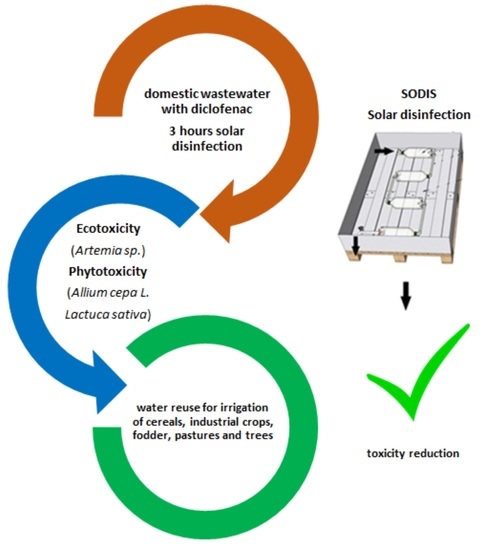
Diclofenac Toxicity Abatement in Wastewater with Solar Disinfection: A Study in the Rural Area of Brazil’s Central−West Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Configuration of the System
2.2. Wastewater Analysis
2.3. Ecotoxicity Assay
2.4. Phytotoxicity Assays
2.5. Toxic Units and Class Weight Score
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wastewater Characteristics and Disinfection Assessment
3.2. Ecotoxicity Assay
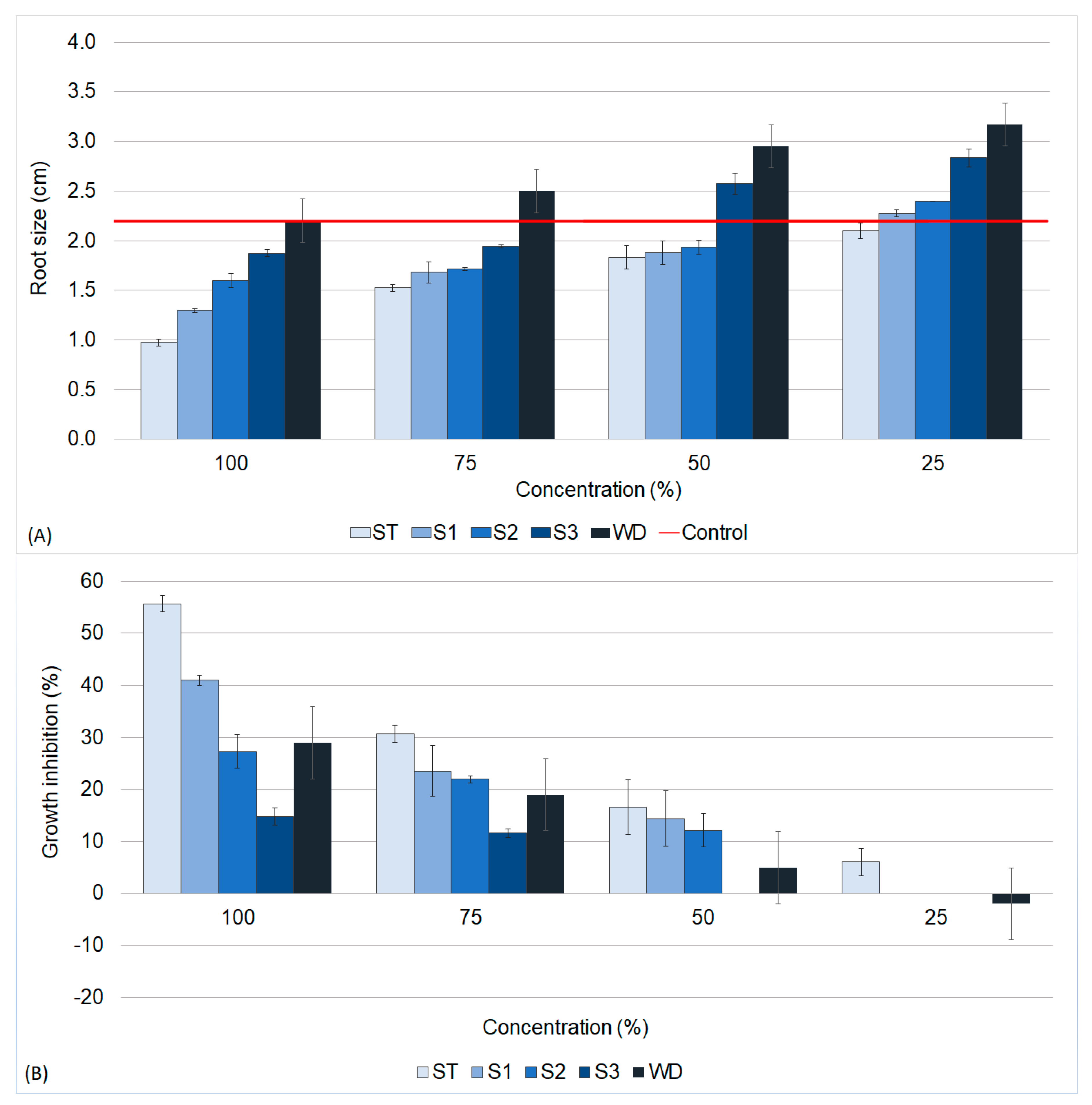
3.3. Phytotoxicity Assays
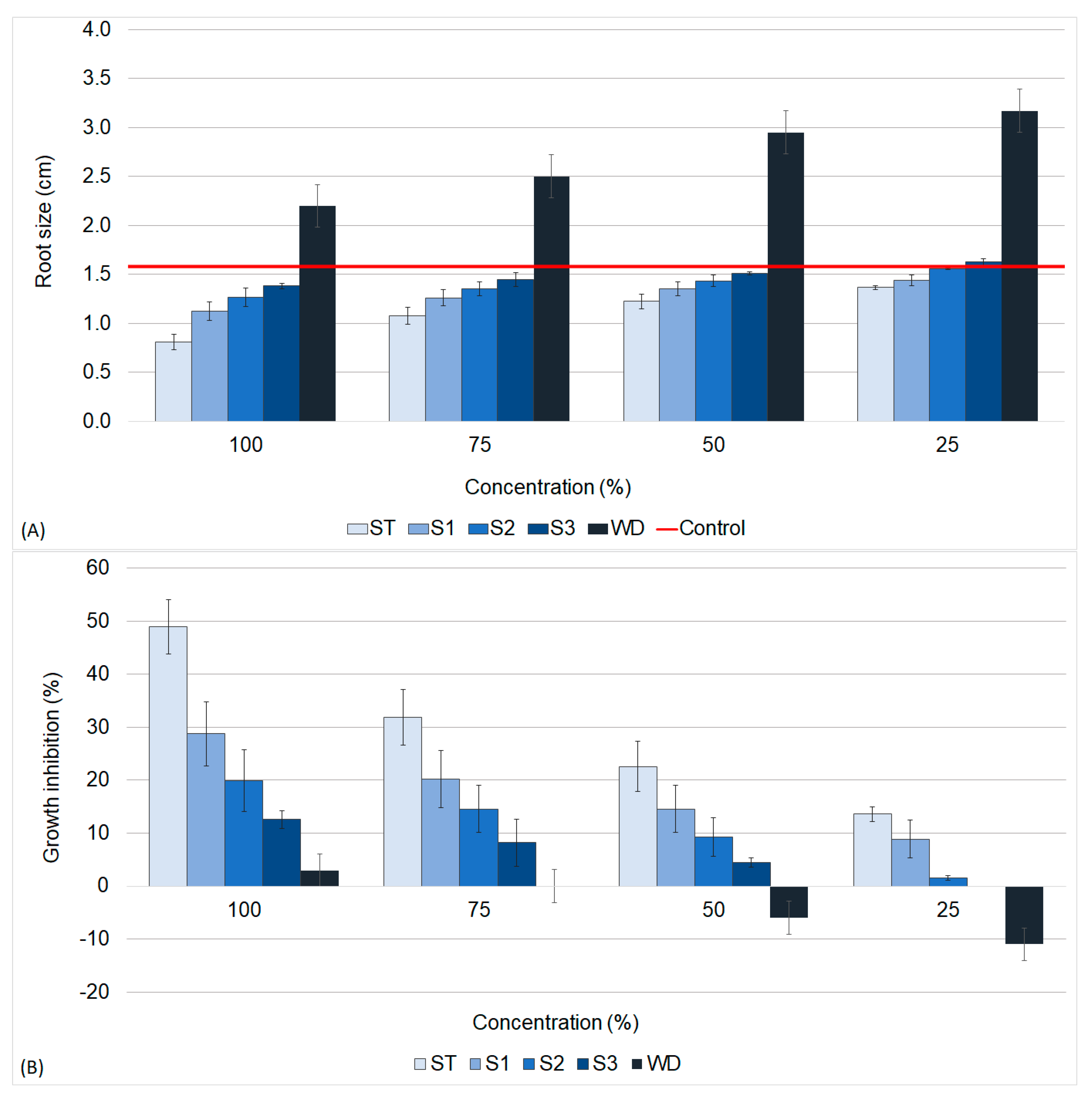
3.3.1. Allium Cepa L.
3.3.2. Lactuca Sativa
3.4. TU and Class Weight Score
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Kimura, S.Y. Water analysis: Emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 546–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Carminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.L.; Anulacion, B.F.; Arkoosh, M.R.; Burrows, D.G.; da Silva, D.A.M.; Dietrich, J.P.; Myers, M.S.; Spromberg, J.; Ylitalo, G.M. Effects of legacy persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in fish—current and future challenges. Fish Physiol. 2013, 33, 53–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé, M.; Desrosiers, M. A review of what is an emerging contaminant. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanakis, A.I.; Becker, J.A. A review of emerging contaminants in water: Classification, sources, and potential risks. In Impact of Water Pollution on Human Health and Environmental Sustainability; McKeown, A.E., Bugyi, G., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 55–80. [Google Scholar]
- Brausch, J.M.; Rand, G.M. A review of personal care products in the aquatic environment: Environmental concentrations and toxicity. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Megharaj, M.; Kirkbride, K.P.; Naidu, R. Illicit drugs and the environment—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezechiáš, M.; Covino, S.; Cajthaml, T. Ecotoxicity and biodegradability of new brominated flame retardants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; De Cicco, L.A.; Lenaker, P.L.; Lutz, M.A.; Sullivan, D.J.; Richards, K.D. Organic contaminants in Great Lakes tributaries: Prevalence and potential aquatic toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bôto, M.; Almeida, C.; Mucha, A. Potential of constructed wetlands for removal of antibiotics from saline aquaculture effluents. Water 2016, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ying, Z.; Ma, M.; Huo, M.; Yang, W. Degradation of Micropollutants by UV–Chlorine Treatment in Reclaimed Water: pH Effects, Formation of Disinfectant Byproducts, and Toxicity Assay. Water 2019, 11, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Blazer, V.S.; Gray, J.L.; Focazio, M.J.; Young, J.A.; Alvarez, D.A.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Foreman, W.T.; Furlong, E.T.; Speiran, G.K.; et al. Chemical contaminants in water and sediment near fish nesting sites in the Potomac River basin: Determining potential exposures to smallmouth bass (Micropterus dolomieu). Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.; Cavalcante, R.P.; Cunha, R.F.; Gozzi, F.; Dantas, R.F.; Oliveira, S.C.; Machulek, A. Tolfenamic acid degradation by direct photolysis and the UV-ABC/ H2O2 process: Factorial design, kinetics, identification of intermediates, and toxicity evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.M.; Gozzi, F.; Sirés, I.; Brillas, E.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Machulek, A. Degradation of 4-aminoantipyrine by electro-oxidation with a boron-doped diamond anode: Optimization by central composite design, oxidation products and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.S.; Santos, L.D.S.; de Souza, A.F.R.; Lange, L.C. A toxicity assessment of 30 pharmaceuticals using Aliivibriofischeri: A comparison of the acute effects of different formulations. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.A.; Lienert, J.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. How to avoid pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 113, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, M.; Frihling, B.E.F.; Velasques, J.; Magalhães Filho, F.J.C.M.; Cavalheri, P.S.; Migliolo, L. Pharmaceuticals residues and xenobiotics contaminants: Occurrence, analytical techniques and sustainable alternatives for wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G.; Sampath, S.; Selvaraj, K.K.; Larsson, D.G.J.; Ramaswamy, B.R. Nom-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Indian rivers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togola, A.; Budzinski, H. Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceutical compounds in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1177, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Isique, W.D.; Torres, N.H.; Machado, A.A.; Carvalho, S.L.; Filho, W.V.V.; Ferreira, L.F.R. Ocorrência de diclofenaco e naproxeno em água superficial no município de Três Lagoas (MS) e a influência da temperatura da água na detecção desses anti-inflamatórios. Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental 2017, 22, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Březinová, T.D.; Koželuh, M.; Kule, L. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals in four full-scale constructed wetlands in the Czech Republic–the first year of monitoring. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.C.G.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbosa, M.O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, C.M.; Tangerino, E.P.; Carvalho, S.L.; Isique, W.D. Removal of diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen and paracetamol in ecological filter followed by granular carbon filter biologically active. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental 2012, 17, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühmland, S.; Wick, A.; Ternes, T.A.; Barjenbruch, M. Fate of pharmaceuticals in a subsurface flow constructed wetland and two ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrubla, J.P.; Cubillos, J.A.; Ramírez, C.A.; Arredndo, J.A. Pharmaceutical and personal care products in domestic wastewater and their removal in anaerobic treatment systems: Septic tank-up flow anaerobic filter. Ingenieria e Investigacion 2016, 36, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger, B.; Kollner, B.; Dietrich, D.R.; Hitzfeld, B. Water-borne diclofenac affects kidney and gill integrity and selected immune parameters in brown trout (Salmo Trutta F. Fario). Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, M.; Karthika, S.; Malarvizhi, A.; Ramesh, M. Ecotoxicological impacts of clofibric acid and diclofenac in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fingerlings: Hematological, biochemical, ionoregulatory and enzymological responses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.J.; Santos, D.R.A.; Buongermino, C.R.P.; Cortez, F.S.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Choeri, R.B.; Cesar, A. Ecotoxicological assessment of four pharmaceuticals compounds through acute toxicity tests. O Mundo da Saúde 2014, 38, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezulka, S.; Kummerová, M.; Babula, P.; Hájková, M.; Oravec, M. Sensitivity of physiological and biochemical endpoints in early ontogenetic stages of crops under diclofenac and paracetamol treatments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 3965–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, D.M.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: A review on its application. Mut. Res. 2009, 682, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, N.; Porte, N.; Fernandes, D.; Barata, C.; Padrós, F.; Carrassón, M.; Monroy, M.; Cano-Rocabayera, O.; Sostoa, A.; Piña, B.; et al. Ecological relevance of biomarkers in monitoring studies of macro- invertebrates and fish in Mediterranean rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalzochio, T.; Rodrigues, G.Z.P.; Petry, I.E.; Gehlen, G.; Silva, L.B. The use of biomarkers to assess the health of aquatic ecosystems in Brazil: A review. Int. Aquat. Res. 2016, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAMA. Ministério do Meio Ambiente (MMA). Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). Resolução CONAMA Nº 357, De 17 de Março de 2005. Dispõe Sobre a Classificação Dos Corpos de áGua E Diretrizes Ambientais Para O Seu Enquadramento, Bem Como Estabelece as CondiçõES E PadrõES de Lançamento de Efluentes, E Dá Outras Providências; Diário Oficial da República Federativa do Brasil: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2005. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- CONAMA. Ministério do Meio Ambiente (MMA). Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). Resolução CONAMA Nº 430, De 11 de Maio de 2011. Dispõe Sobre as CondiçõES E PadrõES de Lançamento de Efluentes, Com-Plementa E Altera a Resolução No 357, De 17 de Março de 2005, Do Conselho Nacional Do Meio Ambiente—CONAMA; Diário Oficial da República Federativa do Brasil: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 2011. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Parrilla, A. Chemical and toxic evaluation of a biological treatment for olive-oil mill wastewater using comercial microbial formulations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudlek, E. Decomposition of contaminants of emerging concern in advanced oxidation processes. Water 2018, 2, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchino, M.; Tigini, V.; Varese, G.C.; Sartor, M.R.; Bona, F. Microalgae treatment removes nutrients and reduces ecotoxicity of diluted piggery digestate. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 570, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, T.B.; Zerwes, F.V.; Kist, L.T.; Machado, Ê.L. Constructed wetland and photocatalytic ozonation for university sewage treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 63, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterbeck, C.A.; Zerwes, F.V.; Radtke, J.F.; Köhler, A.; Kist, L.T.; Machado, E. Integrated system with constructed wetlands for the treatment of domestic wastewaters generated at a rural property—Evaluation of general parameters ecotoxicity and cytogenetics. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros, C.S.C.; Castro, P.M.L.; Gavina, A.; Pereira, R. Toxicity abatement of wastewaters from tourism units by constructed wetlands. Water 2019, 11, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düpont, A.; Lobo, E.A. Evaluation of the efficiency of the sewage treatment plant from the University of Santa Cruz do Sul (UNISC), RS, Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 2012, 24, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silveira, E.O.; Lutterbeck, C.A.; Machado, Ê.L.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Rieger, A.; Beckenkamp, F.; Lobo, E.A. Biomonitoring of urban wastewaters treated by an integrated system combining microalgae and constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 705, 135864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberidou, C.; Kitsiou, V.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Antoniadis, Α.; Ntonou, E.; Zalidis, G.C.; Poulios, I. Evaluation of an alternative method for wastewater treatment containing pesticides using solar photocatalytic oxidation and constructed wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Meza, J.C.; Pacheco-Salazar, V.F.; Pavón-Silva, T.B.; Guirrez-Garca, V.G.; Avila-González, C.J.; Guerrero-García, P. Toxicity assessment of a complex industrial wastewater using aquatic and terrestrial bioassays Daphnia pulex and Lactuca sativa. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2007, 42, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.L.R.; Dezotti, M.; Sant’Anna, G.L. Toxicity evaluation of the process effluent streams of a petrochemical industry. Environ. Technol. 2007, 28, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalwanga, R.; Quilty, B.; Muyanja, C.; Fernandez-Ibañez, P.; McGuigan, K.G. Evaluation of solar disinfection of E. coli under Sub-Saharan field conditions using a 25L borosilicate glass batch reactor fitted with a compound parabolic collector. Solar Energy 2014, 100, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivar, M.; Pichel, N.; Fuentes, M.; López-Vargas, A. Separating the UV and thermal components during real-time solar disinfection experiments: The effect of temperature. Solar Energy 2017, 146, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Vivar, M.; Qin, L.; Cui, L. Photovoltaic and disinfection performance study of a hybrid photovoltaic-solar water disinfection system. Energy 2016, 106, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dababneh, B.F.; Shquirat, W.D.; Abbassi, B.E. Coliform-specific solar disinfection of treated wastewater. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 1577–1581. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani, D.; Hooshyar, H. Application of flat plate solar collector for thermal disinfection of wastewater effluents. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2011, 8, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakis, S.; Darakas, E.; Escalas-Cañellas, A.; Pulgarin, C. The antagonistic and synergistic effects of temperature during solar disinfection of synthetic secondary effluent. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014, 280, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, P.; von Tümpling, W., Jr. Solar radiation influence on the decomposition process of diclofenac in surface waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 374, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, L.; Brar, S.K.; Das, R.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Diclofenac and its transformation products: Environmental occurrence and toxicity—A review. Environ. Int. 2016, 96, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, S.; Tobler, M.; Suter, F.; Meierhofer, R. SODIS Manual—Guidance on Solar Water Disinfection; Sanitation, Water and Solid Waste for Development & Eawag: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Khedikar, I.P.; Tembhurkar, A.R. Inactivation of Escherichia Coli (E. coli), Feacal Coliform (FC) and Total Coliform (TC) in grey water through Batch Solar Disinfection (SODIS) with reflective and absorptive rear surfaces. J. Eng. Res. 2016, 5, 2320–2847. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, V.B.; Machado, B.S.; Atalla, A.A.; Cavalheri, P.S.; Magalhães Filho, F.J.C. Microbiological evaluation of constructed wetlands and solar disinfection in wastewater treatment and reuse. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.D.F.; Junior, G.B.A.; Souza, S.F.L.; Andrade, A.E.F. Comparative study between adhered and suspended growth reactors after septic tanks treating domestic wastewater. AIDIS 2015, 8, 84–101. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, S.F.L.; Júnior, G.B.A.; Oliveira, J.D.F.; Luna, Y.H.D.M. Effect of a peak flow control device on the organic matter removal efficiency in anaerobic filter. AIDIS 2016, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Homlok, R.; Takacs, E.; Wojnarovits, L. Elimination of diclofenac from water using irradiation technology. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.; Pereira, V.J.; Carvalho, G.; Soeiro, R.; Gaffney, V.; Almeida, C.; Vale Cardoso, V.; Ferreira, E.; Benoliel, M.J.; Ternes, T.A.; et al. Photodegradation kinetics and transformation products of ketoprofen, diclofenac and atenolol in pure water and treated wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, I.; Hapeshi, E.; Michael, C.; Varela, A.R.; Kyriakou, S.; Manaia, C.M.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Solar photo—Fenton process on the abatement of antibiotics at a pilot scale: Degradation kinetics, ecotoxicity and phytotoxicity assessment and removal of antibiotic resistant enterococci. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5621–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterniani, J.E.S.; Silva, M.J. Disinfection of effluent of wastewater treated using solar energy (SODIS): Evaluation of a solar concentrator device. Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental 2005, 10, 09–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; AWWA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haap, T.; Triebskorn, R.; Lohler, H.R. Acute effects of diclofenac and DMSO to Daphnia magna: Immobilisation and hsp70-induction. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, M.W.; Soemardji, A.A.; Fidrianny, I.; Yusuf, A. The capability of brine shrimp test as a teratogenicity screening system. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klauck, C.R.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Silva, L.B. Toxicological evaluation of landfill leachate using plant (Allium cepa) and fish (Leporinus obtusidens) bioassays. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G.K.G.F.; Menezes, A.C.S.; Naves, P.L.F.; Bueno, O.C.; Santos, R.G.; Silva Junior, W.M.D. Toxicity of Esenbeckia pumila Pohl (Rutaceae) on Artemia salina an Atta sexdens rubropilosa. Revista Caatinga 2019, 32, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, R.S.; Silva, H.D.; Mello-Andrade, F.; Pires, W.C.; de Castro Pereira, F.; de Lima, A.P.; Santos, S.F.O.; Teixeira, T.M.; da Silva, P.F.F.; Naves, P.L.F.; et al. Ruthenium (II)/Benzonitrile Complex Induces Cytotoxic Effect in Sarcoma-180 Cells by Caspase-Mediated and Tp53/p21-Mediated Apoptosis, with Moderate Brine Shrimp Toxicity. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 198, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaecke, P.; Persoone, G.; Claus, C.; Sorgeloos, P. Research on the development of a short term standard toxicity test with Artemia nauplii. In The Brine Shrimp Artemia. Morphology, Genteics, Radiobiology, Toxicology; Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E., Eds.; Universa Press: Wetteren, Belgium, 1980; Volume 1, p. 345. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, B.N.; Ferrigni, N.R.; Putnam, J.E.; Jacobsen, L.B.; Nichols, D.E.; McLaughlin, J.L. Brine shrimp: A convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. J. Med. Plant Res. Planta Medica 1982, 45, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ABNT NBR 16.530/2016: Ecotoxicologia Aquática—Toxicidade Aguda—Método de Ensaio com Artemia sp. (Crustácea, Brachiopoda); Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 2016. (In Portuguese)
- Fiskesjó, G. The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas 1985, 102, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuchiara, C.; Broges, C.; Bobrowski, V.L. Sistema teste de Allium cepa como bioindicador da citogenotoxicidade de cursos d’ água. Tecnologia e Ciência Agropecuária 2012, 6, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrero, M.C.; Ronco, A. Ensayo de toxicidad aguda con semillas de lechuga Lactuca sativa L. IDRC/IMTA 2004, 4, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Persoone, G.; Marsalek, B.; Blinova, I.; Törökne, A.; Zarina, D.; Manusadzianas, L.; Kolar, B. A practical and user-friendly toxicity classification system with microbiotests for natural waters and wastewaters. Environ. Toxicol. Int. J. 2003, 18, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; David Stensel, H.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Burton, F.L. Wastewater Engineering Treatment and Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; Metcalf & Eddy, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- CETESB. Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo. In Decreto No 8.468, De 08 de Maio de 1976. Dispõe Sobre a Prevenção E O Controle Da Poluição Do Meio Ambiente; CETESB: São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 1976. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- COPAM/CERH-MG. Conselho Estadual de Política Ambiental/Conselho Estadual de Recursos Hídricos do Estado de Minas Gerais. Deliberação Normativa Conjunta No 1, De 05 de Maio de 2008. Dispõe Sobre a Classificação Dos Corpos de áGua E Diretrizes Ambientais Para O Seu Enquadramento, Bem Como Estabelece as CondiçõES E PadrõES de Lançamento de Efluentes, E Dá Outras Providências; COPAM/CERH-MG: Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil, 2008. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- CONSEMA. Conselho Estadual do Meio Ambiente. Resolução No 55, De 21 de Junho de 2012. Dispõe Sobre as CondiçõES E PadrõES de Lançamento de Efluentes Tratados Oriundos de Estação de Tratamento de Esgoto Doméstico Em Galeria de áGuas Pluvial No âMbito Do Estado de Mato Grosso, E Dá Outras Providências; Conselho Estadual do Meio Ambiente: Cuiabá, MT, Brazil, 2012. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Von Sperling, M. Wastewater Characteristics, Treatment and Disposal; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wegelin, M.; Canonica, S.; Mechsner, K.; Fleischmann, T.; Pesaro, F.; Metzler, A. Solar water disinfection: Scope of the process and analysis of radiation experiments. Aqua J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 1994, 43, 154–169. [Google Scholar]
- Bitton, G. Wastewater Microbiology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and greywater: Volume I—Policy and regulatory aspects. World Health 2006, 1, 114. [Google Scholar]
- ABNT NBR 13.969/1997: Tanque Sépticos—Unidades de Tratamento Complementar E Disposição Final de Efluentes Líquidos—Projeto, Construção E Operação; Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas: Sao Paulo, SP, Brasil, 1997. (In Portuguese)
- Sauer, T.P.; Casaril, L.; Oberziner, A.L.B.; José, H.J.; Moreira, R.D.F.P.M. Advanced oxidation processes applied to tannery wastewater containing Direct Black 38—Elimination and degradation kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizato, E.; Lopes, A.C.; Rocha, R.D.C.; Barbosa, A.D.M.; Cunha, M.A.A.D. Textile effluent characterization and evaluation of capacity color removal using the fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae MMPI. Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental 2017, 22, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Athar, H. Textile effluents affected seed germination and early growth of some winter vegetable crops: A case study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 198, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, L.B.; Kummrow, F.; Beijo, L.A.; Lima, C.A.A.; Barbosa, S. Evaluation of the cytogenotoxicity of textile effluents using Allium cepa L. Ambiente e Agua Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 6, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur-González, M.G.; Estepa-Molina, C.; Martin-Peinado, F.; Morales-Ruano, S. Toxicity assessment using Lactuca sativa L. bioassay of the metal(loid)s As, Cu, Mn, Pb and Zn in soluble-in-water saturated soil extracts from an abandoned mining site. J. Soils and Sediments. 2011, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.O.; Moura, D.; Rieger, A.; Machado, Ê.L.; Lutterbeck, C.A. Performance of an integrated system combining microalgae and vertical flow constructed wetlands for urban wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20469–20478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.C.; Bianchini, A. Extraction and concentration of freshwater-and seawater-derived dissolved organic matter for use in aquatic toxicology studies. J. Brazilian Soc. Ecotoxicol. 2007, 2, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barszcz, L.B.; Bellato, F.C.; Benassi, R.F.; Matheus, D.R. Ecotoxicological evaluation of effluents treated by constructed wetlands. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental 2019, 24, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogna, D.; Marotta, R.; Napolitano, A.; Andreozzi, R.; D’Ischia, M. Advanced oxidation of the pharmaceutical drug diclofenac with UV/H2)2 and ozone. Water Res. 2004, 38, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Guo, Y. Degradation of diclofenac by UV-activated persulfate process: Kinetic studies, degradation pathways and toxicity assessments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Sydow, S.; Griebel, J.; Naumov, S.; Elsner, C.; Thomas, I.; Schulze, A. Enhanced removal and toxicity decline of diclofenac by combining UVA treatment and adsorption of photoproducts to polyvinylidene difluoride. Polymers 2020, 12, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.D.; Sans, C.; Agüera, A.; Gómez, M.J.; Esplugas, S.; Dezotti, M. Effects of ozone pre-treatment on diclofenac: Intermediates, biodegradability and toxicity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3572–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Kohler, M.; Meierhofer, R.; Luzi, S.; Wegelin, M. Does the reuse of PET bottles during solar water disinfection pose a health risk due to the migration of plasticisers and other chemicals into the water? Water Res. 2008, 42, 5054–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gil, Á.; Pablos, C.; García-Muñoz, R.A.; McGuigan, K.G.; Marugán, J. Material selection and prediction of solar irradiance in plastic devices for application of solar water disinfection (SODIS) to inactivate viruses, bacteria and protozoa. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubomba-Jaswa, E.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; McGuigan, K.G. A preliminary Ames fluctuation assay assessment of the genotoxicity of drinking water that has been solar disinfected in polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
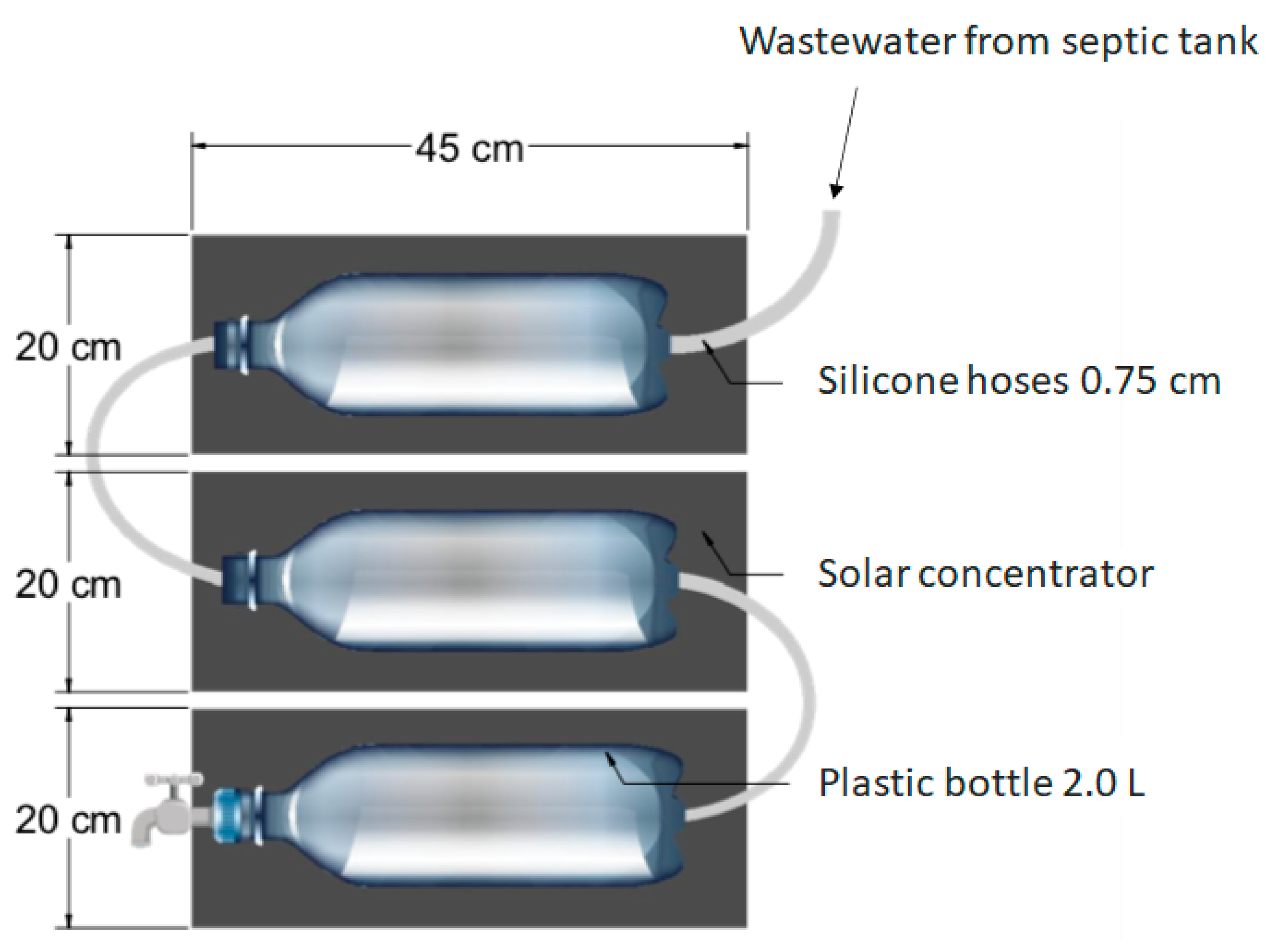
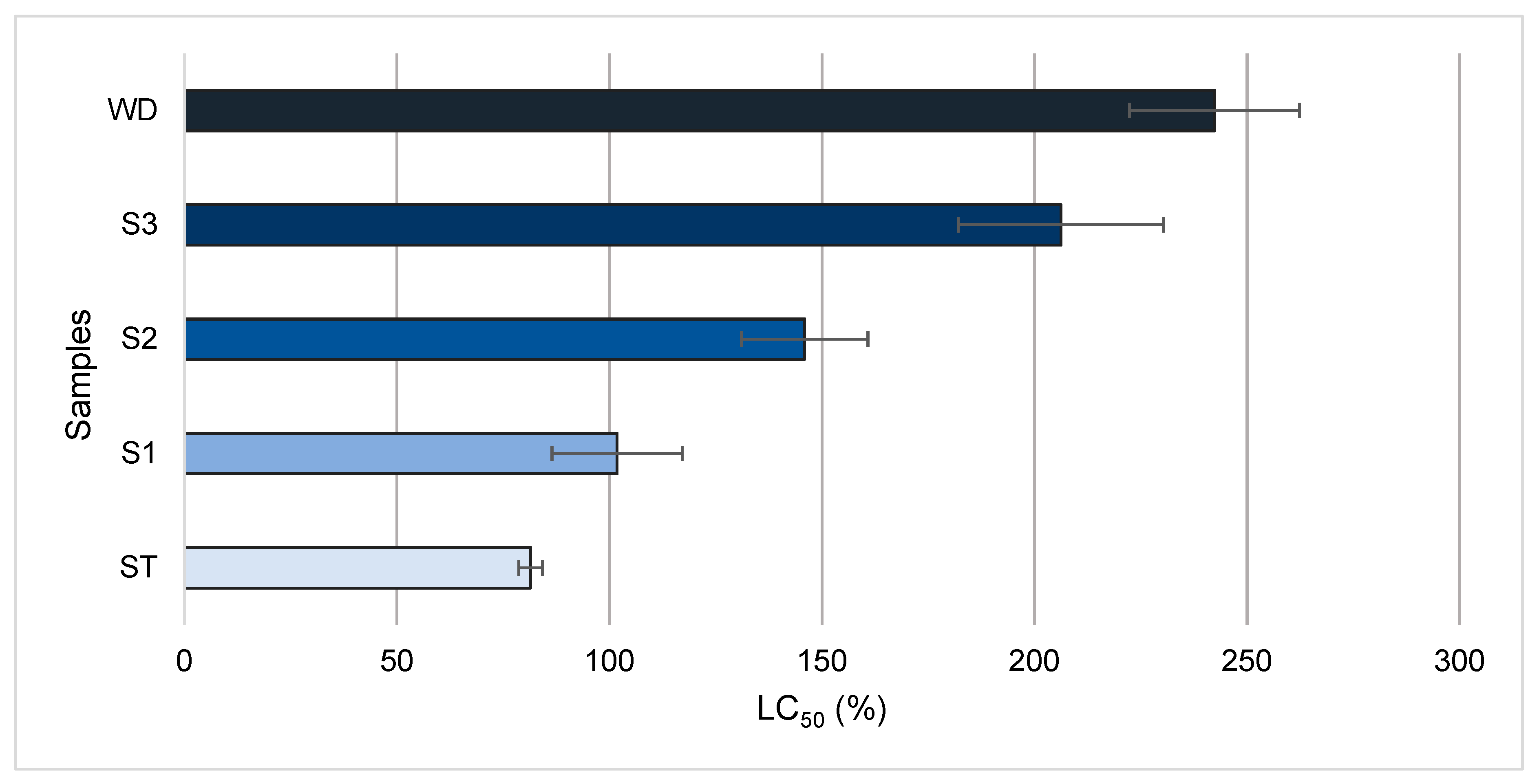
| Parameters | Post-Septic tank |
|---|---|
| pH | 6.9 ± 0.2 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 29.3 ± 0.3 |
| Temperature (°C) | 25 ± 2 |
| Nitrite (mgNO2−·L−1) | 0.9 ± 0.3 |
| Nitrate (mgNO3−·L−1) | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| Total nitrogen (mg·L−1) | 18.0 ± 6.9 |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen (mg·L−1) | 17.5 ± 9.9 |
| Total phosphorus (mg·L−1) | 2.6 ± 0.7 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg·L−1) | 1.1 ± 0.4 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (mg·L−1) | 167 ± 9 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (mg·L−1) | 129 ± 27 |
| Total solids (mg·L−1) | 264 ± 70 |
| Parameters | Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
| Solar radiation (W·m−2) * | – | 768 | 781 | 800 |
| Temperature (°C) * | 24 ± 2 | 31 ± 3 | 36 ± 4 | 40 ± 5 |
| Total coliforms (MPN·100mL−1) | 1.3 × 108 | 2.4 × 107 | 2.4 × 105 | 2.3 × 105 |
| Escherichia coli (MPN·100mL−1) | 8.0 × 106 | 1.7 × 106 | 8.0 × 104 | 5.0 × 104 |
| Samples | Artemia sp. | Allium cepa L. | Lactuca sativa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TU | Test Score | TU | Test Score | TU | Test Score | Class Weight Score | Class Weight Score (%) | |
| ST | 1.2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.7 | 83 |
| S1 | 1 | 2 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 1 | 67 |
| S2 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.4 | 1 | 1 | 50 |
| S3 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.3 | 1 | 1 | 50 |
| WD | 0.4 | 1 | 0.7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 | 67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, N.S.; Marquiza, L.F.; Calheiros, C.S.C.; Cavalheri, P.S.; Machado, B.S.; Cavazzana, G.H.; Filho, F.J.C.M. Diclofenac Toxicity Abatement in Wastewater with Solar Disinfection: A Study in the Rural Area of Brazil’s Central−West Region. Water 2021, 13, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081043
dos Santos NS, Marquiza LF, Calheiros CSC, Cavalheri PS, Machado BS, Cavazzana GH, Filho FJCM. Diclofenac Toxicity Abatement in Wastewater with Solar Disinfection: A Study in the Rural Area of Brazil’s Central−West Region. Water. 2021; 13(8):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081043
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Nathália Sanches, Laura Fernanda Marquiza, Cristina Sousa Coutinho Calheiros, Priscila Sabioni Cavalheri, Beatriz Santos Machado, Guilherme Henrique Cavazzana, and Fernando Jorge Correa Magalhães Filho. 2021. "Diclofenac Toxicity Abatement in Wastewater with Solar Disinfection: A Study in the Rural Area of Brazil’s Central−West Region" Water 13, no. 8: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081043
APA Styledos Santos, N. S., Marquiza, L. F., Calheiros, C. S. C., Cavalheri, P. S., Machado, B. S., Cavazzana, G. H., & Filho, F. J. C. M. (2021). Diclofenac Toxicity Abatement in Wastewater with Solar Disinfection: A Study in the Rural Area of Brazil’s Central−West Region. Water, 13(8), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081043