Impacts of Regional Groundwater Flow and River Fluctuation on Floodplain Wetlands in the Middle Reach of the Yellow River
Abstract
1. Introduction
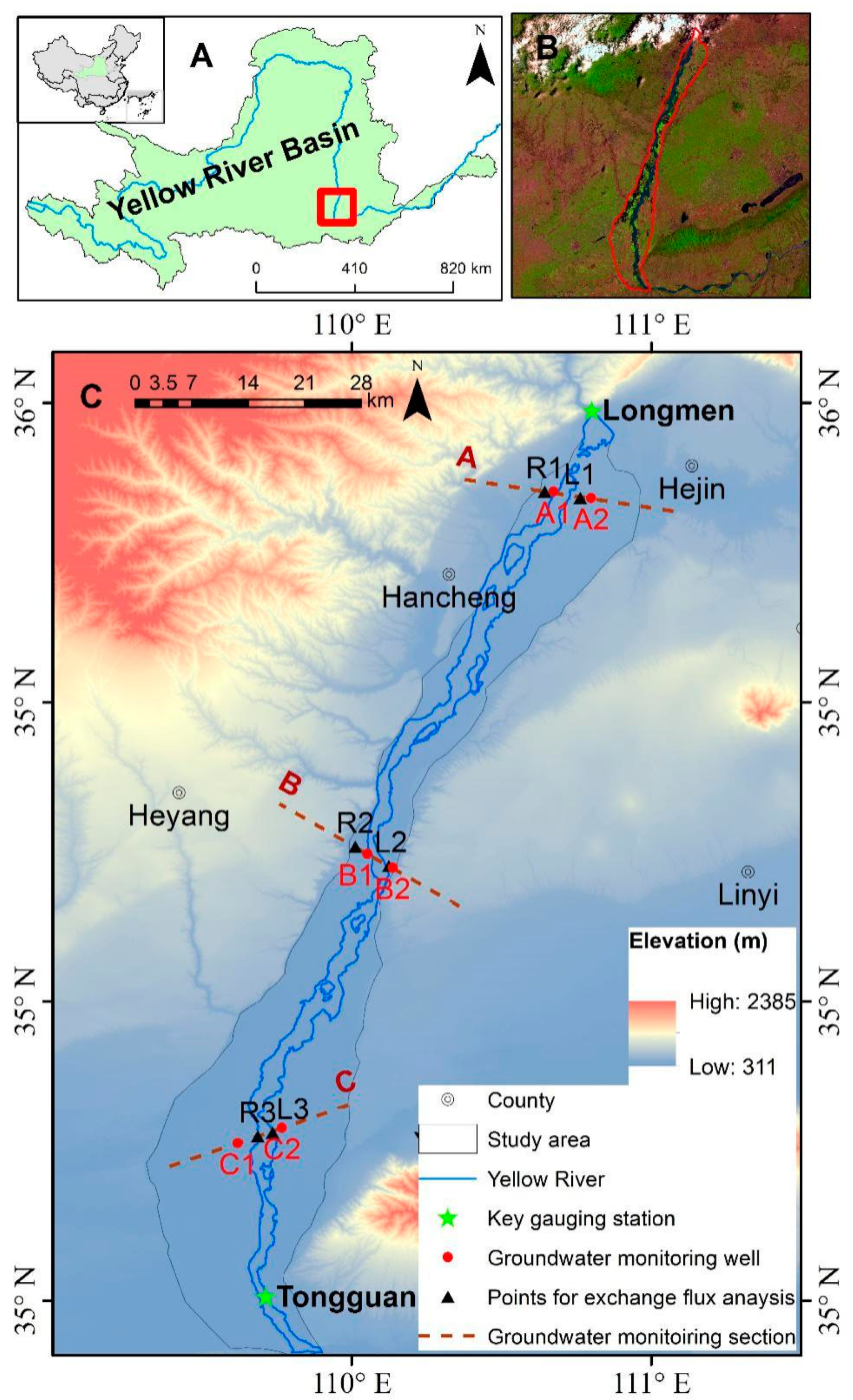
2. Study Area
2.1. Hydrology and Meteorology
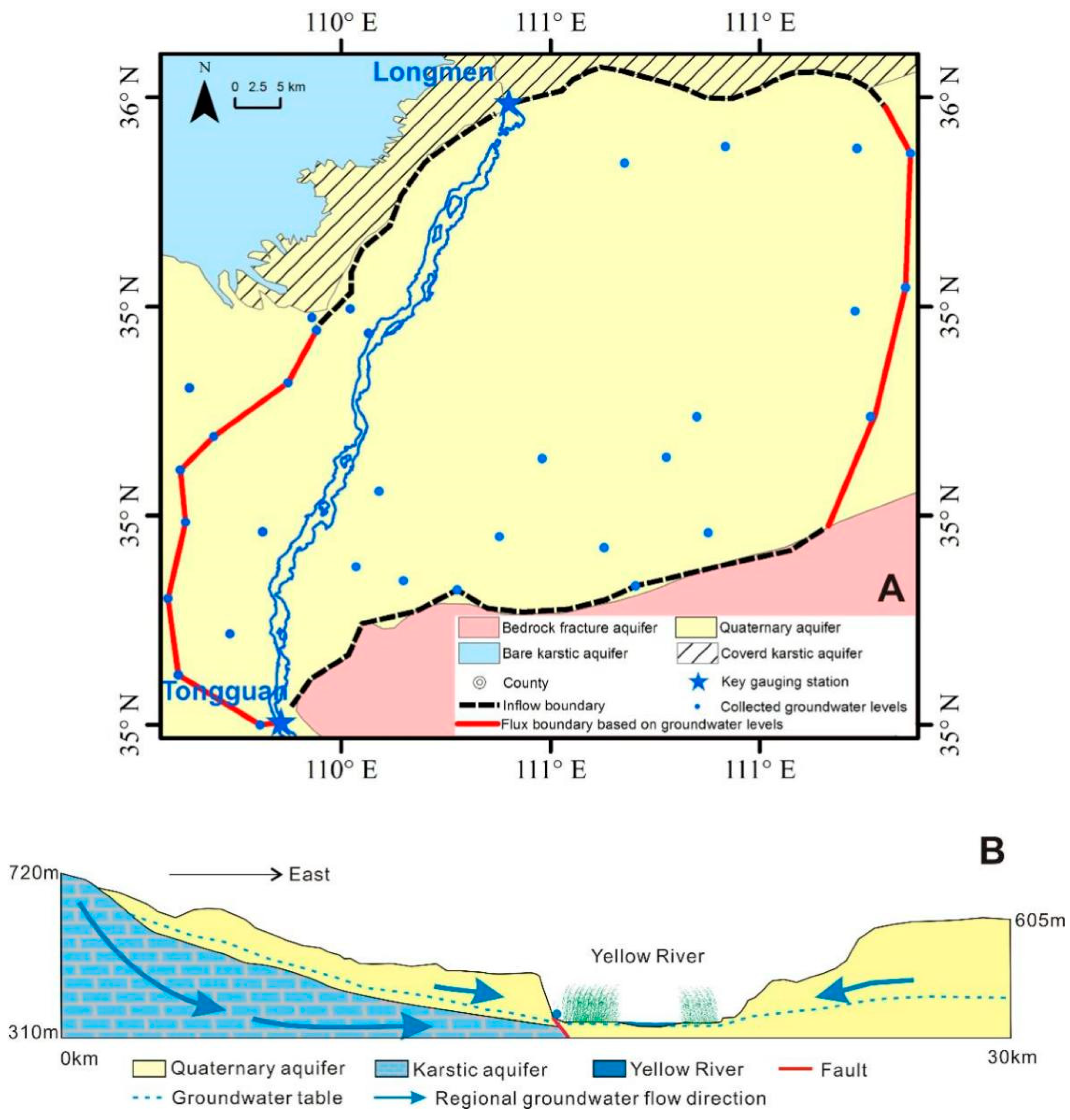
2.2. Geology and Hydrogeology
3. Method
3.1. Remote Sensing and In-Situ Monitoring
3.2. Numerical Modeling
3.2.1. Model Setup
3.2.2. Model Calibration
4. Results and Discussion
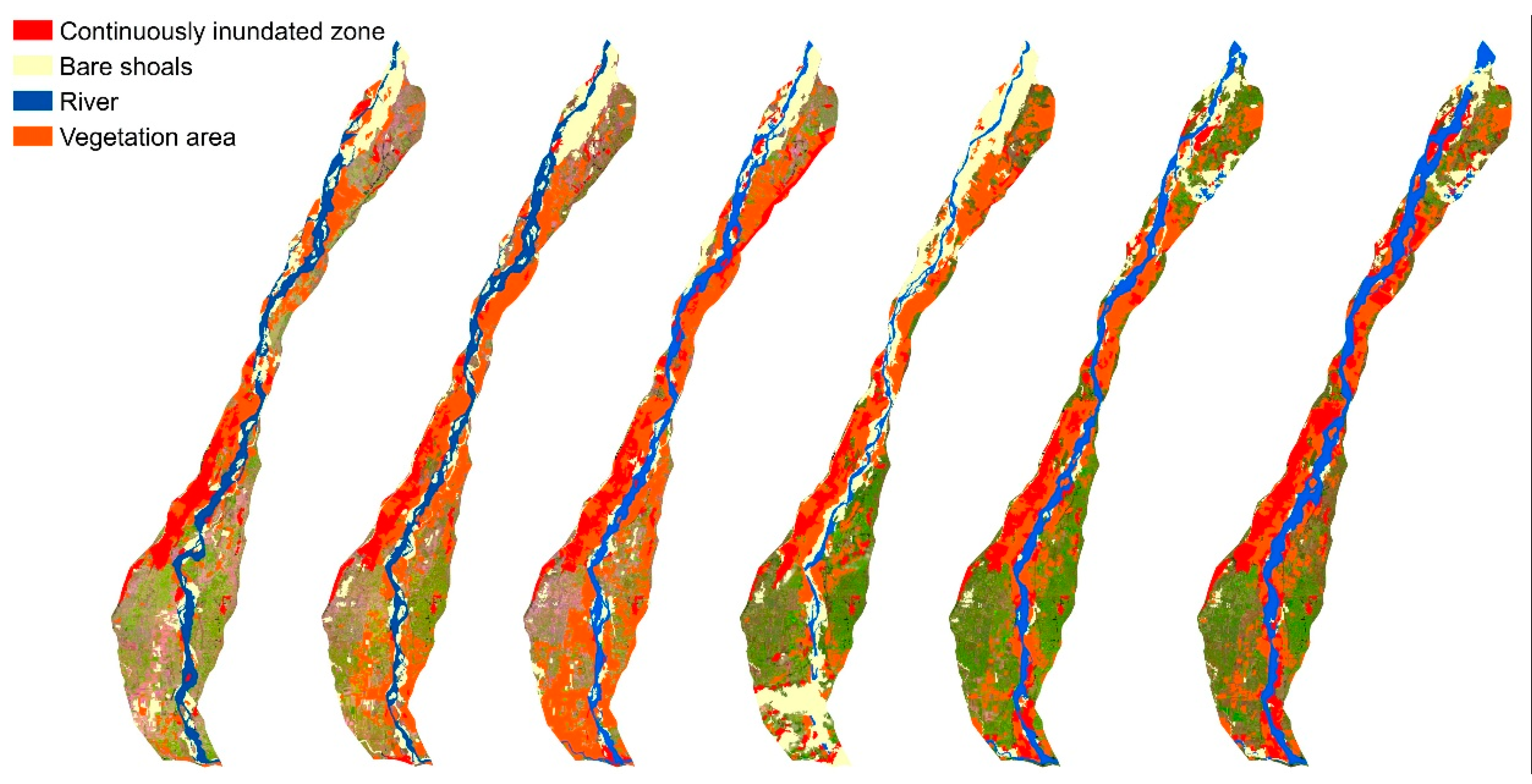
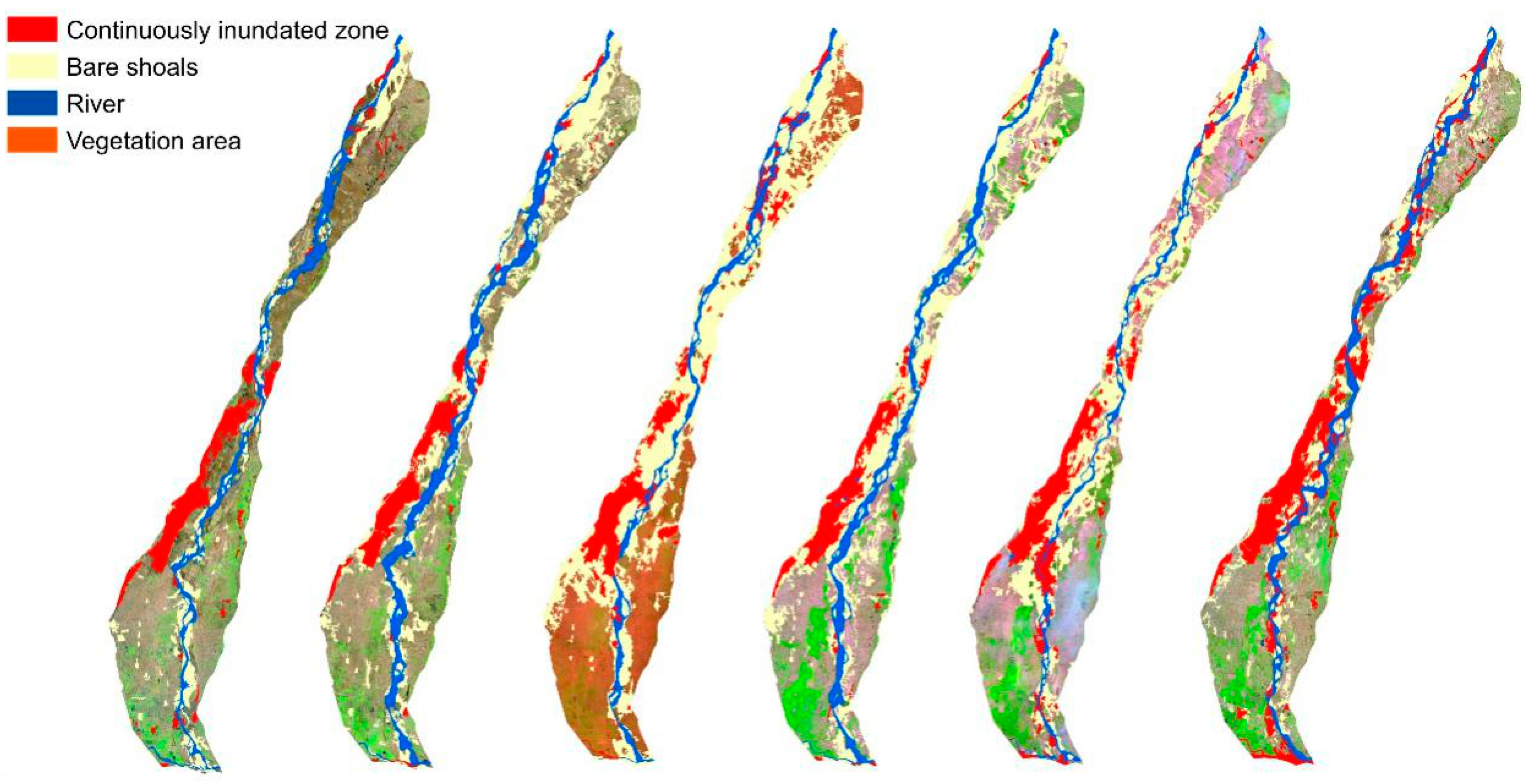
4.1. Remote Sensing and In-Situ Monitoring
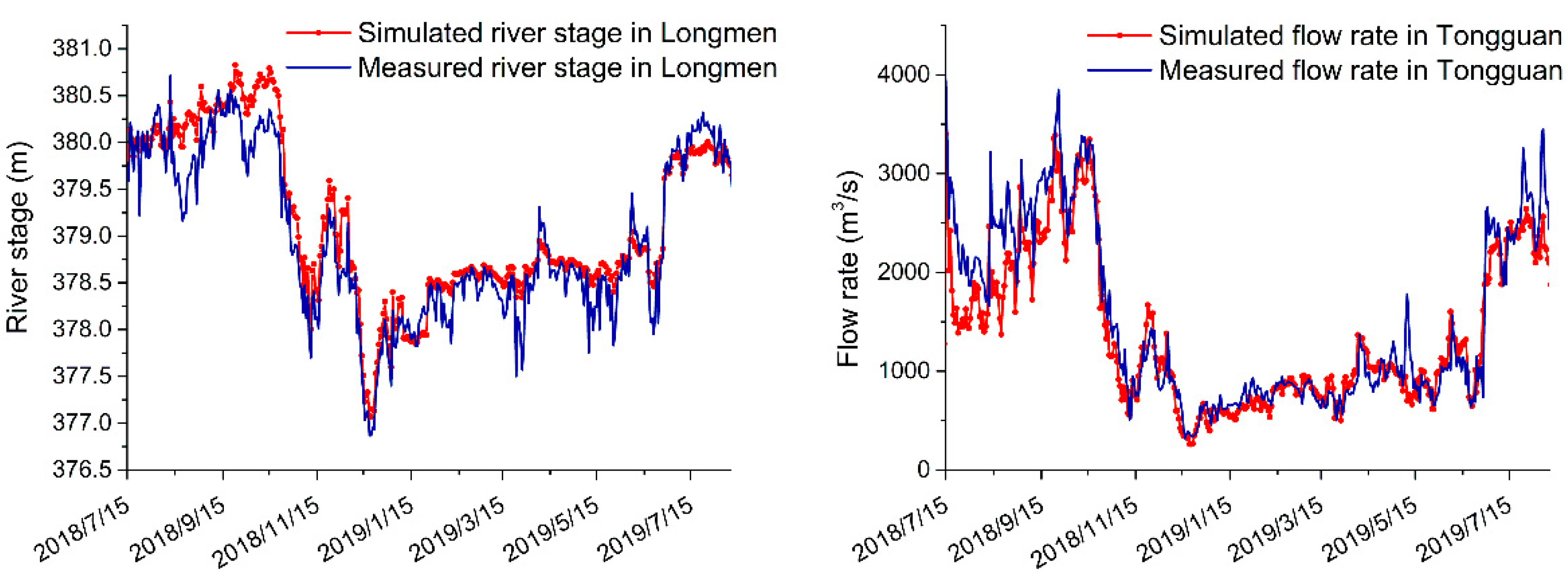
4.2. Model Calibration
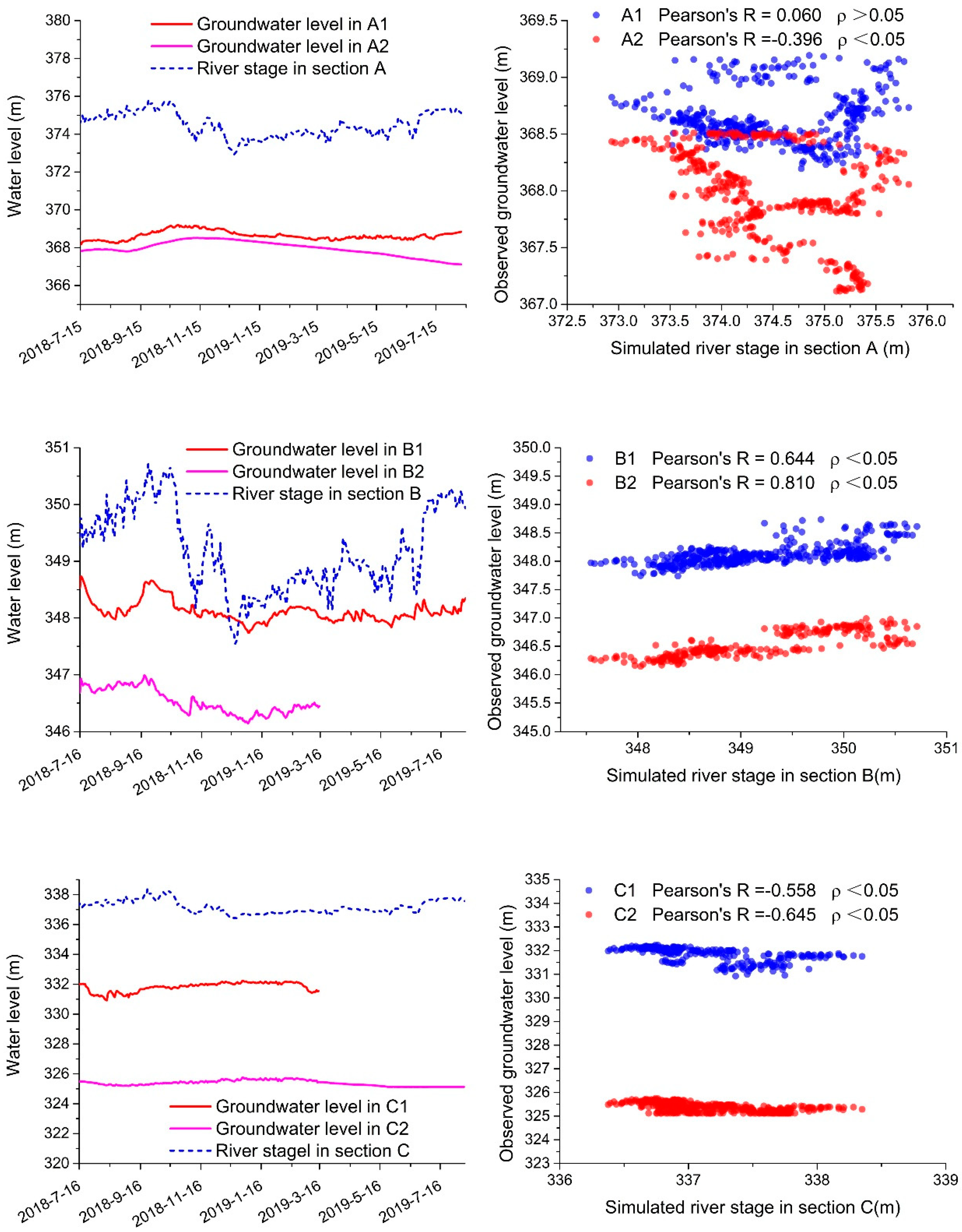
4.3. Connectivity between the River and the Wetland Groundwater
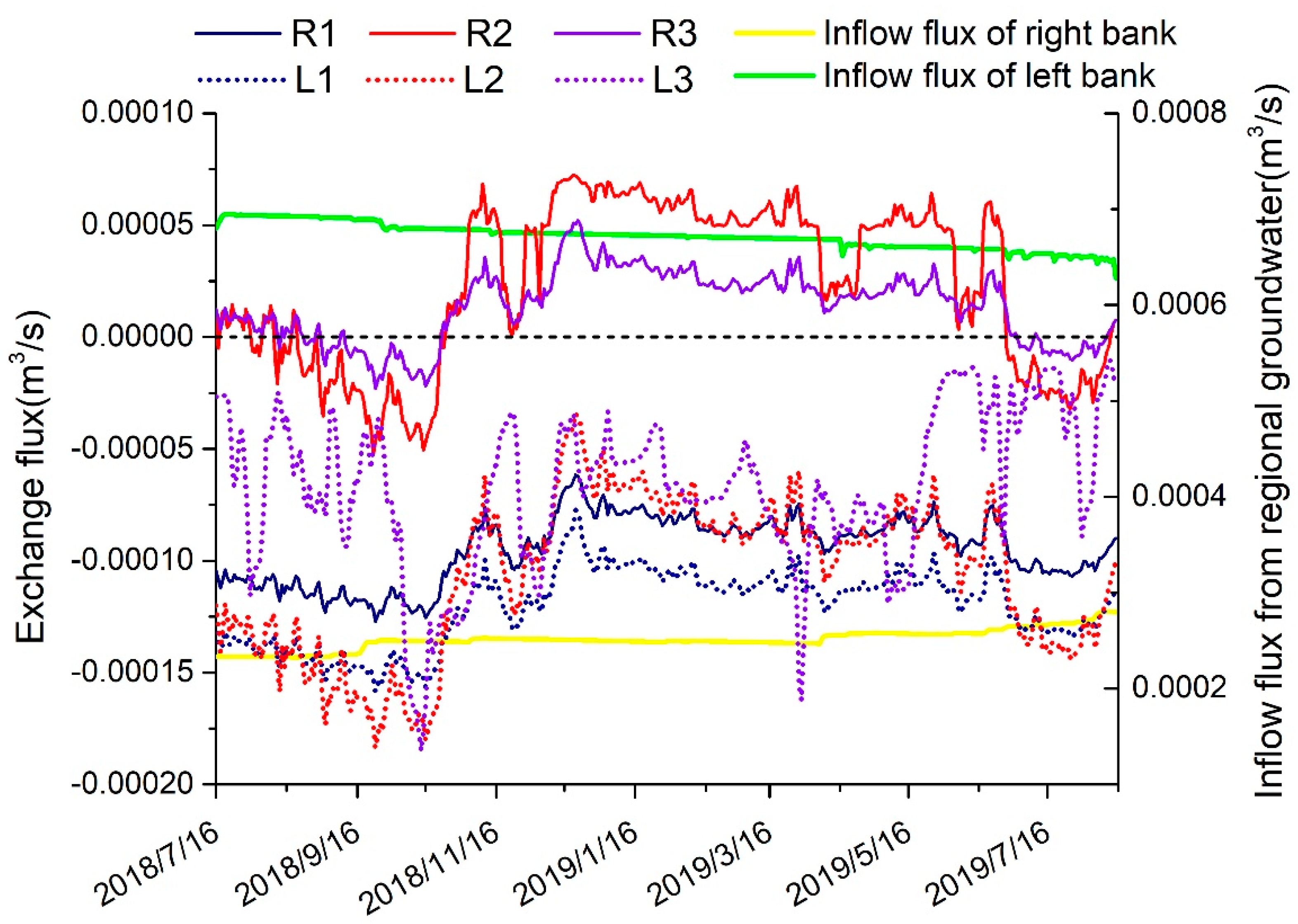
4.4. Difference in the Hydrological Process on Both Banks
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. Wetland resources: Status, trends, ecosystem services, and restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, A.; Acreman, M. The role of wetlands in the hydrological cycle. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperman, J.J.; Luster, R.; McKenney, B.A.; Roberts, M.; Meadows, A.W. Ecologically Functional Floodplains: Connectivity, Flow Regime, and Scale. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Global. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, J.T.A.; Arheimer, B.; Yin, C.; Hefting, M.M. Regional and global concerns over wetlands and water quality. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qi, S.; Na, X. Comparison of land use/land cover change and landscape patterns in Honghe National Nature Reserve and the surrounding Jiansanjiang Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Dong, W.; Lin, X.; Liang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Xie, W. Evolution of wetland in Honghe National Nature Reserve from the view of hydrogeology. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 609, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Sanchez, I.; Phanikumar, M.S.; Niu, J.; Masoner, J.R.; Cozzarelli, I.M.; McGuire, J.T. Quantifying wetland–aquifer interactions in a humid subtropical climate region: An integrated approach. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, T.C. Relation of streams, lakes, and wetlands to groundwater flow systems. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolski, P.; Savenije, H.H.G. Dynamics of floodplain-island groundwater flow in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junk, W.J. Structure and Function of the Large Central Amazonian River Floodplains: Synthesis and Discussion. In The Central Amazon Floodplain: Ecology of a Pulsing System; Junk, W.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Junk, W.J.; Bayley, P.; Sparks, R. The Flood Pulse Concept in River-Floodplain Systems. Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 106, 110–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford, R.T. Ecological impacts of dams, water diversions and river management on floodplain wetlands in Australia. Austral. Ecol. 2000, 25, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Laing, G.; Rinklebe, J.; Vandecasteele, B.; Meers, E.; Tack, F.M.G. Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 407, 3972–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattermann, F.F.; Krysanova, V.; Habeck, A.; Bronstert, A. Integrating wetlands and riparian zones in river basin modelling. Ecol. Model. 2006, 199, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, D.C.; Krempa, H.M. Cumulative Effects of Impoundments on the Hydrology of Riparian Wetlands al ong the Marmaton River, West-Central Missouri, USA. Wetlands 2011, 31, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, A.; Babbar-Sebens, M. On comparison of peak flow reductions, flood inundation maps, and velocity maps in evaluating effects of restored wetlands on channel flooding. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, F.; Kinsey-Henderson, A.; Wallace, J.; Arthington, A.H.; Pearson, R.G. Modelling wetland connectivity during overbank flooding in a tropical floodplain in north Queensland, Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2710–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, X. Development of a SWAT extension module to simulate riparian wetland hydrologic processes at a watershed scale. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 2901–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, I.D.; McEwan, K.L.; Holland, K.L. A review of groundwater-surface water interactions in arid/semi-arid wetlands and the consequences of salinity for wetland ecology. Ecohydrology 2008, 1, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.L.; Hession, W.C. Groundwater influence on water budget of a small constructed floodplain wetland in the Ridge and Valley of Virginia, USA. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rahman, M.M.; Thompson, J.R.; Flower, R.J. An enhanced SWAT wetland module to quantify hydraulic interactions between riparian depressional wetlands, rivers and aquifers. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2016, 84, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, R.J.; Swanson, T.L.; Remo, J.W.F.; Kiss, T. Strategic floodplain reconnection for the Lower Tisza River, Hungary: Opportunities for flood-height reduction and floodplain-wetland reconnection. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Wattayakorn, G.; Supcharoen, R.; Sioudom, K.; Kum, V.; Chanyotha, S.; Kritsananuwat, R. Groundwater discharge and phosphorus dynamics in a flood-pulse system: Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, T.S. Groundwater in the wetlands of the Okavango Delta, Botswana, and its contribution to the structure and function of the ecosystem. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, A.; Bradley, C.; Gerrard, A.J.; Leng, M.J. Using stable isotopes of water to infer wetland hydrological dynamics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Bronstert, A.; Zehe, E. Groundwater—surface water interactions in a North German lowland floodplain—Implications for the river discharge dynamics and riparian water balance. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, A.R.; Thompson, J.R.; Acreman, M.C. Projecting impacts of climate change on hydrological conditions and biotic responses in a chalk valley riparian wetland. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, A.R.; Thompson, J.R.; Sorensen, J.P.R.; Roberts, C.; Acreman, M.C. Modelling groundwater/surface water interaction in a managed riparian chalk valley wetland. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, I.; Werner, A.D.; Woods, J.A. Using geochemistry to discern the patterns and timescales of groundwater recharge and mixing on floodplains in semi-arid regions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, I.; Weaver, T.R.; Simmons, C.T.; Fifield, L.K.; Lawrence, C.R.; Chisari, R.; Varley, S. Physical hydrogeology and environmental isotopes to constrain the age, origins, and stability of a low-salinity groundwater lens formed by periodic river recharge: Murray Basin, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, I.; Hofmann, H.; Sirianos, M.A.; Weaver, T.R.; Simmons, C.T. Geochemical and 222Rn constraints on baseflow to the Murray River, Australia, and timescales for the decay of low-salinity groundwater lenses. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendón, D.I.; Larsen, J.R.; Jones, B.G.; Nanson, G.C.; Rickleman, D.; Hankin, S.I.; Pueyo, J.J.; Maroulis, J. Freshwater recharge into a shallow saline groundwater system, Cooper Creek floodplain, Queensland, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2010, 392, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladouche, B.; Weng, P. Hydrochemical assessment of the Rochefort marsh: Role of surface and groundwater in the hydrological functioning of the wetland. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapes, T.R.; Bradley, C.; Petts, G.E. Hydrodynamics of floodplain wetlands in a chalk catchment: The River Lambourn, UK. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 324–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Gavin, H.; Refsgaard, A.; Sorenson, H.R.; Gowing, D.J. Modelling the hydrological impacts of climate change on UK lowland wet grassland. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, S.; Lischeid, G.; Fleckenstein, J.H. Effects of micro-topography on surface-subsurface exchange and runoff generation in a virtual riparian wetland—A modeling study. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Bronstert, A. An advanced approach for catchment delineation and water balance modelling within wetlands and floodplains. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M. The Influence and Countermeasure Research of High-Speed Railway to the Yellow River. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Shanxi, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, E.; Mu, X.; Zhao, G. Temporal changes in annual runoff and influential factors in the upper and middle reaches of Yellow River from 1919–2010. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Li, F.; He, L.; Lu, M.; Chen, D. Effects of Summer Monsoon and Other Atmospheric Circulation Factors on Periodicities of Runoff in the Middle Huanghe River During 1919–2010. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 917–925. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, G.; Liang, Y.; Su, X.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, Z.; Yin, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Groundwater Systems and Resources in the Ordos Basin, China. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2008, 82, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Currell, M.J.; Cartwright, I.; Bradley, D.C.; Han, D. Recharge history and controls on groundwater quality in the Yuncheng Basin, north China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survey, C.G. Geological Atlas of China; Beijing Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002; p. 348. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Hou, G.; Su, X.; Wang, D.; Dong, J.; Hao, Y.; Wang, X. Isotopes (delta D and delta O-18) in precipitation, groundwater and surface water in the Ordos Plateau, China: Implications with respect to groundwater recharge and circulation. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yan, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Xu, H.; Ma, T.; Tang, Z. Groundwater Resources and Environmental Issues Assessment in the Six Major Basin of Shanxi; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; p. 498. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. Division and characteristics of groundwater system in Guanzhong basin. Geol. Surv. China 2018, 5, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S. Karst Water in the North of Weihe River and Its Environmental Geological Effect; Shaanxi Science and Technology Press: Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X. Groundwater systems and sustainable development countermeasures of groundwater resources in the Guanzhong. Quat. Sci. 2005, 1, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X. Study on the Development and Utilization of Groundwater Resources in Shanxi Province; Shanxi Science and Technology Press: Taiyuan, China, 2013; p. 826. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, G.; Du, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhao, A.; Xu, D. Evaluation and continual using counter measures of groundwater resources in Dali county. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2010, 24, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Study on the Risk of Groundwater Pollution in Yuncheng Basin, Shanxi Province. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, H.J.; Troldborg, L.; Hojberg, A.L.; Refsgaard, J.C. Assessment of exploitable groundwater resources of Denmark by use of ensemble resource indicators and a numerical groundwater-surface water model. J. Hydrol. 2008, 348, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Liu, X.; Sun, T. The effects of groundwater table and flood irrigation strategies on soil water and salt dynamics and reed water use in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Performance Indicator | Excellent | Good | Fair | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| >0.85 | 0.65–0.85 | 0.50–0.65 | <0.50 | |
| R | >0.85 | 0.65–0.85 | 0.50–0.65 | <0.50 |
| Component | Parameter | Unit | Type of Data | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate | Precipitation rate | mm/d | Literature (NOAA) | 1.20–53.60 |
| Net rainfall fraction | - | literature | 0.14–0.32 | |
| Overland flow | Manning’s coefficient | sm−1/3 | calibrated | 0.08 |
| Saturated zone | Hydraulic conductivity for Quaternary aquifer (vertical and horizontal) | m/s | calibrated | 1.4 × 106 |
| Specific yield for Quaternary aquifer | - | literature | 0.02 | |
| Specific storage for Quaternary aquifer | 1/m | calibrated | 1.0 × 104 | |
| Hydraulic conductivity for karstic aquifer (vertical and horizontal) | m/s | calibrated | 4.8 × 105 | |
| Specific yield for karstic aquifer | - | literature | 0.035 | |
| Specific storage for karstic aquifer | 1/m | calibrated | 1.0 × 105 | |
| Drainage level (values relative to ground) | m | calibrated | 0.5 | |
| Drainage time constant | s−1 | calibrated | 5.6 × 106 | |
| River and lakes | River bed resistance | sm−1/3 | measured | 0.058–0.150 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L. Impacts of Regional Groundwater Flow and River Fluctuation on Floodplain Wetlands in the Middle Reach of the Yellow River. Water 2020, 12, 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071922
Fu Y, Dong Y, Xie Y, Xu Z, Wang L. Impacts of Regional Groundwater Flow and River Fluctuation on Floodplain Wetlands in the Middle Reach of the Yellow River. Water. 2020; 12(7):1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071922
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yunmei, Yanhui Dong, Yueqing Xie, Zhifang Xu, and Liheng Wang. 2020. "Impacts of Regional Groundwater Flow and River Fluctuation on Floodplain Wetlands in the Middle Reach of the Yellow River" Water 12, no. 7: 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071922
APA StyleFu, Y., Dong, Y., Xie, Y., Xu, Z., & Wang, L. (2020). Impacts of Regional Groundwater Flow and River Fluctuation on Floodplain Wetlands in the Middle Reach of the Yellow River. Water, 12(7), 1922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071922





