Abstract
Subsurface drainage technology may offer a useful option in improving crop productivity by preventing water-logging in poor drainage paddy fields. The present study compared two paddy fields with and without sheet-pipe type subsurface drainage on land and water productivities in Indonesia. Sheet-pipe typed is perforated plastic sheets with a hole diameter of 2 mm and made from high-density polyethylene. It is commonly installed 30–50 cm below the soil surface and placed horizontally by a machine called a mole drainer, and then the sheets will automatically be a capillary pipe. Two fields were prepared, i.e., the sheet-pipe typed field (SP field) and the non-sheet-pipe typed field (NSP field) with three rice varieties (Situ Bagendit, Inpari 6 Jete, and Inpari 43 Agritan). In both fields, weather parameters and water depth were measured by the automatic weather stations, soil moisture sensors and water level sensors. During one season, the SP field drained approximately 45% more water compared to the NSP field. Thus, it caused increasing in soil aeration and producing a more significant grain yield, particularly for Inpari 43 Agritan. The SP field produced a 5.77 ton/ha grain yield, while the NSP field was 5.09 ton/ha. By producing more grain yield, the SP field was more effective in water use as represented by higher water productivity by 20%. The results indicated that the sheet-pipe type system developed better soil aeration that provides better soil conditions for rice.
1. Introduction
As commonly known, rice is the main staple food for almost half of the world’s population. Asia has the largest rice cultivation areas, approximately 90% of 150.7 million ha total rice area in the world [1]. In Indonesia’s case, the total rice cultivation area in 2018 was 7.1 million ha, which was 0.65 million ha lower compared to 2017. Improving rice production for food self-sufficiency makes more effort, whether by expanding rice or intensifying by modifying plant, water, and nutrient management.
One of the known modified rice cultivations in Indonesia is the System of Rice Intensification (SRI) [2,3,4]. SRI has 6 principles in changing the management of the plant, soil, nutrient, and water [5,6]. Particularly in water management, intermittent irrigation is applied instead of continuous flooded irrigation in which the field is allowed to dry during a particular time. This irrigation has improved water use efficiency by up to 54.2% [3] and water productivity by 73% [7]. The key to improving those parameters is to maintain proper water depth while considering plant growth stages.
However, water depths are not easily controlled in all paddy fields in Indonesia. Some paddy fields located in wetland faced frequent flooding and are influenced by periodic sea tides [8]. Waterlogging with poor drainage became the main problem, and it is difficult to control water depth. Thus, rice productivity is lower compared to other fields. Rice productivity in wetland areas was less than 2 ton/ha, which was approximately 3.5 ton/ha lower than the national average [9]. Thus, water use efficiency and productivity in these areas were poor. The poor water use efficiency and productivity in wetland rice are also affected by more water loss through percolation [10]. Water use efficiency is defined as total rice productivity per water irrigation [11], while water productivity is the ratio of net profit from the crop (rice productivity as an example) to total water used to produce the profit [12]. From the definitions, improving those two parameters can be made by increasing rice productivity with less water used.
Addressing waterlogging in the poor drainage paddy fields, subsurface drainage technology is possibly one attractive option. It has tremendous potential to improve yields [13]. There are some types of subsurface drainage systems, depending on land condition, soil texture, regional climate, and the cropping system [14]. For some specific cases, subsurface drainage enabled a proper water management regime that increased rice yield significantly in Iran [15], Malaysia [16], Korea [17], and India [18]. In addition, this technology solved the salinity problem [19], mitigated greenhouse gas emission by depressing methane gas production potential [20,21], and was possibly used for diverse cropping systems when the water supply is limited [22]. Subsurface drainage is possibly applied with modified rice irrigation regimes such as mid-season drainage regime [15] and alternate wetting and drying regime [23] instead of continuous flooding regime. Water depth can be easily controlled to make an appropriate environment and enable soil sustainability for plant production, particularly during rainy seasons. By this technology, water drainage can be managed well, and water irrigation was used more efficiently, thus improving water use efficiency by 15–20% as reported in Egypt [24] and 12–57% in China [24].
However, there is limited information regarding the utilization of subsurface drainage technology in Indonesia. The fields need to be dug with a heavy machine in installing subsurface drainage pipes, and therefore it requires more time and cost. A sheet-pipe system is possibly used as subsurface drainage technology with more efficiency and cost without digging the soil along the drainage pipes channel. Sheet-pipe typed is commonly installed 30–50 cm below the soil surface and placed horizontally by a machine called a mole drainer, then the sheets will automatically be a perforated pipe [25]. In 2018, this technology was introduced in Indonesia and, firstly, installed in the paddy field belong to the Indonesian Center for Rice Research, Sukamandi West Java. The effectiveness of draining water from the field by the sheet-pipe system and its water flow pattern as affected by rainfall events has been investigated [25]. However, there was no study yet on the performance of the sheet-pipe system with regards to rice yield and water productivity. Thus, the main objective of the present study was to evaluate the performances of the sheet-pipe type as subsurface drainage on land and water productivities, mainly in Indonesia.
2. Materials and Methods
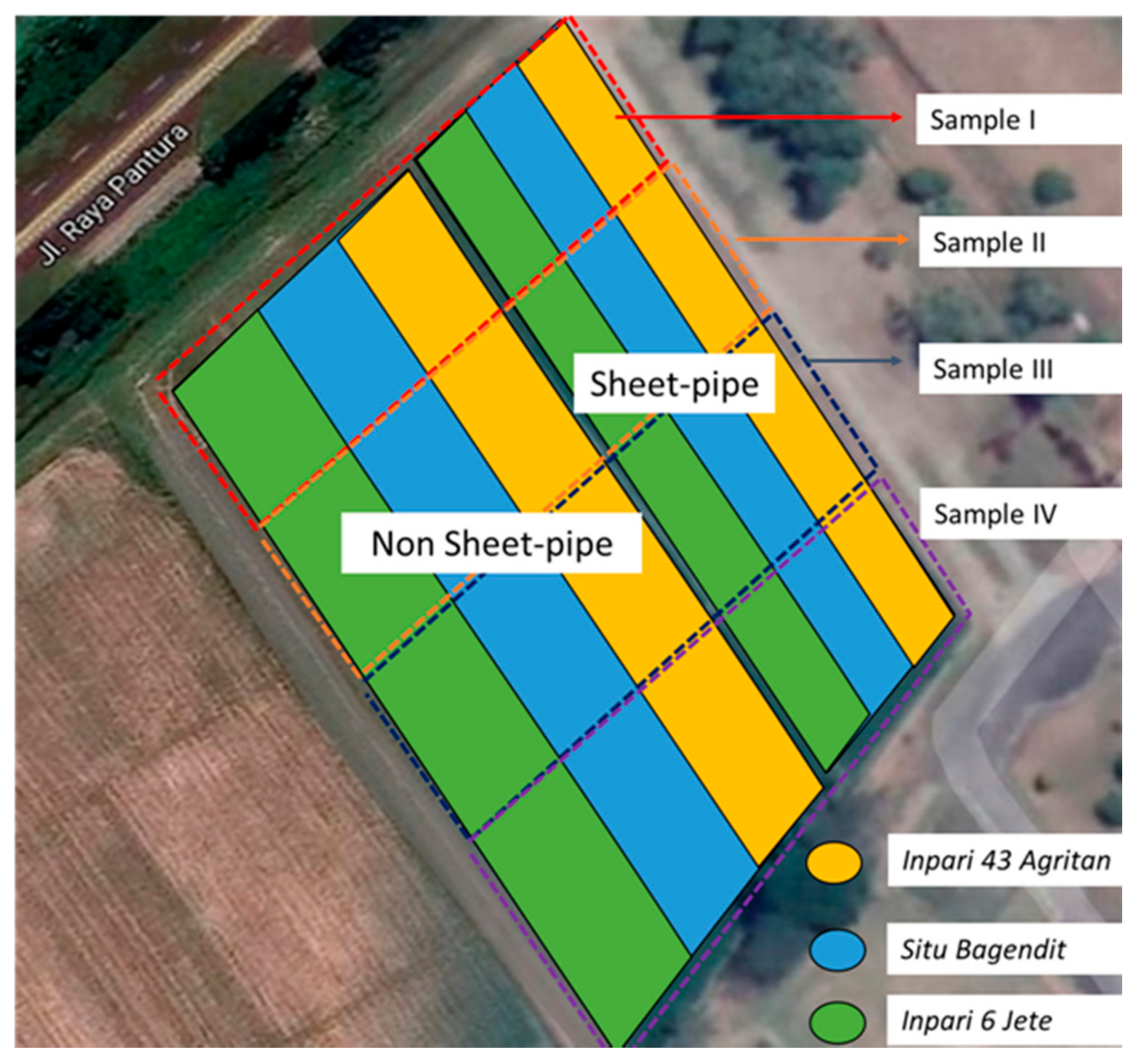
The evaluation was conducted based on one rice season field experiment. Here, we used 1 ha paddy field in the Indonesia Center for Rice Research (BB-Padi), Subang, West Java. Planting time was on 5 May 2018, and harvesting was on 6 August 2018. There were two paddy fields separated by soil bund, i.e., the sheet-pipe typed field (SP field) and non-sheet-pipe type field (NSP field). The SP field is 3600 m2, while the NSP field has an area of 5400 m2. Three rice varieties, namely Situ Bagendit, Inpari 6 Jete, and Inpari 43 Agritan, were planted in The SP field (each variety of approximately 1200 m2) and the NSP field (approximately, Situ Bagendit: 1800 m2, Inpari 6 Jete: 2000 m2, Inpari 43 Agritan: 1600 m2), without any further division into smaller plots. The characteristic of the three varieties are shown in Table 1 and the field layout is as in Figure 1. In both fields, water irrigation was supplied at a similar rate as standard practice by the local farmers, and water depth was not controllable. As a common practice in conventional farming, the water level was kept at shallow water depth (0–5 cm above soil surface) in the NSP field as control treatment. Although supplied at a similar irrigation rate in the SP field, water was drained naturally by the sheet-pipe type.

Table 1.
Agronomic traits of the three varieties planted in the sheet-pipe (SP) and non-sheet-piped (NSP) fields.
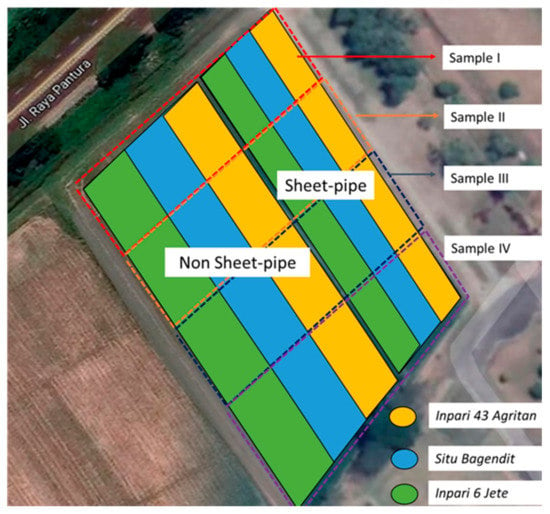
Figure 1.
Layout of the three planted varieties in non sheet-pipe (NSP) and sheet-pipe (SP) fields.
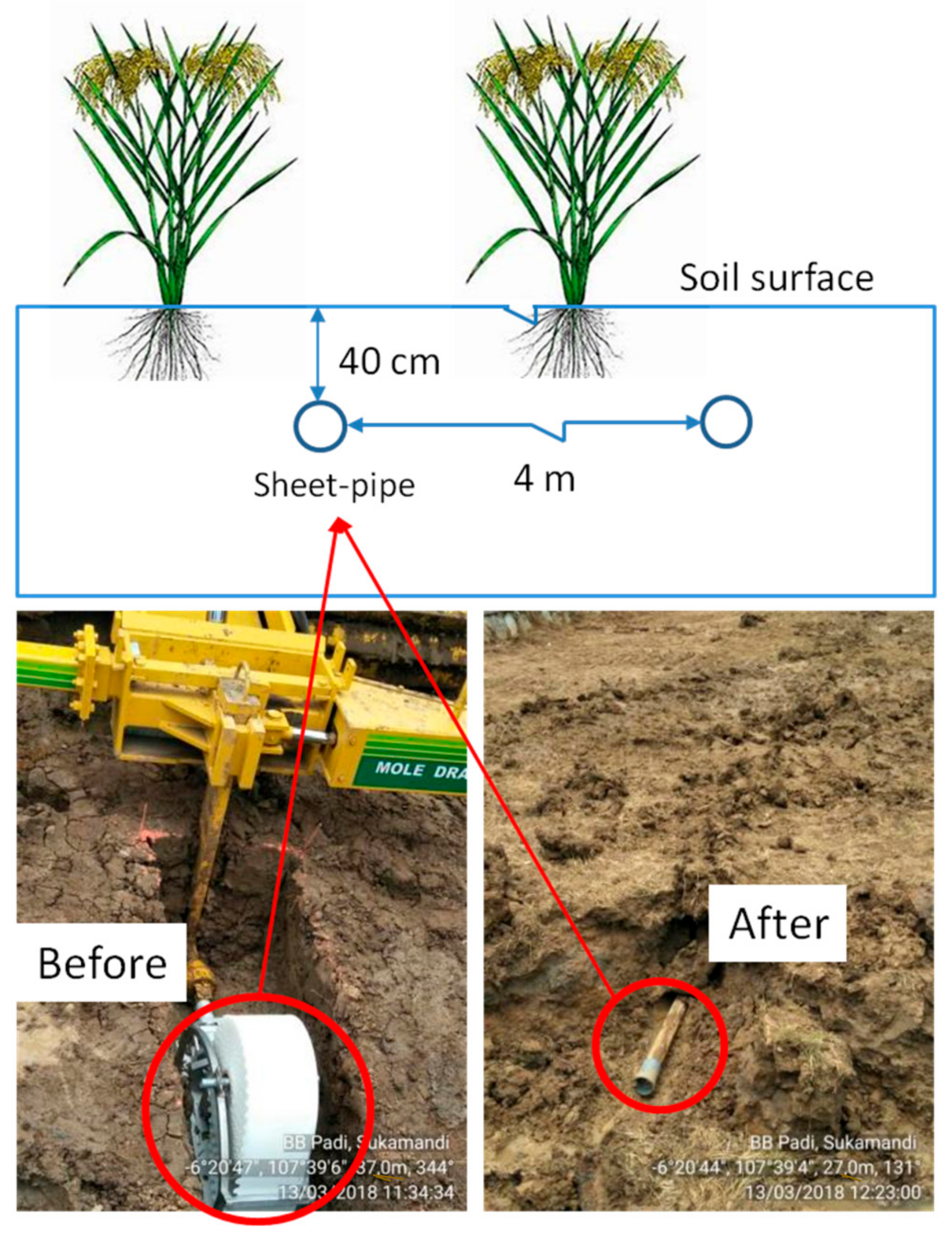
For installation of the sheet-pipe in the SP field, a machine called mole drainer (Komatsu SP30) was used to pull it out at a depth of 40 cm with 100 m length. The sheet-pipe will be a pipe with 5 cm in diameter and 1 mm in thickness during installation. The interval between the sheet-pipes was 4 m spacing (Figure 2). The specification of the sheet-pipe type could be referred from a previous study [26].
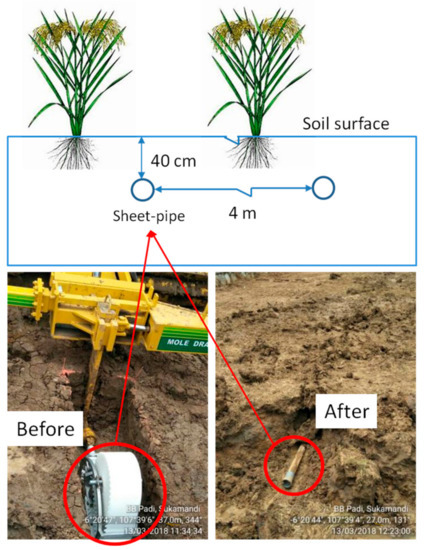
Figure 2.
Sheet-pipe installation in the field.
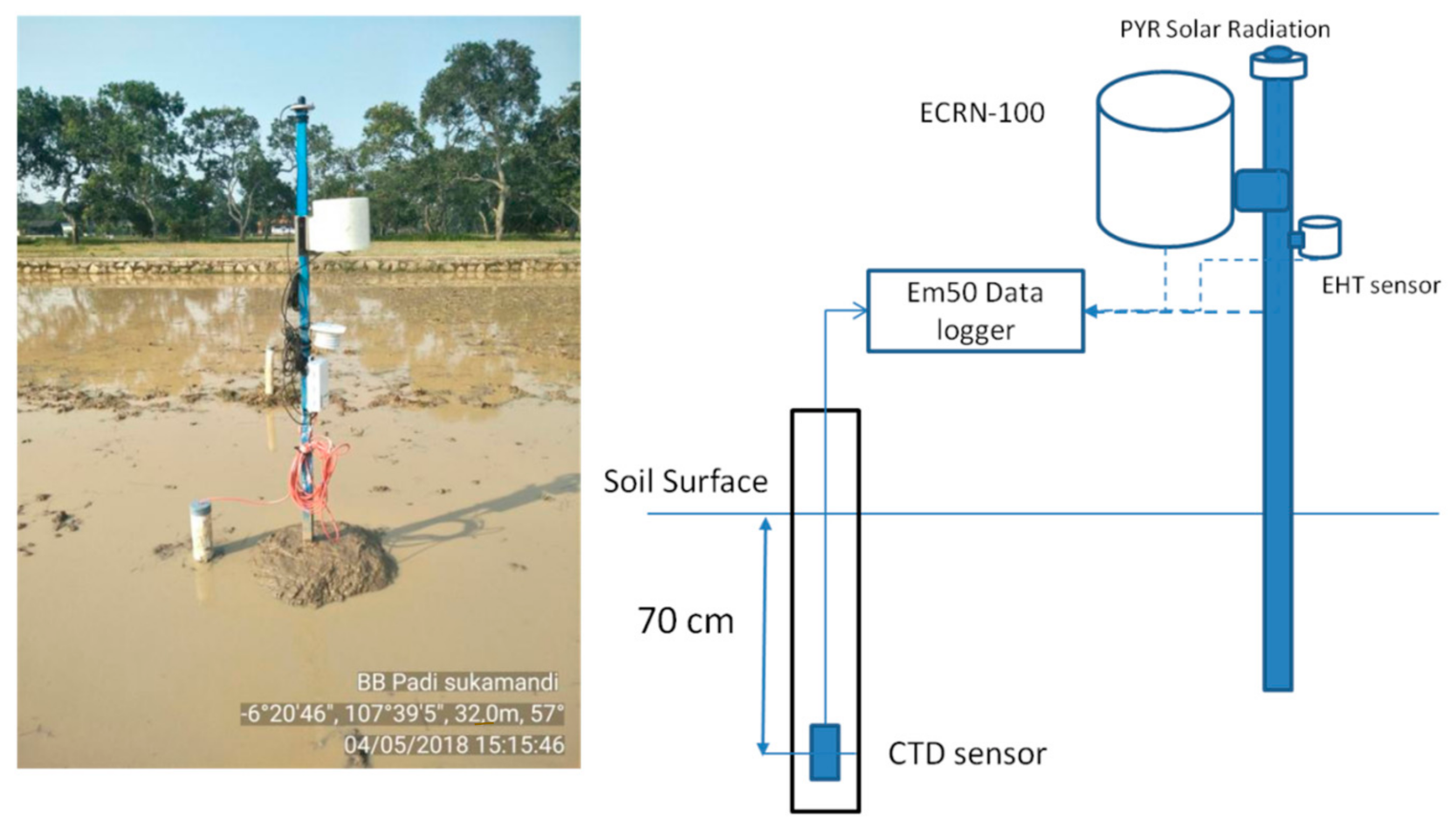
During the field experiments, water depth and weather parameters were measured using the specific sensors. Water depth in the soil was measured by a Conductivity, Temperature, Depth (CTD) sensor from Meter Group, Inc, Pullman, WA, USA. The sensor was placed in the perforated PVC pipe at 70 m depth in both fields. Meanwhile, weather parameters were measured by some weather sensors consisted of ECRN-100 for measuring rainfall, PYR Solar Radiation for measuring solar radiation, and EHT RH/Temp for measuring air temperature and relative humidity (Figure 3). All data were stored in a data logger, Em50 (Meter Group), with an interval of 30 min.
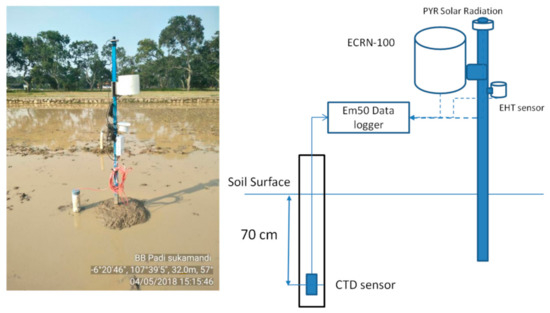
Figure 3.
Field measurements of weather and water level parameters.
Weather data were used to determine reference evapotranspiration according to the following Hargreaves model [26,27]:
where ET is reference evapotranspiration in mm, T is the daily average air temperature in °C, and Rs is daily solar radiation in MJ/m2/d.
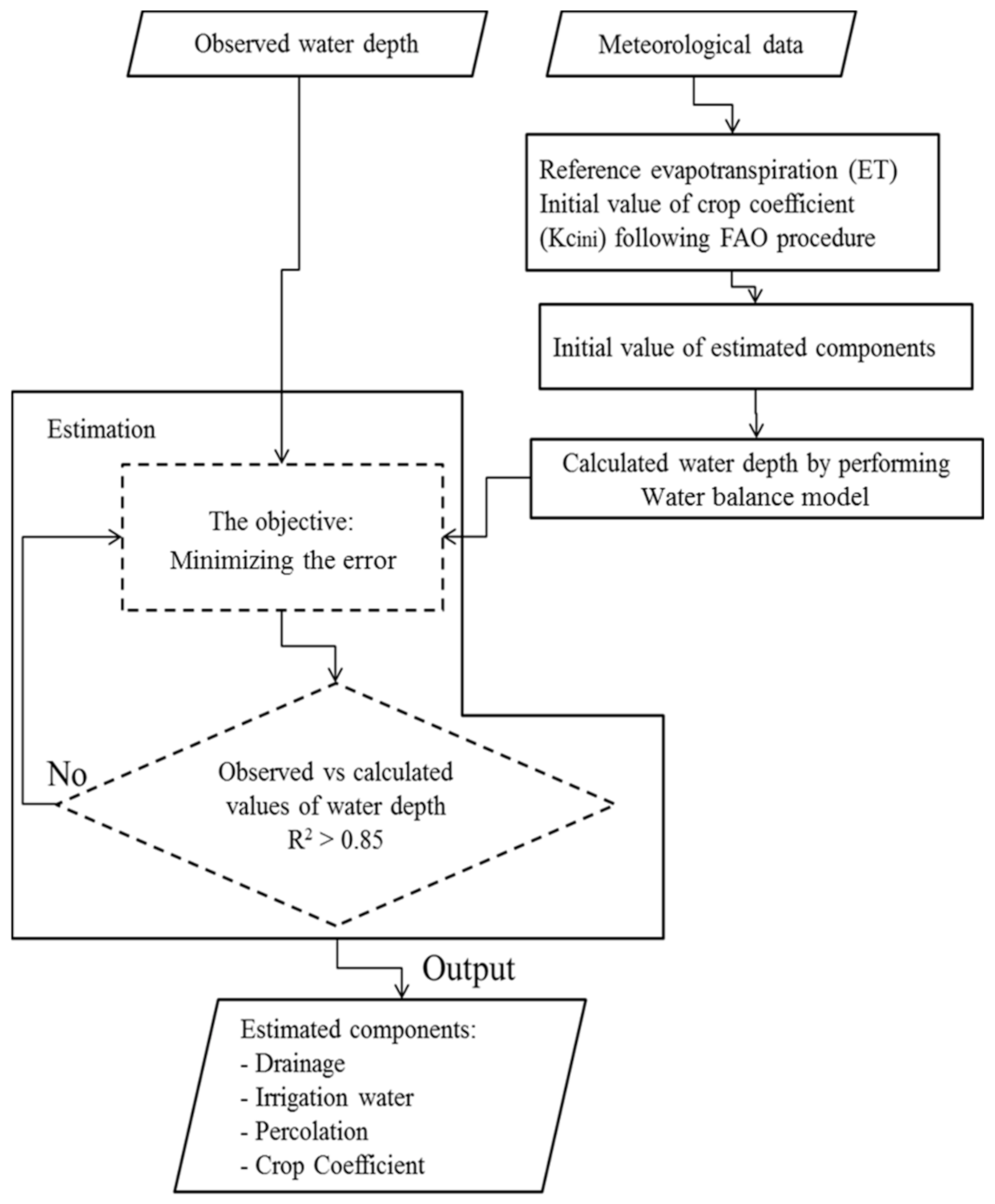
In this study, total irrigation, drainage, percolation were estimated by Excel Solver in MS Excel-based on changes in water depth and weather parameters. The method was applied before, and it was given an effective and accurate estimation of water balance components and crop coefficient in each growth stage [2,28,29], the adjusted procedure for this study is presented in Figure 4.
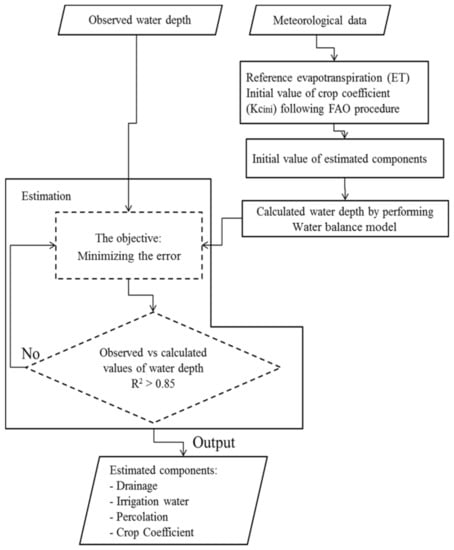
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram for the estimation of non-measurable water balance components.
The estimation method was performed according to the water balance analysis by the following equation:
where ∆WL is the change of water depth (in mm), I is irrigation (in mm), R is rainfall (in mm), DR is drainage (in mm), ETc in crop evapotranspiration (in mm), and DP is percolation (in mm).
ETc was calculated based on the FAO standard by the following equation [30]:
where Kc is the crop coefficient (unitless).
The Excel Solver works based on the linear program in which objective function and constraint should be first formulated. Since the Excel Solver method only estimates 200 data within one process, the estimation process was performed four times according to the crop growth stages that have been defined by previous studies [31,32]. Those four growth stages were initial (21 days), crop development (24 days), mid-season (31 days), and late-season stages (18 days). In each process, the objective function (target cell) was to minimize the following equation:
where ∆WLo is the change of observed water depth (in mm), and ∆WLm is the change of estimated observed water depth (in mm).
Total irrigation was then used to determine water use efficiency index and water productivity. The water use efficiency index was calculated based on the following equation [11]:
where WUE is water use efficiency index (in g grain/kg water).
Water productivity was calculated in two terms, i.e., total yield per total water input (irrigation + rainfall) and total yield per total crop evapotranspiration [33]:
where WPI+R is water productivity with respect to water input in g grain/kg water, WPET is water productivity with respect to total evapotranspiration in g grain/kg water, Y is total yield in ton/ha.
Statistical analysis was performed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) single factor to compare yield, water use efficiency, and productivity between the SP and NSP fields. The difference between the SP and NSP fields treatments means were then compared using the least significant difference (LSD) at the 0.05 probability level (α = 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Weathers Parameters and Their Conditions
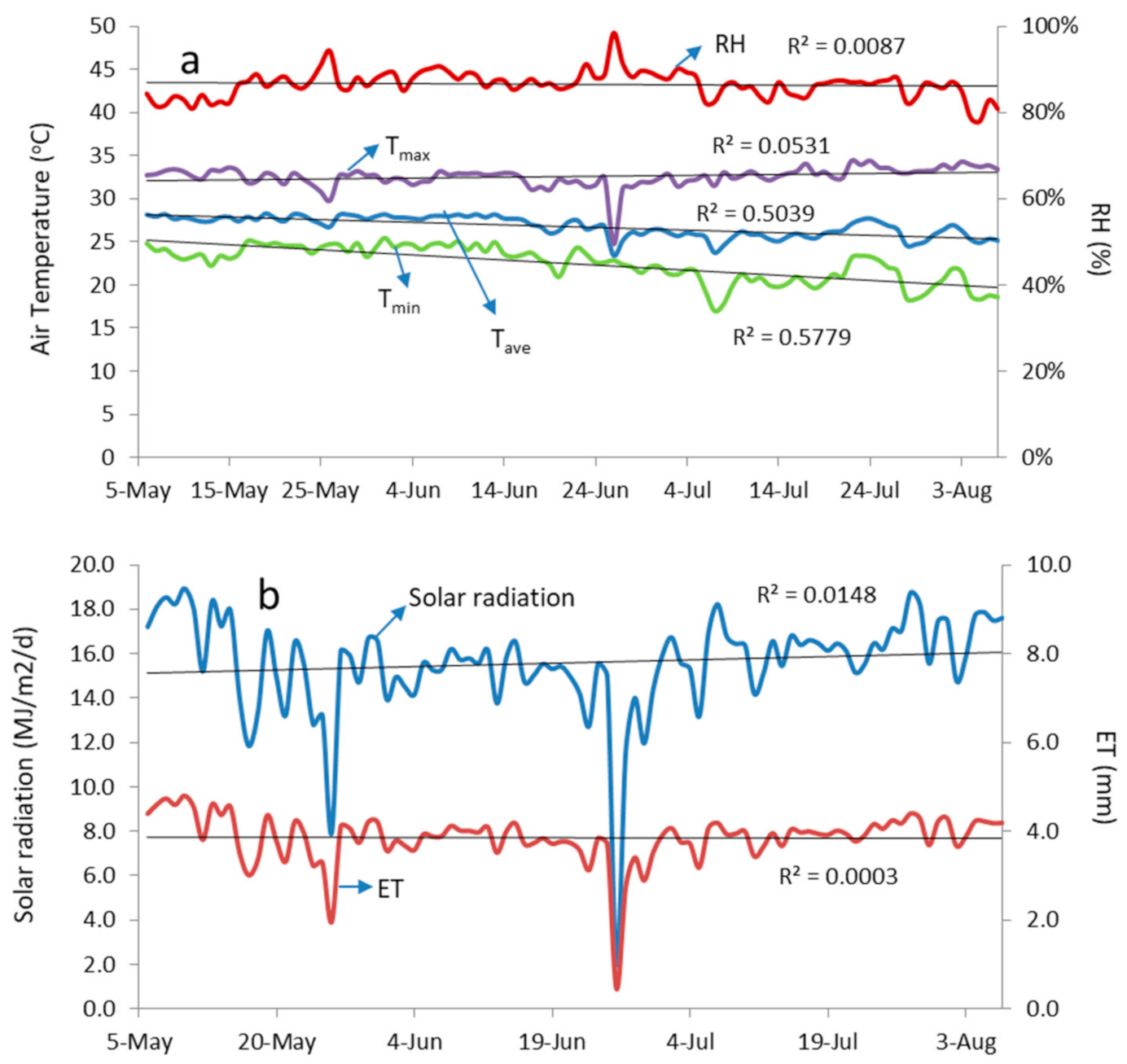
Figure 5 shows daily changes in weather parameters during the planting period. All data fluctuated, and there were two rare events when solar radiation was very low (<10 MJ/m2/d). It occurred on 25 May and 25 June 2018, on which solar radiations were 7.9 and 2.0 MJ/m2/d. These occurrences caused maximum air temperature (Tmax), and average air temperature (Tave) dropped as well as reference evapotranspiration (ET). On the other hand, relative humidity (RH) increased significantly.
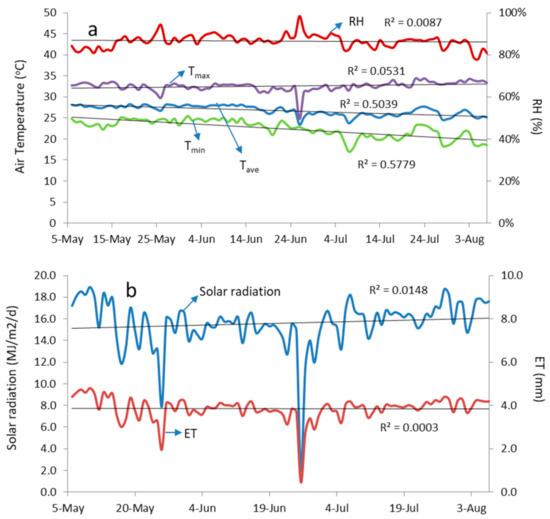
Figure 5.
Weather condition during experiment: (a) air temperature and RH, (b) solar radiation and reference evapotranspiration (ET).
The trend of weather data was insignificantly increased (R2 < 0.1) except for the average and minimum air temperatures. Their trends were decreased (R2 > 0.5). During the planting period, average solar radiation, relative humidity, air temperature, and reference evapotranspiration were 15.6 MJ/m2/d, 86%, 26.78 °C, and 3.85 mm, respectively. Meanwhile, peak solar radiation was 18.9 MJ/m2/d on 9 May 2018 that also caused maximum reference evapotranspiration of 4.8 mm.
3.2. Water Balance in Both Fields
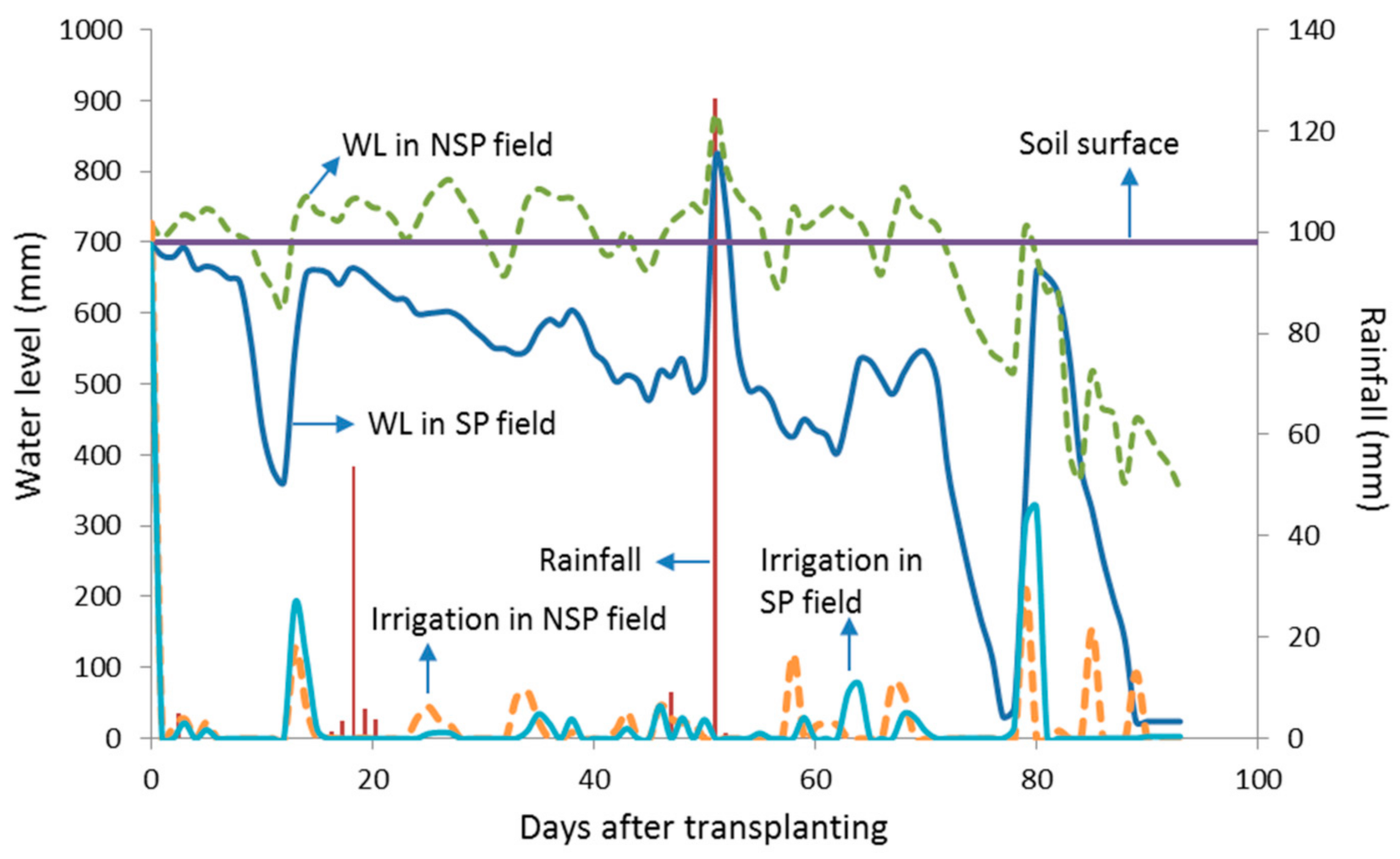
Sheet-pipe system drained water properly as indicated by lower water depth in the SP field than that in the NSP field during the planting period, as shown in Figure 6. A previous study reported that the sheet-pipe system drained water two times faster than the NSP field [25]. The water depth trends in both fields were identical that pointed out irrigation water was supplied at a similar rate and in total (Table 2). In the NSP field, flooded water (0–8 cm water depth above the soil surface) appeared at the end of the initial stage to the end mid-season growth stage. Then, water was drained until harvesting time. On the other hand, water depth in the SP field was lower than the soil surface during the planting period except on 25 June 2018 (51 days after transplanting). On this day, the extreme event occurred by the heavy rains with 126 mm of rainfall. This event raised water depth significantly in both the fields. In the NSP field, water depth reached its maximum level of 880 mm (18 cm water depth above the soil surface), while it also reached its peak of 817 mm in the SP field.
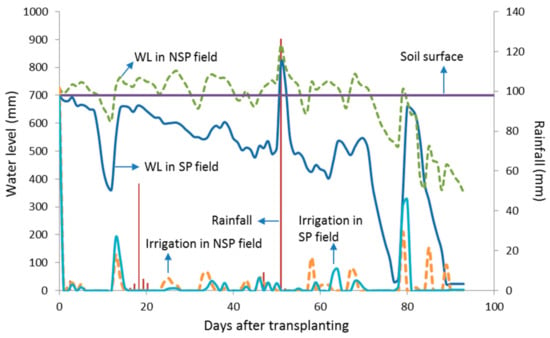
Figure 6.
Actual water depth during the planting period in the sheet-pipe (SP) field and non sheet-pipe (NSP) field.

Table 2.
Water allocation in the SP field and NSP field.
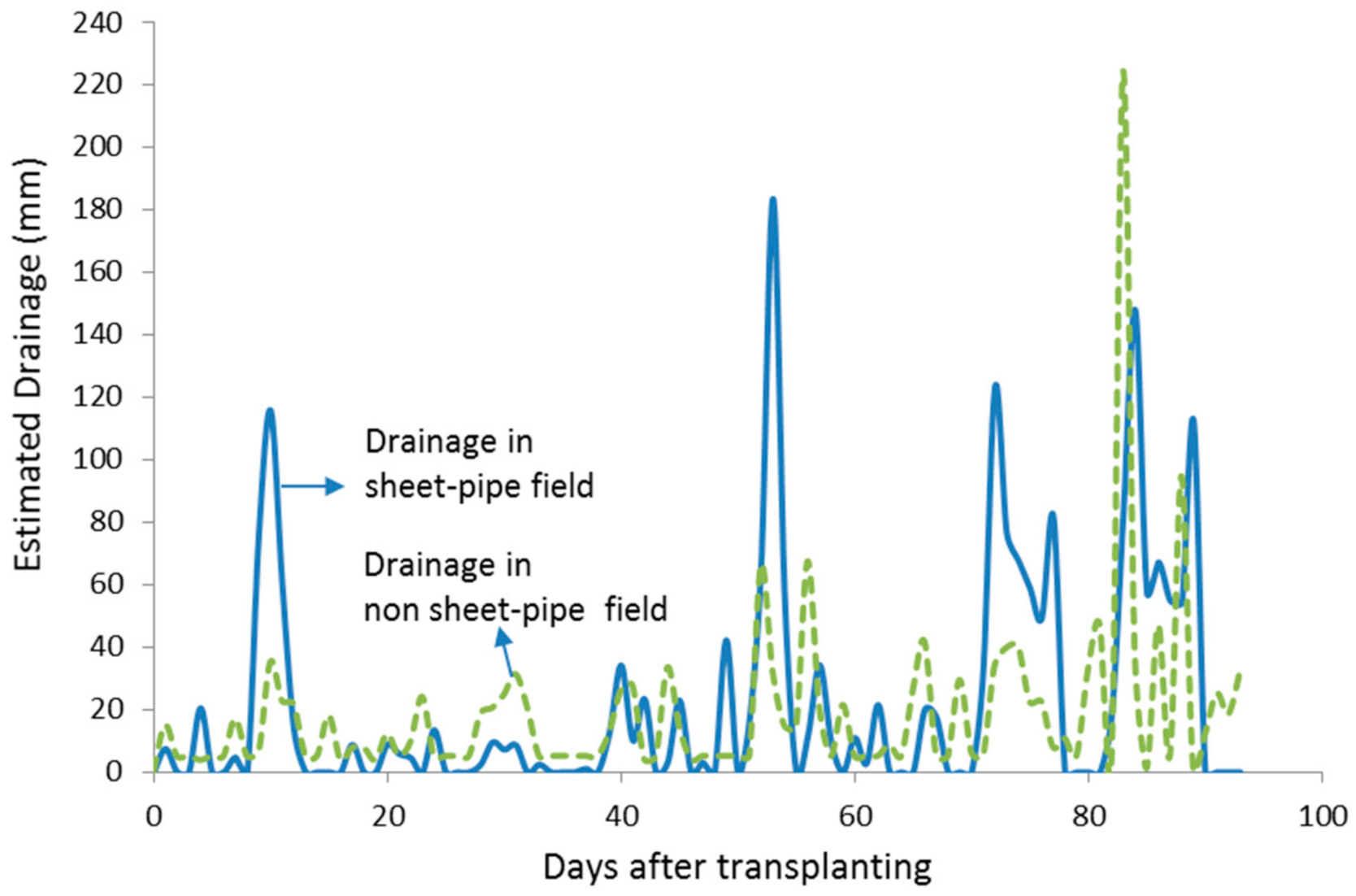
Since irrigation water was supplied at a similar rate in both fields, the SP field drained more water naturally, as shown in Figure 7 and Table 2. More water was initially drained in the SP field 10 days after transplanting when more 115 mm water was drained, then dropped water depth from 561 mm to 442 mm. The peak of drained water occurred two days after the extreme event in which more than 180 mm water was drained, so actual water depth was below the soil surface, increasing soil aeration and oxygen content in the SP field. Meanwhile, in the NSP field, water was drained at moderate levels during the planting period except on 83 and 88 days after transplanting in the late-season stage. The drainage of the NSP field was done by opening the field embankment and flowing water to drainage channel. In this period, water draining was usually done approximately two weeks before harvesting as a standard practice in rice cultivation [34].
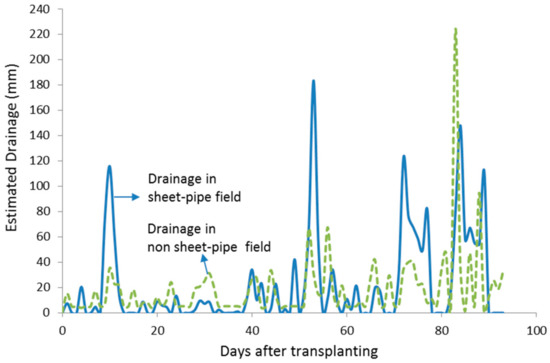
Figure 7.
Drainage during the planting period in the sheet-pipe (SP) field and non sheet-pipe (NSP) field.
Table 2 shows water allocation in both the SP and NSP fields. With similar inflow (rainfall + irrigation), it is apparent that the SP field drained 45% more water. The total water drainage in the SP field and NSP field were 2061 mm and 1422 mm, respectively. However, when water depth was lower than the soil surface (aerobic soil condition) in the SP field, percolation can be significantly reduced. The total percolation was 171 mm in the SP field, while in the NSP field was 377 mm. It means that the total percolation was 55% lower. Percolation is usually affected by physical soil properties and increases with increasing water depth in flooded conditions [35,36,37]. Increasing water depths, such as in the NSP field, will increase hydrostatic pressure that can promote downward water movement by percolation.
Meanwhile, crop evapotranspiration in the SP field was slightly lower than that in the NSP field. It was supposed by more water evaporated under a flooded condition in the NSP field. The average value of Kc in SP was lower than NSP and might arise concern to whether there was worse crop canopy development of SP rice compared to NSP. However, the yield data of SP field was slightly higher than NSP field (Table 3), indicating that this was not the case. The Kc is not solely a function of crop canopy but also land management including water, and the Kc values presented here are specific to our study.

Table 3.
Productivity, water productivity, and water use efficiency index of three rice varieties in the SP field and the NSP field.
3.3. Water Productivity and Water Use Efficiency
The yield of the Inpari 43 Agritan variety in the SP field (5.77 ton/ha) was significantly higher (13.36%) than in the NSP field (5.09 t/ha) (Table 3). The other two rice varieties, namely Inpari 6 Jete and Situ Bagendit, had 3.88% and 0.64% increase of grain yield in the SP field as compared to NSP, but not significantly different. The average grain yield across three varieties was 5.11 ton/ha and 4.80 ton/ha for the SP and NSP fields, respectively.
Following by producing more grain yield, water productivities with respect to total evapotranspiration and total water input in the SP field were higher than those in the NSP field. A significant difference was also found for the rice variety of Inpari 43 Agritan. Water productivities with respect to total evapotranspiration and total water input in the SP field were 20% and 14% higher than those in the NSP field. The same case was also found in the water efficiency index, where the SP field was more efficient in water use than the NSP field as indicated by a 15% higher index for Inpari 43 Agritan.
4. Discussion
Under natural conditions, the water depth in the SP field was lower during the planting period. Lower water depth (below soil surface) in the SP field was known as the aerobic condition in which more oxygen is available in the soil. The sheet-pipe system allows a quicker water depth drawdown then probably improves soil aeration in the soil. This practical was recognized as an alternative irrigation regime conditioned plant growth under non-flooded and non-saturated soil [33]. This regime was suitable for an area with limited water resources such as upland area and water-saving technology with modified rice farming systems such as the system of rice intensification (SRI) [38].
The SP field produced a higher grain yield than that the NSP field. The results show that rice can possibly be produced more under aerobic soil conditions (Table 3). Previous studies supported this finding that rice can be produced under water-saving irrigation, such as intermittent irrigation with SRI as modified rice cultivation [3,39] and alternate wetting drying irrigation [40]. The reason why aerobic soil conditions in the SP field possibly can produce more grain yield is that the SP field conditions promote more root activities, enable a deeper root system, and better nutrient uptake [5]. The aerobic soil condition by the sheet-pipe system improves the transport of nutrients such as nitrate, so fertilizer could be absorbed more effectively by the rice plants. Water management is the main factor in the nitrogen use efficiency in which alternate wetting drying irrigation improved it [40]. In addition, this condition enhanced shoot activities when optimal water and oxygen available under such soil conditions [41].
Aerobic rice cultivation is a promising rice cultivation for water saving and conservation due to climate change and possible maintain high-productivity. As reported previous study [42] aerobic rice increased water productivity up to 148% than flooded rice in two year experiments and two field locations under different climate. In addition, aerobic rice maintained high yield and produced 6.2% more rice yield than that flooded rice. The main reason the aerobic condition maintained high yield is due to more vigorous nitrogen uptake particularly in the reproductive growth stage, thus rice plants could produce more biomass and spikelet [43]. However, adopting aerobic rice cultivation must be accompanied by proper fertilization management, so nitrogen demand can be well fulfilled. In addition, it is necessary to control irrigation in maintaining optimum soil moisture to anticipate water deficit, thus plant transpiration can be well managed. Previous study found the optimum soil moisture for aerobic rice was ranged from a water potential of −15 kPa to −25 kPa at a depth of 20 cm, which is the threshold for plants to maintain the transpiration process [44,45].
With the comparable irrigation, lower crop evapotranspiration, and more grain yield, the water productivities under the SP field were higher than those in the NSP field. Under natural conditions, ponding water in the NSP field evaporated more water. The lower ETc value in the SP field was not caused by water shortages to the crop that caused unfavorable crop growth. The low ETc value was due to the water level that was below the ground surface. From several research results, especially on the system of rice intensification (SRI), crops grew optimally in water table conditions approximately 5 cm below the soil surface, avoiding continuous inundation. Therefore, we suspect that in the SP field, the lower water level allows the plants to grow better with stronger roots and led to a good production, as shown by the results presented in Table 3.
It is indicated that the absence of ponded water in the SP field under aerobic rice reduced the evapotranspiration rate and lower leaf area index [46], and therefore saving more irrigation water and increased water productivity. Furthermore, the sheet-pipe system improved water use efficiency (Table 3). The result was similar to the previous study in Egypt that showed subsurface drainage could improve 15–20% water use efficiency without any yield reduction [47]. Based on the current findings, the sheet-pipe type subsurface drainage created more aerated soil that more suitable for producing more rice since oxygen is optimally available.
According to our empirical results, it was not certain whether high ETc was positively correlated with high production, although it had been known that higher ETc will result in a higher rice yield in a conventional. The lower ETc value on the SP Field is due to the lower Kc value. The average value of Kc in the SP Field was 0.97, while in the NSP field was 1.03. The lower Kc value is due to the absence of standing water in the aerobic conditions of the SP Field, thereby reducing the ETc value. These results are in line with previous studies which show that the average of Kc value in the aerobic conditions was 19% lower than in the flooded conditions [48]. This is an opportunity to further examine the relationship between ETc and production for aerobic rice and alternative systems such as SRI in further study. Controlling water depth is the main key in conditioning soil for suitable plant growth. A framework and conceptual design of an automatic water depth control system with the sheet-pipe system has been introduced and needs to be tested in the fields.
5. Conclusions
The sheet-pipe typed subsurface drainage system effectively drained water from the soil. The sheet-pipe field (SP field) was more rapidly drained than the non-sheet-pipe field (NSP field). This condition promoted aerobic soil conditions for better soil and water environments in producing more grain yields. Although having lower ETc, the SP field produced more grain yield up to 13.36% and higher water productivities, i.e., 20% and 14% higher with respect to evapotranspiration and water input, respectively. Based on the current finding, there is an opportunity to further examine the relationship between ETc and production for aerobic rice. It is recommended to manage irrigation water and develop a water depth control system for improving more efficient water use, so that water input (irrigation and rainfall) can be used more effectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, C.A., S.K.S., and B.I.S.; data collection, C.A., Z.M.H., N.N., N.A.; funding, S.K.S., K.T., Y.I.; writing—review and editing, C.A., S.K.S., B.I.S., H.M., and W.B.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Kyouwa Kensetsu Kogyo Co., Ltd., Japan and the Ministry of Research and Technology/National Research and Innovation Agency under research project with the title “Development of Eco-friendly Paddy Field Water Management System with Sheetpipe Sub-surface Drainage Technology” according to contract number of 1/AMD/E1.KP.PTNBH/2020.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to due the owenership is shared between all parties that contributed to the research.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Indonesia Center for Rice Research for the facility and staff supports in their on-site research, Kyouwa Kensetsu Kogyo Co., Ltd., for providing sheetpipe technology and technical support during the research as well as to the Directorate General of Higher Education, Ministry of Education and Culture, Republic of Indonesia for all their support on this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Antonopoulos, V.Z. Modelling of Water and Nitrogen Balances in the Ponded Water and Soil Profile of Rice Fields in Northern Greece. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, C.; Toriyama, K.; Nugroho, B.D.A.; Mizoguchi, M. Crop Coefficient and Water Productivity in Conventional and System of Rice Intensification (SRI) Irrigation Regimes of Terrace Rice Fields in Indonesia. J. Teknol. (Sci. Eng.) 2015, 75, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, L.; Wu, M.; Li, Y. Nutrient Uptake and Water Use Efficiency as Affected by Modified Rice Cultivation Methods with Reduced Irrigation. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Animesh, S.; Zhu, D.; Uphoff, N. Comparisons of Yield, Water Use Efficiency, and Soil Microbial Biomass as Affected by the System of Rice Intensification. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uphoff, N.; Kassam, A.; Harwood, R. SRI as a Methodology for Raising Crop and Water Productivity: Productive Adaptations in Rice Agronomy and Irrigation Water Management. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoop, W.A. The Scientific Case for System of Rice Intensification and Its Relevance for Sustainable Crop Intensification. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2011, 9, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Mohanty, R.K.; Patil, D.U.; Kumar, A. Impact of Water Management on Yield and Water Productivity with System of Rice Intensification (SRI) and Conventional Transplanting System in Rice. Paddy Water Environ. 2014, 12, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riza, I.A.; Alkasuma, A. Argicultural Land Tidal Swamp and Development Strategy Era of Regional Autonomy. J. Sumberd. Lahan 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nursyamsi, D.; Noor, M.; Maftu’ah, E. Peatland Management for Sustainable Agriculture. In Tropical Peatland Ecosystems; Osaki, M., Tsuji, N., Eds.; Springer: Japan, Tokyo, 2016; pp. 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.D.; Das, B.S.; Bhadoria, P.B.S. A Simple Bund Plugging Technique for Improving Water Productivity in Wetland Rice. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hoek, W.; Sakthivadivel, R.; Renshaw, M.; Silver, J.; Birley, M.; Konradsen, F. Alternate Wet/Dry Irrigation in Rice Cultivation: A Practical Way to Save Water and Control Malaria and Japanese Encephalitis? Research Report 47; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Molden, D.; Oweis, T.; Steduto, P.; Bindraban, P.; Hanjra, M.A.; Kijne, J. Improving Agricultural Water Productivity: Between Optimism and Caution. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E.; Evans, R.G. Subsurface Drainage—What’s Next? Irrig. Drain. 2015, 64, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bhakar, S.R.; Singh, P.K. Evaluation of Hydraulics Characteristics and Management Strategies of Subsurface Drainage System in Indira Gandhi Canal Command. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2013, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Darzi-Naftchali, A.; Shahnazari, A. Influence of Subsurface Drainage on the Productivity of Poorly Drained Paddy Fields. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 56, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Cheong, A.W. Subsurface Drainage Effect on Soil and Rice Crop. J. Trop. Agric. Food Sci. 2001, 29, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.Y.; Yun, E.S.; Park, K.D.; Lee, Y.H.; Hwang, J.B.; Park, C.Y.; Ramos, E.P. Effect of Subsurface Drainage for Multiple Land Use in Sloping Paddy Fields. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, E.K.; Panda, R.K.; Nair, M. Influence of Subsurface Drainage on Crop Production and Soil Quality in a Low-Lying Acid Sulphate Soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 47, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzema, H.P.; Satyanarayana, T.V.; Raman, S.; Boonstra, J. Subsurface Drainage to Combat Waterlogging and Salinity in Irrigated Lands in India: Lessons Learned in Farmers’ Fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Furukawa, Y.; Tsuruta, H.; Inubushi, K. Effectiveness of a Subsurface Drainage System in Poorly Drained Paddy Fields on Reduction of Methane Emissions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 53, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Shiratori, Y.; Inubushi, K. Depression of Methane Production Potential in Paddy Soils by Subsurface Drainage Systems. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 54, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi-Naftchali, A.; Mirlatifi, S.M.; Shahnazari, A.; Ejlali, F.; Mahdian, M.H. Effect of Subsurface Drainage on Water Balance and Water Table in Poorly Drained Paddy Fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 130, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi-Naftchali, A.; Ritzema, H.; Karandish, F.; Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A.; Ghasemi-Nasr, M. Alternate Wetting and Drying for Different Subsurface Drainage Systems to Improve Paddy Yield and Water Productivity in Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, C.; Lu, P.; Bakour, A. Effects of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinity and Yield of Summer Maize (Zea mays L.) in Subsurface Drainage System. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, B.; Saptomo, S.; Arif, C.; Sulaiman, A.; Herodian, S.; Matsuda, H.; Tamura, K.; Inoue, Y. Waterflow in the Paddy Field Installed with Sheetpipe Mole Drains. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 355, 12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.P. A Simple Evapotranspiration Model for Hawaii: The Hargreaves Model; CTAHR Fact Sheet Engeineer’s Notebook 106; University of Hawaii: Manoa, HI, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Allen, R.G. History and Evaluation of Hargreaves Evapotranspiration Equation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, C.; Setiawan, B.I.; Mizoguchi, M.; Doi, R. Estimation of Water Balance Components in Paddy Fields under Non-Flooded Irrigation Regimes by using Excel Solver—SciAlert Responsive Version. J. Agron. 2012, 11, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, C.; Setiawan, B.I.; Sofiyuddin, H.A.; Martief, L.M.; Mizoguchi, M.; Doi, R. Estimating Crop Coefficient in Intermittent Irrigation Paddy Fields Using Excel Solver. Rice Sci. 2012, 19, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Pareira, L.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56. Crop Evapotranspiration (Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements); Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, N.K.; Sharma, D.K.; Luthra, S.K. Determination of Evapotranspiration and Crop Coefficients of Rice and Sunflower with Lysimeter. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 45, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, S.H.; Watanabe, H.; Takagi, K. Application of FAO-56 for Evaluating Evapotranspiration in Simulation of Pollutant Runoff from Paddy Rice Field in Japan. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Peng, S.; Castañeda, A.R.; Visperas, R.M. Yield and Water Use of Irrigated Tropical Aerobic Rice Systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 74, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, C.; Setiawan, B.I.; Sofiyuddin, H.A.; Martief, L.M. Enhanced Water Use Efficiency by Intermittent Irrigation for Irrigated Rice in Indonesia. J. Islamic Perspect. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2013, 1, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kalita, P.K.; Kanwar, R.S.; Rahman, M.A. Modeling percolation losses from a ponded field under variable water-table conditions. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1992, 28, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, L.C.; Bhuiyan, S.I.; Tuong, T.P.; Barker, R. Producing More Rice with Less Water from Irrigated Systems; International Irrigation Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tuong, T.P.; Bhuiyan, S.I. Increasing Water-Use Efficiency in Rice Production: Farm-Level Perspectives. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhu, D.; Lin, X. Effects of Water Management and Organic Fertilization with SRI Crop Practices on Hybrid Rice Performance and Rhizosphere Dynamics. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Yamaji, E.; Kuroda, T. Strategies and Engineering Adaptions to Disseminate SRI Methods in Large-Scale Irrigation Systems in Eastern Indonesia. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaman, K.; Mel, V.C.; Diop, L.; Sow, A.; El-Namaky, R.; Manneh, B.; Saito, K.; Futakuchi, K.; Irmak, S. Effects of Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation Regime and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Irrigated Rice in the Sahel. Water 2018, 10, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crop Management Techniques to Enhance harvest Index in Rice|Journal of Experimental Botany|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jxb/article/61/12/3177/425540 (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Kato, Y.; Okami, M.; Katsura, K. Yield Potential and Water Use Efficiency of Aerobic Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Japan. Field Crop. Res. 2009, 113, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Katsura, K. Rice Adaptation to Aerobic Soils: Physiological Considerations and Implications for Agronomy. Plant Prod. Sci. 2014, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Okami, M. Root Growth Dynamics and Stomatal Behaviour of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Grown under Aerobic and Flooded Conditions. Field Crop. Res. 2010, 117, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Okami, M. Root Morphology, Hydraulic Conductivity and Plant Water Relations of High-Yielding Rice Grown under Aerobic Conditions. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, M.C.R.; Wassmann, R.; Hirano, T.; Miyata, A.; Hatano, R.; Kumar, A.; Padre, A.; Amante, M. Comparisons of Energy Balance and Evapotranspiration between Flooded and Aerobic Rice Fields in the Philippines. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1417–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, M.A.S.; Christen, E.W.; Amer, M.H. Irrigation Water Saving by Management of Existing Subsurface Drainage in Egypt. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, M.D.M.; Mylavarapu, R.S.; Li, Y.C.; Reddy, G.B.; Reddy, M.D. Impact of Aerobic Rice Cultivation on Growth, Yield, and Water Productivity of Rice–Maize Rotation in Semiarid Tropics. Agron. J. 2012, 104, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).