New Advances in Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology Using Continuous Flow Reactors: Engineering and Microbiological Aspects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characterization of Aerobic Granular Sludge Biomass
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization
- (a)
- Regular shape
- (b)
- Excellent settleability
- (c)
- Dense structure
- (d)
- Removal of organic matter and nutrients within the reactor
- (e)
- Tolerance to a high organic loading ratio and high biomass retention
- (f)
- High toxicity resistance
2.2. Advantages over Conventional Activated Sludge
3. Granular Formation Mechanisms and Technological Characterization
3.1. Extracellular Polymeric Substance Segregation
3.2. Technological Operation
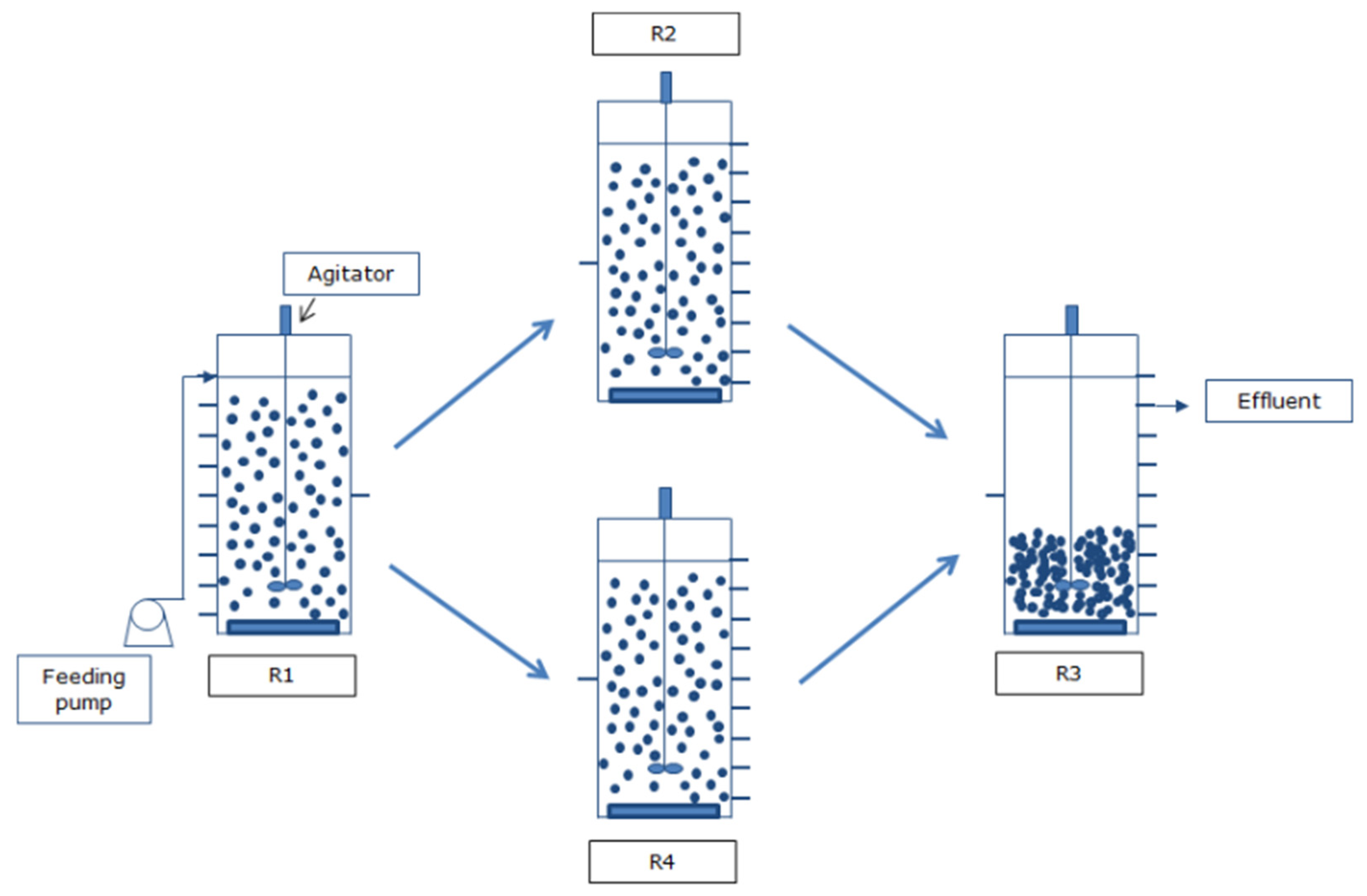
4. Aspects of AGS in Continuous-Flow Reactors
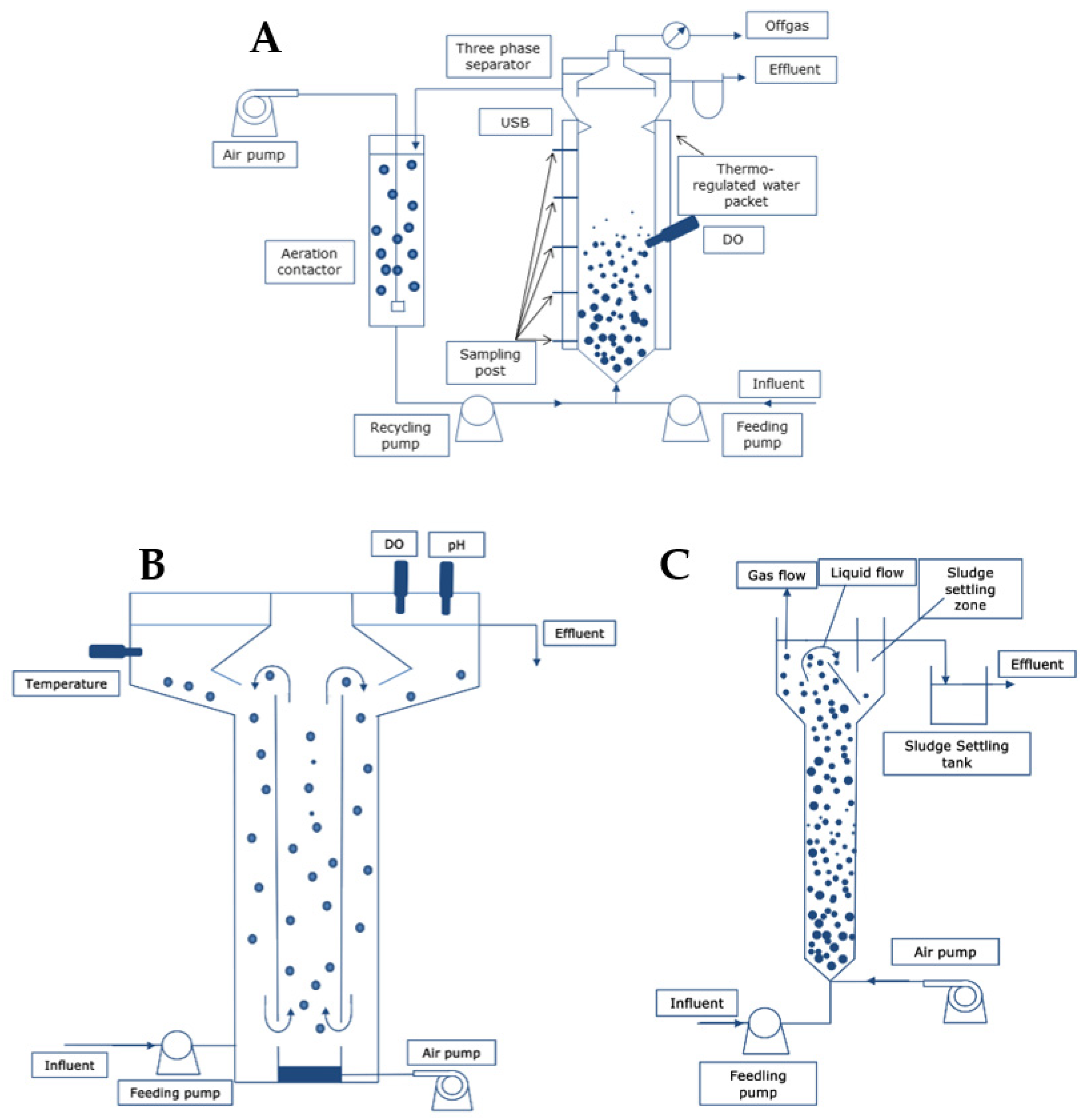
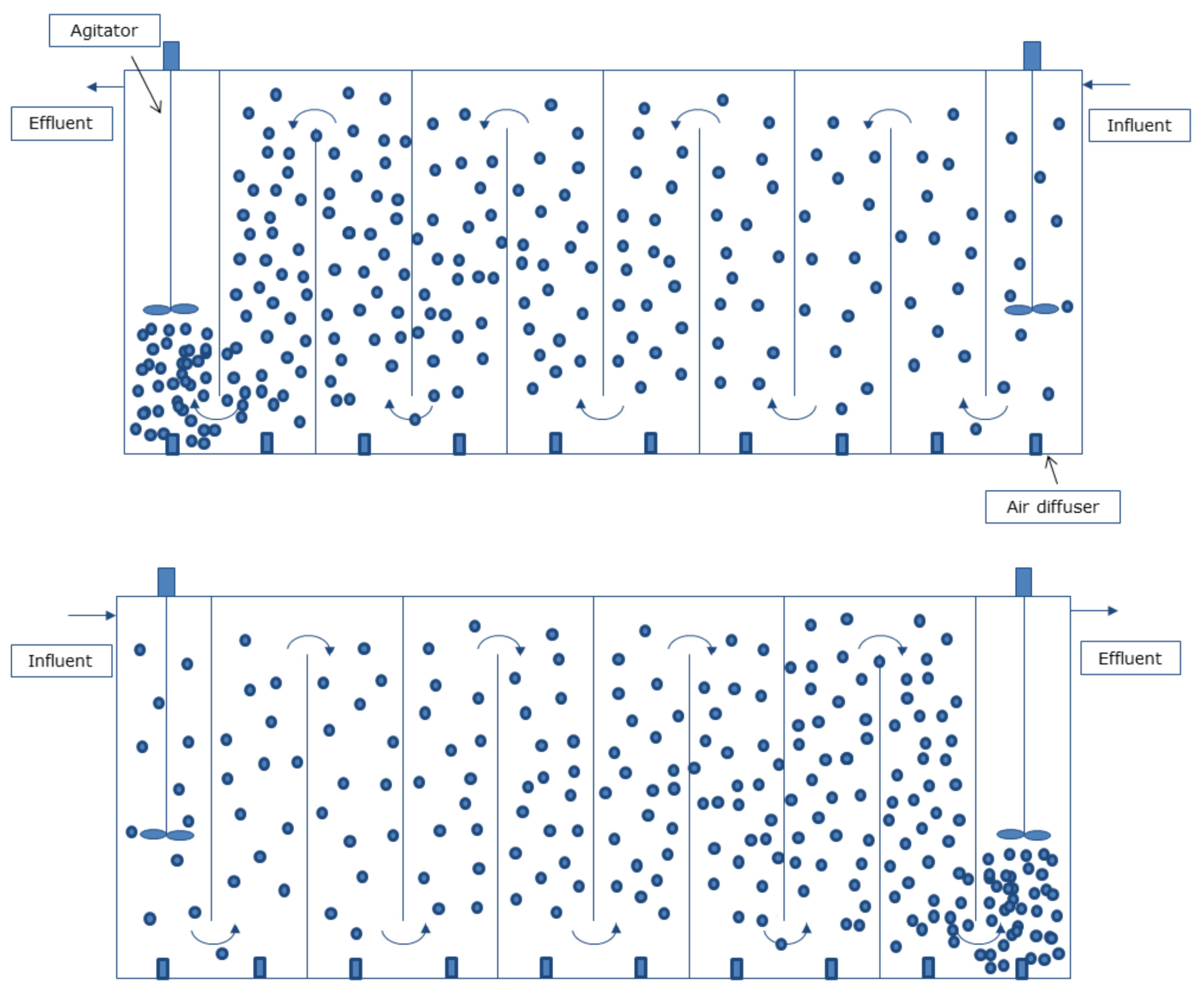
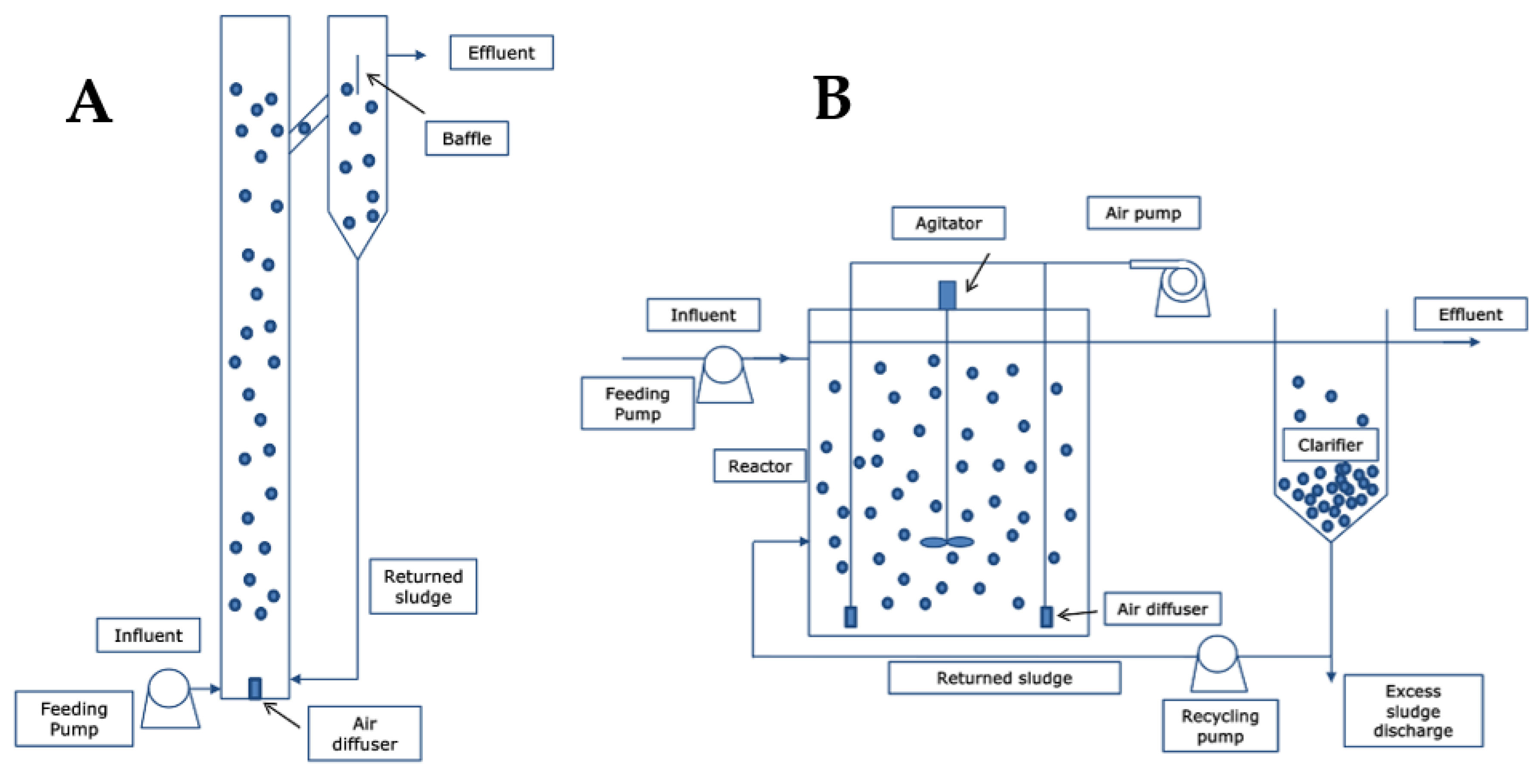
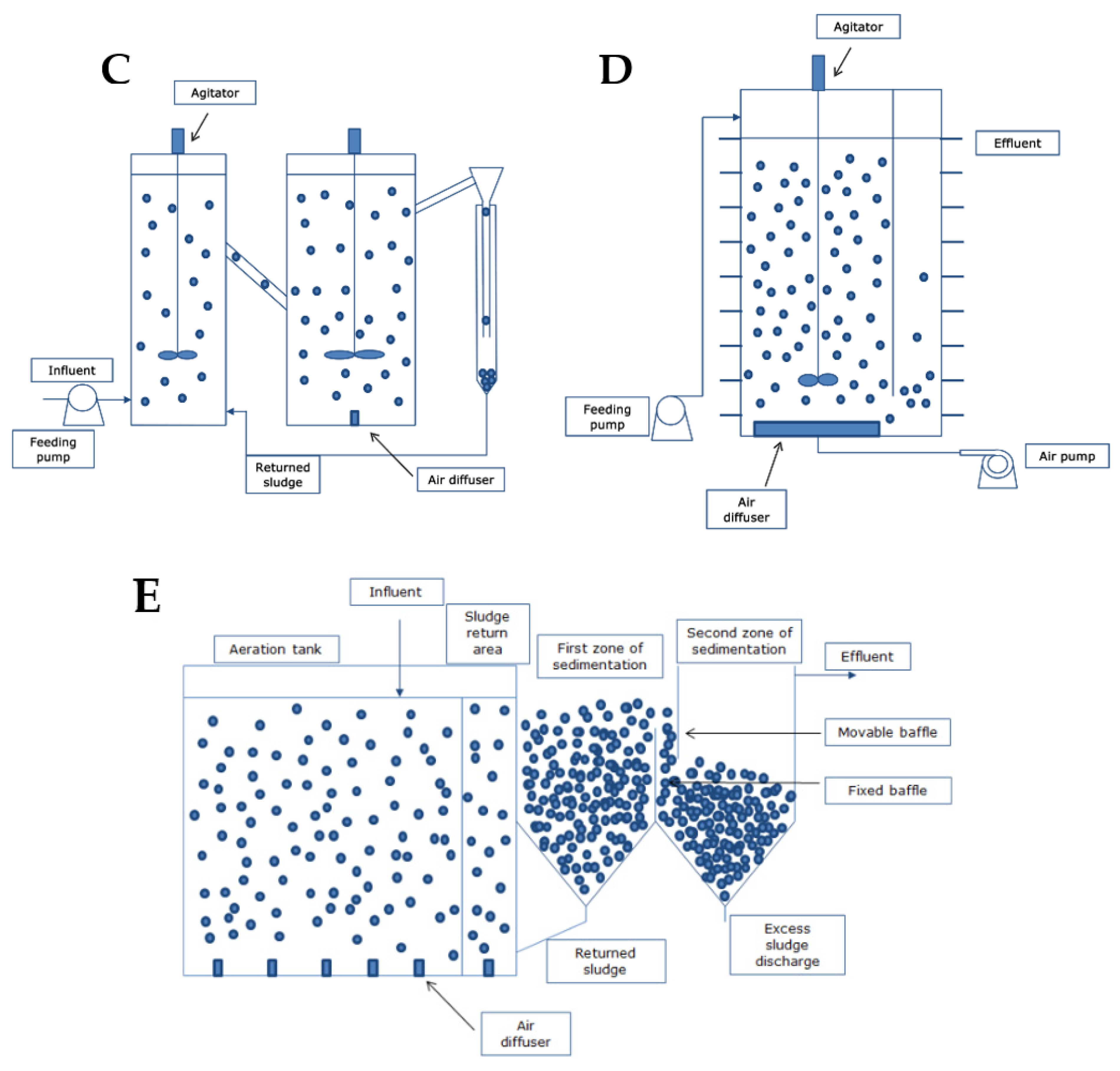
4.1. Design Reactors and Engineering Aspects
- (a)
- Bubble columns with baffles
- (b)
- Serial multiple chambers
- (c)
- Use of clarifiers
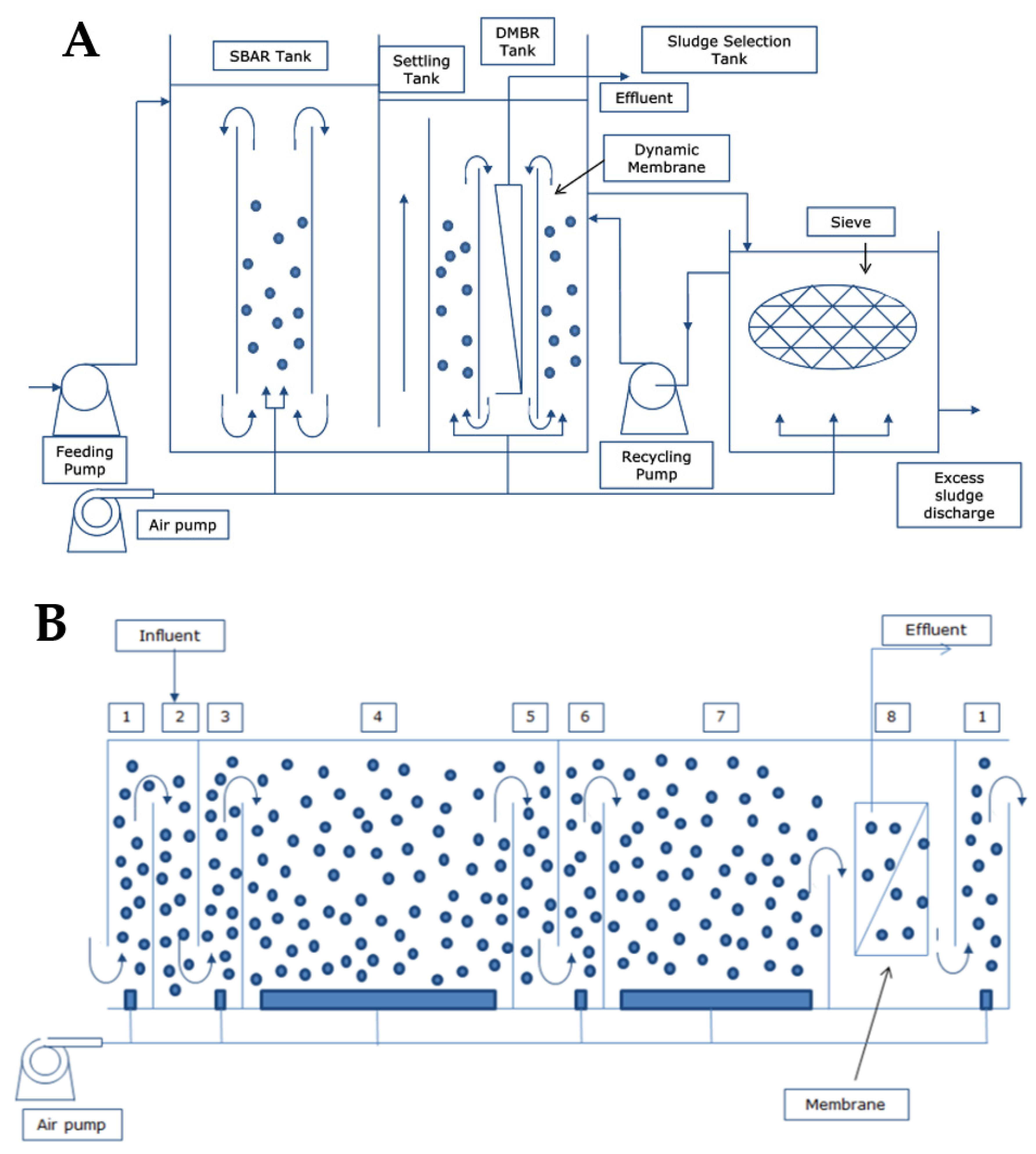
- (d)
- CFR with submerged membranes
- (e)
- Hybrid SBR-CFR system
4.2. Physicochemical Parameters and Granular Formation in CFR Systems
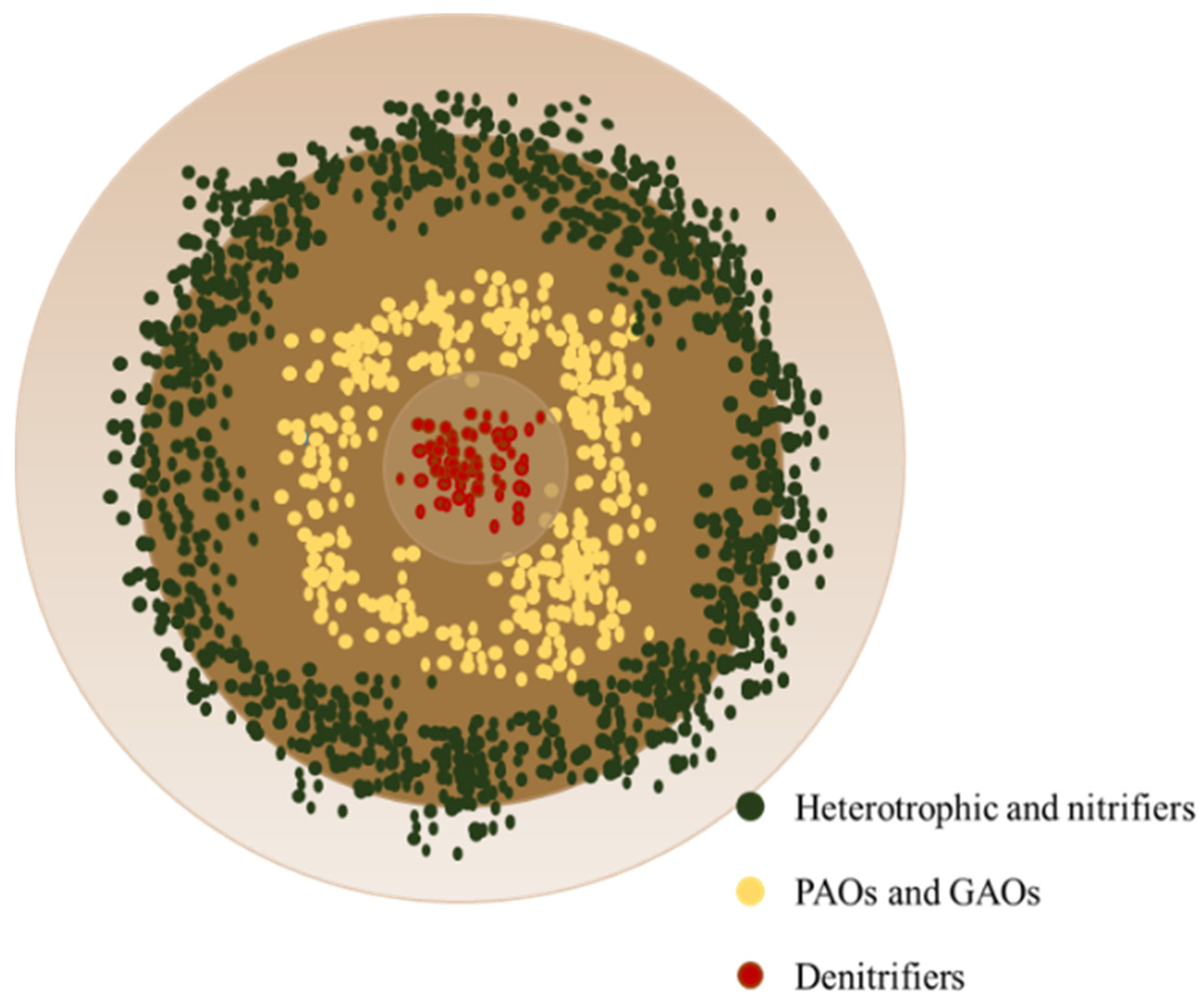
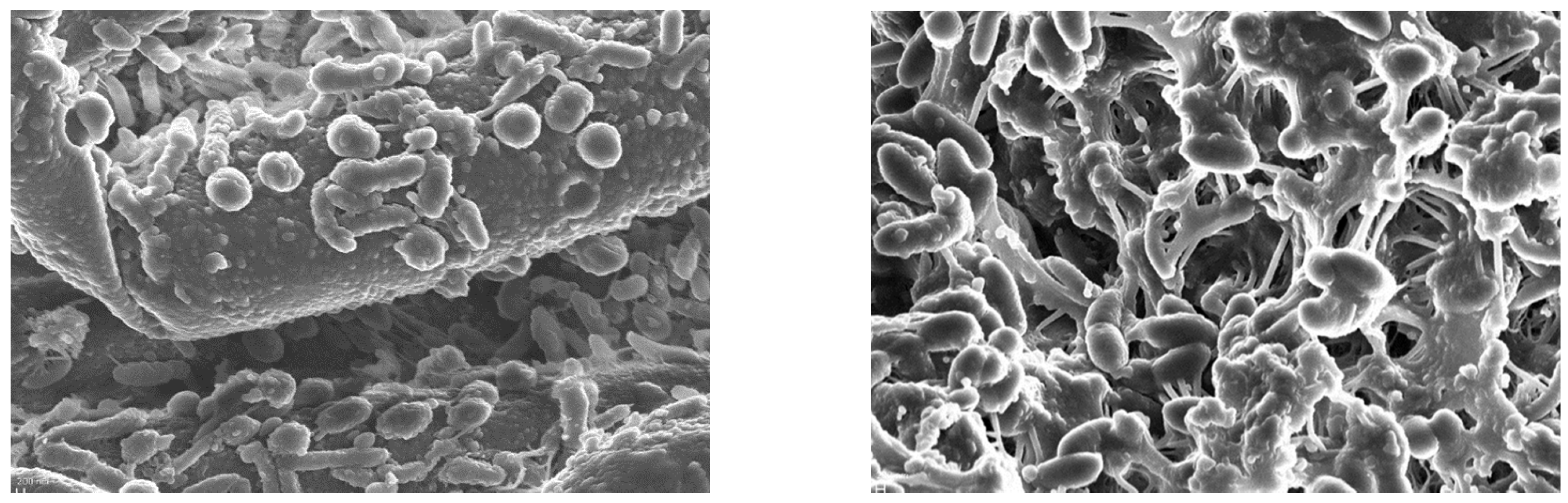
4.3. Granular Biomass in CFR Systems: Microbial Aspects
5. Technical Application of Aerobic Granular Continuous Flow Systems: Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACFR | advanced continuous flow reactor |
| AGR | aerobic granular sludge |
| AOB | ammonia oxidizing-bacteria |
| AUFB | aerobic upflow fluidized bed |
| CAFB | continuous flow airlift fluidized bed |
| CAS | conventional activated sludge |
| CFAGR | continuous-flow aerobic granular reactor |
| CFR | continuous flow reactor |
| CFR-TST | continuous-flow reactor with two-zone sedimentation tank |
| CGSFDMBR | continuous-flow granular self-forming dynamic membrane bioreactor |
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| CSTR | completely stirred tank reactor |
| D | diameter |
| DCCAGR | double column cyclic aerobic granular reactor |
| DMBR | dynamic membrane bioreactor |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| EBPR | enhanced biological phosphorus removal |
| EPS | extracellular polymeric substances |
| GAO | glycogen-accumulating organism |
| H | height |
| HRT | hydraulic retention time |
| MBR | membrane bioreactor |
| MLSS | mixed liquor suspended solids |
| NOB | nitrite oxidizing bacteria |
| OLR | organic loading rate |
| PAO | polyphosphate-accumulating organism |
| QS | quorum sensing |
| quorum quenching | |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| SBAR | sequencing batch airlift reactor |
| SBR | sequential batch reactor |
| USB | upflow sludge bed |
| WWTP | wastewater treatment plant |
References
- Cai, F.; Lei, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. A review of aerobic granular sludge (AGS) treating recalcitrant wastewater: Refractory organics removal mechanism, application and prospect. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettinga, G.; Van Velsen, A.F.M.; Hobma, S.W.; De Zeeuw, W.; Klapwijk, A. Use of the upflow sludge blanket (USB) reactor concept for biological wastewater treatment, especially for anaerobic treatment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1980, 22, 699–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Eikelboom, D.; Gjaltema, A.; Mulder, A.; Tijhuis, L.; Heijnen, J.J. Biofilm structures. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 32, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenroth, E.; Sherden, T.; Van Loosdrecht, M.; Heijnen, J.; Wilderer, P. Aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 1997, 31, 3191–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ma, R.; Hu, Y.; Lin, J.; Sun, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, T.; Liao, Q.; Luo, J. Reviewing bottlenecks in aerobic granular sludge technology: Slow granulation and low granular stability. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. Overcoming the instability of aerobic granular sludge under nitrogen deficiency through shortening settling time. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, E.J.; Pronk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. A settling model for full-scale aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; van Lier, J.B.; de Kreuk, M. Digestibility of waste aerobic granular sludge from a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment system. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaff, D.R.; Van Dijk, E.J.H.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pronk, M. Strength characterization of full-scale aerobic granular sludge. Environ. Technol. 2018, 41, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, A.; van Loosdrecht, M.; de Bruin, B.; van der Roest, H.; Pronk, M. Full-scale experiences with aerobic granular biomass technology for tratment of urban and industrial wastewater. In Proceedings of the International Water Week Amsterdam, Amsterda, The Netherlands, 4–8 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nancharaiah, Y.; Reddy, G.K.K. Aerobic granular sludge technology: Mechanisms of granulation and biotechnological applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1128–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Palazón, B.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification Processes in Granular Sludge Technology. In Nitrogen Cycle; Informa UK Limited: London, UK, 2021; pp. 222–244. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; de Castro, I.M.; Juarez-Jimenez, B.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Performance and microbial community structure of an aerobic granular sludge system at different phenolic acid concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 376, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J.; Show, K.-Y.; Tay, J.-H. Aerobic granular sludge: Recent advances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Robles-Arenas, V.M.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Biological nitrate removal from groundwater by an aerobic granular technology to supply drinking water at pilot-scale. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 40, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, L.D.A.; Ibiyeye, H.T.; Yuzir, A.; Mohamad, S.E.; Iwamoto, K.; Zamyadi, A.; Abdullah, N. Various applications of aerobic granular sludge: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Pfetzing, P.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A. Performance and microbial community structure of aerobic granular bioreactors at different operational temperature. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 33, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasina, M.; Kleyböcker, A.; Michalik, M.; Würdemann, H. Extremely fast increase in the organic loading rate during the co-digestion of rapeseed oil and sewage sludge in a CSTR—Characterization of granules formed due to CaO addition to maintain process stability. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, M.J.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Osorio, F. Performance and microbial community structure of an anammox biofilter treating real wastewater from a sludge return. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martínez, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Kruglova, A.; Vilpanen, M.; Kuokkanen, A.; Mikola, A.; Heinonen, M. Performance and microbial community structure of a full-scale ANITATMMox bioreactor for treating reject water located in Finland. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; Capodici, M.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Fate of aerobic granular sludge in the long-term: The role of EPSs on the clogging of granular sludge porosity. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kreuk, M.; Pronk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M. Formation of aerobic granules and conversion processes in an aerobic granular sludge reactor at moderate and low temperatures. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4476–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamis, S.; Katsou, E.; Fatone, F. Integration of energy efficient processes in carbon and nutrient removal from sewage. In Sewage Treatment Plants: Economic Evaluation of Innovative Technologies for Energy Efficiency; Stamatelatou, K., Tsagarakis, K.P., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2015; pp. 71–94. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Huang, W.; Li, H.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tay, J.H.; Lee, D.-J. Species and distribution of inorganic and organic phosphorus in enhanced phosphorus removal aerobic granular sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Fang, W.; Wang, Y.-P.; Sheng, G.-P.; Zeng, R.J.; Li, W.-W.; Yu, H.-Q. Phosphorus Removal in an Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal Process: Roles of Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11482–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, A.; Cui, D.; Cui, C.; Ma, F. Evolution of microbial community and key genera in the formation and stability of aerobic granular sludge under a high organic loading rate. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Yang, C.-Z.; Pu, W.-H.; Yang, J.-K.; Liu, F.-B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, K. Tolerance to organic loading rate by aerobic granular sludge in a cyclic aerobic granular reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, H.; Van Hullebusch, E.D. The Influence of Design and Operational Factors on the Removal of Personal Care Products by Constructed Wetlands. Water 2020, 12, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Martin-Ramos, D.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Poyatos, J.M.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Biofouling Formation and Bacterial Community Structure in Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor-Membrane Bioreactors: Influence of Salinity Concentration. Water 2018, 10, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Lee, D.-J. Aerobic granular processes: Current research trends. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, M.; Giesen, A.; Thompson, A.; Robertson, S.; Van Loosdrecht, M. Aerobic granular biomass technology: Advancements in design, applications and further developments. Water Pract. Technol. 2017, 12, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwaites, B.J.; Short, M.D.; Stuetz, R.M.; Reeve, P.J.; Gaitan, J.-P.A.; Dinesh, N.; Akker, B.V.D. Comparing the performance of aerobic granular sludge versus conventional activated sludge for microbial log removal and effluent quality: Implications for water reuse. Water Res. 2018, 145, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Hernández, M.L.; Pronk, M.; Garcia, H.; Boersma, A.; Brdjanovic, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Hooijmans, C.M. Removal of bacterial and viral indicator organisms in full-scale aerobic granular sludge and conventional activated sludge systems. Water Res. X 2020, 6, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Li, W.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Seo, Y.; Tang, C.-J.; Li, Q.; Xiao, R. Sorption and biodegradation of pharmaceuticals in aerobic activated sludge system: A combined experimental and theoretical mechanistic study. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Palazon, B.M.; Maza-Márquez, P.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Vahala, R. Performance and microbial community structure of a polar Arctic Circle aerobic granular sludge system operating at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Palazon, B.M.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Maza-Márquez, P.; Mikola, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Vahala, R. Start-up and operation of an aerobic granular sludge system under low working temperature inoculated with cold-adapted activated sludge from Finland. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Tay, J.H.; Chu, A. Finding Knowledge Gaps in Aerobic Granulation Technology. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-C.; Zhu, J.-R. Role of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL)-based quorum sensing (QS) in aerobic sludge granulation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7623–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.H.; Koh, K.S.; Xie, C.; Zhang, J.; Tan, X.H.; Lee, G.P.; Zhou, Y.; Ng, W.J.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Community quorum sensing signalling and quenching: Microbial granular biofilm assembly. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2015, 1, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilén, B.-M.; Liébana, R.; Persson, F.; Modin, O.; Hermansson, M. The mechanisms of granulation of activated sludge in wastewater treatment, its optimization, and impact on effluent quality. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5005–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.L.; Maia, A.S.; Mesquita, R.B.; Rangel, A.O.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Tiritan, M.E.; Castro, P.M. Performance of aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch bioreactor exposed to ofloxacin, norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin. Water Res. 2014, 50, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reino, C.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E.; Pérez, J.; Carrera, J. Kinetic and microbiological characterization of aerobic granules performing partial nitritation of a low-strength wastewater at 10 °C. Water Res. 2016, 101, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Liu, D.; Pan, Y.; Xi, L.; Yang, D.; Huang, W. Enhanced amount and quality of alginate-like exopolysaccharides in aerobic granular sludge for the treatment of salty wastewater. BioResources 2019, 14, 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Avendaño-Romero, G.C.; López-Malo, A.; Palou, E. Propiedades del alginato y aplicaciones en alimentos. Temas Sel. Ing. Aliment. 2013, 7, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Seviour, T.W.; Lambert, L.K.; Pijuan, M.; Yuan, Z. Selectively inducing the synthesis of a key structural exopolysaccharide in aerobic granules by enriching for Candidatus “Competibacter phosphatis”. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Hua, Z.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Characteristics of aerobic biogranules from membrane bioreactor system. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Chen, H.-L.; Fu, S.-Y.; Zhan, H.-Y. Cultivation of Biogranules in a Continuous Flow Reactor at Low Dissolved Oxygen. Water, Air, Soil Pollution: Focus 2009, 9, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, T.R.; Bott, C.B.; Wang, Z.-W. State of the art of aerobic granulation in continuous flow bioreactors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1139–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, S.; Cui, N.; Gao, L. Granulation of activated sludge in a continuous flow airlift reactor by strong drag force. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2013, 18, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Yang, X.; Lee, D.-J.; Liu, X.; Sun, S.; Chen, C. Partial nitrification of wastewaters with high NaCl concentrations by aerobic granules in continuous-flow reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, N.; Kono, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Tsuneda, S. Formation of Aerobic Granular Sludge in a Continuous-Flow Reactor—Control Strategy for the Selection of Well-Settling Granular Sludge. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2010, 8, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kishida, N.; Totsuka, R.; Tsuneda, S. Challenge for Formation of Aerobic Granular Sludge in a Continuous-Flow Reactor. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2012, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, A.; Ding, L.; Sellamuthu, B.; Perreault, J. Aerobic sludge granulation in a Reverse Flow Baffled Reactor (RFBR) operated in continuous-flow mode for wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Yang, C.-Z.; Pu, W.-H.; Yang, J.-K.; Liu, F.-B.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, K. Rapid cultivation of aerobic granular sludge in a continuous flow reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2966–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, L.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Nie, K. Cultivation of aerobic granular sludge in a conventional, continuous flow, completely mixed activated sludge system. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 9, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lv, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J. Long term operation of continuous-flow system with enhanced biological phosphorus removal granules at different COD loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Lv, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J. Startup and long term operation of enhanced biological phosphorus removal in continuous-flow reactor with granules. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 212, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Angelotti, B.; Wang, Z.-W. Continuous-flow aerobic granulation in plug-flow bioreactors fed with real domestic wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Angelotti, B.; Brooks, M.; Wang, Z.-W. Feast/famine ratio determined continuous flow aerobic granulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, J. Startup and stable operation of advanced continuous flow reactor and the changes of microbial communities in aerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Ma, T.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S. Rapid granulation of aerobic sludge in a continuous-flow reactor with a two-zone sedimentation tank by the addition of dewatered sludge. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 41, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; Campo, R.; Di Bella, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Study of aerobic granular sludge stability in a continuous-flow membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, R.; Lubello, C.; Lotti, T.; Di Bella, G. Aerobic Granular Sludge–Membrane BioReactor (AGS–MBR) as a Novel Configuration for Wastewater Treatment and Fouling Mitigation: A Mini-Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.P.; Stensel, H.D.; Quoc, B.N.; Stahl, D.A.; Huang, X.; Lee, P.-H.; Winkler, M.-K. Flocs in disguise? High granule abundance found in continuous-flow activated sludge treatment plants. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Pu, W.; He, L.; Bo, F. Stable aerobic granules in continuous-flow bioreactor with self-forming dynamic membrane. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 121, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J. Aerobic granular sludge operation and nutrients removal mechanism in a novel configuration reactor combined sequencing batch reactor and continuous-flow reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 122024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiao, H.; Huang, S.; Ma, H.; Liu, H. Aerobic granules cultivated and operated in continuous-flow bioreactor under particle-size selective pressure. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, X. Achieving high performance completely autotrophic nitrogen removal in a continuous granular sludge reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 118, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Ju, S.-P.; Lee, D.-J. Aerobic granulation of protein-rich granules from nitrogen-lean wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebrich, M.; Kleyböcker, A.; Kasina, M.; Miethling-Graff, R.; Kassahun, A.; Würdemann, H. Process Recovery after CaO Addition Due to Granule Formation in a CSTR Co-Digester—A Tool to Influence the Composition of the Microbial Community and Stabilize the Process? Microorganisms 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Han, Y.; Ma, D.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Bioaugmentation of a continuous-flow self-forming dynamic membrane bioreactor for the treatment of wastewater containing high-strength pyridine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 3437–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Yang, X.; Lee, D.J.; Sun, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P. Influence of hydraulic retention time on partial nitrification of continuous-flow aerobic granular-sludge reactor. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Yang, X.; Lee, D.-J.; Liu, X.; Sun, S. Partial nitrification using aerobic granule continuous-flow reactor: Operations and microbial community. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y. Magnesium carbonate precipitate strengthened aerobic granules. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 183, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, Y.-C.; Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H. Stable aerobic granules for continuous-flow reactors: Precipitating calcium and iron salts in granular interiors. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8051–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollemberg, S.L.D.S.; Barros, A.R.M.; Firmino, P.I.M.; dos Santos, A.B. Aerobic granular sludge: Cultivation parameters and removal mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Hao, T.; Wei, L.; Mackey, H.R.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G.-H. Impact of influent COD/N ratio on disintegration of aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2014, 62, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Huang, W.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Application of aerobic granules-continuous flow reactor for saline wastewater treatment: Granular stability, lipid production and symbiotic relationship between bacteria and algae. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, C.M.; Camejo, P.; Oshlag, J.Z.; Noguera, D.R. Ammonia-oxidizing microbial communities in reactors with efficient nitrification at low-dissolved oxygen. Water Res. 2015, 70, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, J.-W.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.-R.; Wang, W.-Q.; Zhang, J. Aerobic Granular Sludge Operation and Nutrient Removal Mechanism from Domestic Sewage in an Anaerobic/Aerobic Alternating Continuous Flow System. Huan Jing ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tan, X.; Wan, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Lee, D.-J. Biodegradation of real industrial wastewater containing ethylene glycol by using aerobic granular sludge in a continuous-flow reactor: Performance and resistance mechanism. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 161, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E.; Carrera, J. Biodegradation of a high-strength wastewater containing a mixture of ammonium, aromatic compounds and salts with simultaneous nitritation in an aerobic granular reactor. Process. Biochem. 2016, 51, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | CAS | AGS |
|---|---|---|
| Settling ability | <10 m h−1 | 15 to 140 m h−1 |
| Size | <0.2 mm | 0.2 to 50 mm |
| Redox | Aerobic | Aerobic, anoxic and anaerobic |
| Compactness | Absence | High |
| EPS production | Low | High |
| Resistance to toxicity | Low | High |
| Type of Reactor | Settling Velocity (max)(mh−1) | Mean Size (mm) | SVI (mL g−1) | Nucleus Core Formation (d) | Temperature (°C) | HRT (h) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFR system with baffled bubble column | - | 0.2–2 | 33.5 | - | 20 ± 2 | 4.08–24 | [53] |
| CFR system with serial multiple chambers | - | 0.135 | 43 | 21 | - | 5.5–16.4 | [54] |
| CFR system with clarifiers/sieve | 35.4 | 0.34–0.42 | 25–56 | 14 | 25 ± 5 | 16 | [62] |
| CFR system with MBR | 15–25 | 1.0–6.0 | 25–40 | Inoculated with granules | 22.5 ± 2.5 | 13 | [66] |
| Hybrid CFR/SBR system | - | - | 56.2–101.7 | Inoculated with granules | - | 6–12 | [67] |
| Conventional SBR system | 138 | 14 | - | 35 | 8–26 | 6 | [17] |
| Conventional SBR system | - | 1.2 | 15 (SVI8) * | Inoculated with granules | 8–20 | 5.6 | [22] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosa-Masegosa, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Fenice, M.; Gorrasi, S.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. New Advances in Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology Using Continuous Flow Reactors: Engineering and Microbiological Aspects. Water 2021, 13, 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131792
Rosa-Masegosa A, Muñoz-Palazon B, Gonzalez-Martinez A, Fenice M, Gorrasi S, Gonzalez-Lopez J. New Advances in Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology Using Continuous Flow Reactors: Engineering and Microbiological Aspects. Water. 2021; 13(13):1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131792
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosa-Masegosa, Aurora, Barbara Muñoz-Palazon, Alejandro Gonzalez-Martinez, Massimiliano Fenice, Susanna Gorrasi, and Jesus Gonzalez-Lopez. 2021. "New Advances in Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology Using Continuous Flow Reactors: Engineering and Microbiological Aspects" Water 13, no. 13: 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131792
APA StyleRosa-Masegosa, A., Muñoz-Palazon, B., Gonzalez-Martinez, A., Fenice, M., Gorrasi, S., & Gonzalez-Lopez, J. (2021). New Advances in Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology Using Continuous Flow Reactors: Engineering and Microbiological Aspects. Water, 13(13), 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131792











