Removal of Cobalt (II) from Waters Contaminated by the Biomass of Eichhornia crassipes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
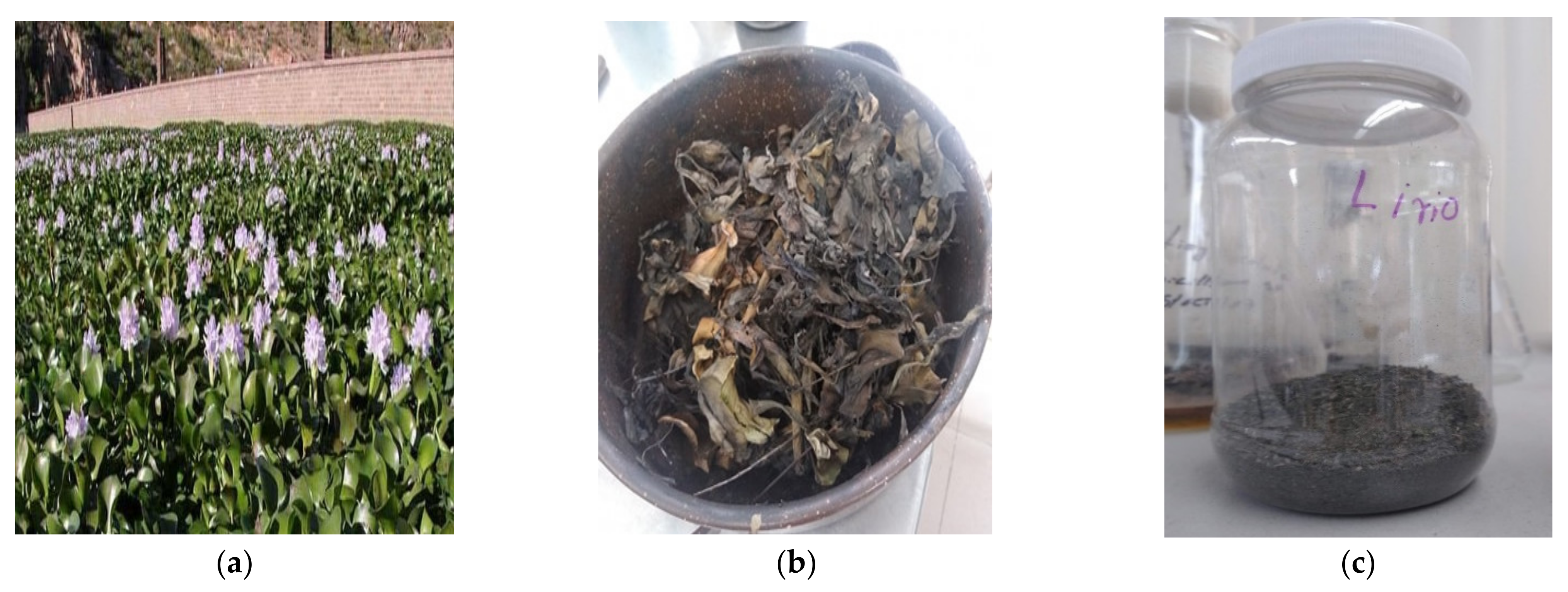
2.1. Bioadsorbent Used
2.2. Cobalt Solutions
2.3. Determination of the Concentration of Divalent Cobalt
3. Results
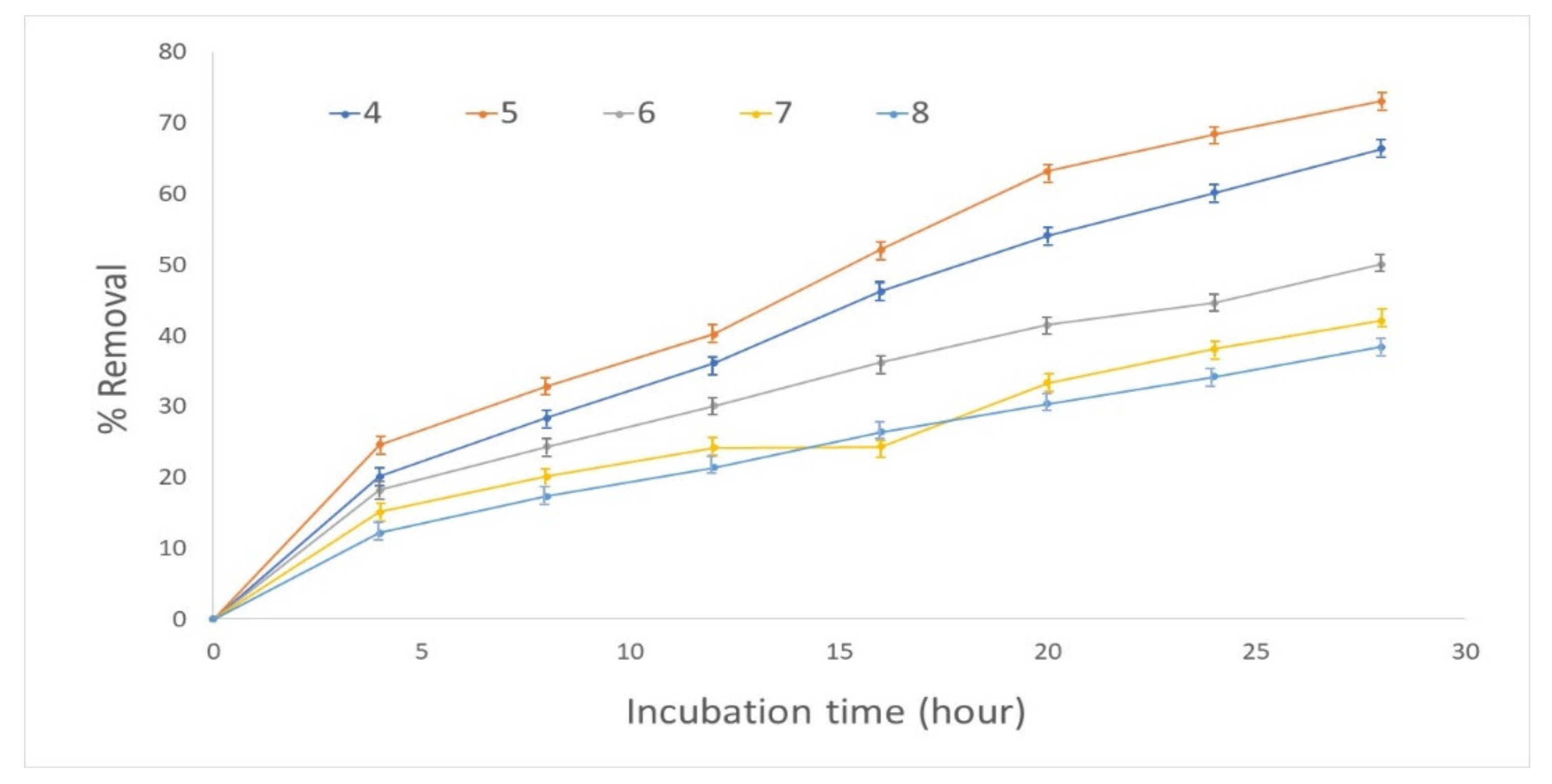
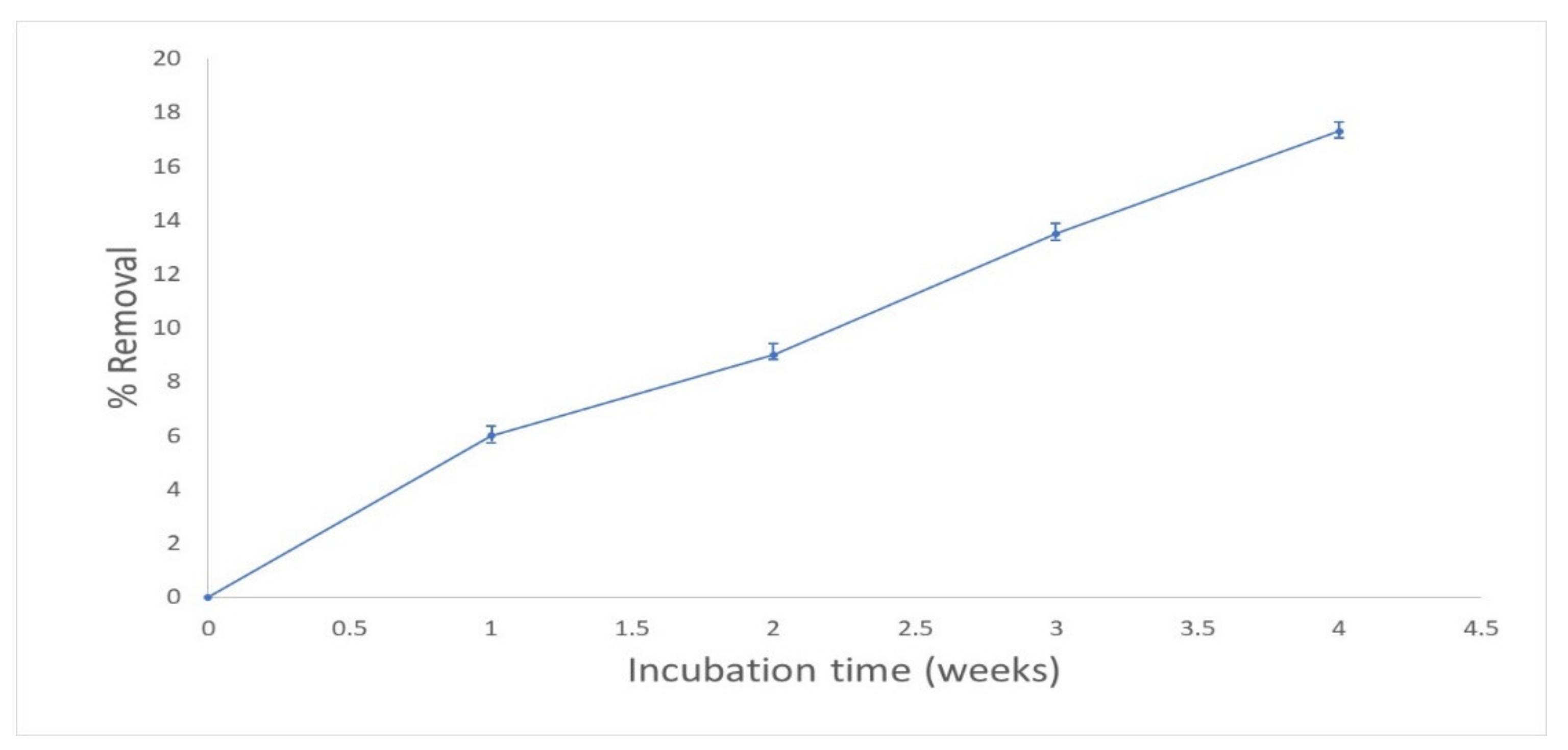
3.1. Effect of Incubation Time and pH
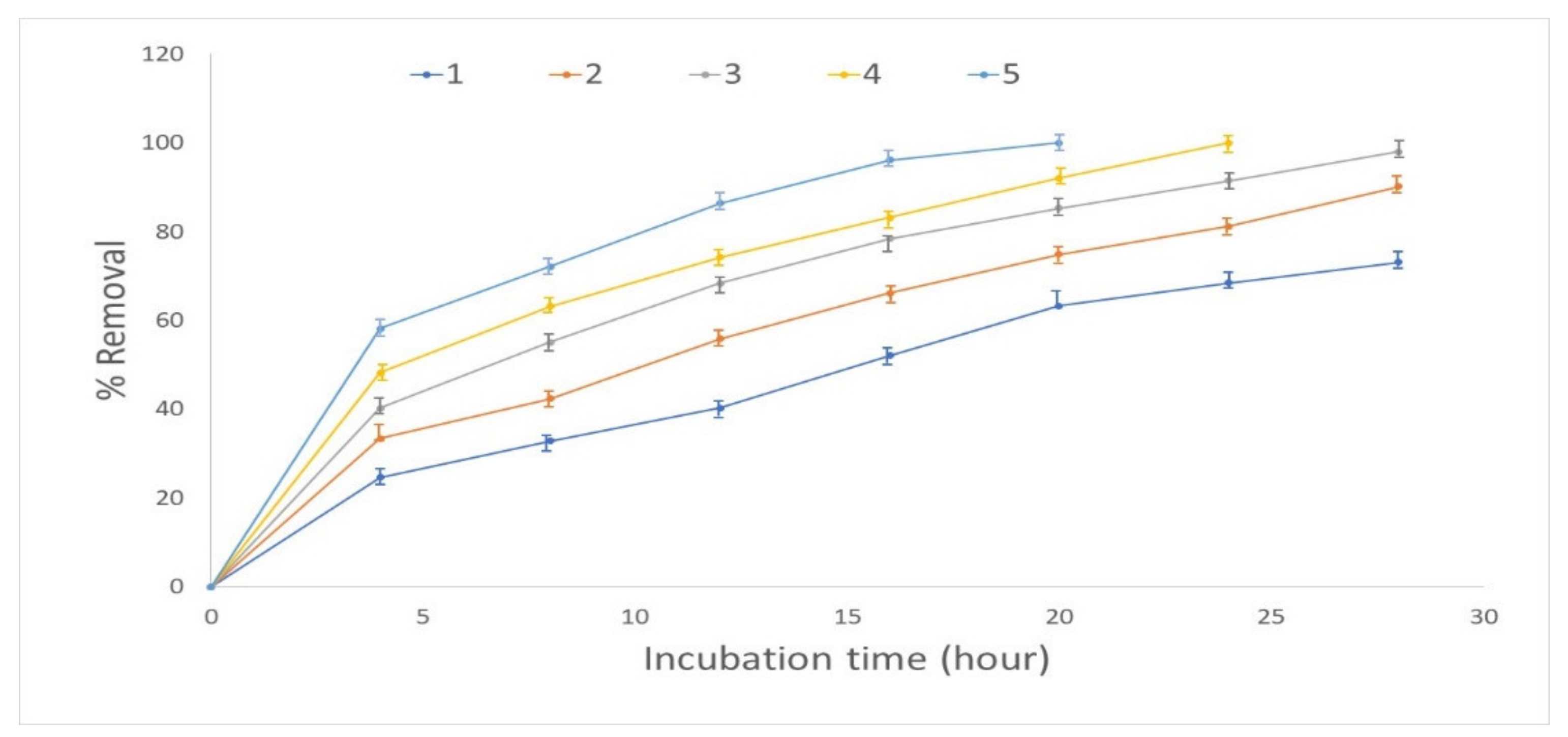
3.2. Effect of Temperature
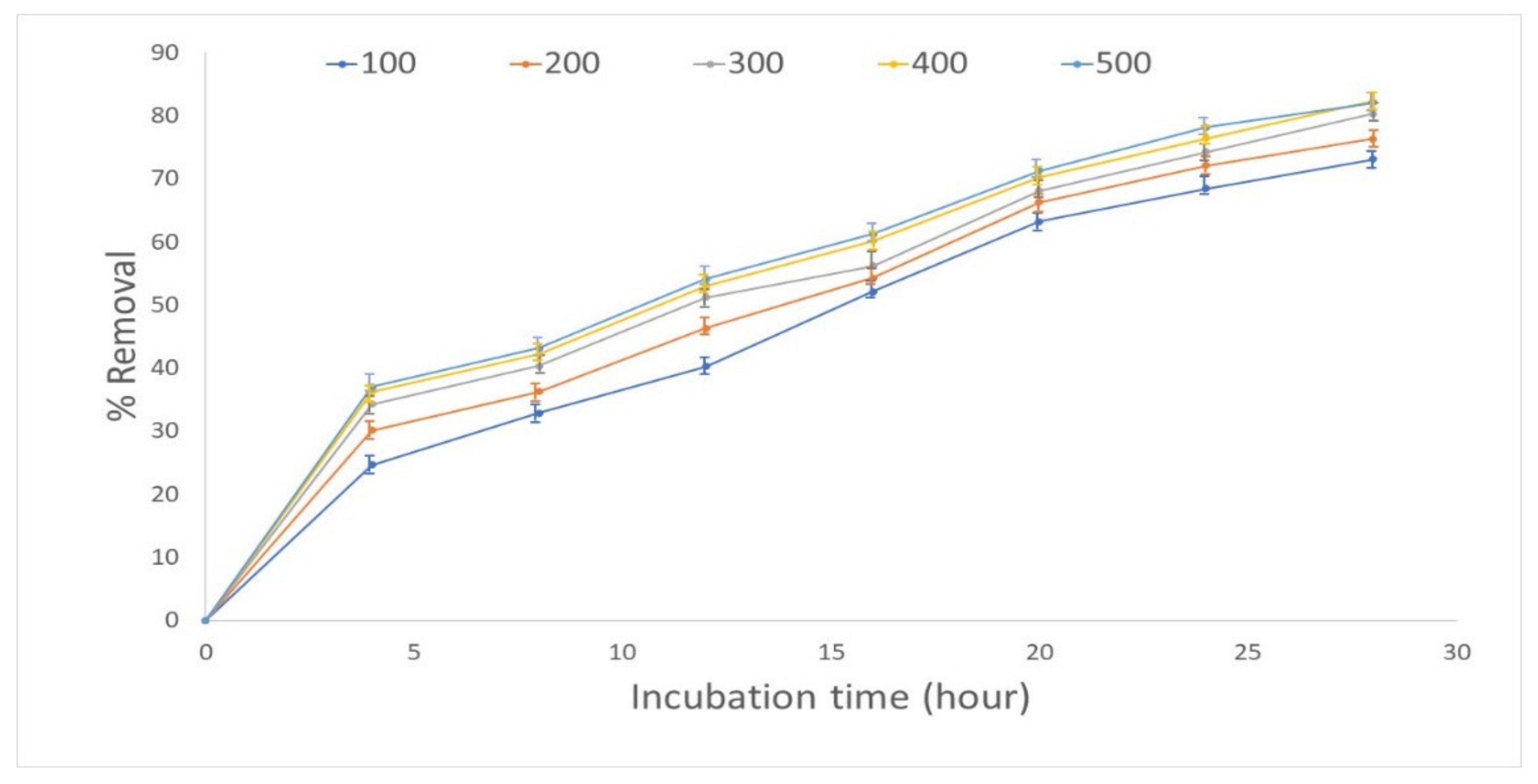
3.3. Effect of the Concentration of Cobalt (II)
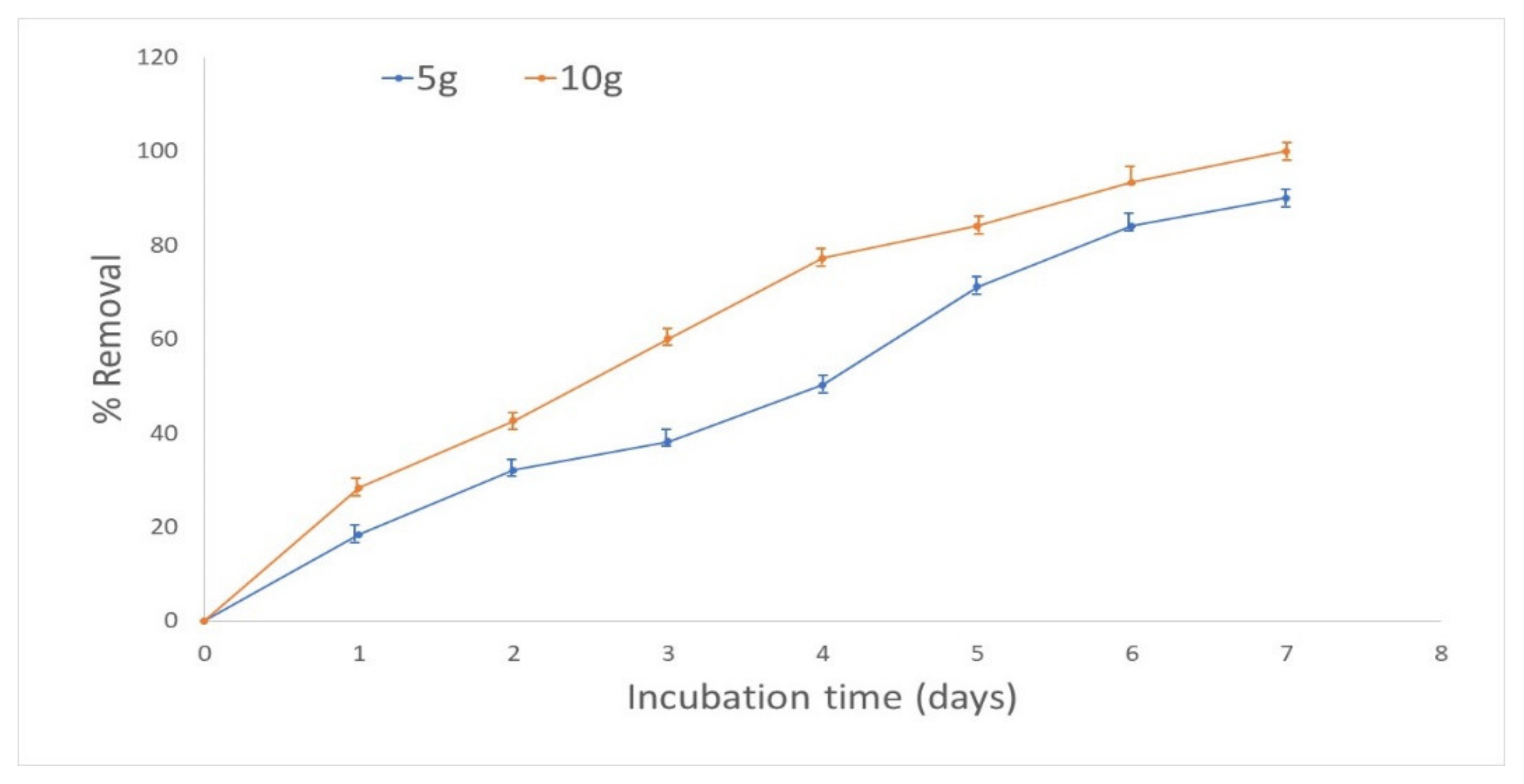
3.4. Effect of Initial Biomass Concentration
3.5. Removal of Co (II) in Industrial Wastes
3.6. Removal of Cobalt (II) In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Díaz de Alba, M.I.; Gestoso Rojas, J.A.; Granado Castro, M.D.; Galindo Riaño, M.D.; Casanueva Marenco, M.J. Potencial uso de residuos agroalimentarios en la eliminación de metales contaminantes para la mejora del medioambiente. In Proceedings of the XLI Jornadas de Viticultura y Enología de la tierra de Barros. I Congreso Agroalimentario de Extremadura, Almendralejo, Spain, 7–10 May 2019; pp. 367–385. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7617885 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Kapahy, M.; Sachdeva, S. Bioremediation options for heavy metals pollution. J. Health Poll. 2019, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, S.; Ramontja, J. Natural bentonite clay and it composites for dye removal: Current state and future potential. Am. J. Chem. Appl. 2016, 3, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Vacar, C.L.; Covaci, E.; Chakraborty, S.; Li, B.; Weindorf, D.C.; Frentiu, T.; Parve, M.; Podar, D. Heavy metals-resistant filamentous fungi as potential mercury bioremediators. J. Fung. 2021, 7, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharangate-Lad, A.; D’Souza, N.C. Current Approaches in Bioremediation of Toxic Contaminants by Application of Microbial Cells; Biosurfactants and Bioemulsifiers of Microbial Origin. In Rhizobiont in Bioremediation of Hazardous Waste; Kumar, V., Prasad, R., Kumar, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, G.; Mehmood, A.; Shahid, M.; Ashraf, R.S.; Altaf, M.; Hussain, M.A.; Raza, M.A. Biochemical Methods for Water Purification. In Methods for Bioremediation of Water and Wastewater Pollution. Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Ahamed, M.I., Lichtfouse, E., Asiri, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Mandari, K.K.; Kim, J.W.; Kang, M.; Fosso-Kankeau, E. Recent Advancement in Visible-Light-Responsive Photocatalysts in Heterogeneous Photocatalytic Water Treatment Technology; Fosso-Kankeu, E., Pandey, S., Ray, S.S., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Salem, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 167–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S. A comprehensive review on recent developments in bentonite-based materials used as adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 1091–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imessaoudene, D.; Bensacia, N.; Chenoufi, F. Removal of Cobalt (II) from aqueous solution by spent green teleaves. J. Radioan. Nucl. Chem. 2020, 324, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Do, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Kang, M. Fast and highly efficient catalytic degradation of dyes using κ-carrageenan stabilized silver nanoparticles nanocatalyst. Carbo. Polym. 2020, 230, 115971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, V.I.; Acevedo, B.J.; Hernández, S.C. Distribution and potential of bioenergy resources from agricultural activities in Mexico. Ren. Sust. Ener. Rev. 2010, 14, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Silva, J.M.; González-Estrada, R.R.; Blancas-Benitez, F.J.; Fonseca-Cantabrana, A. Utilización de subproductos agroindustriales para la bioadsorción de metales pesados. TIP Rev. Esp. Cien. Quím. Biol. 2020, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Chaudhar, K.; Kumar, M.; Yadab, P.; Sachdev, K.; Janud, C.; Gupta, J. Highly efficient, economic, and recyclable glutathione decorated magnetically separable nanocomposite for uranium (VI) adsorption from aqueous solution. Mat. Tod. Chem. 2020, 18, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Doa, J.Y.; Kimb, A.; Hang, M. Fast and highly efficient removal of dye from aqueous solution locust gum based hydrogels as adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macrom. 2020, 143, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Jiménez, X.; Favela-Torres, E.; Volke-Sepulveda, T.L.; Escalante-Espinosa, E.; Diaz-Ramírez, I.J.; Córdova-López, J.A.; Tellez-Jurado, A. Influence of the geographical area and morphological part of the water hyacinth on its chemical composition. Ing. Agríc. Biosist. 2019, 11, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonilla-Barbosa, J.R.; Santamaría, B. Plantas acuáticas exóticas y traslocadas invasoras. In Especies Acuáticas Invasoras en México, 1st ed.; Mendoza, R., Koleff, P., Eds.; Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad: México City, Mexico, 2014; pp. 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenu, S.; Sheela, D. Impact of Co and Cu (heavy metals) on Eichhornia crassipes (Mart) solms, with special reference to bioaccumulation and phytoremediation. Asian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 2996–2998. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas Adrianzen, L.P.; Suyon Diaz, E.P. Eficiencia de Fitoremediación con Jacinto de Agua (Eichhornia crassipes) Para Disminuir Concentraciones de Arsénico en Aguas del Centro Poblado Cruz del Medano-Morrope-2019. Bachelor’s Thesis, Escuela Profesional de Ingeniería Ambiental, Facultad de Ciencias e Ingeniería, Universidad de Lambayeque, Chiclayo, Perú, 2020. Available online: https://repositorio.udl.edu.pe/handle/UDL/314 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Gallardo Pazmiño, A.S. Bioensayos estáticos para determinar la acumulación de plata en lirio Acuático (Eichhornia crassipes). Master’s Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Ambientales, Universidad Internacional SEK, Quito, Ecuador, 2015. Available online: http://repositorio.uisek.edu.ec/handle/123456789/1090 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Sandoval Vilchez, J.D. Eficiencia del Jacinto de Agua Eichhornia crassipes y Lenteja de Agua Lemna minor L. en la Remoción de Cadmio en Aguas Residuales. Bachelor’s Thesis, Ingeniero Ambiental, Facultad de Ingeniería Geográfica, Ambiental y Ecoturismo, Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal, Lima, Perú, 2019. Available online: http://repositorio.unfv.edu.pe/handle/UNFV/3256 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Gómez Gutiérrez, C.; Guarín Álvarez, S.L. Evaluar el Efecto del Proceso de Fitorremediación con Eichhornia crassipes en un agua Cianurada Mediante Cromatografía de Gases. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Ingeniería y Arquitectura, Universidad Católica de Manizales, Manizales, Colombia, 2020. Available online: http://repositorio.ucm.edu.co (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Islas Olvera, J. Fitoextracción de Arsénico, Cadmio y Cobre, Mediante las Especies Eichhornia crassipes, Miriophyllum aquaticum y Wolffia colombiana. Master’s Thesis, División de Ciencias Básicas e Ingeniería, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana, Unidad Azcapotzalco, México City, México, 2020. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11191/6850 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Ali, S.; Abbas, S.; Rizwan, M.; Zaheer, I.E.; Yava, I.; Ünay, A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Kalderis, Application of Floating Aquatic Plants in Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals Polluted Water: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eid, M.E.; Shaltout, K.S.; Moghanm, F.S.; Youssef, M.S.G.; El-Mohsnawy, E.; Haroun, S.A. Bioaccumulation and translocation of nine heavy metals by Eichhornia crassipes in Nile Delta, Egypt: Perspectives for phytoremediation. Int. J. Phytorem. 2019, 21, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.C.; Gómez, S.; Ardila, A.N. Fitorremediación de mercurio presente en aguas residuales provenientes de la industria minera. UG Ciencia 2016, 22, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, N.; Idrees, I.; Danish, P.; Ahmad, S.; Ali, Q.; Malik, A. Potential of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes L.) for phytoremediation of heavy metals from wastewater. Biol. Clin. Sci. Res. J. 2020, 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lara González, L. Fitorremediación para la extracción del colorante “azul de metileno” mediante el uso de Eichhornia crassipes. Bachelor’s Thesis, Facultad de Planeación Urbana y Regional, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México, Toluca de Lerdo, México, 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11799/67471 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Charlot, G. Colorimetric Determination of Elements, 12th ed.; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Ziwa, G.; Crane, R.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Geochemistry, Mineralogy and Microbiology of Cobalt in Mining-Affected Environments. Minerals 2021, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency of Toxic substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Public Health Service; U.S. Departament of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Drinking Water Regulations and Contaminants United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/drinking-water-regulations-and-contaminants (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Dusengemungu, L.; Kasali, G.; Gwanama, C.; Ouma, K.O. Recent advances in biosorption of copper and cobalt by filamentous fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas González, J.F.; Rodríguez Pérez, A.S.; Vargas Morales, J.M.; Martínez Juárez, V.M.; Acosta Rodríguez, I.; Michel Cuello, C.; Gallegos Fonseca, G.; Escalera Chávez, M.E.; Muñoz Morales, A. Biosorption of Cobalt (II) from aqueous solutions by fungal biomasses. Bioinor. Chem. Appl. 2019, 2019, 8757149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Ali, I.; Rasheed, S.; Shah, M.; Munir, T.; Nawaz, S. Adsorptive Removal of Cobalt (II) and Chromium (III) from Aqueous Solution onto Citrus Limon Leaves Powder. Lett. Appl. Nano Biosci. 2021, 10, 2446–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucaci, A.R.; Bulgariu, D.; Ahmad, I.; Bulgariu, L. Equilibrium and Kinetics Studies of Metal Ions Biosorption on Alginate Extracted from Marine Red Algae Biomass (Callithamnion corymbosum sp.). Polymers 2020, 12, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Kilinc, E.; Fatih, S. A novel biosorbent for preconcentrations of Co(II) and Hg(II) in real samples. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouzida, A.; Djedid, M.; Ad, C.; Benalia, M.; Hafez, B.; Elmsellem, H. Biosorption of CO (II) ions from aqueous solutions using selected local Luffa Cylindrica: Adsorption and characterization studies. Mor. J. Chem. 2021, 9, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.H. Biosorption of Cobalt (II) ions using palm kernel mesocarp fiber. Bachelor’s Thesis, Faculty of Engineering and Green Technology, University Tunku Abdul Ramhan, Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 2019. Available online: http://eprints.utar.edu.my/id/eprint/3913 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Vafajoo, L.; Cheraghi, R.; Dabbagh, R.; McKay, G. Removal of cobalt (II) ions from aqueous solutions utilizing the pre-treated 2-Hypnea Valentiae algae: Equilibrium, thermodynamic, and dynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 31, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Fang, L. The effect of environmental factors on the uptake of 60Co by Paecilomyces catenlannulatus. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 299, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymavathi, D.; Prabhakar, G. Optimization, equilibrium, and kinetic studies of adsorptive removal of cobalt(II) from aqueous solutions using Cocos nucifera L. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymavathi, D.; Prabhakar, G. Studies on the removal of cobalt(II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption with Ficus benghalensis leaf powder through response Surface methodology. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaadaoui, Y.; Lebkiri, A.; EL Houssein, R.; Kadiri, L.; Ouass, A. Adsorption of cobalt from aqueous solutions onto Bark of Eucalyptus. Med. J. Chem. 2018, 7, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannela, R.; Verma, S.K. Co2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ Accumulation by Cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilvanathan, S.; Shanthakumar, S. Column Adsorption Studies on Nickel and Cobalt Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Native and Biochar Form of Tectona grandis. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Ener. 2017, 36, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabanal Atalaya, M.M. Estudio de la biosorción de Co (II) por el alga marina Macrocistis piryfera. Bachelor’s Thesis, Profesional Químico, Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Lima, Perú, 2006. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12672/3282 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Swelam, A.A.; Awad, M.B.; Salem, A.S.M.A.; El-Feky, A.S. Biosorption of Cobalt(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution using Rice Straw and its Modification. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2017, 4, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Montes de Oca, R.; Solache-Ríos, M.; Jimenez-Reyes, M.; García-Sánchez, J.J.; Almazán-Sánchez, P.T. Adsorption of cobalt by using inorganic components of sediment samples from water bodies. Int. J. Sed. Res. 2021, 36, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Sindhu, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar Dhaka, R.; Chahar, M.; Singh, S.; Nain, L. Restoration of heavy metals-contaminated soil and water through biosorbents: A review of current understanding and future challenge. Phys. Plant. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Ponce. L. Aplicación de Residuos Vegetales en el Tratamiento de aguas Contaminadas por Metales. Bachelor’s Thesis, Grado en Química, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Cadiz, Cadiz, Spain, 2018. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10498/23560 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Soltan, M.E.; Rashed, M.N. Laboratory study on the survival of water hyacinth under several conditions of heavy metal concentrations. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palihakkara, C.R.; Dassanayake, S.; Jayawardena, C.; Senanayake, I.P. Floating Wetland Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage using Eichhornia crassipes (Water Hyacinth). J. Health Poll. 2018, 8, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.T.; Mahmood, T.; Malik, S.A. Phytoremediation technologies for Ni++ by water Hyacinth. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 8648–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acosta-Rodríguez, I.; Rodríguez-Pérez, A.; Pacheco-Castillo, N.C.; Enríquez-Domínguez, E.; Cárdenas-González, J.F.; Martínez-Juárez, V.-M. Removal of Cobalt (II) from Waters Contaminated by the Biomass of Eichhornia crassipes. Water 2021, 13, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131725
Acosta-Rodríguez I, Rodríguez-Pérez A, Pacheco-Castillo NC, Enríquez-Domínguez E, Cárdenas-González JF, Martínez-Juárez V-M. Removal of Cobalt (II) from Waters Contaminated by the Biomass of Eichhornia crassipes. Water. 2021; 13(13):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131725
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcosta-Rodríguez, Ismael, Adriana Rodríguez-Pérez, Nancy Cecilia Pacheco-Castillo, Erika Enríquez-Domínguez, Juan Fernando Cárdenas-González, and Víctor-Manuel Martínez-Juárez. 2021. "Removal of Cobalt (II) from Waters Contaminated by the Biomass of Eichhornia crassipes" Water 13, no. 13: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131725
APA StyleAcosta-Rodríguez, I., Rodríguez-Pérez, A., Pacheco-Castillo, N. C., Enríquez-Domínguez, E., Cárdenas-González, J. F., & Martínez-Juárez, V.-M. (2021). Removal of Cobalt (II) from Waters Contaminated by the Biomass of Eichhornia crassipes. Water, 13(13), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131725




