A Quantitative Evaluation Method for Xanthan Enhanced Transport Uniformity and Factors Affecting This Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Xanthan Gum Solution
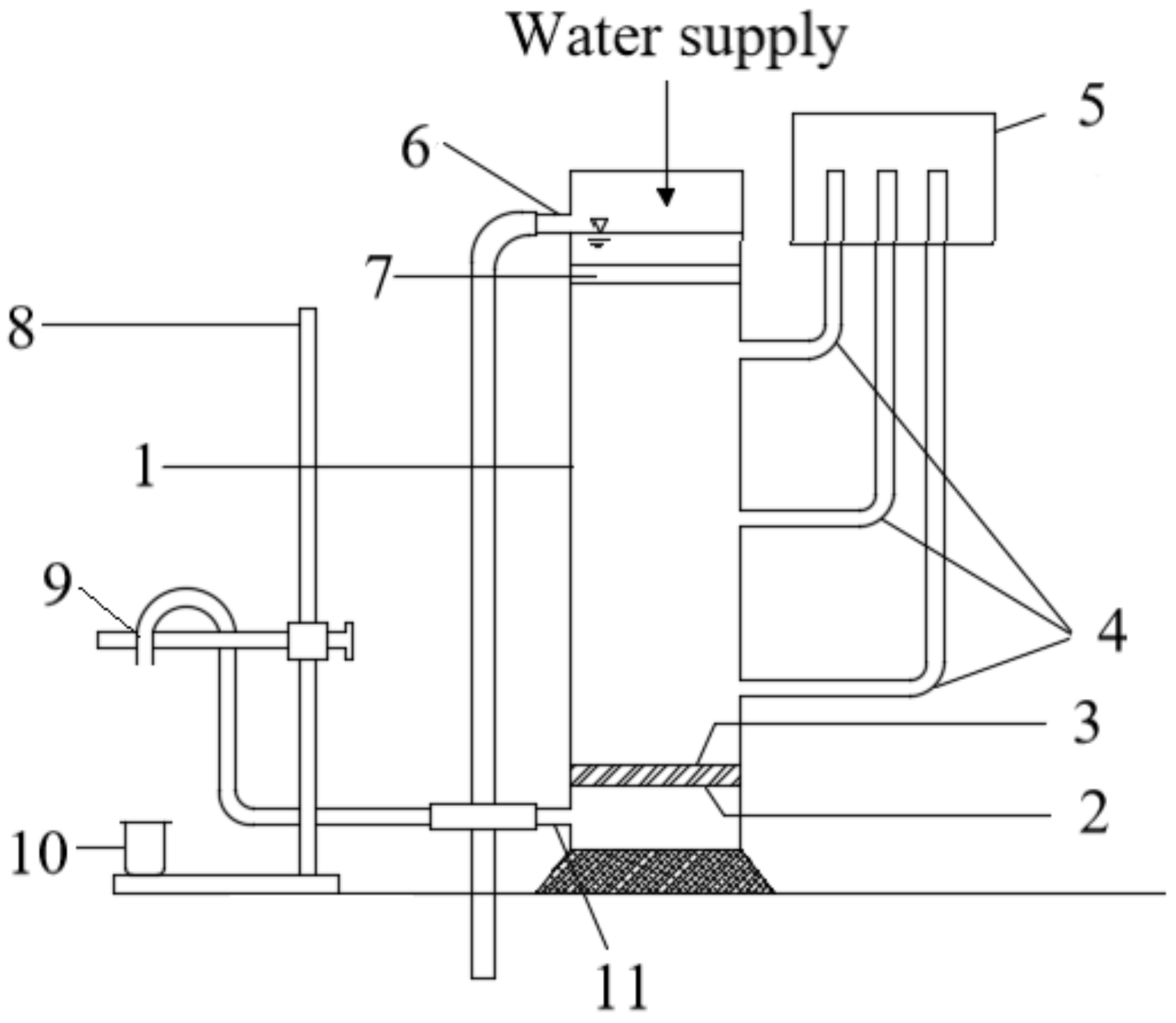
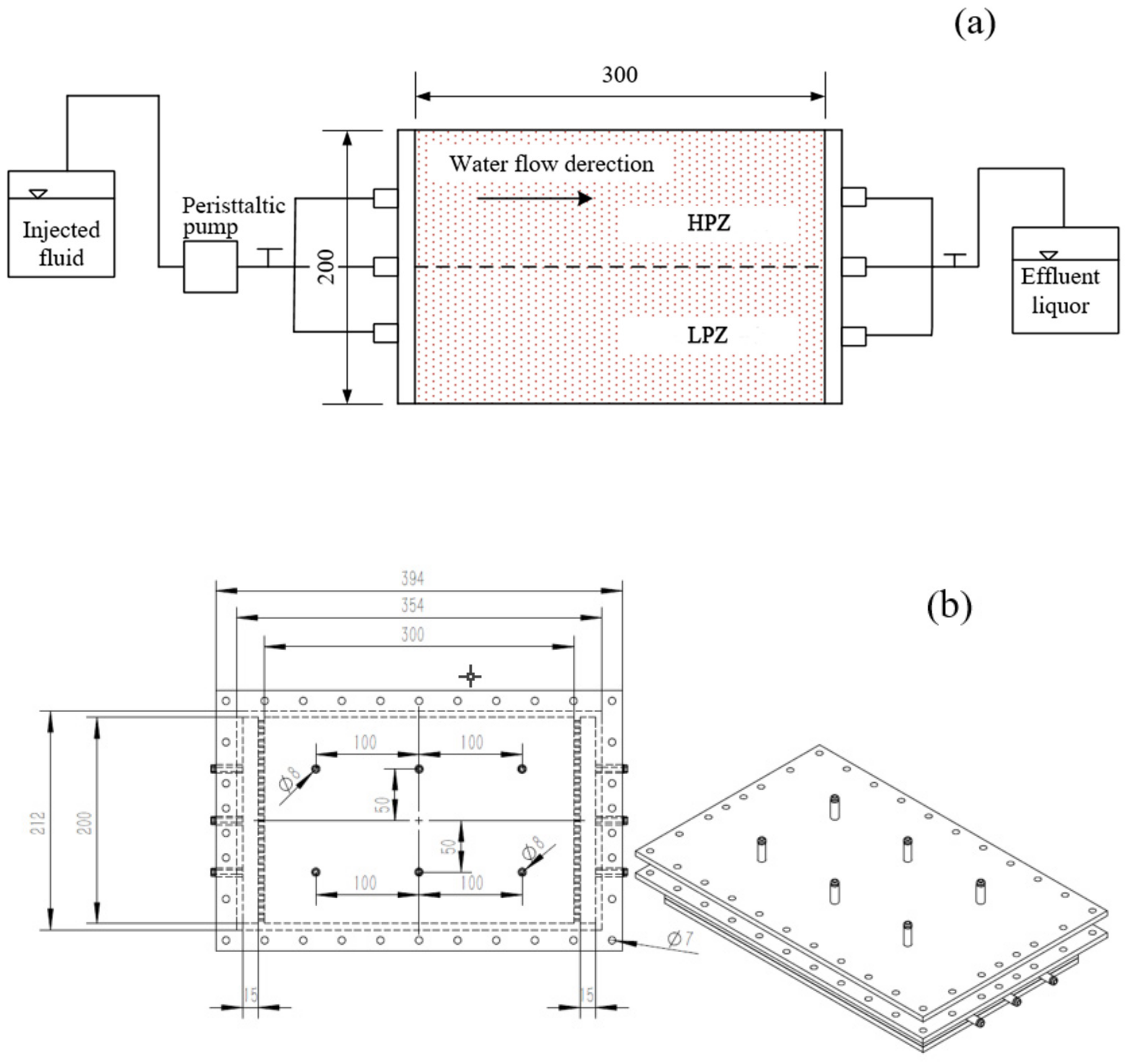
2.2. Experimental Equipment and Process
2.2.1. One-Dimensional Column Experiment
2.2.2. Two-Dimensional Cell Experiment
2.3. Characterization of Transmission Uniformity
3. Results
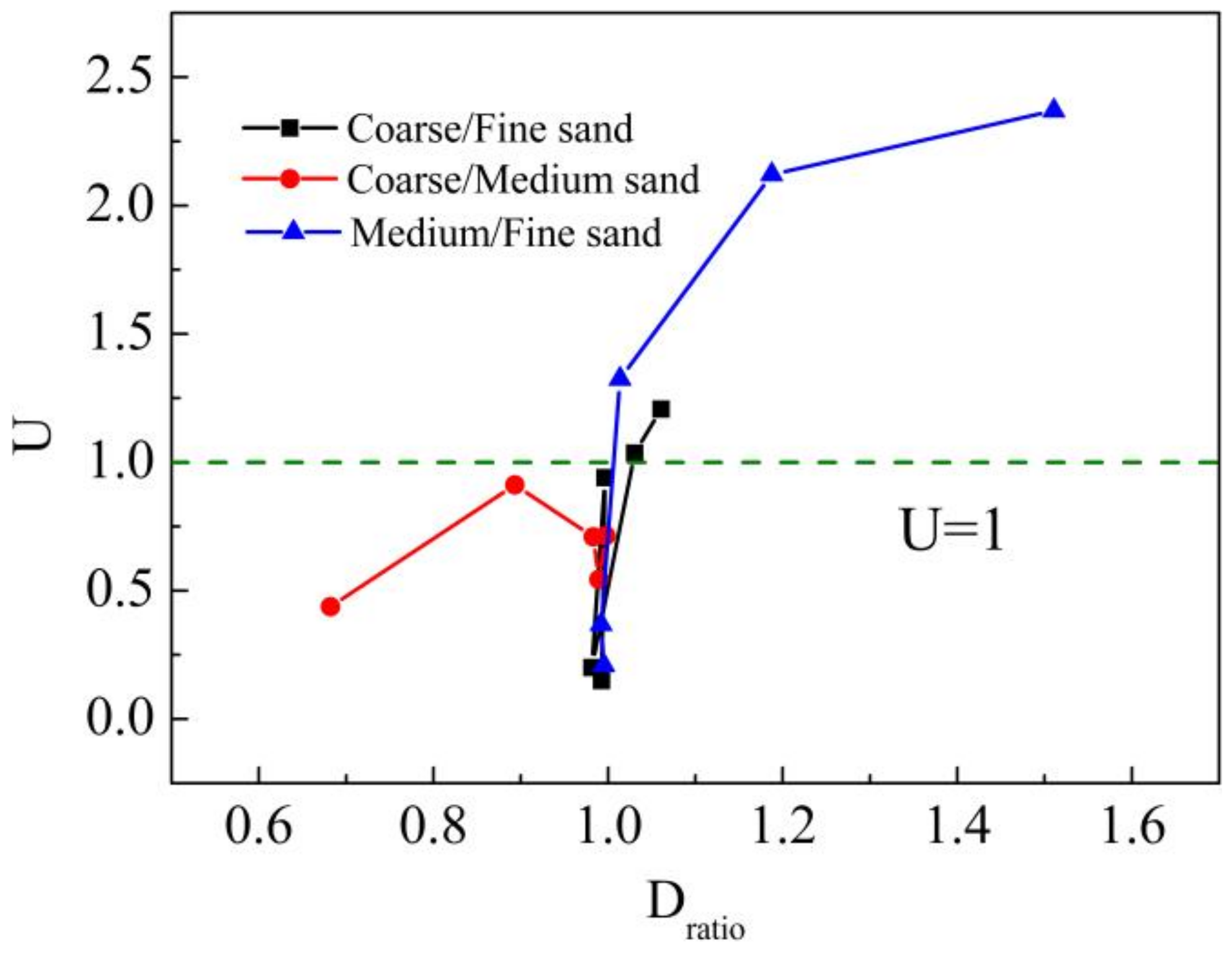
3.1. Factors Influencing U
3.1.1. Permeability Contrast
3.1.2. Polymer Concentration
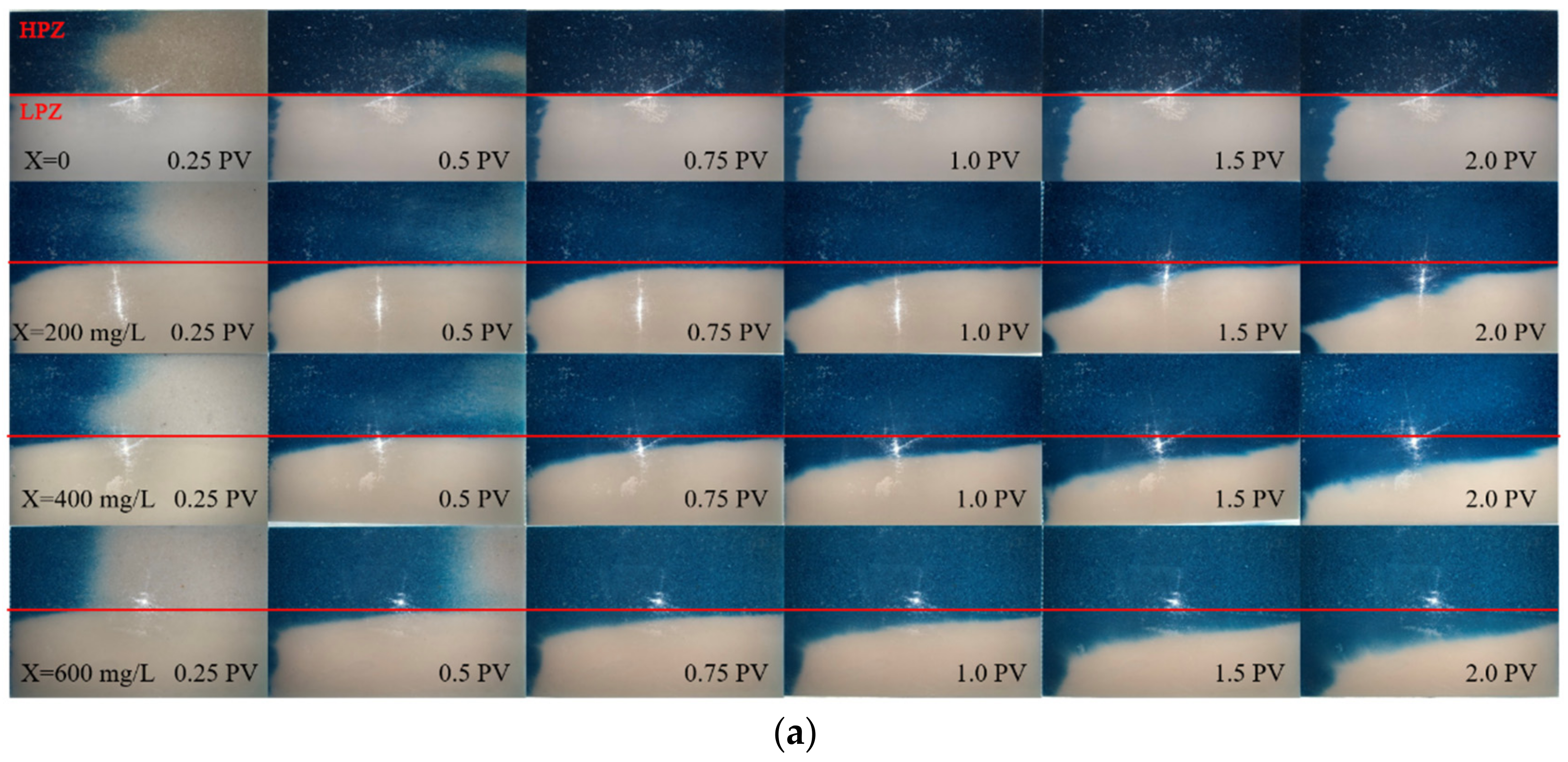
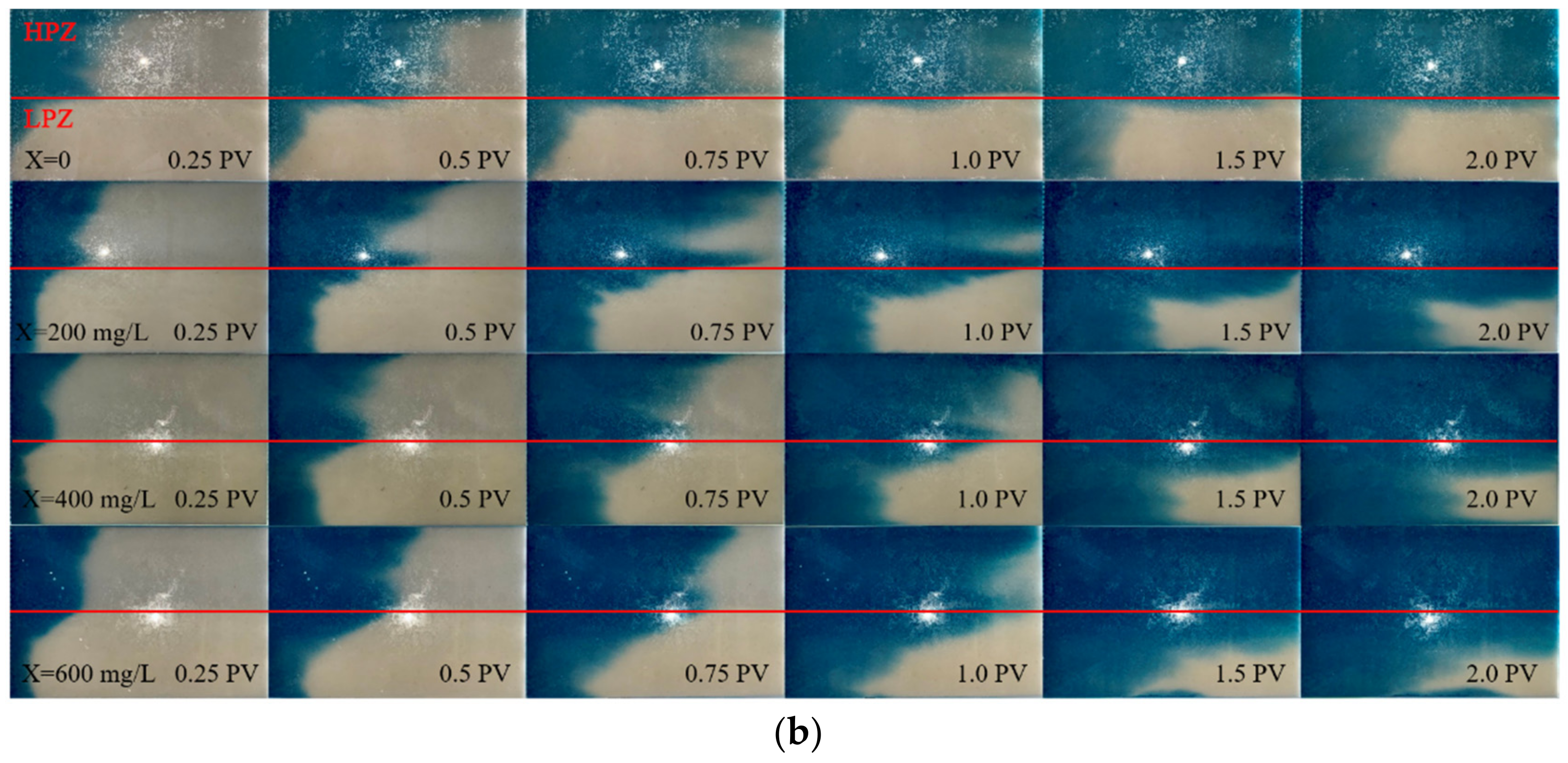
3.2. Polymer Transport in Heterogeneous Media
3.3. Migration of Xanthan Gum
4. Discussion
4.1. Permeability Reduction
4.2. Hydraulic Conductivity Decrease
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The transmission uniformity control coefficient is affected by both hydraulic conductivity changes and permeability changes. The characterization method, which uses the U express transmission uniformity control coefficient, is shown to be reasonable and effective based on experimental results.
- (2)
- The permeability contrast and polymer concentration influence the transmission uniformity in heterogeneous media. Xanthan solution is more easily uniformly transmitted in heterogeneous media with a smaller permeability contrast.
- (3)
- The adsorption of polymers on the surface of porous media affects the permeability of the media. When the viscosity of polymer is too large, blockage can easily occur in the LPZ, which is not conducive to uniform transmission, thus influencing the degree of U.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Symbol | Implication |
| K (cm/s) | Hydraulic conductivity |
| Rcfw | Ratio of hydraulic conductivity of coarse sand to that of fine sand for water |
| Rmfw | Ratio of hydraulic conductivity of medium sand to that of fine sand for water |
| Rcmw | Ratio of hydraulic conductivity of coarse sand to that of medium sand for water |
| Rcfp | Ratio of hydraulic conductivity of coarse sand to that of fine sand for polymer solution |
| Rmfp | Ratio of hydraulic conductivity of medium sand to that of fine sand for polymer solution |
| Rcmp | Ratio of hydraulic conductivity of coarse sand to that of medium sand for polymer solution |
| Ucf | Transmission uniformity control coefficient of coarse sand/ fine sand heterogeneous media. |
| Umf | Transmission uniformity control coefficient of medium sand/ fine sand heterogeneous media. |
| Ucm | Transmission uniformity control coefficient of coarse sand/medium sand heterogeneous media. |
References
- Krembs, F.J.; Siegrist, R.L.; Crimi, M.L.; Furrer, R.F.; Petri, B.G. ISCO for Groundwater Remediation: Analysis of Field Applications and Performance. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2010, 30, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, B.X. The co-effect of heterogeneity and solute concentration on representative elementary volume of DNAPL in groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A.; Smith, M.M.; Munakata-Marr, J.; McCray, J.E. The effect of system variables on in situ sweep-efficiency improvements via viscosity modification. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 136–137, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.M.; Silva, J.A.; Munakata-Marr, J.; McCray, J.E. Using Polymer Floods to Overcome Heterogeneity Effects during Bioremediation and Chemical Oxidation Ground Water Treatments. Ground Water Summit. 2008. Available online: https://ngwa.confex.com/ngwa/2008gws/techprogram/P5026.HTM (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Jackson, R.E.; Dwarakanath, V.; Meinardus, H.W.; Young, C.M. Mobility control: How injected surfactants and biostimulants may be forced into low-permeability unit. Remediat. J. 2003, 13, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algharaib, M.; Alajmi, A.; Gharbi, R. Improving polymer flood performance in high salinity reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 115, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokejaroenrat, C.; Kananizadeh, N.; Sakulthaew, C.; Comfort, S.; Li, Y. Improving the Sweeping Efficiency of Permanganate into Low Permeable Zones To Treat TCE: Experimental Results and Model Development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13031–13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCray, J.E.; Munakata-Marr, J.; Silva, J.A.; Davenport, S.; Smith, M.M. Multi-Scale Experiments to Evaluate Mobility Control Methods for Enhancing the Sweep Efficiency of Injected Subsurface Remediation Amendments; Colorado School of Mines Golden: Golden, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, R.; Hébert, A.; Lefebvre, R.; Gélinas, P.; Gabriel, U. Displacement and sweep efficiencies in a DNAPL recovery test using micellar and polymer solutions injected in a five-spot pattern. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 75, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Chen, J.J.; Wei, M.; Shi, L.X. Improving the Sweeping Efficiency of Amendment by Using Polymer. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 744, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truex, M.J.; Vermeul, V.R.; Adamson, D.T.; Oostrom, M.; Zhong, L.; Mackley, R.D.; Fritz, B.G.; Horner, J.A.; Johnson, T.C.; Thomle, J.N.; et al. Field Test of Enhanced Remedial Amendment Delivery Using a Shear-Thinning Fluid. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2015, 35, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.M.; Silva, J.A.; Munakata-Marr, J.; McCray, J.E. Compatibility of Polymers and Chemical Oxidants for Enhanced Groundwater Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9296–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcıa-Ochoa, F.; Santos, V.E.; Casas, J.A.; Gómez, E. Xanthan gum: Production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 549–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokejaroenrat, C.; Comfort, S.; Sakulthaew, C.; Dvorak, B. Improving the treatment of non-aqueous phase TCE in low permeability zones with permanganate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.A.; Crimi, M.; Palaia, T.; Ko, S.; Davenport, S. Field demonstration of polymer-amended in situ chemical oxidation (PA-ISCO). J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 199, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Szecsody, J.; Oostrom, M.; Truex, M.; Shen, X.; Li, X. Enhanced remedial amendment delivery to subsurface using shear thinning fluid and aqueous foam. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 191, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.A.; Liberatore, M.; McCray, J.E. Characterization of Bulk Fluid and Transport Properties for Simulating Polymer-Improved Aquifer Remediation. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, L.; Thomson, N. Laboratory-scale in situ chemical oxidation of a perchloroethylene pool using permanganate. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2002, 56, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Oostrom, M.; Wietsma, T.; Covert, M. Covert, Enhanced remedial amendment delivery through fluid viscosity modifications: Experiments and numerical simulations. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2008, 101, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Fu, Y.; Guo, C.; He, Y.; Qin, C. Performance of polymer-enhanced KMnO4 delivery for remediation of TCE contaminated heterogeneous aquifer: A bench-scale visualization. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 225, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
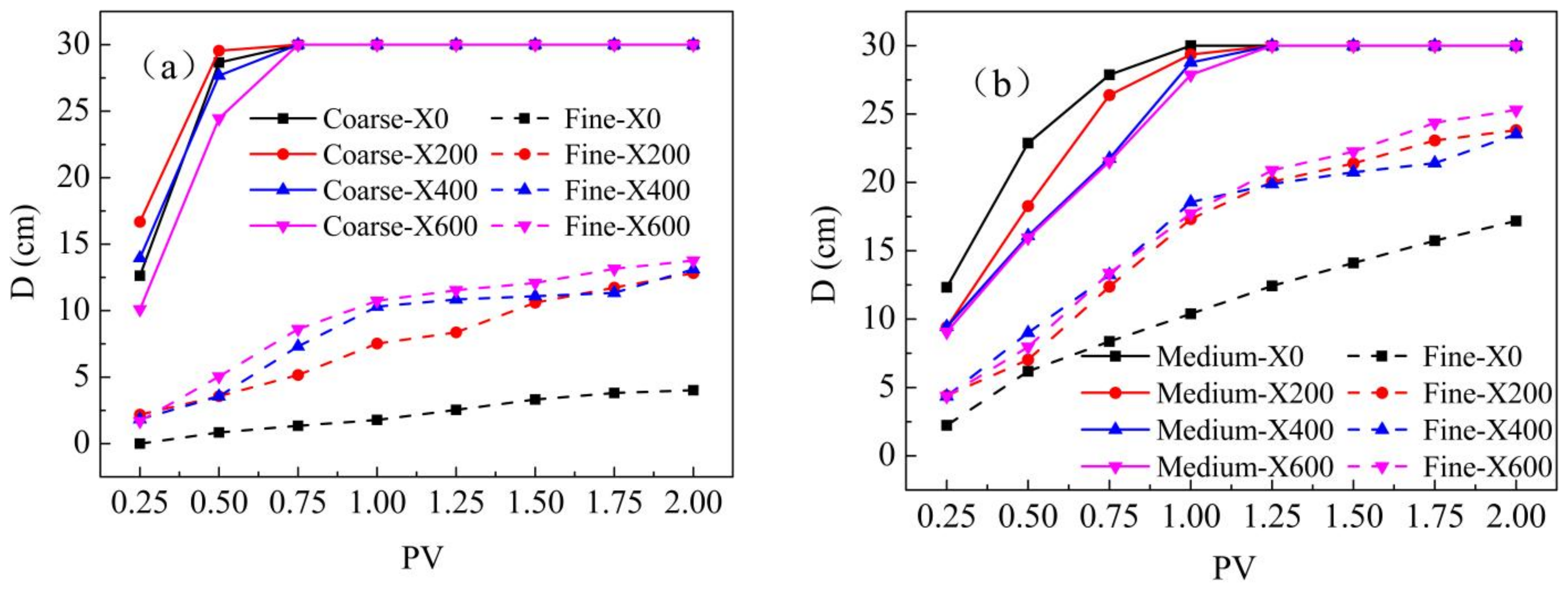
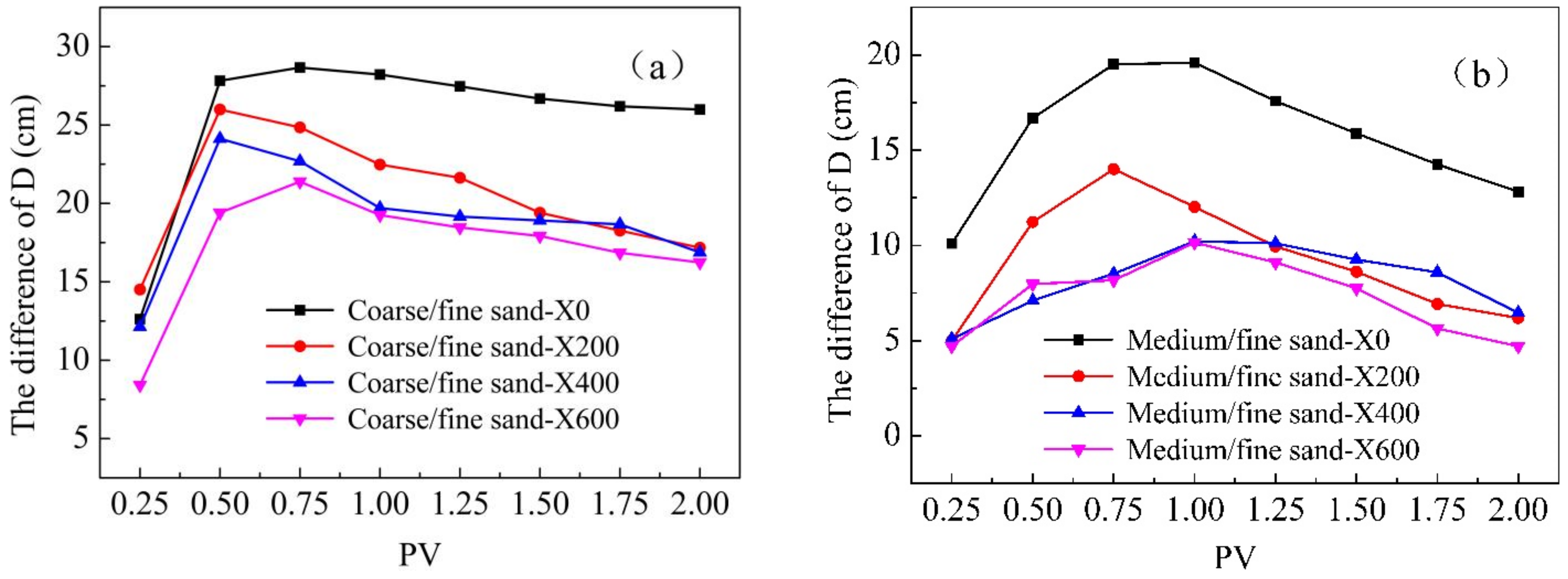
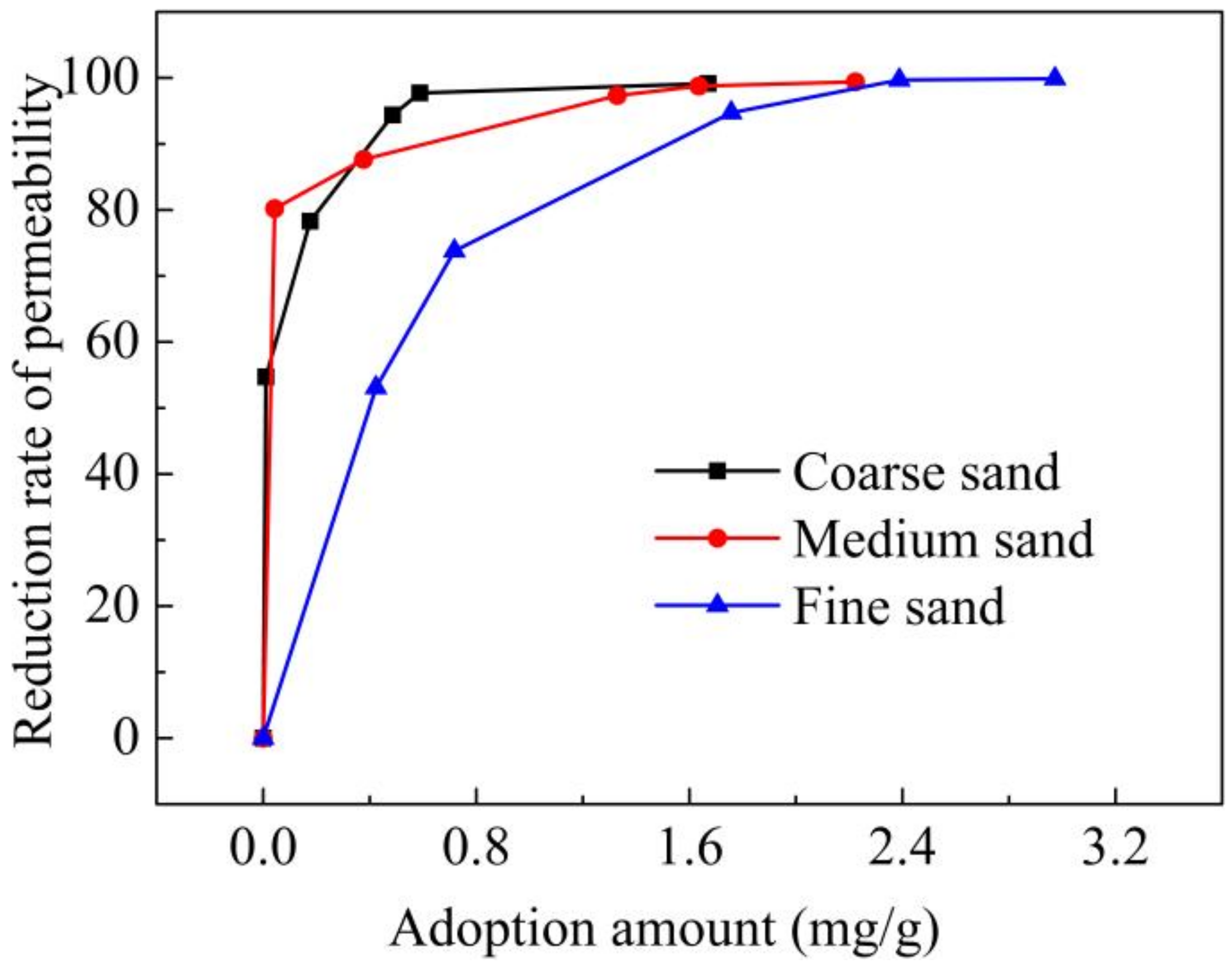
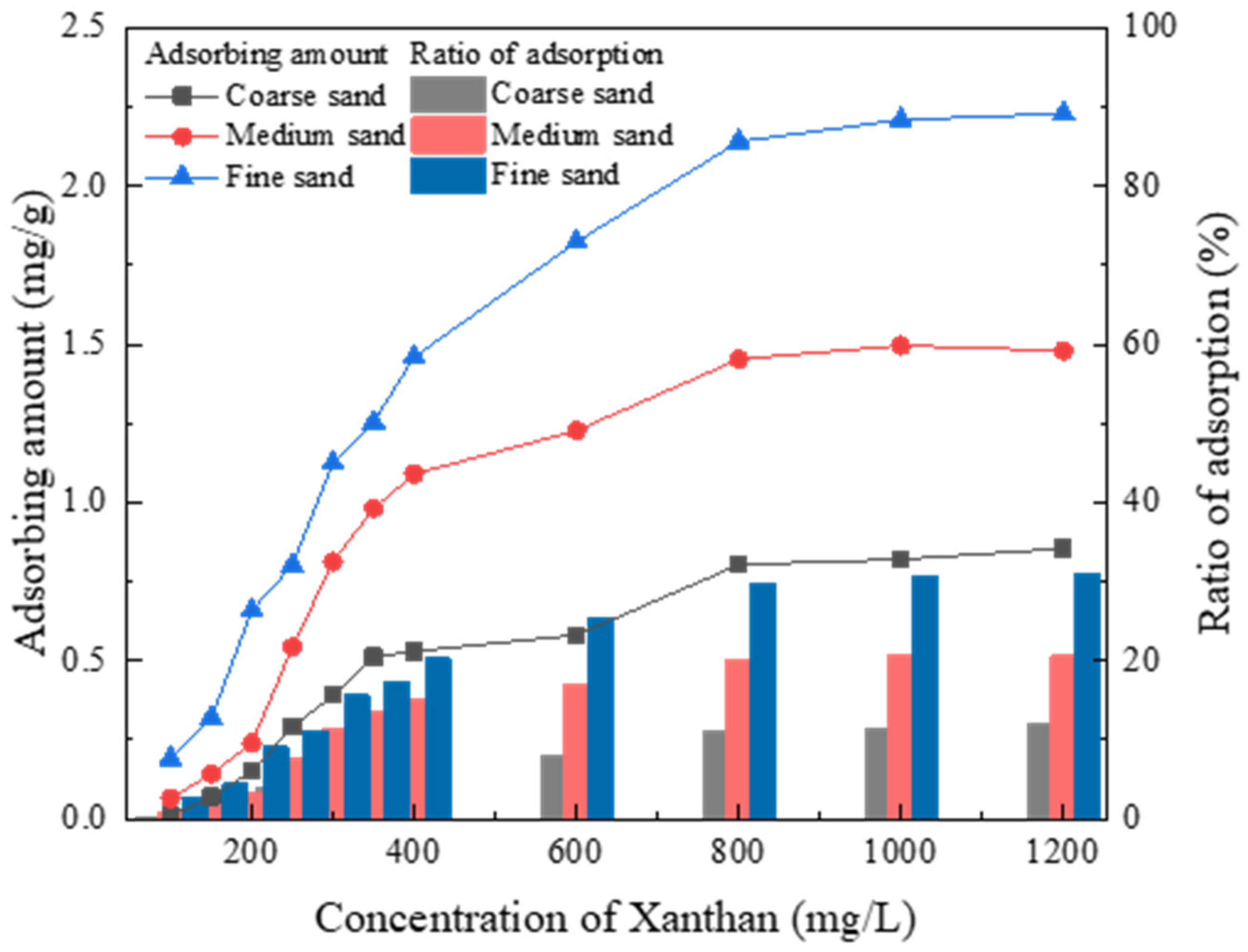
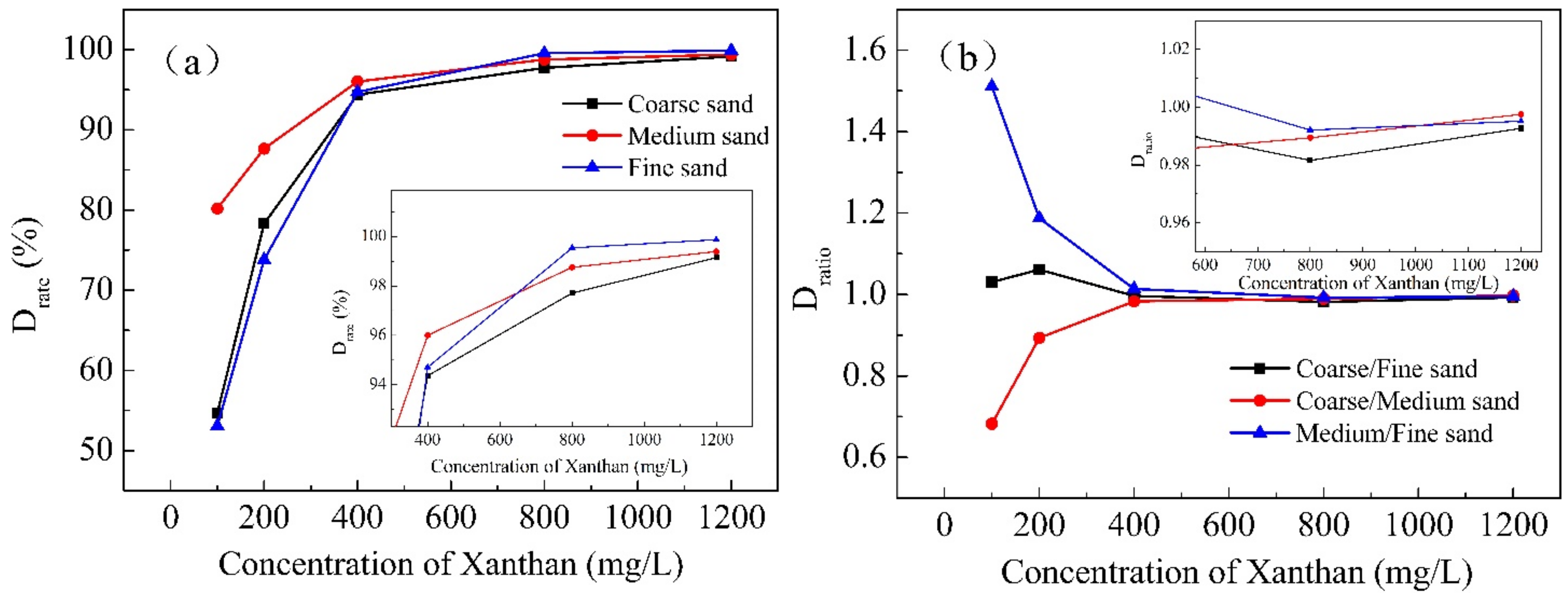
| Xanthan (mg/L) | 0 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1200 |
| Viscosity (cP) | 1.00 | 2.88 | 3.66 | 4.80 | 6.00 | 6.66 | 7.62 | 8.52 | 11.64 | 14.40 | 17.76 | 23.22 |
| Xanthan (mg/L) | Kc | n | Rheological Equation | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.606 | 0.598 | 0.995 | 0.99667 | |
| 200 | 0.598 | 0.581 | 0.988 | 0.99700 | |
| 400 | 0.960 | 0.895 | 0.984 | 0.98821 | |
| 600 | 1.747 | 1.496 | 0.988 | 0.99666 | |
| 1200 | 2.661 | 2.222 | 0.978 | 0.98383 |
| (a) Physical properties of each medium | ||||||||
| Media | Particle Size (mm) | Unit Weight (N/cm3) | Pore Volume (mL) | Porosity (%) | ||||
| Coarse sand | 0.841~2 | 0.0155 | 712 | 34.2 | ||||
| Medium sand | 0.42~0.841 | 0.0151 | 720 | 34.6 | ||||
| Fine sand | 0.25~0.42 | 0.0146 | 752 | 36.2 | ||||
| (b) Hydraulic conductivity of different medium under pure water injection | ||||||||
| Media | K (cm/s) | (cm/s) | σ | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| Coarse sand | 1.1404 | 1.1677 | 0.9206 | 0.8776 | 0.9294 | 1.2739 | 1.0516 | 0.1632 |
| Medium sand | 0.1195 | 0.108 | 0.1122 | 0.1087 | 0.1062 | 0.1367 | 0.1152 | 0.0115 |
| Fine sand | 0.0285 | 0.028 | 0.0271 | 0.0274 | 0.027 | 0.0227 | 0.0268 | 0.0021 |
| Combination Media | Coarse Sand/Fine Sand | Coarse Sand/Medium Sand | Medium Sand/Fine Sand |
|---|---|---|---|
| kbs | 41.27 | 8.90 | 4.63 |
| R0 | 39.26 | 9.13 | 4.30 |
| U0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| (a) Transmission uniformity control coefficients corresponding to different xanthan gum concentrations | ||||||
| Xanthan (mg/L) | 0 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | 1200 |
| Rcfp | 41.27 | 33.74 | 32.61 | 42.29 | 216.26 | 262.48 |
| Ucf | 1.00 | 1.22 | 1.27 | 0.98 | 0.19 | 0.16 |
| Rmfp | 4.63 | 1.90 | 2.03 | 3.29 | 11.38 | 20.53 |
| Umf | 1.00 | 2.44 | 2.28 | 1.41 | 0.41 | 0.23 |
| Rcmp | 2.26 | 17.79 | 16.08 | 12.87 | 19.00 | 12.79 |
| Ucm | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.18 |
| (b) Standard deviations for medias’ hydraulic conductivity under different xanthan concentration | ||||||
| Media | σ | |||||
| 0 mg/L | 100 mg/L | 200 mg/L | 400 mg/L | 800 mg/L | 1200 mg/L | |
| Coarse sand | ||||||
| Medium sand | ||||||
| Fine sand | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q. A Quantitative Evaluation Method for Xanthan Enhanced Transport Uniformity and Factors Affecting This Process. Water 2022, 14, 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172630
Wang Y, Zhou H, Chen J, Xu Q. A Quantitative Evaluation Method for Xanthan Enhanced Transport Uniformity and Factors Affecting This Process. Water. 2022; 14(17):2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172630
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yiti, Hongbo Zhou, Jiajun Chen, and Qi Xu. 2022. "A Quantitative Evaluation Method for Xanthan Enhanced Transport Uniformity and Factors Affecting This Process" Water 14, no. 17: 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172630
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhou, H., Chen, J., & Xu, Q. (2022). A Quantitative Evaluation Method for Xanthan Enhanced Transport Uniformity and Factors Affecting This Process. Water, 14(17), 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14172630





