Magnetic Sorbent for the Removal of Selenium(IV) from Simulated Industrial Wastewaters: Determination of Column Kinetic Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Carbon Supported Magnetic Nanoparticle Adsorbents (C-MNA) Synthesis
2.2. Column Set Up
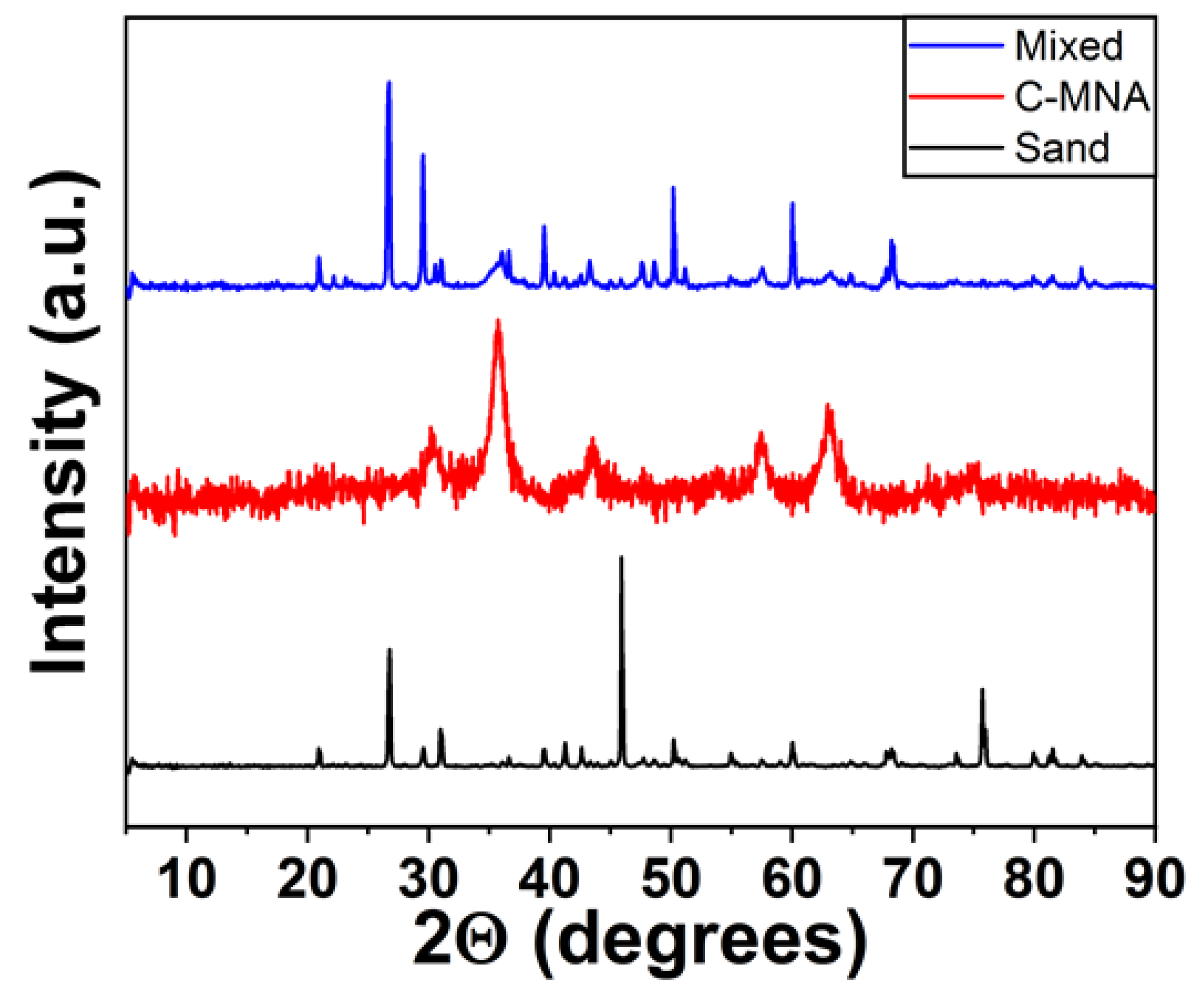
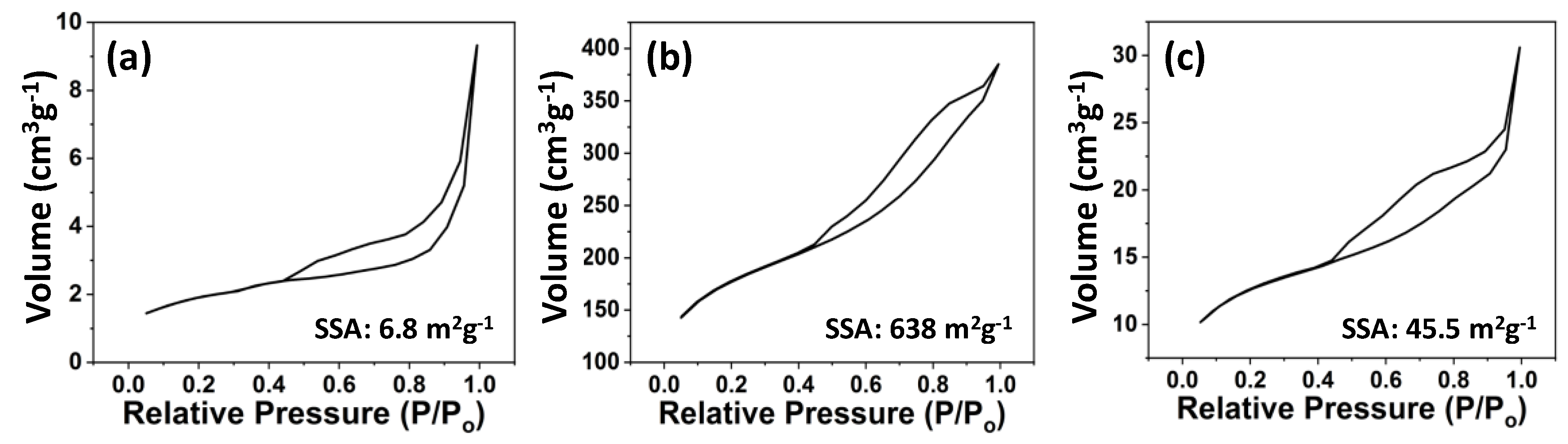
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Kinetic Model
- The quantity 1 at the denominator of Equation (7) is thus regarded as insignificant.
- Since the time of the experiment far outweighs the residence time, the residence-time term can be ignored.
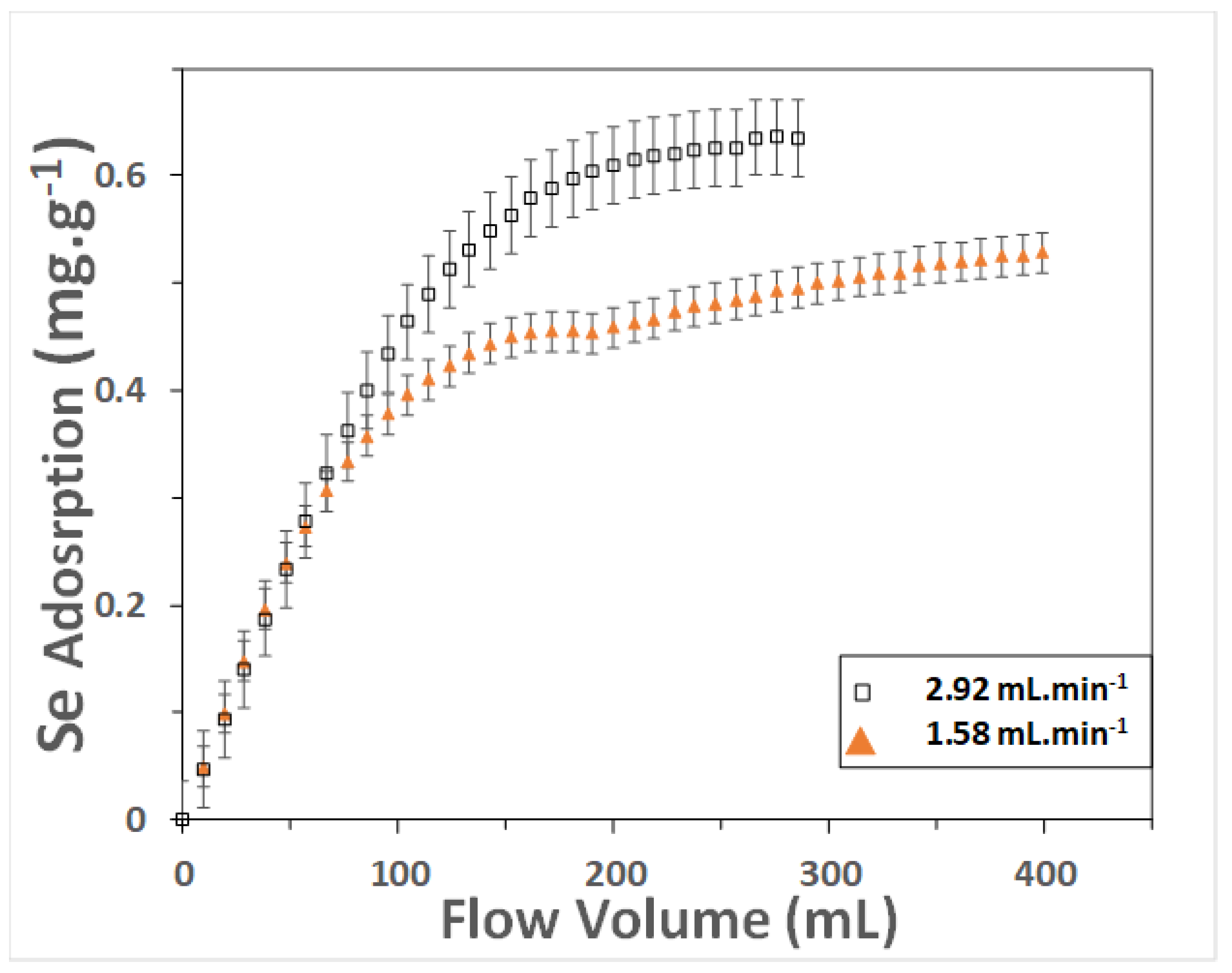
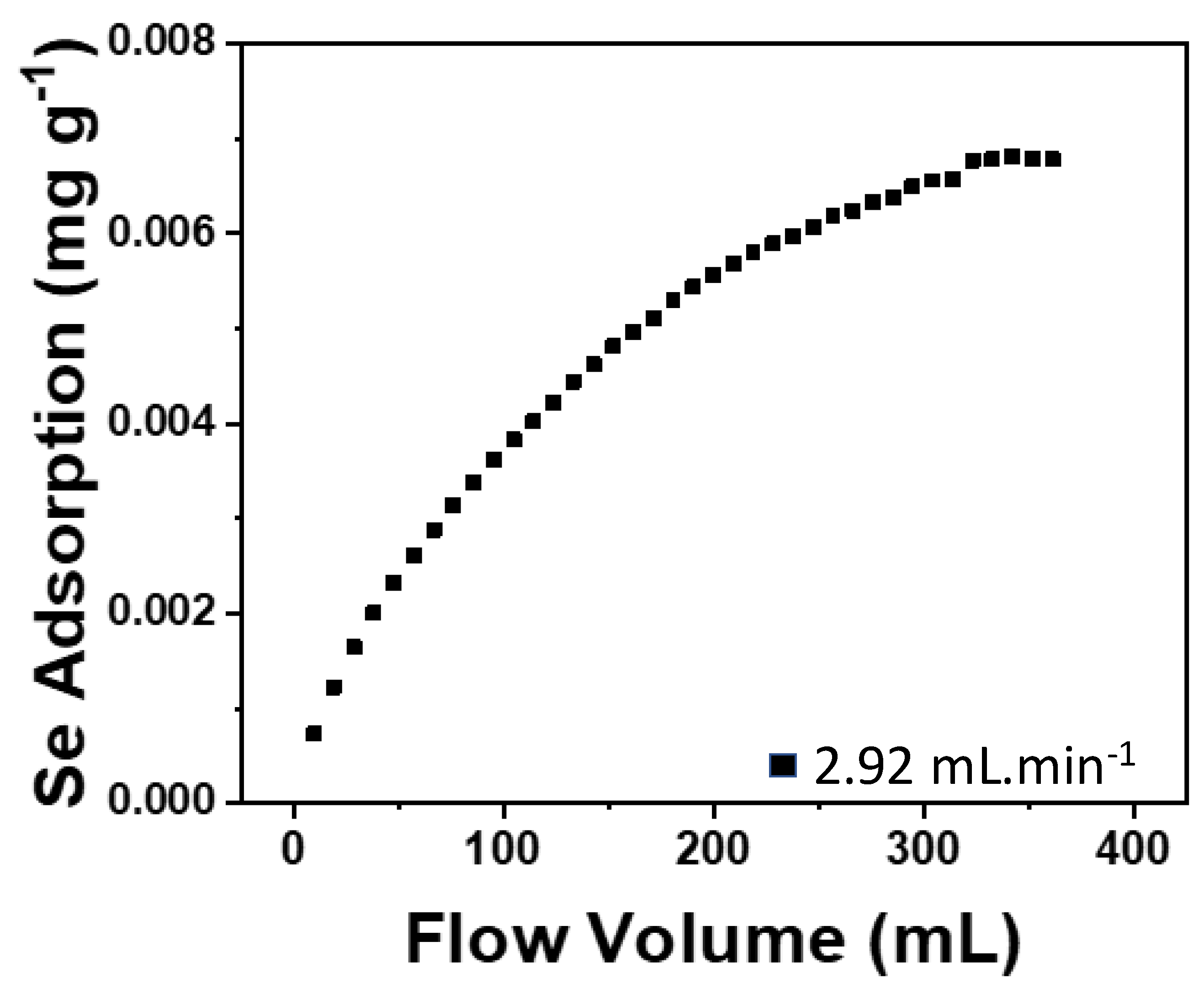
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rate Law
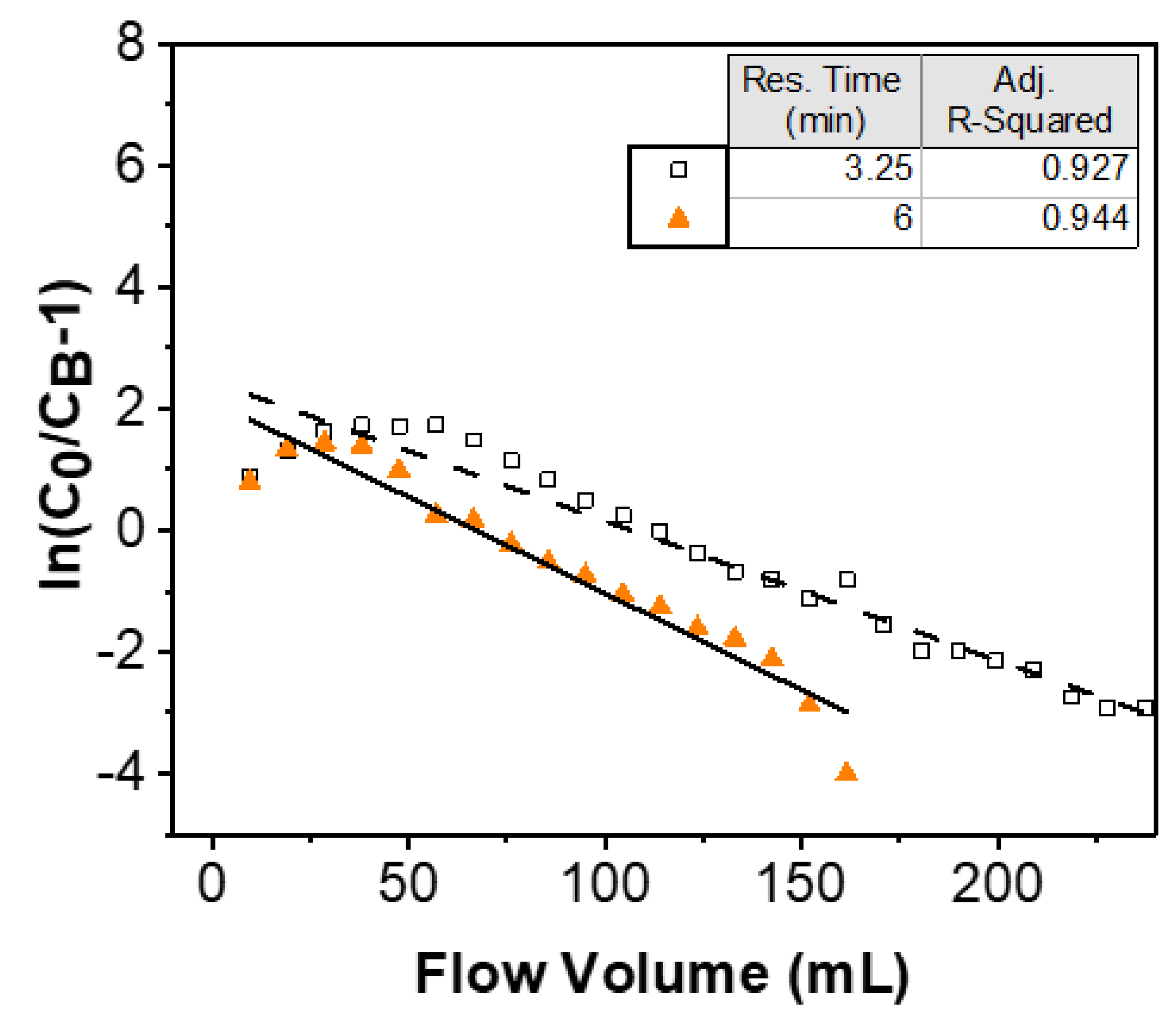
3.2. Adams–Bohart Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Relevant Variables | |
| k | kinetic constant (g mg−1 min−1) |
| qe | equilibrium concentration (mg g−1) |
| qt | concentration at time t (mg g−1) |
| t | time (min) |
| CB | breakthrough concentration (mg cm−3) |
| C | sorbate concentration in bulk (mg cm−3) |
| C0 | initial sorbate concentration in feed (mg cm−3) |
| kAB | Adams–Bohart rate constant (cm3 mg−1 s−1) |
| M | mass of adsorbent (g) |
| N0 | sorption capacity per unit volume of fixed bed (mg cm−3) |
| q | sorbate concentration in adsorbent (mg g−1) |
| q0 | sorption capacity per unit mass of adsorbent (mg g−1) |
| Q | flow rate (cm3 s−1) |
| tB | breakthrough time (s) |
| u | superficial velocity (cm s−1) |
| ν | interstitial velocity (cm s−1) |
| V | volume of solution (mL) |
| Z | total bed depth (cm) |
| ε | column void fraction |
| ρP | apparent adsorbent density (g cm−3) |
References
- Liu, Y.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Mackebee, W.G.; Ruhl, L.; Vengosh, A.; Hsu-Kim, H. Selenium Speciation in Coal Ash Spilled at the Tennessee Valley Authority Kingston Site. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14001–14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, S.J.; Jones, D.S.; Stojak, A.R.; Carriker, N.E. Ecological risk assessment for residual coal fly ash at Watts Bar Reservoir, Tennessee: Site setting and problem formulation. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2015, 11, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamkhash, A.; Srivastava, V.; Ghosh, T.; Akdogan, G.; Ganguli, R.; Aggarwal, S. Mining-related selenium contamination in Alaska, and the state of current knowledge. Minerals 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemly, A.D. Aquatic selenium pollution is a global environmental safety issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimalt, J.O.; Ferrer, M.; Macpherson, E. The mine tailing accident in Aznalcollar. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 242, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B. Chemical and microbiological characteristics of mineral spoils and drainage waters at abandoned coal and metal mines. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2003, 3, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deonarine, A.; Kolker, A.; Doughten, M.W. Trace Elements in Coal Ash; US Geological Survey: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 2327–6932. [Google Scholar]
- Hartuti, S.; Kambara, S.; Takeyama, A.; Kumabe, K.; Moritomi, H. Direct quantitative analysis of arsenic in coal fly ash. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, S.F.; Ivancevic, M.R.; Yan, J.; Naskar, A.K.; Levine, A.M.; Lee, R.J.; Tsouris, C.; Paranthaman, M.P. Magnetic adsorbents for selective removal of selenite from contaminated water. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, M.F.F.; Lee, V.K.C.; McKay, G. Simplified fixed bed column model for adsorption of organic pollutants using tapered activated carbon columns. Desalination 2008, 218, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Gönen, F. Biosorption of phenol by immobilized activated sludge in a continuous packed bed: Prediction of breakthrough curves. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Wang, K.; Gamo, T. Land and Marine Hydrogeology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Ihara, T.; Yaita, T. Mesoporous silica based novel conjugate adsorbent for efficient selenium (IV) detection and removal from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, H. Water-dispersible magnetic nanoparticle–graphene oxide composites for selenium removal. Carbon 2014, 77, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheha, R.; El-Shazly, E. Kinetics and equilibrium modeling of Se (IV) removal from aqueous solutions using metal oxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiabi, H.; Yamini, Y.; Shamsayei, M. Highly selective and efficient removal of arsenic(V), chromium(VI) and selenium(VI) oxyanions by layered double hydroxide intercalated with zwitterionic glycine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.J.; Katz, M.J.; Wang, T.C.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Chapman, K.W.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. High Efficiency Adsorption and Removal of Selenate and Selenite from Water Using Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7488–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption study of selenium ions from aqueous solutions using MgO nanosheets synthesized by ultrasonic method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardi, G.; Mpouras, T.; Dermatas, D.; Verdone, N.; Polydera, A.; Di Palma, L. Nanomaterials application for heavy metals recovery from polluted water: The combination of nano zero-valent iron and carbon nanotubes. Competitive adsorption non-linear modeling. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakpour, H.; Younesi, H.; Mohammadhosseini, M. Two-stage biosorption of selenium from aqueous solution using dried biomass of the baker’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A. Biosorption of selenium from aqueous solution by green algae (Cladophora hutchinsiae) biomass: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettem, K.; Almusallam, A.S. Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies on the Biosorption of Selenium (IV) Ions onto Ganoderma Lucidum Biomass. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Artal, R.; García-Amorós, J.; Sepúlveda, B.; Gómez, E.; Nogués, J.; Philippe, L. Hybrid Ni@ZnO@ZnS-Microalgae for Circular Economy: A Smart Route to the Efficient Integration of Solar Photocatalytic Water Decontamination and Bioethanol Production. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.M. Review of Available Technologies for the Removal of Selenium from Water; Final Report for North American Metals Council: Washington, DC, USA, June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Keijer, T.; Bakker, V.; Slootweg, J.C. Circular chemistry to enable a circular economy. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Saenz-Arana, R.; Hernandez, C.; Guinto, T.; Ahsan, M.A.; Bragg, D.T.; Wang, H.; Alvarado-Tenorio, B.; Noveron, J.C. Conversion of waste tire rubber into a high-capacity adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue, methyl orange, and tetracycline from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D. Pseudo-second-order kinetic equations for modeling adsorption systems for removal of lead ions using multi-walled carbon nanotube. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2013, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooney David, O. Adsorption Design for Wastewater Treatment; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.-S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.H. Fixed bed sorption: Setting the record straight on the Bohart–Adams and Thomas models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, D.; Davis, J.; Anderson, L.; Rea, B. Transport of chromium and selenium in a pristine sand and gravel aquifer: Role of adsorption processes. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.A.; Qazi, I.A.; Khalid, I. Removal of heavy metals through adsorption using sand. J. Environ. Sci. 2003, 15, 413–416. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, A.; DasGupta, S.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Batch and column study: Adsorption of arsenate using untreated laterite as adsorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Preparation and characterization of a novel chitosan/Al2O3/magnetite nanoparticles composite adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies of Methyl Orange adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


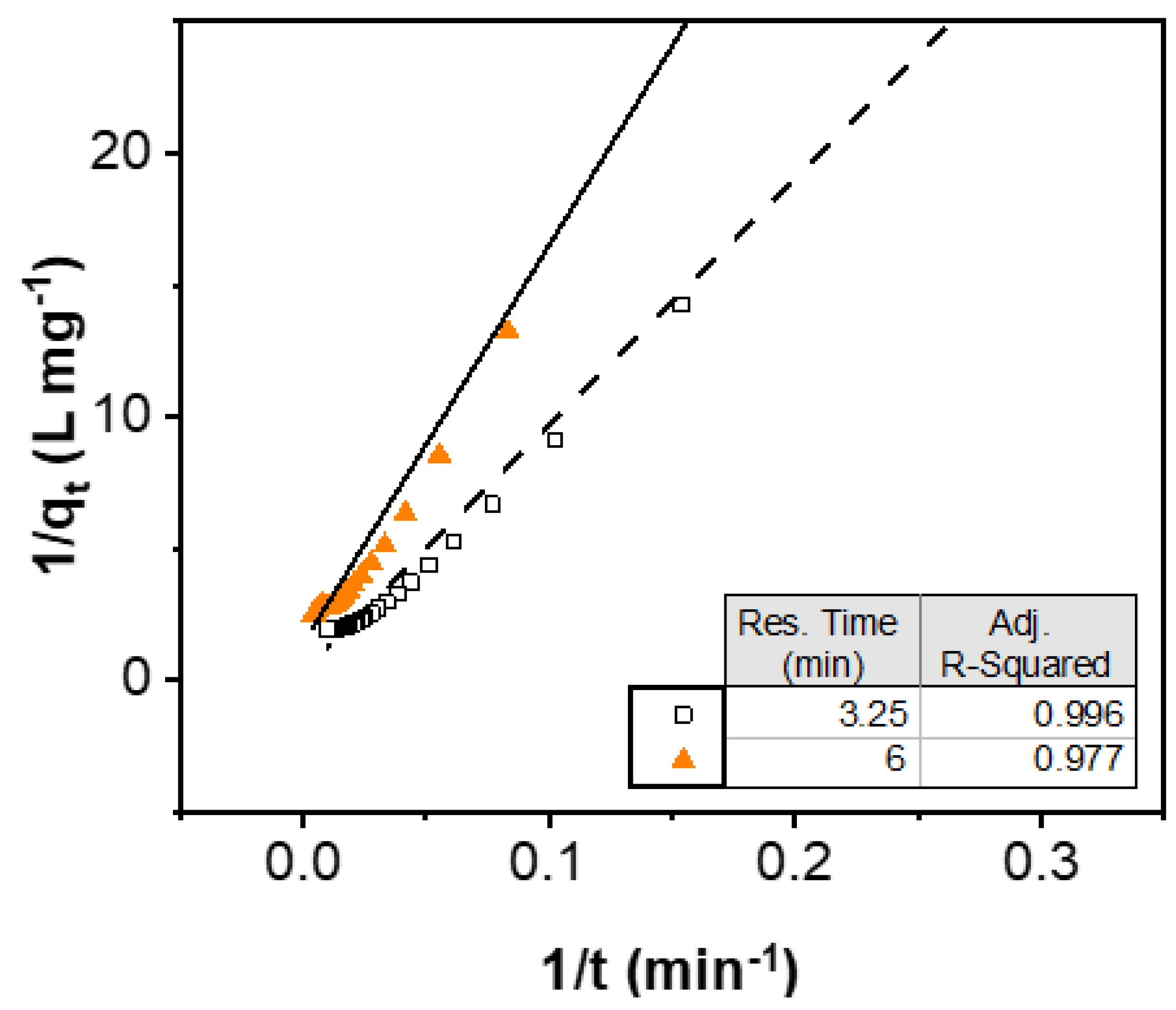
| Residence Time (min) | Theoretical Se Uptake (mg g−1) | Observed Se Uptake (mg g−1) | Kinetic Constant (g mg−1 min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.25 | 3.305 | 0.513 | 0.001 |
| 6 | 0.724 | 0.407 | 0.013 |
| Residence Time (min) | Equation Used | kAB (mL/mg/min) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.25 | 9 | 0.011 |
| 10 | 0.013 | |
| 6 | 9 | 0.009 |
| 10 | 0.009 |
| Residence Time (min) | Equation Used | kAB (mL/mg/min) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.25 | 9 | 0.002 |
| 10 | 2.167 | |
| 6 | 9 | 0.005 |
| 10 | 4.661 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, A.; Evans, S.F.; Tsouris, C.; Paranthaman, M.P. Magnetic Sorbent for the Removal of Selenium(IV) from Simulated Industrial Wastewaters: Determination of Column Kinetic Parameters. Water 2020, 12, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051234
Ying A, Evans SF, Tsouris C, Paranthaman MP. Magnetic Sorbent for the Removal of Selenium(IV) from Simulated Industrial Wastewaters: Determination of Column Kinetic Parameters. Water. 2020; 12(5):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051234
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Andrew, Samuel F. Evans, Costas Tsouris, and M. Parans Paranthaman. 2020. "Magnetic Sorbent for the Removal of Selenium(IV) from Simulated Industrial Wastewaters: Determination of Column Kinetic Parameters" Water 12, no. 5: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051234
APA StyleYing, A., Evans, S. F., Tsouris, C., & Paranthaman, M. P. (2020). Magnetic Sorbent for the Removal of Selenium(IV) from Simulated Industrial Wastewaters: Determination of Column Kinetic Parameters. Water, 12(5), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051234







