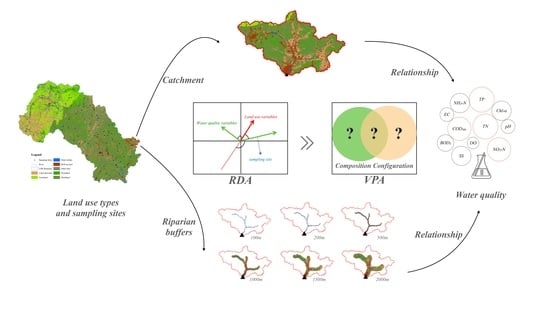
Catchment versus Riparian Buffers: Which Land Use Spatial Scales Have the Greatest Ability to Explain Water Quality Changes in a Typical Temperate Watershed?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling and Parameter Measurements
2.3. Quantification of Land Use Indicators
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Land Use Variables and Water Quality Characteristics
3.2. Relationship between Land Use and Water Quality at Multiple Scales
3.3. Differences in the Capability of Land Use Composition and Configuration to Explain Water Quality at Different Scales
4. Discussion
4.1. Effective Spatial Scale Identification of Land Use Patterns on Water Quality
4.2. Main Land-Use Variables That Affect Water Quality at Different Spatial Scales
4.3. Implications for Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Davies, P.M. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, C.K.; Fernandes, M.R.; Ferreira, M.T.; Hering, D.; Ormerod, S.J.; Venohr, M.; Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C. Evaluating riparian solutions to multiple stressor problems in river ecosystems—a conceptual study. Water Res. 2018, 139, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Hou, Z.; He, K.; Jiang, Y. Relationship between dissolved organic matter and phytoplankton community dynamics in a human-impacted subtropical river. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient explored by geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, J.; Chang, H. Landscape and anthropogenic factors affecting spatial patterns of water quality trends in a large river basin, South Korea. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.E.; Fernandes, J.N.; David, L.M. Key issues for sustainable urban stormwater management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6787–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, R. Scale effects on spatially varying relationships between urban landscape patterns and water quality. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafi’Shehab, Z.; Jamil, N.R.; Aris, A.Z.; Shafie, N.S. Spatial variation impact of landscape patterns and land use on water quality across an urbanized watershed in Bentong, Malaysia. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, E.G. The Global Risks Report 2020. In World Economic Forum. 2020. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/reports/the-global-risks-report-2020 (accessed on 28 January 2020).
- Sliva, L.; Williams, D.D. Buffer zone versus whole catchment approaches to studying land use impact on river water quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, S.; Andersen, D.K.; Kronvang, B.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A. Structural and functional characteristics of buffer strip vegetation in an agricultural landscape–high potential for nutrient removal but low potential for plant biodiversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, P.; Shu, W.; Ding, M.; Zhang, H. Influence of landscape structures on river water quality at multiple spatial scales: A case study of the Yuan river watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuchástegui, G.; Di Franco, L.; Feijoó, C. Catchment morphometric characteristics, land use and water chemistry in Pampean streams: A regional approach. Hydrobiologia 2016, 767, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, C.G.; Barlow, J.; Gardner, T.A.; Hughes, R.M.; Leitão, R.P.; Mac Nally, R.; Pompeu, P.S. Is environmental legislation conserving tropical stream faunas? A large-scale assessment of local, riparian and catchment-scale influences on Amazonian fish. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meixler, M.S.; Bain, M.B. Landscape scale assessment of stream channel and riparian habitat restoration needs. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 6, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosskey, M.G.; Vidon, P.; Gurwick, N.P.; Allan, C.J.; Duval, T.P.; Lowrance, R. The role of riparian vegetation in protecting and improving chemical water quality in streams 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chi, G.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z. Identifying the critical riparian buffer zone with the strongest linkage between landscape characteristics and surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Multi-scale analysis of relationship between landscape pattern and urban river water quality in different seasons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Dong, R.; Jiang, C.; Ni, M. Influences of land use metrics at multi-spatial scales on seasonal water quality: A case study of river systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gove, N.E.; Edwards, R.T.; Conquest, L.L. Effects of scale on land use and water quality relationships: A longitudinal basin-wide perspective 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.G.; Bennett, E.M.; Gonzalez, A. Linking landscape connectivity and ecosystem service provision: Current knowledge and research gaps. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, F.; Ruiz, J.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Blais, D.; Campeau, S. Landscape diversity and forest edge density regulate stream water quality in agricultural catchments. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Marks, B.J. Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; Gen. Tech. Rep. PNW-GTR-351; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1995; pp. 1–122.
- Ricart, A.M.; Dalmau, A.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J. Effects of landscape configuration on the exchange of materials in seagrass ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 532, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Hou, X.; Li, W.; Aini, G. Relating landscape characteristics to non-point source pollution in a typical urbanized watershed in the municipality of Beijing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 123, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Antrop, M.; Roosaare, J.; Marja, R.; Mander, Ü. Landscape metrics and indices: An overview of their use in landscape research. Living Rev. Landsc. Res. 2009, 3, 1–28. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1854/LU-695518 (accessed on 9 June 2018). [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Mander, Ü.; Marja, R. Trends in the use of landscape spatial metrics as landscape indicators: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 28, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guhathakurta, S.; Dai, G.; Wu, L.; Yan, L. The control of land-use patterns for stormwater management at multiple spatial scales. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wu, J. Landscape composition or configuration: Which contributes more to catchment hydrological flows and variations? Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, R. Modeling the non-point source pollution risks by combing pollutant sources, precipitation, and landscape structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2019, 26, 11856–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dong, M.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Using a water quality index to assess the water quality of the upper and middle streams of the Luanhe River, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebei Province Bureau of Statistics. Hebei Province Statistical Yearbook 2017; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Bureau of Statistics. Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Statistical Yearbook 2017; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. The National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002); Chinese Environmental Sciences Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Booth, D.; Hill, K.; Coburn, B.; Avolio, C.; Coe, S.; Spirandelli, D. The impact of urban patterns on aquatic ecosystems: An empirical analysis in Puget lowland sub-basins. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, J.A. Landscape ecology and biogeography: Rethinking landscape metrics in a post-FRAGSTATS landscape. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 36, 400–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps. Computer Software Program Produced by the Authors at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. 2012. Available online: http://www. umass. edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Braak, C.J.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0. Ithaca USA: Microcomputer Power; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Jongman, E.; Jongman, S.R.R. Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; Available online: www.cambridge.org/9780521475747 (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Økland, R.H.; Eilertsen, O. Canonical correspondence analysis with variation partitioning: Some comments and an application. J. Veg. Sci. 1994, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; dos Santos, A.C.A.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Effects of land use and land cover on water quality of low-order streams in Southeastern Brazil: Watershed versus riparian zone. Catena 2018, 167, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, R.; Dwivedi, P. Impact of land cover on groundwater quality in the Upper Floridan Aquifer in Florida, United States. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Ma, K.; Yang, L.; He, K. Testing a Dynamic Complex Hypothesis in the Analysis of Land Use Impact on Lake Water Quality. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1313–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, W.; Skidmore, A.K.; Toxopeus, A.G.; Hao, F. Long-term vegetation landscape pattern with non-point source nutrient pollution in upper stream of Yellow River basin. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidary, A.; Amiri, B.J.; Adamowski, J.; Fohrer, N.; Nakane, K. Assessing the impacts of four land use types on the water quality of wetlands in Japan. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Santos, R.M.B.; Fernandes, L.S.; Pereira, M.G.; Cortes, R.M.V. Controls and forecasts of nitrate yields in forested watersheds: A view over mainland Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 537, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahearn, D.S.; Sheibley, R.W.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Anderson, M.; Johnson, J.; Tate, K.W. Land use and land cover influence on water quality in the last free-flowing river draining the western Sierra Nevada, California. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Hwang, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; Hwang, H.S.; Sung, H.C. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennen, J.G.; Riva-Murray, K.; Beaulieu, K.M. Determining hydrologic factors that influence stream macroinvertebrate assemblages in the northeastern US. Ecohydrol. Ecosyst. Land Water Process Interact. Ecohydrogeomorphology 2010, 3, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namugize, J.N.; Jewitt, G.; Graham, M. Effects of land use and land cover changes on water quality in the uMngeni river catchment, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A B C 2018, 105, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Bahn, R.A.; Webster, J.R. Water quality signals from rural land use and exurbanization in a mountain landscape: What’s clear and what’s confounded? J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 1212–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Q.; Kang, M. Impacts of land use on surface water quality in a subtropical River Basin: A case study of the Dongjiang River Basin, Southeastern China. Water 2015, 7, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tudesque, L.; Tisseuil, C.; Lek, S. Scale-dependent effects of land cover on water physico-chemistry and diatom-based metrics in a major river system, the Adour-Garonne basin (South Western France). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, B.J.; Nakane, K. Modeling the linkage between river water quality and landscape metrics in the Chugoku District of Japan. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 931–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, W.; Huang, X. Spatial and seasonal patterns in stream water contamination across mountainous watersheds: Linkage with landscape characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarram, M.; Saber, A.; Sheykhi, V. Effects of heavy metal contamination on river water quality due to release of industrial effluents. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.D.F.; de Souza, A.L.; Tanaka, M.O. Can the structure of a riparian forest remnant influence stream water quality? A tropical case study. Hydrobiologia 2014, 724, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Hu, H.; Ma, L.; Sheng, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Characterizing the spatial variations of the relationship between land use and surface water quality using self-organizing map approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

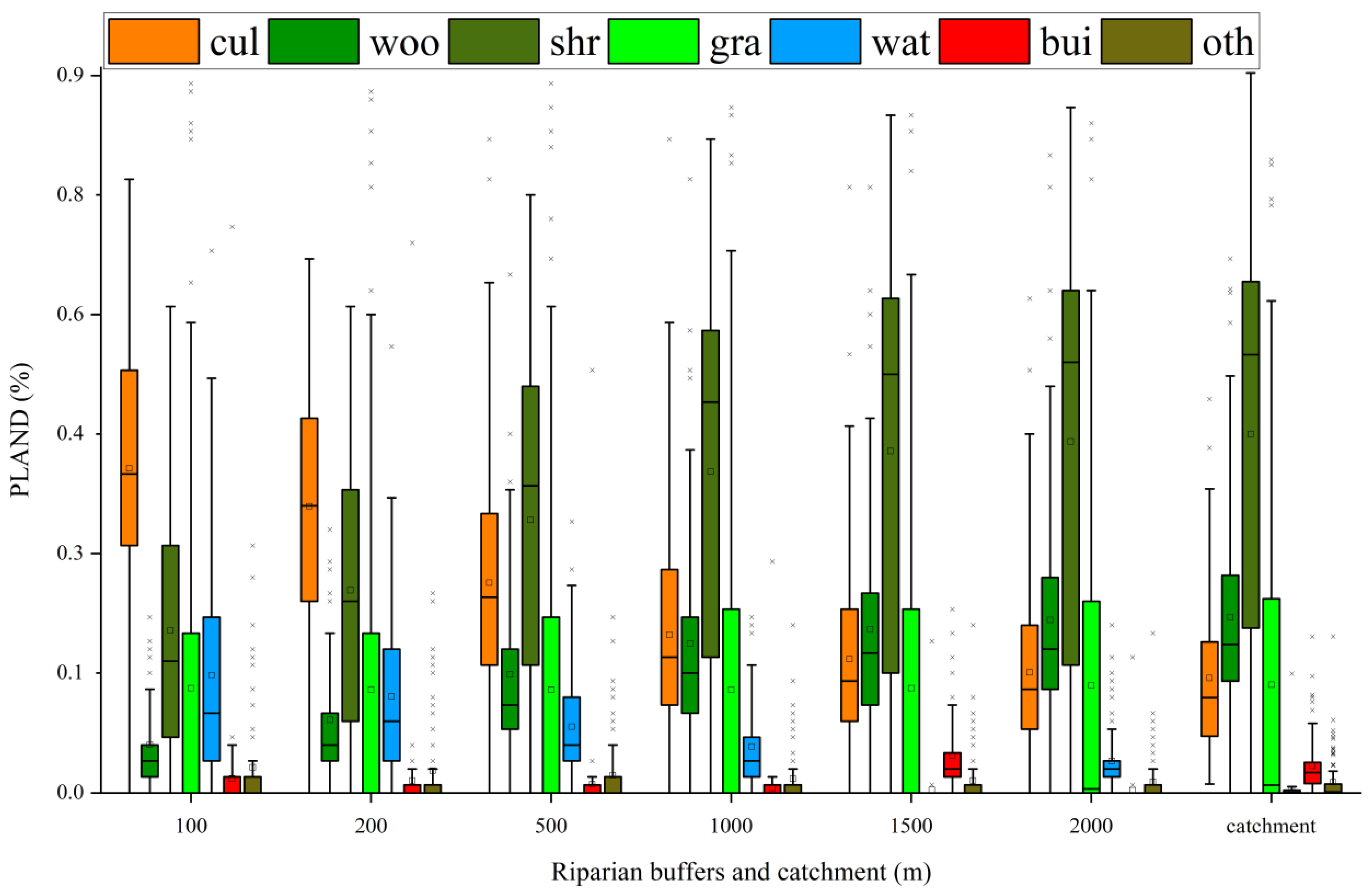
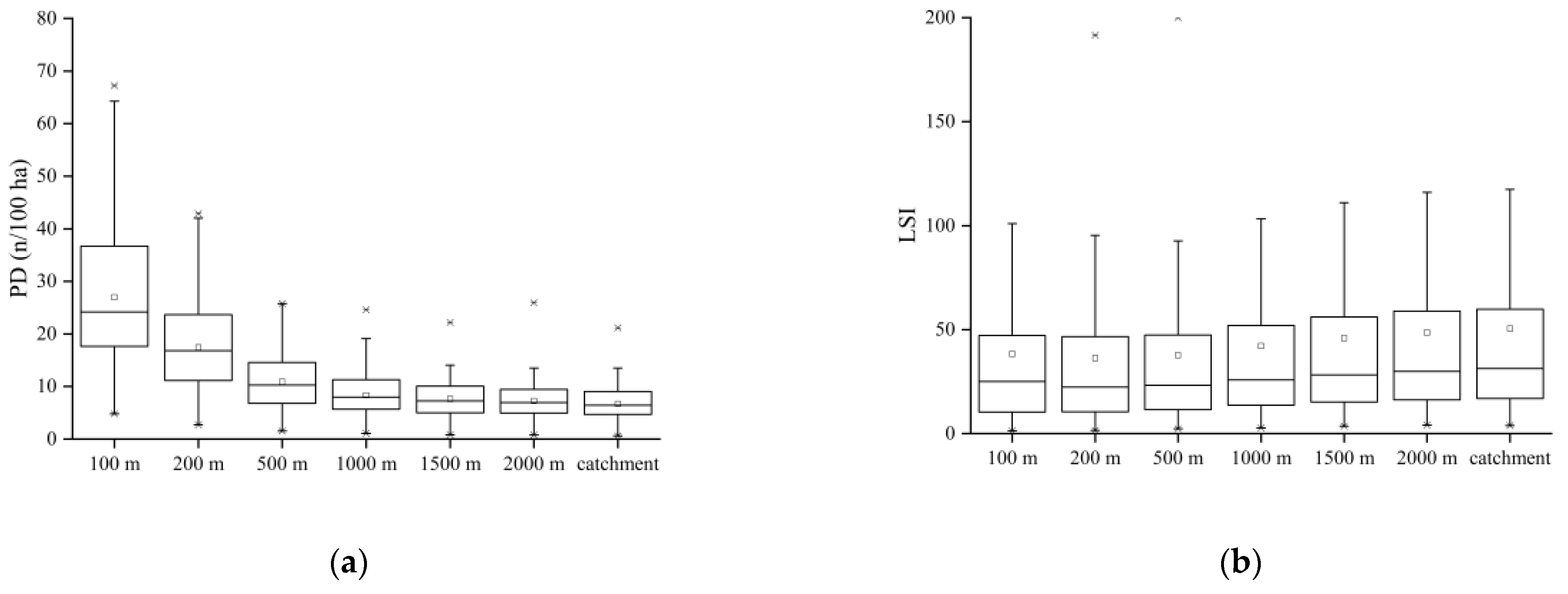
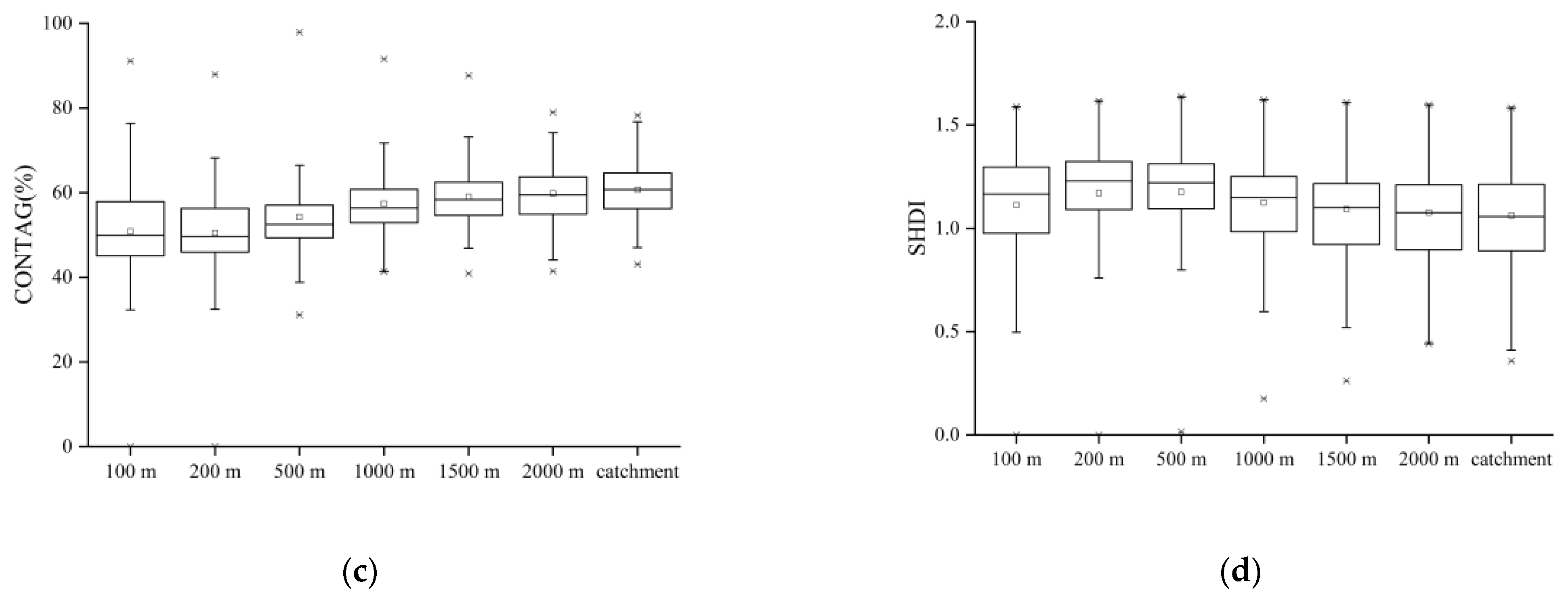
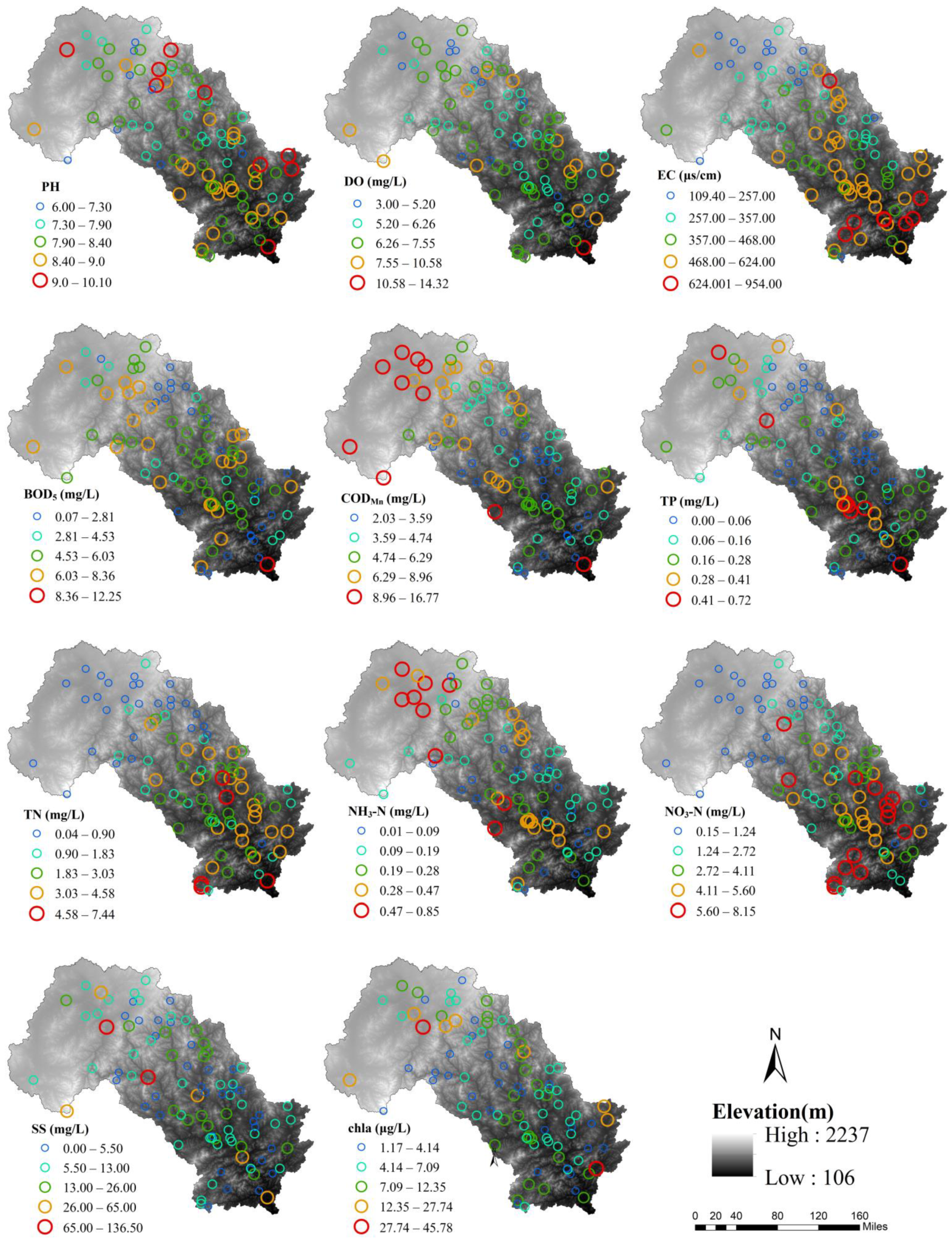

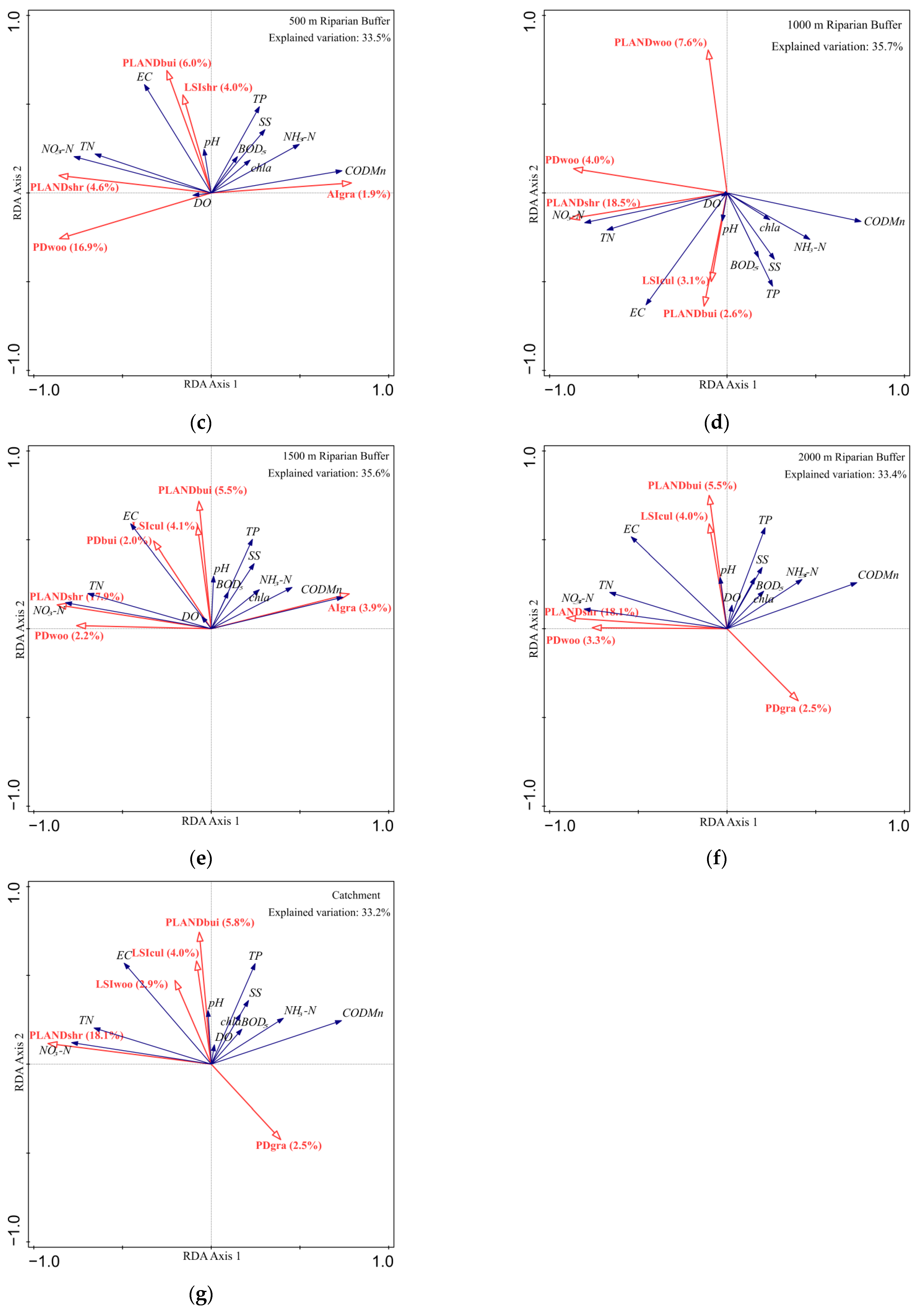
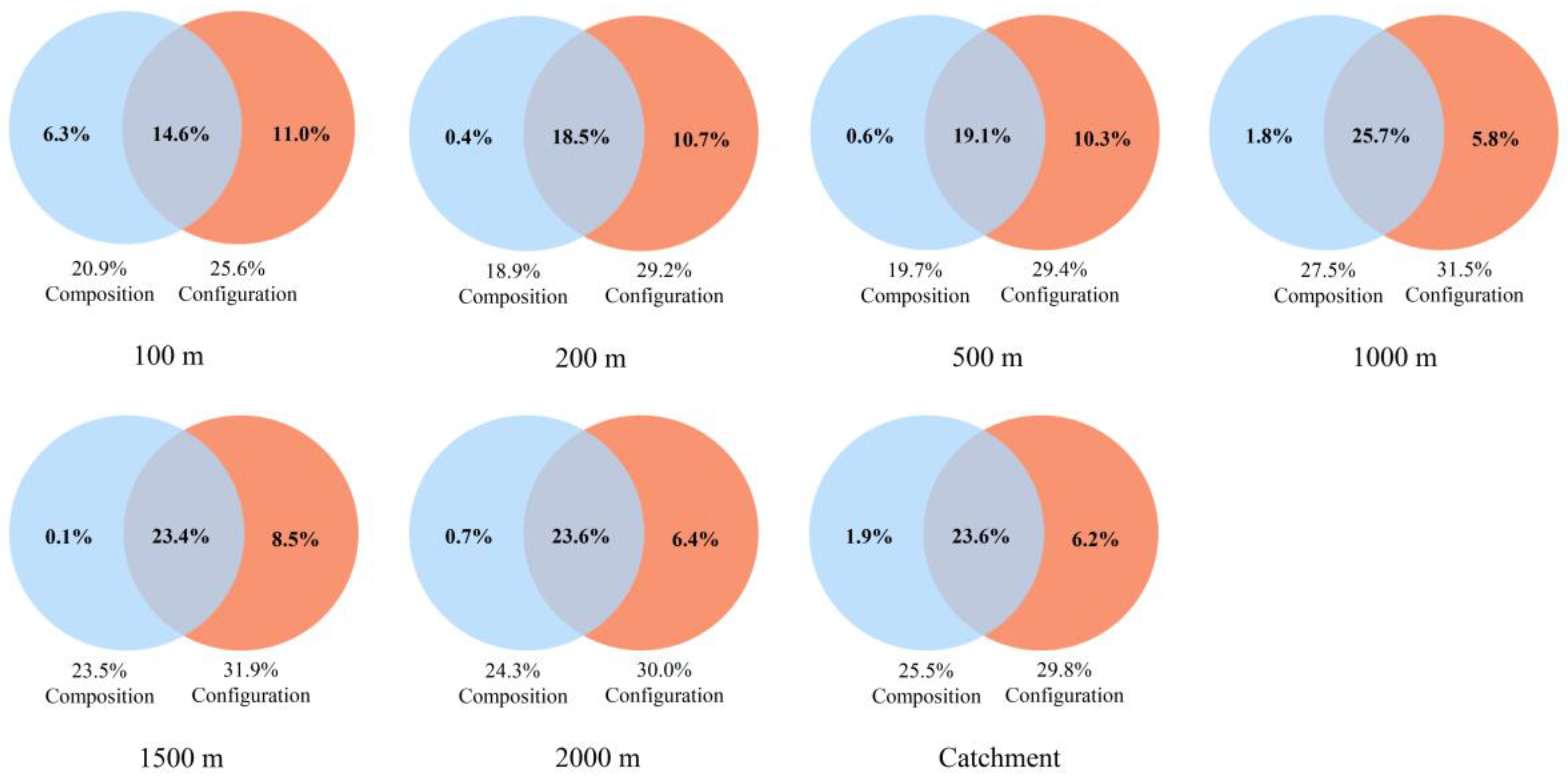
| Land Use Types | Cultivated Land | WoodLand | ShrubLand | GrassLand | Built-Up Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average slope (°) | 9.20 | 19.07 | 19.59 | 8.66 | 9.55 |
| Scales | Explanatory Variables | |
|---|---|---|
| Riparian buffer width | 100 m | PLANDcul, PDcul, LSIcul, PDwoo, PLANDshr, LSIshr, PLANDgra, AIgra, LSIgra, PDgra, PLANDbui |
| 200 m | PLANDcul, LPIcul, PDwoo, AIwoo, AIshr, PDshr, AIgra, LSIgra, LSIbui, PLANDbui, PDbui | |
| 500 m | LSIcul, PDwoo, PLANDshr, LSIshr, LPIgra, LSIgra, AIgra, AIbui, PLANDbui | |
| 1000 m | PLANDcul, LSIcul, LSIwoo, PLANDwoo, PDwoo, PLANDshr, AIshr, LPIgra, AIgra, AIbui, PLANDbui | |
| 1500 m | LSIcul, LSIwoo, PDwoo, PLANDshr, LSIshr, AIgra, LPIgra, PLANDbui, AIbui, PDbui | |
| 2000 m | LSIcul, PLANDwoo, PDwoo, PLANDshr, LSIgra, AIgra, PDgra, PLANDbui | |
| Catchment | LSIcul, PLANDwoo, LSIwoo, PLANDshr, AIgra, PDgra, LSIgra, PDbui, PLANDbui | |
| Scales | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | Axis 4 | Explained Variance (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Riparian buffer width | 100 m | |||||
| EV | 0.205 | 0.076 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 29.8 | |
| CPC (%) | 68.87 | 94.47 | 98.87 | 99.55 | ||
| 200 m | ||||||
| EV | 0.212 | 0.086 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 33.8 | |
| CPC (%) | 67.56 | 95.17 | 98.75 | 99.58 | ||
| 500 m | ||||||
| EV | 0.222 | 0.097 | 0.0009 | 0.005 | 33.5 | |
| CPC (%) | 66.18 | 95.26 | 98.02 | 99.54 | ||
| 1000 m | ||||||
| EV | 0.234 | 0.109 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 35.7 | |
| CPC (%) | 65.45 | 95.89 | 98.46 | 99.56 | ||
| 1500 m | ||||||
| EV | 0.233 | 0.098 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 35.6 | |
| CPC (%) | 65.53 | 92.90 | 96.09 | 99.19 | ||
| 2000 m | ||||||
| EV | 0.220 | 0.090 | 0.019 | 0.003 | 33.4 | |
| CPC (%) | 65.82 | 92.81 | 98.52 | 99.54 | ||
| Catchment | EV | 0.212 | 0.097 | 0.017 | 0.005 | 33.2 |
| CPC (%) | 63.80 | 92.85 | 98.02 | 99.57 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Kang, M. Catchment versus Riparian Buffers: Which Land Use Spatial Scales Have the Greatest Ability to Explain Water Quality Changes in a Typical Temperate Watershed? Water 2021, 13, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131758
Song M, Jiang Y, Liu Q, Tian Y, Liu Y, Xu X, Kang M. Catchment versus Riparian Buffers: Which Land Use Spatial Scales Have the Greatest Ability to Explain Water Quality Changes in a Typical Temperate Watershed? Water. 2021; 13(13):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131758
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Minmin, Yuan Jiang, Qi Liu, Yulu Tian, Yang Liu, Xia Xu, and Muyi Kang. 2021. "Catchment versus Riparian Buffers: Which Land Use Spatial Scales Have the Greatest Ability to Explain Water Quality Changes in a Typical Temperate Watershed?" Water 13, no. 13: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131758
APA StyleSong, M., Jiang, Y., Liu, Q., Tian, Y., Liu, Y., Xu, X., & Kang, M. (2021). Catchment versus Riparian Buffers: Which Land Use Spatial Scales Have the Greatest Ability to Explain Water Quality Changes in a Typical Temperate Watershed? Water, 13(13), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131758