Assessment of Trophic Responses of a Reservoir to Seasonal and Annual Variations in Monsoon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
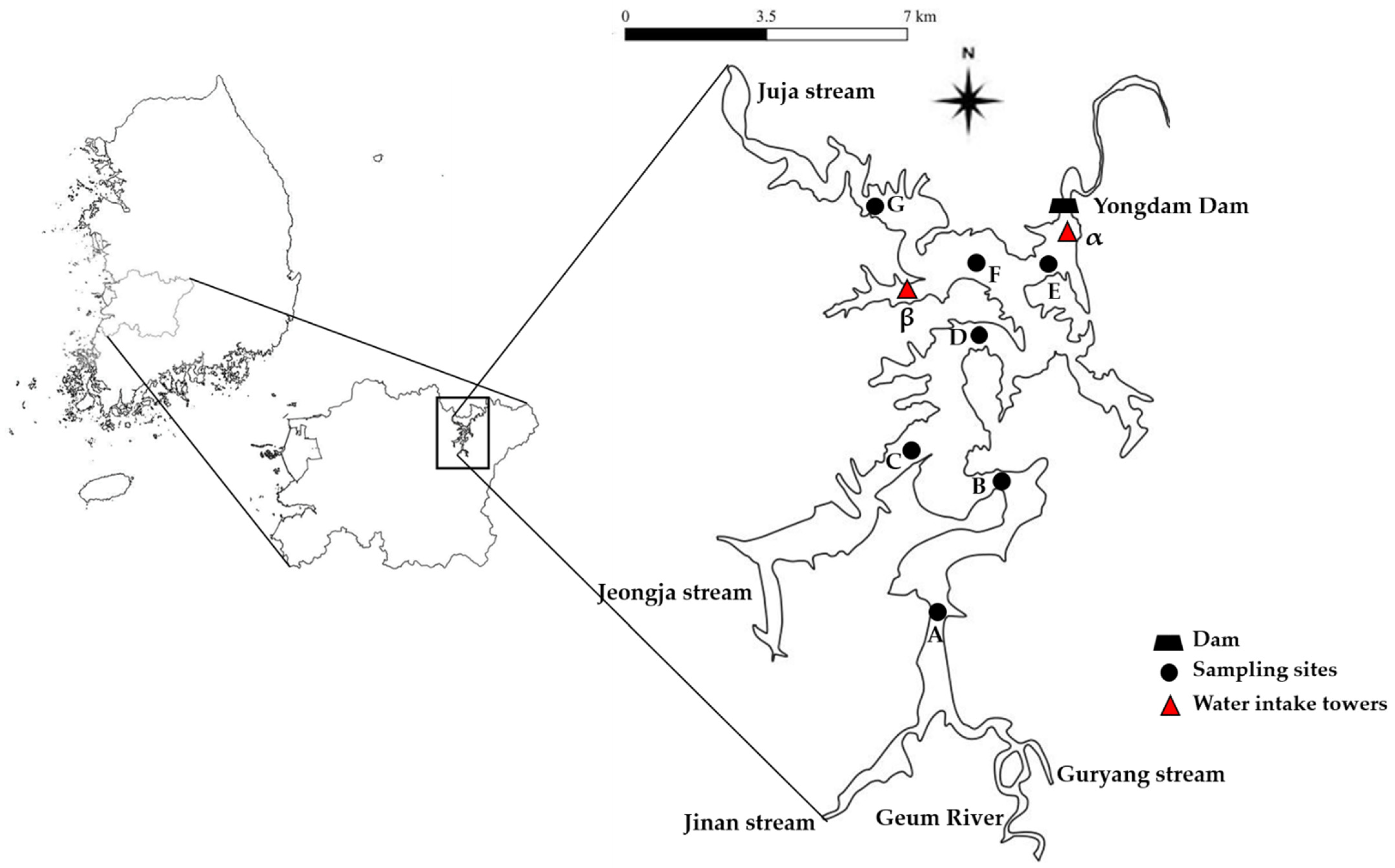
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Trophic State Index and Non-Algal Light Attenuation Coefficient
2.5. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
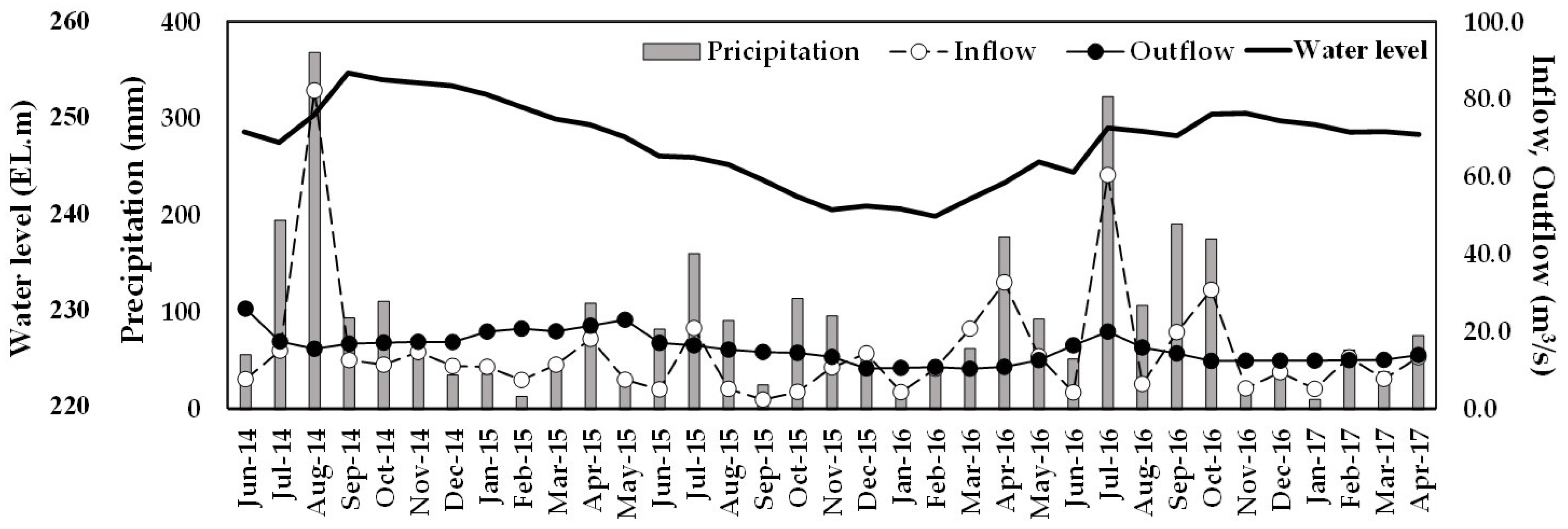
3.1. Precipitation Pattern and Flow Regime
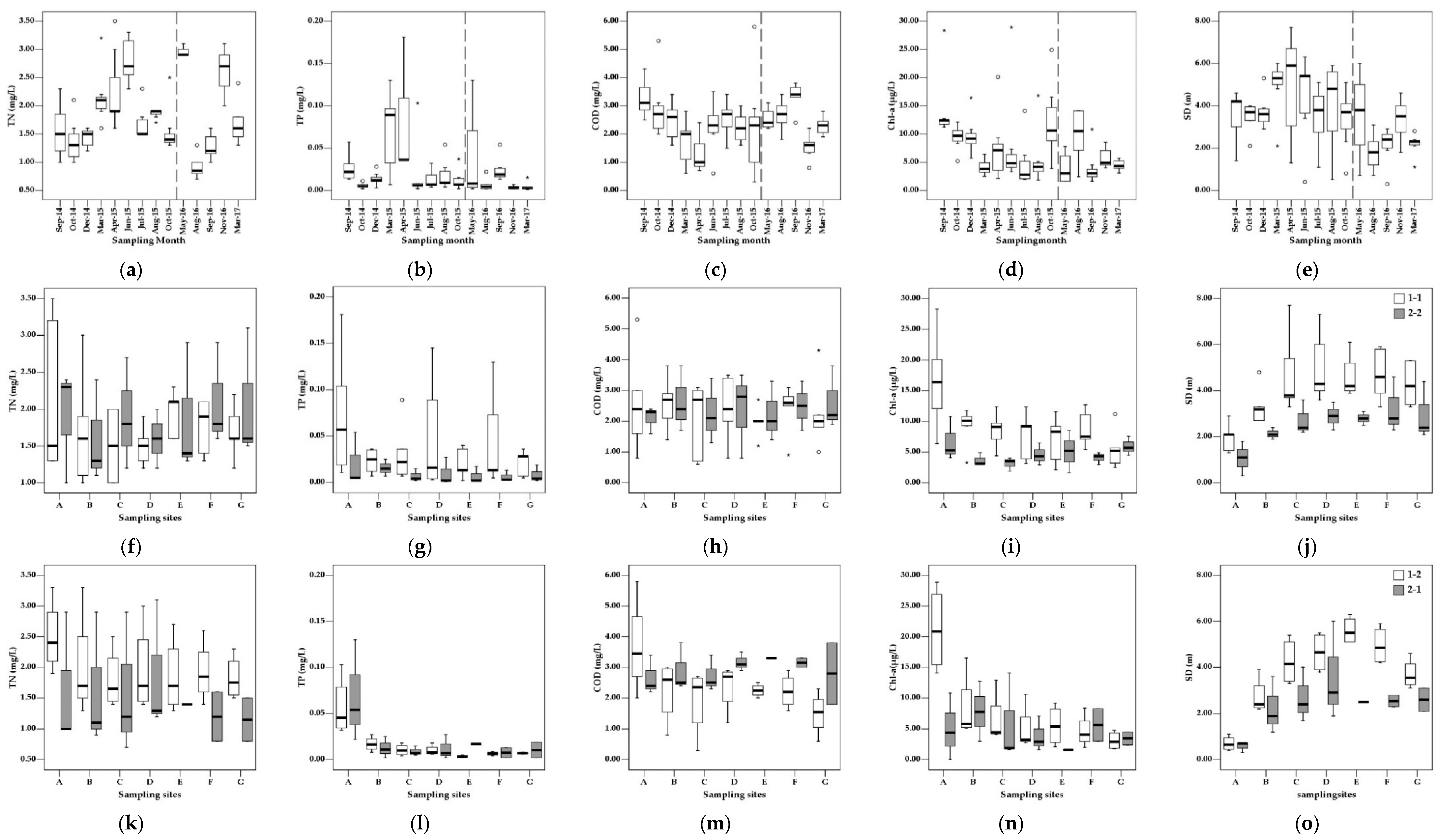
3.2. Water Quality Parameters
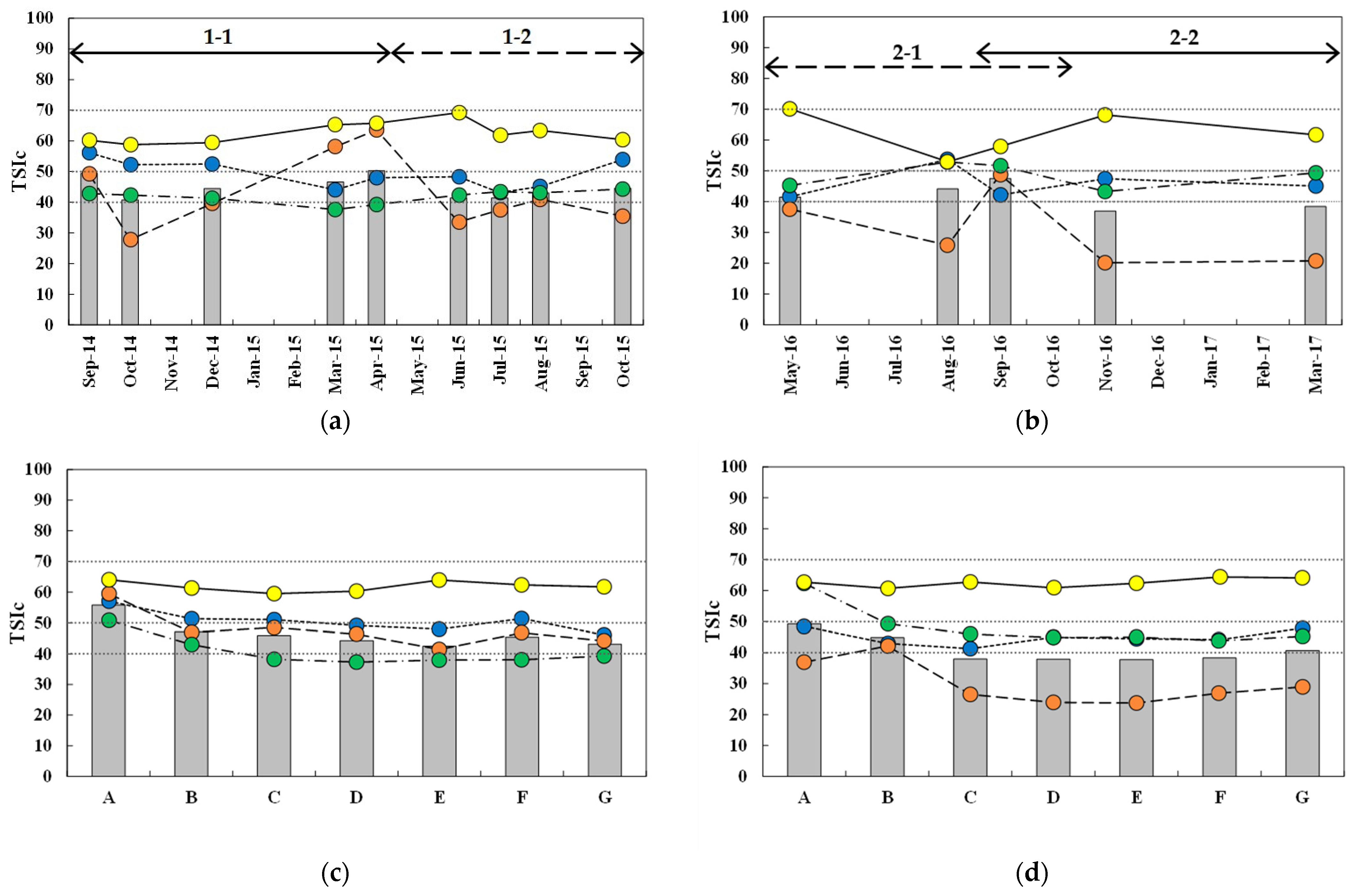
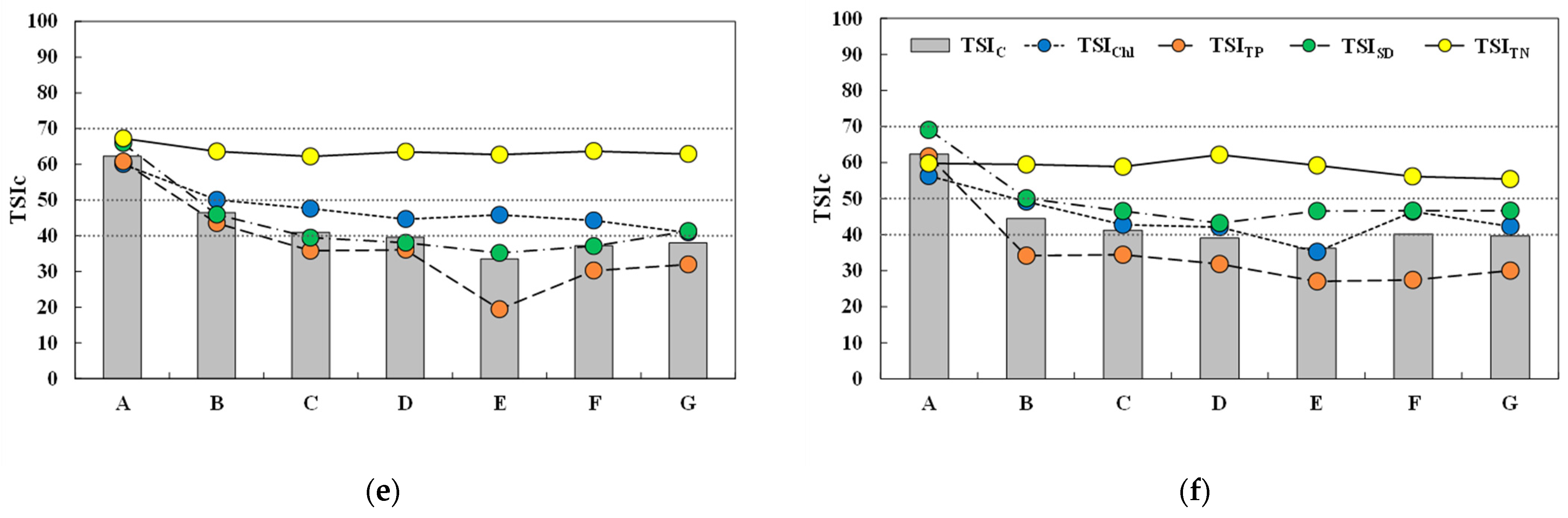
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Trophic State Index
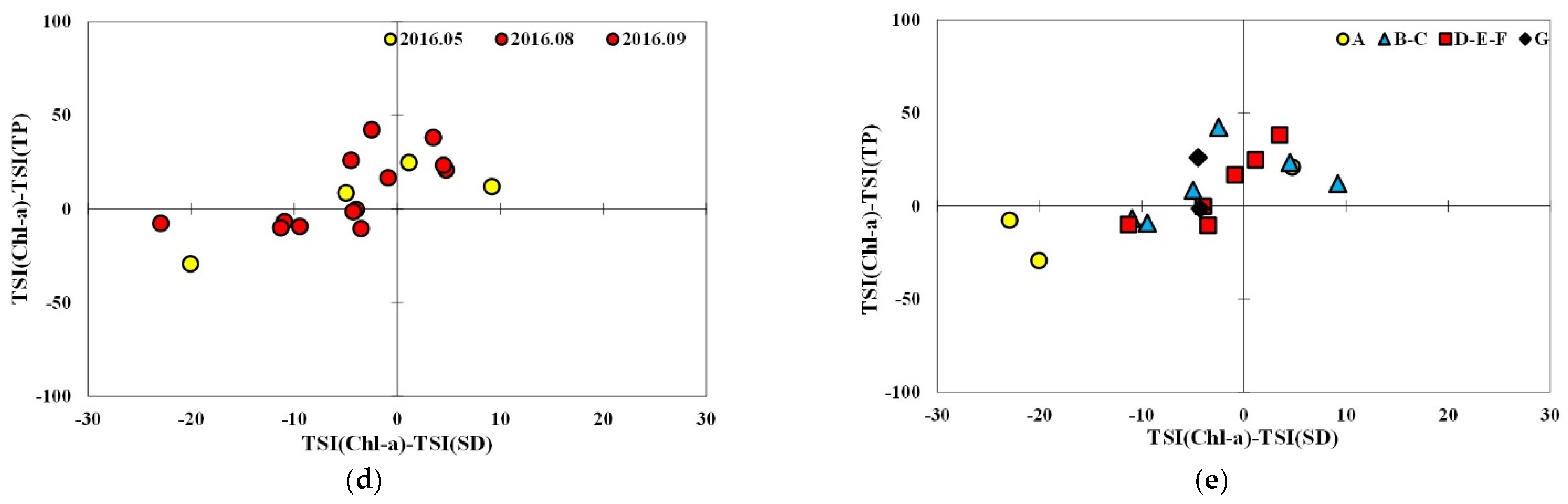
3.4. Trophic State Index Deviation
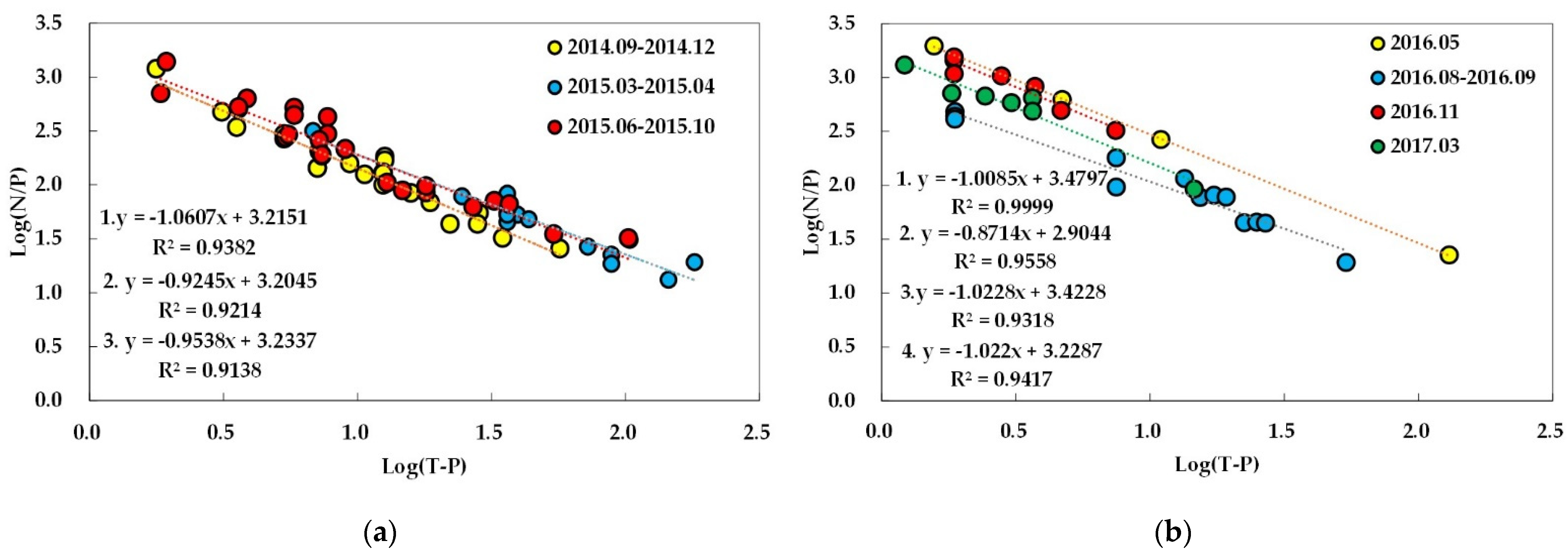
3.5. Empirical Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations in Water Quality Parameters
4.2. Nutritional Limitation
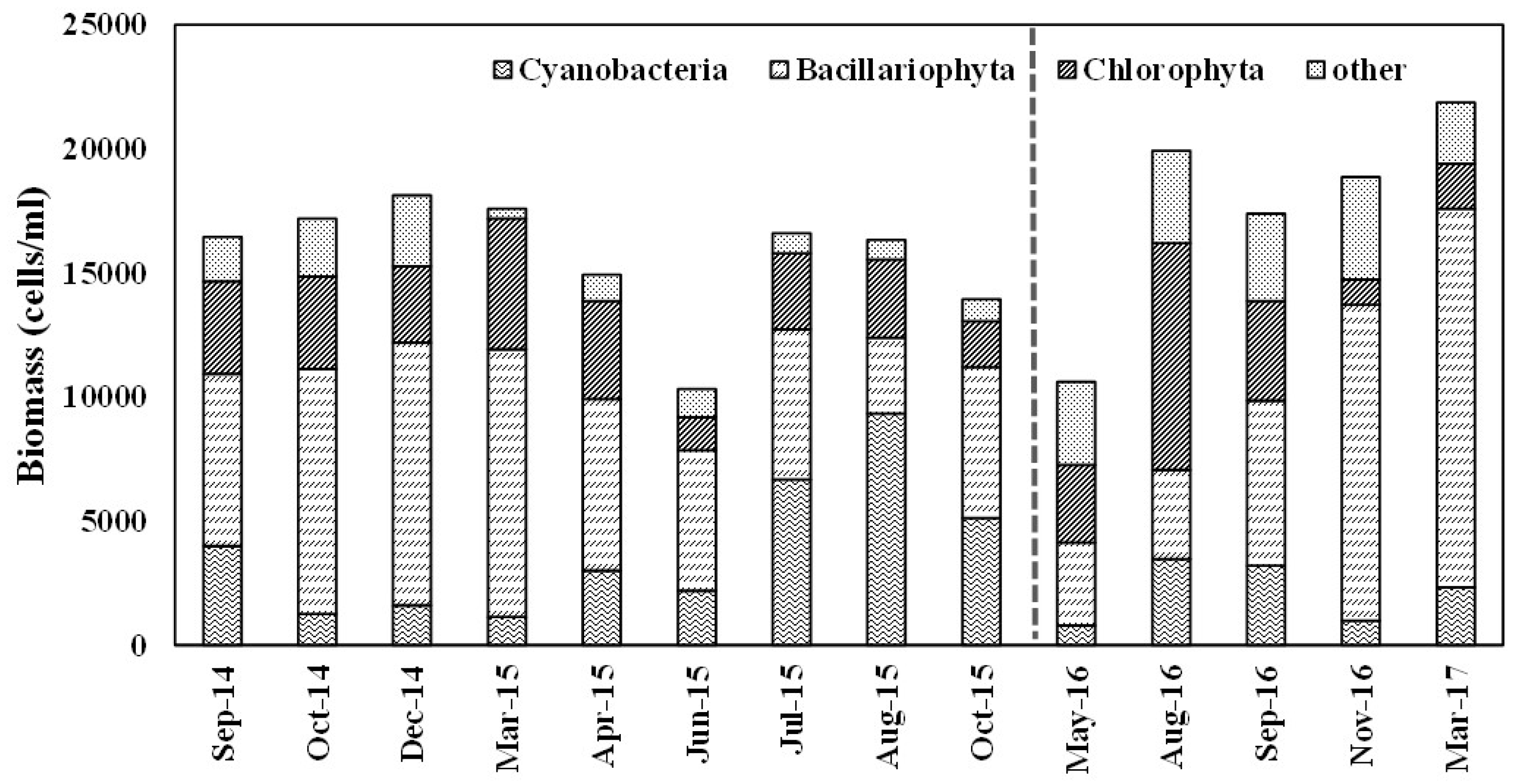
4.3. Trophic Limiting Factors
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ingole, N.P.; An, K.G. Modifications of nutrient regime, chlorophyll-a, and trophic state relations in daechung reservoir after the construction of an upper dam. J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Atique, U.; An, K.G. Reservoir water quality assessment based on chemical parameters and the chlorophyll dynamics in relation to nutrient regime. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhot, A.; Talbot, G.; Ricard, S.; Turcotte, R.; Guinard, K. Assessing the potential impacts of dam operation on daily flow at ungauged river reaches. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology Lake and River Ecosystem; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780127447605. [Google Scholar]
- Atique, U.; An, K.G. Landscape heterogeneity impacts water chemistry, nutrient regime, organic matter and chlorophyll dynamics in agricultural reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markad, A.T.; Landge, A.T.; Nayak, B.B.; Inamdar, A.B.; Mishra, A.K. Trophic state modeling for shallow freshwater reservoir: A new approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haande, S.; Rohrlack, T.; Semyalo, R.P.; Brettum, P.; Edvardsen, B.; Lyche-Solheim, A.; Sørensen, K.; Larsson, P. Phytoplankton dynamics and cyanobacterial dominance in Murchison Bay of Lake Victoria (Uganda) in relation to environmental conditions. Limnologica 2011, 41, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, B.M.; Carvalho, L.; Dudley, B.; May, L. Variation in chlorophyll a to total phosphorus ratio across 94 UK and Irish lakes: Implications for lake management. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 115, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.P.; Liu, L.S.; Zheng, B.H. Eutrophication development and its key regulating factors in a water-supply reservoir in North China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am. Sci. 1958, 46, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.H. The nitrogen and phosphorus dependence of algal biomass in lakes: An empirical and theoretical analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, F.E.; North, R.L.; McEachern, P.; Obrecht, D.V.; Gurung, T.B.; Jones, S.B.; Jones, J.R. Phytoplankton nutrient deficiencies vary with season in sub-tropical lakes of Nepal. Hydrobiologia 2019, 833, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maberly, S.C.; King, L.; Dent, M.M.; Jones, R.I.; Gibson, C.E. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton and periphyton growth in upland lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 2136–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.C.; Brezonik, P.; Heaney, J.P.; Dickinson, R.E.; Preston, S.D. A Classification of Florida Lakes; Final Report; Department of Environmental Regulations: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Ptacnik, R.; Andersen, T.; Tamminen, T. Performance of the Redfield ratio and a family of nutrient limitation indicators as thresholds for phytoplankton N vs. P limitation. Ecosystems 2010, 13, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Wan, J.; Pan, X.; Wan, C.; Peng, J.; Chang, J.; Xie, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus relationships to chlorophyll a in 139 reservoirs of China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, J.; Han, B.; Naselli-Flores, L. The effects of absolute and relative nutrient concentrations (N/P) on phytoplankton in a subtropical reservoir. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, E. The scope and chief problems of regional limnology. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1929, 22, 129–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.J.; Rigler, F.H. The phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, C.R.; Brezonik, P.L. A Carlson-type trophic state index for nitrogen in Florida Lakes. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1981, 17, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, N.M.; Rutherford, J.C.; Clayton, J.S. A monitoring and classification system for New Zealand lakes and reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1999, 15, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, W.T. Secchi disk and chlorophyll. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. Expanding the trophic state concept to identify non-nutrient limited lakes and reservoirs. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Enhancing the States’ Lake Management Programs. Monitoring and Lake Impact Assessment, Chicago, IL, USA; 1991; pp. 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Havens, K.E. Using trophic state index (TSI) values to draw inferences regarding phytoplankton limiting factors and seston composition from routine water quality monitoring data. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2000, 33, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, J.; Atique, U.; An, K.G. Multiyear links between water chemistry, algal chlorophyll, drought-flood regime, and nutrient enrichment in a morphologically complex reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.-G. Long-term interannual and seasonal links between the nutrient regime, sestonic chlorophyll and dominant bluegreen algae under the varying intensity of monsoon precipitation in a drinking water reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhu, G.; Cai, Y.; Vilmi, A.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Relationships between nutrient, chlorophyll a and Secchi depth in lakes of the Chinese Eastern Plains ecoregion: Implications for eutrophication management. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 109923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R.; Knowlton, M.F.; An, K.G. Trophic state, seasonal patterns and empirical models in South Korean Reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2003, 19, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, M.F.; Jones, J.R. Temporal and spatial dynamics of suspended sediment, nutrients, and algal biomass in Mark Twain Lake, Missouri. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1995, 135, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; An, K.G. Major nutrients and chlorophyll dynamics in Korean agricultural reservoirs along with an analysis of trophic state index deviation. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers 2017, 10, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; An, G.K. Evaluation of algal chlorophyll and nutrient relations and the N:P ratios along with trophic status and light regime in 60 Korea reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kim, J.Y.; An, G.K. Trophic responses of the Asian reservoir to long-term seasonal and interannual dynamic monsoon. Water 2020, 12, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, E.J.; Cichra, M.; Havens, K.; Hanton, C.; Badylak, S.; Rueter, B.; Randall, M.; Hansen, P. Relationships between phytoplankton dynamics and the availability of light and nutrients in a shallow sub-tropical lake. J. Plankton Res. 1997, 19, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talling, J.F. Phytoplankton-zooplankton seasonal timing and the ‘clear-water phase’ in some English lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirok, K.; Gaedke, U. Spring weather determines the relative importance of ciliates, rotifers and crustaceans for the initiation of the clear-water phase in a large, deep lake. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, M. Spatial gradient and seasonal variation of trophic status in a large water supply reservoir for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, R.; Garg, J.K. Trophic state assessment of Bhindawas Lake, Haryana, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Mahajan, A.K.; Meena, N.K. Evaluation of trophic status and its limiting factors in the Renuka Lake of Lesser Himalaya, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, A. Trophic state and limiting nutrient evaluations using trophic state/level index methods: A case study of Borcka Dam Lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOE. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water Quality Contamination, 7th ed.; Ministry of Environemnt (MOE): Gwacheon, Korea, 2014; p. 435. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E.; Simpson, J. A Coordinator’s Guide to Volunteer Lake Monitoring Methods. North Am. Lake Manag. Soc. 1996, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, W.W. An empirical analysis of phosphorus, nitrogen, and turbidity effects on reservoir chlorophyll-a levels. Can. Water Resour. J. 1982, 7, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cade, B.S.; Noon, B.R. A gentle introduction to quantile regression for ecologists. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, M.S.; An, K.G. Spatio-temporal variabilities of nutrients and chlorophyll, and the trophic state index deviations on the relation of nutrients-chlorophyll–light availability. J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 39, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.W.; Lee, H.; Jung, Y. The effect of hydrodynamic flow regimes on the algal bloom in a monomictic reservoir. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.G.; Park, S.S. Indirect influence of the summer monsoon on chlorophyll-total phosphorus models in reservoirs: A case study. Ecol. Model. 2002, 152, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Kwun, S.K.; Yoon, C.G. Water quality and limnology of Korean reservoirs. Paddy Water Environ. 2003, 1, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, G.; Jun, M.S.; Choi, K. Eutrophication of reservoirs in South Korea. Limnology 2001, 2, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.D.; Yi, Y.; Ko, I.H.; Kim, W.G. Water quality management by reservoir discharge control through selective withdrawal. In Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference, Korea, 1 May 2005; pp. 454–458. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Lim, K.J.; Choi, J.H. Contribution of internal nutrients loading on the water quality of a reservoir. Water 2019, 11, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, T.; Völkner, C.; Koschorreck, M. A sediment core incubation method to measure the flux of dissolved organic carbon between sediment and water. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, J.L.; Pierzynski, G.M. Methods of Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals, and Waters, 2nd ed.; South Coop Ser Bull, Virginia Tech University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009; Volume 408, pp. 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Geng, J.; Yin, H.; Chen, K. Sediment internal nutrient loading in the most polluted area of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its contribution to lake eutrophication. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, M.; Tammeorg, P.; Niemistö, J.; Simojoki, A.; Tammeorg, O. Internal phosphorus loading in a small shallow Lake: Response after sediment removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.A.; Fleck, R.; Pace, M.L.; Wilkinson, G.M. Scaling relationships between lake surface area and catchment area. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, M. Growth responses of several diatom species isolated from various environments to temperature. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by bluegreen algae in lake phytoplankton. Science 1983, 221, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimbee, A.M.; Prepas, E.E. Evaluation of total phosphorus as a predictor of the relative biomass of blue-green algae with emphasis on Alberta lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquatic. Sci. 1987, 44, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; McCauley, E.; Downing, J.A. Patterns in phytoplankton taxonomic composition across temperate lakes of differing nutrient status. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, C.; Ryding, S.O. Eutrophication parameters and trophic state indices in 30 Swedish waste-receiving lakes. Arch Hydrobiol. 1980, 89, 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Hellström, T. An empirical study of nitrogen dynamics in lakes. Water Environ. Res. 1996, 68, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marberly, S.C.; Pitt, J.; Davies, P.S.; Carvalho, L. Nitrogen and phosphorus limitation and the management of small productive lakes. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Metabolic sensitivities of lacustrine ecosystems to anthropogenic forcing. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 61, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankto; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S.; Moisander, P.H.; Dyble, J. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an amphasis on cyanobacteria. Sci. World 2001, 1, 139109. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.S. Cyanobacterial water-blooms. Adv. Bot. Res. 1987, 13, 67–143. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W. Nuisance phytoplankton blooms in coastal, estuarine and inland waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 823–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. The long, the short and the stalled: On the attributes of phytoplankton selected by physical mixing in lakes and rivers. Hydrobiologia 1994, 289, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Kiesling, R.; Sterner, R.; Kilham, S.; Johnson, F.A. Green, blue-green and diatom algae—Taxonomic differences in competitive ability for phosphorus, silica and nitrogen. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1986, 106, 473–485. [Google Scholar]
- McQueen, D.J.; Lean, D.R.S. Influence of water temperature and nitrogen–phosphorus ratios on the dominant bluegreen algae in Lake St. George, Ontario. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1987, 44, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilham, S.S. A hypothesis concerning silica and the freshwater plankton diatoms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1971, 16, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W. Resource competition during seasonal succession toward dominance by cyanobacteria. Ecology 1989, 70, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, J.F. Field studies on zooplankton-cyanobacteria interactions. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1987, 21, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryding, S.O.; Rast, W. The Control of Eutrophication of Lakes and Reservoirs; Man and the Biosphere Series; UNESCO and The Parthenon Publishing Group: Nashville, TN, USA, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- An, K.; Jones, J.R. Factors regulating bluegreen dominance in a reservoir directly influenced by the Asian monsoon. Hydrobiologia 2000, 432, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onandia, G.; Dias, J.D.; Miracle, M.R. Zooplankton grazing on natural algale and bacteria under hypertrophic conditions. Limnetica 2015, 34, 541–560. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, R.D.; Demott, W.R. The role of food quality for zooplankton: Remarks on the state-of-the-art, perspectives and priorities. Freshw. Biol. 1997, 38, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, W.R.; Gulati, R.D.; Van Donk, E. Daphnia food limitation in three hypereutrophic Dutch lakes: Evidence for exclusion of large-bodied species by interfering filaments of cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leflaive, J.P.; Ten-Hage, L. Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: A comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, J.; Attayde, J.L.; Vasconcelos, F.R.; Dantas, D.D.F.; Huszar, V.L.M. Drought induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2016, 770, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Period | Statistic | Chl-a (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | SD (m) | TSIChl | TSITP | TSITN | TSISD | Kna | Phytoplankton Concentration (cells/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | Max | 28.3 | 0.181 | 3.5 | 7.7 | 63.3 | 79.2 | 72.5 | 56.2 | 0.32 | 3933 |
| Min | 2.1 | 0.002 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 37.9 | 12.4 | 53.9 | 30.6 | −0.10 | 1333 | |
| Avg | 9.0 | 0.036 | 1.8 | 4.1 | 50.6 | 47.7 | 61.9 | 40.6 | 0.06 | 2410 | |
| Stdev | 5.3 | 0.041 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 5.8 | 16.2 | 4.5 | 5.8 | 0.09 | 667 | |
| 1-2 | Max | 28.9 | 0.103 | 3.3 | 6.3 | 63.6 | 71.0 | 71.7 | 73.2 | 1.78 | 5933 |
| Min | 1.8 | 0.002 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 36.5 | 13.0 | 58.3 | 33.4 | −0.04 | 933 | |
| Avg | 7.7 | 0.016 | 2.0 | 3.8 | 47.6 | 36.8 | 63.7 | 43.3 | 0.26 | 2043 | |
| Stdev | 6.9 | 0.021 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 7.6 | 13.6 | 4.0 | 10.5 | 0.41 | 987 | |
| 2-1 | Max | 55.0 | 0.130 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 69.9 | 74.4 | 70.6 | 76.9 | 2.95 | 3667 |
| Min | 1.1 | 0.002 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 31.6 | 10.6 | 49.7 | 33.7 | 0.05 | 1000 | |
| Avg | 7.2 | 0.021 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 44.3 | 38.0 | 60.2 | 48.4 | 0.44 | 2283 | |
| Stdev | 11.6 | 0.031 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 9.6 | 18.2 | 7.8 | 10.9 | 0.63 | 717 | |
| 2-2 | Max | 10.8 | 0.054 | 3.1 | 4.6 | 54.0 | 61.6 | 70.6 | 76.9 | 2.95 | 3600 |
| Min | 1.6 | 0.001 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 35.3 | 7.0 | 54.9 | 38.0 | 0.04 | 2000 | |
| Avg | 4.7 | 0.011 | 1.9 | 2.5 | 44.9 | 29.9 | 62.6 | 48.1 | 0.43 | 2768 | |
| Stdev | 2.2 | 0.013 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 4.5 | 16.0 | 4.9 | 8.0 | 0.60 | 469 |
| Periods | Variables | Chl-a | TP | TN | SD | COD | Precipitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | Chl-a | 1 | |||||
| TP | 0.01 | 1 | |||||
| TN | −0.06 | 0.58 ** | 1 | ||||
| SD | −0.66 ** | 0.14 | −0.05 | 1 | |||
| COD | 0.47 ** | −0.35 * | −0.40 * | −0.48 ** | 1 | ||
| Precipitation | 0.24 | −0.07 | −0.05 | −0.11 | 0.16 | 1 | |
| 1-2 | Chl-a | 1 | |||||
| TP | 0.80 ** | 1 | |||||
| TN | 0.25 | 0.36 | 1 | ||||
| SD | −0.73 ** | −0.75 ** | −0.07 | 1 | |||
| COD | 0.36 | 0.40 * | 0.34 | −0.34 | 1 | ||
| Precipitation | −0.10 | −0.12 | −0.49 ** | −0.18 | 0.11 | 1 | |
| 2-1 | Chl-a | 1 | |||||
| TP | 0.00 | 1 | |||||
| TN | −0.28 | 0.29 | 1 | ||||
| SD | −0.46 | −0.50 * | 0.54 * | 1 | |||
| COD | 0.08 | −0.17 | −0.18 | 0.04 | 1 | ||
| Precipitation | −0.22 | 0.01 | −0.46 | −0.24 | 0.64 ** | 1 | |
| 2-2 | Chl-a | 1 | |||||
| TP | 0.18 | 1 | |||||
| TN | 0.33 | −0.61 ** | 1 | ||||
| SD | −0.07 | −0.55 ** | 0.59 ** | 1 | |||
| COD | −0.49 * | 0.52 * | −0.66 ** | −0.32 | 1 | ||
| Precipitation | −0.26 | 0.78 ** | −0.67 ** | −0.34 | 0.83 ** | 1 | |
| * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-m.; Kim, H.-s. Assessment of Trophic Responses of a Reservoir to Seasonal and Annual Variations in Monsoon. Water 2021, 13, 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152117
Kim S-m, Kim H-s. Assessment of Trophic Responses of a Reservoir to Seasonal and Annual Variations in Monsoon. Water. 2021; 13(15):2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152117
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Su-mi, and Hyun-su Kim. 2021. "Assessment of Trophic Responses of a Reservoir to Seasonal and Annual Variations in Monsoon" Water 13, no. 15: 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152117
APA StyleKim, S.-m., & Kim, H.-s. (2021). Assessment of Trophic Responses of a Reservoir to Seasonal and Annual Variations in Monsoon. Water, 13(15), 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152117






