Countrywide Groundwater Quality Trend and Suitability for Use in Key Sectors of Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
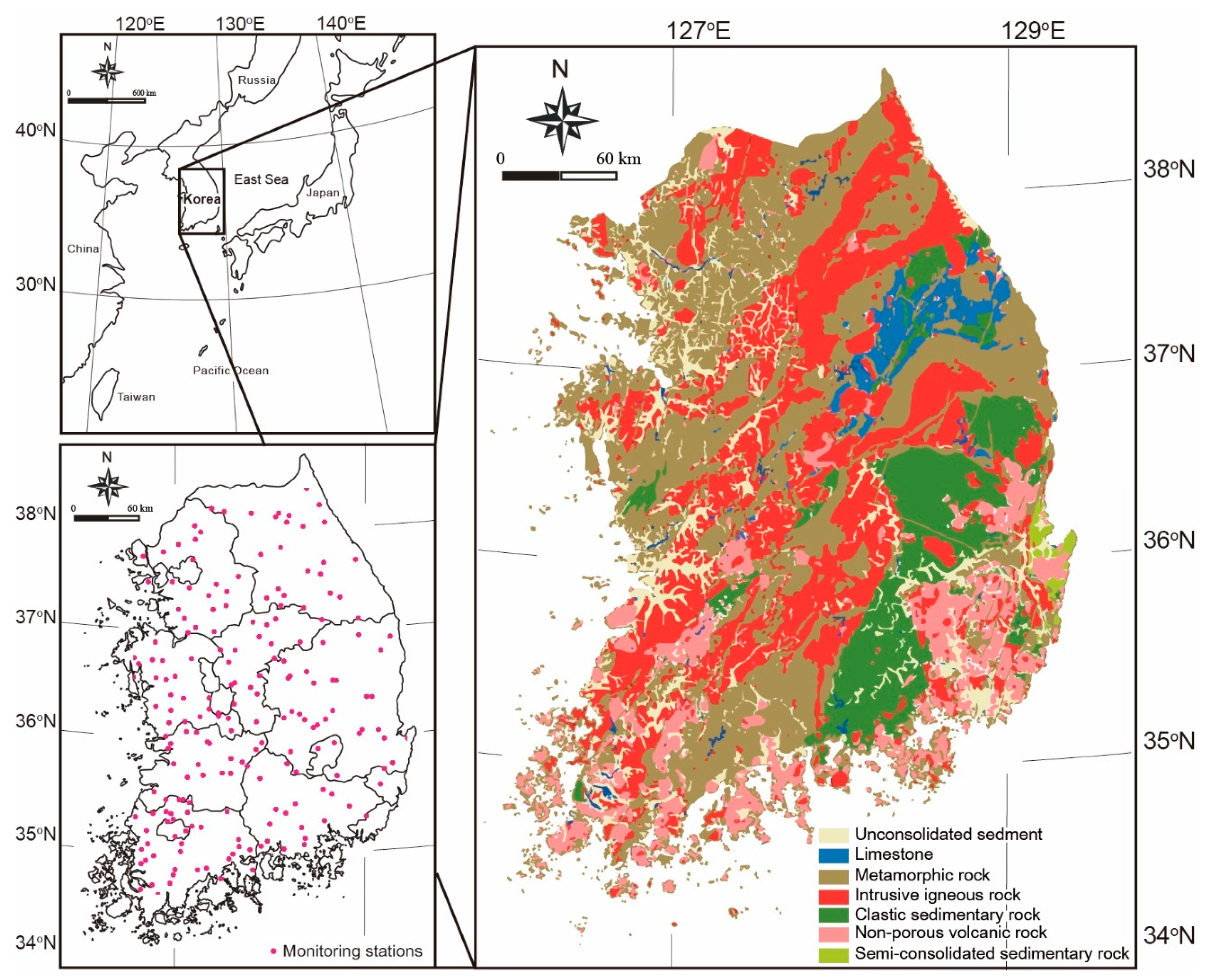
2.1. Study Area Location and Hydrometeorology
2.2. Geological Settings
2.3. Data Collection and Analysis
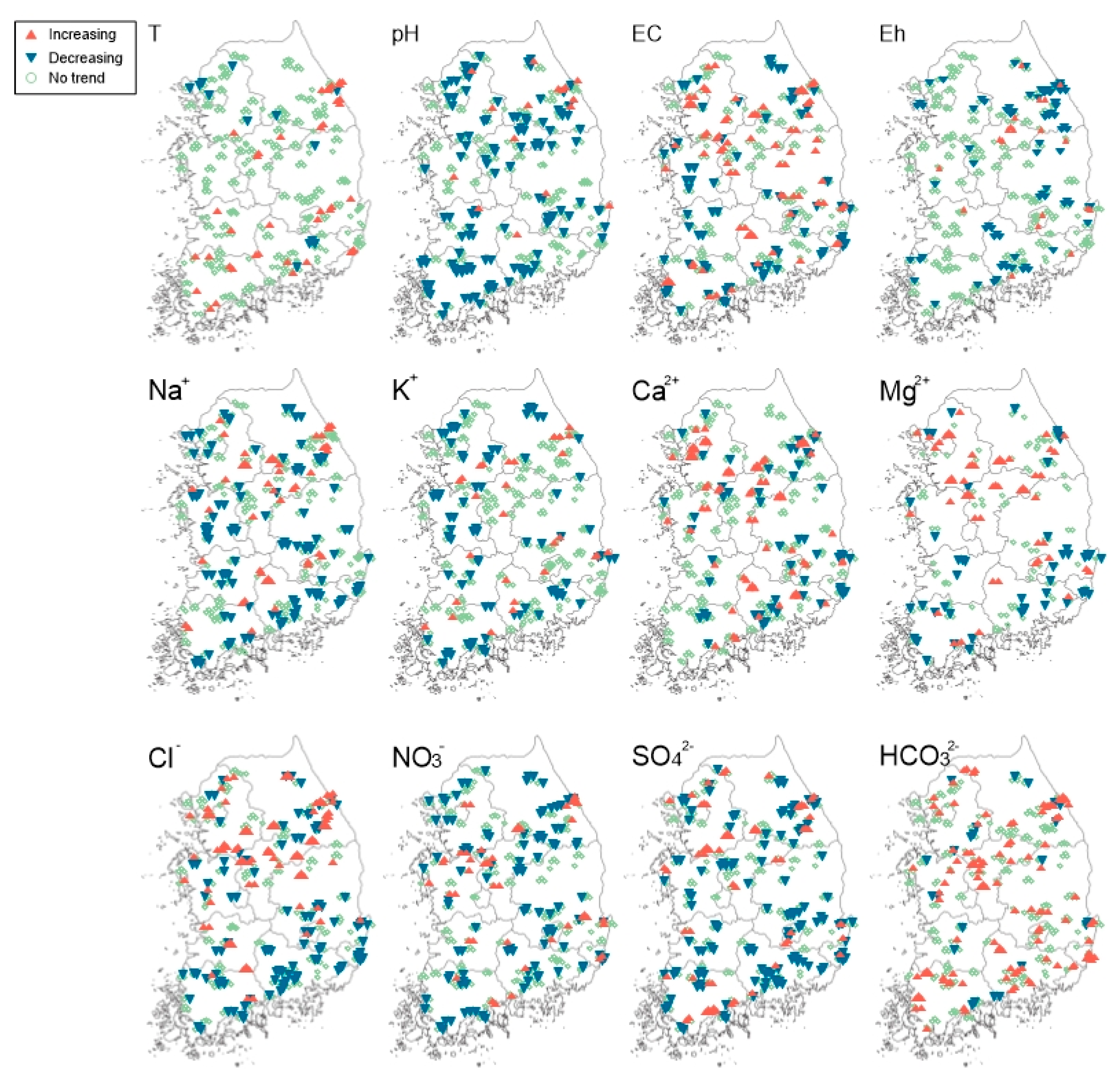
2.4. Statistical Trend Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of Groundwater Suitability
- The EC values in groundwater were compared with EC based classification (from unfit to excellent for irrigation) given by Richard [37].
- The Na % was calculated by using following equation given by Wilcox [39]:
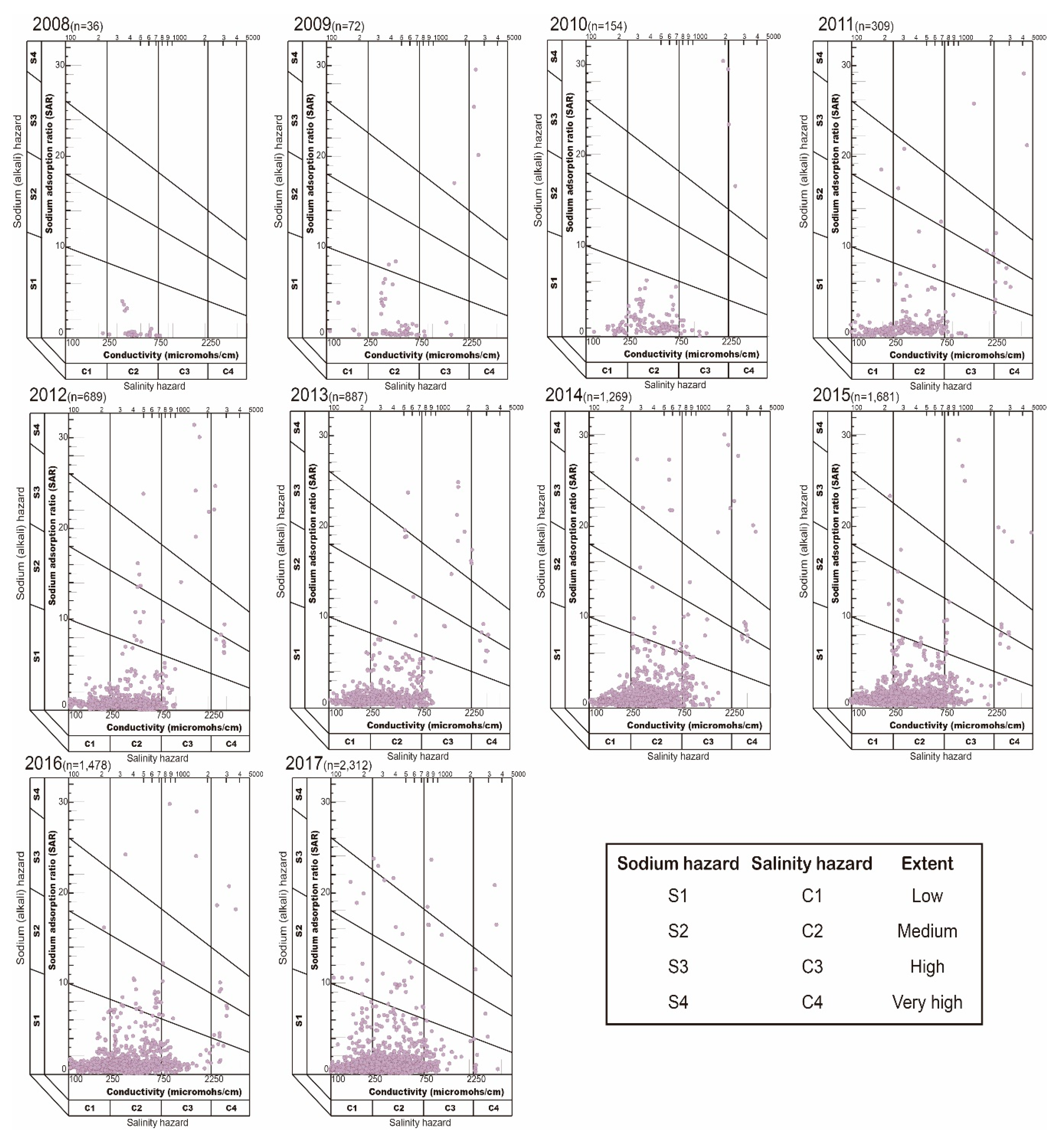
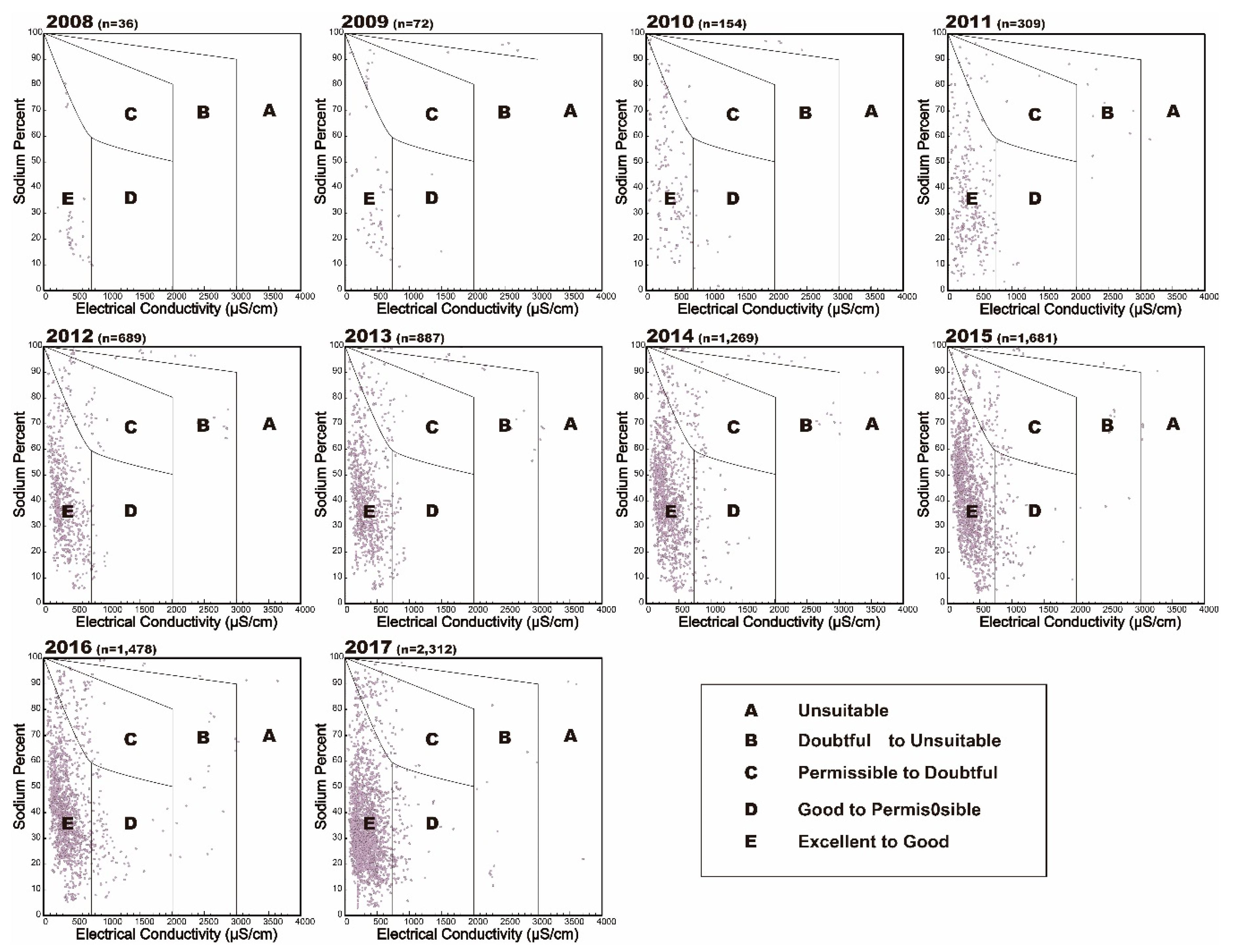
- The suitability class of groundwater data were also described using a USSL diagram that specifies the combined effect of salinity hazard (EC) and sodium hazard (SAR) [2]. Wilcox diagram was used to calculate combined effect of sodium hazard as sodium percent (Na+ %) and salinity hazard (EC), to evaluate groundwater suitability for irrigation [39].
3. Results and Discussion
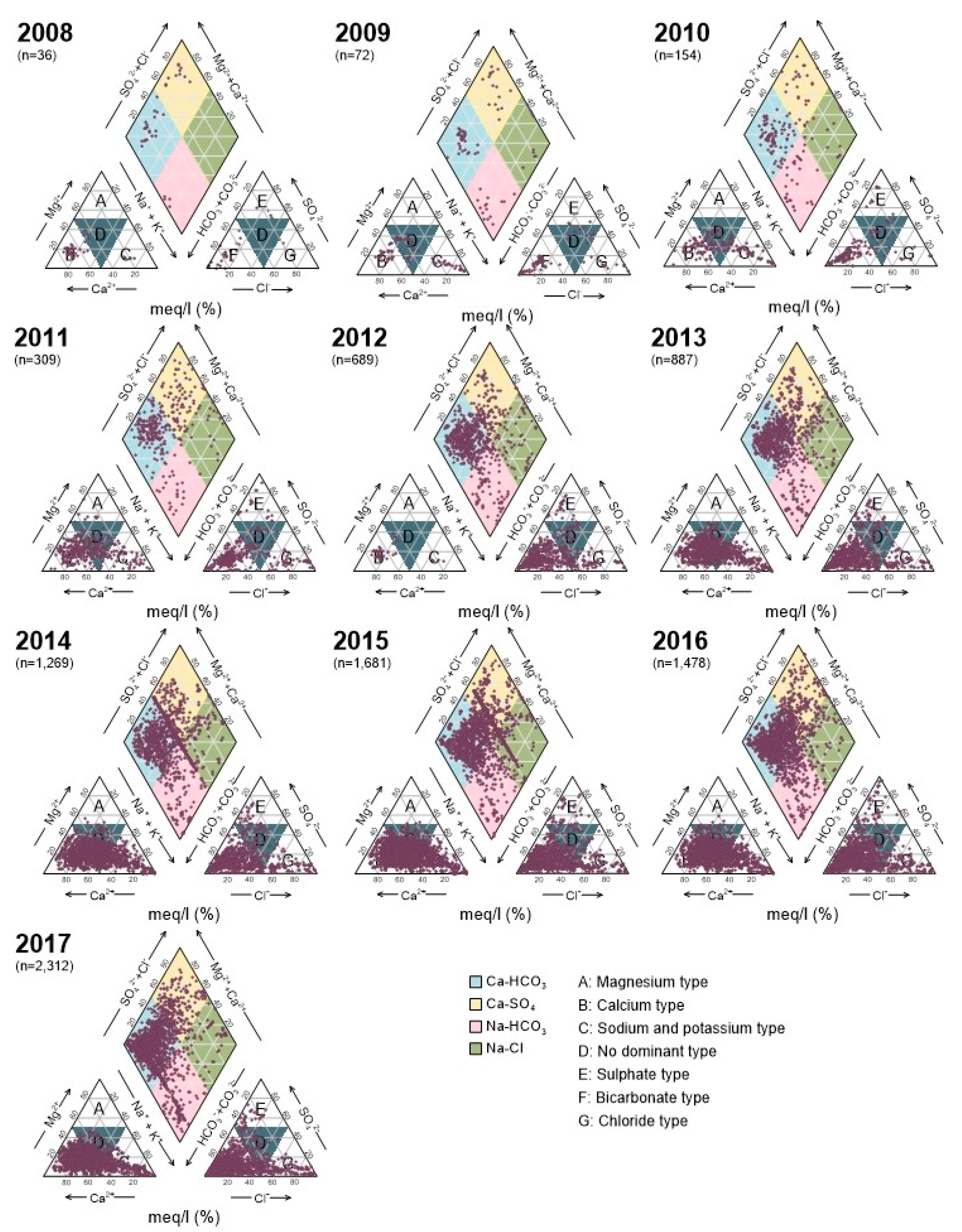
3.1. Nationwide Groundwater Chemistry
3.2. Trend Analysis of Groundwater Quality Parameters
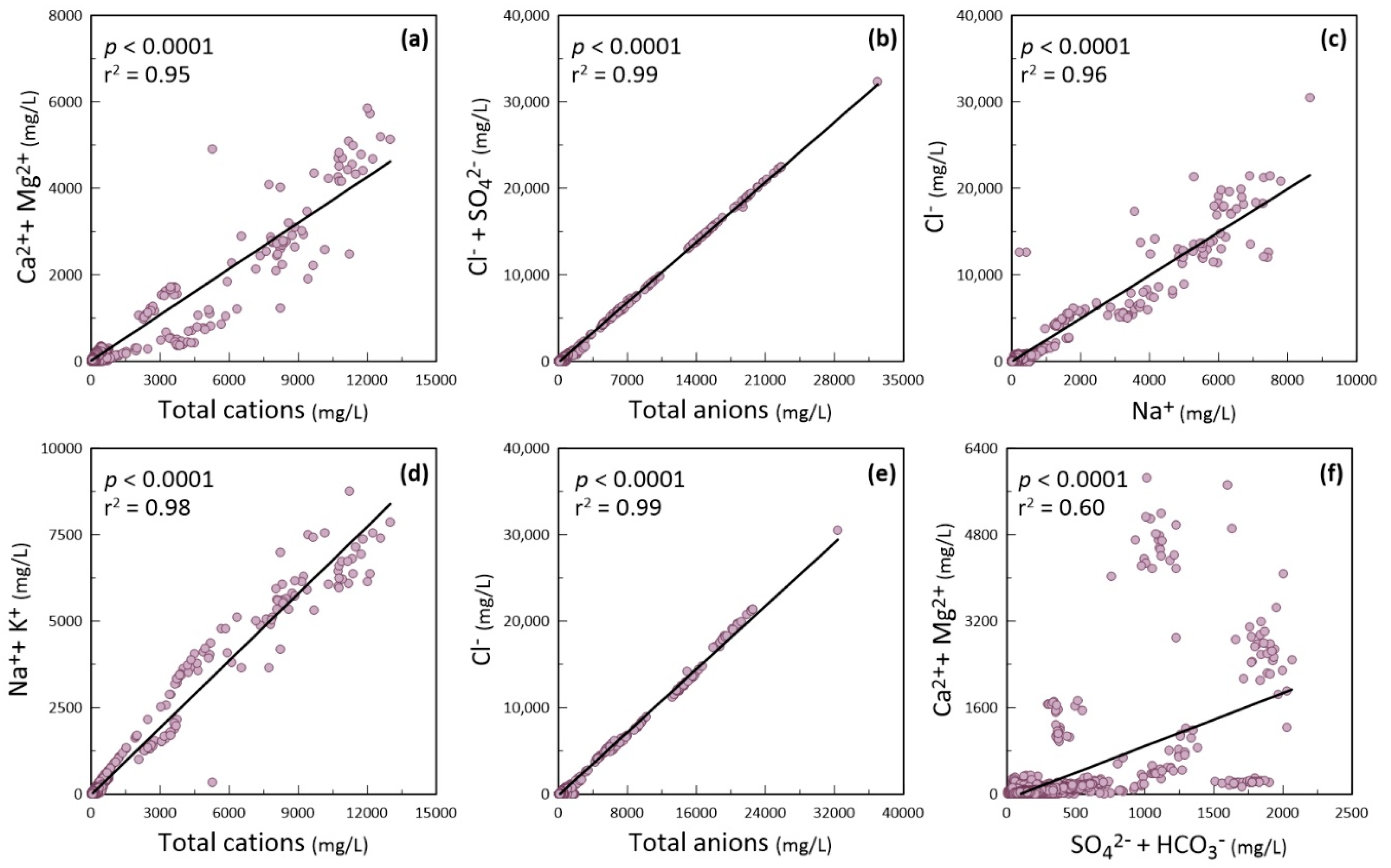
Bivariate Plots and Geochemistry of Water Quality Parameters
3.3. Groundwater Suitability
3.3.1. Suitability for Drinking
3.3.2. Suitability for Irrigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prasanth, S.S.; Magesh, N.; Jitheshlal, K.; Chandrasekar, N.; Gangadhar, K. Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the coastal stretch of Alappuzha District, Kerala, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staff, U.S.L. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. USDA Agric. Handb. 1954, 60, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, I.W.; Bae, D.H.; Kim, G. Recent trends of mean and extreme precipitation in Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.-H.; Hayes, M.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Tadesse, T.; Wilhite, D.A. Drought hazard assessment in the context of climate change for South Korea. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kwon, K.D.; Raza, M. Current water uses, related risks, and management options for Seoul megacity, Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kwon, K.D. Estimation of quantitative spatial and temporal distribution for groundwater storage in agricultural basin of Korea: Implications for rational water use. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KNCLD. Korea National Committee on Large Dams. Available online: http://www.kncold.or.kr/eng/ds6_1.html. (accessed on 12 December 2018).
- Lee, J.-Y.; Raza, M.; Park, Y.-C. Current status and management for the sustainable groundwater resources in Korea. Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2018, 41, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kwon, K. Current status of groundwater monitoring networks in Korea. Water 2016, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.; Hamm, S.-Y.; Jang, S.; Cheong, J.-Y.; Kim, G.-B. Relationship between groundwater and climate change in South Korea. Geosci. J. 2014, 18, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Hussain, F.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shakoor, M.B.; Kwon, K.D. Groundwater status in Pakistan: A review of contamination, health risks, and potential needs. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1713–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoye, S.; Fontaine, C.; Gaye, C.; Razack, M. Groundwater quality and suitability for different uses in the Saloum area of Senegal. Water 2018, 10, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.; Farooqi, A.; Niazi, N.K.; Ahmad, A. Geochemical control on spatial variability of fluoride concentrations in groundwater from rural areas of Gujrat in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirataee, B.; Zeinalzadeh, K. Trends analysis of quantitative and qualitative changes in groundwater with considering the autocorrelation coefficients in west of Lake Urmia, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.W.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, H.G. Variation of stream water quality and baseflow contribution from groundwater during rainfall event in the Haean basin. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2015, 51, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Lee, J.-Y. Factors affecting spatial pattern of groundwater hydrochemical variables and nitrate in agricultural region of Korea. Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2019, 42, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Song, S.-H. Evaluation of groundwater quality in coastal areas: Implications for sustainable agriculture. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Jeon, W.-H.; Lee, K.-K. Groundwater environment in Seoul, Republic of Korea. In Groundwater Environment in Asian Cities; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 413–449. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, G.-T.; Yun, S.-T.; Choi, B.-Y.; Yu, S.-Y.; Jo, H.-Y.; Mayer, B.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-Y. Hydrochemistry of urban groundwater, Seoul, Korea: The impact of subway tunnels on groundwater quality. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2008, 101, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-C.; Jo, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-Y. Trends of groundwater data from the Korean National groundwater monitoring stations: Indication of any change? Geosci. J. 2011, 15, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaown, D.; Hyun, Y.; Bae, G.-O.; Oh, C.W.; Lee, K.-K. Evaluation of spatio-temporal trends of groundwater quality in different land uses using Kendall test. Geosci. J. 2012, 16, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Park, S.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Jo, H.-J.; Kim, J.-I.; Lee, G.-M.; Shin, I.-K.; Kim, T.-S. Hydrochemistry for the assessment of groundwater quality in Korea. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2017, 6, 72576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.; Venkatramanan, S.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.; Ramkumar, T. Influence of hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of suitability for groundwater uses in Busan City, Korea. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.-S.; Kim, G. Seasonal and spatial variations of tritium in precipitation in Northeast Asia (Korea) over the last 20 years. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KMA. Korea Meteorological Administration, Rainfall. Available online: http://web.kma.go.kr/eng/index.jsp (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Groundwater Management Basic Plan; Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs (MLTMA): Sejong, Korea, 2012; p. 159.
- Korea Ministry of Environment. A Master Plan for Expansion and Revision of the Groundwater Quality Monitoring Network. Available online: http://eng.me.go.kr/eng/web/main.do (accessed on 5 December 2018).
- Mann, H. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M. Rank Correlation Measures; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Tabari, H.; Abghari, H.; Hosseinzadeh Talaee, P. Temporal trends and spatial characteristics of drought and rainfall in arid and semiarid regions of Iran. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3351–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampata, J.M.; Parida, B.P.; Moalafhi, D. Trend analysis of rainfall in the headstreams of the Zambezi River Basin in Zambia. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2008, 33, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis, 3; confidence regions for the parameters of polynomial regression equations. Indag. Math. 1950, 1, 467–482. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Some’e, B.S.; Ezani, A.; Tabari, H. Spatiotemporal trends and change point of precipitation in Iran. Atmos. Res. 2012, 113, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sayemuzzaman, M.; Jha, M.K. Seasonal and annual precipitation time series trend analysis in North Carolina, United States. Atmos. Res. 2014, 137, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 216, pp. 303–304.
- Richard, L. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkaline Soils, USDA; USA Government, Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; p. 60.
- Todd, D.K. Ground Water Hydrology; Education Revolucionaria, El Instituto Cubano del Libro: La Habana, Cuba, 1970; p. 336. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; USA Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955; pp. 1–19.
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Zahid, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.; Akter, Y.; Shammi, M.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Roy, B. Investigation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the south central part of the coastal region in Bangladesh. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, M.; Shimada, J.; Uemura, T. Transient effects of surface temperature and groundwater flow on subsurface temperature in Kumamoto Plain, Japan. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2003, 28, 477–486. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.M.; Kwon, E.H.; Woo, N.C. Natural and human-induced drivers of groundwater sustainability: A case study of the Mangyeong river basin in Korea. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, D.A.; Rishi, M.S.; Keesari, T. Evaluation of groundwater quality and suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in southwest Punjab, India using hydrochemical approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3137–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvakumar, S.; Ramkumar, K.; Chandrasekar, N.; Magesh, N.; Kaliraj, S. Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and irrigational use in the Southern Tiruchirappalli district, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J. Aquatic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 1022. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.; Keesari, T.; Mohokar, H.; Sinha, U.K.; Bitra, S. Assessment of groundwater quality in hard rock aquifer of central Telangana state for drinking and agriculture purposes. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hölting, B.; Coldewey, W.G. Groundwater classifications. In Hydrogeology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, O.L. Concepts and Modeling in Ground-Water Hydrology: A Self-Paced Training Course; USA Geological Survey: Reston, VA. USA, 1991; Volume 90, p. 707.
- Hosseinifard, S.J.; Aminiyan, M.M. Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater quality for drinking and agricultural purposes: A case study in Rafsanjan plain, Iran. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2015, 7, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ako, A.A.; Shimada, J.; Hosono, T.; Ichiyanagi, K.; Nkeng, G.E.; Fantong, W.Y.; Eyong, G.E.T.; Roger, N.N. Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking, domestic, and agricultural uses in the Banana Plain (Mbanga, Njombe, Penja) of the Cameroon Volcanic Line. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-H. Mineral-water interaction and hydrogeochemistry in the Samkwang mine area, Korea. Geochem. J. 2001, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, M. Subsurface water responses to land cover/use changes: An overview. In Subsurface Hydrological Responses to Land Cover and Land Use Changes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazavi, R.; Vali, A.B.; Eslamian, S. Impact of flood spreading on groundwater level variation and groundwater quality in an arid environment. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 6, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurylyk, B.L.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B.; McKenzie, J.M. Climate change impacts on groundwater and soil temperatures in cold and temperate regions: Implications, mathematical theory, and emerging simulation tools. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Groundwater recharge and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka, S.; Ka, S.; Ra, P.; Sa, G.; CS, S. An evaluation of hydrogeochemistry of groundwater in upper Vellar sub–basin using mineral stability and solute transport modelling. Aquat. Proc. 2015, 4, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, M.; Krishnaswami, S.; Dilli, K.; Somayajulu, B.; Moore, W. Major ion chemistry of the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system: Weathering processes and fluxes to the Bay of Bengal. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Tyagi, S. Major ion chemistry of groundwater in Delhi area: Chemical weathering processes and groundwater flow regime. J. Geol. Soc. India 1996, 47, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Rajmohan, N.; Elango, L. Identification and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment in an area of the Palar and Cheyyar River Basins, Southern India. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhari, F.; Meddi, M.; Mehaiguene, M.; Razack, M. Hydrogeochemical assessment of the upper Cheliff groundwater (North West Algeria). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3043–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, R.S.; Mullican, W.F. III Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulfate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the northern Chihuahuan Desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 1997, 5, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerling, T.; Pederson, B.; Von Damm, K. Sodium-calcium ion exchange in the weathering of shales: Implications for global weathering budgets. Geology 1989, 17, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, G.S.; Keshavarzi, A.; Shit, P.K.; Omran, E.-S.E.; Bagherzadeh, A. Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and irrigation using GIS and geostatistics techniques in semiarid region of Neyshabur, Iran. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebong, E.D.; Akpan, A.E.; Emeka, C.N.; Urang, J.G. Groundwater quality assessment using geoelectrical and geochemical approaches: Case study of Abi area, southeastern Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2463–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houatmia, F.; Azouzi, R.; Charef, A.; Bédir, M. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical mechanisms evolution in Northeastern, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.; Kaushik, C.P.; Kaushik, A.; Kansal, A.; Yadav, A.K. Suitability assessment of groundwater for drinking, irrigation and industrial use in some North Indian villages. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 145, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Year (Data No.) | 2008 (36) | 2009 (72) | 2010 (154) | 2011 (309) | 2012 (689) | 2013 (887) | 2014 (1269) | 2015 (1681) | 2016 (1478) | 2017 (2312) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T 1 | Range | 9.4–21.9 | 6.5–20.1 | 4.4–22.7 | 8.2–23.7 | 5.2–24.2 | 8.1–22.9 | 10.4–25.4 | 10.8–25.3 | 11.2–21.8 | 4.7–191.0 |
| Median | 14.1 | 14.6 | 14.4 | 15.4 | 15.9 | 15.7 | 16.1 | 16.1 | 16.1 | 16.3 | |
| SD | 2.5 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 4.6 | |
| pH | Range | 5.5–8.7 | 5.4–8.5 | 5.0–8.7 | 5.6–9.2 | 5.1–10.4 | 5.2–10.4 | 4.3–10.0 | 5.0–10.0 | 3.9–10.2 | 4.4–10.8 |
| Median | 7.0 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 7.1 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 6.6 | |
| SD | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 | |
| EC 2 | Range | 220.0–759.0 | 50.0–35,600.0 | 47.0–35,300.0 | 46.0–23,000.0 | 53.0–46,400.0 | 55.0–46,600.0 | 57.0–48,100.0 | 56.0–47,300.0 | 43.0–47,620.0 | 42.0–36,610.0 |
| Median | 414.0 | 259.0 | 349.5 | 330.0 | 305.0 | 317.0 | 327.0 | 331.0 | 334.0 | 311.0 | |
| SD | 132.1 | 4293.2 | 5178.0 | 4190.1 | 4157.5 | 3680.7 | 3401.4 | 3216.6 | 2997.2 | 986.1 | |
| Eh 3 | Range | −56.0–606.0 | −159.0–801.0 | −30.0–533.0 | −109.0–813.0 | −148.0–638.0 | −128.0–798.0 | −150.0–685.0 | −325.0–604.0 | −306.9–659.3 | −425.0–892.0 |
| Median | 415.5 | 374.5 | 331.5 | 318.0 | 291.0 | 310.0 | 322.0 | 309.0 | 280.0 | 299.5 | |
| SD | 178.3 | 206.2 | 128.9 | 142.3 | 137.5 | 130.5 | 131.2 | 115.4 | 101.5 | 98.4 | |
| TDS | Range | 121.0–418.0 | 28.0–19,580.0 | 26.0–19,415.0 | 25.0–2035.0 | 29.0–25,520.0 | 30.0–25,630.0 | 28.0–24,000.0 | 27.0–23,650.0 | 21.6–23,330.0 | 20.3–2312.0 |
| Median | 228.0 | 259.0 | 192.0 | 182.0 | 168.0 | 174.0 | 160.0 | 162.0 | 164.0 | 199.0 | |
| SD | 72.8 | 4293.2 | 2847.9 | 2304.6 | 2286.6 | 2024.4 | 1663.9 | 1587.7 | 1472.0 | 1410.0 | |
| Na+ | Range | 7.7–64.8 | 7.8–8640.0 | 0.0–7420.0 | 0.1–6350.0 | 2.9–6363.0 | 3.1–6720.0 | 1.4–7795.0 | 2.2–7480.0 | 2.3–7075.0 | 1.4–4981.0 |
| Median | 10.7 | 23.1 | 26.7 | 15.4 | 16.7 | 19.2 | 19.8 | 18.6 | 19.4 | 15.3 | |
| SD | 16.5 | 1578.1 | 921.4 | 756.7 | 667.5 | 599.2 | 571.3 | 477.2 | 455.4 | 256.2 | |
| K+ | Range | 1.3–8.5 | 0.5–114.5 | 0.5–3200.0 | 0.2–124.0 | 0.6–106.9 | 0.1–97.6 | 0.3–129.1 | 0.3–122.7 | 0.3–120.2 | 0.1–135.4 |
| Median | 3.4 | 3.9 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 1.9 | |
| SD | 1.9 | 22.6 | 257.8 | 13.0 | 12.1 | 10.0 | 9.8 | 9.2 | 8.3 | 6.8 | |
| Ca2+ | Range | 11.2–107.5 | 0.1–1832.0 | 0.1–3400.0 | 1.7–3830.0 | 0.1–2668.0 | 0.1–3155.8 | 0.1–4000.0 | 0.1–3327.0 | 0.1–2914.8 | 1.3–1506.4 |
| Median | 55.4 | 49.9 | 28.8 | 27.4 | 23.0 | 26.9 | 25.0 | 25.1 | 225.7 | 33.9 | |
| SD | 21.3 | 381.4 | 338.5 | 394.1 | 292.5 | 237.8 | 224.9 | 188.9 | 167.6 | 87.2 | |
| Mg2+ | Range | 3.0–18.3 | 0.2–824.0 | 0.3–776.0 | 0.2–2357.0 | 0.2–21,180.8 | 0.1–1731.0 | 0.1–1794.0 | 0.1–1662.0 | 0.0–1564.0 | 0.1–633.0 |
| Median | 8.9 | 14.1 | 7.2 | 7.63 | 5.9 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 7.3 | 6.4 | |
| SD | 4.4 | 170.6 | 114.3 | 218.1 | 141.0 | 116.9 | 95.0 | 97.5 | 83.0 | 32.0 | |
| Cl− | Range | 1.0–100.0 | 0.6–30,479.0 | 2.0–12,594.0 | 1.4–21,324.0 | 2.0–19,776.1 | 1.9–18,256.3 | 0.1–21,430.0 | 1.9–21,407.0 | 1.5–19,942.0 | 0.1–11,992.5 |
| Median | 12.0 | 18.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 12.7 | 14.3 | 13.4 | 14.3 | 14.0 | 13.1 | |
| SD | 23.6 | 4309.3 | 1907.9 | 2535.7 | 1722.8 | 1527.7 | 1442.7 | 1244.5 | 1154.4 | 553.9 | |
| NO3− | Range | 0.1–170.9 | 0.1–335.6 | 0.1–344.0 | 0.1–325.4 | 0.1–248.9 | 0.1–218.5 | 0.1–220.1 | 0.1–227.3 | 0.1–368.9 | 0.1–327.8 |
| Median | 23.3 | 8.2 | 5.6 | 6.2 | 7.9 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 6.5 | 4.8 | |
| SD | 47.4 | 63.7 | 60.8 | 46.2 | 28.9 | 31.0 | 29.0 | 26.9 | 29.0 | 22.0 | |
| SO42− | Range | 0.1–92.7 | 0.1–1817.0 | 0.1–1909.0 | 0.1–1921.0 | 0.1–1863.5 | 0.1–1854.5 | 0.1–1950.0 | 0.1–1821.9 | 1.9–1983.2 | 0.1–1612.5 |
| Median | 24.5 | 29.0 | 18.7 | 19.0 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 14.6 | 14.5 | 14.7 | 11.9 | |
| SD | 28.1 | 397.5 | 296.4 | 255.3 | 171.3 | 154.4 | 142.6 | 125.1 | 125.0 | 69.9 | |
| CO32− | Range | 0.1–1.5 | 0.1–23.0 | 0.1–10.0 | 0.1–32.0 | 0.1–118.0 | 0.1–178.0 | 0.1–111.0 | 0.1–89.0 | 0.1–83.0 | 0.1–121.8 |
| Median | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| SD | 0.2 | 2.7 | 3.5 | 1.9 | 5.8 | 8.7 | 5.5 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 4.1 | |
| HCO3− | Range | 23.2–200.0 | 13.0–290.0 | 10.0–266.0 | 2.0–804.0 | 10.0–825.0 | 8.0–881.0 | 0.1–1095.0 | 1.0–974.0 | 0.0–990.0 | 0.1–940.3 |
| Median | 110.7 | 157.5 | 115.0 | 80.2 | 94.0 | 98.0 | 105.0 | 96.0 | 99.0 | 122.0 | |
| SD | 55.4 | 84.9 | 95.6 | 121.4 | 91.8 | 89.5 | 98.9 | 94.6 | 93.9 | 88.5 |
| Parameter | Trend | Mann–Kendall Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% | Z Value Range | 99% | Z Value Range | ||
| T | Increasing | 52 1 (13.1% 2) | 1.96~3.59 | 17 (4.3%) | 2.58~3.59 |
| Decreasing | 13 (3.3%) | −2.82~−2.00 | 2 (0.5%) | −2.82~−2.78 | |
| No trend | 333 (83.7%) | −1.92~1.94 | 379 (95.2%) | −2.35~2.57 | |
| pH | Increasing | 20 (5.0%) | 1.97~5.19 | 11 (2.8%) | 2.58~5.19 |
| Decreasing | 116 (29.1%) | −5.67~−1.96 | 77 (19.3%) | −5.67~−2.63 | |
| No trend | 262 (65.8%) | −1.94~1.94 | 310 (77.9%) | −2.57~2.56 | |
| EC (μS/cm) | Increasing | 78 (19.6%) | 1.97~6.62 | 50 (12.6%) | 2.74~6.62 |
| Decreasing | 71 (17.8%) | −5.42~−1.98 | 44 (11.1%) | −5.42~−2.67 | |
| No trend | 249 (62.6%) | −1.94~1.95 | 304 (76.4%) | −2.56~2.57 | |
| Eh (mV) | Increasing | 20 (5.0%) | 2.08~4.13 | 8 (2.0%) | 2.64~4.13 |
| Decreasing | 80 (20.1%) | −5.05~−1.97 | 51 (12.8%) | −5.05~−2.58 | |
| No trend | 298 (74.9%) | −1.90~1.96 | 339 (85.2%) | −2.54~2.56 | |
| Na+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 50 (12.6%) | 1.96~5.76 | 25 (6.3%) | 2.59~5.76 |
| Decreasing | 96 (24.1%) | −4.63~−1.98 | 56 (14.1%) | −4.63~−2.58 | |
| No trend | 252 (63.3%) | −1.94~1.95 | 317 (79.6%) | −2.57~2.54 | |
| K+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 32 (8.0%) | 1.96~4.46 | 16 (4.0%) | 2.64~4.46 |
| Decreasing | 75 (18.8%) | −4.86~−2.04 | 44 (11.1%) | −4.86~−2.59 | |
| No trend | 291 (73.1%) | −1.93~1.96 | 338 (84.9%) | −2.54~2.57 | |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 74 (18.6%) | 1.98~7.50 | 52 (13.1%) | 2.58~7.50 |
| Decreasing | 43 (10.8%) | −6.90~−2.01 | 22 (5.5%) | −6.90~−2.58 | |
| No trend | 281 (70.6%) | −1.96~1.95 | 324 (81.4%) | −2.54~2.57 | |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 82 (20.6%) | 1.98~5.26 | 56 (14.1%) | 2.58~5.26 |
| Decreasing | 48 (12.1%) | −4.52~−1.96 | 32 (8.0%) | −4.52~−2.81 | |
| No trend | 268 (67.3%) | −1.93~1.96 | 310 (77.9%) | −2.57~2.57 | |
| Cl− (mg/L) | Increasing | 85 (21.4%) | 1.98~7.90 | 64 (16.1%) | 2.58~7.90 |
| Decreasing | 98 (24.6%) | −6.75~−1.97 | 70 (17.6%) | −6.75~−2.58 | |
| No trend | 215 (54.0%) | −1.95~1.85 | 264 (66.3%) | −2.56~2.48 | |
| NO3− (mg/L) | Increasing | 46 (11.6%) | 2.01~5.77 | 30 (7.5%) | 2.63~5.77 |
| Decreasing | 96 (24.1%) | −7.03~−2.06 | 62 (15.6%) | −7.03~−2.59 | |
| No trend | 256 (64.3%) | −1.96~1.93 | 306 (76.9%) | −2.57~2.54 | |
| SO42− (mg/L) | Increasing | 65 (16.3%) | 2.00~5.44 | 49 (12.3%) | 2.59~5.44 |
| Decreasing | 123 (30.9%) | −6.21~−1.98 | 87 (21.9%) | −6.21~−2.59 | |
| No trend | 210 (52.8%) | −1.89~1.89 | 262 (65.8%) | −2.57~2.52 | |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | Increasing | 114 (28.6%) | 1.96~6.41 | 71 (17.8%) | 2.59~6.41 |
| Decreasing | 23 (5.8%) | −3.91~−1.98 | 10 (2.5%) | −3.91~−2.59 | |
| No trend | 261 (65.6%) | −1.90~1.96 | 317 (79.6%) | −2.56~2.57 | |
| Parameter | Trend | Sen’s Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% and 99% | Qmed (minimum) | Qmed (maximum) | ||
| T | Increasing | 245 (61.6%) | 0.00 | 0.30 |
| Decreasing | 132 (33.2%) | −0.50 | 0.00 | |
| No trend | 21 (5.3%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| pH | Increasing | 90 (22.6%) | 0.00 | 0.08 |
| Decreasing | 283 (71.1%) | −0.14 | 0.00 | |
| No trend | 25 (6.3%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| EC (μS/cm) | Increasing | 217 (54.5%) | 0.01 | 213.33 |
| Decreasing | 174 (43.7%) | −57.57 | −0.01 | |
| No trend | 7 (1.8%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Eh (mV) | Increasing | 135 (33.9%) | 0.09 | 11.55 |
| Decreasing | 259 (65.1%) | −19.00 | −0.13 | |
| No trend | 4 (1.0%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Na+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 159 (39.9%) | 0.00 | 49.2 |
| Decreasing | 234 (58.8%) | −34.25 | 0.00 | |
| No trend | 5 (1.3%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| K+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 135 (33.9%) | −1.26 | 2.35 |
| Decreasing | 210 (52.8%) | −2.59 | 0.78 | |
| No trend | 53 (13.3%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 230 (57.8%) | 0.01 | 53.12 |
| Decreasing | 165 (41.5%) | −0.30 | −0.01 | |
| No trend | 3 (0.8%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | Increasing | 219 (55.0%) | 0.00 | 2.67 |
| Decreasing | 159 (39.9%) | −25.45 | 0.00 | |
| No trend | 20 (5.0%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Cl− (mg/L) | Increasing | 183 (46.0%) | 0.00 | 34.56 |
| Decreasing | 205 (51.5%) | −15.60 | 0.00 | |
| No trend | 10 (2.5%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| NO3− (mg/L) | Increasing | 107 (26.9%) | 0.01 | 3.30 |
| Decreasing | 211 (53.0%) | −8.34 | 0.00 | |
| No trend | 80 (20.1%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| SO42− (mg/L) | Increasing | 145 (36.4%) | 0.00 | 20.28 |
| Decreasing | 232 (58.3%) | 0.00 | −27.70 | |
| No trend | 21 (5.3%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | Increasing | 268 (67.3%) | 0.01 | 10.32 |
| Decreasing | 111 (27.9%) | −17.2 | −0.01 | |
| No trend | 19 (4.8%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Parameter | pH | EC | TDS | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | CO32− | HCO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| EC | 0.51 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| TDS | 0.48 | 0.98 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Na+ | 0.48 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 1.00 | |||||||
| K+ | 0.39 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Ca2+ | 0.47 | 0.90 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.66 | 1.00 | |||||
| Mg2+ | 0.52 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 1.00 | ||||
| Cl− | 0.52 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.77 | 0.87 | 0.98 | 1.00 | |||
| SO42− | 0.51 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 1.00 | ||
| CO32− | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.17 | −0.12 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 1.00 | |
| HCO3− | −0.45 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 1.00 |
| Parameter | Range | Median | WHO Guideline 2011 (% Samples Exceeding Limit) | Korean Guideline (% Samples Exceeding Limit) | Effects on Human |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3.9–10.8 | 6.9 | 6.5–8.5 (33.4%) | 5.8–8.5 (7.9%) | Taste |
| EC (µS/cm) | 42.0–48,100.0 | 1325.0 | 1400 (2.6%) | − | Laxative effects |
| TDS (mg/L) | 21.6–25,630.0 | 168.0 | 1000 (28.0%) | − | Gastrointestinal |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 0.1–4000.0 | 27.8 | 200 (1.5%) | − | Kidney and bladder |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 0.1–2357.0 | 6.8 | 100 (1.5%) | − | Laxative effects |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 0.1–8640.0 | 17.8 | 200 (2.9%) | − | Taste |
| K+ (mg/L) | 0.1–3200.0 | 2.4 | 12 (3.7%) | − | Laxative effects |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 0.1–30,479.0 | 13.8 | 250 (3.0%) | 250 (3.0%) | Taste, indigestion |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 0.1–1983.2 | 14.2 | 250 (2.1%) | 200 (2.5%) | Gastrointestinal |
| Parameters | Reference | Range | Classification for Irrigation Use | Sample Number 1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (µS/cm) | Richards (1954) | 100–250 | Excellent | 2642 (29.73%) |
| 250–750 | Good | 6240 (70.21%) | ||
| 750–2250 | Doubtful | 5 (0.06%) | ||
| >2250 | Unsuitable | 0 (0.00%) | ||
| SAR | Todd (1959) and Richards (1954) | <10 | Excellent | 8649 (97.32%) |
| 10–18 | Good | 68 (0.77%) | ||
| 18–26 | Doubtful | 84 (0.95%) | ||
| >26 | Unsuitable | 86 (0.97%) | ||
| Na+ hazard (%) | Wilcox (1955) | <20 | Excellent | 1060 (11.93%) |
| 20–40 | Good | 3830 (43.10%) | ||
| 40–60 | Permissible | 2488 (28.00%) | ||
| 60–80 | Doubtful | 984 (11.07%) | ||
| >80 | Unsuitable | 525 (5.91%) | ||
| RSC | Eaton (1950) and Richards (1954) | <1.25 | Suitable | 8362 (94.09%) |
| 1.25–2.5 | Marginal | 313 (3.52%) | ||
| >2.5 | Unsuitable | 212 (2.39%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, C.; Raza, M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, B.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, R.-H.; Lee, S.-W. Countrywide Groundwater Quality Trend and Suitability for Use in Key Sectors of Korea. Water 2020, 12, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041193
Jeon C, Raza M, Lee J-Y, Kim H, Kim C-S, Kim B, Kim J-W, Kim R-H, Lee S-W. Countrywide Groundwater Quality Trend and Suitability for Use in Key Sectors of Korea. Water. 2020; 12(4):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041193
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Chanhyeok, Maimoona Raza, Jin-Yong Lee, Heejung Kim, Chang-Seong Kim, Bora Kim, Jeong-Woo Kim, Rak-Hyeon Kim, and Sun-Woo Lee. 2020. "Countrywide Groundwater Quality Trend and Suitability for Use in Key Sectors of Korea" Water 12, no. 4: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041193







