Application of Machine Learning Techniques for the Estimation of the Safety Factor in Slope Stability Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geotechnical Database
2.2. Data Acquisition
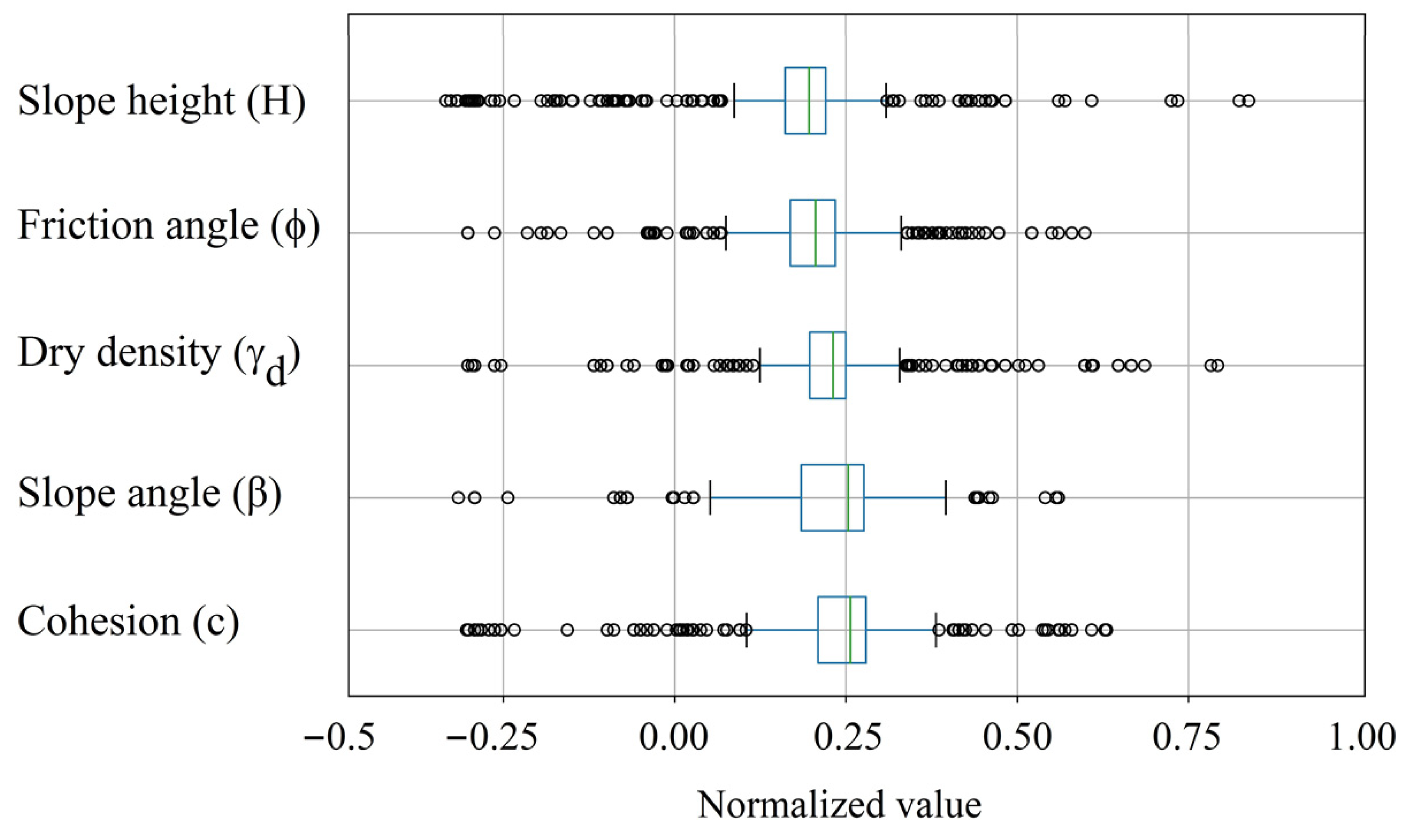
2.3. Predictive Model Implementations and Adjustment
2.4. Model Performance Evaluations
3. Results and Discussion
| Classifier | Parameter | Assessment Score | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |||
| MLP | Stable | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.938 |
| Unstable | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.89 | ||
| SVM | Stable | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.756 |
| Unstable | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.75 | ||
| k-NN | Stable | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.849 |
| Unstable | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.85 | ||
| DT | Stable | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.808 |
| Unstable | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | ||
| RF | Stable | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.700 |
| Unstable | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.65 | ||
| Classifier | MAE | MSE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | 0.103367 | 0.102566 | 0.098470 |
| SVM | 0.145631 | 0.130764 | 0.128836 |
| k-NN | 0.125682 | 0.123009 | 0.120957 |
| DT | 0.125369 | 0.121942 | 0.120454 |
| RF | 0.138980 | 0.135124 | 0.126821 |
| Aim | Applied Models | Target Model | Accuracy | Precision | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS calculation | LR, DT, RF, GBM, SVM, MLP | MLP | 0.84 | - | [17] |
| RF, DT, SVM, k-NN, GBDT, AdaBoost, Bagging, MLP | MLP | 0.88 | - | [18] | |
| AdaBoost, GBM, Bagging, ET, RF, MLP | MLP | 0.84 | - | [34] | |
| MLP, GPR, MLR, SVM, SLR | SVM | - | - | [35] | |
| MLP, RBFR, MLR, SVM, k-NN, RF, RT | MLP | 0.50 | - | [22] | |
| BR, LR, ENR, ABR, SVM, GBR, ETR, DTR, KNR, Bagging | SVM | 0.86 | - | [36] | |
| MLP, SVM, k-NN, DT, RF | MLP | 0.938 | 0.90 | This study |
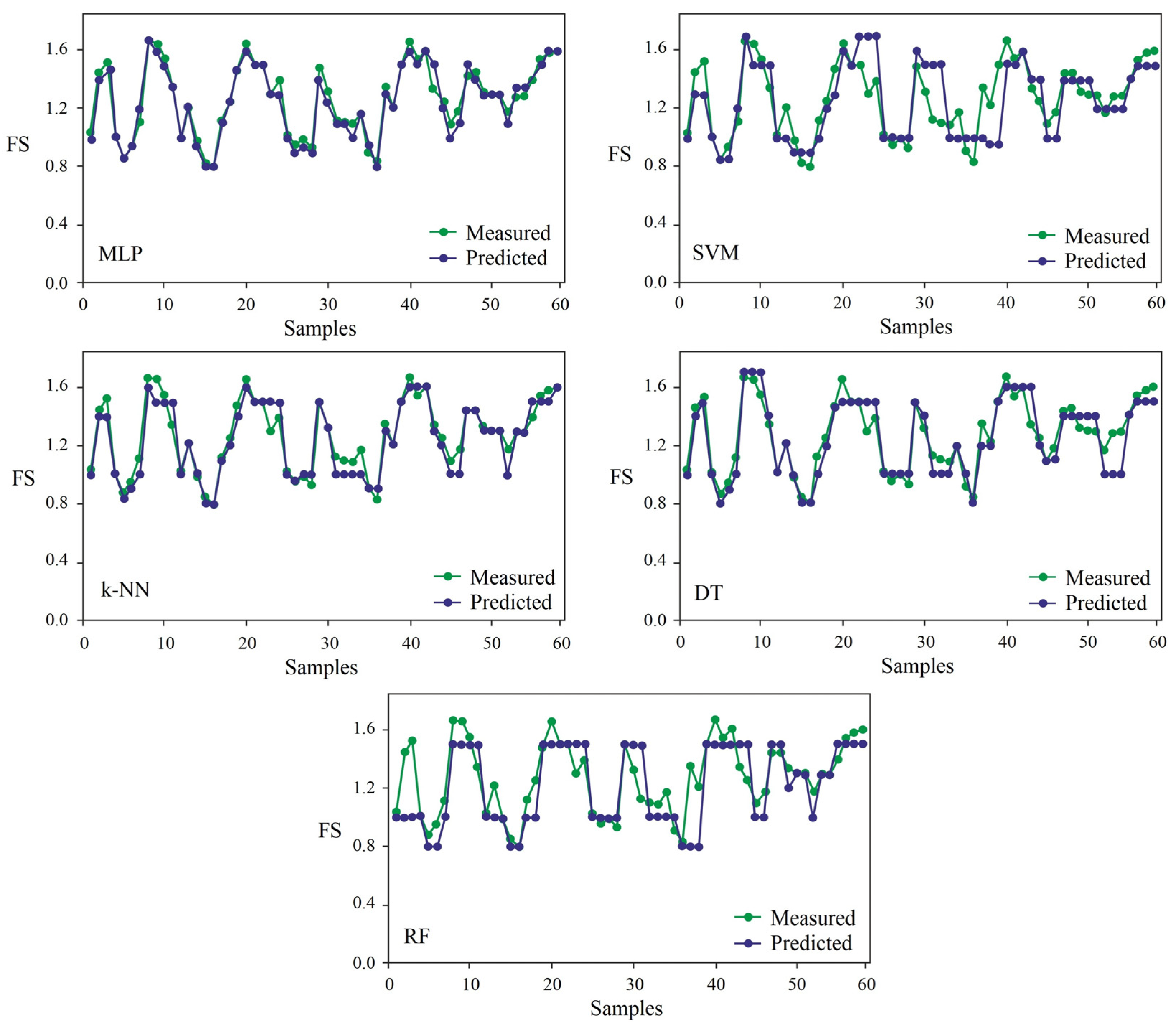
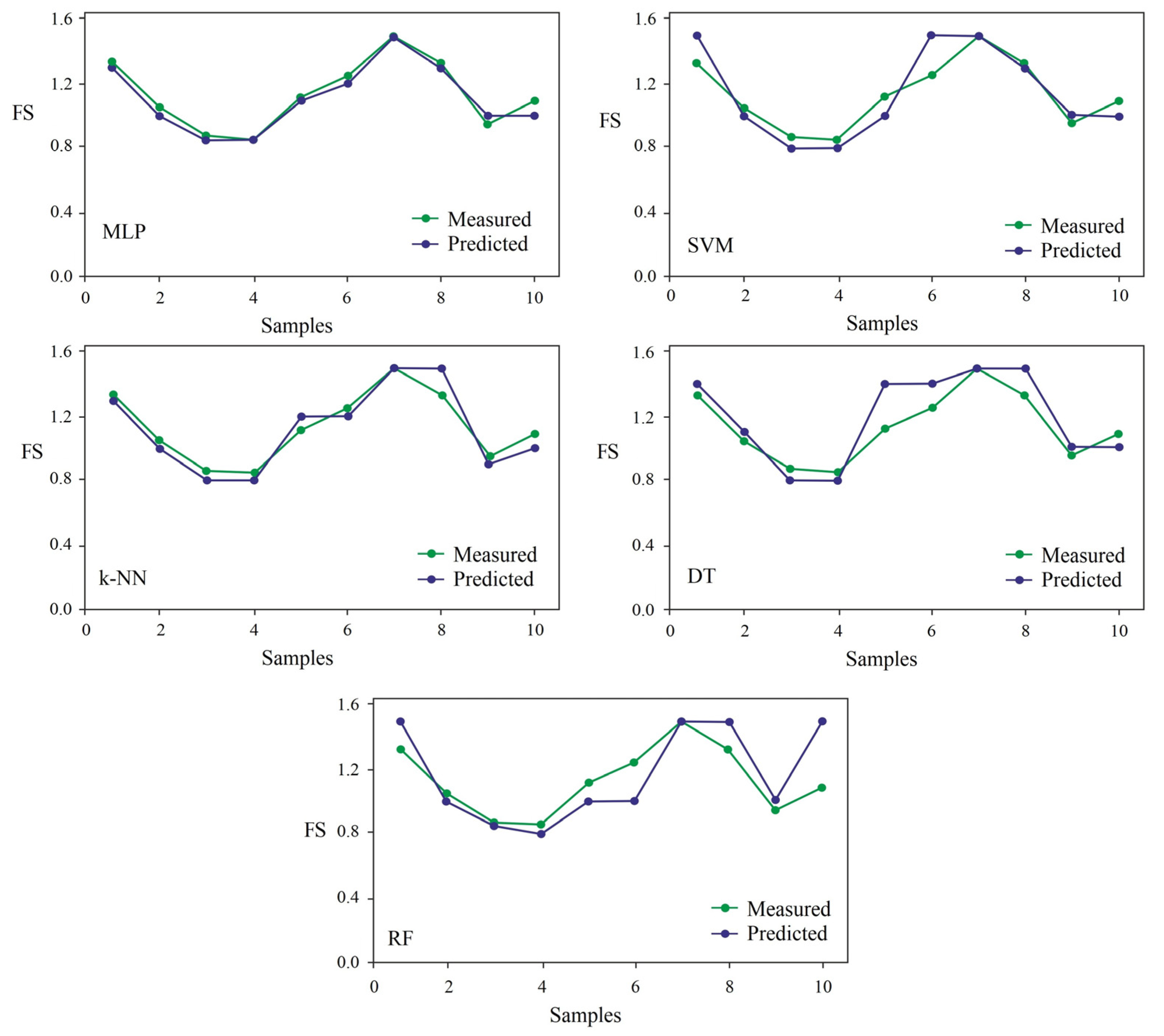

4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FS | Factor of safety | MLP | Multilayer perceptron |
| H | Slope height | SVM | Support vector machines |
| β | Slope angle | k-NN | k-nearest neighbors |
| γd | Dry density | DT | Decision tree |
| c | Cohesion | RF | Random forest |
| ϕ | Internal friction angle | TP | True positive |
| Su | Total cohesion | TN | True negative |
| Cu | Undrained cohesion | FP | False positive |
| Gs | Specific gravity | FN | False negative |
| R | Forces resultant vector | MSE | Mean squared error |
| W | Movable mass weight | MAE | Mean absolute error |
| c′ | Effective cohesion | RMSE | Root mean square error |
| ϕ′ | Effective friction angle |
References
- Azarafza, M.; Akgün, H.; Ghazifard, A.; Asghari-Kaljahi, E.; Rahnamarad, J.; Derakhshani, R. Discontinuous rock slope stability analysis by limit equilibrium approaches—A review. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1918–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarafza, M.; Hajialilue Bonab, M.; Derakhshani, R. A novel empirical classification method for weak rock slope stability analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H. Slope Stability Analysis by the Limit Equilibrium Method; ASCE Publications: Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Abramson, L.W.; Lee, T.S.; Sharma, S.; Boyce, G.M. Slope Stability Concepts: Slope Stabilisation and Stabilisation Methods, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Millburn, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Azarafza, M.; Nikoobakht, S.; Asghari-Kaljahi, E.; Moshrefy-Far, M.R. Stability analysis of jointed rock slopes using block theory (case study: Gas flare site in phase 7 of South Pars Gas Complex). In Proceedings of the 32th National & 1st International Geosciences Congress of Iran, Tehran, Iran, 3–4 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Agam, M.W.; Hashim, M.H.M.; Murad, M.I.; Zabidi, H. Slope Sensitivity Analysis Using Spencer’s Method in Comparison with General Limit Equilibrium Method. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alejano, L.; Ferrero, A.M.; Ramírez-Oyanguren, P.; Álvarez Fernández, M.I. Comparison of Limit-Equilibrium, Numerical and Physical Models of Wall Slope Stability. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Goswami, D. State of the art: Three dimensional (3D) slope-stability analysis. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 10, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromhead, E. The Stability of Slopes; Spon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mafi, R.; Javankhoshdel, S.; Cami, B.; Jamshidi Chenari, R.; Gandomi, A.H. Surface altering optimisation in slope stability analysis with non-circular failure for random limit equilibrium method. Georisk Ass. Manag. Risk Eng. Sys. Geohaz. 2021, 15, 260–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mi, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, F. A Simplified Method for 3D Slope Stability Analysis. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.M. A limit equilibrium method of slope stability analysis. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Landslides, Lausanne, Switzerland, 10–15 July 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D. Limit Equilibrium Solution for the Rock Slope Stability under the Coupling Effect of the Shear Dilatancy and Strain Softening. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 134, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniyaz, A.; Azmoon, B.; Liu, Z. Coupled transient saturated–unsaturated seepage and limit equilibrium analysis for slopes: Influence of rapid water level changes. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 2139–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, E.; Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Shi, X.; Yao, S.; Mitri, H.S. Slope Stability Prediction for Circular Mode Failure Using Gradient Boosting Machine Approach Based on an Updated Database of Case Histories. Saf. Sci. 2019, 118, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, J. Performance Evaluation of HybridWoa-Svr and Hho-Svr Models with Various Kernels to Predict Factor of Safety for Circular Failure Slope. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Tang, X. Slope stability prediction using integrated metaheuristic and machine learning approaches: A comparative study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 118, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Hou, Y.; Wan, B.; An, N.; Yan, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D. Performance Evaluation and Engineering Verification of Machine Learning Based Prediction Models for Slope Stability. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, M.; Ju, Z. Preliminary discussion regarding SVM kernel function selection in the twofold rock slope prediction model. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2015, 30, 04015031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Goswami, D. Prediction of slope stability using multiple linear regression (MLR) and artificial neural network (ANN). Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagan, J.; Meghana, G.; Samui, P. Determination of stability number of layered slope using ANFIS, GPR, RVM and ELM. Int. J. Comput. Res. 2016, 23, 371. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, D.T.; Moayedi, H.; Gör, M.; Jaafari, A.; Foong, L.K. Predicting slope stability failure through machine learning paradigms. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inform. 2019, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardhan, A.; Samui, P. Probabilistic slope stability analysis of Heavy-haul freight corridor using a hybrid machine learning paradigm. Transport. Geotech. 2022, 37, 100815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karir, D.; Ray, A.; Bharati, A.K.; Chaturvedi, U.; Rai, R.; Khandelwal, M. Stability prediction of a natural and man-made slope using various machine learning algorithms. Transport. Geotech. 2022, 34, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.; Che Mamat, R.; Abdul Rasam, A.R.; Ramli, A.; Samad, A. Artificial intelligence application for predicting slope stability on soft ground: A comparative study. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Explor. 2021, 8, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2166; Standard Test Method for Unconfined Compressive Strength of Cohesive Soil. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006.
- ASTM D3080; Standard Test Method for Direct Shear Test of Soils under Consolidated Drained Conditions. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Zhou, J.; Qin, C. A Novel Procedure for 3D Slope Stability Analysis: Lower Bound Limit Analysis Coupled with Block Element Method. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 1815–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarafza, M.; Asghari-Kaljahi, E.; Akgün, H. Assessment of Discontinuous Rock Slope Stability with Block Theory and Numerical Modeling: A Case Study for the South Pars Gas Complex, Assalouyeh, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.Y.; Lee, C.F.; Jiang, H.D. Generalised Framework of Limit Equilibrium Methods for Slope Stability Analysis. Geotechnique 2003, 53, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, L.; Fredlund, L. A General Limit Equilibrium Model for Three-Dimensional Slope Stability Analysis. Can. Geotech. J. 1993, 30, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.C.; Guido, S. Introduction to Machine Learning with Python: A Guide for Data Scientists; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning: A Textbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Zheng, H.; Han, B.; Li, Y.; Han, C.; Li, W. Comparative performance of eight ensemble learning approaches for the development of models of slope stability prediction. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 1477–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayedi, H.; Bui, D.T.; Kalantar, B.; Kok Foong, L. Machine-learning-based classification approaches toward recognizing slope stability failure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Zheng, H.; Han, C.; Han, B.; Li, W. Evaluation and prediction of slope stability using machine learning approaches. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2021, 15, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocscience Inc. Slide Geotechnical Software. Available online: https://www.rocscience.com/software/slide2 (accessed on 1 August 2022).
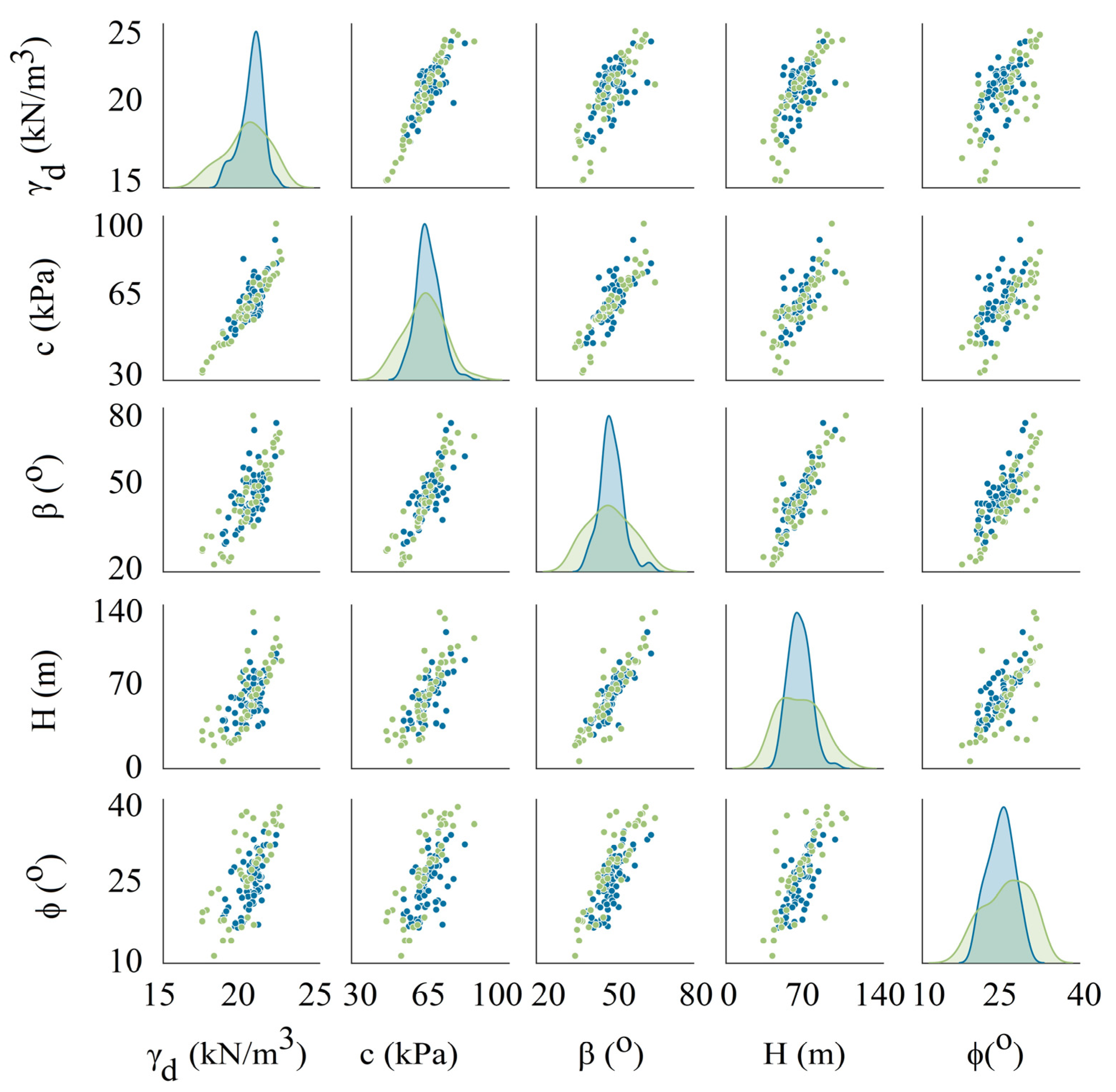
| Parameter | Unit | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water content | % | 6.22 | 1.73 | 3.97 | 2.24 |
| Specific gravity (Gs) | - | 2.85 | 2.49 | 2.67 | 0.16 |
| γd | kN/m3 | 18.99 | 18.69 | 18.84 | 0.18 |
| Slope height | m | 135 | 12 | 73.5 | 50.21 |
| Slope angle | Degree | 77 | 43 | 60 | 13.88 |
| Cohesion (c) | kPa | 97 | 39 | 68 | 23.9 |
| Friction (φ) | Degree | 35 | 20 | 27.5 | 7.51 |
| Classifier | Hyperparameters | Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Multilayer perceptron (MLP) | Hidden layers’ size Learning rate Optimization | Activation = ‘relu’; Optimization = ‘rmsprop’; Loss_function = ‘mse’; Metrics = ‘mae’ |
| Support vector machines (SVM) | Kernels C value | Kernel = ‘poly’; Degree = 2 C = 100; Epsilon = 0.1 |
| K-nearest neighbors (k-NN) | Number of neighbors | n_Neighbors = 3 |
| Decision tree (DT) | Max depth Random state | Criterion = ‘Gini’; Max_depth = 5 Ccp_alpha = 0.0; Min_samples_leaf = 1 Random_state = 100 |
| Random forest (RF) | Number of estimators Max depth | Criterion = ‘entropy’; N_estimators = 10; Max_depth = 5; Min_samples_leaf = 1; Min_sanmples_split = 2 |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity (Gs) | - | 2.63 |
| γd | kN/m3 | 20.00 |
| Slope height (H) | m | 14.5 |
| Slope angle (β) | Degree | 65 |
| Cohesion (c) | kPa | 125 |
| Friction (φ) | Degree | 35 |
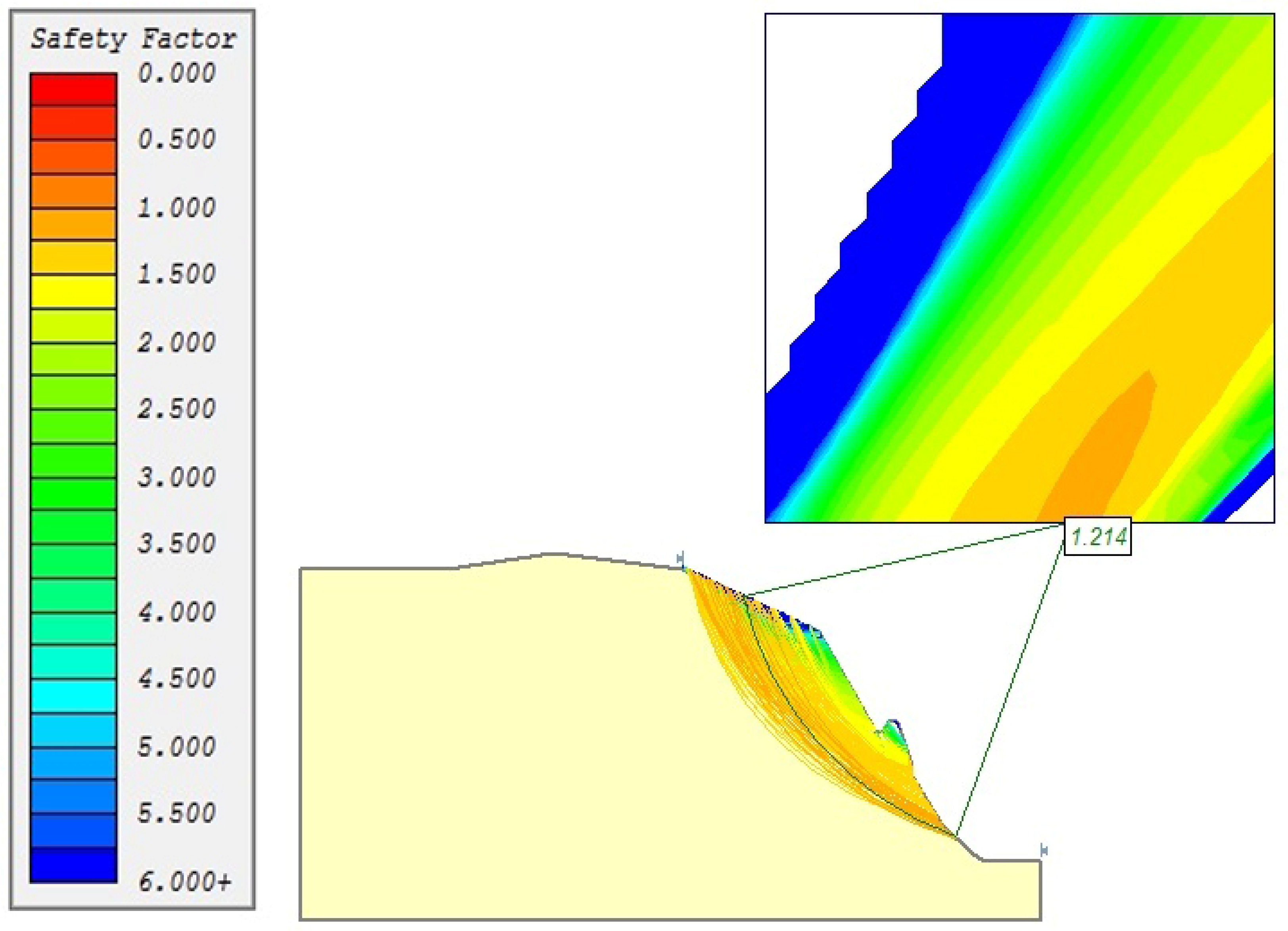
| No. | Analysis Method | Estimated FS |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MLP | 1.18 |
| 2 | SVM | 1.1 |
| 3 | DT | 1.1 |
| 4 | RF | 1.4 |
| 5 | SLIDE | 1.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahangari Nanehkaran, Y.; Pusatli, T.; Chengyong, J.; Chen, J.; Cemiloglu, A.; Azarafza, M.; Derakhshani, R. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for the Estimation of the Safety Factor in Slope Stability Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223743
Ahangari Nanehkaran Y, Pusatli T, Chengyong J, Chen J, Cemiloglu A, Azarafza M, Derakhshani R. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for the Estimation of the Safety Factor in Slope Stability Analysis. Water. 2022; 14(22):3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223743
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhangari Nanehkaran, Yaser, Tolga Pusatli, Jin Chengyong, Junde Chen, Ahmed Cemiloglu, Mohammad Azarafza, and Reza Derakhshani. 2022. "Application of Machine Learning Techniques for the Estimation of the Safety Factor in Slope Stability Analysis" Water 14, no. 22: 3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223743
APA StyleAhangari Nanehkaran, Y., Pusatli, T., Chengyong, J., Chen, J., Cemiloglu, A., Azarafza, M., & Derakhshani, R. (2022). Application of Machine Learning Techniques for the Estimation of the Safety Factor in Slope Stability Analysis. Water, 14(22), 3743. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223743











