Assessment of Acute and Short-Term Developmental Toxicity of Mercury Chloride to Rare Minnow (Gobiocypris rarus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Test Chemicals and Animals
2.2. Acute Toxicity Assays of Hg2+ to Rare Minnow
2.3. Short-Term Toxicity Test of Hg2+ on Rare Minnow at Embryo and Sac-Fry Stages
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters of the Test Solutions
3.2. Acute Toxicity of Hg2+ to Rare Minnow
3.3. Sub-Chronic Toxicity of Hg2+ to Rare Minnow
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Okpala, C.O.R.; Sardo, G.; Vitale, S.; Bono, G.; Arukwe, A. Hazardous properties and toxicological update of mercury: From fish food to human health safety perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1986–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Nurchi, V.M.; Sahoo, S.K. Mercury toxicity and detection using chromo-fluorogenic chemosensors. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okereafor, U.; Makhatha, M.; Mekuto, L. Toxic Metal Implications on Agricultural Soils, Plants, Animals, Aquatic life and Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, S.; Wu, D.; Hua, X.; Li, Y.; Song, X.; Chu, Q.; Hou, S. The toxicological effects of mercury exposure in marine fish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Comparison of species sensitivity distributions for species from China and the USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrington, G.A.Y.; Grist, E.P.M.; Jeong, S.W.; Rattikansukha, C.; Roe, S.; Schneider, U.S.S.; Suter, G.W.; Van, D.R.; Van, S.P.; Wang, J.; et al. Water quality guidelines for chemicals: Learning lessons to deliver meaningful environmental metrics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciorowski, H.D.; Clarke, R. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Invertebrates in Toxicity Testing. Aquat. Invertebr. Bioassays 1980, 715, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Zeng, J.; Huang, W.; Xu, X.; Shou, L.; Chen, Q. Development of marine water quality criteria for inorganic mercury in China based on the retrievable toxicity data and a comparison with relevant criteria or guidelines. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallare, A.V.; Factor, P.A.; Santos, E.K.; Hollert, H. Assessing the impact of fish cage culture on taal lake (philippines) water and sediment quality using the zebrafish embryo assay. Philipp. J. Sci. 2009, 138, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, V.P.; Ventura, M.A.; Amarillo, P.B. Ecotoxicological assessment of water and sediment in areas of Taal Lake with heavy aquaculture practices using Allium cepa and Daphnia magna assay. Philipp. J. Sci. 2022, 151, 969–974. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, P. Mercury concentration and speciation in mine wastes in Tongren mercury mining area, southwest china and environmental effects. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 106, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadra, M.; Planas, D.; Brodeur, P.; Amyot, M. Mercury and selenium distribution in key tissues and early life stages of yellow perch (perca flavescens). Environ. Pollution. 2019, 254, 112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, L.I.; Zelikoff, J.T. Toxicology and immunotoxicology of mercury: A comparative review in fish and humans. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2001, 4, 161–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Abbott, L.C.; Moussa, E.A. The effect of mercury on the morphology of developing zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). J. Vet. Anat. 2017, 10, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Chen, C.Z.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Chai, Y.; Li, Z.H. Chronic toxic effects of waterborne Mercury on Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) Larvae. Water 2022, 14, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, S.B.; Reistad, N.A.; Rumbold, D.G. Mercury in neonatal and juvenile blacktip sharks (Carcharhinus limbatus). Part II: Effects assessment. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massányi, P.; Massányi, M.; Madeddu, R.; Stawarz, R.; Lukáč, N. Effects of cadmium, lead, and mercury on the structure and function of reproductive organs. Toxics 2020, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praskova, E.; Voslarova, E.; Siroka, Z.; Plhalova, L.; Macova, S.; Marsalek, P. Assessment of diclofenac LC50 reference values in juvenile and embryonic stages of the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Pang, S.; Sun, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Evaluation of acute and developmental effects of difenoconazole via multiple stage zebrafish assays. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Domingues, I.; Koppe Grisolia, C.; Soares, A.M. Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.Q.; Li, H.Y.; Qiu, N.; Su, L.X.; Huang, Z.L.; Song, L.R.; Wang, J.W. Bioconcentration and depuration of cadmium in the selected tissues of rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) and the effect of dietary mulberry leaf supplementation on depuration. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 73, 103278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Administration SEP. Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals China Environmental Science; Administration SEP: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, P.; Li, Y.F.; Ni, Z.H. Effects of mercury on oxidative stress and gene expression of potential biomarkers in larvae of the Chinese rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Wu, B.; Xiong, X.Q.; Wang, J.W. Short-term toxicity of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate to early life stages of the rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Wu, Z.F.; Li, J.; Wang, G.X. Single and joint action toxicity of heavy metals on early developmental stages of Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos-Muñoz, S.; Abad-Rosales, S.M.; Aguilar-Juárez, M.; Frías-Espericueta, M.G.; Voltolina, D. Acute toxicity of mercury and nervous tissue damage in postlarvae and juveniles of Litopenaeus vannamei. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 35, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, M.K.S.; Stultz, A.E.; Smith, A.W.; Stephens, D.A.; Rawlings, J.M.; Belanger, S.E.; Oris, J.T. The fish embryo toxicity test as a replacement for the larval growth and survival test: A comparison of test sensitivity and identification of alternative endpoints in zebrafish and fathead minnows. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, G.; Xiu, R. Toxicity of mercury, copper, nickel, lead, and cobalt to embryos and larvae of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 21, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boening, D.W. Ecological effects, transport, and fate of mercury: A general review. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 1335–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.B.; Wang, J.W.; Cao, W.X. The embryonic development of Gobiocypris rarus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1995, 19, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Cao, W.; Wang, J. The identification of metallothionein in rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) and its expression following heavy metal exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, T.H.; Solbe, J.; Kloepper-Sams, P.J. Analysis of the ecetoc aquatic toxicity (EAT) database III—comparative toxicity of chemical substances to different life stages of aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cao, L.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Dou, S. Short-term mercury exposure affecting the development and antioxidant biomarkers of Japanese flounder embryos and larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Li, Y.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, Q.L. Exposure to mercuric chloride induces developmental damage, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in zebrafish embryos-larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 181, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezierska, B.; Ługowska, K.; Witeska, M. The effects of heavy metals on embryonic development of fish (a review). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Wei, L.; Jingfeng, Y.; Chernick, M.; Hinton, D.E. Developmental toxicity from exposure to various forms of mercury compounds in medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) embryos. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Test | Stages | Temperature (°C) | pH | DO (mg/L) | Nominal Hg2+(mg/L) | Measured Hg2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute toxicity assays | Embryo | 24.84 ± 0.36 | 7.58 ± 0.36 | 7.52 ± 1.26 | Control | ND |
| 24.78 ± 0.42 | 7.62 ± 0.42 | 7.49 ± 1.64 | 0.20 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | ||
| 24.63 ± 0.55 | 7.68 ± 0.29 | 7.63 ± 1.79 | 0.40 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | ||
| 24.47 ± 0.54 | 7.69 ± 0.66 | 7.58 ± 1.26 | 0.60 | 0.56 ± 0.03 | ||
| 25.03 ± 0.32 | 7.70 ± 0.48 | 7.69 ± 1.39 | 0.80 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | ||
| Newly hatched larvae | 24.62 ± 0.47 | 7.72 ± 0.42 | 7.74 ± 1.62 | Control | ND | |
| 24.83 ± 0.36 | 7.63 ± 0.38 | 7.66 ± 1.37 | 0.08 | 0.07 ± 0.003 | ||
| 25.02 ± 0.28 | 7.58 ± 0.52 | 7.70 ± 1.68 | 0.10 | 0.09 ± 0.004 | ||
| 24.75 ± 0.37 | 7.66 ± 0.46 | 7.71 ± 1.46 | 0.12 | 0.10 ± 0.007 | ||
| 24.66 ± 0.58 | 7.57 ± 0.62 | 7.68 ± 1.08 | 0.14 | 0.12 ± 0.015 | ||
| Juvenile fish | 25.03 ± 0.47 | 7.61 ± 0.41 | 7.72 ± 1.28 | Control | ND | |
| 24.86 ± 0.39 | 7.58 ± 0.50 | 7.66 ± 1.48 | 0.09 | 0.084 ± 0.003 | ||
| 24.79 ± 0.46 | 7.62 ± 0.47 | 7.70 ± 1.38 | 0.10 | 0.092 ± 0.003 | ||
| 24.82 ± 0.53 | 7.60 ± 0.42 | 7.73 ± 1.06 | 0.11 | 0.101 ± 0.007 | ||
| 25.12 ± 0.37 | 7.56 ± 0.64 | 7.63 ± 1.20 | 0.12 | 0.105 ± 0.007 | ||
| Sub-chronic toxicity tests | Embryo and sac-fry | 25.03 ± 0.67 | 7.62 ± 0.39 | 7.64 ± 1.66 | Control | ND |
| 24.78 ± 0.53 | 7.59 ± 0.42 | 7.70 ± 1.78 | 0.001 | 0.0009 ± 0.0001 | ||
| 25.16 ± 0.48 | 7.60 ± 0.53 | 7.72 ± 1.16 | 0.005 | 0.0046 ± 0.0002 | ||
| 24.84 ± 0.39 | 7.58 ± 0.47 | 7.69 ± 1.25 | 0.01 | 0.093 ± 0.003 | ||
| 24.76 ± 0.47 | 7.61 ± 0.36 | 7.71 ± 1.62 | 0.05 | 0.043 ± 0.002 | ||
| 25.18 ± 0.52 | 7.59 ± 0.44 | 7.74 ± 1.58 | 0.1 | 0.092 ± 0.003 |
| Stages | Time (h) | LC50 (mg/L) | 95% Confidence Limit (mg/L) | Regression Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embryos | 24 | 0.86 | 0.75–1.05 | Y = −1.88 + 2.18X |
| 48 | 0.83 | 0.72–1.00 | Y = −1.77 + 2.13X | |
| 72 | 0.72 | 0.64–0.84 | Y = −1.67 + 2.30X | |
| 96 | 0.56 | 0.51–0.62 | Y = −1.82 + 3.25X | |
| Newly hatched larvae | 24 | 0.16 | 0.14–0.22 | Y = −3.36 + 21.42X |
| 48 | 0.12 | 0.11–0.15 | Y = −2.13 + 17.18X | |
| 72 | 0.10 | 0.08–0.11 | Y = −1.65 + 17.36X | |
| 96 | 0.07 | 0.06–0.08 | Y = −1.90 + 25.97X | |
| Juvenile fish | 24 | 0.14 | 0.12–0.31 | Y = −3.71 + 27.07X |
| 48 | 0.12 | 0.11–0.15 | Y = −4.02 + 33.17X | |
| 72 | 0.11 | 0.11–0.13 | Y = −2.19 + 18.50X | |
| 96 | 0.10 | 0.09–0.11 | Y = −2.16 + 21.63X |
| Concentration (mg/L) | Time (hpf) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 | 120 | 144 | 168 | |
| 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| 0.001 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 1.67 ± 2.89 | 3.33 ± 2.89 | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| 0.005 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 1.67 ± 2.89 | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 5.00 ± 0.00 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| 0.01 | 3.33 ± 2.89 | 3.33 ± 2.89 | 5.00 ± 5.00 | 6.67 ± 3.33 | 6.67 ± 3.33 | 10.00 ± 5.00 | 10.00 ± 5.00 |
| 0.05 | 3.33 ± 2.89 | 3.33 ± 2.89 | 3.33 ± 2.89 | 8.33 ± 5.77 * | 10.00 ± 8.66 * | 16.67 ± 7.64 * | 20.00 ± 13.23 * |
| 0.10 | 3.33 ± 2.89 | 5.00 ± 5.00 | 51.67 ± 12.58 * | 88.33 ± 2.89 * | 98.33 ± 2.89 * | 100.00 ± 0.00 * | 100.00 ± 0.00 * |
| Concentration (mg/L) | Time (hpf) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 72 | 84 | 96 | |
| 0.00 | 3.33 ± 5.77 | 63.33 ± 7.64 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| 0.001 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 80.00 ± 10.00 | 98.33 ± 2.89 |
| 0.005 | 5.00 ± 5.00 | 60.00 ± 8.66 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| 0.01 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 63.33 ± 7.56 | 93.33 ± 7.64 |
| 0.05 | 5.00 ± 5.00 | 88.33 ± 10.41 | 93.33 ± 7.64 |
| 0.10 | 16.67 ± 10.41 * | 21.67 ± 10.41 * | 23.33 ± 7.64 * |
| Endpoints | LOEC (mg/L) | NOEC (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
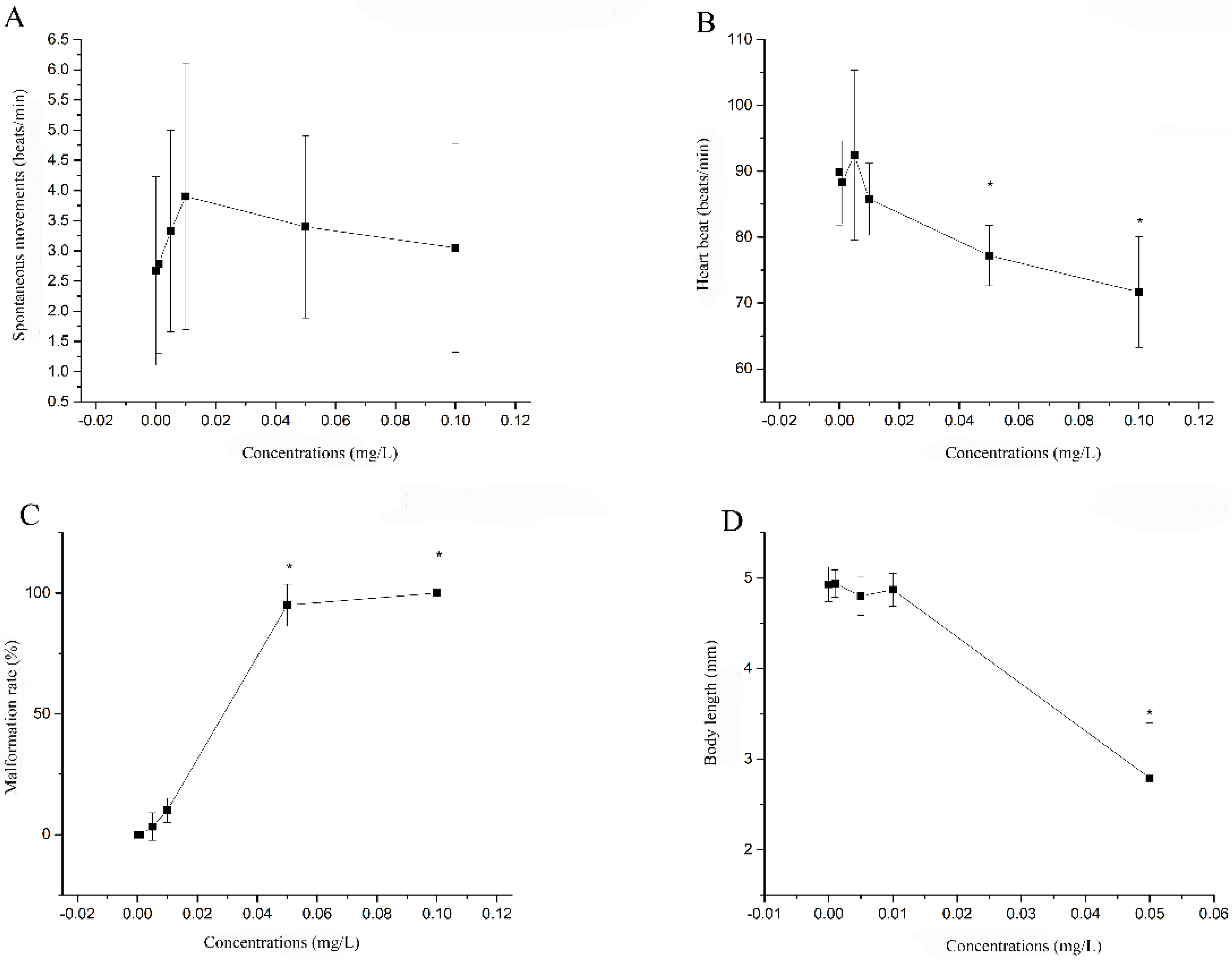
| Spontaneous movements (36 hpf) | >0.1 | >0.1 |
| Hatching rate (96 hpf) | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| Heartbeat (48 hpf) | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Mortality (96 hpf) | 0.05 | 0.01 |
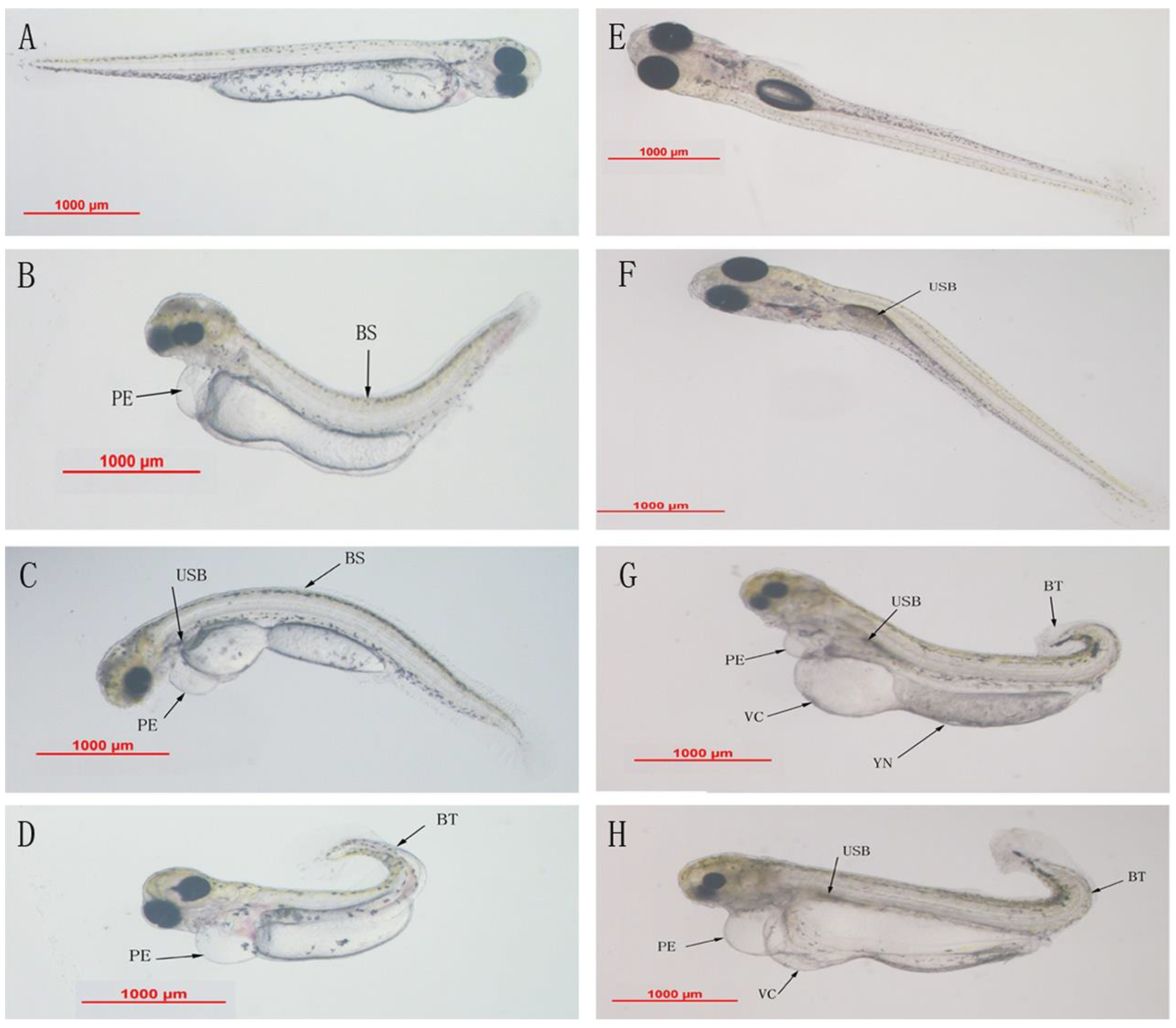
| Malformation rate (96 hpf) | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Body length | 0.05 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, X.; Shi, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; Hu, P.; Wen, Z.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Assessment of Acute and Short-Term Developmental Toxicity of Mercury Chloride to Rare Minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Water 2022, 14, 2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182825
Xiong X, Shi Q, Liu H, Zhou Q, Li H, Hu P, Wen Z, Wang J, Zou Y, Zeng Y, et al. Assessment of Acute and Short-Term Developmental Toxicity of Mercury Chloride to Rare Minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Water. 2022; 14(18):2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182825
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Xiaoqin, Qingchao Shi, Hao Liu, Qian Zhou, Huatao Li, Peng Hu, Zhengyong Wen, Jianwei Wang, Yuanchao Zou, Yu Zeng, and et al. 2022. "Assessment of Acute and Short-Term Developmental Toxicity of Mercury Chloride to Rare Minnow (Gobiocypris rarus)" Water 14, no. 18: 2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182825
APA StyleXiong, X., Shi, Q., Liu, H., Zhou, Q., Li, H., Hu, P., Wen, Z., Wang, J., Zou, Y., Zeng, Y., & Hao, Y. (2022). Assessment of Acute and Short-Term Developmental Toxicity of Mercury Chloride to Rare Minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Water, 14(18), 2825. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182825






