Twenty-First Century Science Calls for Twenty-First Century Groundwater Use Law: A Retrospective Analysis of Transboundary Governance Weaknesses and Future Implications in the Laurentian Great Lakes Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Outcomes (Y): The Emerging Problem of Groundwater Insecurity and Linked Governance Gaps
- Characterizing Sub-Watershed-Scale GWS Decline
- Characterizing Present-Day GWS Governance Weaknesses
3.2. Causal Mechanisms: Linking Historical GWS Governance to Current Outcomes
- Fundamental Legal and Scientific Principles Underpinning the Evolution of GWS Governance
- The Evolution of Binational GWS Governance
- The Evolution of Federal GWS Governance
- The Evolution of State/Provincial GWS Governance
- Ontario
- II.
- Pennsylvania
- III.
- Minnesota
- IV.
- Wisconsin
- V.
- Indiana
- VI.
- Michigan
- VII.
- New York
- VIII.
- Illinois
- IX.
- Ohio
4. Discussion
- Causes and Outcomes
- Empirical Manifestations and Causal Mechanisms
- Causal Linkages
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coon, W.F.; Sheets, R.A. Estimate of Groundwater in Storage in the Great Lakes Basin, United States, 2006; USGS Scientific Investigations Report 2006–5180; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2006; 19p.
- Great Lakes Commission. Annual report of the Great Lakes regional water use data base-representing 2016 water use data. In Proceedings of the Great Lakes and St Lawrence Governors and Premiers, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 29 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kavcic, R. A Special report on the Great Lakes and St Lawrence Regional Economy. In Proceedings of the Great Lakes and St Lawrence Governors and Premiers, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 29 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency (NOAA). Basin Map of Great Lakes; Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2004. Available online: http://www.flickr.com/photos/noaaglerl/4037600466/ (accessed on 2 January 2019).
- Lofgren, B.; Hunter, T.; Wilbarger, J. Effects of using air temperature as a proxy for potential evapotranspiration in climate change scenarios of Great Lakes Basin hydrology. J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 27, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Halpenny, J.; van der Wal, W.; Klatt, C.; James, T.; Rivera, A. Detecting Groundwater Storage Change within the Great Lakes Water Basin using GRACE. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, B08401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, K.; Gerber, R. Impacts of urban areas and urban growth on groundwater in the Great Lakes Basin of North America. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, P.; Pattberg, P.; Schroeder, H. Multi-Actor Governance and the Environment. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 365–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, S.; Loucks, D. Non-Renewable Groundwater Resources: A Guidebook on Socially-Sustainable Management for Policy Makers; IHP-VI, Series on Groundwater No. 10; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2006; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000146997 (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Majidipour, F.; Mohammad, S.; Taheri, K.; Fathollahi, J.; Missimer, T. Index-Based Groundwater Sustainability Assessment in the Socio Economic Context: A Case Study in the Western Iran. Environ. Manag. 2021, 67, 648–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimone, M. Defining and Managing Sustainable Yield. Groundwater 2004, 42, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granneman, N.G.; Van Stempvoort, D. Groundwater Science Relevant to the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement: A Status Report for the Great Lakes Executive Committee. 2016. Available online: https://binational.net//wpcontent/uploads/2016/05/GW-Report-final-EN.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Kreutzwiser, R.; Lo, R.; Durley, J.; Priddle, C. Water Allocation and the Permit to Take Water Program in Ontario: Challenges and Opportunities. Can. Water Resour. J. 2013, 29, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, A.; Mubako, S.; Ruddel, B. Developing the greatest blue economy: Water productivity, freshwater depletion and virtual water trade in the Great Lakes Basin. Earths Future 2016, 4, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemper, K.E. Instruments and institutions for groundwater management. In the Agricultural Groundwater Revolution: Opportunities and Threats to Development; Giordano, M., Villholth, K.G., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2007; pp. 153–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hodge, R.A. Groundwater in the Great Lakes Basin: The Natural System, Use and Abuse, and Policy Implications. Chi. Kent L. Rev. 1989, 65, 439. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, J. Law and Management of the Great Lakes Basin. Can. J. Water Resour. 2000, 25, 209–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karkkainen, B. The Great Lakes Water Resources Compact and Agreement: Transboundary Normativity without International Law. William Mitchell Law Rev. 2013, 39, 1001–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Dellapenna, J. Emerging Challenges to Good Governance in the Great Lakes: Changing Legal Regimes: Changing State Water Allocations Laws to Protect the Great Lakes. Ind. Int. Comp. L. Rev. 2014, 9, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, A. Transboundary aquifers along the Canada-USA Border: Science, Policy and Social Issues. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 623–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weekes, K.; Krantzberg, G.; Vizeu, M. Identifying Groundwater Sustainability Implications of Water Policy in High-Use Situations in the Laurentian Great Lakes Basin. Can. Water Resour. J. 2019, 44, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megdal, S.; Gerlak, A.; Varady, R.; Huang, L. Groundwater Governance in the United States: Common Priorities and Challenges. Groundwater 2014, 53, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.; Quevauviller, P. Groundwater law. In Integrated Groundwater Management; Jakeman, A.J., Barreteau, O., Hunt, R.J., Rinaudo, J.D., Ross, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beach, D. It’s all about mechanisms—What process-tracing case studies should be tracing. New Political Econ. J. 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waltz, K.; Bull, H.; Butterfield, H. Theory of International Politics. Saltzman Institute of War and Peace, Columbia University; Waveland Press Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Beach, P.; Pedersen, R. Process-Tracing Methods: Foundations and Guidelines; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, H.; Ahmad, I.; Anjum, M.; Khan, Z.; Iqbal, M.; Shakoor, A.; Mubeen, M. Assessing seasonal and long-term changes in groundwater quality due to over-abstraction using geostatistical techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. J. 2019, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pophare, A.; Lamsoge, B.; Katpatal, Y.; Nawale, V. Impact of over-exploitation on groundwater quality: A case study from WR-2 Watershed, India. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 123, 1541–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galloway, D.; Jones, D.; Ingebritsen, S. Land Subsidence in the United States; USGS Circular 1182; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 1999. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlow, P.; Leake, S. Streamflow Depletion by Wells: Understanding and Managing the Effects of Groundwater Pumping on Streamflow; USGS Circular 1376; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/1376/ (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- Custodio, E.; Kretsinger, V.; Llamas, M. Intensive development of groundwater: Concept, facts and suggestions. Water Policy 2005, 7, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.; Faunt, C.; Longuevergne, L.; Reedy, R.; Alley, W.; McGuire, V.; McMahon, P. Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Expert Panel on Groundwater. The Sustainable Management of Groundwater in Canada; The Council of Canadian Academies Report: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, W.; McLane, C. Aspects of Groundwater Supply Sustainable Yield. Groundw. Tech. Comment. 2013, 51, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lin, H. Determination of groundwater sustainable yield using a numerical modelling approach for the Table Mountain Group sandstone aquifer, Rawsonville, South Africa. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheets, R.A.; Simonson, L.A. Compilation of Regional Ground-Water Divides for Principal Aquifers Corresponding to the Great Lakes Basin; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2006–5102; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2006; 23p.
- Granneman, N.G.; Hunt, R.J.; Nicholas, J.R.; Reilly, T.E.; Winter, T.C. The Importance of Groundwater in the Great Lakes Region; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 00-4008; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2000; 14p.
- Luczaj, J.; Masarik, K. Groundwater Quantity and Quality Issues in a Water-Rich Region: Examples from Wisconsin, USA. Resources 2015, 4, 323–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Great Lakes Science Advisory Board to the International Joint Commission. Groundwater in the Great Lakes Basin. International Joint Commission. 2010. Available online: https://legacyfiles.ijc.org/publications/E43.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Great Lakes Executive Committee. Progress Report of the Parties for 2019. Pursuant to the 2012 Canada-United States Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement. 2019. Available online: https://binational.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Final-2019-PROP-English-June-7.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Xu, S.; Frey, S.; Erler, A.; Khader, O.; Berg, S.; Hwang, H.; Callaghan, M.; Davison, J.; Sudicky, E. Investigating groundwater-lake interactions in the Laurentian Great Lakes with a fully-integrated surface water-groundwater model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtschlag, D.; Nicholas, J. Indirect Ground-Water Discharge to the Great Lakes; Open-File Report 98-579; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1998; 25p. [CrossRef]
- Helmuth, J.; Johnon, D.; Karklins, S.; Lindorff, D. Status of Groundwater Quantity in Wisconsin; PUBL-DG-043-97; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, MI, USA, 1997.
- National Research Council. Mitigating Losses from Land Subsidence in the United States; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keqiang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, S. Karst collapse related to over pumping and a criterion for its stability. Environ. Geol. 2003, 43, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A. Final Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement for the Central United States. First Responder Network Authority 6; 2019. Available online: https://firstnet.gov/sites/default/files/FirstNet%20FPEIS%20Central%20Chapter%208%20Michigan%20June%202017.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Curtis, Z.; Li, S.; Sampath, P.; Liao, H. Groundwater Sustainability in the Michigan Lowlands—Understanding the Complex Interplay of Natural Brine Upwelling, Human Activity, and Climate Change. In Proceedings of the Fall Meeting, Warszawa, Poland, 15–18 September 2015; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. abstract id. H33I-1731. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, Z.; Liao, H.; Li, S. Ottawa County Water Resources Study—Phase 2. Final Report. Institute for Water Research. 2018. Available online: https://www.miottawa.org/GroundWater/pdf/phase2_report.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Asher, M.; Cleary, E.; Olawoyin, R. Medical Geology of Arsenic in Groundwater and Well Water in South East Michigan. Environ. Dis. 2017, 2, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Galasinski, U.; Cho, S.; Hwang, C. A Spatiotemporal Analysis of Groundwater Level Changes in Relation to Urban Growth and Groundwater Recharge Potential for Waukesha County, Wisconsin. Geogr. Anal. 2012, 44, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, H. Water Availability and Use Pilot. A Multiscale Assessment of the US Great Lakes; United States Geological Society: Madison, MI, USA, 2011.
- Grand River Conservation Authority. Groundwater Resources. 2019. Available online: https://www.grandriver.ca/en/our-watershed/Groundwater-resources.aspx (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Bruneau, J.; Dupont, D.; Renzetti, S. Economic Instruments, Innovation, and Efficient Water Use. Can. Public Policy Anal. Polit. 2013, 39, S11–S22. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/23594768 (accessed on 21 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Annin, P. The Great Lakes Water Wars; The Center for Resource Economics: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sterner, R.; Ostrom, P.; Ostrom, N.; Klump, J.V.; Steinman, A.; Dreelin, E.; Zanden, M.V.; Fisk, A. Grand Challenges for Research in the Laurentian Great Lakes Basin. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 2510–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.; Luoma, D.S.S.; Love, N.; Austin, J. Leveraging the Great Lakes Region’s Water Assets for Economic Growth. Metropolitan Policy Program at Brookings. 2010. Available online: https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/0927_great_lakes_water.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- International Joint Commission. Groundwater in the Great Lakes Basin; International Joint Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Ecofiscal Commission. Only Pipes Should be Hidden: Best Practices for Pricing and Improving Municipal Water and Wastewater Services. 2017. Available online: http://ecofiscal.ca/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Ecofiscal-Commission-Report-Onlythe-Pipes-Should-be-Hidden-FINAL-Sept-26-2017.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Gardner, A.; Bartlett, R.H.; Gray, J.; Carney, G. Water Resources Law; LexisNexis Butterworths: Sydney, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, J. Groundwater as the Cinderella of water laws, policies and institutions in Australia. Ecol. Econ. J. 2007, 141, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshein, J.S.; Moore, J.E.; Lohman, S.W.; Chase, E.B. Two Hundred Years of Hydrogeology in the United States; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 86-480; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 1986.
- National Research Council. Legal considerations, valuations and groundwater policy—Chapter 5. In Valuing Ground Water: Economic Concepts and Approaches; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; Available online: https://www.nap.edu/read/5498/chapter/1#xi (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- IJC. Impacts of a Proposed Coal Mine in the Flathead River Basin; International Joint Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, C. Standing Under the Great Lakes Compact: A Broad-Based Argument Infused with Public Trust Principles for those with Diversion Aversion. Mich. State Law Rev. 2018, 251, 252–306. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, K.; Cook, C. Water governance in Canada: Innovation and fragmentation. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2011, 27, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlan, L. Out of sight, out of mind? Taking Canada’s groundwater for granted. In Eau Canada; Bakker, K., Ed.; UBC Press: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leshy, J. Interstate groundwater resources: The federal role. Hastings North West J. Environ. Law Policy 2008, 14, 1475–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Kilbert, K.; Merkle, A.; Miller, F. An Assessment of the Great Lakes States’ Implementation of the Water Management and Conservation Provisions of the Great Lakes—St Lawrence River Basin Water Resources Compact; University of Toledo College of Laws Legal Institute of the Great Lakes: Toledo, OH, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Minnesota Statewide Drought Plan. 2009. Available online: https://files.dnr.state.mn.us/natural_resources/climate/drought/drought_plan_matrix.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Kent, P.; Dudiak, T. Wisconsin Water Law: A Guide to Water Rights and Regulations; University of Wisconsin extension: Madison, WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein, G.; Hardberger, A. Groundwater Laws and Regulations: A Preliminary Survey of Thirteen U.S. States. Texas A&M University School of Law Program in Natural Resources Systems. 2017. Available online: https://law.tamu.edu/docs/default-source/faculty-documents/groundwater-laws-reg-13states.pdf?sfvrsn=0 (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Lusch, D. An Overview of Existing Water Law in Michigan Related to Irrigation Water Use and Riparian Considerations; Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J. A Critical Look at Michigan Citizens for Water Conservation v. Nestle Waters North America & the Michigan Supreme Court’s Recent Jurisprudence. 2008. Available online: https://digitalcommons.law.msu.edu/king/118 (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Negro, S.; Porter, K. Water Stress in New York State: The Regional Imperative? J. Water Law 2009, 20, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, J.E. From divining rods to dams: Creating a comprehensive water resource management strategy for New York. Commem. Pace Law Rev. 1995, 1995, 105–139. [Google Scholar]
- Janasie, C. An Overview of Water Law in Illinois; NSGLC-20-04-02; Sea Grant Law Center: Oxford, MS, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, P. Understanding Water Rights in Ohio; Law Notes; The Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gosman, S. The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Implementation of the Great Lakes Compact; National Wildlife Association: Reston, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, P. A Short Review of Pennsylvania Water Law. PA Department of Environmental Protection Presentation. 2006. Available online: http://files.dep.state.pa.us/Water/BSDW/WaterAllocation/water_law_review_022806.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Great Lakes Science Advisory Board. Great Lakes Surface and Groundwater Model Integration Review: Literature Review, Options and Approaches and Preliminary Action Plan for the Great Lakes Basin. International Joint Commission Report. 2018. Available online: https://www.ijc.org/sites/default/files/2019-01/Great_Lakes_Surface_and_Groundwater_Model_Integration_Review_Oct2018.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Burlakova, L.E.; Hincheyb, E.; Karatayeva, A.; Rudstamc, L.G. U.S. EPA Great Lakes National Program Office monitoring of the Laurentian Great Lakes: Insights from 40years of data collection. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerna, L. The Nature of Policy Change and Implementation: A Review of Different Theoretical Approaches; OECD: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/education/ceri/The%20Nature%20of%20Policy%20Change%20and%20Implementation.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Hansen, R. Globalization, embedded realism and path dependence: The other immigrants to Europe. Comp. Political Stud. 2002, 35, 259–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, P. Increasing returns, path dependence and the study of politics. Am. Political Sci. Rev. 2000, 94, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greener, I. Understanding NHS reform: The policy-transfer, social learning and path-dependency perspectives. Governance 2002, 15, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoccia, G.; Kelemen, D. The study of critical junctures: Theory, narrative and counterfactuals in historical institutionalism. World Politics 2007, 59, 341–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, T.J.; Mohapatra, S.P.; Mitchell, A. Conflicts, costs and environmental degradation—Impacts of antiquated groundwater allocation policies in the Great Lakes Basin. Water Policy 2008, 10, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watershed Council. Great Lakes Water Use and Diversions. 2020. Available online: https://www.watershedcouncil.org/great-lakes-water-use-and-diversions.html (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Kane, K. The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River basin agreement: What happens in the Great Lakes Won’t Stay in the Great Lakes. Mich. State Int. Law Rev. 2017, 25, 432–453. [Google Scholar]
- Chaloux, A.; Paquin, S. Green Paradiplomacy and Water Resource Management in North America: The Case of the Great Lakes-St Lawrence River Basin. Can. Foreign Policy J. 2013, 19, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G. Groundwater the Sixth Great Lake. Great Lakes Now. 2018. Available online: https://www.greatlakesnow.org/2018/09/groundwater-the-sixth-great-lake/ (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- Pentland, R.; Mayer, A. Ten Year Review of the International Joint Commission’s Report on “Protection of the Waters of the Great Lakes”. Alliance for the Great Lakes. 2015. Available online: http://fbheron.issuelab.org/resource/on_track_ensuring_the_resilience_of_the_great_lakes_compact (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Sun, A.; Scanlon, B. How can Big Data and machine learning benefit environment and water management: A survey of methods, applications, and future directions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marçais, J.; de Dreuzy, J.-R. Prospective interest of deep learning for hydrological inference. Groundwater 2017, 55, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fienen, M.N.; Nolan, B.T.; Feinstein, D.T.; Starn, J. Metamodels to bridge the gap between modeling and decision support. Groundwater 2015, 53, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Water Systems Council. Who Owns the Water; National AG Law Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; Available online: http://nationalaglawcenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Who-Owns-the-Water-2016-Update-FINAL.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Abrams, R. Legal Convergence of the East and West in contemporary Water Law. Environ. Law J. 2012, 42, 65–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kotkin, J.; Schill, M. A Map of America’s Future: Where Growth Will Be over the Next Decade. New Geogr. 2013. Available online: http://www.newgeography.com/content/003914-a-map-of-americas-future-where-growth-will-be-over-the-next-decade (accessed on 10 September 2020).
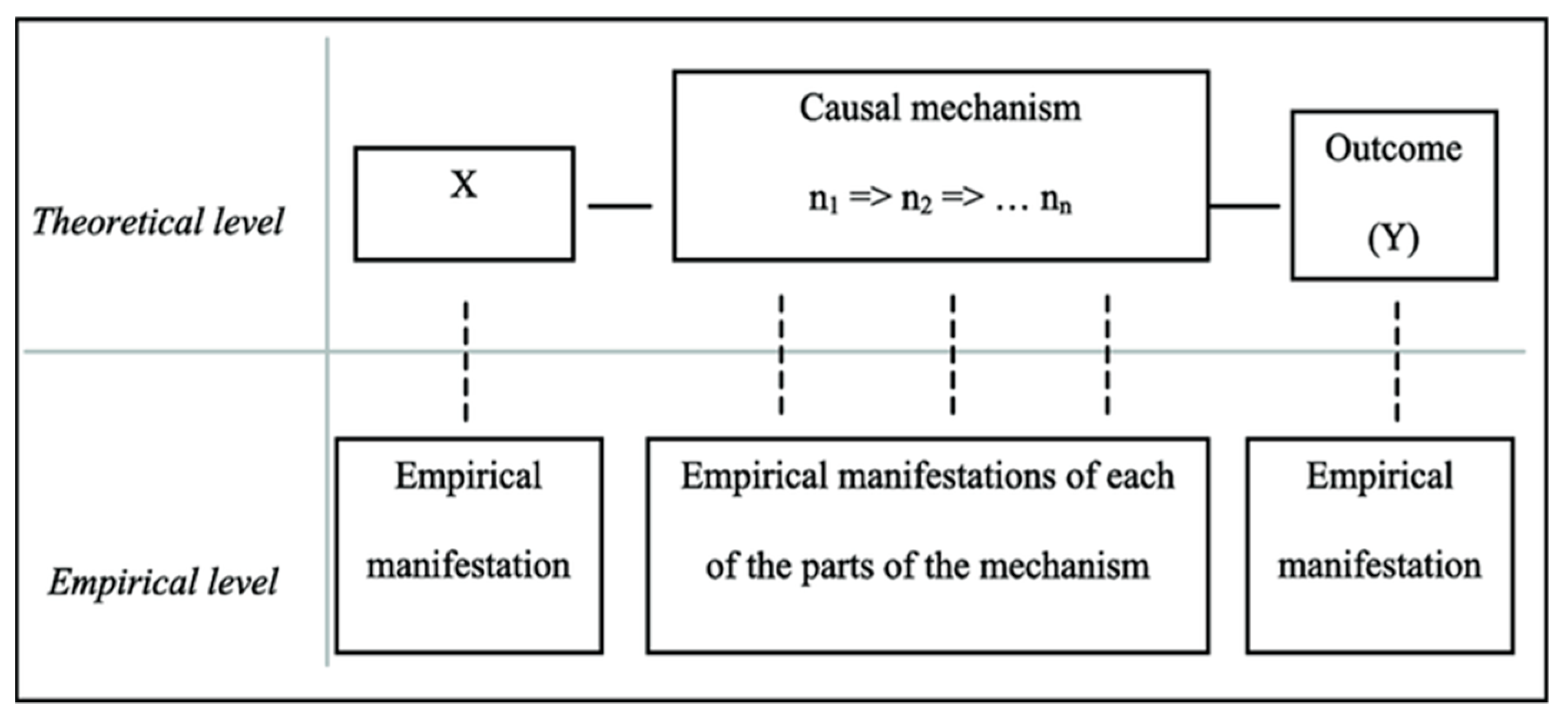
| CPT ELEMENT | APPLICATION IN RESEARCH |
|---|---|
| Causes (X) | Foundational policies and decision-making standards of the current GWS governance framework. |
| Outcomes (Y) |
|
| Causal mechanism | Multilevel governance processes, which have evolved over time, defining groundwater uses and environmental safeguards relevant to maintaining GWS. |
| Empirical manifestation/events (nx) | Milestones and/or changes in policies and decision-making standards over the timeframe of the evolution of the GWS governance framework, e.g., successive binational treaties, statute amendments, major court decisions, and other governance mechanisms influencing GWS. |
| Causal linkages (=>) | Established by interpretation and detailed descriptions of policies and decision-making standards over time based on the hypothesis and sustainable aquifer yield theory. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weekes, K.; Krantzberg, G. Twenty-First Century Science Calls for Twenty-First Century Groundwater Use Law: A Retrospective Analysis of Transboundary Governance Weaknesses and Future Implications in the Laurentian Great Lakes Basin. Water 2021, 13, 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131768
Weekes K, Krantzberg G. Twenty-First Century Science Calls for Twenty-First Century Groundwater Use Law: A Retrospective Analysis of Transboundary Governance Weaknesses and Future Implications in the Laurentian Great Lakes Basin. Water. 2021; 13(13):1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131768
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeekes, Khafi, and Gail Krantzberg. 2021. "Twenty-First Century Science Calls for Twenty-First Century Groundwater Use Law: A Retrospective Analysis of Transboundary Governance Weaknesses and Future Implications in the Laurentian Great Lakes Basin" Water 13, no. 13: 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131768
APA StyleWeekes, K., & Krantzberg, G. (2021). Twenty-First Century Science Calls for Twenty-First Century Groundwater Use Law: A Retrospective Analysis of Transboundary Governance Weaknesses and Future Implications in the Laurentian Great Lakes Basin. Water, 13(13), 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131768







