Integration of Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling for Assessing Surface Water Quality in Qaroun Lake, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analyses
2.3. Indexing Approach
2.3.1. Weighted Arithmetic Water Quality Index (WAWQI)
2.3.2. Pollution Indices (PIs)
Heavy Element Pollution Index (HPI)
Metal Index (MI)
Contamination Index (Cd)
Pollution Index (PI)
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Support Vector Machine Regression
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Data
3.2. Water Quality Indices
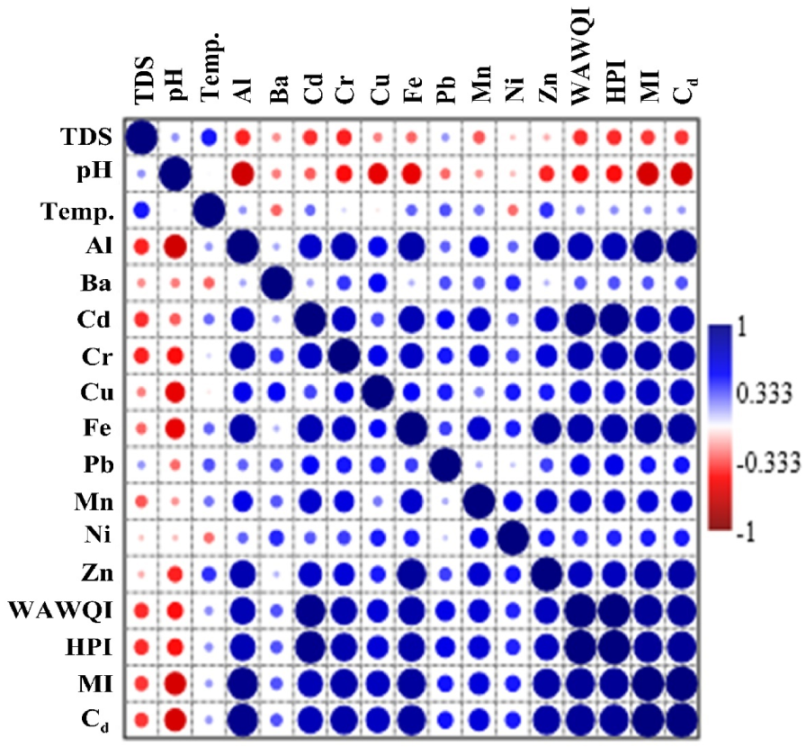
3.3. Correlation Matrix between WQIs and Physicochemical Parameters
3.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3.4.1. Cluster Analysis
3.4.2. Principal Component Analysis
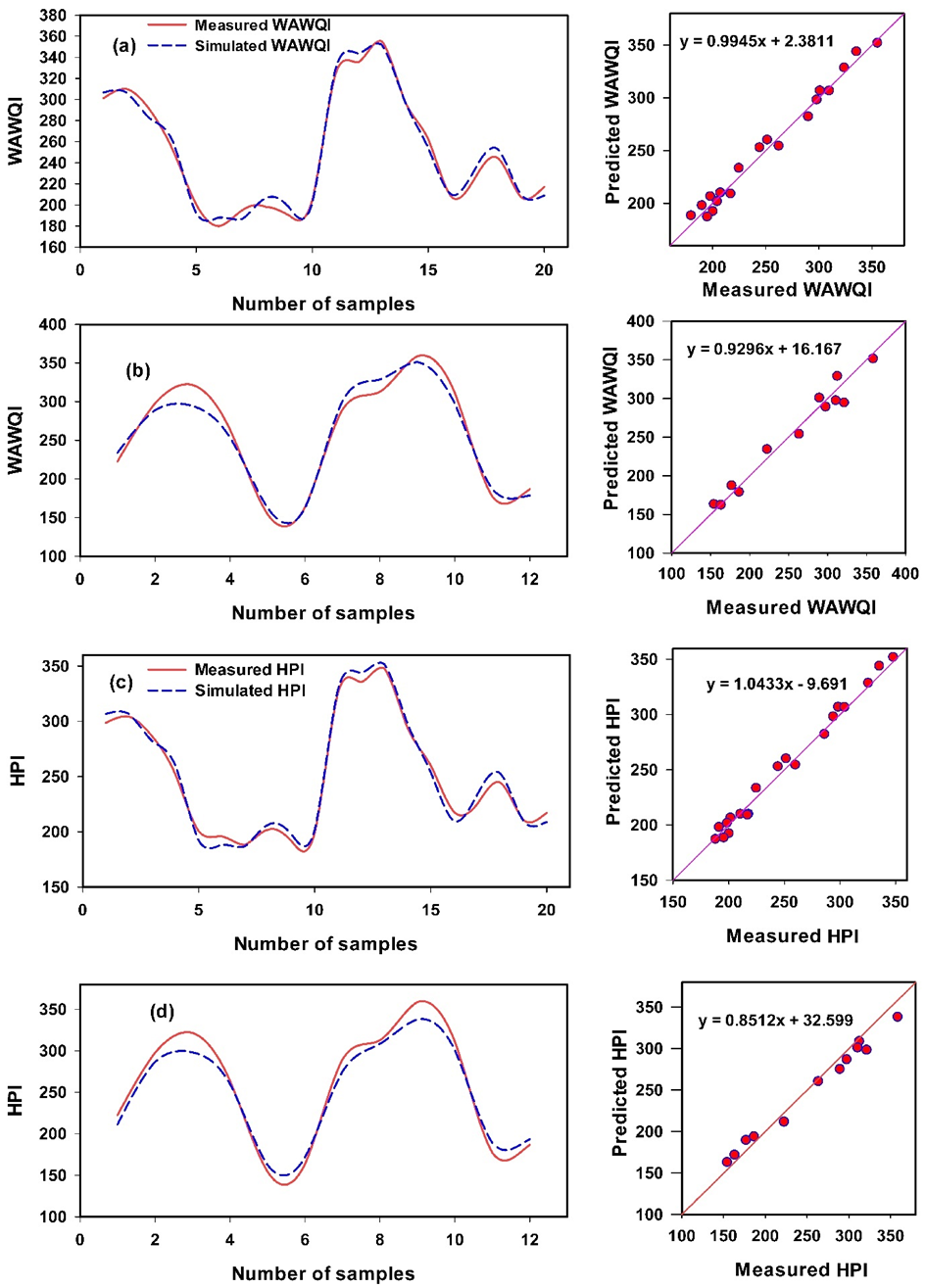
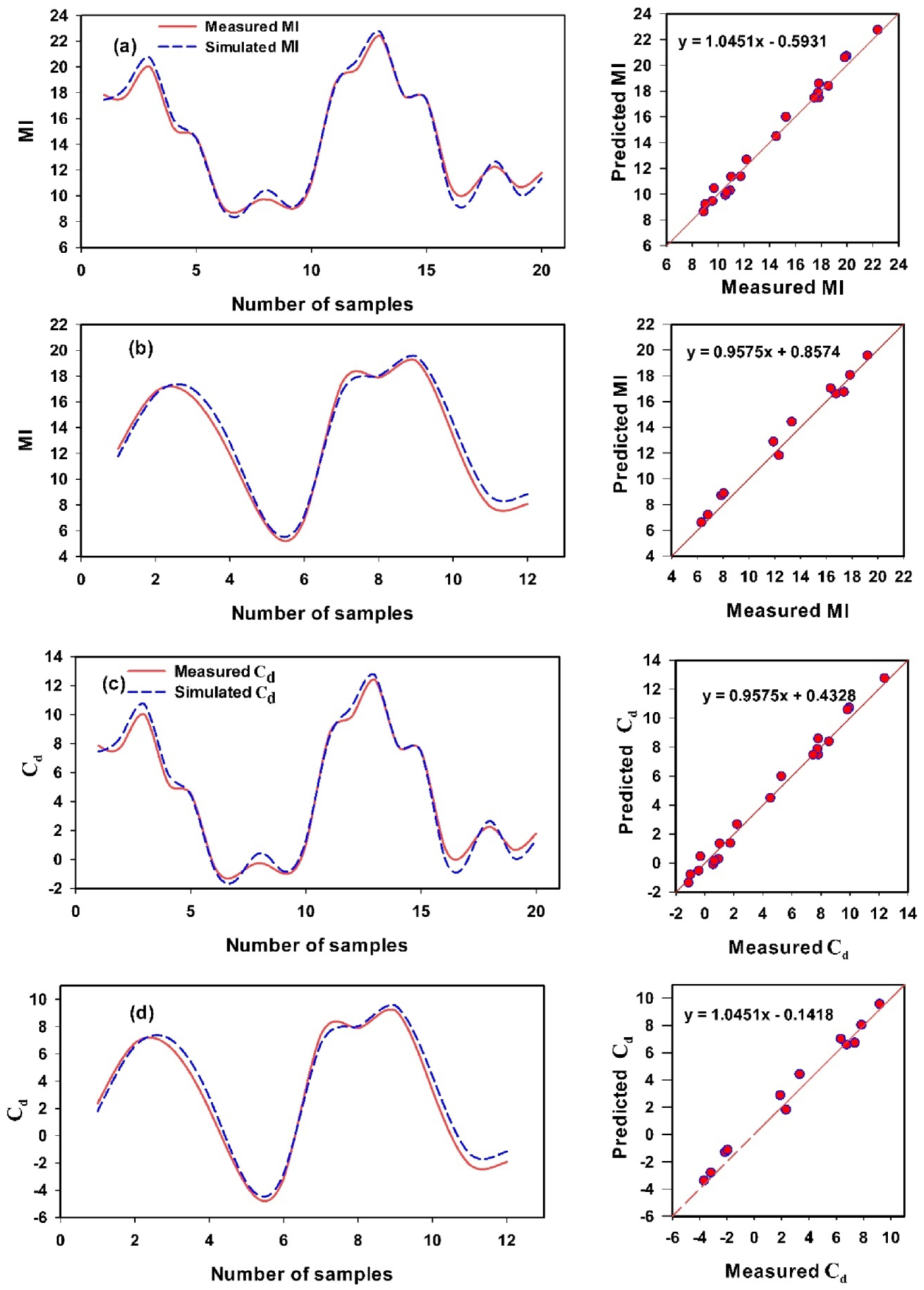
3.5. The Support Vector Machine Regression Models to Predict Water Quality Indices
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shakweer, L.M.; Abbas, M.M. Effect of ecological and biological factors on the uptake and concentration of trace elements by aquatic organisms at EdkuLake. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2005, 31, 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Jolly, Y.N.; Begum, B.A.; Choudhury, T.R.; Fatema, K.J.; Islam, M.S.; Ali, M.M.; Idris, A.M. Assessment of trace element toxicity in surface water of a fish breeding river in Bangladesh: A novel approach for ecological and health risk evaluation. Toxin Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, G.M.; Neary, J.P. Water quality for ecosystem and human health. United Nations Environment Programme Global Environment Monitoring System/Water Programme; GEMS Burlington: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, P.; Spoto, S.E.; Saiano, F.; Sprovieri, M.; Mazzola, S.; Nardone, G.; Ottonello, D. Heavy metals in coastal water systems. A case study from the northwestern Gulf of Thailand. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, V.F.; Ogunkuade, O.O.; Kanife, U.C. Biomarkers of oxidative stress and heavy metal levels as indicators of environmental pollution in some selected fishes in Lagos, Nigeria. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2010, 7, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- El-Zeiny, A.M.; El Kafrawy, S.B.; Ahmed, M.H. Geomatics based approach for assessing Qaroun Lake pollution. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2019, 22, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, M.; Fishar, M.R.A. Information sheet on Ramsar wetlands (RIS)—2009–2012. Ramsar Site 2012, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- EEAA/NCS (Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency/Nature Conservation Sector). Qaroun Protected Area Management Plane—Draft; EEAA: Cairo, Egypt, 2007; p. 73. Available online: https://www.eeaa.gov.eg/portals/0/eeaaReports/NCSCB/Management%20Plans/QPA%20MP.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, F. Assessment of water quality in Baiyangdian Lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Deng, J. Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.H.; Abdel-Satar, A.M. Studies of some heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and fish diets in some fish farms in El-Fayoum Province, Egypt. Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2005, 31, 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- Rifaat, A.E.; Ahdy, H.H.H.; Saadawy, M.M. Metal fluxes across sediment-water interface in Lake Qarun, Egypt. JAKU Earth Sci. 2012, 23, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.A.; Moussa, E.M.M.; El-Sabagh, M.E.I. Evaluation of heavy metal content in Qaroun Lake, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Part I: Bottom sediments. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalakoti, H.; Mishra, S.; Chaudhary, M.; Singal, S.K. Appraisal of water quality in the lakes of Nainital District through numerical indices and multivariate statistics, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2017, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupakheti, D.; Tripathee, L.; Kang, S.; Sharma, C.M.; Paudyal, R.; Sillanpää, M. Assessment of water quality and health risks for toxic trace elements in urban Phewa and remote Gosainkunda lakes, Nepal. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2017, 23, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kükrer, S.; Mutlu, E. Assessment of surface water quality using water quality index and multivariate statistical analyses in Saraydüzü Dam Lake, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Cui, B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, K.; Deng, W.; Gao, H.; Xiao, R. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China. Ecol. Modell. 2011, 222, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Effects of eutrophication on maximum algal biomass in lake and river ecosystems. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Taş, B.; Tepe, Y.; Topaldemir, H. Comprehensive assessment of water quality and associated health risk by using physicochemical quality indices and multivariate analysis in Terme River, Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, R.O.; Church, R.L. Water quality indexing and scoring. J. Environ. Eng. 1980, 106, 757–771. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.M.; Ahmed, M.S.; Adnan, R.; Shafiquzzaman, M. Water quality indices to assess the spatiotemporal variations of Dhaleshwari river in central Bangladesh. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2020, 8, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, V.; Kamboj, N.; Bisht, A. An overview of water quality indices as promising tools for assessing the quality of water resources. In Advances in Environmental Pollution Management: Wastewater Impacts and Treatment Technologies; Agriculture and Environmental Science Academy: Haridwar, India, 2020; pp. 188–214. [Google Scholar]
- Sheykhi, V.; Moore, F. Geochemical characterization of Kor River water quality, Fars Province, Southwest Iran. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2012, 4, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhanardakani, S.; Yari, A.R.; Taghavi, L.; Tayebi, L. Water quality pollution indices to assess the heavy metal contamination, case study: Groundwater resources of Asadabad Plain in 2012. Arch. Hyg. Sci. 2016, 5, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.; Saxena, A.; Shukla, S.; Sekar, S.; Senapathi, V.; Wu, J. Environmental contamination by heavy metals and associated human health risk assessment: A case study of surface water in Gomti River Basin, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goher, M.E.; Mahdy, E.M.; Abdo, M.H.; El Dars, F.M.; Korium, M.A.; Elsherif, A.S. Water quality status and pollution indices of Wadi El-Rayan lakes, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; El-Hattab, M. Integration of water pollution indices and DRASTIC model for assessment of groundwater quality in El Fayoum Depression, Western Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 158, 103554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Moghanm, F.S.; Almarshadi, M.H.; Alshammari, A.S.; Khedher, K.M.; Eid, E.M.; Hussein, H. Combining water quality indices and multivariate modeling to assess surface water quality in the Northern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; McCleiland, N.J.; Deininger, R.A.; O’Connor, M.F. A Water Quality Index—Crossing the Psychological Barrier. Proc. Int. Conf. Water Poll. Res. 1972, 6, 787–797. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, B.; Kumari, S. Heavy metal pollution index of ground water of an abandoned open cast mine filled with fly ash: A case study. Mine Water Environ. 2008, 27, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, R.; Singh, G.; Manish, J. Application of heavy metal pollution index for ground water quality assessment in Angul District of Orissa, India. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2011, 1, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Caerio, S.; Costa, M.H.; Ramos, T.B.; Fernandes, F.; Silveira, N.; Coimbra, A.; Painho, M. Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: An index analysis approach. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 5, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bartolomeo, A.; Poletti, L.; Sanchini, G.; Sebastiani, B.; Morozzi, G. Relationship among parameters of lake polluted sediments evaluated by multivariate statistical analysis. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamaras, N.; Michalopoulou, H.; Byun, H.R. Detection of drought events in Greece using daily precipitation. Hydrol. Res. 2010, 41, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Markert, B.; Chen, W.; Peng, C.; Ouyang, Z. Identification of heavy metal pollutants using multivariate analysis and effects of land uses on their accumulation in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 5889–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, M.V.; Praveena, S.M.; Chidambaram, S.; Nagarajan, R.; Elayaraja, A. Evaluation of water quality pollution for heavy metal contamination monitoring: A case study from Curtin Lake, Miri City, East Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1987–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, R.S.; Shah, M.H.; Shaheen, N.; Khalique, A.; Manzoor, S.; Jaffar, M. Multivariate analysis of selected metals in tannery effluents and related soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 122, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jiao, J.J.; Huang, J.; Huang, R. Multivariate statistical evaluation of trace elements in groundwater in a coastal area in Shenzhen, China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazidi, A.; Saidi, S.; Mbarek, N.B.; Darragi, F. Contribution of GIS to evaluate surface water pollution by heavy metals: Case of Ichkeul Lake (Northern Tunisia). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 134, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Leng, P.; Zhu, N.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, F. Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Dissolved Trace Elements in Groundwater in southern China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeih, S.F.; El-Zeiny, A.M. Qualitative assessment of groundwater quality based on land use spectral retrieved indices: Case study Sohag Governorate, Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 10, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliqi, E.; Jusufi, K.; Singh, S.K. Assessment and Spatial Mapping of Groundwater Quality Parameters Using Metal Pollution Indices, Graphical Methods and Geoinformatics. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2020, 10, 152–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidu, H.; Halilu, F.B.; Yerima, K.M.; Garba, L.M.; Suleiman, A.A.; Kankara, A.I.; Abdullahi, I.M. Heavy metals pollution indexing, geospatial and statistical approaches of groundwater within Challawa and Sharada industrial areas, Kano City, North-Western Nigeria. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Mumtaz, R.; Anwar, H.; Shah, A.A.; Irfan, R.; García-Nieto, J. Efficient water quality prediction using supervised machine learning. Water 2019, 11, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Ren, X.; Yang, Z.; Long, H.; Xiao, J. Influence of landscape structures on water quality at multiple temporal and spatial scales: A case study of Wujiang River Watershed in Guizhou. Water 2019, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsayed, S.; Hussein, H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Khedher, K.M.; Eid, E.M.; Gad, M. Application of irrigation water quality indices and multivariate statistical techniques for surface water quality assessments in the Northern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C. Prediction modeling of potentially toxic elements’ hydrogeopollution using an integrated Q-mode HCs and ANNs machine learning approach in SE Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamasi, G.; Cini, R. Heavy metals in drinking waters from Mount Amiata (Tuscany, Italy) possible risks from arsenic for public health in the province of Siena. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 327, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Haghiabi, A.H.; Parsaie, A. Prediction of side weir discharge coefficient by support vector machine technique. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noori, R.; Yeh, H.-D.; Abbasi, M.; Kachoosangi, F.T.; Moazami, S. Uncertainty analysis of support vector machine for online prediction of five-day biochemical oxygen demand. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Wu, F.-C. Support vector machine approach for longitudinal dispersion coefficients in natural streams. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2011, 11, 2902–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Wahed, M.S.M.; Mohamed, E.A.; Wolkersdorfer, C.; El-Sayed, M.I.; Adel M’nif, A.; Sillanpa, M. Assessment of water quality in surface waters of the Fayoum watershed, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 1765–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baioumy, H.M.; Kayanne, H.; Tada, R. Reconstruction of lake-level and climate changes in Lake Qarun, Egypt, during the last 7000 years. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, R.J.; Stickley, C.; Rose, N.L.; Peglar, S.; Fathi, A.A.; Appleby, P.G. Environmental changes at the desert margin: An assessment of recent paleolimnological records in Lake Qarun, Middle Egypt. J. Paleolimnol. 2006, 35, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.R.; Abdel Kawy, W.A.M. Land degradation risk assessment of El Fayoum depression, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 2767–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment). For the protection of aquatic life. In Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, B.; Bose, J.M. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution index for surface and spring water near a limestone mining area of the Lower Himalayas. Environ. Geol. 2001, 41, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brraich, O.S.; Jangu, S. Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring in the water of Harike Wetland (Ramsar site), India. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Backman, B.; Bodis, D.; Lahermo, P.; Rapant, S.; Tarvainen, T. Application of a groundwater contamination index in Finland and Slovakia. Environ. Geol. 1997, 36, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, A.E.; Offong, O.E. Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring. A study case from Akpabuyo-Odukpani area, Lower Cross River Basin (south Nigeria). Geo. J. 2002, 4, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, T. An index approach to metallic pollution in river waters. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Goher, M.E.; Farhat, H.I.; Abdo, M.H.; Salem, S.G. Metal pollution assessment in the surface sediment of Lake Nasser, Egypt. Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matiatos, I.; Alexopoulos, A.; Godelitsas, A. Multivariate statistical analysis of the hydrogeochemical and isotopic composition of the groundwater resources in northeastern Peloponnesus (Greece). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamtchueng, B.T.; Fantong, W.Y.; Wirmvem, M.J. Hydrogeochemistry and quality of surface water and groundwater in the vicinity of Lake Monoun, West Cameroon: Approach from multivariate statistical analysis and stable isotopic characterization. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Chawla, A.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K. Water quality assessment of River Beas, India, using multivariate and remote sensing techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakotondrabe, F.; Ngoupayou, J.R.; Mfonka, Z. Water quality assessment in the Betare-Oya gold mining area (East-Cameroon): Multivariate statistical analysis approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrough, P.A. Principles of geographical information systems for land resources assessment. Geo. Int. 1986, 1, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.F. Contouring: A guide to the analysis and display of spatial data. Comput. Methods Geosci. 1992, 10, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, N. Population dynamics of Rotifera in Ismailia Canal, Egypt. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2014, 4, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Aal, R.F.; El Sayed, S.M.; Attia, M.S.; Donia, N.S.; Goher, M.E. Pollution indices and distribution pattern of heavy metals in Qarun Lake water, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.H.; Abdel-Satar, A.M.; Goher, M.E.-M. Present Status and Long-Term Changes of Water Quality Characteristics in Heavily Polluted Mediterranean Lagoon, Lake Mariut, Egypt. IJRDO J. Appl. Sci. 2017, 3, 66–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.H. Assessment of some water quality characteristics and determination of some heavy metals in Lake Manzalah, Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2008, 12, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nafea, E.M.A.; Zyada, M.A. Biomonitoring of heavy metals pollution in Lake Burullus, Northern Delta, Egypt. Affrican J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.M.; Shaker, I.M. Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution in Water and Sediments and Their Effect on Oreochromis niloticus in The Northern Delta Lakes, Egypt. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture, Cairo, Egypt, 12–14 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, P.F.; Oliveira, J.S.; da Silva, E.F.; Fonseca, E.C. Geochemical signatures and mechanisms of trace elements dispersion in the area of the Vale das Gatas mine (Northern Portugal). J. Geochem. Explor. 2005, 85, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.H.; El-Fakharany, I.I.; Abd El-Razik, M.A.S. Monitoring of some agrochemical pollutants in surface water in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate. J. Pest. Cont. Environ. Sci. 2007, 15, 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Bao, F.; Wang, S.; Cui, F. Water quality assessment of the Huaihe River segment of Bengbu (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Water Res. 2016, 43, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Lam, P.K. Multivariate statistical evaluation of dissolved trace elements and a water quality assessment in the middle reaches of Huaihe River, Anhui, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Assessment of heavy-metal pollution in three different Indian water bodies by combination of multivariate analysis and water pollution indices. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattigod, S.V.; Page, A.L. Assessment of metal pollution in soils. In Applied Environmental Geochemistry; Thornton, I., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: London, UK, 1983; pp. 355–394. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Shih, K.; Zeng, E.Y.; Cheng, H. Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6150–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Karbassi, A.R.; Moghaddamnia, A.; Han, D.; Zokaei-Ashtiani, M.H.; Farokhnia, A.; Gousheh, M.G. 2011. Assessment of input variables determination on the SVMmodel performance using PCA, Gamma test, and forwardselection techniques for monthly stream flow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Liu, W.C. Water quality modeling in reservoirs using multivariate linear regression and two neural network models. Adv. Artif. Neural. Syst. 2015, 2015, 521721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Parameter | Aquatic Life * | Arithmetic Weight (Wi) | Sub-Quality Index (Qi) | WAWQI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. | 28 | 0.00007 | 92.22 | 0.006379047 |
| pH | 6.5–9 | 0.00002 | 107.85 | 0.002398024 |
| TDS | 500 | 0.00001 | 6908.32 | 0.008601328 |
| Al | 0.1 | 0.00623 | 170.00 | 1.058306921 |
| Ba | 0.05 | 0.01245 | 97.60 | 1.215185358 |
| Cd | 0.001 | 0.62253 | 240.00 | 149.4080359 |
| Cr | 0.01 | 0.06225 | 38.00 | 2.365627235 |
| Cu | 0.004 | 0.15563 | 275.00 | 42.79917694 |
| Fe | 0.3 | 0.00208 | 5.26 | 0.010928921 |
| Pb | 0.007 | 0.08893 | 97.14 | 8.63924017 |
| Mn | 0.05 | 0.01245 | 9.40 | 0.117036295 |
| Ni | 0.025 | 0.02490 | 59.20 | 1.474159287 |
| Zn | 0.05 | 0.01245 | 143.64 | 1.788414189 |
| ∑wi = 1 |
| Trace Element (mg/L) | Si (mg/L) (CCME, 2007) | MACi | Unit Weight Wi | Sub Index Qi | Wi × Qi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 0.1 | 100 | 0.00623 | 130 | 0.809368515 |
| Ba | 0.05 | 50 | 0.01245 | 88.2 | 1.098250815 |
| Cd | 0.001 | 1 | 0.62259 | 220 | 136.9700563 |
| Cr | 0.01 | 10 | 0.06226 | 33 | 2.054550845 |
| Cu | 0.004 | 4 | 0.15565 | 317.5 | 49.41817373 |
| Fe | 0.3 | 300 | 0.00208 | 4.53 | 0.009408044 |
| Pb | 0.007 | 7 | 0.08894 | 82.85 | 7.369446444 |
| Mn | 0.05 | 50 | 0.01245 | 8.2 | 0.102104951 |
| Ni | 0.025 | 25 | 0.02490 | 56.8 | 1.414527127 |
| Zn | 0.05 | 50 | 0.01245 | 191 | 2.378298251 |
| ∑(Wi) = 1 | ∑(Wi × Qi) |
| Class | PI Value | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | <1 | No effect |
| 2 | 1–2 | Slightly affected |
| 3 | 2–3 | Moderately affected |
| 4 | 3–5 | Strongly affected |
| 5 | >5 | Seriously affected |
| Water Quality Parameters | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T °C | pH | TDS | Al | Ba | Cd | Cr | Cu | Fe | Pb | Mn | Ni | Zn | |
| First year 2018 (n = 16) | |||||||||||||
| Min | 29.4 | 7.800 | 27,652.270 | 0.040 | 0.045 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.061 |
| Max | 34.2 | 8.400 | 38,752.040 | 0.720 | 0.068 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.022 | 0.029 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.163 |
| Mean | 31.356 | 8.244 | 35,580.940 | 0.299 | 0.053 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.102 |
| SD | 1.168 | 0.136 | 2634.437 | 0.246 | 0.007 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.037 |
| Second year 2019 (n = 16) | |||||||||||||
| Min | 29.4 | 7.8 | 28,840.43 | 0.04 | 0.0447 | 0.0024 | 0.003 | 0.0017 | 0.0155 | 0.0057 | 0.0042 | 0.011 | 0.06052 |
| Max | 34.2 | 8.4 | 39,056.09 | 0.72 | 0.0678 | 0.0045 | 0.0054 | 0.0219 | 0.029 | 0.0081 | 0.0077 | 0.0204 | 0.16271 |
| Mean | 31.35625 | 8.24375 | 35,777.81 | 0.2985 | 0.053025 | 0.003259 | 0.004075 | 0.012551 | 0.021119 | 0.0068 | 0.005638 | 0.016256 | 0.101624 |
| SD | 1.167886 | 0.136473 | 2442.075 | 0.245747 | 0.00724 | 0.001757 | 0.000686 | 0.00525 | 0.004255 | 0.000593 | 0.001052 | 0.002841 | 0.037036 |
| Data across two years (n = 32) | |||||||||||||
| Min | 29.4 | 7.8 | 27,652.27 | 0.04 | 0.0447 | 0.0024 | 0.003 | 0.0017 | 0.0155 | 0.0057 | 0.0042 | 0.011 | 0.06052 |
| Max | 34.2 | 8.4 | 39,056.09 | 0.72 | 0.0678 | 0.0045 | 0.0054 | 0.0219 | 0.029 | 0.0081 | 0.0077 | 0.0204 | 0.16271 |
| Mean | 31.35625 | 8.24375 | 35,679.37 | 0.29 | 0.053025 | 0.003259 | 0.004075 | 0.012551 | 0.021119 | 0.0068 | 0.005638 | 0.016256 | 0.101624 |
| SD | 1.148895 | 0.134254 | 2500.774 | 0.24175 | 0.007122 | 0.001745 | 0.000674 | 0.005165 | 0.004186 | 0.000584 | 0.001035 | 0.002795 | 0.036433 |
| Egyptian Lakes | Fe | Mn | Zn | Cu | Cd | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qaroun | 0.015–0.029 | 0.004–0.007 | 0.060–0.162 | 0.001–0.021 | 0.0024–0.0045 | Present study |
| Mariut | 0.522–1.952 | 0.02–0.085 | 0.023–0.0865 | 0.003–0.088 | 0.0025–0.0127 | [72] |
| Manzalah | 0.447–1.212 | 0.334–0.925 | 0.036–0.093 | 0.003–0.008 | 0.0022–0.0056 | [73] |
| Burullus | 0.025–0.06 | - | 0.018–0.055 | 0.011–0.033 | 0.0029–0.0085 | [74] |
| Idku | 0.08–1.89 | 0.003–0.088 | 0.004–0.05 | 0.002–0.024 | ND–0.008 | [75] |
| Permissible level | 0.3 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.002 | 0.001 | [57] |
| Water Quality Indices (WQIs) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WAWQI | HPI | MI | Cd | |
| First year 2018 (n = 16) | ||||
| Min | 154.591 | 154.5875 | 6.343048 | −3.65695 |
| Max | 321.625 | 321.6374 | 20.69338 | 10.69338 |
| Mean | 234.5054 | 234.5096 | 12.9214 | 2.921396 |
| SD | 55.81393 | 55.81947 | 4.366384 | 4.366384 |
| Second year 2019 (n = 16) | ||||
| Min | 177.240 | 177.2382 | 7.883352 | −2.11665 |
| Max | 358.788 | 358.8039 | 22.7259 | 12.7259 |
| Mean | 269.1347 | 270.424 | 14.68734 | 4.687343 |
| SD | 63.3035 | 61.37765 | 4.753074 | 4.753074 |
| Data across two years (n = 32) | ||||
| Min | 154.591 | 154.5875 | 6.343048 | −3.65695 |
| Max | 358.788 | 358.8039 | 22.7259 | 12.7259 |
| Mean | 252.461 | 252.4668 | 13.80437 | 3.804369 |
| SD | 60.51976 | 60.5257 | 4.578364 | 4.578364 |
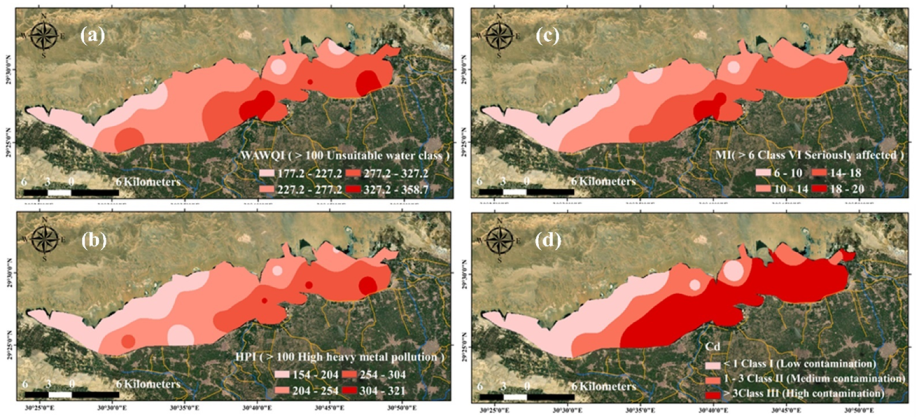
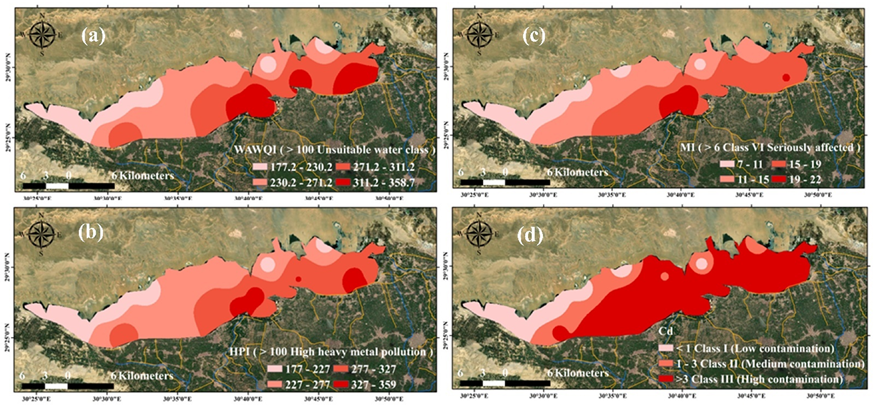
| WQIs | Range | Water Class | Samples (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Year (2018) | Second Year (2019) | Across Two Years | |||
| Weighted arithmetic water quality index (WAWQI) | 0–25 | Excellent | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 26–50 | Good | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 51–75 | Poor | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 76–100 | Very poor | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| >100 | Unsuitable | 100% (16 samples) | 100% (16 samples) | 100% (32 samples) | |
| Metal index (HPI) | <100 | Low polluted | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| >100 | High polluted | 100% (16 samples) | 100% (16 samples) | 100% (32 samples) | |
| Trace element evaluation index (MI) | <0.3 | Very pure | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.3–1.0 | Pure | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1.0–2.0 | Slightly affected | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2.0–3.0 | Moderately affected | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3.0–6.0 | Strongly affected | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| >6.0 | Seriously affected | 100% (16 samples) | 100% (16 samples) | 100% (32 samples) | |
| Contamination index (Cd) | >1 | Low | 37% (6 samples) | 31% (5 samples) | 34% (11 samples) |
| 1–3 | Medium | 19% (3 sample) | 13% (2 sample) | 16% (5 samples) | |
| <3 | High | 44% (7 samples) | 56% (9 samples) | 50% (16 sample) | |
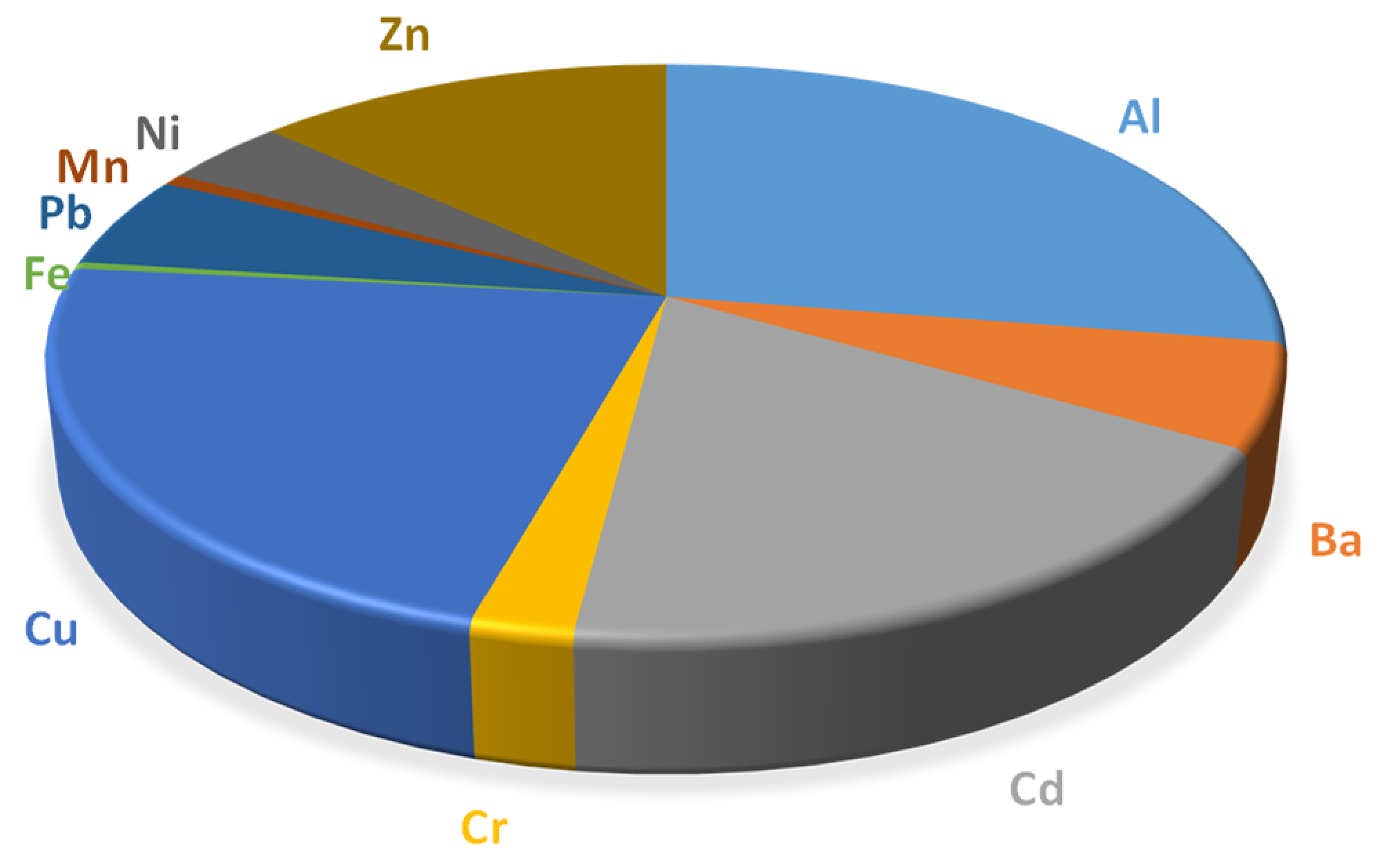
| Trace Element | PI | Class | Effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Year | Second Year | Across Two Years | |||
| Al | 3.41 | 3.61 | 3.51 | IV | Strongly affected |
| Ba | 0.72 | 0.81 | 0.765 | I | No effect |
| Cd | 2.30 | 2.55 | 2.425 | III | Moderately affected |
| Cr | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.295 | I | No effect |
| Cu | 2.77 | 2.75 | 2.76 | III | Moderately affected |
| Fe | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | I | No effect |
| Pb | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.68 | I | No effect |
| Mn | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.085 | I | No effect |
| Ni | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.47 | I | No effect |
| Zn | 1.63 | 1.74 | 1.685 | II | Slightly affected |
| Water Quality Indices (WQIs) | Performance Criteria | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | MAD | Acc | ||
| Calibration models | WAWQI | 0.99 *** | 6.70 | 6.14 | 0.995 |
| HPI | 0.99 *** | 6.18 | 5.60 | 0.997 | |
| MI | 0.99 *** | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.999 | |
| Cd | 0.99 *** | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.996 | |
| Validation models | WAWQI | 0.97 *** | 12.64 | 11.16 | 0.998 |
| HPI | 0.99 *** | 12.65 | 11.23 | 0.989 | |
| MI | 0.99 *** | 0.63 | 0.56 | 0.966 | |
| Cd | 0.99 *** | 0.63 | 0.56 | 0.970 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gad, M.; Abou El-Safa, M.M.; Farouk, M.; Hussein, H.; Alnemari, A.M.; Elsayed, S.; Khalifa, M.M.; Moghanm, F.S.; Eid, E.M.; Saleh, A.H. Integration of Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling for Assessing Surface Water Quality in Qaroun Lake, Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162258
Gad M, Abou El-Safa MM, Farouk M, Hussein H, Alnemari AM, Elsayed S, Khalifa MM, Moghanm FS, Eid EM, Saleh AH. Integration of Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling for Assessing Surface Water Quality in Qaroun Lake, Egypt. Water. 2021; 13(16):2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162258
Chicago/Turabian StyleGad, Mohamed, Magda M. Abou El-Safa, Mohamed Farouk, Hend Hussein, Ashwaq M. Alnemari, Salah Elsayed, Moataz M. Khalifa, Farahat S. Moghanm, Ebrahem M. Eid, and Ali H. Saleh. 2021. "Integration of Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling for Assessing Surface Water Quality in Qaroun Lake, Egypt" Water 13, no. 16: 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162258
APA StyleGad, M., Abou El-Safa, M. M., Farouk, M., Hussein, H., Alnemari, A. M., Elsayed, S., Khalifa, M. M., Moghanm, F. S., Eid, E. M., & Saleh, A. H. (2021). Integration of Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling for Assessing Surface Water Quality in Qaroun Lake, Egypt. Water, 13(16), 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162258













