Hotspots of Legacy Phosphorus in Agricultural Landscapes: Revisiting Water-Extractable Phosphorus Pools in Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Characteristics
2.2. Soil Collection
2.3. Sample Extractions
2.4. Sample Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
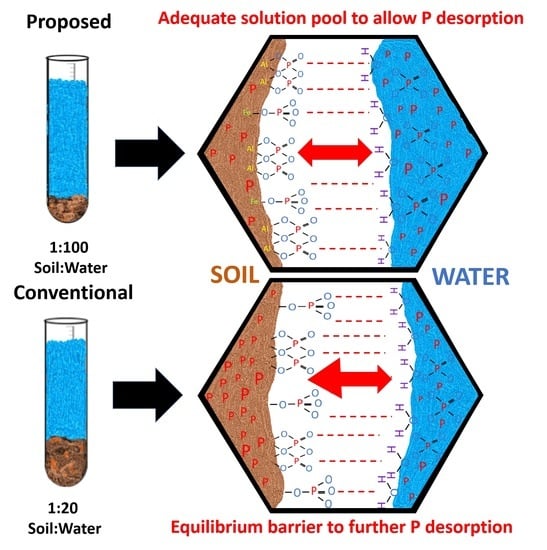
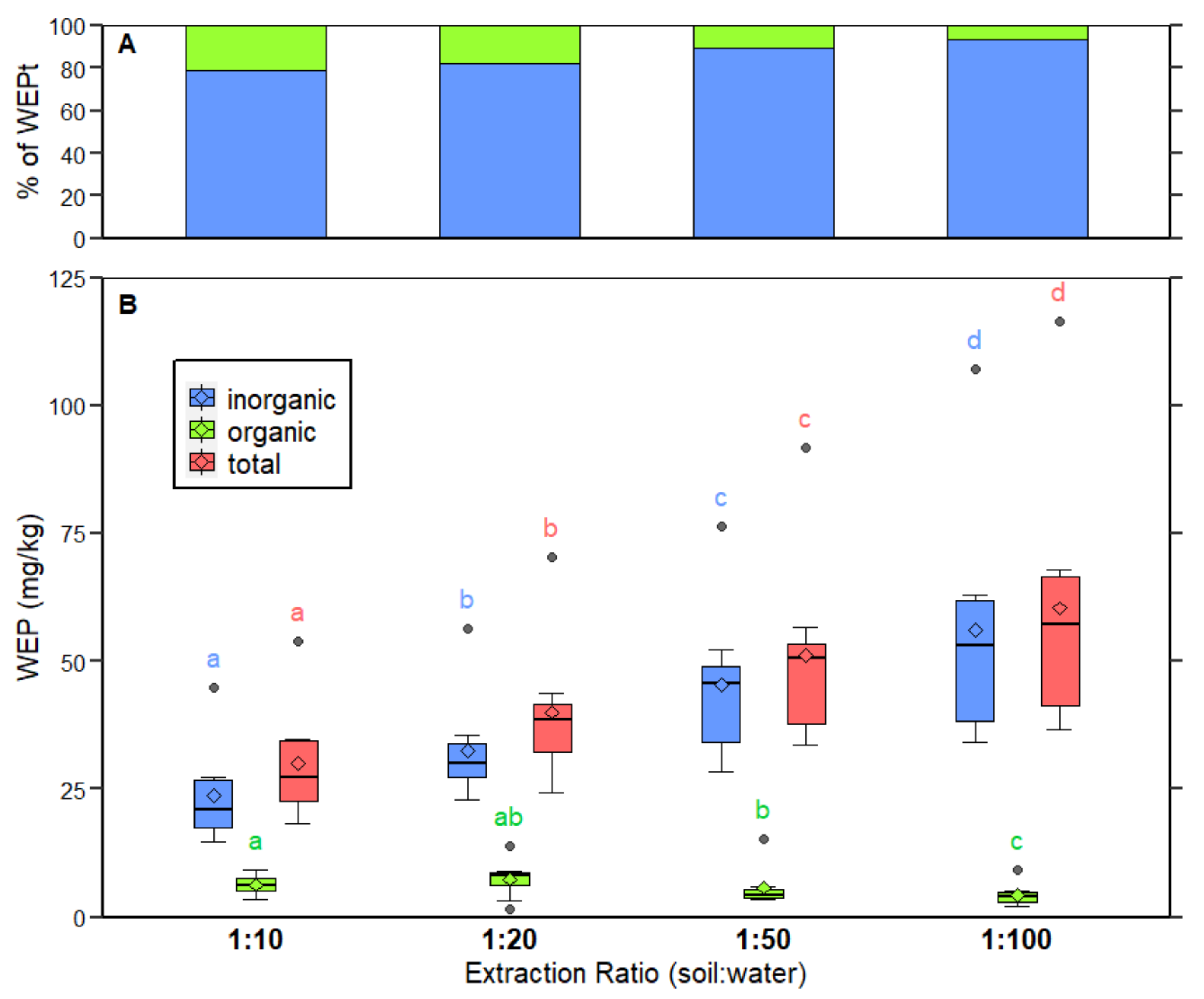
3.1. Water-Extractable Phosphorus across Extraction Ratios
3.2. Water-Extractable Phosphorus as a Proportion of Mehlich 3–Phosphorus and Total Phosphorus
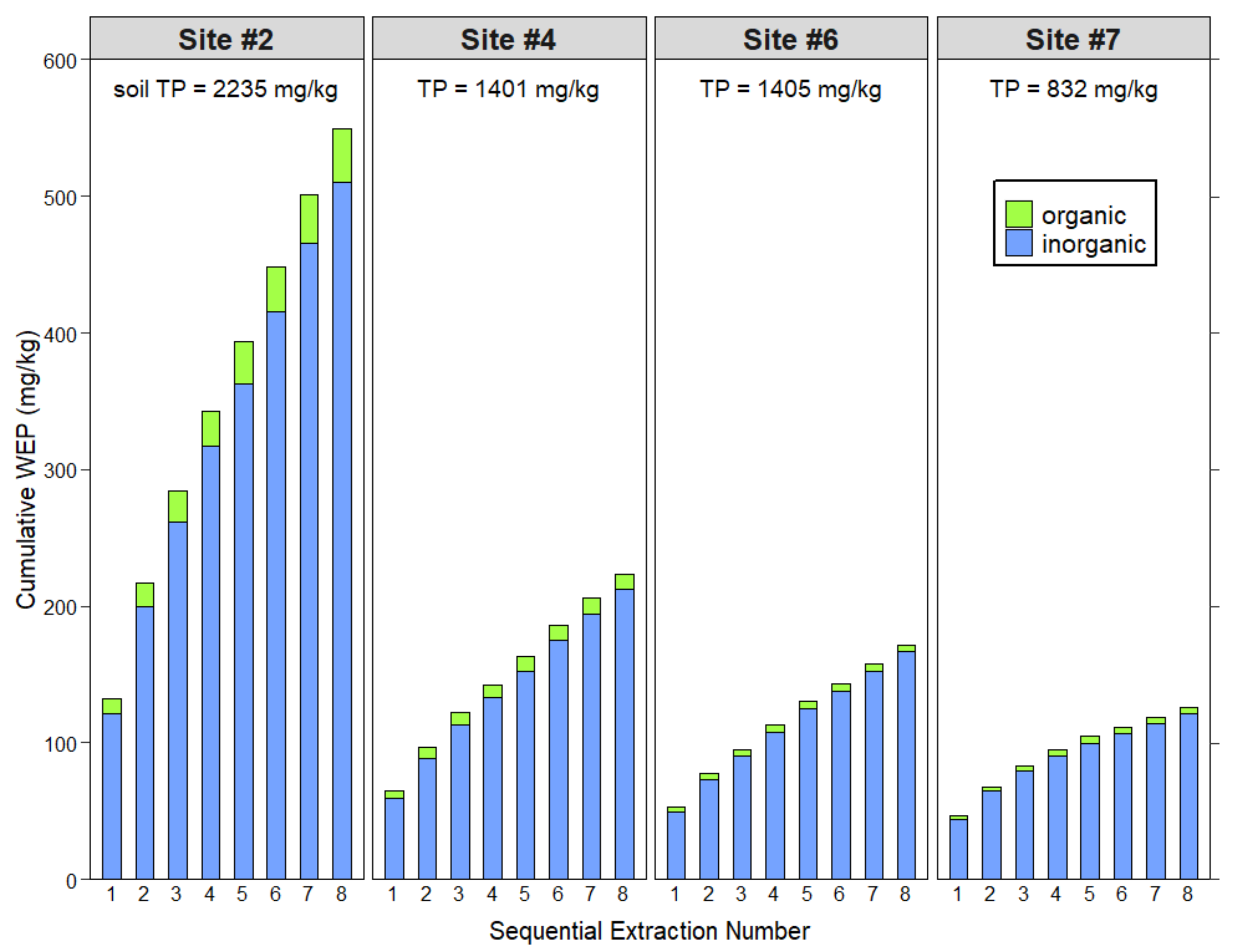
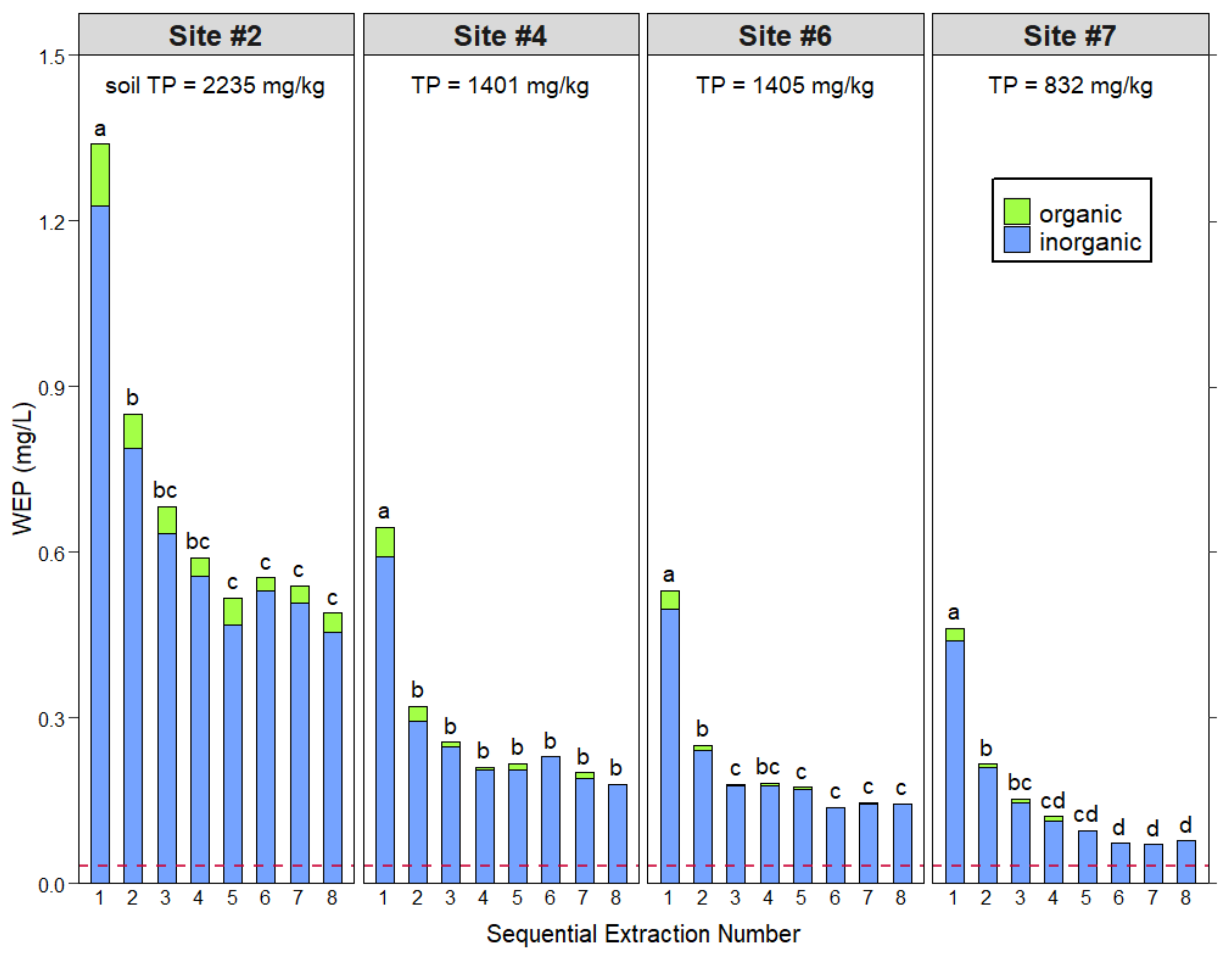
3.3. Sequential Water Extractions to Exhaust Water-Extractable Phosphorus
3.4. Impact of Phosphorus Saturation on the Magnitude of Water-Extractable Phosphorus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Extraction Ratio | Site 1 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 | Site 6 | Site 7 | Site 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ––––––––––––––––––––––––mg kg−1––––––––––––––––––––––––––– | |||||||||
| WEPt | 1:10 | 18.4 | 54.0 | 34.4 | 34.7 | 25.4 | 29.1 | 23.0 | 21.4 |
| 1:20 | 24.3 | 70.4 | 43.6 | 40.8 | 38.2 | 38.9 | 32.6 | 31.3 | |
| 1:50 | 33.7 | 91.7 | 56.6 | 52.1 | 51.1 | 50.0 | 35.3 | 38.4 | |
| 1:100 | 41.7 | 132.2 | 68.0 | 63.0 | 66.1 | 52.7 | 45.3 | 36.5 | |
| WEPi | 1:10 | 14.8 | 44.7 | 26.8 | 27.2 | 19.8 | 22.1 | 17.6 | 16.8 |
| 1:20 | 22.9 | 56.5 | 35.5 | 33.4 | 29.9 | 30.1 | 24.2 | 28.2 | |
| 1:50 | 28.4 | 76.5 | 52.1 | 47.9 | 47.2 | 44.2 | 31.9 | 34.9 | |
| 1:100 | 38.5 | 121.1 | 62.9 | 57.8 | 61.5 | 49.2 | 43.1 | 34.2 | |
| WEPo | 1:10 | 3.5 | 9.2 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 5.6 | 7.0 | 5.3 | 4.6 |
| 1:20 | 1.4 | 13.9 | 8.2 | 7.4 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 8.5 | 3.1 | |
| 1:50 | 5.3 | 15.2 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 3.9 | 5.8 | 3.4 | 3.5 | |
| 1:100 | 3.2 | 11.0 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 2.2 | 2.4 | |
| Extraction Ratio | Site 1 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 | Site 6 | Site 7 | Site 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ––––––––––––––––––––––––% of Mehlich 3–P–––––––––––––– | |||||||||
| WEPt:M3–P | 1:10 | 3.4 | 4.8 | 4.3 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.4 |
| 1:20 | 4.6 | 6.2 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 7.6 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 5.0 | |
| 1:50 | 6.3 | 8.1 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 10.2 | 6.4 | 5.9 | 6.2 | |
| 1:100 | 7.8 | 11.7 | 8.4 | 9.1 | 13.2 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 5.9 | |
| WEPi:M3–P | 1:10 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 4.0 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.7 |
| 1:20 | 4.3 | 5.0 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 6.0 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 4.6 | |
| 1:50 | 5.3 | 6.8 | 6.5 | 6.9 | 9.4 | 5.6 | 5.3 | 5.6 | |
| 1:100 | 7.2 | 10.7 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 12.3 | 6.3 | 7.2 | 5.5 | |
| WEPo:M3–P | 1:10 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
| 1:20 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 0.5 | |
| 1:50 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 1:100 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| Extraction Ratio | Site 1 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 | Site 6 | Site 7 | Site 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| –––––––––––––––––––––% of total P–––––––––––––––––––––– | |||||||||
| WEPt:TP | 1:10 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 2.9 |
| 1:20 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.9 | 4.2 | |
| 1:50 | 4.9 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 5.1 | |
| 1:100 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 4.7 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 3.7 | 5.4 | 4.9 | |
| WEPi:TP | 1:10 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 2.2 |
| 1:20 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 3.8 | |
| 1:50 | 4.1 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 4.7 | |
| 1:100 | 5.6 | 5.4 | 4.3 | 4.1 | 4.3 | 3.5 | 5.2 | 4.6 | |
| WEPo:TP | 1:10 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| 1:20 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.4 | |
| 1:50 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |
| 1:100 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Sequential Extraction Number | Site 2 1 | Site 4 | Site 6 | Site 7 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | |
| ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– mg L−1 ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 1.34 | 1.23 | 0.11 | 0.65 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.53 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
| 4 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| 5 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.07 | −0.01 |
| 7 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.00 |
| 8 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| Sequential Extraction Number | Site 2 1 | Site 4 | Site 6 | Site 7 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | WEPt | WEPi | WEPo | |
| –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– mg kg−1 –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 132.2 | 121.1 | 11.0 | 63.0 | 57.8 | 5.2 | 52.7 | 49.2 | 3.5 | 45.3 | 43.1 | 2.2 |
| 2 | 84.0 | 77.9 | 6.2 | 32.0 | 29.3 | 2.6 | 24.7 | 23.9 | 0.8 | 21.5 | 20.9 | 0.7 |
| 3 | 67.5 | 62.7 | 4.8 | 25.5 | 24.7 | 0.8 | 17.8 | 17.4 | 0.3 | 15.2 | 14.4 | 0.7 |
| 4 | 58.3 | 54.9 | 3.4 | 20.9 | 20.4 | 0.5 | 18.0 | 17.5 | 0.5 | 12.1 | 11.2 | 0.9 |
| 5 | 51.0 | 46.1 | 4.9 | 21.4 | 20.3 | 1.2 | 17.1 | 16.7 | 0.4 | 9.5 | 9.4 | 0.2 |
| 6 | 54.7 | 52.3 | 2.4 | 22.8 | 22.9 | −0.1 | 13.3 | 13.5 | −0.2 | 6.6 | 7.2 | −0.6 |
| 7 | 53.2 | 50.1 | 3.1 | 19.9 | 18.9 | 1.0 | 14.5 | 14.1 | 0.3 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 0.0 |
| 8 | 48.4 | 45.0 | 3.4 | 17.6 | 17.8 | −0.2 | 13.8 | 14.2 | −0.4 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 0.0 |
| Cumulative (1–8) | 549.3 | 510.1 | 39.3 | 223.1 | 212.1 | 11.0 | 171.8 | 166.6 | 5.2 | 124.9 | 120.8 | 4.1 |
References
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Fanelli, R.M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Buda, A.R.; Easton, Z.M.; Wainger, L.A.; Brosch, C.; Lowenfish, M.; Collick, A.S.; Shirmohammadi, A.; et al. Phosphorus and the Chesapeake Bay: Lingering Issues and Emerging Concerns for Agriculture. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmer, A.S.; Goyette, J.-O.; Macdonald, G.K.; Bennett, E.M.; Maranger, R.; Withers, P.J.A. Watershed Buffering of Legacy Phosphorus Pressure at a Regional Scale: A Comparison Across Space and Time. Ecosystems 2019, 22, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, G.S.; Sims, J.T. Managing Phosphorus Leaching in Mid-Atlantic Soils: Importance of Legacy Sources. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, G.S.; Yang, Y.; Morris, M.; Schwartz, P.; Darwish, Y.; Gaylord, G.; Webb, K. Phosphorus Pools in Soils Under Rotational and Continuous Grazed Pastures. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, 20103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Sharpley, A.N.; Edwards, D.R.; Wedepohl, R.; Lemunyon, J.L. Minimizing Surface Water Eutrophication from Agriculture by Phosphorus Management. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1994, 49, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R. Phosphorus Control is Critical to Mitigating Eutrophication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11039–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholz, W.R.; Hanrahan, B.R.; King, K.W. Legacy Phosphorus Concentration–Discharge Relationships in Surface Runoff and Tile Drainage from Ohio Crop Fields. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, G.S.; Sims, J.T. Phosphorus Leaching in Soils Amended with Animal Manures Generated from Modified Diets. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, G.S.; Sims, J.T. Managing Legacy and New Sources of Phosphorus to Reduce Leaching in Mid-Atlantic Soils. Crop. Soils 2016, 49, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.; Allen, A.L.; Needelman, B.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Vadas, P.A.; Saporito, L.S.; Folmar, G.J.; Bryant, R.B. Dynamics of Phosphorus Transfers from Heavily Manured Coastal Plain Soils to Drainage Ditches. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 62, 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Weld, J.L.; Beegle, D.B.; Kleinman, P.J.; Gburek, W.J.; Moore, P.A.; Mullins, G. Development of Phosphorus Indices for Nutrient Management Planning Strategies in the United States. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 58, 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Osmond, D.L.; Cabrera, M.L.; Feagley, S.E.; Hardee, G.E.; Mitchell, C.C.; Moore, P.A.; Mylavarapu, R.S.; Oldham, J.L.; Stevens, J.C.; Thom, W.O.; et al. Comparing Ratings of the Southern Phosphorus Indices. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 61, 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Maryland Department of Agriculture. Soils Data Collection and Verification as of January 2019; Maryland Department of Agriculture: Annapolis, MD, USA, 2019.
- Sharpley, A.N. Dependence of Runoff Phosphorus on Extractable Soil Phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pote, D.H.; Daniel, T.C.; Moore, P.A.; Nichols, D.J.; Sharpley, A.N.; Edwards, D.R. Relating Extractable Soil Phosphorus to Phosphorus Losses in Runoff. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, P.S.; Rendell, A.R.; Edwards, A.C.; Withers, P.J.A.; Aitken, M.N.; Truesdale, V.W. Relating Soil Phosphorus Indices to Potential Phosphorus Release to Water. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, R.O.; Sims, J.T. Soil Testing to Predict Phosphorus Leaching. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self-Davis, M.L.; Moore, P.A., Jr.; Joern, B.C. Determination of Water- and/or Dilute Salt-extractable Phosphorus. In Methods Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals, and Waters; Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin No. #396; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2000; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchemin, S.; Hesterberg, D.; Chou, J.; Beauchemin, M.; Simard, R.R.; Sayers, D.E. Speciation of Phosphorus in Phosphorus-Enriched Agricultural Soils Using X-Ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Spectroscopy and Chemical Fractionation. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in Inorganic and Organic Soil Phosphorus Fractions Induced by Cultivation Practices and by Laboratory Incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; McDowell, R.W.; Kleinman, P.J.A. Amounts, Forms, and Solubility of Phosphorus in Soils Receiving Manure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.; Sullivan, D.; Wolf, A.; Brandt, R.; Dou, Z.; Elliott, H.; Kovar, J.; Leytem, A.; Maguire, R.; Moore, P.; et al. Selection of a Water-Extractable Phosphorus Test for Manures and Biosolids as an Indicator of Runoff Loss Potential. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Wolf, A.M.; Beegle, D.B.; Moore, P.A. Measuring Water-Extractable Phosphorus in Manure as an Indicator of Phosphorus in Runoff. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, G.S.; Haggard, B.E.; Reiter, M.S.; Daniel, T.C.; Donoghue, A.M. Phosphorus Solubility in Poultry Litters and Granulates: Influence of Litter Treatments and Extraction Ratios. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N. Depth of Surface Soil-runoff Interaction as Affected by Rainfall, Soil Slope, and Management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, P.A.; Mallarino, A.P.; McFarland, A. The Importance of Sampling Depth When Testing Soils for their Potential to Supply Phosphorus to Surface Runoff. In Extension Fact Sheets; 2005; p. 14. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/research/publications/publication/?seqNo115=188150 (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J. A Modified Single Solution Method for the Determination of Phosphate in Natural Waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Orr, D. 2.4 Particle-Size Analysis. Methods Soil Anal. 2002, 5, 255–293. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, A.M.; Beegle, D.B. Recommended Soil Tests for Macronutrients. Recomm. Soil Test. Proced. Northeast. USA 2011, 493, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Method 3050B Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils; Revision 2; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 1–12. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/epa-3050b.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2021).
- Fuhrman, J.K.; Zhang, H.; Schroder, J.L.; Davis, R.L.; Payton, M.E. Water-Soluble Phosphorus as Affected by Soil to Extractant Ratios, Extraction Times, and Electrolyte. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N. Effect of Soil Properties on the Kinetics of Phosphorus Desorption. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leytem, A.B.; Mikkelsen, R.L.; Gilliam, J.W. Sorption of Organic Phosphorus Compounds in Atlantic Coastal Plain Soils. Soil Sci. 2002, 167, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrip, H.M.; Pagliari, P.H.; He, Z.; Harmel, R.D.; Cole, N.A.; Zhang, M. Legacy Phosphorus in Calcareous Soils: Effects of Long-Term Poultry Litter Application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, G.F.; Chardon, W.J.; McDowell, R.W. Phosphorus Movement and Speciation in a Sandy Soil Profile after Long-Term Animal Manure Applications. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, R.; Sharpley, A. Recognizing the Role of Soil Organic Phosphorus in Soil Fertility and Water Quality. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Ambient Water Quality Criteria Recommendations Information Supporting the Development of State and Tribal Nutrient Criteria Rivers and Streams in Nutrient Ecoregion XIV; EPA 822-B-00-022; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.D.; Portier, K.M.; Graetz, D.A.; Walker, M.L. An Environmental Threshold for Degree of Phosphorus Saturation in Sandy Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.T.; Maguire, R.O.; Leytem, A.B.; Gartley, K.L.; Pautler, M.C. Evaluation of Mehlich 3 as an Agri-Environmental Soil Phosphorus Test for the Mid-Atlantic United States of America. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 2016–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, B.; Nair, V.D.; Sharpley, A.N.; Kleinman, P.; Franklin, D.; Harris, W.G. Consistency of the Threshold Phosphorus Saturation Ratio across a Wide Geographic Range of Acid Soils. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2018, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, E.R.; Toor, G.S.; McGrath, J.M. Agronomic and Environmental Phosphorus Decline in Coastal Plain Soils after Cessation of Manure Application. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 107337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Characteristics | Site 1 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 | Site 6 | Site 7 | Site 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.55 | 7.25 | 6.56 | 6.36 | 6.14 | 6.22 | 6.35 | 6.38 |
| Organic Matter (%) | 0.56 | 1.87 | 1.87 | 2.11 | 2.89 | 2.08 | 1.00 | 0.99 |
| CEC (meq/100 g) | 6.40 | 15.10 | 11.70 | 12.50 | 13.20 | 10.20 | 5.90 | 8.30 |
| % Sand | 77.7 | 53.9 | 67.7 | 51.3 | 56.9 | 53.6 | 85.0 | 86.1 |
| % Silt | 17.5 | 40.6 | 23.7 | 39.2 | 32.7 | 38.6 | 12.1 | 11.4 |
| % Clay | 4.8 | 5.5 | 8.6 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 7.8 | 3.0 | 2.5 |
| Texture | Loamy Sand | Sandy Loam | Sandy Loam | Loam | Sandy Loam | Sandy Loam | Loamy Sand | Loamy Sand |
| USDA-NRCS soil classification | Coarse-loamy, siliceous, semiactive, mesic Typic Hapludults | Fine-loamy, mixed, active, mesic Typic Endoaquults | Fine-loamy, mixed, semiactive, mesic Typic Hapludults | Fine-loamy, mixed, active, mesic Typic Endoaquults | Fine-loamy, mixed, active, mesic Typic Endoaquults | Fine-loamy, mixed, active, mesic Typic Endoaquults | Coarse-loamy, siliceous, semiactive, mesic Aquic Hapludults | Coarse-loamy, siliceous, semiactive, mesic Aquic Hapludults |
| WRB Soil Classification | Acrisol | Gleysol | Acrisol | Gleysol | Gleysol | Gleysol | Acrisol | Acrisol |
| Acidity (meq/100 g) | 2.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 3.9 | 2.8 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Total P (mg/kg) | 691.9 | 2235.2 | 1460.7 | 1401.1 | 1446.4 | 1405.4 | 832.4 | 749.4 |
| M3–P (mg/kg) | 534.0 | 1127.0 | 806.0 | 692.0 | 502.0 | 785.0 | 602.0 | 620.0 |
| M3–Fe (mg/kg) | 281.6 | 270.5 | 357.8 | 316.7 | 275.6 | 183.0 | 185.4 | 164.1 |
| M3–Al (mg/kg) | 789.1 | 586.4 | 784.4 | 586.7 | 905.0 | 1006.0 | 767.3 | 615.1 |
| M3–PSR | 0.50 | 1.37 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.42 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.78 |
| M3–P:Total P | 0.77 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.35 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 0.83 |
| M3–Ca (mg/kg) | 721.4 | 2662.4 | 1375.1 | 1605.3 | 1495.1 | 1203.7 | 591.7 | 995.3 |
| M3–Mg (mg/kg) | 58.0 | 167.0 | 180.0 | 162.0 | 158.0 | 104.0 | 89.0 | 111.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roswall, T.; Lucas, E.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Burgis, C.; Scott, I.S.P.C.; Toor, G.S. Hotspots of Legacy Phosphorus in Agricultural Landscapes: Revisiting Water-Extractable Phosphorus Pools in Soils. Water 2021, 13, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081006
Roswall T, Lucas E, Yang Y-Y, Burgis C, Scott ISPC, Toor GS. Hotspots of Legacy Phosphorus in Agricultural Landscapes: Revisiting Water-Extractable Phosphorus Pools in Soils. Water. 2021; 13(8):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081006
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoswall, Taylor, Emileigh Lucas, Yun-Ya Yang, Charles Burgis, Isis S.P.C. Scott, and Gurpal S. Toor. 2021. "Hotspots of Legacy Phosphorus in Agricultural Landscapes: Revisiting Water-Extractable Phosphorus Pools in Soils" Water 13, no. 8: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081006
APA StyleRoswall, T., Lucas, E., Yang, Y.-Y., Burgis, C., Scott, I. S. P. C., & Toor, G. S. (2021). Hotspots of Legacy Phosphorus in Agricultural Landscapes: Revisiting Water-Extractable Phosphorus Pools in Soils. Water, 13(8), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081006