Automatic Extraction of Open Water Using Imagery of Landsat Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
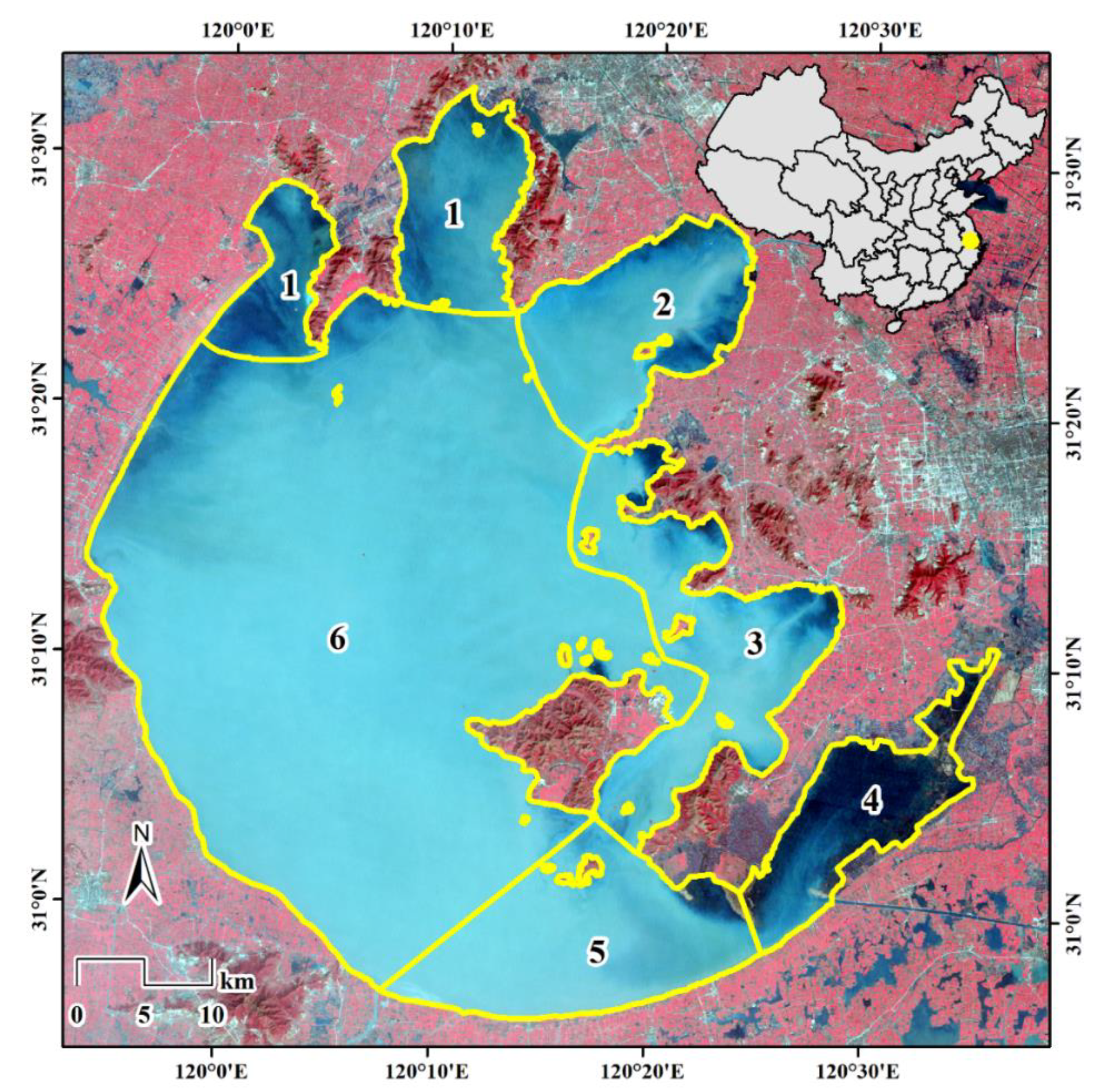
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
3.1.1. Landsat Images
3.1.2. Precipitation, Water Level, and Pondage Data for Taihu Lake
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Pre-Processing of Landsat Single Bands
3.2.2. Spatial Autocorrelation for the Standardized NumPy Array
3.2.3. Post-Processing for Open Surface Water Extraction
3.2.4. The Effects of Low Filter Image Process on Water Extraction
3.2.5. Time Series Analysis and Segmented Linear Regression for Climate and Survey Data
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Open Water Extraction from Different Landsat Bands
4.2. The Effects of Low Filter Image Processing on Water Extraction
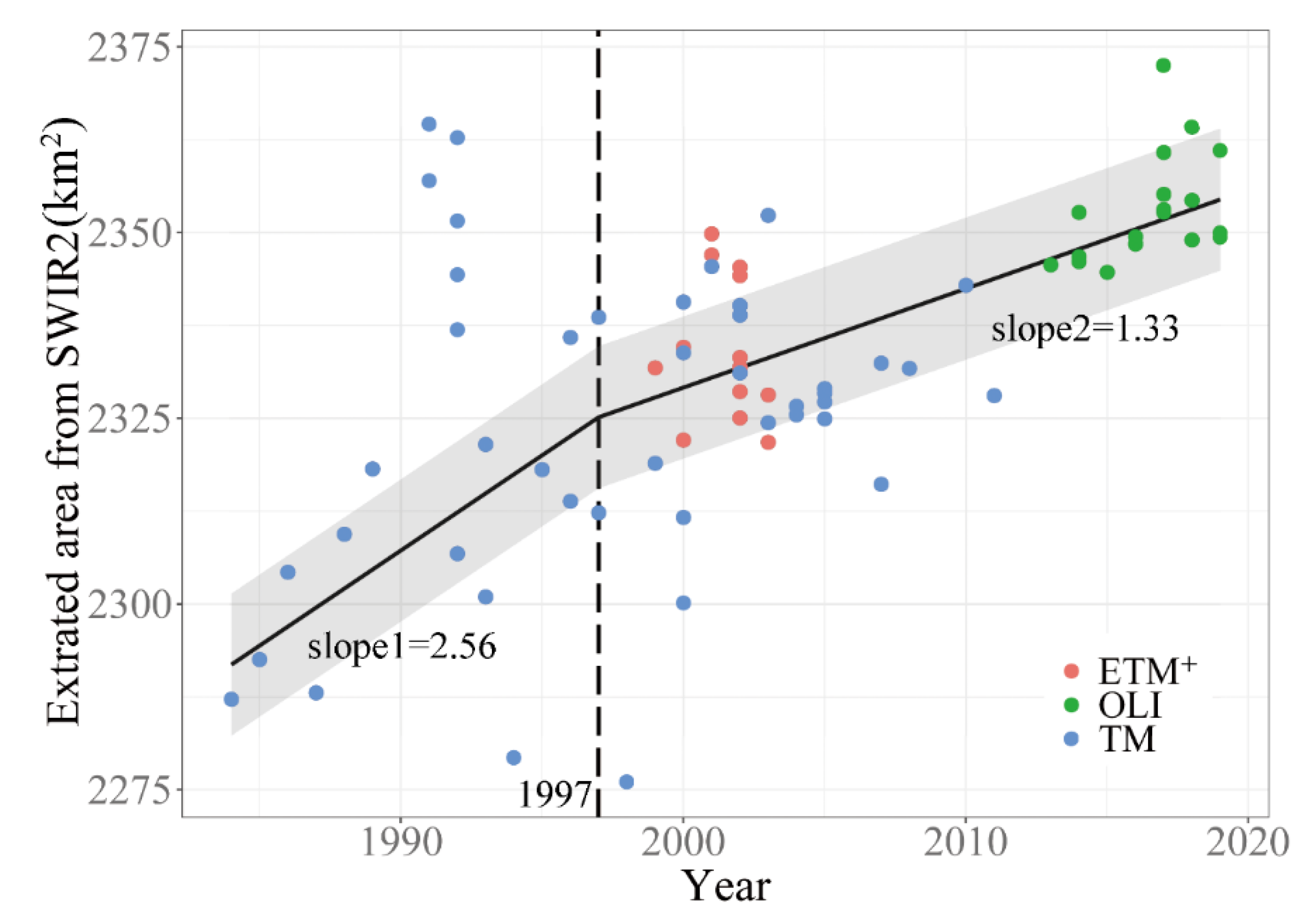
4.3. Temporal Trend of Extracted Area of Taihu Lake
4.4. Inter-Annual Dynamics of Precipitation, Water Level and Pondage
4.5. Water Extraction in Different Sections of Taihu Lake
4.6. Error Sources of Automatic Open Water Extraction from Landsat Series
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartsch, A.; Pathe, C.; Scipal, K.; Wagner, W. Detection of permanent open water surfaces in central Siberia with ENVISAT ASAR wide swath data with special emphasis on the estimation of methane fluxes from tundra wetlands. Hydrol. Res. 2008, 39, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. Divergent trends of open-surface water body area in the contiguous United States from 1984 to 2016. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3810–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crasto, N.; Hopkinson, C.; Forbes, D.L.; Lesack, L.; Marsh, P.; Spooner, I.; van der Sanden, J.J. A LiDAR-based decision-tree classification of open water surfaces in an Arctic delta. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Xiao, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zou, Z.; Qin, Y. Open surface water mapping algorithms: A comparison of water-related spectral indices and sensors. Water 2017, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colditz, R.R.; Troche Souza, C.; Vazquez, B.; Wickel, A.J.; Ressl, R. Analysis of optimal thresholds for identification of open water using MODIS-derived spectral indices for two coastal wetland systems in Mexico. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 70, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wang, R. Assessing methods of identifying open water bodies using Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, A.; Ettritch, G.; Cross, D.E.; Bunting, P.; Liywalii, F.; Sakala, J.; Silumesii, A.; Singini, D.; Smith, M.; Willis, T.; et al. Automatic detection of open and vegetated water bodies using sentinel 1 to map African malaria vector mosquito breeding habitats. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticehurst, C.; Guerschman, J.P.; Chen, Y. The strengths and limitations in using the daily MODIS open water likelihood algorithm for identifying flood events. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11791–11809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, M.E.; Elliott, N.; Veloz, S.; Jongsomjit, D.; Hickey, C.M.; Merrifield, M.; Reynolds, M.D. Spatio-temporal patterns of open surface water in the central valley of California 2000–2011: Drought, land cover, and waterbirds. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1722–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Wegmueller, U.; Lamarche, C.; Bontemps, S.; Defoumy, P.; Arino, O. Strengths and weaknesses of multi-year Envisat ASAR backscatter measurements to map permanent open water bodies at global scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Wegmueller, U.; Wiesmann, A.; Lamarche, C.; Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; Arino, O. Assessing fnvisat ASAR and sentinel-1 multi-temporal observations to map open water bodies. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Singapore, 1–4 September 2015; pp. 614–619. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, P.J.; Schwartzkopf, W.C.; Koehler, F.W. Robust automated thresholding of SAR imagery for open-water detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 11–15 May 2015; pp. 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.; Wegmueller, U. Multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar metrics applied to map open water bodies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3225–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioresita, F.; Puissant, A.; Stumpf, A.; Malet, J.-P. A method for automatic and rapid mapping of water surfaces from sentinel-1 imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, B.; Tobak, Z.; Kovacs, F. Sentinel-1 and-2 based near real time inland excess water mapping for optimizedwater management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldsetzer, T.; Yackel, J.J. Sea ice type and open water discrimination using dual co-polarized C-band SAR. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 35, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvonen, J.; Simila, M.; Makynen, M. Open water detection from Baltic Sea ice Radarsat-1 SAR imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, A.S.; Buehner, M. Automated detection of ice and open water from dual-polarization RADARSAT-2 images for data assimilation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5755–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, A.S.; Buehner, M. Adaptive probability thresholding in automated ice and open water detection from RADARSAT-2 images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M. Potential of large-scale inland water body mapping from Sentinel-1/2 data on the example of Bavaria′s lakes and rivers. PFG J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovakoglou, G.; Alexandridis, T.K.; Crisman, T.L.; Skoulikaris, C.; Vergos, G.S. Use of MODIS satellite images for detailed lake morphometry: Application to basins with large water level fluctuations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 51, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffi, A.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.A.; Bordogna, G.; Boschetti, M. Towards an automated approach to map flooded areas from Sentinel-2 MSI data and soft integration of water spectral features. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Paavel, B.; Kaljurand, K.; Ligi, M.; Randla, M. Mapping shallow waters of the Baltic sea with Sentinel-2 imagery. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/OES Baltic International Symposium, Klaipèda, Lithuania, 12–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arvor, D.; Daher, F.R.G.; Briand, D.; Dufour, S.; Rollet, A.-J.; Simoes, M.; Ferraz, R.P.D. Monitoring thirty years of small water reservoirs proliferation in the southern Brazilian Amazon with Landsat time series. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekertekin, A. A survey on global thresholding methods for mapping open water body using sentinel-2 satellite imagery and normalized difference water index. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated water extraction index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Liu, Y. Method for delineating open water bodies based on the deeply clear waterbody delineation index. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, J. Segmentation and morphology of open water bodies from multispectral images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4015–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Su, H.; Cao, G.; Wang, S.; Guan, Q. Learning from data: A post classification method for annual land cover analysis in urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemin, Y.; Rabbani, U. A new methodology for virtual water level gauges. Int. J. Geoinf. 2016, 12, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Diao, C.; Ji, W.; Yin, D. A survey of methods incorporating spatial information in image classification and spectral unmixing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3870–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, Z.A.; Evans, J.S. Using fuzzy C-means and local autocorrelation to cluster satellite-inferred burn severity classes. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2010, 19, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowe, P.; Mutanga, O.; Odindi, J.; Dube, T. Exploring the spatial patterns of vegetation fragmentation using local spatial autocorrelation indices. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Fang, S.; Yang, G.; Ge, M. Using a hidden markov model for improving the spatial-temporal consistency of time series land cover classification. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-inf. 2017, 6, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Pu, R.; Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Mao, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiao, Q. Evaluating the influences of harvesting activity and eutrophication on loss of aquatic vegetations in Taihu Lake, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Li, Y.M.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H.; Le, C.F.; Huang, C.C.; Gong, S.Q. A neural-network model to retrieve CDOM absorption from in situ measured hyperspectral data in an optically complex lake: Lake Taihu case study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 4005–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Le, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, L. Parameterization of water component absorption in an inland eutrophic lake and its seasonal variability: A case study in Lake Taihu. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3549–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. Detecting aquatic vegetation changes in Taihu Lake, China using multi-temporal satellite imagery. Sensors 2008, 8, 3988–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Yao, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, M. Spatiotemporal variation in particulate organic carbon based on long-term MODIS observations in Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhai, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y. Long-term and inter-monthly dynamics of aquatic vegetation and its relation with environmental factors in Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhu, A.X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, H.; Huang, T.; Zou, J.; Li, Y. Evaluation of the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) to monitor the dynamic characteristics of suspension sediment in Taihu Lake. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 3859–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quan, W. Using Landsat/TM imagery to estimate nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Zhang, X.; Dong, R. Long-term spatial and temporal monitoring of cyanobacteria blooms using MODIS on google earth engine: A case study in Taihu Lake. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring the river plume induced by heavy rainfall events in large, shallow, Lake Taihu using MODIS 250 m imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Duan, H.; Barnes, B.B.; Ma, R. An EOF-based algorithm to estimate chlorophyll a concentrations in Taihu Lake from MODIS land-band measurements: Implications for near real-time applications and forecasting models. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10694–10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Li, Y.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, C.; Lu, H. A four-band semi-analytical model for estimating chlorophyll a in highly turbid lakes: The case of Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wei, Y.; Lv, G.; Yuan, Z. Remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid water using a spectral index: A case study in Taihu Lake, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Deriving total suspended matter concentration from the near-infrared-based inherent optical properties over turbid waters: A case study in Lake Taihu. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, C.; Shen, Q.; Barnes, B.B.; Murch, B.; Feng, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, B. Recovering low quality MODIS-Terra data over highly turbid waters through noise reduction and regional vicarious calibration adjustment: A case study in Taihu Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 197, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Tian, L.; Ye, H.; Wang, S.; Lu, Z. A soft-classification-based chlorophyll-a estimation method using MERIS data in the highly turbid and eutrophic Taihu Lake. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 74, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y. Temporal and spatial dynamics of phytoplankton primary production in Lake Taihu derived from MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Hu, W.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W.; Lin, C. A new method for modifying thresholds in the classification of tree models for mapping aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake with satellite images. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7442–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Loiselle, S.; Li, J.; Hu, M. A MODIS-based novel method to distinguish surface cyanobacterial scums and aquatic macrophytes in Lake Taihu. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.D.; Guo, X.L.; Li, Z.Q.; Yang, X.H.; Yin, H. Measuring the dead component of mixed grassland with Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, P.S.; Page, K.J. Water body detection and delineation with Landsat TM data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Tang, J. Water property monitoring and assessment for China’s inland Lake Taihu from MODIS-Aqua measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Finlay, J.C.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of Landsat 8 and Landsat 7 for regional measurements of CDOM and water clarity in lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Shi, D.; Luan, Z. Automatic Extraction of Open Water Using Imagery of Landsat Series. Water 2020, 12, 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071928
Xu D, Zhang D, Shi D, Luan Z. Automatic Extraction of Open Water Using Imagery of Landsat Series. Water. 2020; 12(7):1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071928
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Dandan, Dong Zhang, Dan Shi, and Zhaoqing Luan. 2020. "Automatic Extraction of Open Water Using Imagery of Landsat Series" Water 12, no. 7: 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071928
APA StyleXu, D., Zhang, D., Shi, D., & Luan, Z. (2020). Automatic Extraction of Open Water Using Imagery of Landsat Series. Water, 12(7), 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071928





