The Fate of Anthropogenic Nanoparticles, nTiO2 and nCeO2, in Waste Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
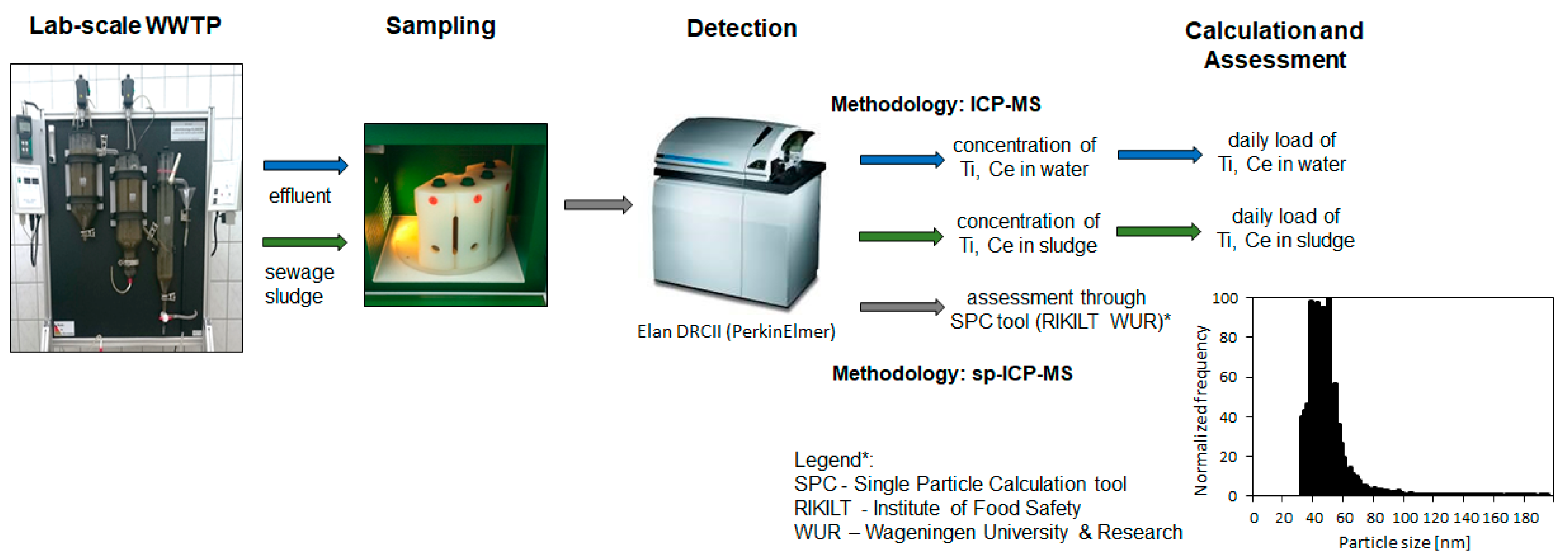
2.1. NM Measuring Technique
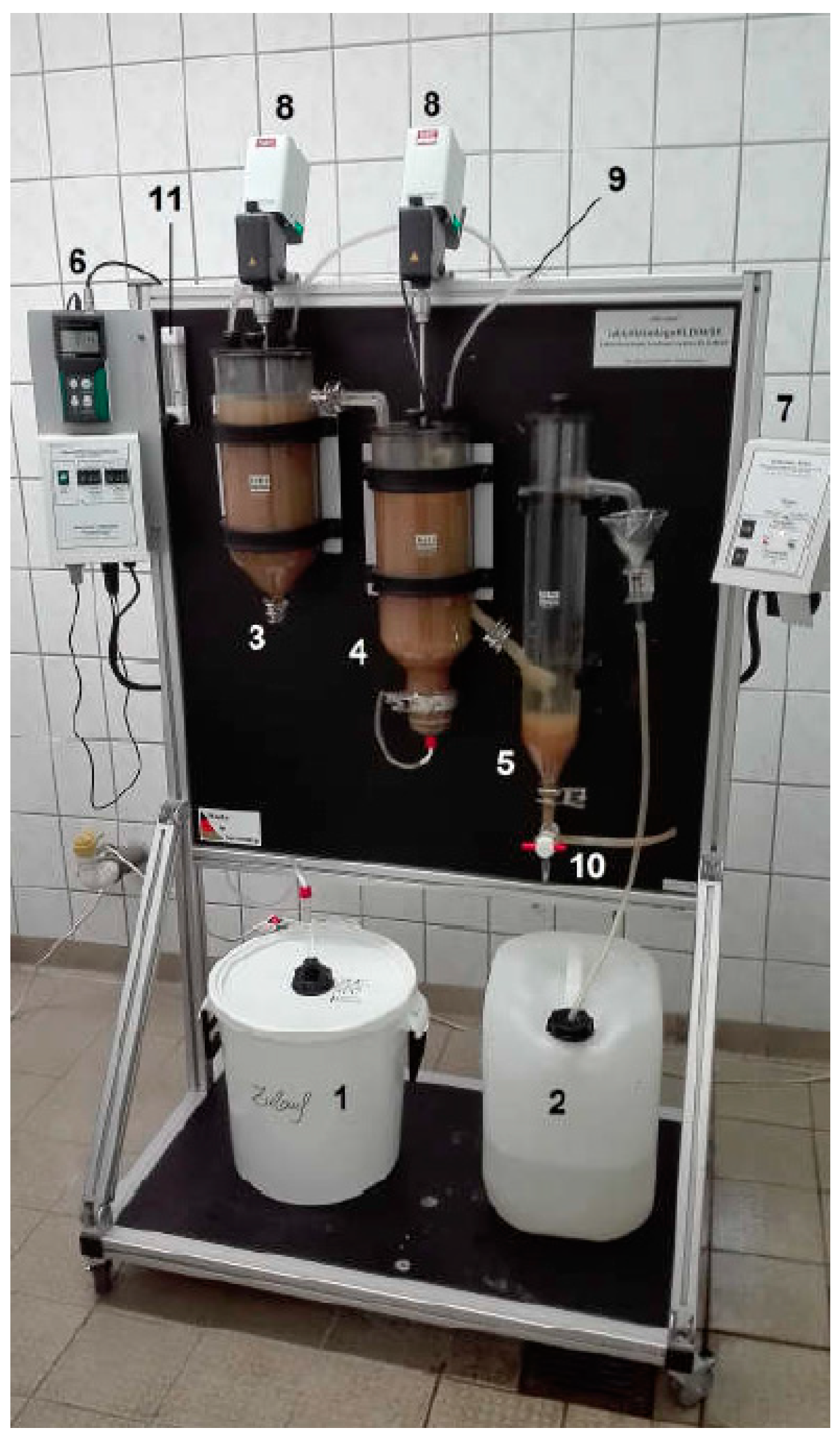
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Operational Setting of the Lab-Scale Wastewater Treatment System
2.4. Input: Synthetic Wastewater
2.5. NM Investigation Methodology
2.6. Sampling and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Operational Monitoring of the Lab-Scale Sewage Treatment Systems
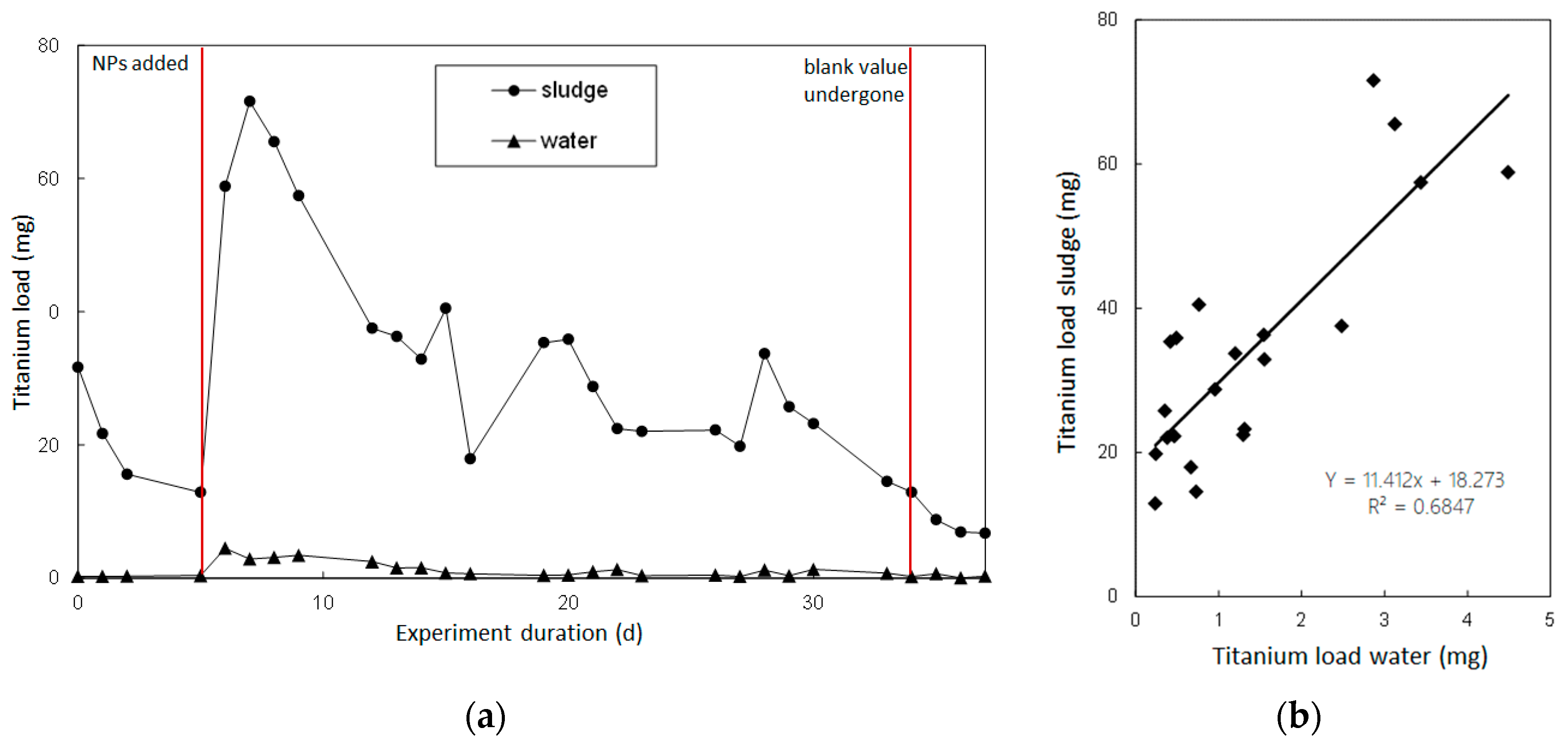
3.2. Discharge Loads of Titanium NP-Spike Particle Addition
3.3. Discharge Loads of Titanium NP-Continuous Particle Addition
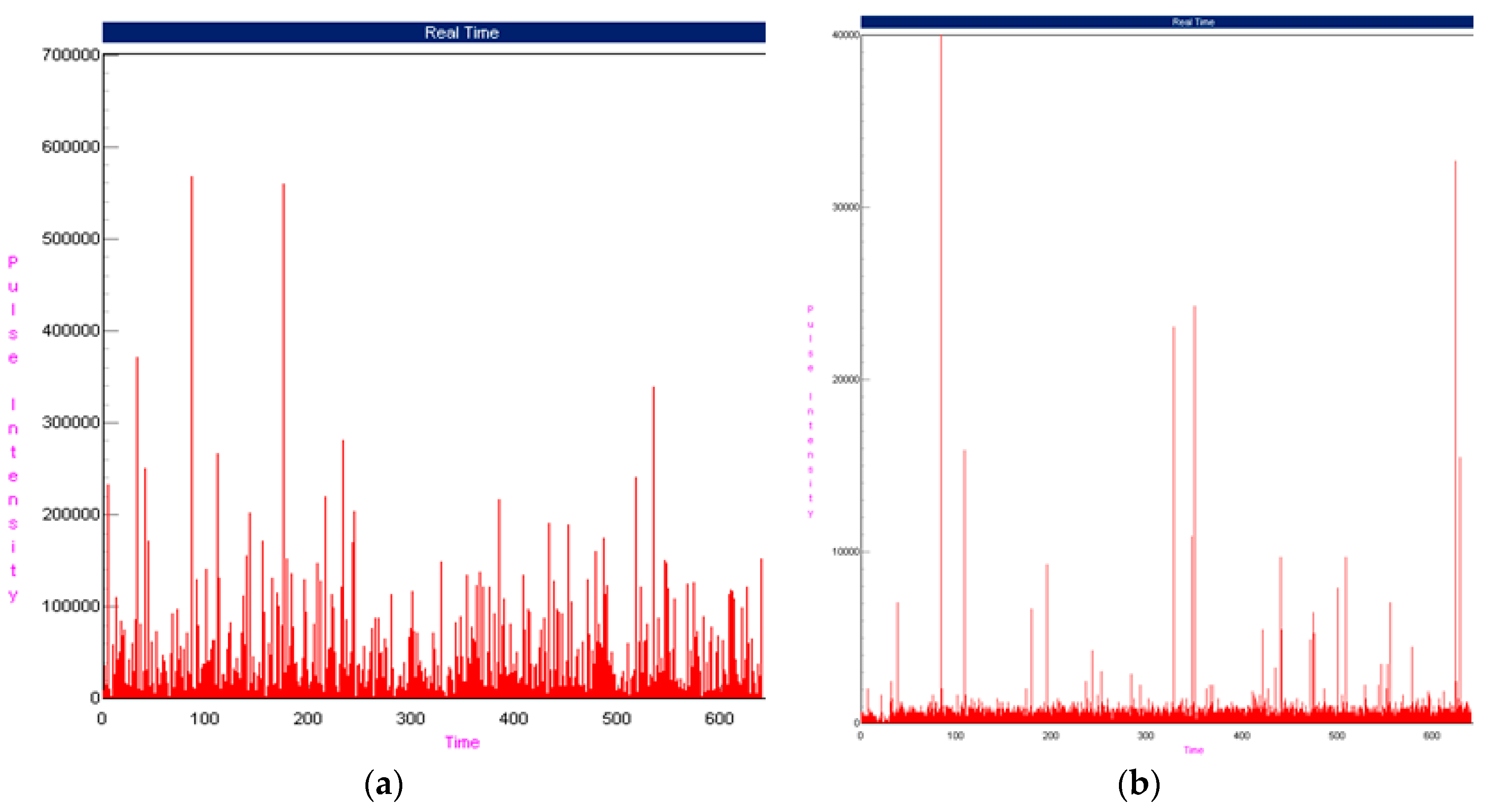
3.4. nTiO2 Characteristics of Added NP Suspension and Effluent
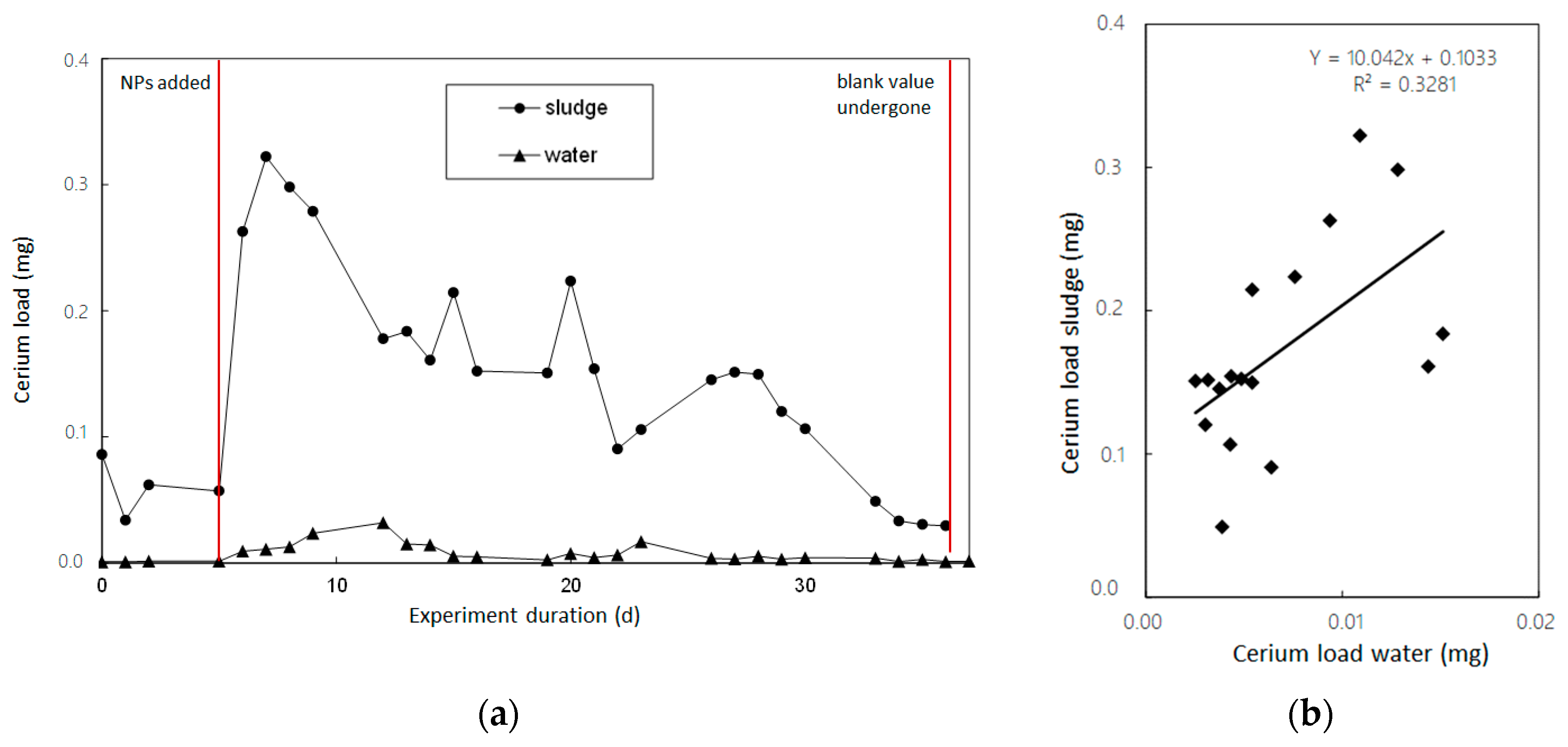
3.5. Discharge Loads of Cerium NP-Spike Particle Addition
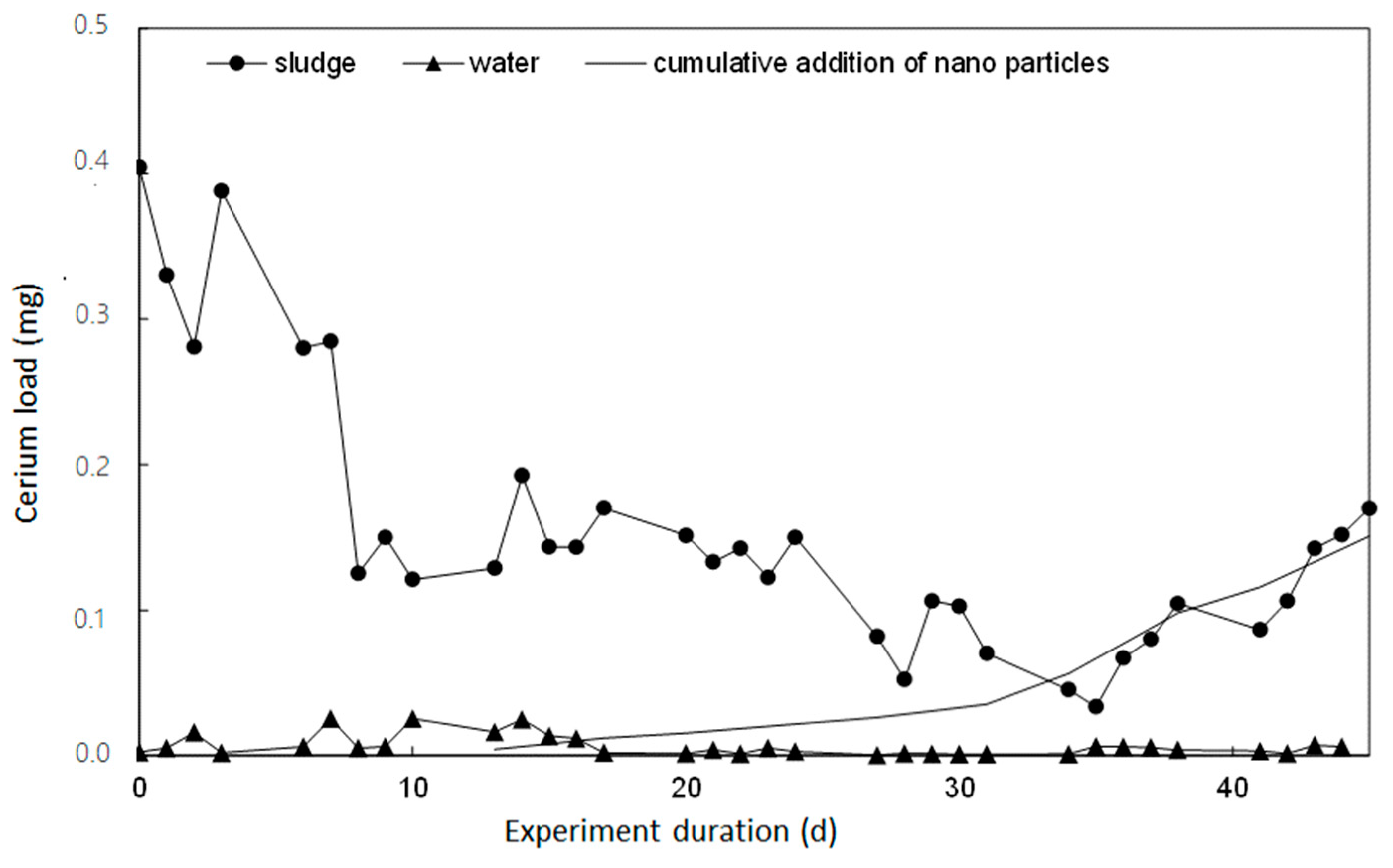
3.6. Discharge Loads of Cerium NP-Continuous Particle Addition
3.7. nCeO2 Characteristics of Added NP Suspension and Effluent, Particle Size Distribution
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.Y.; Man, C.; Bo, H.Z. Effective removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution by amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Colvin, V.L. The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, S.; Gondikas, A.; Neubauer, E.; Hofmann, T.; von der Kammer, F. Spot the Difference: Engineered and Natural Nanoparticles in the Environment—Release, Behavior, and Fate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12398–12419. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.H.M.; Chiche, A.; Krausch, G.; Rosenfeldt, R.; Ballauff, M.; Harnau, L.; Göttker-Schnetmann, I.; Tong, Q.; Mecking, S. Single Lamella Nanoparticles of Polyethylene. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Engineered nanoparticles in wastewater and wastewater sludge—Evidence and impacts. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSalvo, R.M., Jr.; McCollum, G.R. Evaluating the Impact of Nanoparticles on Wastewater Collection and Treatment Systems in Virginia. In Proceedings of the Water JAM 2008, Virginia Beach, VA, USA, 7–11 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Mashima, Y.; Iyoda, T. Reversible Size Control of Liquid-Metal Nanoparticles under Ultrasonication. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 13000–13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendren, C.O.; Badireddy, A.R.; Casman, E.; Wiesner, M.R. Modeling nanomaterial fate in wastewater treatment: Monte Carlo simulation of silver nanoparticles (nano-Ag). Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Naz, I.; Khan, Z.M.; Sultan, M.; Isalm, T.; Abbasi, I.A. Phytogenic magnetic nanoparticles for wastewater treatment: A review. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40158–40178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Stoller, M.; Wang, T.; Bao, Y.; Hao, H. An Overview of Nanomaterials for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1687–8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, H.S.; Das, R.; Bhattachajee, C. Influence of Nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment—A Short Review. Austin Chem. Eng. 2016, 3, 1036. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y. Contradictory effects of silver nanoparticles on activated sludge wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Li, K.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Li, X. Removal of silver nanoparticles in simulated wastewater treatment processes and its impact on COD and NH4 reduction. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Al-Obaidi, H.; King, S.M. Fate of Silica Nanoparticle in Simulated Primary Wastewater Treastment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8622–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Choi, S.B.; Noh, J.H.; Hunyoon, S.; Lee, S.; Noh, T.H.; Frank, A.J.; Hong, K.S. Synthesis of CdSe-TiO2 nanocomposites and their applications to TiO2 sensitized solar cells. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5348–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Murayama, M.; Colmane, B.P.; Hochella, M.F., Jr. Characterization and environmental implications of nano- and larger TiO2 particles in sewage sludge, and soils amended with sewage sludge. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartiser, S.; Flach, F.; Nickel, C.; Stintz, M.; Damme, S.; Schaeffer, A.; Erdinger, L.; Kuhlbusch, T.J.A. Behavior of nanoscale titanium dioxide in laboratory wastewatertreatment plants according to OECD 303 A. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbach, L.K.; Bereiter, R.; Müller, E.; Krebs, R.; Gälli, R.; Stark, W.J. Removal of Oxide Nanoparticles in a Model Wastewater Treatment Plant: Influence of Agglomeration and Surfactants on Clearing Efficiency. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5828–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Z. Impact of metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles on wastewater treatment and anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Hollert, H. Comparison of sewage sludge toxicity to plants and invertebrates in three different soils. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, A.; Pedersen, A.L.; Jensen, K.A. Effects of C60 fullerene nanoparticles on soil bacteria and protozoans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, C.; Gabsch, S.; Hellack, B.; Nogowski, A.; Babick, F.; Stintz, M.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J. Mobility of coated and uncoated TiO2 nanomaterials in soil columns–Applicability of the tests methods of OECD TG 312 and 106 for nanomaterials. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzleben, C.; Hansen, S.F. Environmental Exposure to Nanomaterials—Data Scoping Study: Final Report; Milieu: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gladkova, M.M.; Terekhova, V.A. Engineered nanomaterials in soil: Sources of entry and migration pathways. Mosc. Univ. Soil Sci. Bull. 2013, 68, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sonderer, T.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, fullerenes) for different regions Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9216–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.C.; Bowes, M.J.; Crossley, A.; Jarvie, H.P.; Jurkschat, K.; Jürgens, M.D.; Lawlor, A.J.; Park, B.; Rowland, P.; Spurgeon, D.; et al. An assessment of the fate, behaviour and environmental risk associated with sunscreen TiO2 nanoparticles in UK field scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Gondikas, A.P.; Marinakos, S.M.; Auffan, M.; Liu, J.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Meyer, J.N. Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticle Toxicity Is Dependent on Dissolved Silver and Surface Coating in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.E.; Therezien, M.; Auffan, M.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Wiesner, M.R. Theory and Methodology for Determining Nanoparticle Affinityfor Heteroaggregation in Environmental Matrices UsingBatch Measurements. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.; Hund-Rinke, K.; Van den Brink, N.W.; Nickel, C. Fate and Bioavailability of Engineered Nanoparticles in Soils: A Review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2720–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy Guzmán, K.A.; Taylor, M.R.; Banfield, J.F. Environmental Risks of Nanotechnology: National Nanotechnology Initiative Funding, 2000–2004. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotze, E.M.; Phenrat, T.; Lowry, G.V. Nanoparticles aggregation: Challanges to understanding transport and reactivity in the envioenment. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Biswas, P. Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomerationstate of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santiago-Martín, A.; Constantin, B.; Guesdon, G.; Kagambega, N.; Raymond, S.; Galvez Cloutier, R. Bioavailability of engineered nanoparticles in soil systems. J. Hazard. Toxic. Radioact. Waste 2016, 20, B4015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.E.; Junin, R.; Shamshirband, S.; Chong, W.T. Transport and retention of engineered Al2O3, TiO2 and SiO2 nanoparticles through various sedimentary rocks. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, G.; Thomas, C.D.M.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Kirby, J.K.; Beak, D.G.; Chittleborough, D. Retention and Dissolution of Engineered Silver Nanoparticles in Natural Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Shan, X.; Wen, B.; Lin, J.; Owens, G. Stability of titania nanoparticles in soil suspensions and transport in saturated homogeneous soil columns. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.A.; Jacobson, A.R.; Kim, B.; Isley, S.L.; Penn, R.L.; Baveye, P.C. Influence of Ionic Strength, pH, and Cation Valence on Aggregation Kinetics of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogos, A.; Knauer, K.; Bucheli, T.D. Nanomaterials in plant protection and fertilization: Current state, foreseen applications, and research priorities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9781–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salim, N.; Barraclough, E.; Burgess, E. Quantum dots transport in soil, plants and insects. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3237–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, M.; Martins, J.M.F.; Uzu, G.; Vince, E.; Richaume, A. Combined Study of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Transport and Toxicity on Microbial Nitrifying Communities under Single and Repeated Exposures in Soil Columns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10693–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, K.; Fang, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, M.; Han, J. Transport of TiO2 nanoparticles in soil in the presence of surfactants. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Shijirbaatar, A.; Fang, J.; Owen, G.; Lin, D.; Zhang, K. Distinguishable Transport Behavior of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Silica Sand and Soil Columns. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourinho, P.S.; Cornelis, A.; Van Gestel, M.; Lofts, S.; Svendsen, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Lourero, S. Metal-based Nanoparticles in Soil: Fate, Baheviour, and Effects on Soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1679–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Varela-Ramirez, A.; Castillo-Michel, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Aguilera, R.J.; Keller, A.A.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Effect of surface coating and organic matter on the uptake of CeO2 NPs by corn plants grown in soil: Insight into the uptake mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225–226, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaegi, R.; Voegelin, A.; Sinnet, B.; Zuleeg, Z.; Hagendorfer, H.; Burkhardt, M.; Siegrist, H. Behavior of metallic silver nanoparticles in a pilot wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3902–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Tapia Ramirez, J.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silvernanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.K.; Lyon, D.Y.; McIntosh, A.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Comparative toxicity of nano-scale TiO2, SiO2 and ZnO water suspensions. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Cao, J.; Shen, Z.; Ho, W.; Lee, S.C. Environment-Friendly Carbon Quantum Dots/ZnFe2O4 Photocatalysts: Characterization, Biocompatibility, and Mechanisms for NO Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2924–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Feng, W.-Y.; Wang, T.-C.; Jia, G.; Wang, M.; Shi, J.-W.; Zhang, F.; Zhaoa, Y.-L.; Chai, Z.-F. Acute toxicity of nano- and micro-scale zinc powder in healthy adult mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 161, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exbrayat, J.-M.; Moudilou, E.N.; Lapied, E. Harmful Effects of Nanoparticles on Animals. J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 2015, 861092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinlaan, M.; Ivask, A.; Blinova, I.; Dubourguier, H.C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemets, K.; Ivask, A.; Dubourguier, H.-C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Harper, B.J.; Harper, S.L. Comparative dissolution, uptake, and toxicity of zinc oxide particles in individual aquatic species and mixed populations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, D.; Zhang, X.J.; Rooney-Varga, J.N. Impacts of single-walled carbon nanotubes on microbial community structure in activated sludge. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, N.; Top, E.M.; Verstraete, W.; Siciliano, S.D. Bioaugmentation as a tool to protect the structure and function of an activated-sludge microbial community against a 3-chloroaniline shock load. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, I.D.S.; Love, N.G. The role of extracellular polymeric substances in the toxicity response of activated sludge bacteria to chemical toxins. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4177–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roco, M.C. The long view of nanotechnology development: The National Nanotechnology Initiative at 10 years. J. Nanopart. Res. 2001, 13, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, W.; Rui, Y. Interactions between nanoparticles and plants: Phytotoxicity and defense mechanisms. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Kammer, F.; Ferguson, P.L.; Holden, P.A.; Masion, A.; Rogers, K.R.; Klaine, S.J.; Koelmans, A.A.; Horne, N.; Unrine, J.M. Analysis of engineered nanomaterials in complex matrices (environment and biota): General considerations and conceptual case studies. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Xing, B. Applications and implications of manufactured nanoparticles in soils: A review. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, H. Nanosicherheitsforschung–sind wir auf dem richtigenWeg? Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 12502–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durenkamp, M.; Pawlett, M.; Ritz, K.; Harris, J.A.; Neal, A.L.; McGrath, S.P. Nanoparticles within WWTP sludges have minimal impact on leachate quality and soil microbial community structure and function. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Stephan, C. Single-Particle ICP-MS: A Key Analytical Technique for Characterizing Nanoparticles. Spectroscopy 2017, 32, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, A.R.; Adams, C.D.; Ma, Y.; Stephan, C.; Eichholz, T.; Shi, H. Detection of zinc oxide and cerium dioxide nanoparticles during drinking water treatment by rapid single particle ICP-MS methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5137–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgantzopoulou, A.; Almeida Carvalho, P.; Vogelsang, C.; Tilahun, M.; Ndungu, K.; Booth, A.M.; Thomas, K.; Macken, A. Ecotoxicological Effects of Transformed Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in the Effluent from a Lab-Scale Wastewater Treatment System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9431–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, A.R.; Adams, C.D.; Ma, Y.; Stephan, C.; Eichholz, T.; Shi, H. Single particle ICP-MS characterization of titanium dioxide, silver, and gold nanoparticles during drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Shih, Y.H.; Su, C.H.; Ho, H.C. Comparison of three analytical methods to measure the size of silver nanoparticles in real environmental water and wastewater samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théoret, T.; Wilkinson, K.J. Evaluation of enhanced darkfield microscopy and hyperspectral analysis to analyse the fate of silver nanoparticles in wastewaters. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3920–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining transport efficiency for the purpose of counting and sizing nanoparticles via single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Lesher, K.; Bednar, A.; Monserud, J.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Detecting nanoparticulate silver using single-particle inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozhayeva, D.; Engelhard, C. A critical review of single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry—A step towards an ideal method for nanomaterial characterization. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt (LfU). Umweltrelevante Eigenschaften Synthetischer Nanopartikel–Abschlussbericht, Analysis of Engineered Nanomaterials in Complex Matrices (Environment and Biota): General Considerations and Conceptual Case Studies Investigation on Likely Effects of Ag, TiO2, and ZnO Nanoparticles on Sewage Treatment. 2013. Available online: https://www.lfu.bayern.de/analytik_stoffe/nanopartikel/doc/abschlussbericht_nanoprojekt.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Burkhardt, M.; Zuleeg, S.; Kägi, R.; Sinnet, B.; Eugster, J.; Bollen, M.; Siegrist, H. Verhalten von nanosilber in Kläranlagen und dessen Einfluss auf die Nitrifikationsleistung in Belebtschlamm. Umweltwiss. Schadst. Forsch. 2010, 22, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Youa, H. Fate and transformation of nanoparticles (NPs) in municipal wastewater treatment systems and effects of NPs on the biological treatment of wastewater: A review. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 37065–37075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Operational Parameter | System 1 | System 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic retention time | 3.0 h | 2.4 h |
| Volume flow inlet pump | 0.5 L/h | 0.5 L/h |
| Volume flow recirculation pump | 1.7 L/h | 2.4 L/h |
| Volume flow draw-back pump | 0.5 L/h | 0.4 L/h |
| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Injection tube | 2 mm, quartz |
| Sprayer | concentric |
| Sprayer chamber type | cyclone |
| Scan mode | Peak hopping |
| Dwell time | 150 ms |
| Sweeps | 20 |
| Readings | 1 |
| Replicates | 3 |
| Detector mode | Pulse |
| Nebulizer Gas Flow | 0.76 L/min Ar |
| Auxiliary Gas Flow | 1.2 L/min Ar |
| Plasma Gas Flow | 16 L/min Ar |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lange, T.; Schneider, P.; Schymura, S.; Franke, K. The Fate of Anthropogenic Nanoparticles, nTiO2 and nCeO2, in Waste Water Treatment. Water 2020, 12, 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092509
Lange T, Schneider P, Schymura S, Franke K. The Fate of Anthropogenic Nanoparticles, nTiO2 and nCeO2, in Waste Water Treatment. Water. 2020; 12(9):2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLange, Thomas, Petra Schneider, Stefan Schymura, and Karsten Franke. 2020. "The Fate of Anthropogenic Nanoparticles, nTiO2 and nCeO2, in Waste Water Treatment" Water 12, no. 9: 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092509
APA StyleLange, T., Schneider, P., Schymura, S., & Franke, K. (2020). The Fate of Anthropogenic Nanoparticles, nTiO2 and nCeO2, in Waste Water Treatment. Water, 12(9), 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092509






