Water Dynamics in an Infiltration Trench in an Urban Centre in Brazil: Monitoring and Modelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
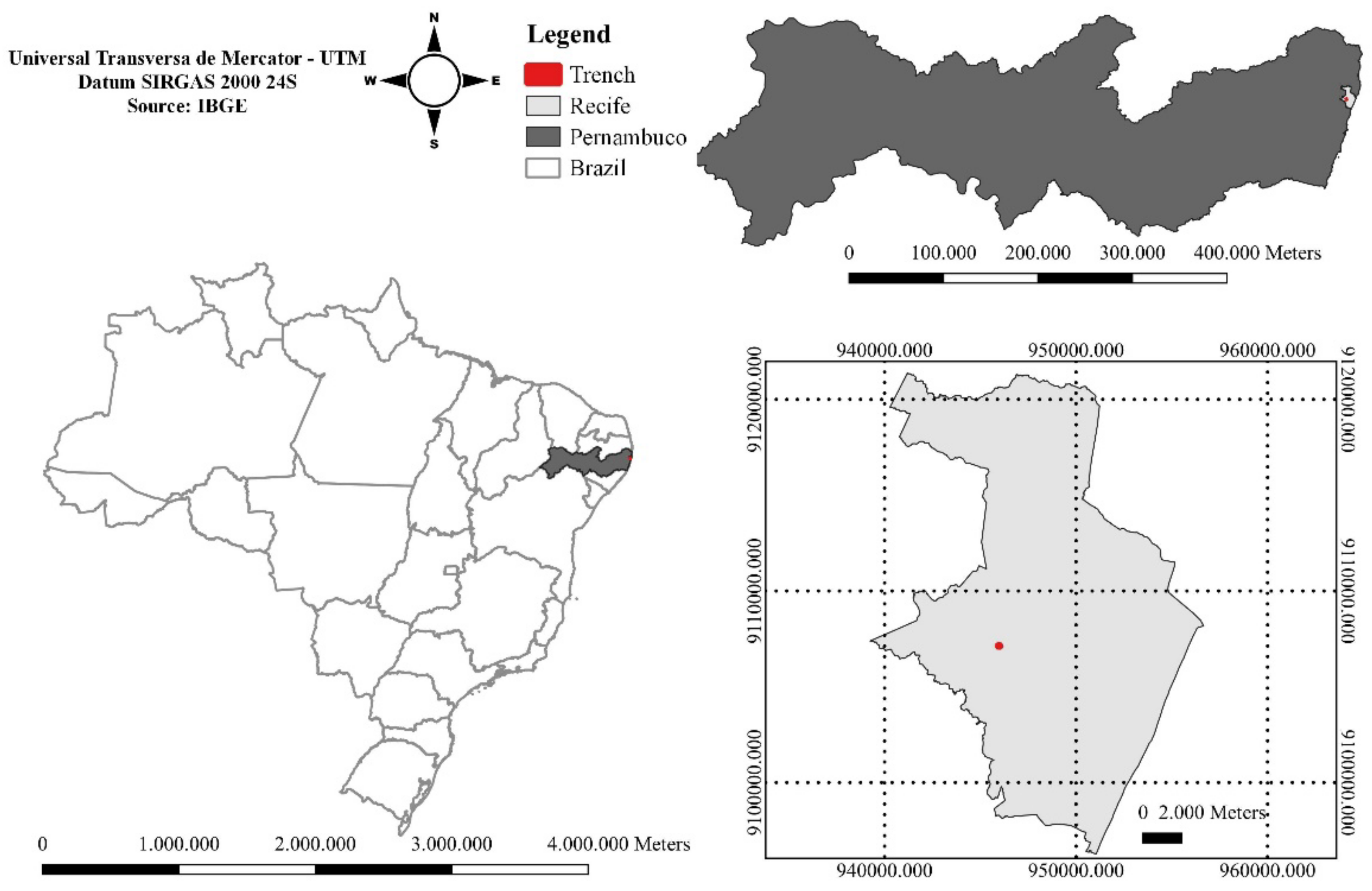
2.1. Study Area
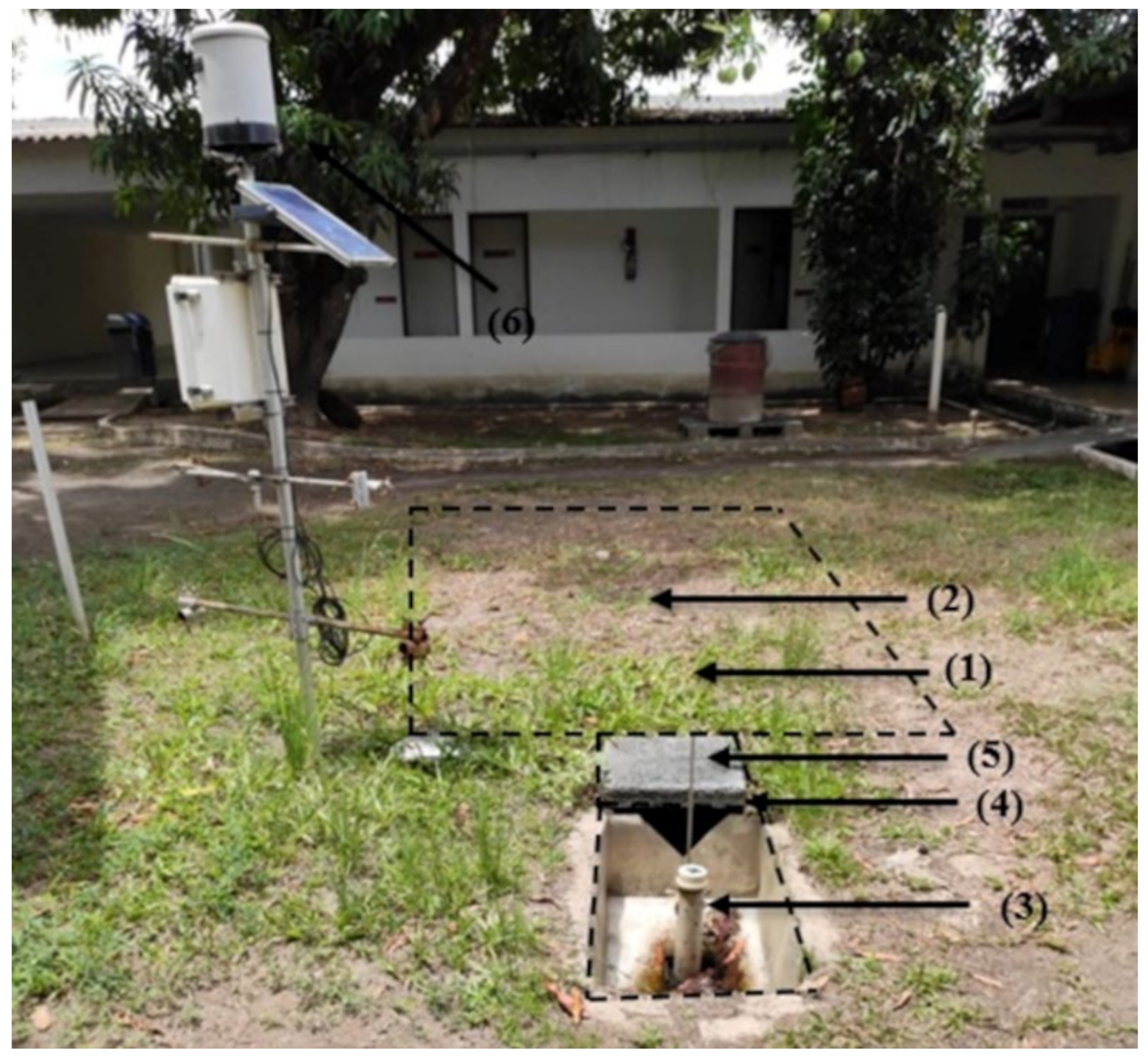
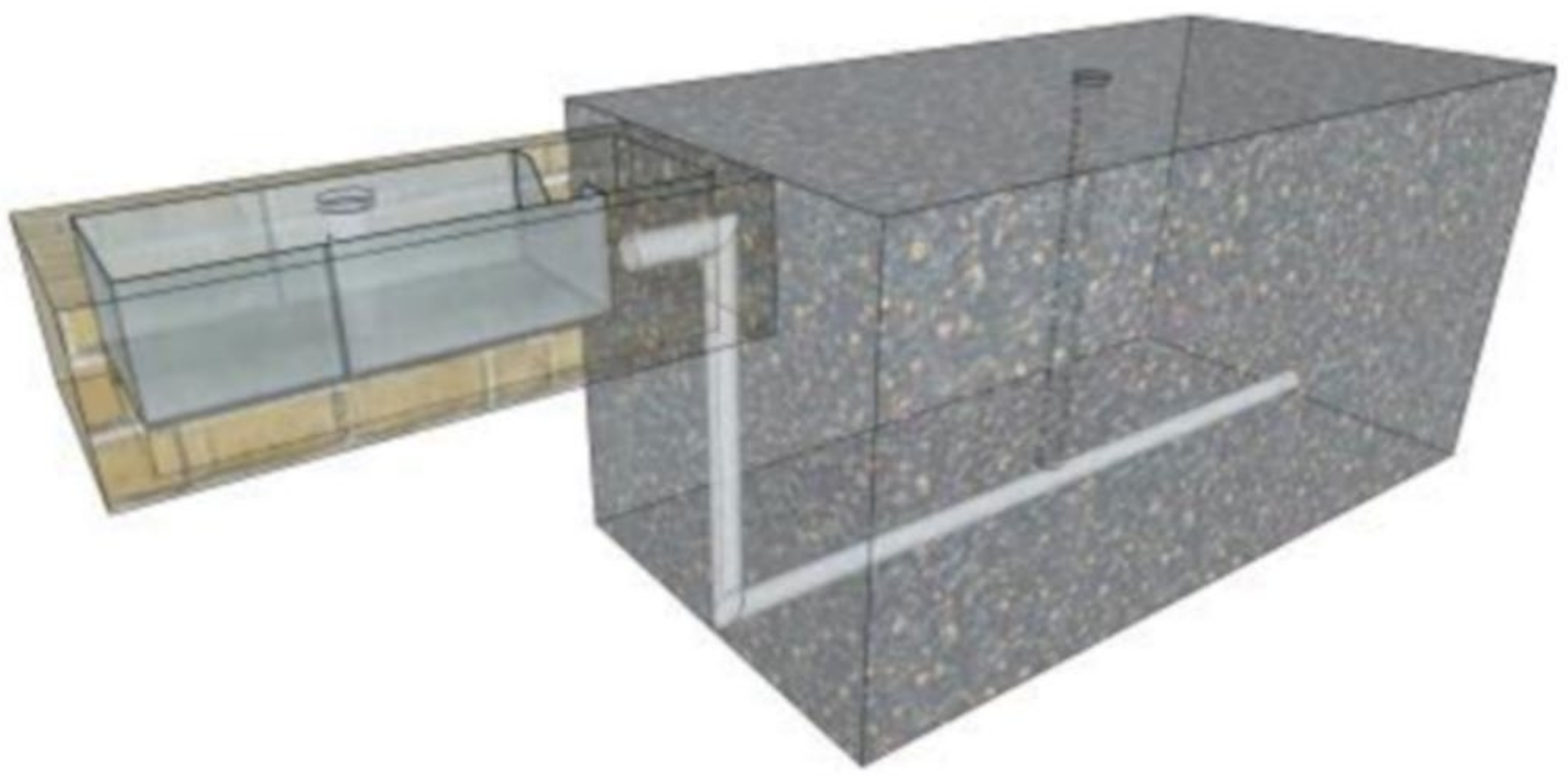
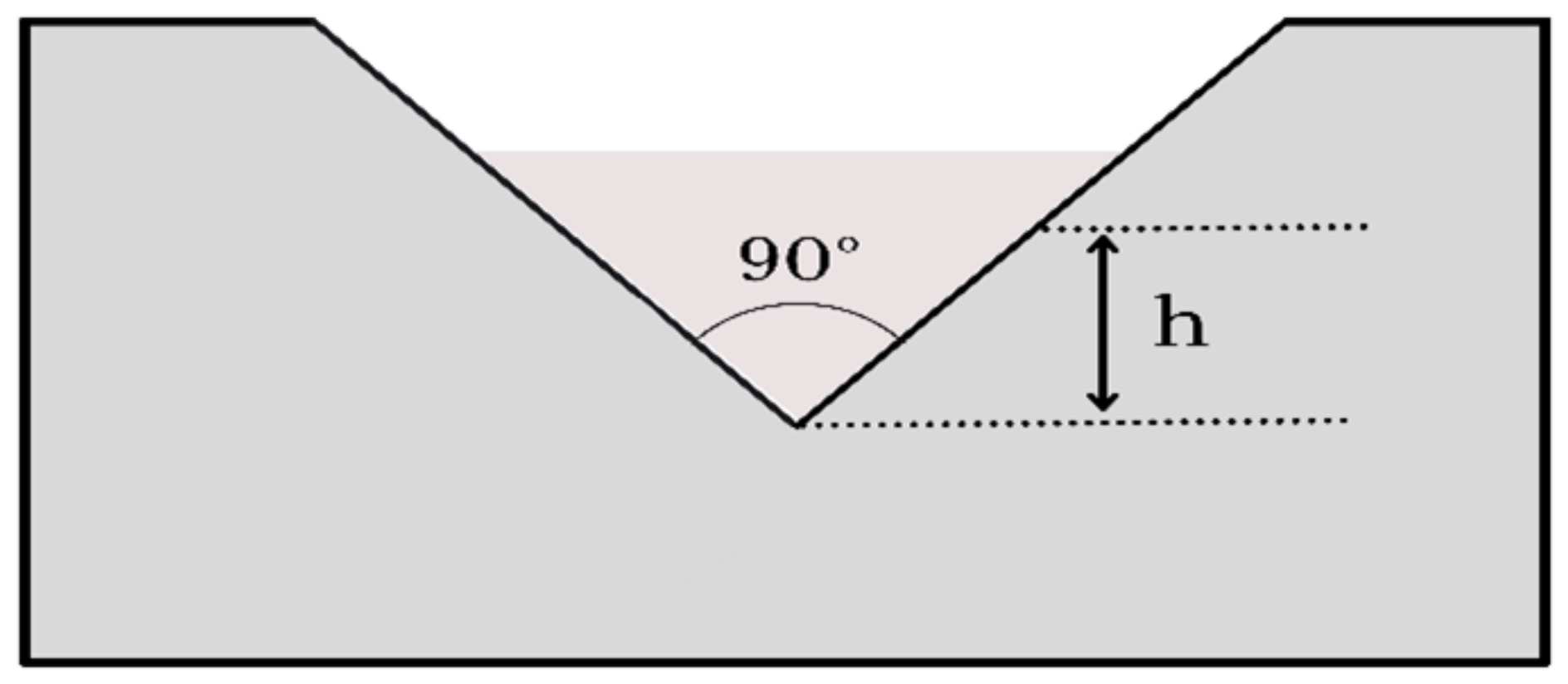
2.2. Infiltration Trench Monitoring and Analysis
2.3. Infiltration Trench Modelling
2.4. Simulated Rainfall Events and Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
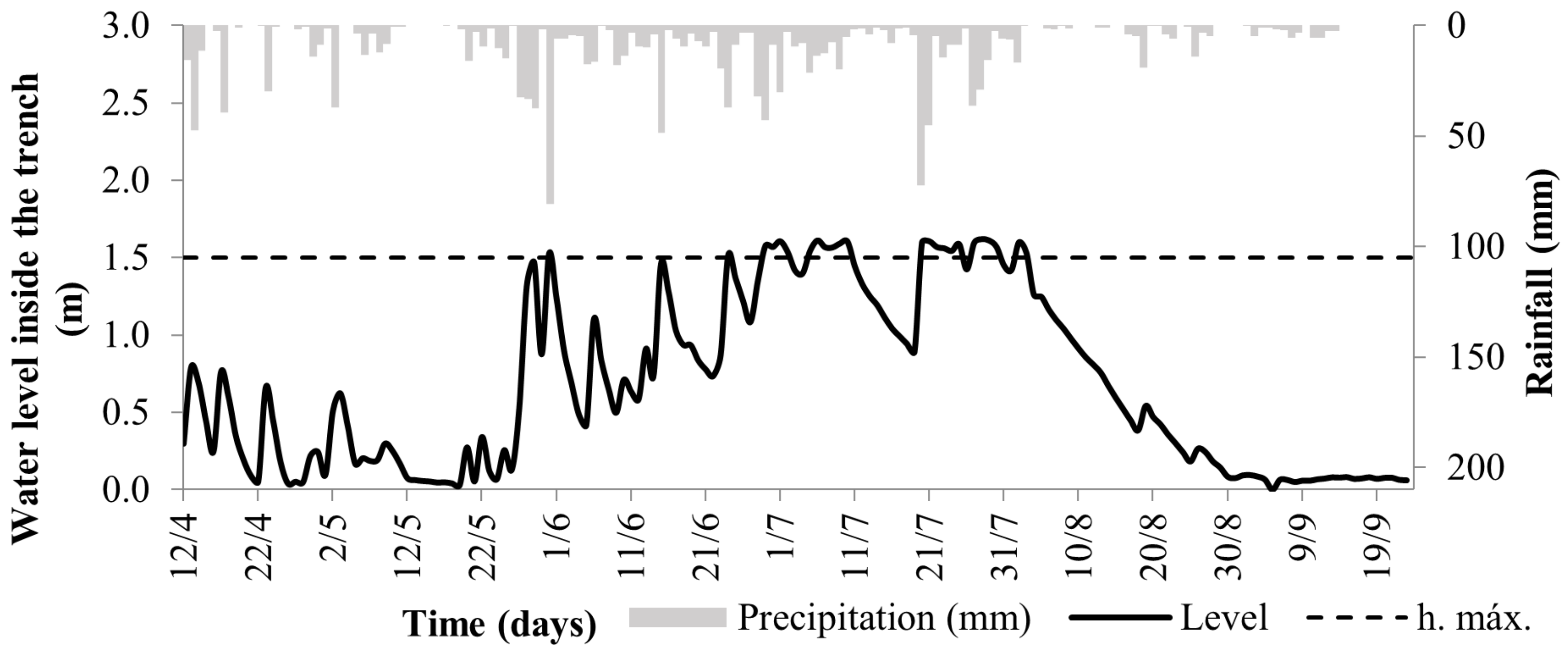
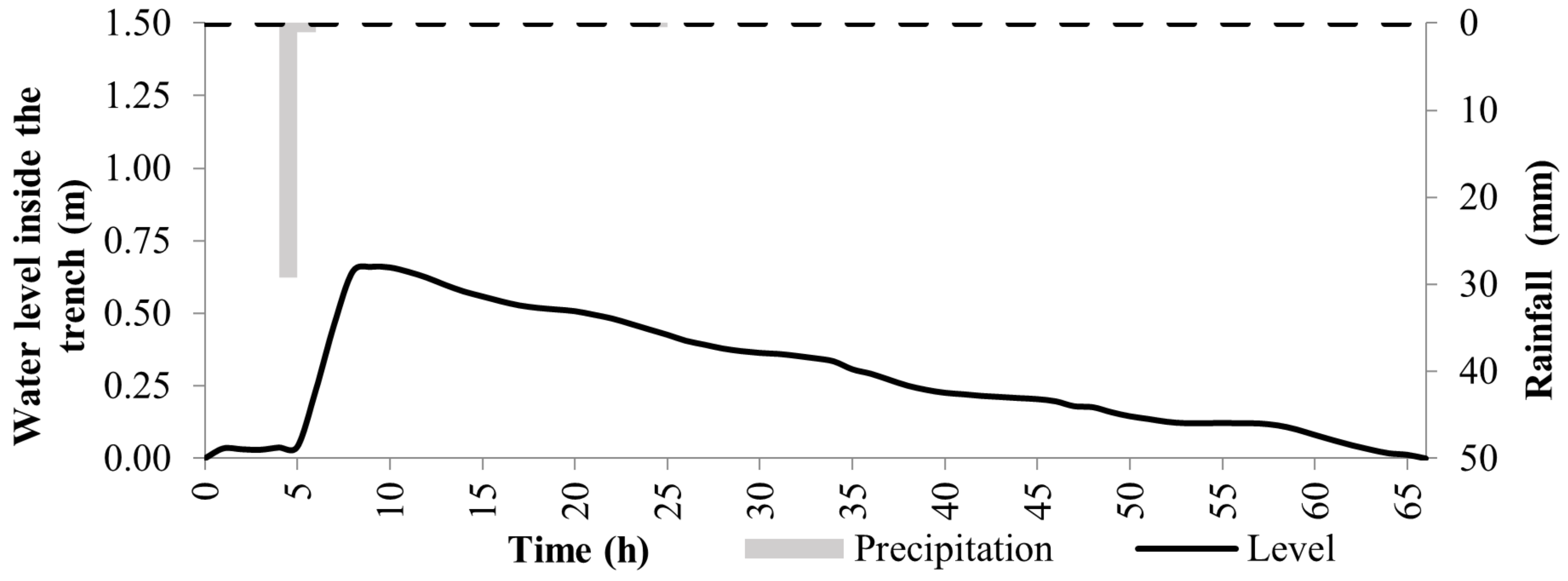
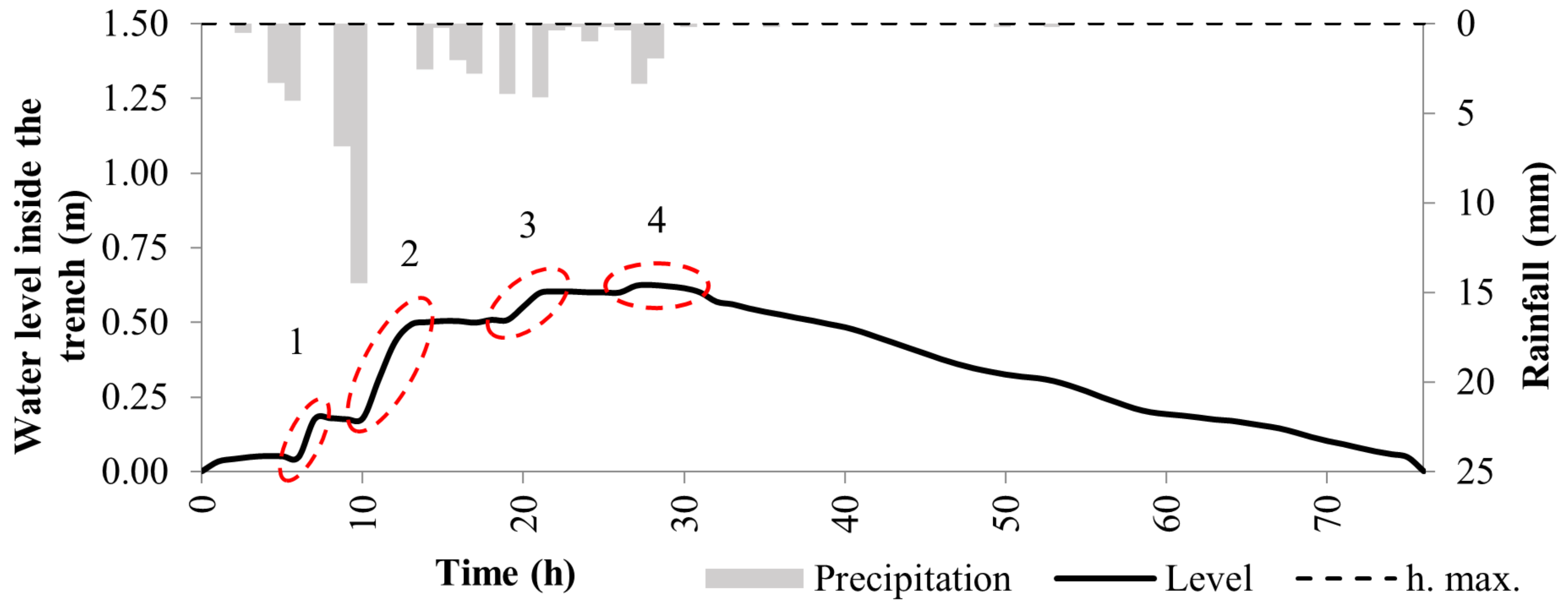
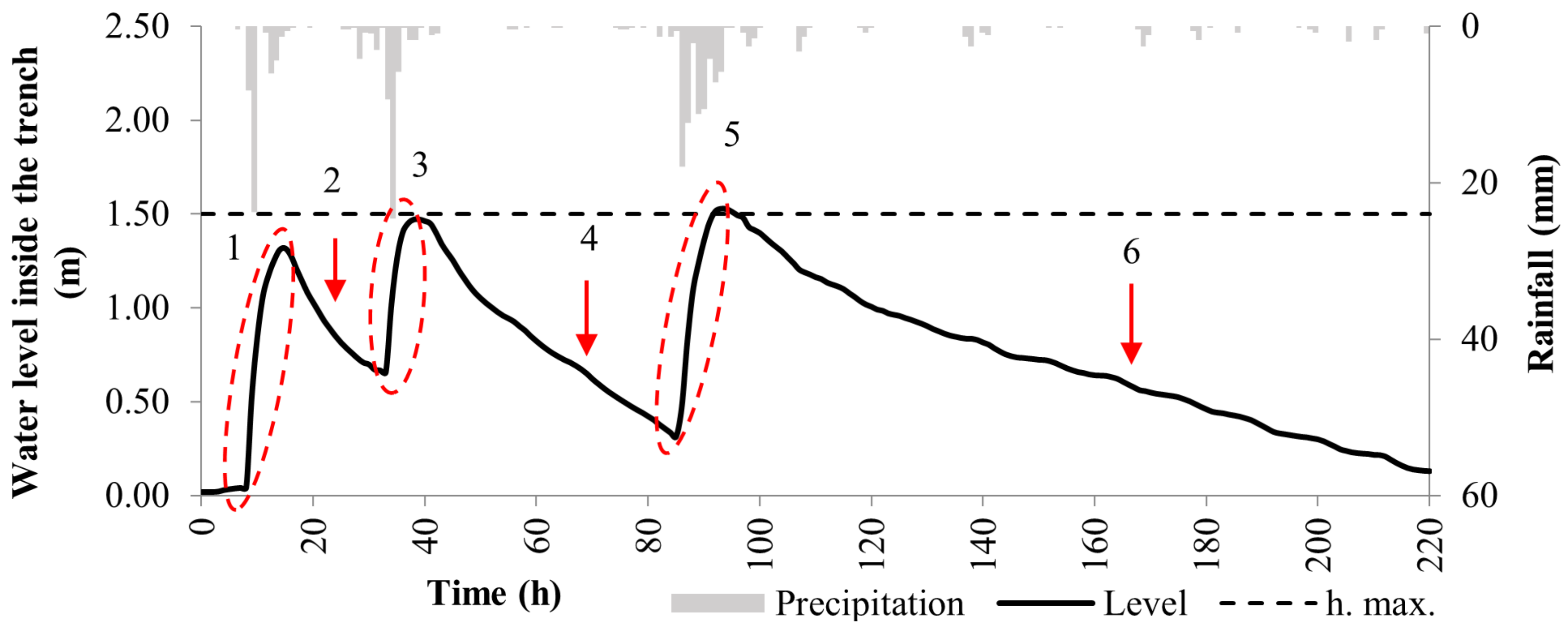
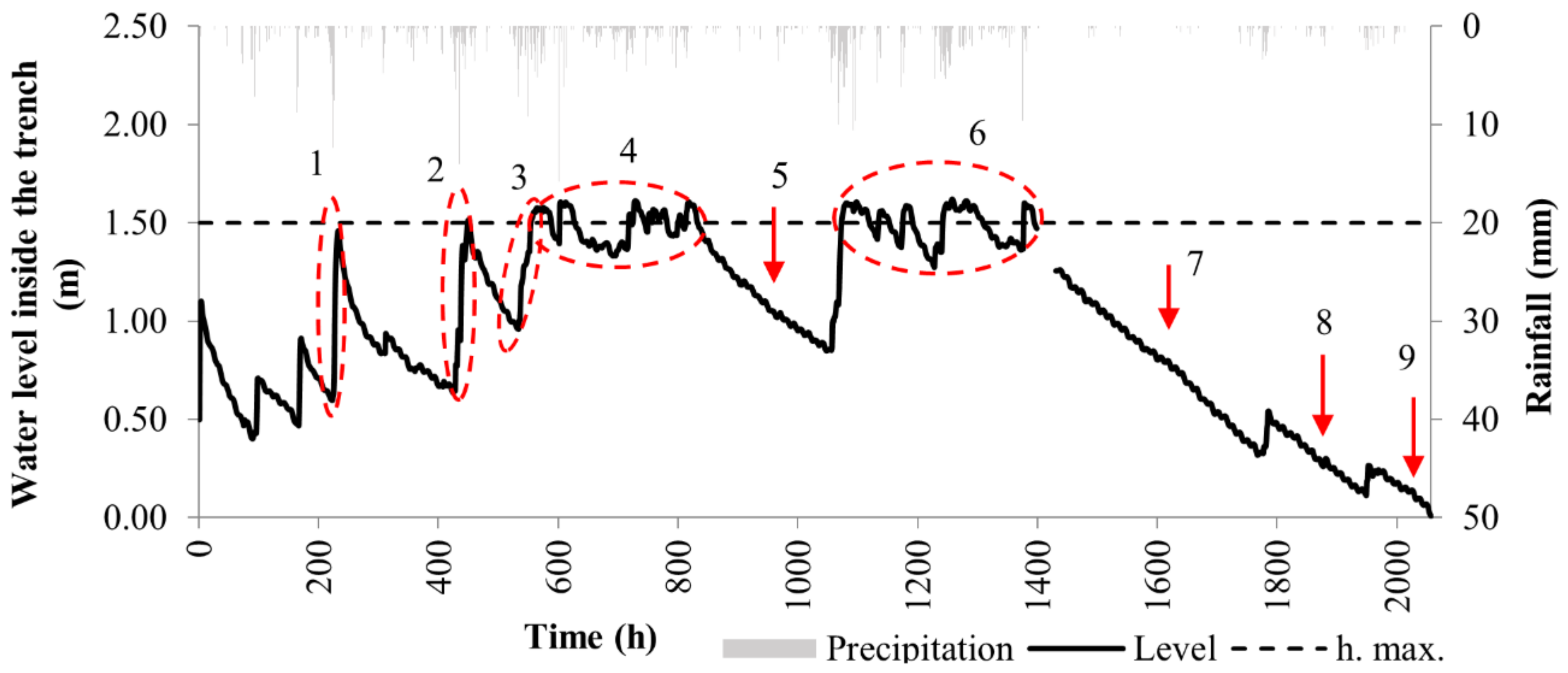
3.1. Infiltration Trench Monitoring and Analysis
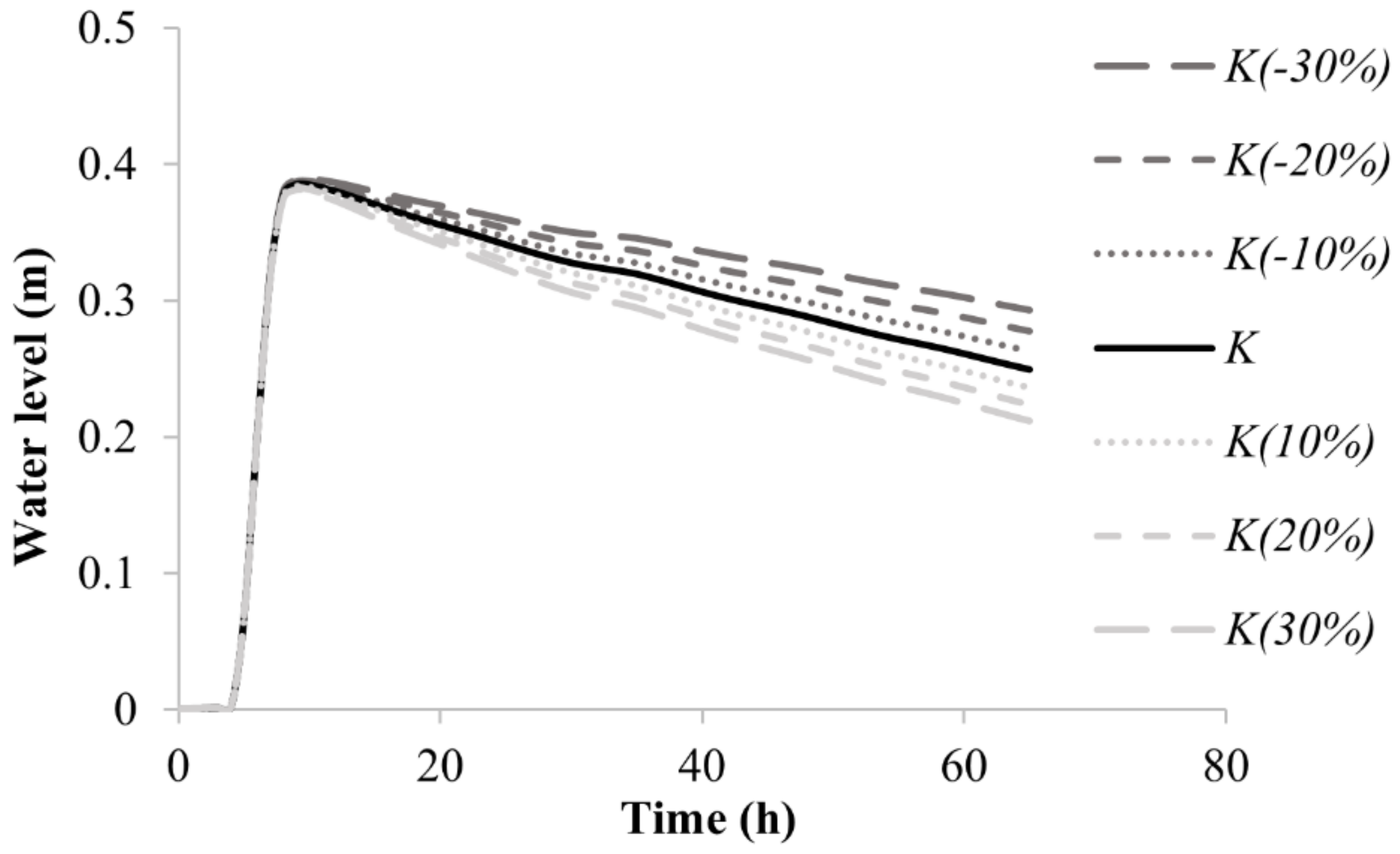
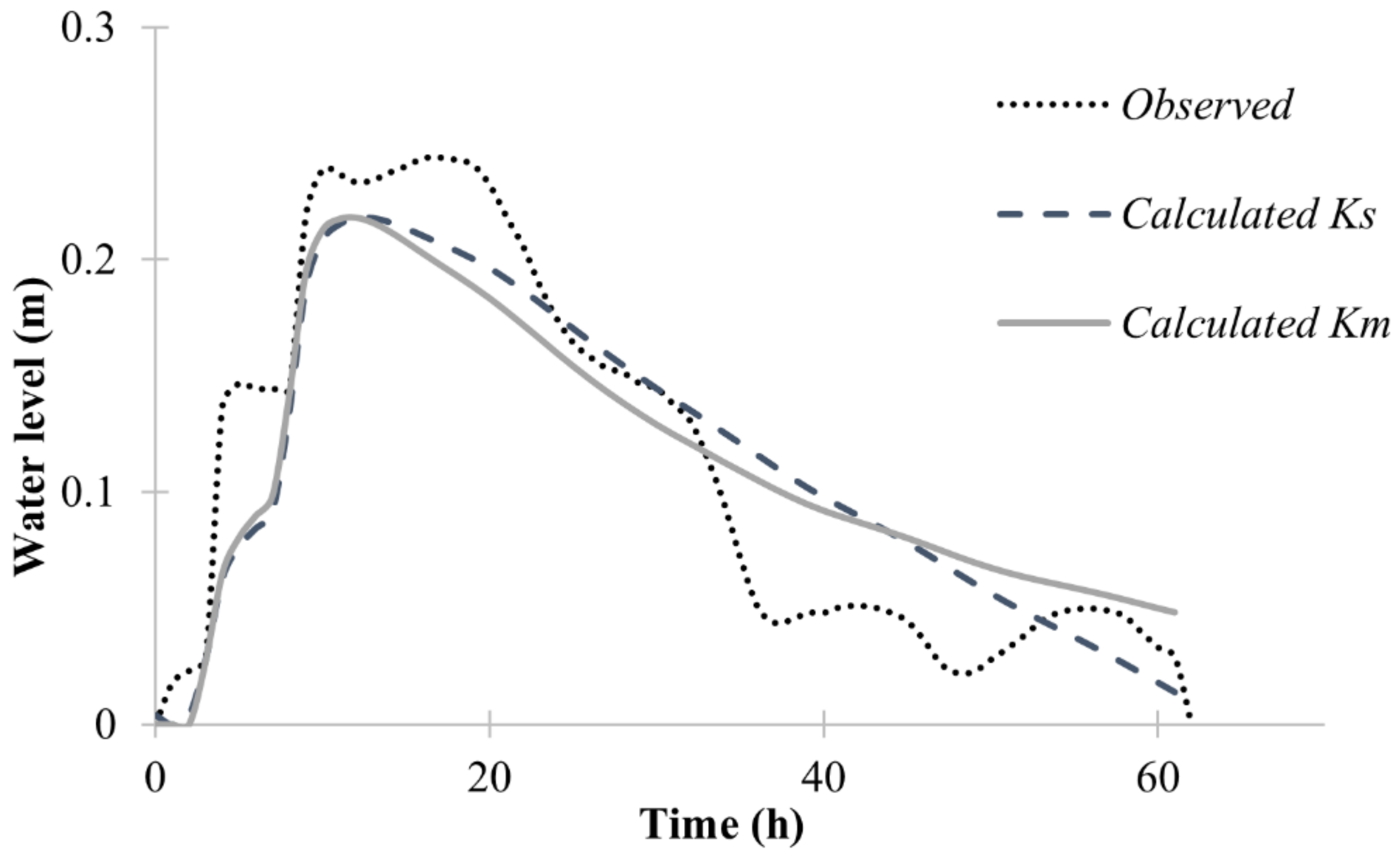
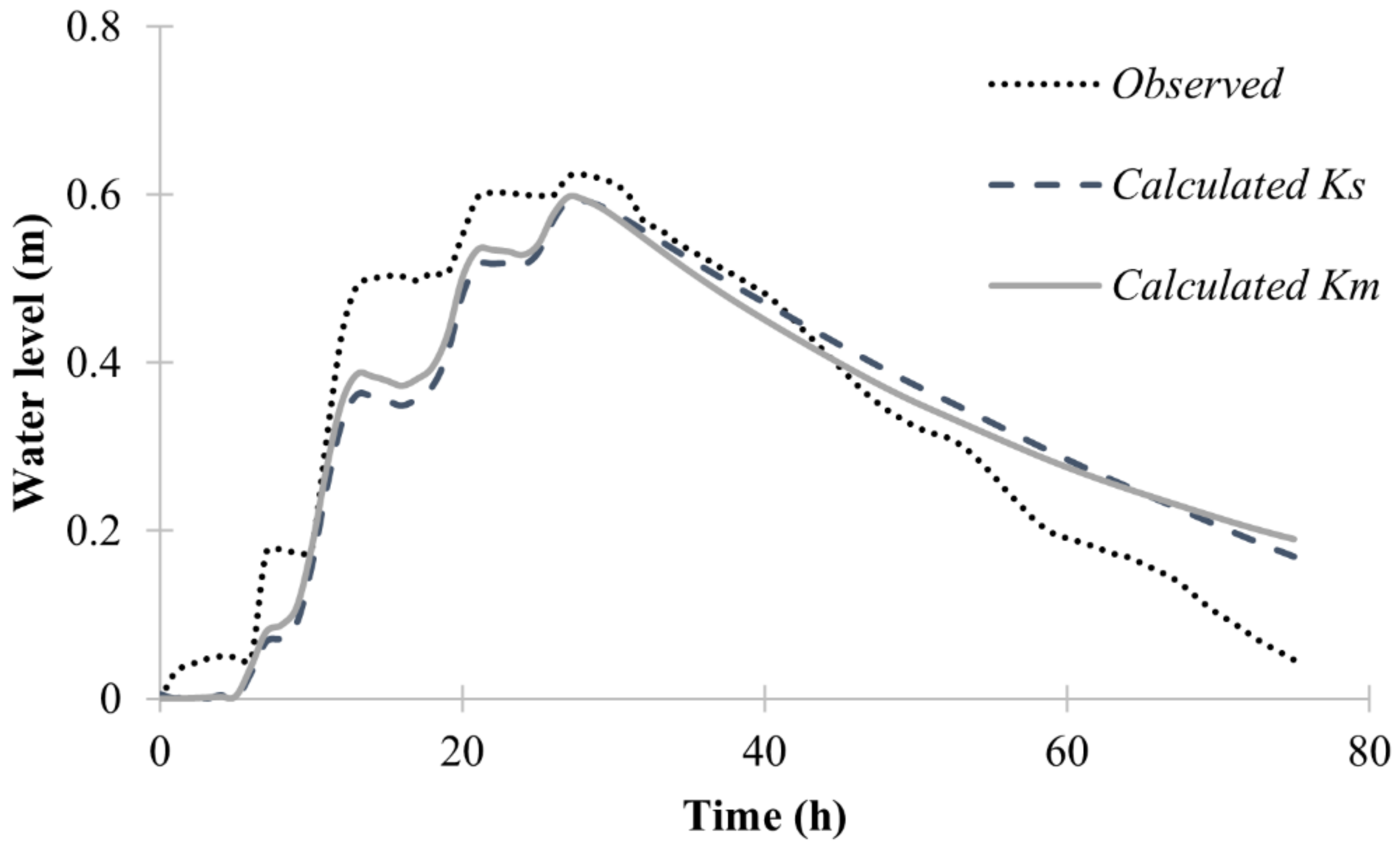
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis of the Model
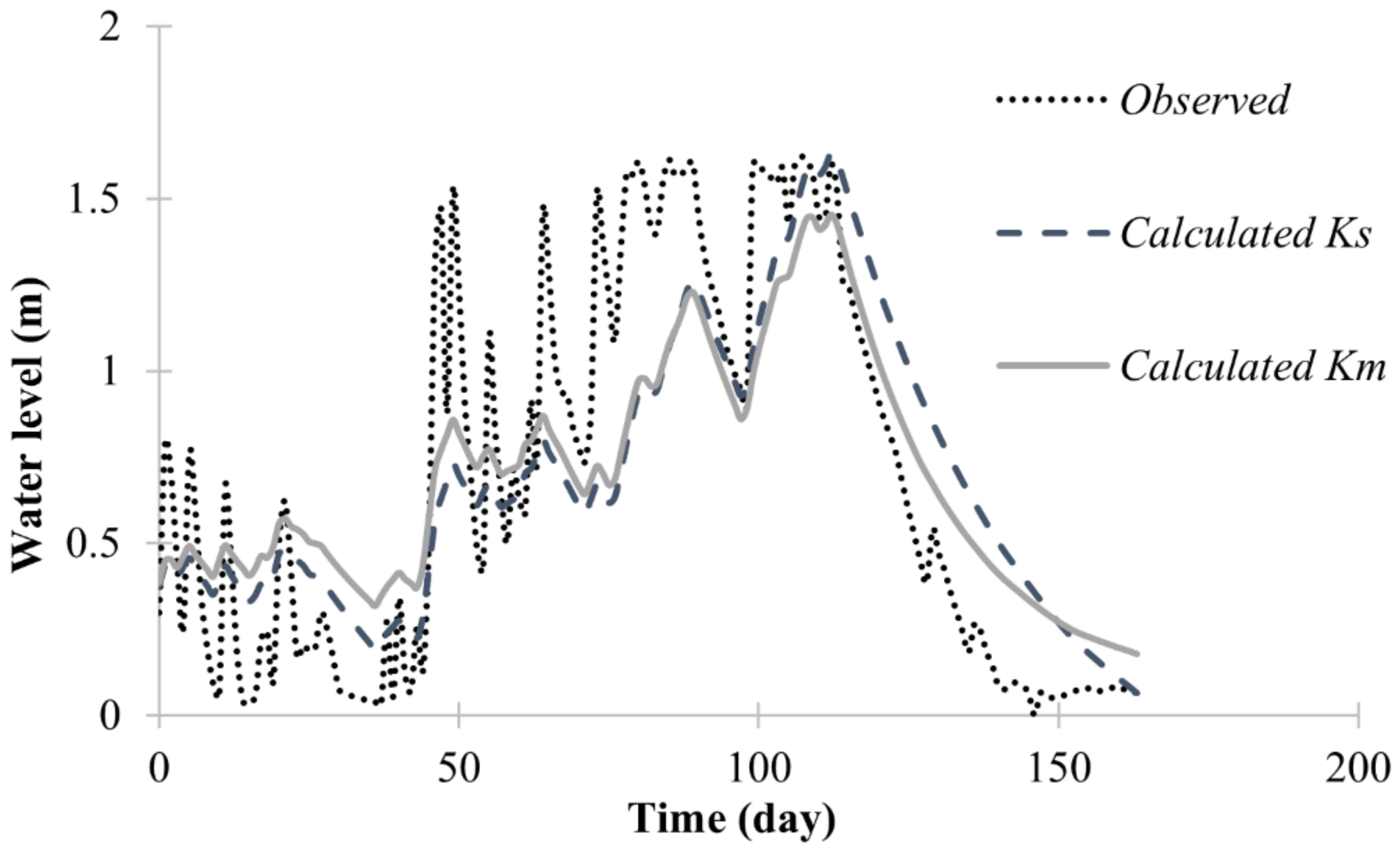
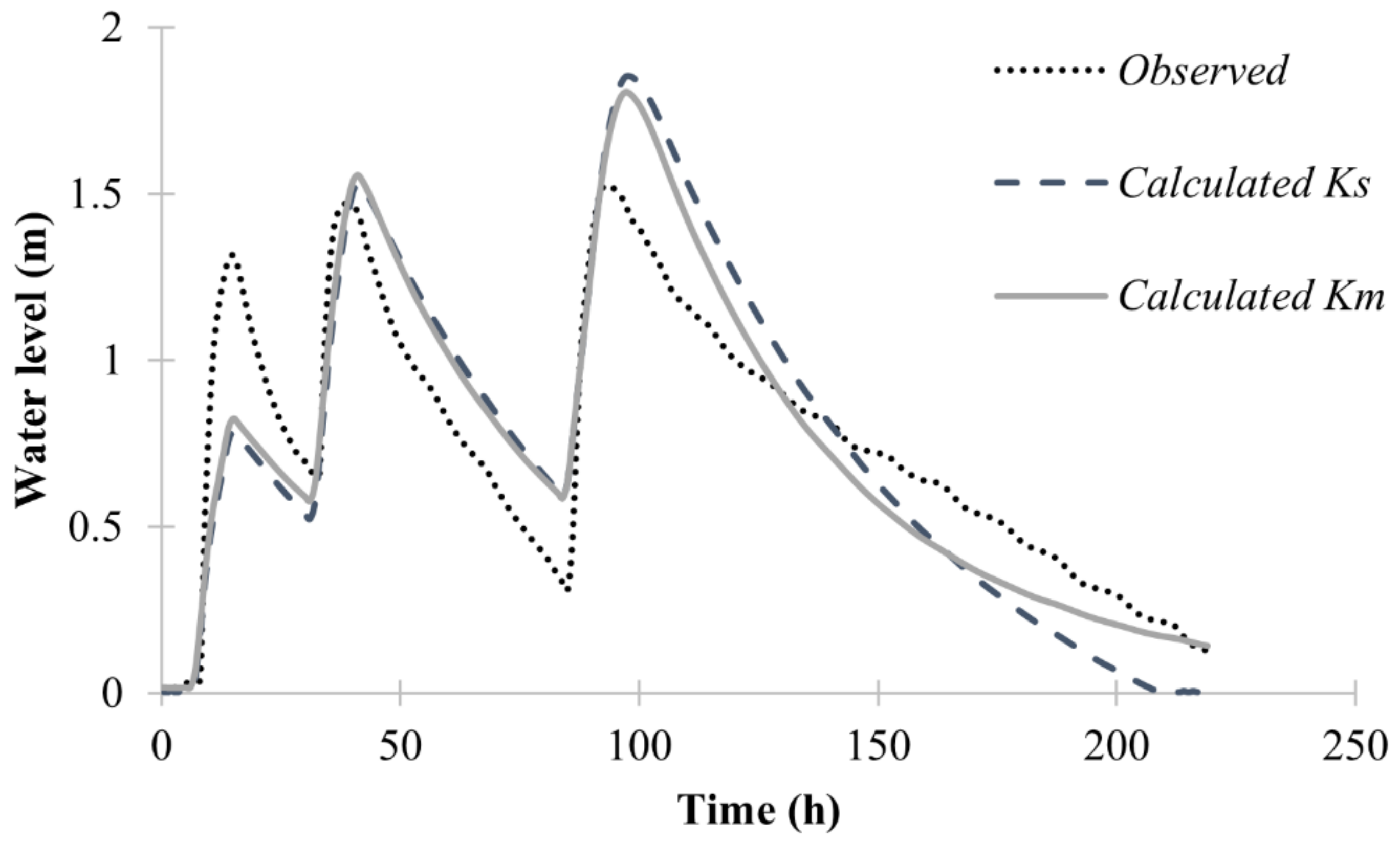
3.3. Modeled Data of the Infiltration Trench
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamel, P.; Daly, E.; Fletcher, T.D. Source-control stormwater management for mitigating the impacts of urbanisation on baseflow: A review. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, T.A.T.; Coutinho, A.P.; Cabral, J.J.S.P.; Antonino, A.C.D.; Cirilo, J.A. Jardim de Chuva: Sistema de Biorretenção Para o Manejo Das Águas Pluviais Urbanas. Ambiente Construído Porto Alegre 2014, 14, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Xiang, L.L.; Che, W.; Ge, R.L. Design and Hydrologic Estimation Method of Multi-Purpose Rain Garden: Beijing Case Study. In Low Impact Development for Urban Ecosystem and Habitat Protection, Proceedings of the International Low Impact Development Conference 2008, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–19 November 2008; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2009; Volume 67, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, T.; Coutinho, A.P.; Dos Santos, J.B.F.; Cabral, J.J.D.S.P.; Antonino, A.C.D.; Lassabatere, L. Trincheira de Infiltração Como Técnica Compensatória No Manejo Das Águas Pluviais Urbanas. Ambiente Construído 2016, 16, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coutinho, A.P.; Lassabatere, L.; Winiarski, T.; Cabral, J.J.S.P.; Antonino, A.C.D.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R. Vadose Zone Heterogeneity Effect on Unsaturated Water Flow Modeling at Meso-Scale. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 7, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Mufleh, A.; Béchet, B.; Ruban, V.; Legret, M.; Clozel, B.; Barraud, S.; Gonzalez-Merchan, C.; Bedell, J.-P.; Delolme, C. Review on Physical and Chemical Characterizations of Contaminated Sediments from Urban Stormwater Infiltration Basins within the Framework of the French Observatory for Urban Hydrology (SOERE URBIS). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5329–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, A.A.; Borst, M.; O’Connor, T.P. Pervious Pavement System Evaluation. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2009, Great River, Kansas City, MS, USA, 17–21 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, A.P.; Lassabatere, L.; Montenegro, S.; Antonino, A.C.D.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R.; Cabral, J.J.S.P. Hydraulic Characterization and Hydrological Behaviour of a Pilot Permeable Pavement in an Urban Centre, Brazil. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4242–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabur, A.S.; Dornelles, F.; Silveira, A.L.L.; Goldenfum, J.A.; Okawa, C.M.P.; Gasparini, R.L. Determination of the Infiltration Capacity of Permeable Pavements. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos 2015, 20, 937–945. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, A.H.; Sobrinha, L.A.; Moruzzi, R.B.; Barbassa, A.P. Evaluation of Best Management Practices’ Construction and Operation: The Fine Particles Transportation, the Infiltration Capacity, the Soil Infiltration Loading Rate and the Geotextile Permeability. Eng. Sanit. E Ambient. 2015, 20, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascimento, N.O.; Baptista, M.B. Técnicas Compensatórias em Águas Pluviais. In Manejo Águas Pluviais; ABES: Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 2009; pp. 148–197. Available online: http://www.finep.gov.br/images/apoio-e-financiamento/historico-de-programas/prosab/prosab5_tema_4.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and More—The Evolution and Application of Terminology Surrounding Urban Drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarizadeh, A.; Rippy, M.A.; Fletcher, T.D.; Feldman, D.L.; Peng, J.; Bowler, P.; Mehring, A.S.; Winfrey, B.K.; Vrugt, J.A.; AghaKouchak, A.; et al. From Rain Tanks to Catchments: Use of Low-Impact Development to Address Hydrologic Symptoms of the Urban Stream Syndrome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11264–11280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houle, J.J.; Roseen, R.M.; Ballestero, T.P.; Puls, T.A.; Sherrard, J., Jr. Comparison of Maintenance Cost, Labor Demands, and System Performance for LID and Conventional Stormwater Management. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiablame, L.M.; Engel, B.A.; Chaubey, I. Effectiveness of Low Impact Development Practices in Two Urbanized Watersheds: Retrofitting with Rain Barrel/Cistern and Porous Pavement. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 119, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhen, X.; Clar, M.; Yu, S.L. China’s Sponge City Construction: A Discussion on Technical Approaches. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, S.U. Sustainable Drainage Systems as Ecosystem Services Case Study: Urban Catchment in Montevideo, Uruguay; UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thorne, C.R.; Lawson, E.C.; Ozawa, C.; Hamlin, S.L.; Smith, L.A. Overcoming Uncertainty and Barriers to Adoption of Blue-Green Infrastructure for Urban Flood Risk Management. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S960–S972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.C.; Ren, N.; Li, G.; Ding, J.; Liang, H. Implementation of a Specific Urban Water Management—Sponge City. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevenbergen, C.; Fu, D.; Pathirana, A. Transitioning to Sponge Cities: Challenges and Opportunities to Address Urban Water Problems in China. Water 2018, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reis, R.P.A.; Ilha, M.S.D.O.; Teixeira, P.D.C. Sistemas Prediais de Infiltração de Água de Chuva: Aplicações, Limitações e Perspectivas. REEC—Rev. Eletrôn. Eng. Civ. 2013, 7, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Buchberger, S.G.; Sansalone, J.J. Variably Saturated Flow in Storm-Water Partial Exfiltration Trench. J. Environ. Eng. 1999, 125, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, A.A.; Da Silva, L.P.; Mendiondo, E.M. Input Flows for the Infiltration Trench Household. Cienc. Eng. Sci. Eng. J. 2015, 24, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locatelli, L.; Mark, O.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Wong, T.; Binning, P.J. Determining the Extent of Groundwater Interference on the Performance of Infiltration Trenches. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duchêne, M.; McBean, E.A.; Thomson, N.R. Modeling of Infiltration from Trenches for Storm-Water Control. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1994, 120, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SWMMWW. Stormwater Management Manual for Western Washington. Available online: https://ecology.wa.gov/Regulations-Permits/Guidance-technical-assistance/Stormwater-permittee-guidance-resources/Stormwater-manuals (accessed on 8 June 2017).
- Lucas, A.H.; Barbassa, A.P.; Moruzzi, R.B. Modelagem de Um Sistema Filtro-Vala-Trincheira de Infiltração Pelo Método de Puls Adaptado Para Calibração de Parâmetros. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos 2013, 18, 135–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chui, T.F.M. A Review on Implementing Infiltration-Based Green Infrastructure in Shallow Groundwater Environments: Challenges, Approaches, and Progress. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecedor, N. Monitoramento e Modelagem Hidrológica de Plano de Infiltração Construído em Escala Real. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, P.H.L. Dinâmica da Água em Trincheira de Infiltração em Lote Urbano. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, S.R.; de Sousa Araújo, G.R. Algoritmo Para Determinação da Equação de Chuvas Intensas (Algorithm to Determine the Equation of Intense Rain). Rev. Bras. Geogr. Fís. 2013, 6, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- APAC. Agência Pernambucana de Águas e Clima. Available online: http://old.apac.pe.gov.br/meteorologia/monitoramento-pluvio.php (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Silva, F.C. Manual de Análises Químicas de Solos, Plantas e Fertilizantes; Embrapa Informação Tecnológica: Brasília, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, J.B.F. Monitoramento e Simulação Hidráulica de Uma Trincheira de Infiltração. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McCuen, R.H. Hydrologic Analysis and Design, 4th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-0-13-431312-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tucci, C.E. Modelos Hidrológicos; Editora da UFRGS: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2005; ISBN 978-85-7025-823-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Zhu, J.L.; Dollard, L.A. Infiltration Trenches for Urban Runoff Control. In Hydraulic Engineering; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1989; pp. 1029–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.T.L.M.; das Neves, M.G.F.P.; de Souza, V.C.B. Puls Method for Events Simulation in a Lot Scale Bioretention Device. RBRH 2019, 24, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baptista, M.; Nascimento, N.; Barraud, S. Técnicas Compensatórias Em Drenagem Urbana [Compensatory Techniques for Urban Drainage]; ABRH: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Emerson, C.H.; Wadzuk, B.M.; Traver, R.G. Hydraulic Evolution and Total Suspended Solids Capture of an Infiltration Trench. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.A.; Clausen, B. Streamflow Recession in Basins with Multiple Water Storages. J. Hydrol. 1997, 190, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, T.D.A.T. Avaliação Hidrodinâmica de Trincheira de Infiltração No Manejo Das Águas Pluviais Urbanas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Barbassa, A.P.; Angelini Sobrinha, L.; Moruzzi, R.B. Poço de Infiltração Para Controle de Enchentes Na Fonte: Avaliação Das Condições de Operação e Manutenção. Ambiente Construído Porto Alegre 2014, 14, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunetti, G.; Šimůnek, J.; Piro, P. A comprehensive analysis of the variably saturated hydraulic behavior of a green roof in a mediterranean climate. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15, vzj2016.04.0032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farahi, G.; Khodashenas, S.R.; Alizadeh, A.; Ziaei, A.N. New model for simulating hydraulic performance of an infiltration trench with finite-volume one-dimensional Richards’ equation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, A.; Cimorelli, L.; Cozzolino, L.; Pianese, D. The effect of geological heterogeneity and groundwater table depth on the hydraulic performance of stormwater infiltration facilities. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1147–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Šimůnek, J.; Turco, M.; Piro, P. On the use of global sensitivity analysis for the numerical analysis of permeable pavements. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freni, G.; Mannina, G. Long term efficiency analysis of infiltration trenches subjected to clogging. In New Trends in Urban Drainage Modelling; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimian, A.; Wadzuk, B.; Sokolovskaya, N. Temporal Variation of Infiltration in Green Infrastructure. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. H44E-08. [Google Scholar]




| Layers (m) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | Textural Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2–0.3 | 11.72 | 13.27 | 74.58 | Loam Sand |
| 0.3–0.4 | 14.07 | 22.69 | 63.24 | Sandy Loam |
| 0.4–0.5 | 23.45 | 29.31 | 47.24 | Loam |
| 0.6–0.7 | 17.59 | 20.98 | 61.43 | Sandy Loam |
| 1.1–1.2 | 23.45 | 19.93 | 56.62 | Sandy Clay Loam |
| 1.3–1.4 | 21.11 | 12.90 | 65.99 | Sandy Clay Loam |
| 1.4–1.5 | 26.97 | 21.10 | 51.93 | Sandy Clay Loam |
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4.6 | E5.5 | E5.7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.14 | 0.52 | 1.27 | 1.10 | 0.32 | 0.25 |
| Simulation | Km | Ks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| kb | kw | k | |
| Event 2 | 1.26 × 10−4 | 5.99 × 10−3 | 1.42 × 10−3 |
| Event 3 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 4.09 × 10−3 | 1.84 × 10−3 |
| Event 4 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 4.05 × 10−3 | 2.63 × 10−3 |
| Complete event | 1.27 × 10−4 | 8.35 × 10−3 | 4.98 × 10−3 |
| Average values | 1.25 × 10−4 | 5.62 × 10−3 | 2.72 × 10−3 |
| Standard deviation | 1.05 × 10−6 | 2.03 × 10−3 | 1.59 × 10−3 |
| Coefficient of variation | 8.34 × 10−3 | 3.62 × 10−1 | 5.85 × 10−1 |
| Simulation | Km | Ks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | DR | CRM | R2 | DR | CRM | |
| Event 2 | 0.86 | 1.86 | 3.24 × 10−7 | 0.84 | 1.45 | 1.27 × 10−6 |
| Event 3 | 0.89 | 1.43 | −3.12 × 10−14 | 0.86 | 1.38 | −2.26 × 10−7 |
| Event 4 | 0.84 | 0.69 | −1.32 × 10−9 | 0.82 | 0.56 | −4.23 × 10−9 |
| Complete event | 0.80 | 2.79 | 5.96 × 10−7 | 0.68 | 1.93 | 4.35 × 10−8 |
| Average | 0.85 | 1.69 | 2.31 × 10−7 | 0.80 | 1.33 | 2.70 × 10−7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes Bezerra, P.H.; Coutinho, A.P.; Lassabatere, L.; Santos Neto, S.M.d.; Melo, T.d.A.T.d.; Antonino, A.C.D.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R.; Montenegro, S.M.G.L. Water Dynamics in an Infiltration Trench in an Urban Centre in Brazil: Monitoring and Modelling. Water 2022, 14, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040513
Lopes Bezerra PH, Coutinho AP, Lassabatere L, Santos Neto SMd, Melo TdATd, Antonino ACD, Angulo-Jaramillo R, Montenegro SMGL. Water Dynamics in an Infiltration Trench in an Urban Centre in Brazil: Monitoring and Modelling. Water. 2022; 14(4):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes Bezerra, Paulo Henrique, Artur Paiva Coutinho, Laurent Lassabatere, Severino Martins dos Santos Neto, Tassia dos Anjos Tenório de Melo, Antonio Celso Dantas Antonino, Rafael Angulo-Jaramillo, and Suzana Maria Gico Lima Montenegro. 2022. "Water Dynamics in an Infiltration Trench in an Urban Centre in Brazil: Monitoring and Modelling" Water 14, no. 4: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040513
APA StyleLopes Bezerra, P. H., Coutinho, A. P., Lassabatere, L., Santos Neto, S. M. d., Melo, T. d. A. T. d., Antonino, A. C. D., Angulo-Jaramillo, R., & Montenegro, S. M. G. L. (2022). Water Dynamics in an Infiltration Trench in an Urban Centre in Brazil: Monitoring and Modelling. Water, 14(4), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040513






