Control of Runoff Peak Flow for Urban Flooding Mitigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
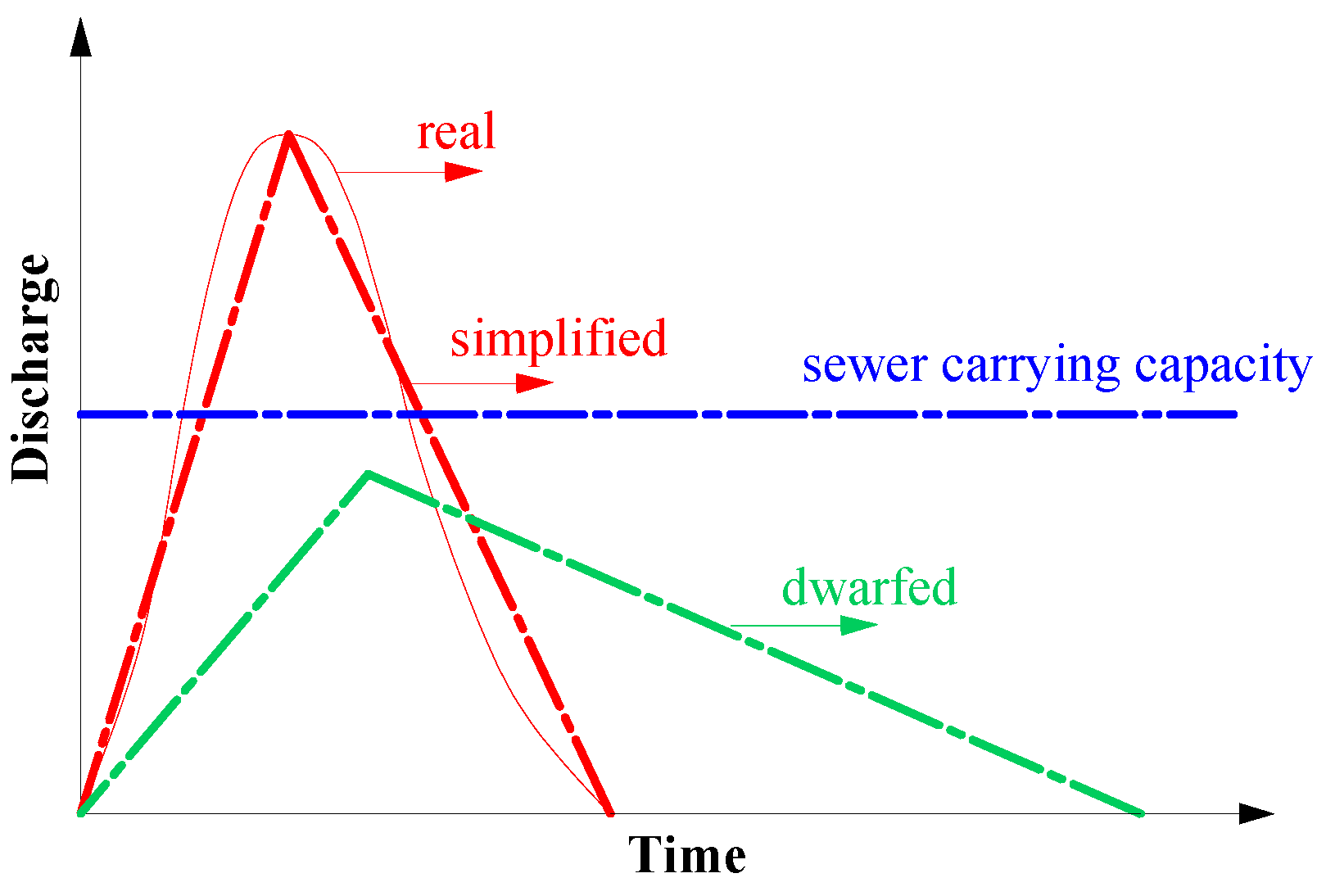
2. Concept of Peak-Flow Control
3. Theory, Experiment, and Numerical Simulations
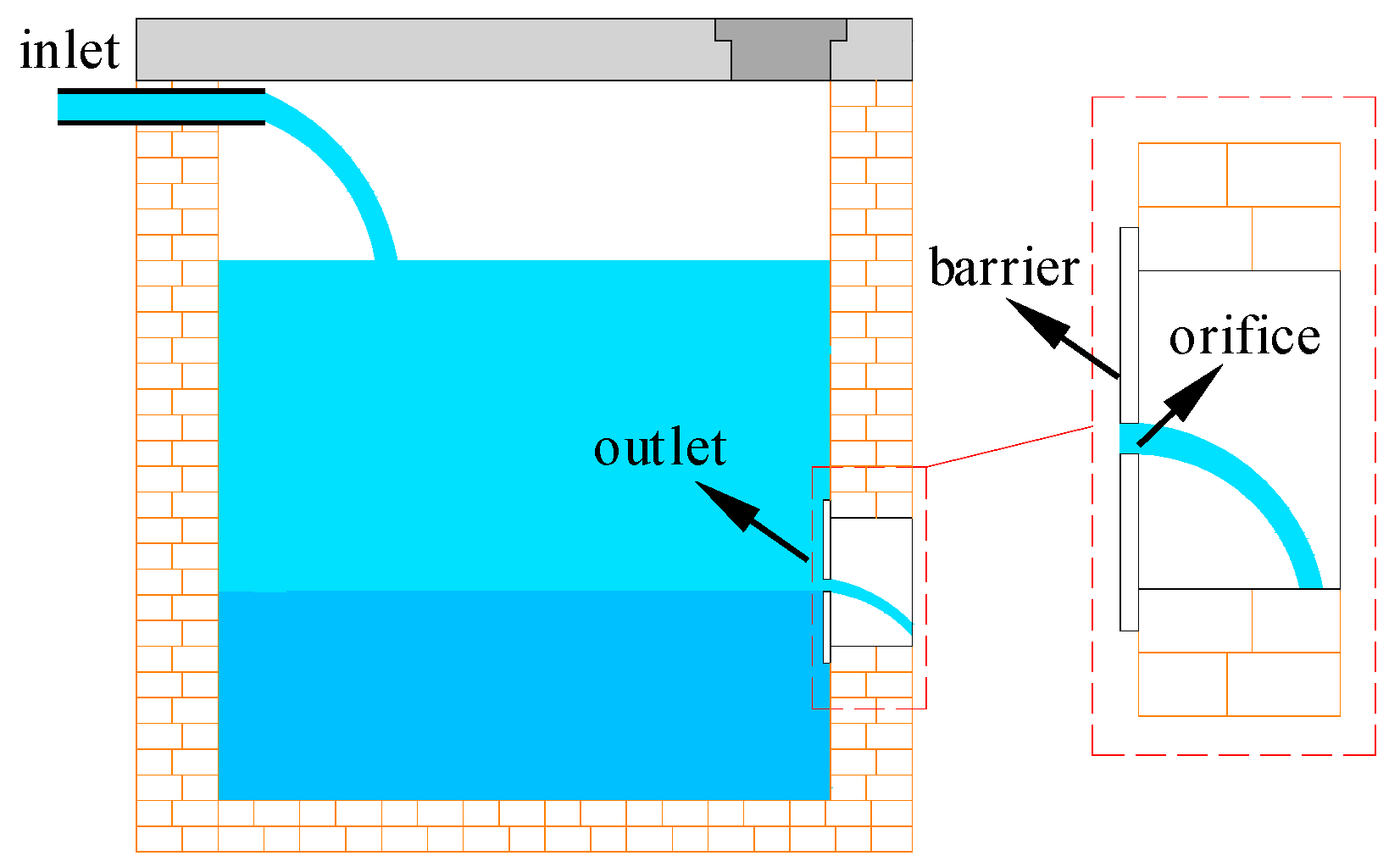
3.1. Drop of Water Head in a Tank with a Drain Hole
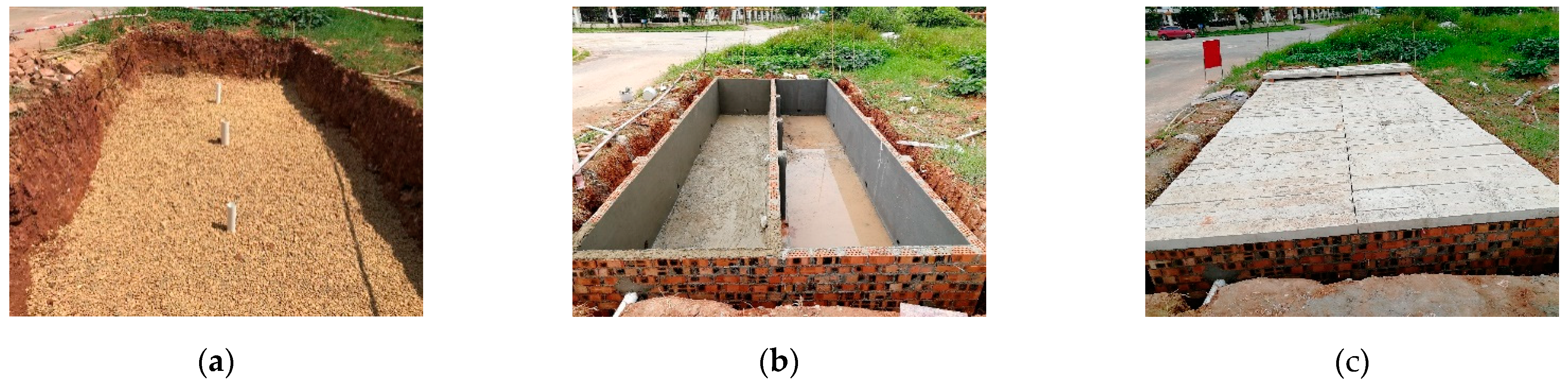
3.2. Experiments
- (1)
- Add water to the buffer tank until the water head is 50 cm above the center of the drain orifice;
- (2)
- Open the drain orifice and record the water head dropping in the tank until the water dropping rate is less than 0.1 cm/hour;
- (3)
- Replace the glass plate with different diameter of drain orifice and then repeat steps (1) and (2).
3.3. Numerical Simulations
4. Result
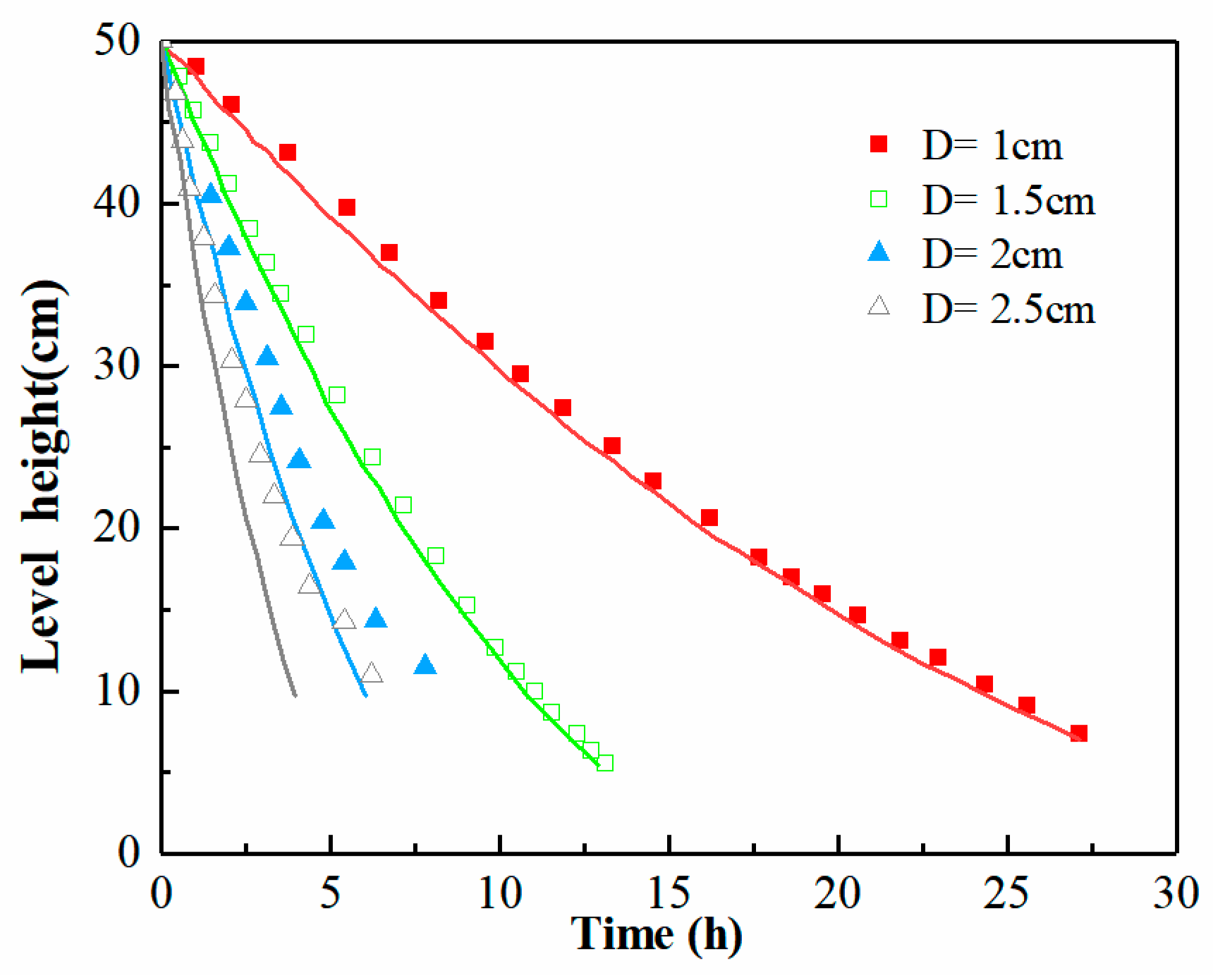
4.1. Water Head Dropping in the Water Tank Obeys the Torricelli Law
4.2. The Buffer Tank Effectively Attenuates the Peak Flow in Case of Heavy Rain
4.3. The Peak-Flow Attenuation Rate Is Controlled by the Drain Orifice
4.4. The Buffer Tank Keeps Empty in Case of Small Rain
4.5. Buffer Tank Works Better in Case of Heavy Rain
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schreider, S.Y.; Smith, D.I.; Jakeman, A.J. Climate Change Impacts on Urban Flooding. Clim. Chang. 2000, 47, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, H.T.L.; Pathirana, A. Urbanization and climate change impacts on future urban flooding in Can Tho city, Vietnam. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietz, M.E. Low Impact Development Practices: A Review of Current Research and Recommendations for Future Directions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 186, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc, H.H.; Duyen, P.M.; Ballatore, T.J.; Lan, N.H.M.; Das Gupta, A. Applicability of sustainable urban drainage systems: an evaluation by multi-criteria analysis. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2017, 37, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, V.G. Applying Integrated Urban Water Management Concepts: A Review of Australian Experience. Environ. Manag. 2006, 37, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khastagir, A.; Jayasuriya, L. Impacts of using rainwater tanks on stormwater harvesting and runoff quality. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mei, C.; Liu, J.; Shao, W. A new strategy for integrated urban water management in China: Sponge city. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Lu, X.X. Sustainable urban stormwater management in the tropics: An evaluation of Singapore’s ABC Waters Program. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiablame, L.M.; Engel, B.A.; Chaubey, I. Effectiveness of Low Impact Development Practices: Literature Review and Suggestions for Future Research. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4253–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNardo, J.C.; Jarrett, A.R.; Manbeck, H.B.; Beattie, D.J.; Berghage, R.D. Stormwater mitigation and surface temperature reduction by green roofs. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolani, G.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Gandolfi, C.; Castelli, F.; Masseroni, D. Evaluating performances of green roofs for stormwater runoff mitigation in a high flood risk urban catchment. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.; Jackson, C.R. Vegetated roofs for stormwater management at multiple spatial scales. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.M.; Akib, S.; Karim, M.R. Permeable pavement and stormwater management systems: a review. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2649–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coughlin, J.; Campbell, C.; Mays, D. Infiltration and Clogging by Sand and Clay in a Pervious Concrete Pavement System. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 17, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Baetz, B.W. Sizing of Rainwater Storage Units for Green Building Applications. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnaars, E.; Larsen, A.V.; Jacobsen, P.; Mikkelsen, P.S. Hydrologic behaviour of stormwater infiltration trenches in a central urban area during 2¾ years of operation. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardene, N.R.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D. Clogging of stormwater gravel infiltration systems and filters: Insights from a laboratory study. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kia, A.; Wong, H.S.; Cheeseman, C.R. Clogging in permeable concrete: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. Urban Flooding Mitigation Techniques: A Systematic Review and Future Studies. Water 2020, 12, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.K. Storm-Water Infiltration for Peak-Flow Control. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1995, 121, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ŞEN, Z.; Eljadid, A.G. Rainfall distribution function for Libya and rainfall prediction. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1999, 44, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U.; Netzer, L.; Livshitz, Y. Land cover properties and rain water harvesting in urban environments. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, A.A.; Adeel, A.A.; Hopkins, A.; Litofsky, A.L.; Wellstead, S.W. Rain Barrel-Urban Garden Stormwater Management Performance. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Babin, N.; Turner, A.J.; Hoffa, C.R.; Peel, S.; Prokopy, L.S. Understanding urban-suburban adoption and maintenance of rain barrels. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2016, 153, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, G.; Deroubaix, J.-F.; de Gouvello, B.; Deutsch, J.-C.; Bompard, P.; Tassin, B. Rainwater harvesting to control stormwater runoff in suburban areas. An experimental case-study. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palla, A.; Gnecco, I.; Lanza, L.G.; La Barbera, P. Performance analysis of domestic rainwater harvesting systems under various European climate zones. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 62, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
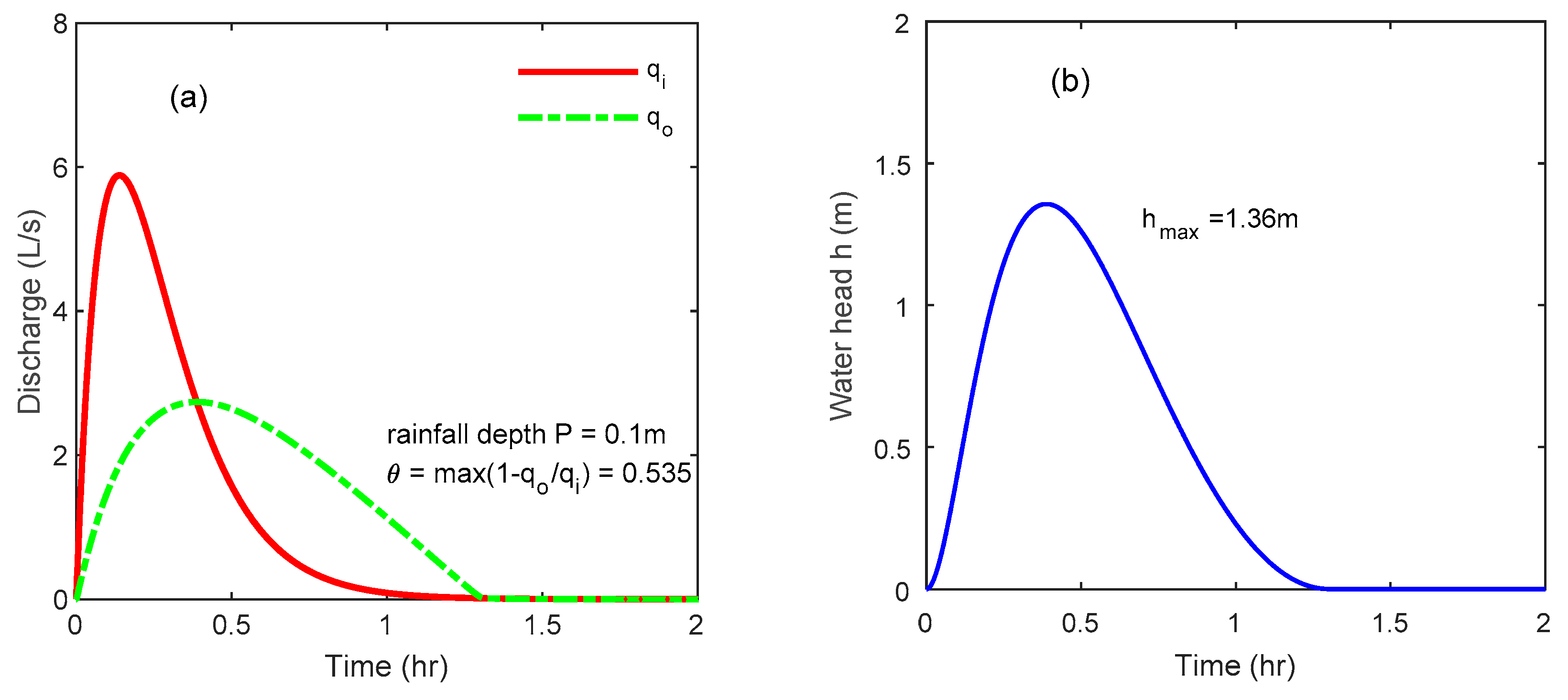
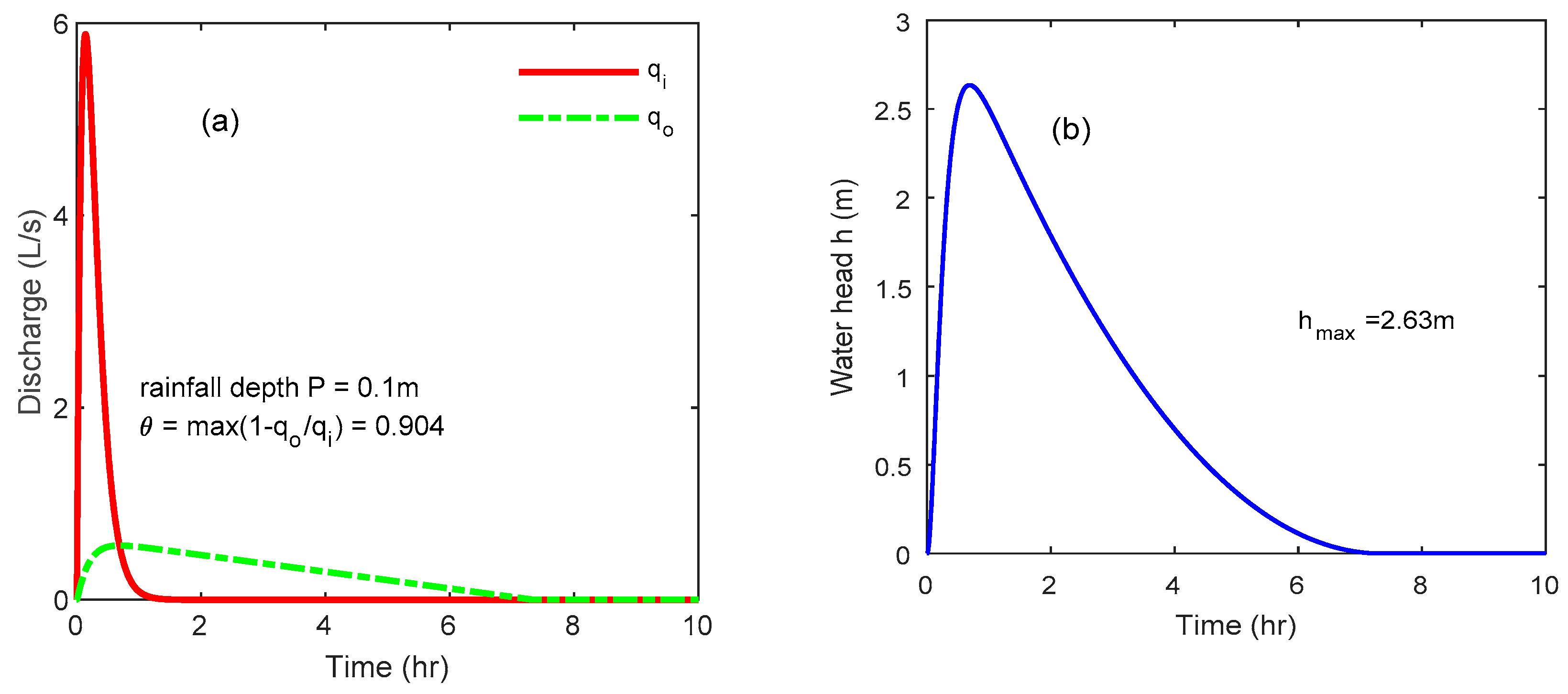
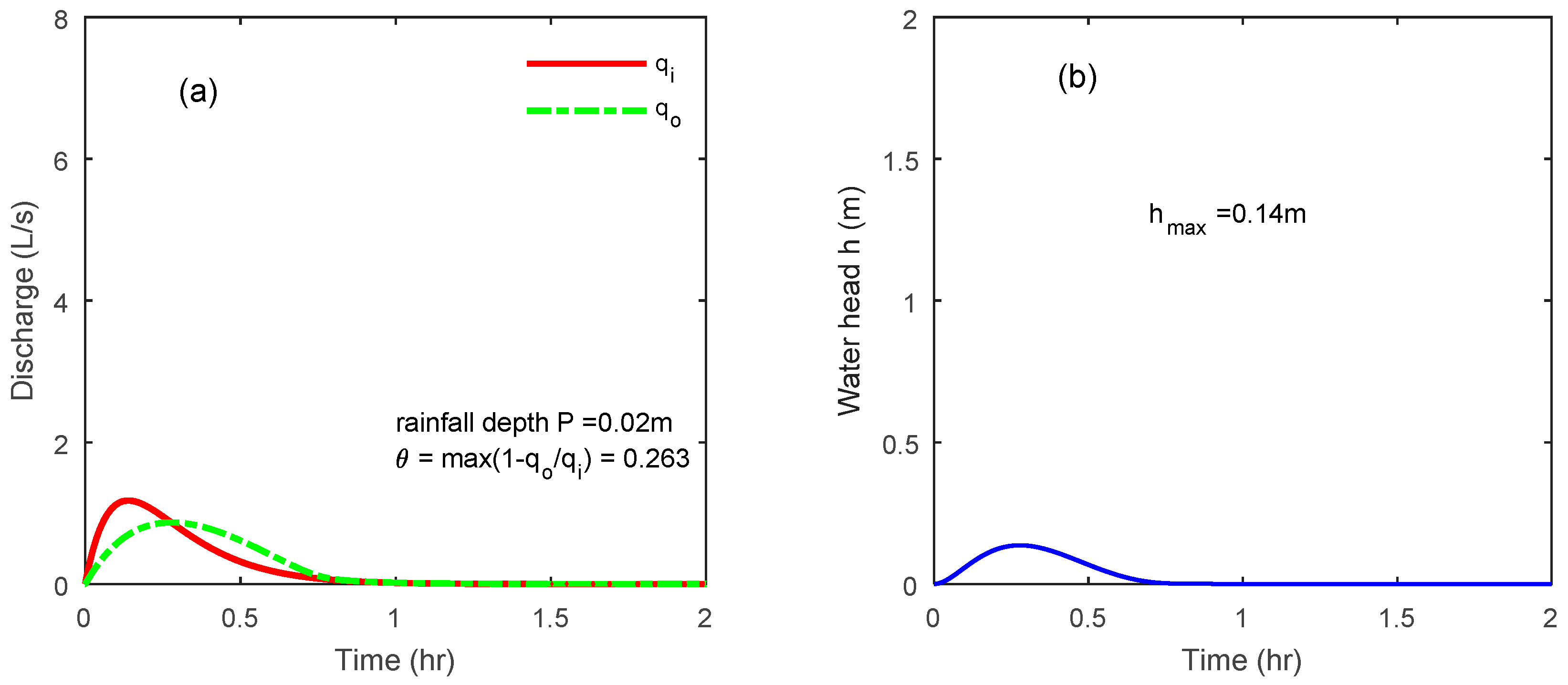
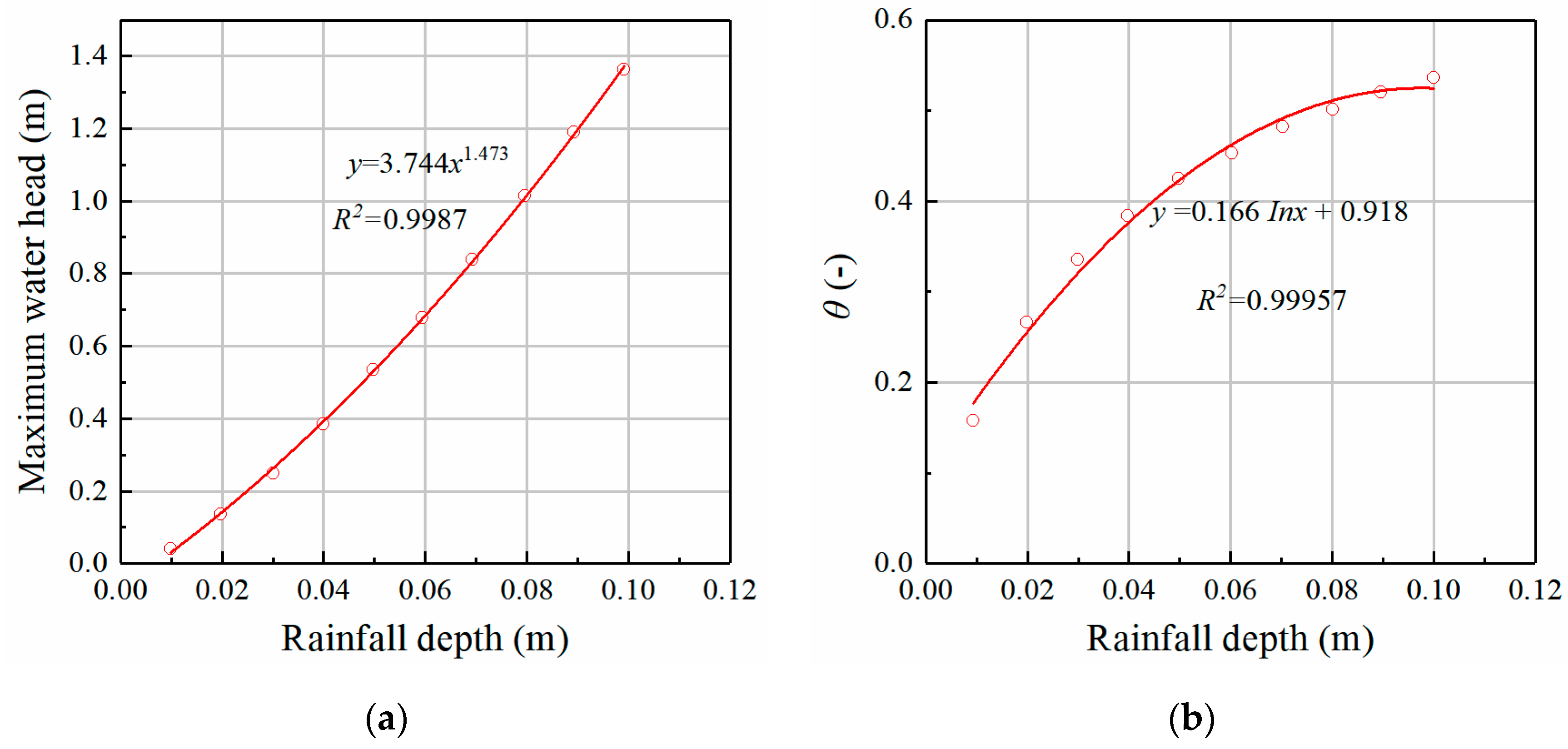
| Rainfall Distribution f | Rainfall Depth P | Buffer Tank Size | Outlet Orifice | Catchment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f = βα tα−1e−βt/Γ(α) | P = 10 cm or | m × m × m | 2.6 cm in diameter | Ac = 100 m2 |
| α = 2 and β = 1/500 | P = 2 cm | R = 0.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, C.; Qin, Y. Control of Runoff Peak Flow for Urban Flooding Mitigation. Water 2021, 13, 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131796
Lu Y, Xie J, Yang C, Qin Y. Control of Runoff Peak Flow for Urban Flooding Mitigation. Water. 2021; 13(13):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131796
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yunan, Jinli Xie, Cheng Yang, and Yinghong Qin. 2021. "Control of Runoff Peak Flow for Urban Flooding Mitigation" Water 13, no. 13: 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131796
APA StyleLu, Y., Xie, J., Yang, C., & Qin, Y. (2021). Control of Runoff Peak Flow for Urban Flooding Mitigation. Water, 13(13), 1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131796







