Diversity and Activity of Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria Isolated from Sedimentary Water in the Littoral Zone of Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
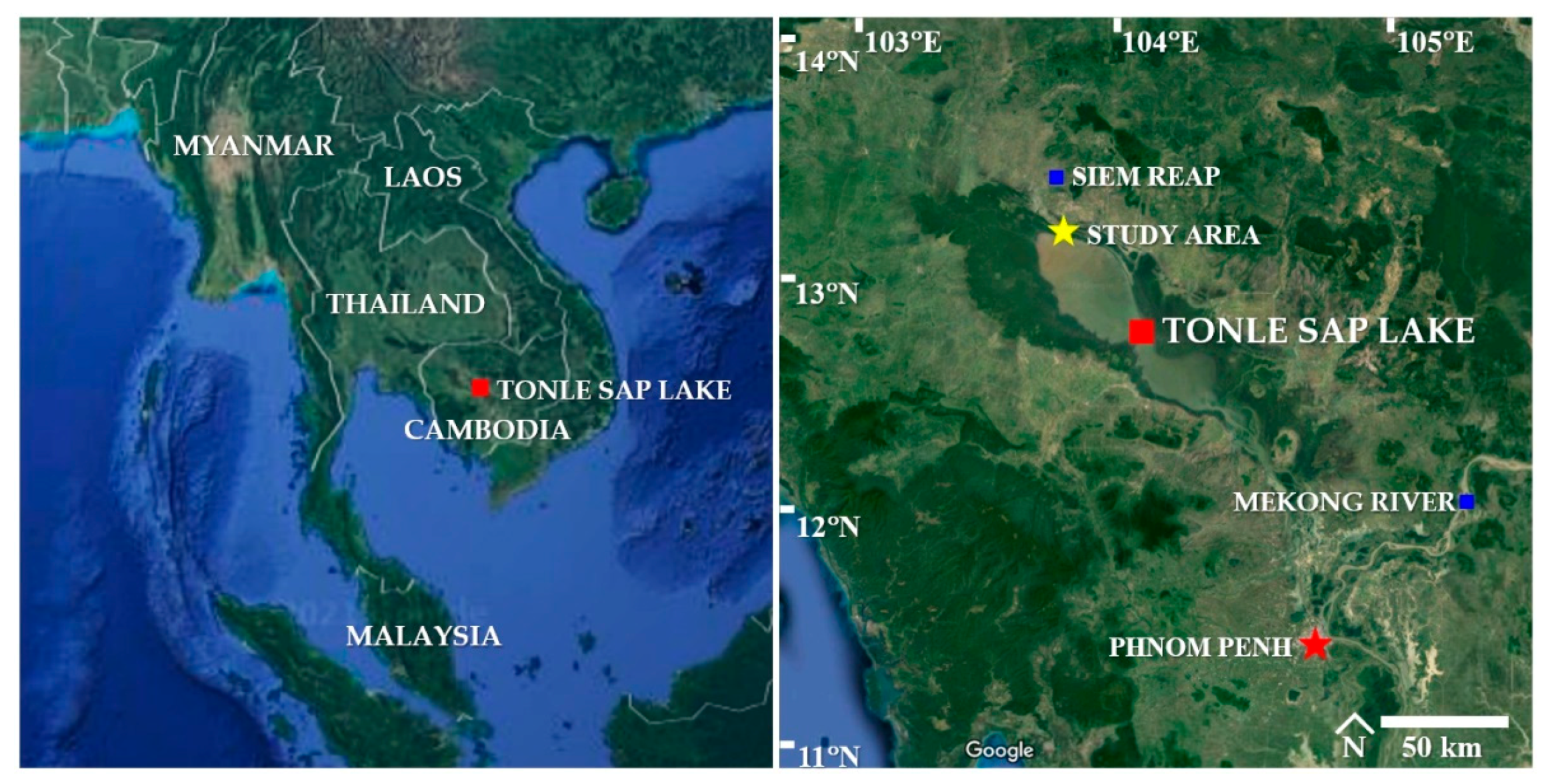
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling of Sedimentary Water Samples
2.3. Isolation, Screening, and Purification of Cellulolytic Bacteria from the Sedimentary Water Samples
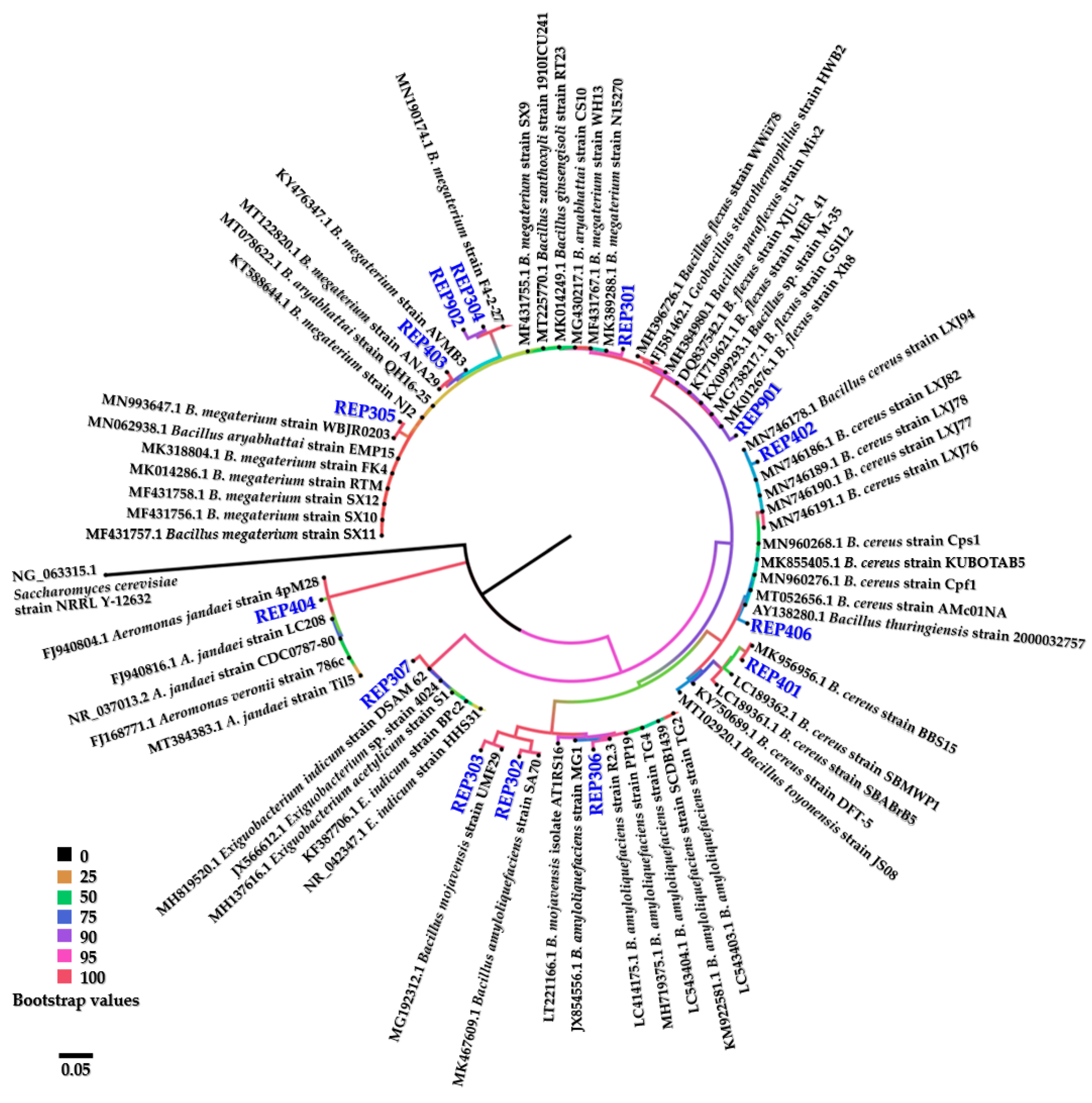
2.4. Genetic Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Isolated Bacteria
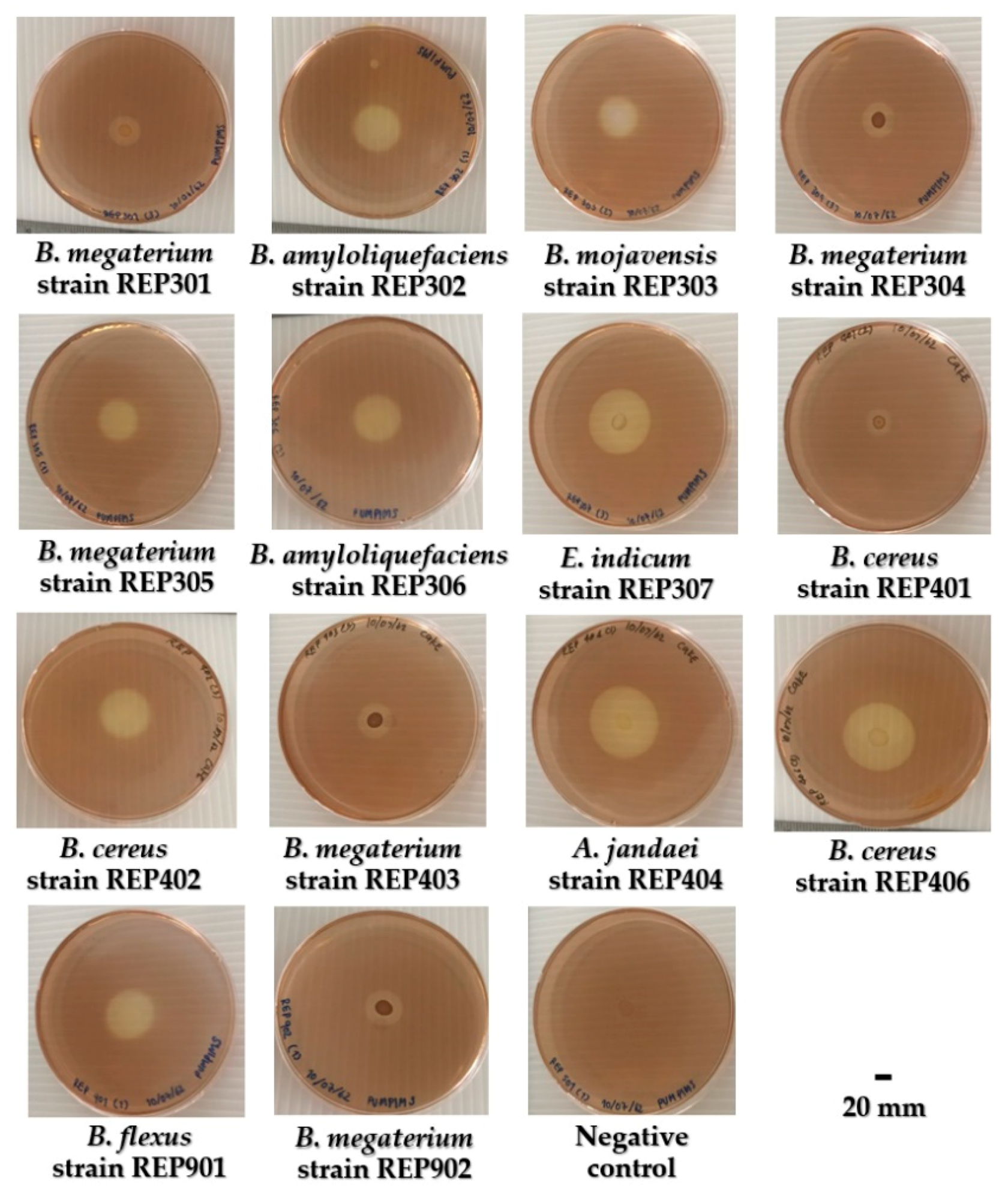
2.5. Determination of Hydrolysis Capacity of Isolated Bacteria
2.6. Preparation of the Crude Cellulases
2.7. Determination of Cellulolytic Activity of the Crude Cellulases
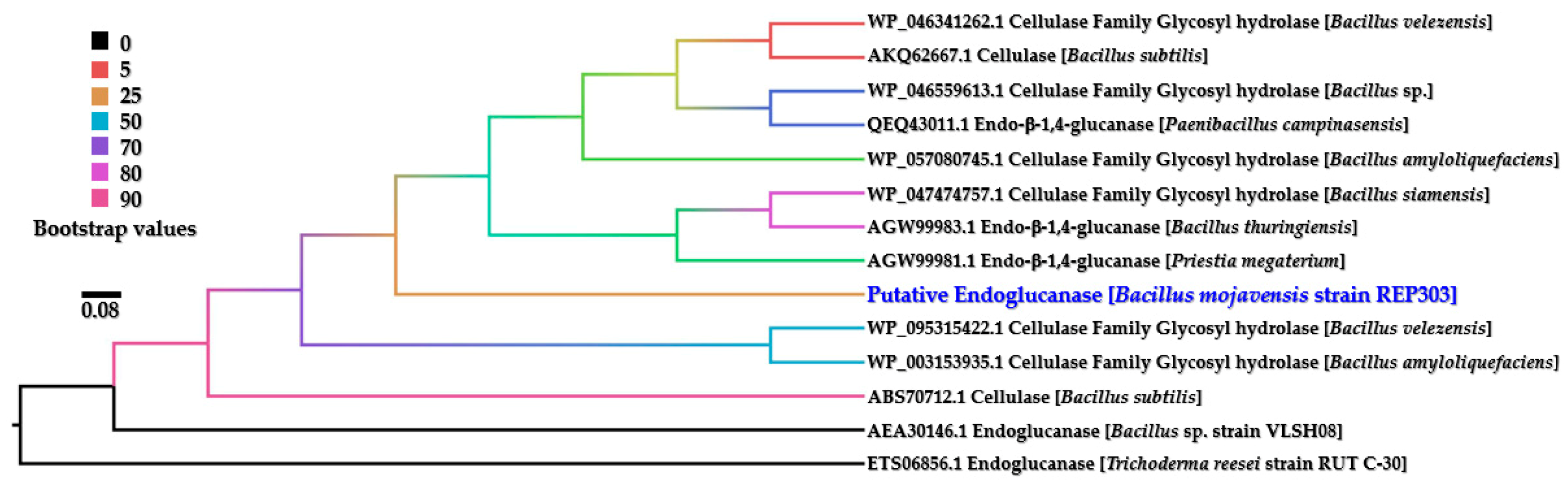
2.8. Bioinformatic Analysis of the Endoglucanase from the Most Active Cellulolytic Bacterium
2.9. Enzymatic Characterization of the Cellulases from the Most Active Cellulolytic Bacterium
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sampling of Sedimentary Water Samples
3.2. Phenotypic Morphology and Genetic Identification of the Isolated Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria
3.3. Hydrolysis Capacity (HC) and Cellulolytic Activity of Isolated Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria
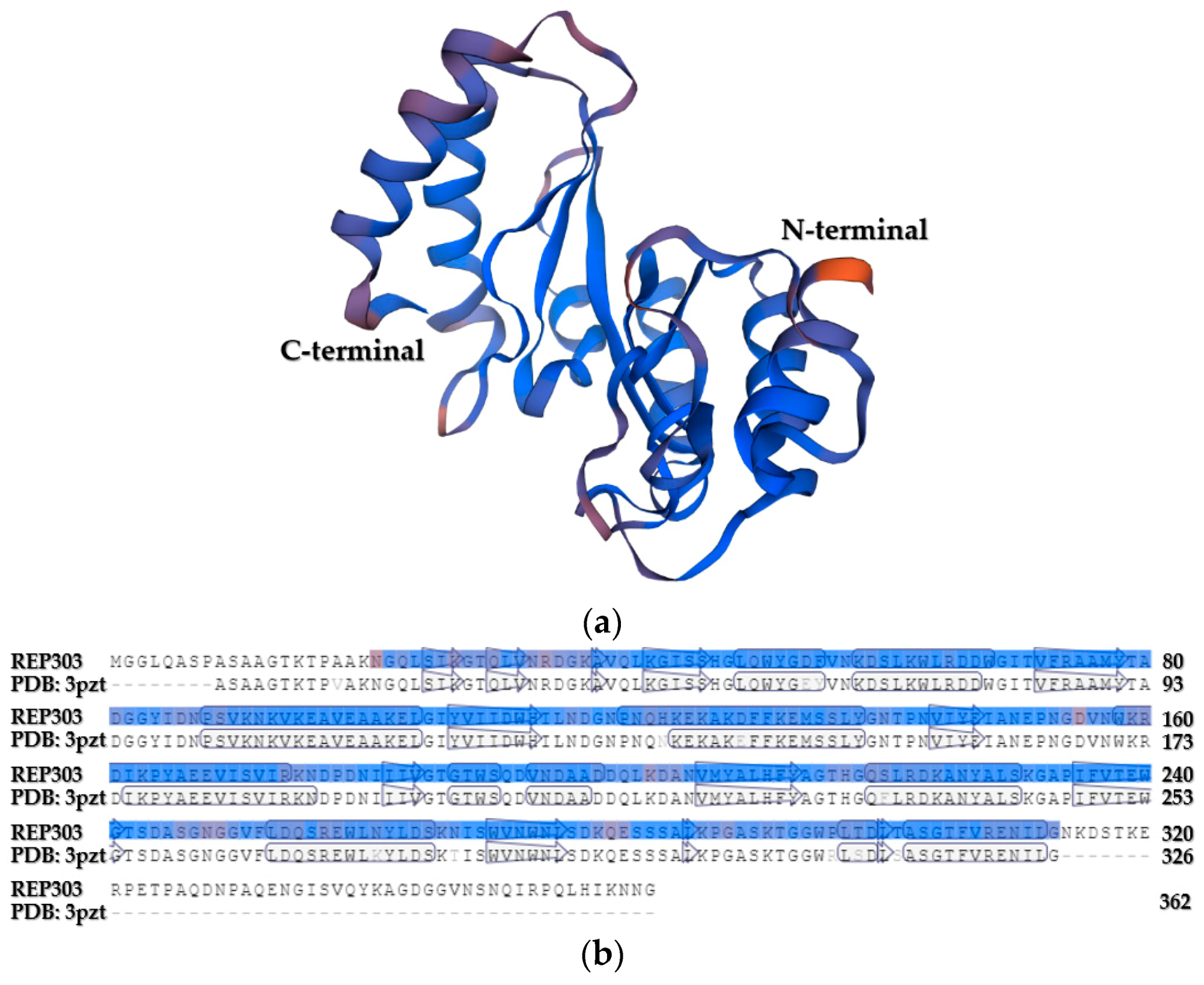
3.4. Bioinformatic Analysis of the Endoglucanase from B. mojavensis Strain REP303
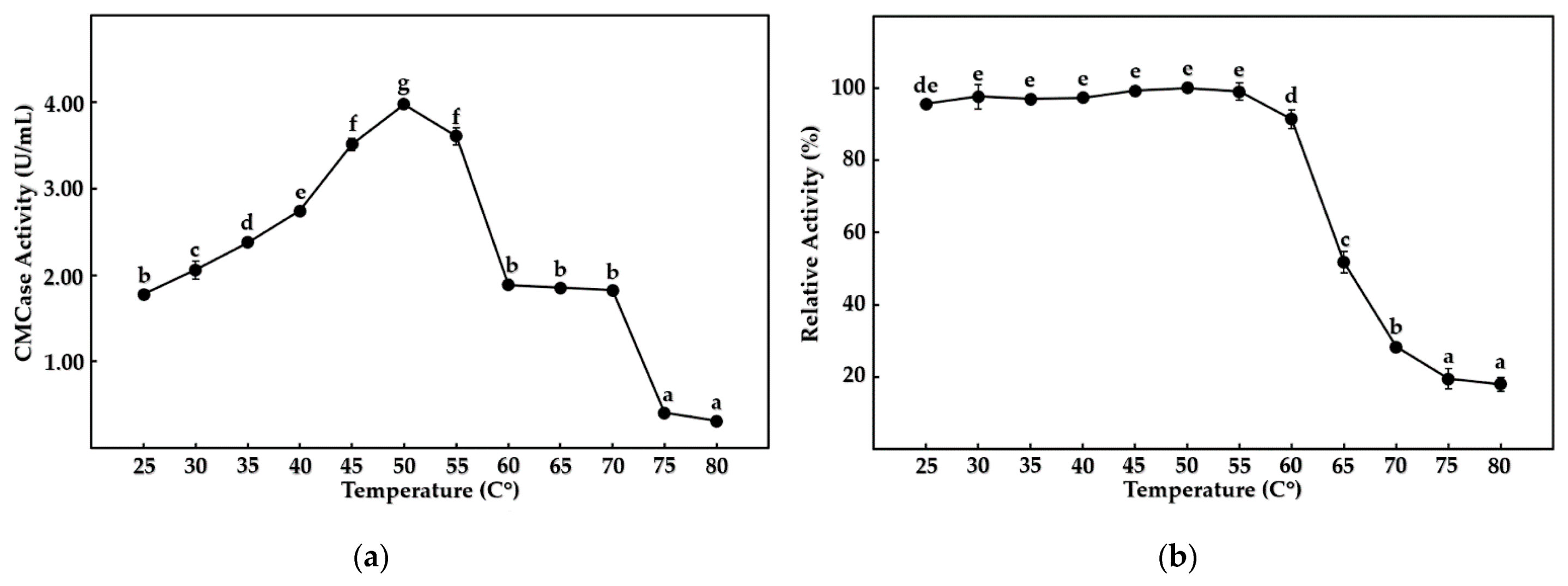
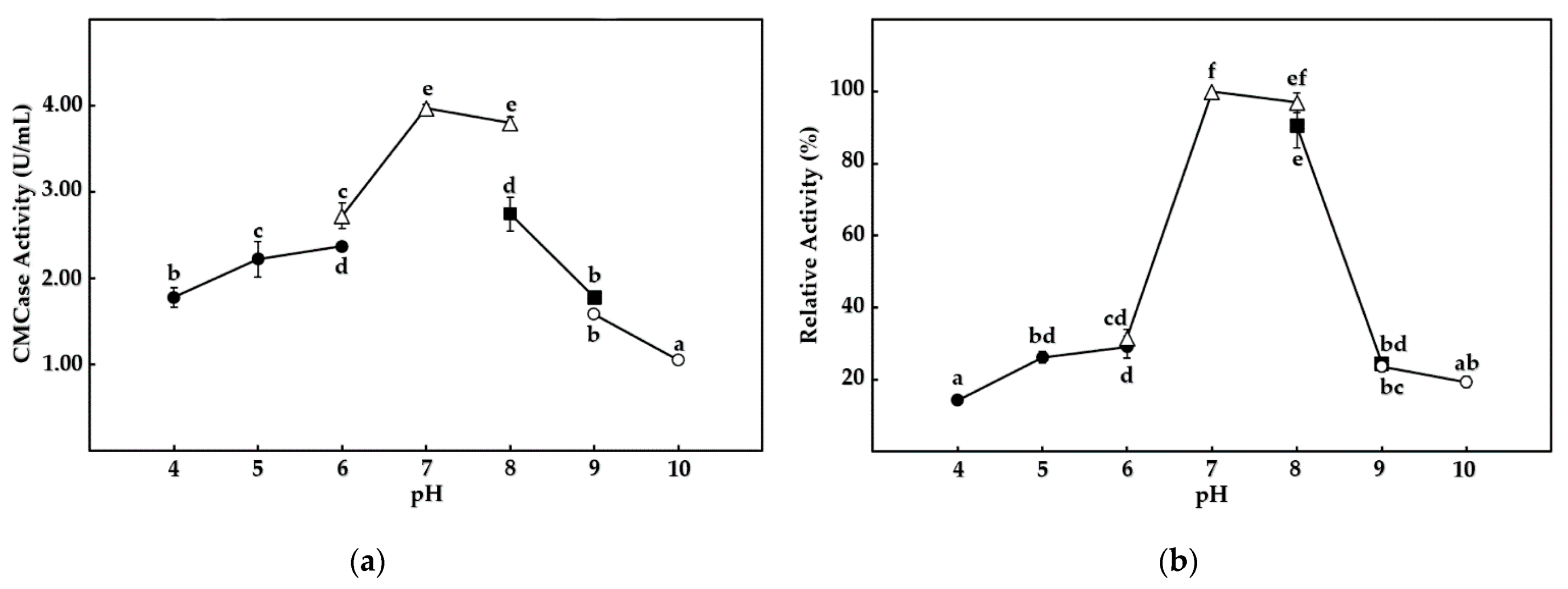
3.5. Enzymatic Characterization of Cellulases from B. mojavensis Strain REP303
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eiler, A.; Bertilsson, S. Composition of freshwater bacterial communities associated with cyanobacterial blooms in four Swedish lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søndergaard, M.; Johansson, L.S.; Levi, E.E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jeppesen, E. Lake types and their definition: A case study from Denmark. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Leonardi, M.; Monticelli, L.S.; Decembrini, F.; Azzaro, F.; Crisafi, E.; Zappalà, G.; Bergamasco, A.; Vizzini, S. Assessment of the ecological status of transitional waters in Sicily (Italy): First characterisation and classification according to a multiparametric approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Azzaro, M.; Monticelli, L.S.; Maimone, G.; Azzaro, F.; La Ferla, R.; Caruso, G. Nutrient regeneration mediated by extracellular enzymes in water column and interstitial water through a microcosm experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sekar, R.; Visser, P.M. Editorial: Microbial ecology in reservoirs and lakes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.N.; Yadav, N.; Kour, D.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, K.; Kumar, A.; Rastegari, A.A.; Sachan, S.G.; Singh, B.; Chauhan, V.S.; et al. Bacterial community composition in lakes. In Freshwater Microbiology: Perspectives of Bacterial Dynamics in Lake Ecosystems, 1st ed.; Bandh, S.A., Shafi, S., Shameem, N., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Gucht, K.; Vandekerckhove, T.; Vloemans, N.; Cousin, S.; Muylaert, K.; Sabbe, K.; Gillis, M.; Declerk, S.; Meester, L.D.; Vyverman, W. Characterization of bacterial communities in four freshwater lakes differing in nutrient load and food web structure. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 53, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G. Distinct factors shape aquatic and sedimentary microbial community structures in the lakes of western China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Xi, W.; Ye, W.; Yang, H. Bacterial community composition of a shallow hypertrophic freshwater lake in China, revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humbert, J.F.; Dorigo, U.; Cecchi, P.; Berre, B.L.; Debroas, D.; Bouvy, M. Comparison of the structure and composition of bacterial communities from temperate and tropical freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudryk, Z.J.; Podgorska, B. Enzymatic activity of bacterial strains isolated from marine beach sediments. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Roy, R.N.; Sen, S.K.; Ray, A.K. Characterization of cellulase-producing bacteria from the digestive tract of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambica (Peters) and grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes). Aquac. Res. 2006, 37, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathy, K.; Pandiarajan, J. Cellulolytic potential of gut bacterial biomass in silkworm Bombyx mori. L. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 14, 100045. [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, Y.P.; Qin, W. Characterization of novel cellulase-producing bacteria isolated from rotting wood samples. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, P.; Li, Y.; Marshall, S.D.G.; Zhang, H. High genetic diversity of microbial cellulase and hemicellulase genes in the hindgut of Holotrichia parallela larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16545–16559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Lu, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Screening of cellulolytic bacteria from rotten wood of Qinling (China) for biomass degradation and cloning of cellulases from Bacillus methylotrophicus. BMC Biotechnol. 2020, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chantarasiri, A. Novel halotolerant cellulolytic Bacillus methylotrophicus RYC01101 isolated from ruminant feces in Thailand and its application for bioethanol production. KMUTNB Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croos, A.M.B.; Rajendran, S.; Ranganathan, K. Isolation of a cellulase producing Bacillus cereus from cow dung and determination of the kinetic properties of the crude enzyme. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lunka 2019, 47, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarasiri, A. Aquatic Bacillus cereus JD0404 isolated from the muddy sediments of mangrove swamps in Thailand and characterization of its cellulolytic activity. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 41, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pramono, H.; Mariana, A.; Ryandini, D.; Sudiana, E. Short communication: Diversity of cellulolytic bacteria isolated from coastal mangrove sediment in Logending Beach, Kebumen, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2021, 22, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, H.; Pourbabaee, A.A.; Asgharzadeh, A.; Besharati, H. Isolation and identification of effective cellulolytic bacteria in composting process from different sources. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Gao, X.; Shan, M.; Sun, C.; Niu, Y.D.; Shan, A. Screening of cellulose degradation bacteria from Min pigs and optimization of its cellulase production. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriariyanun, M.; Tantayotai, P.; Yasurin, P.; Pornwongthong, P.; Cheenkachorn, K. Production, purification and characterization of an ionic liquid tolerant cellulase from Bacillus sp. isolated from rice paddy field soil. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 19, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pangsri, T.; Wuttipornpun, T.; Songserm, W. Mannanase and cellulase enzyme production from the agricultural wastes by the Bacillus subtilis P2-5 strain. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarasiri, A.; Boontanom, P.; Yensaysuk, N.; Ajwichai, P. Isolation and identification of a cellulase-producing Bacillus sp. strain BR0302 from Thai coastal wetland soil. KMUTNB Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chantarasiri, A. Diversity of cellulolytic bacteria isolated from a freshwater wetland reserve in Thailand and their cellulolytic activity. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 5965–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; Cole, J.J.; Middelburg, J.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Prairie, Y.T.; Laube, K.A. Sediment organic carbon burial in agriculturally eutrophic impoundments over the last century. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, GB1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, D.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q. Endoglucanase activity of cellulolytic bacteria from lake sediments and its application in hydrophyte degradation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2020, 367, fnaa200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Mannivannan, A.; Narendhirakannan, R.T. Screening of cellulase producing microorganisms from lake area containing water hyacinth for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, G.; Mansoor, S.; Jan, S.; Kaur, B.; Paray, B.A.; Ahmad, A. Response surface optimization of cellulase production from Aneurinibacillus aneurinilyticus BKT-9: An isolate of urban Himalayan freshwater. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2333–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Feng, J.X. Isolation, screening, and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from natural reserves in the subtropical region of China and optimization of cellulase production by Paenibacillus terrae ME27-1. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 512497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menendez, E.; Garcia-Fraile, P.; Rivas, R. Biotechnological applications of bacterial cellulases. AIMS Bioeng. 2015, 2, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinza, E.M.; Mwakilili, A.D.; Mpinda, C.B.; Lyantagaye, S.L. Cellulase-producing bacteria isolated from Mufindi Paper Mill industrial effluent, Iringa Tanzania. Tanzan. J. Sci. 2021, 47, 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Juturu, V.; Wu, J.C. Microbial cellulases: Engineering, production and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.C.; Sethi, B.K.; Mishra, R.R.; Dutta, S.K.; Thatoi, H.N. Microbial cellulases-diversity & biotechnology with reference to mangrove environment: A review. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Handelsman, J. Metagenomics: Application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cucurachi, M.; Busconi, M.; Marudelli, M.; Soffritti, G.; Fogher, C. Direct amplification of new cellulase genes from woodland soil purified DNA. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 4317–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A. The importance of bacterial culture to food microbiology in the age of genomics. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keskinen, M. The lake with floating villages: Socio-economic analysis of the Tonle Sap Lake. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2006, 22, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, P.; Peng, C.; Yuk, S.; Tan, R.; Ann, V.; Miyanaga, K.; Tanji, Y. Dynamics of bacterial community in Tonle Sap Lake, a large tropical flood-pulse system in Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberts, D. The Tonle Sap Lake as a productive ecosystem. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2006, 22, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, Y.; Gasith, A. The littoral zone. In Lake Kinneret: Ecology and Management; Zohary, T., Sukenik, A., Berman, T., Nishri, A., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 517–532. [Google Scholar]
- Ferbiyanto, A.; Rusmana, I.; Raffiudin, R. Characterization and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from gut of worker Macrotermes gilvus. Hayati 2015, 22, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boontanom, P.; Chantarasiri, A. Short communication: Diversity of culturable epiphytic bacteria isolated from seagrass (Halodule uninervis) in Thailand and their preliminary antibacterial activity. Biodiversitas 2020, 21, 2907–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gascuel, O. BIONJ: An improved version of the NJ algorithm based on a simple model of sequence data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, G. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samira, M.; Mohammad, R.; Gholamreza, G. Carboxymethyl-cellulase and filter-paperase activity of new strains isolated from Persian Gulf. Microbiol. J. 2011, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shobharani, P.; Yogesh, D.; Halami, P.M.; Sachindra, N.M. Potential of cellulase from Bacillus megaterium for hydrolysis of Sargassum. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2013, 22, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, S.; Vinitchaikul, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Gu, Z.; Leng, J.; Gou, X.; Deng, M.; Sun, L.; et al. Directed modification of a ruminal cellulase gene (CMC-1) from a metagenomic library isolated from Yunnan gayal (Bos frontalis). Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Annamalai, N.; Rajeswari, M.V.; Elayaraja, S.; Balasubramanian, T. Thermostable, haloalkaline cellulase from Bacillus halodurans CAS 1 by conversion of lignocellulosic wastes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K.; Park, T.S.; Kwon, I.H.; Piao, M.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Ha, J.K. Characterization of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes of Bacillus licheniformis JK7 isolated from the rumen of a native Korean goat. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, C.R.; Paiva, J.H.; Sforça, M.L.; Neves, J.L.; Navarro, R.Z.; Cota, J.; Akao, P.K.; Hoffmam, Z.B.; Meza, A.N.; Smetana, J.H.; et al. Dissecting structure-function-stability relationships of a thermostable GH5-CBM3 cellulase from Bacillus subtilis 168. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsukawaki, S.; Okawara, M.; Lao, K.L.; Tada, M. Preliminary study of sedimentation in Lake Tonle Sap, Cambodia. J. Geogr. 1994, 103, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Chen, D. Changes of inundation area and water turbidity of Tonle Sap Lake: Responses to climate changes or upstream dam construction? Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 0940a1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Cottrell, M.T.; Lovejoy, C. The structure of bacterial communities in the western Arctic Ocean as revealed by pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA genes. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, W.L. Roles of Bacillus endospores in the environment. CMLS Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vary, P.S.; Biedendieck, R.; Fuerch, T.; Meinhardt, F.; Rohde, M.; Deckwer, W.D.; Jahn, D. Bacillus megaterium-from simple soil bacterium to industrial protein production host. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, B.H.; Jo, K.I.; Lee, N.K.; Chung, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, J.W. Purification and characterization of cellulase produced by Bacillus amyoliquefaciens DL-3 utilizing rice hull. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Blom, J.; Klenk, H.P.; Borriss, R. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus velezensis, and Bacillus siamensis form an “operational group B. amyloliquefaciens” within the B. subtilis species complex. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, M.; Sun, L.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.; Qi, K.Z. The optimization of fermentation conditions for producing cellulase of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its application to goose feed. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 171012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurniawan, A.; Sari, S.P.; Asriani, E.; Kurniawan, A.; Sambah, A.B.; Prihanto, A.A. Molecular identification of cellulolytic bacteria from mangrove sediment at tin mining region in West Bangka. Int. J. Appl. Biol. 2019, 3, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bottone, E.J. Bacillus cereus, a volatile human pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trivedi, N.; Gupta, V.; Kumar, M.; Kumari, P.; Reddy, C.R.K.; Jha, B. An alkali-halotolerant cellulase from Bacillus flexus isolated from green seaweed Ulva lactuca. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.S.; Nakamura, L.K.; Cohan, F.M. Bacillus mojavensis sp. nov., distinguishable from Bacillus subtilis by sexual isolation, divergence in DNA sequence, and differences in fatty acid composition. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blacutt, A.A.; Mitchell, T.R.; Bacon, C.W.; Gold, S.E. Bacillus mojavensis RRC101 lipopeptides provoke physiological and metabolic changes during antagonism against Fusarium verticillioides. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2016, 29, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jasim, B.; Sreelakshmi, S.; Mathew, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Identification of endophytic Bacillus mojavensis with highly specialized broad spectrum antibacterial activity. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, K.V.; Vijayalashmi, T.; Ranjit, P.; Raju, M.N. Characterization of some efficient cellulase producing bacteria isolated from pulp and paper mill effluent contaminated soil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2017, 60, e17160226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souii, A.; Guesmi, A.; Ouertani, R.; Cherif, H.; Chouchane, H.; Cherif, A.; Neifar, M. Carboxymethyl cellulase production by extremotolerant bacteria in low-cost media and application in enzymatic saccharification of stevia biomass. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Shivaji, S. Exiguobacterium indicum sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium from the Hamta glacier of the Himalayan mountain ranges of India. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2765–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, T.H.A.; Tam, N.H.; Huu, N.N.; Tu, N.H.K. Characterization of Exiguobacterium indicum Pn04 isolated from hot spring. Glob. J. Biol. Agric. Health Sci. 2016, 5, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Xiao, W. Characterization of a novel bacteriophage specific to Exiguobacterium indicum isolated from a plateau eutrophic lake. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayalaxmi, S.; Anu Appaiah, K.A.; Jayalakshmi, S.K.; Mulimani, V.H.; Sreeramulu, K. Production of bioethanol from fermented sugars of sugarcane bagasse produced by lignocellulolytic enzymes of Exiguobacterium sp. VSG-1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabria, G.L.; Argayosa, V.B.; Lazaro, J.E.; Argayosa, A.M.; Arcilla, C.A. Draft genome sequence of haloalkaliphilic Exiguobacterium sp. strain AB2 from Manleluag Ophiolitic Spring, Philippines. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00840-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasana, R.C.; Pandey, C.B. Exiguobacterium: An overview of a versatile genus with potential in industry and agriculture. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.W.; Carnahan, A.M.; Brayton, P.R.; Fanning, G.R.; Almazan, R.; Drabick, C.; Trudo, E.W., Jr.; Colwell, R.R. Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii dual infection of a human wound following aquatic exposure. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balsalobre, L.C.; Dropa, M.; Lincopan, N.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Matté, G.R.; Matté, M.H. Detection of metallo-β-lactamases-encoding genes in environmental isolates of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas jandaei. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.T.; Techatanakitarnan, C.; Jindakittikul, P.; Thaiprayoon, A.; Taengphu, S.; Charoensapsri, W.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Wirth, S.; Hao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zou, H.; Li, W.; Wang, G. Diversity and activity of cellulolytic bacteria, isolated from the gut contents of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) (Valenciennes) fed on Sudan grass (Sorghum sudanense) or artificial feedstuffs. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, S.; Maiti, T.K. Cellulase production by bacteria: A review. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2013, 3, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, B.; Nigar, S.; Shah, S.S.A.; Bashir, S.; Ali, J.; Yousaf, S.; Bangash, J.A. Isolation and identification of cellulose degrading bacteria from municipal waste and their screening for potential antimicrobial activity. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 27, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, D.M.; Turowski, V.R.; Murakami, M.T. Effects of the linker region on the structure and function of modular GH5 cellulases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, S.T.C.; Freund, H.L.; Kasanjian, J.; Berlemont, R. Function, distribution, and annotation of characterized cellulases, xylanases, and chitinases from CAZy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Aizhan, R.; Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Cloning and characterization of low-temperature adapted GH5-CBM3 endo-cellulase from Bacillus subtilis 1AJ3 and their application in the saccharification of switchgrass and coffee grounds. AMB Express 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Kushwah, J.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, R.; Somvanshi, V.S.; Nain, L.; Saxena, A.K. Cloning and expression of -1, 4-endoglucanase gene from Bacillus subtilis isolated from soil long term irrigated with effluents of paper and pulp mill. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanadumkerng, P.; Sakka, M.; Sakka, K.; Wiwat, C. Characterization and secretive expression in Bacillus subtilis of endoglucanase from Bacillus safensis isolated from freshwater swamp forest. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Chantarasiri, A.; Meevootisom, V.; Wiyakrutta, S. Strategies for alleviating in vitro low protein solubility in applied biotechnology and microbiology. KMUTNB Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeep; Liu, H.; Shukla, P. Synthetic biology and biocomputational approaches for improving microbial endoglucanases toward their innovative applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 6055–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeka, Y.S.; Sulistiani. Production and characterization of cellulase from the newly isolated Bacillus subtilis A8 on rice bran and corncob. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 308, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, E.O.; Omafuvbe, B.O.; Adewale, I.O.; Bakare, M.K. Purification and characterisation of a cellulase obtained from cocoa (Theobroma cacao) pod-degrading Bacillus coagulans Co4. Turk. J. Biochem. 2012, 37, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, H.; Ishikawa, H. Enzymes which are stable in the presence of organic solvents. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 91, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, H.Y. Purification and characterization of an organic-solvent-tolerant cellulase from a halotolerant isolate, Bacillus sp. L1. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 39, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pigmentation (Percentage) | Shape (Percentage) | Margin (Percentage) | Elevation (Percentage) | Diameter of the Colony (Percentage) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 85.72 | Circular | 85.72 | Entire | 71.43 | Convex | 50.00 | <2.00 mm | 21.43 |
| Pale brown | 7.14 | Irregular | 14.28 | Undulate | 28.57 | Raised | 50.00 | 2.00–4.00 mm | 71.43 |
| Orange | 7.14 | Other | 0.00 | Other | 0.00 | Other | 0.00 | >4.00 mm | 7.14 |
| Total | 100.00 | Total | 100.00 | Total | 100.00 | Total | 100.00 | Total | 100.00 |
| Bacterial Isolate | Closely Related Bacteria | GenBank Accession Number (References) | Query Cover (%) | Identity (%) * | GenBank Accession Number (Deposited) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REP301 | Bacillus megaterium strain WH13 | MF431767.1 | 99 | 99.04 | MW344078 |
| REP302 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain SA70 | MK467609.1 | 99 | 98.97 | MW344081 |
| REP303 | Bacillus mojavensis strain UMF29 | MG192312.1 | 99 | 98.66 | MW344082 |
| REP304 | Bacillus megaterium strain F4-2-27 | MN190174.1 | 99 | 98.50 | MW344088 |
| REP305 | Bacillus megaterium strain WBJR0203 | MN993647.1 | 99 | 98.82 | MW344090 |
| REP306 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain R2.3 | LC414175.1 | 99 | 98.61 | MW344118 |
| REP307 | Exiguobacterium indicum strain DSAM 62 | MH819520.1 | 99 | 98.72 | MW344117 |
| REP401 | Bacillus cereus strain BBS15 | MK956956.1 | 99 | 99.09 | MW344120 |
| REP402 | Bacillus cereus strain LXJ77 | MN746190.1 | 99 | 98.35 | MW344123 |
| REP403 | Bacillus megaterium strain ANA29 | MT122820.1 | 99 | 99.06 | MW344267 |
| REP404 | Aeromonas jandaei strain 4pM28 | FJ940804.1 | 99 | 98.78 | MW344263 |
| REP406 | Bacillus cereus strain KUBOTAB5 | MK855405.1 | 99 | 98.12 | MW344274 |
| REP901 | Bacillus flexus strain Xh8 | MK012676.1 | 99 | 99.10 | MW344273 |
| REP902 | Bacillus megaterium strain F4-2-27 | MN190174.1 | 99 | 98.13 | MW344292 |
| Bacterial Strain | HC Value | Cellulolytic Activity (U/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMCase | Avicelase | β-Glucosidases | FPase | ||
| B. megaterium strain REP301 | 1.88 ± 0.07 a | 2.45 ± 0.05 bc | 1.27 ± 0.08 ab | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 1.23 ± 0.01 bc |
| B. amyloliquefaciens strain REP302 | 3.39 ± 0.18 d | 3.26 ± 0.06 e | 1.50 ± 0.19 ac | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 1.48 ± 0.04 f |
| B. mojavensis strain REP303 | 3.19 ± 0.06 cd | 3.97 ± 0.05 g | 1.94 ± 0.11 c | 0.16 ± 0.01 b | 1.76 ± 0.05 h |
| B. megaterium strain REP304 | 2.25 ± 0.18 ab | 2.36 ± 0.04 ab | 1.28 ± 0.27 ab | 0.12 ± 0.00 ab | 1.16 ± 0.01 ab |
| B. megaterium strain REP305 | 2.67 ± 0.28 bc | 2.43 ± 0.02 bc | 1.66 ± 0.22 bc | 0.12 ± 0.01 ab | 1.19 ± 0.02 ac |
| B. amyloliquefaciens strain REP306 | 3.17 ± 0.04 cd | 3.72 ± 0.07 f | 1.68 ± 0.20 bc | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 1.66 ± 0.05 g |
| E. indicum strain REP307 | 4.44 ± 0.25 e | 2.31 ± 0.06 ab | 1.25 ± 0.02 ab | 0.11 ± 0.00 a | 1.18 ± 0.01 ac |
| B. cereus strain REP401 | 1.87 ± 0.02 a | 2.79 ± 0.15 d | 1.30 ± 0.13 ab | 0.13 ± 0.00 ab | 1.36 ± 0.02 e |
| B. cereus strain REP402 | 3.55 ± 0.27 d | 2.69 ± 0.05 d | 1.41 ± 0.13 ab | 0.12 ± 0.01 ab | 1.33 ± 0.02 de |
| B. megaterium strain REP403 | 2.30 ± 0.13 ab | 2.20 ± 0.06 a | 1.02 ± 0.07 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 ab | 1.12 ± 0.02 a |
| A. jandaei strain REP404 | 4.72 ± 0.20 ef | 2.71 ± 0.03 d | 1.20 ± 0.15 ab | 0.11 ± 0.00 a | 1.12 ± 0.01 a |
| B. cereus strain REP406 | 5.14 ± 0.26 f | 2.61 ± 0.03 cd | 1.26 ± 0.12 ab | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 1.26 ± 0.05 cd |
| B. flexus strain REP901 | 3.53 ± 0.31 d | 2.34 ± 0.10 ab | 1.31 ± 0.31 ab | 0.11 ± 0.00 a | 1.15 ± 0.04 ab |
| B. megaterium strain REP902 | 2.28 ± 0.15 ab | 2.36 ± 0.07 ab | 1.12 ± 0.18 a | 0.11 ± 0.00 a | 1.17 ± 0.02 ab |
| Chemical Additives | Relative Activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 102.58 ± 2.44 d |
| Co2+ | 133.48 ± 5.36 e |
| Cu2+ | 102.73 ± 3.32 d |
| Fe2+ | 104.75 ± 6.56 d |
| Hg2+ | 105.88 ± 6.14 d |
| K+ | 98.98 ± 2.18 cd |
| Mg2+ | 95.54 ± 1.80 bd |
| Mn2+ | 161.62 ± 2.40 f |
| Na+ | 98.83 ± 3.28 cd |
| Ni2+ | 95.89 ± 2.43 bd |
| Pb2+ | 136.80 ± 4.14 e |
| Sr2+ | 98.72 ± 1.96 cd |
| Zn2+ | 100.95 ± 3.51 d |
| EDTA | 44.51 ± 4.90 a |
| Acetone | 87.97 ± 5.06 bc |
| Dichloromethane | 99.35 ± 0.51 cd |
| Ethanol | 88.06 ± 1.46 bc |
| Ethyl-acetate | 33.23 ± 3.95 a |
| Methanol | 85.89 ± 3.32 b |
| n-Hexane | 98.90 ± 3.55 cd |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chantarasiri, A. Diversity and Activity of Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria Isolated from Sedimentary Water in the Littoral Zone of Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia. Water 2021, 13, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131797
Chantarasiri A. Diversity and Activity of Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria Isolated from Sedimentary Water in the Littoral Zone of Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia. Water. 2021; 13(13):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131797
Chicago/Turabian StyleChantarasiri, Aiya. 2021. "Diversity and Activity of Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria Isolated from Sedimentary Water in the Littoral Zone of Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia" Water 13, no. 13: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131797
APA StyleChantarasiri, A. (2021). Diversity and Activity of Aquatic Cellulolytic Bacteria Isolated from Sedimentary Water in the Littoral Zone of Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia. Water, 13(13), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131797






