Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and the Water Quality Identification Index for the Qinhuai River Basin, East China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Water Quality Identification Index (WQII)
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Techiniques (MST)
3. Results
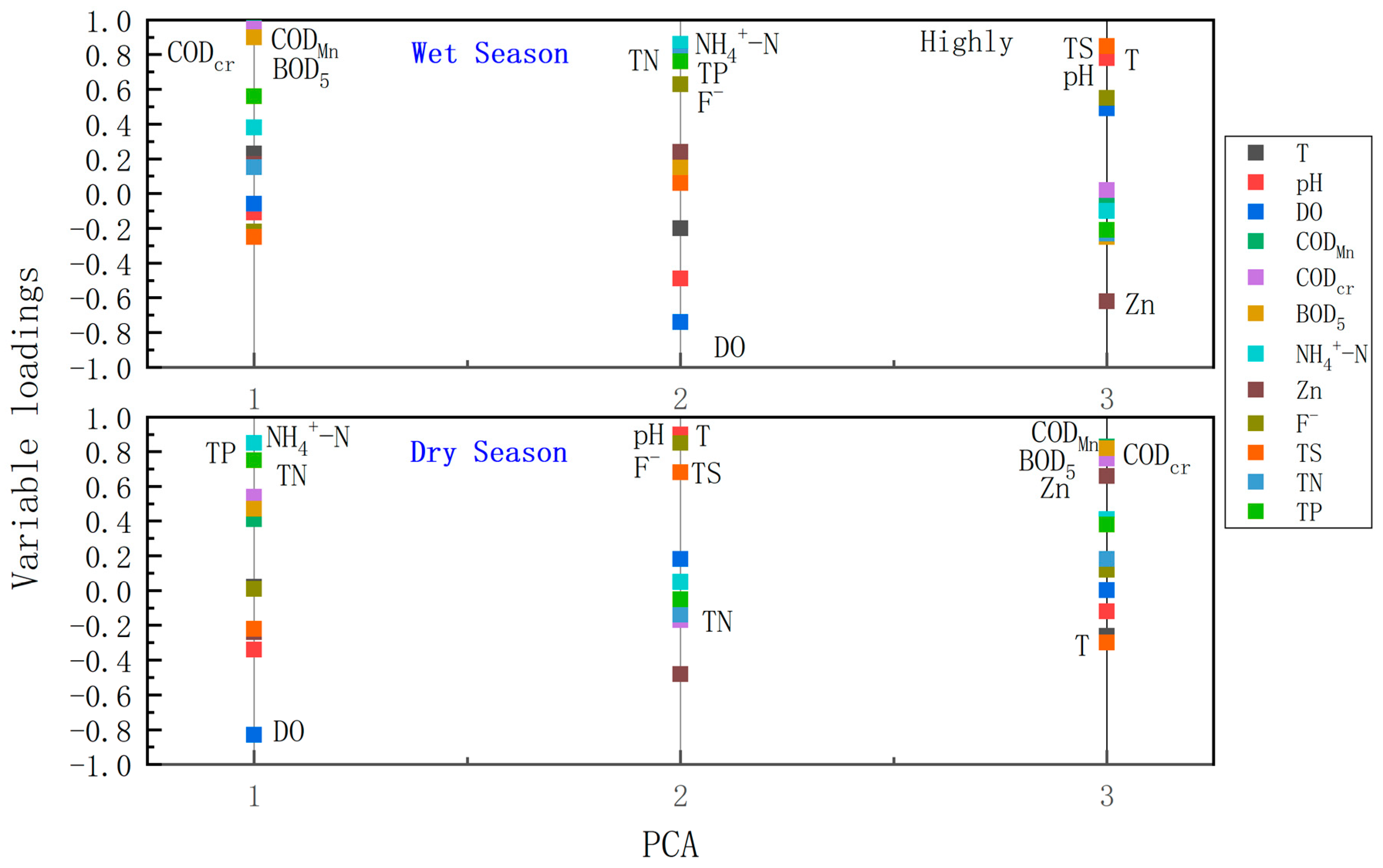
3.1. Identification of Potential Pollution Sources in Wet and Dry Seasons
3.1.1. Wet and Dry Seasons
3.1.2. Identification of Potential Pollution Sources in the Wet Season
3.1.3. Identification of Potential Pollution Sources in the Dry Season
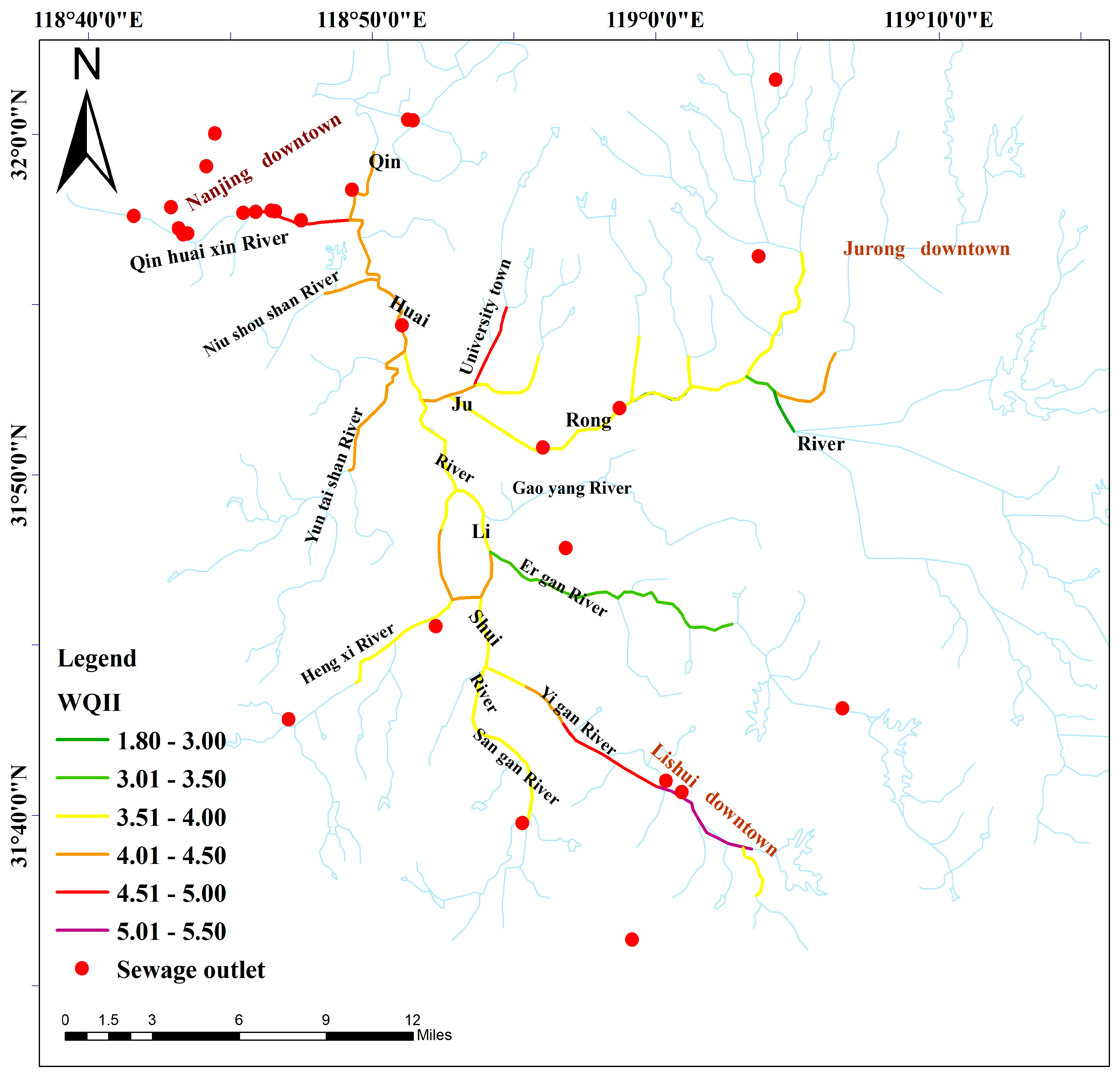
3.2. Spatiotemporal Trends of Water Quality Based on the WQII
3.2.1. Temporal Trend of Water Quality Based on the WQII
3.2.2. Spatial Pattern of Water Quality Based on the WQII
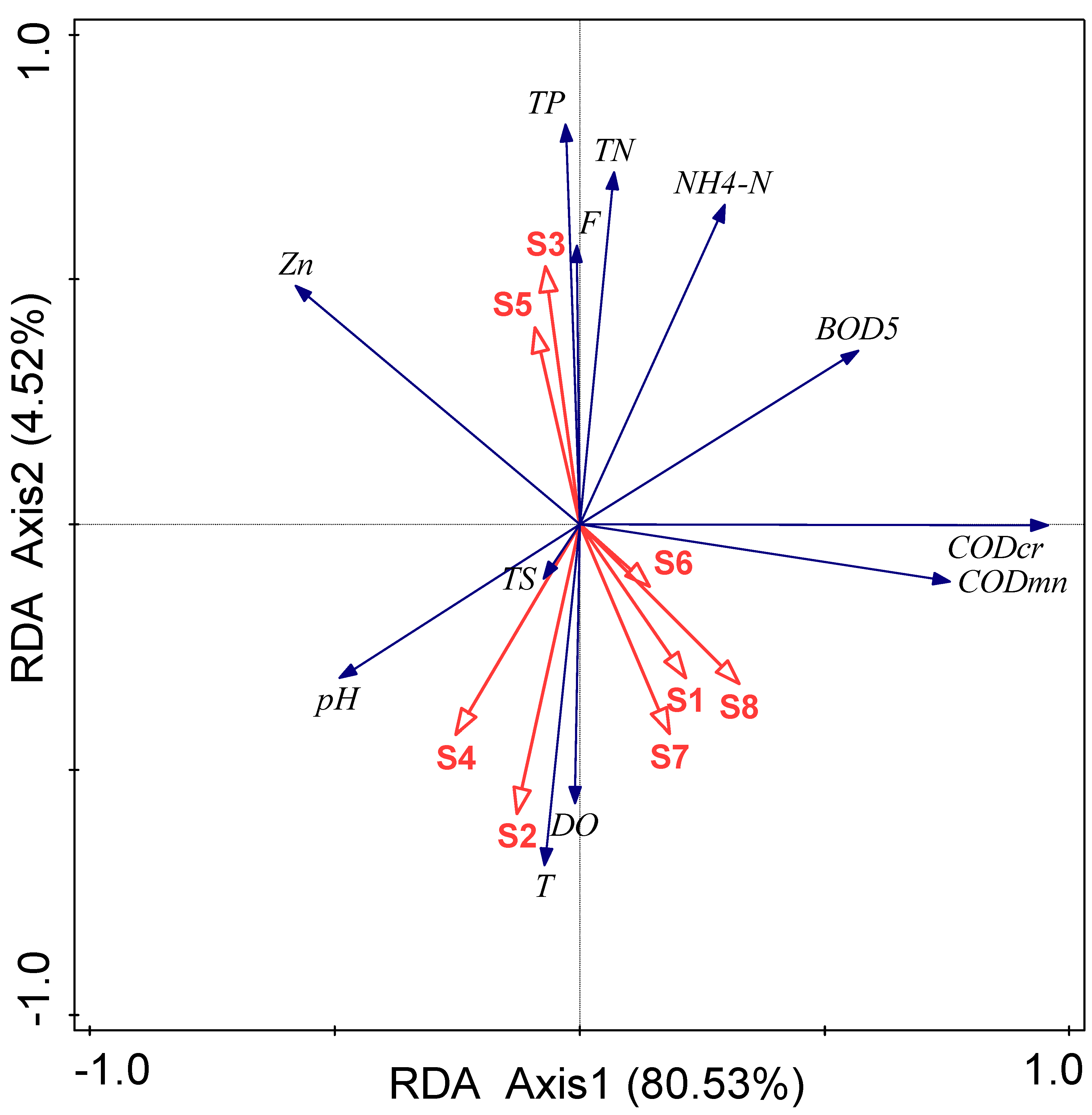
3.3. Analying Influence Factors of Water Quality Using RDA Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal Variation in Water Quality
4.2. Spatial Variation in Water Quality
4.3. Control the Pollution Sources in Wet Season
4.4. Limitation and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Flower, R.J.; Thompson, J.R. Sustaining China’s water resources. Science 2013, 339, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, R.A.; Gani, K.M. Water quality evaluation of the upper stretch of the river Jhelum using multivariate statistical techniques. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiyaka, H.A.; Mustapha, A.; Juahir, H.; Phil-Eze, P. Water quality modelling using artificial neural network and multivariate statistical techniques. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 5, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Huang, T.; Huang, H. Analyses on the temporal and spatial characteristics of water quality in a seagoing river using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study in the Duliujian River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Kumar, M.S. Use of water quality index and multivariate statistical techniques for the assessment of spatial variations in water quality of a small river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, G.H.; Yan, Z.H.; Liu, J.C.; Dong, H.K.; Jiang, R.R.; Zhou, R.R.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Nkooma, M. Occurrence, spatial-temporal distribution and ecological risks of pharmaceuticals and personal care products response to water diversion across the rivers in Nanjing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Gökot, B.; Bekleyen, A.; Şen, B. Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River Basin, Turkey. Catena 2012, 92, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques—A case study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, A.; Bombardelli, F.A.; Pitton, B.J.L.; Oki, L.R.; Haver, D.L.; Young, T.M. Uncertainty in the parameterization of sediment build-up and wash-off processes in the simulation of water quality in urban areas. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 111, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumb, A.; Sharma, T.C.; Bibeault, J.F. A review of genesis and evolution of water quality index (wqi) and some future directions. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2011, 3, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debels, P.; Figueroa, R.; Urrutia, R.; Barra, R.; Niell, X. Evaluation of water quality in the Chillán River (Central Chile) using physicochemicalparameters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 110, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannel, P.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kanel, S.; Khan, S. Application of water quality indices and dissolved oxygen as indicators for river water classification and urban impact assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquía River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, C.S.; Mitchell, T.W.; Rizvi, F.Z.; Rehman, Y.; Faisal, M.; Hasnain, S.; McInerney, M.J.; Krumholz, L.R. Exposure of soil microbial communities to chromium and arsenic alters their diversity and structure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhao, B.; Qin, J.; Peng, T. Combined multivariate statistical techniques, water pollution index (WPI) and daniel trend test methods to evaluate temporal and spatial variations and trends of water quality at Shanchong River in the Northwest Basin of Lake Fuxian, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.D.; Riegel, R.P.; de Quevedo, D.M.; Osório, D.M.M.; da Costa, G.M.; do Nascimento, C.A.; Telöken, F. Seasonal assessment and apportionment of surface water pollution using multivariate stati stical methods: Sinos River, southern Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotondrabe, F.; Ngoupayou, J.R.N.; Mfonka, Z.; Rasolomanana, E.H.; Nyangono, A.J.A.; Ako, A.A. Water quality assessment in the Betare-Oya gold mining area (East-Cameroon): Multivariate statistical analysis approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanbakhsh, M.; Birgani, Y.T.; Dastoorpoor, M.; Angali, K.A. Evaluation of Zohreh River water quality, impacted by natural and anthropogenic pollution sources, using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2019, 16, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, C.C.; Calazans, G.M.; Oliveira, S.C. Assessment of spatial variations in the surface water quality of the Velhas River Basin, Brazil, using multivariate statistical analysis and nonparametric statistics. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Muhib, M.I.; Shammi, M.; Zahid, A.; Akter, Y.; Kurasaki, M. A study of groundwater irrigation water quality in south-central Bangladesh: A geo-statistical model approach using GIS and multivariate statistics. Acta Geochim. 2017, 37, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.X.; Wang, L.C.; Wu, H.; Li, N.; Ma, L.; Zeng, C.F.; Yang, J. Impact of Yangtze River water transfer on the water quality of the Lixia River watershed, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 10, e0119720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.S.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.J.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.W. Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in Lake Poyang: The largest freshwater lake in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, E.; Colmenarejo, M.F.; Vicente, J.; Rubio, A.; García, M.G.; Travieso, L.; Borja, R. Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of basins pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 7, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, S.; Sener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankari, S.G.; Prasanna, S.M.; Madhurambal, G. Evaluation of water quality suitability for drinking using drinking water quality index in Nagapattinam district, Tamil Nadu in Southern India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 6, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.K. An index number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A water quality index: Do we dare? Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Cude, C.G. Oregon water quality index: A tool for evaluating water quality management effectiveness. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 37, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaghi, F.; Delgosha, F.; Razzaghmanesh, M.; Myersb, B. Introducing a water quality index for assessing water for irrigation purposes: A case study of the Ghezel Ozan River. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howladar, M.F.; Al Numanbakth, M.A.; Faruque, M.O. An application of water quality index (wqi) and multivariate statistics to evaluate the water quality around Maddhapara granite mining industrial area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouayti, A.; Khattacha, D.; Hilalib, M.; Nouaytiac, N.; Arabid, M. Assessment of groundwater quality using statistical techniques in high Basin of Guir (Eastern High Atlas, Morocco). Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 13, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabuk, A.; Al-Madhlom, Q.; Al-Maliki, A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Hussain, H.M.; Laue, J. Water quality assessment along Tigris river (Iraq) using water quality index (wqi) and gis software. Arab. J. Geoences 2020, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Mi, T.; Xia, L.; Yan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, Y. Understanding the patterns and mechanisms of urban water ecosystem degradation: Phytoplankton community structure and water quality in the Qinhuai river, Nanjing city, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5003–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Lai, L.J.; Yao, M.; Ma, Z.Z. Water environment quality assessment based on normal cloud-fuzzy variable set evaluation model. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 93, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, D.; Singh, S.K.; Shukla, D.N. Assessment of river water quality and ecological diversity through multivariate statistical techniques, and earth observation dataset of rivers Ghaghara and Gandak, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2017, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wang, X.; Lou, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J. Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lep, J.; Milauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hülya, B.; Hayal, B. Water pollution sources assessment by multivariate statistical methods in the Tahtali Basin, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Simeonov, V.; Stratis, J.A.; Samara, C.; Zachariadis, G.; Voutsa, D.; Anthemidis, A.; Sofoniou, M.; Kouimtzis, T. Assessment of the surface water quality in northern Greece. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, G.M.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.X. Impact of Environmental Change on Water Environmental and Hydrological-Case Study of Qinhuai River Watershed; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Zhi, J.; Lou, L.; Huang, F.; Chen, X.; Wu, J. Spatio-temporal patterns and source apportionment of pollution in Qiantang River (China) using neural-based modeling and multivariate statistical techniques. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjing Statistics Bureau (NSB). Statistical Yearbook of Nanjing (1990–2014). Available online: http://221.226.86.104/file/index.htm (accessed on 1 August 2015).
- Yilma, M.; Kiflie, Z.; Windsperger, A.; Gessese, N. Assessment and interpretation of river water quality in Little Akaki River using multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). Outline of China’s 11th Five-Year Economic and Social Development Program. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/gdzt/ghjd/quanwen/ (accessed on 24 March 2006).
- Yang, H.; Ma, M.; Thompson, J.R.; Flower, R.J. Waste management, informal recycling, environmental pollution and public health. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2018, 72, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Chou, N.T.; Wang, L. Dynamic coupling analysis of urbanization and water resource utilization systems in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Thompson, J.R.; Bright, R.M.; Astrup, R. The crushing weight of urban waste. Science 2016, 351, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wright, J.A.; Gundry, S.W. Boost water safety in rural China. Nature 2012, 484, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Paruch, L.; Chen, X.J.; van Eerde, A.; Skomedal, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, D.; Clarke, J.L. Antibiotic application and resistance in swine production in China: Current situation and future perspectives. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shen, X.Y.; Lai, L.; Huang, X.J.; Zhou, Y. Spatio-temporal variations of health costs caused by chemical fertilizer utilization in China from 1990 to 2012. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yang, H.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Jin, B.S.; Tong, C. Production and uptake of dissolved carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in overlying water of aquaculture shrimp ponds in subtropical estuaries, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21565–21578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Flower, R.J.; Thompson, J.R. Rural factories won’t fix Chinese pollution. Nature 2012, 490, 342–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.C.; Zhang, X.Q.; Siu, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.P. Flood mitigation by permeable pavements in Chinese sponge city construction. Water 2018, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kattel, G.; Arp, H.P.H.; Yang, H. Towards threshold-based management of freshwater ecosystems in the context of climate change. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Flower, R.J.; Thompson, J.R. China’s new leaders offer green hope. Nature 2013, 493, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.X.; Mao, X.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Zhao, H.Y.; Yang, H. Tracing the sources of air pollutant emissions embodied in exports in the Yangtze River Delta, China: A four-level perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Wang, X.X.; Yang, H.; Zhou, B.T.; Song, L.R.; Shang, M.S. Use statistical machine learning to detect nutrient thresholds in Microcystis blooms and microcystin management. Harmful Algae 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, K.; Shang, M.; Zhou, B.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Song, L. Application of Bayesian network including Microcystis morphospecies for microcystin risk assessment in three cyanobacterial bloom-plagued lakes, China. Harmful Algae 2019, 83, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.Z.; Yin, P.H.; Sharpley, A.N. A coupled model system to optimize the best management practices for nonpoint source pollution control. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
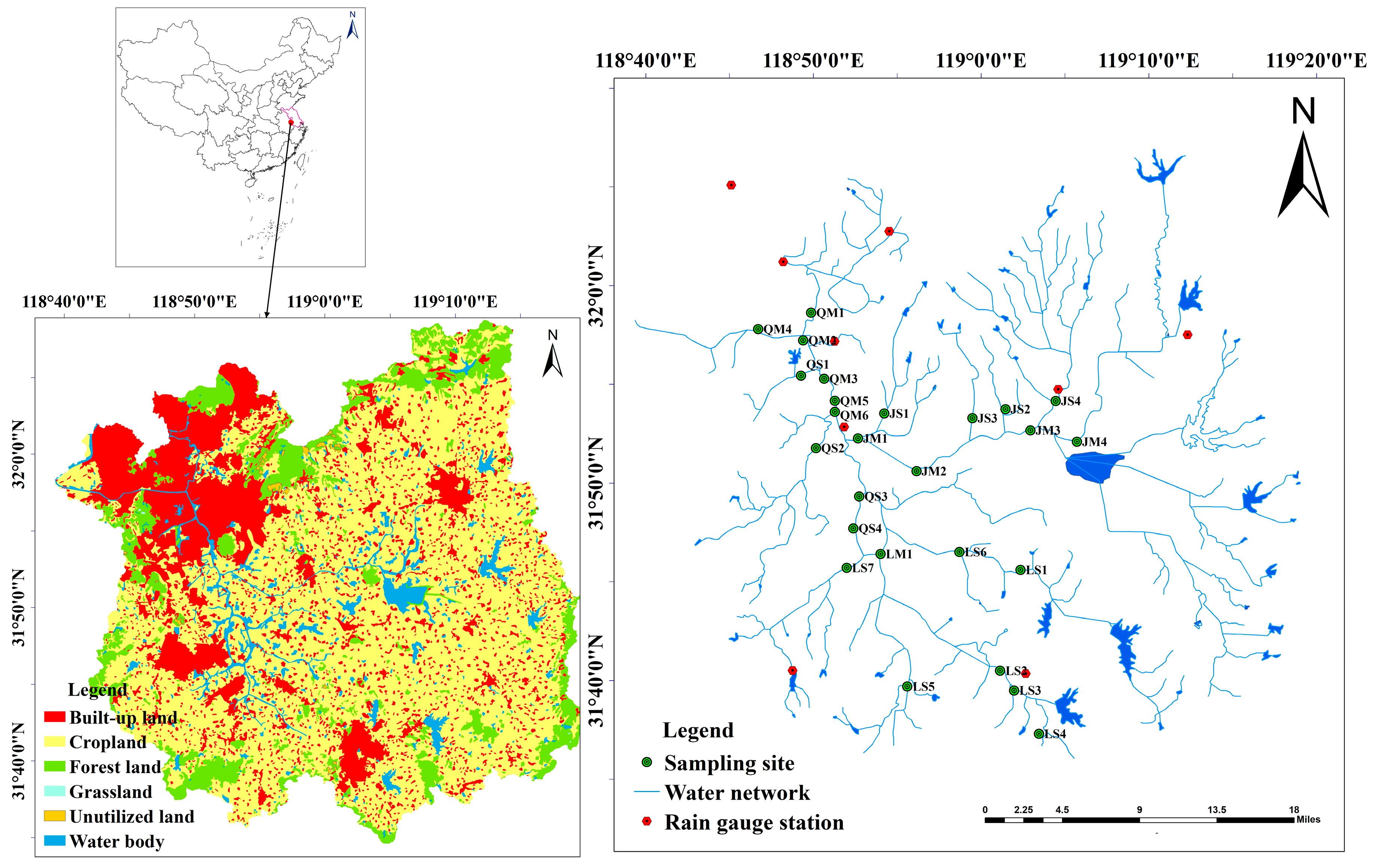
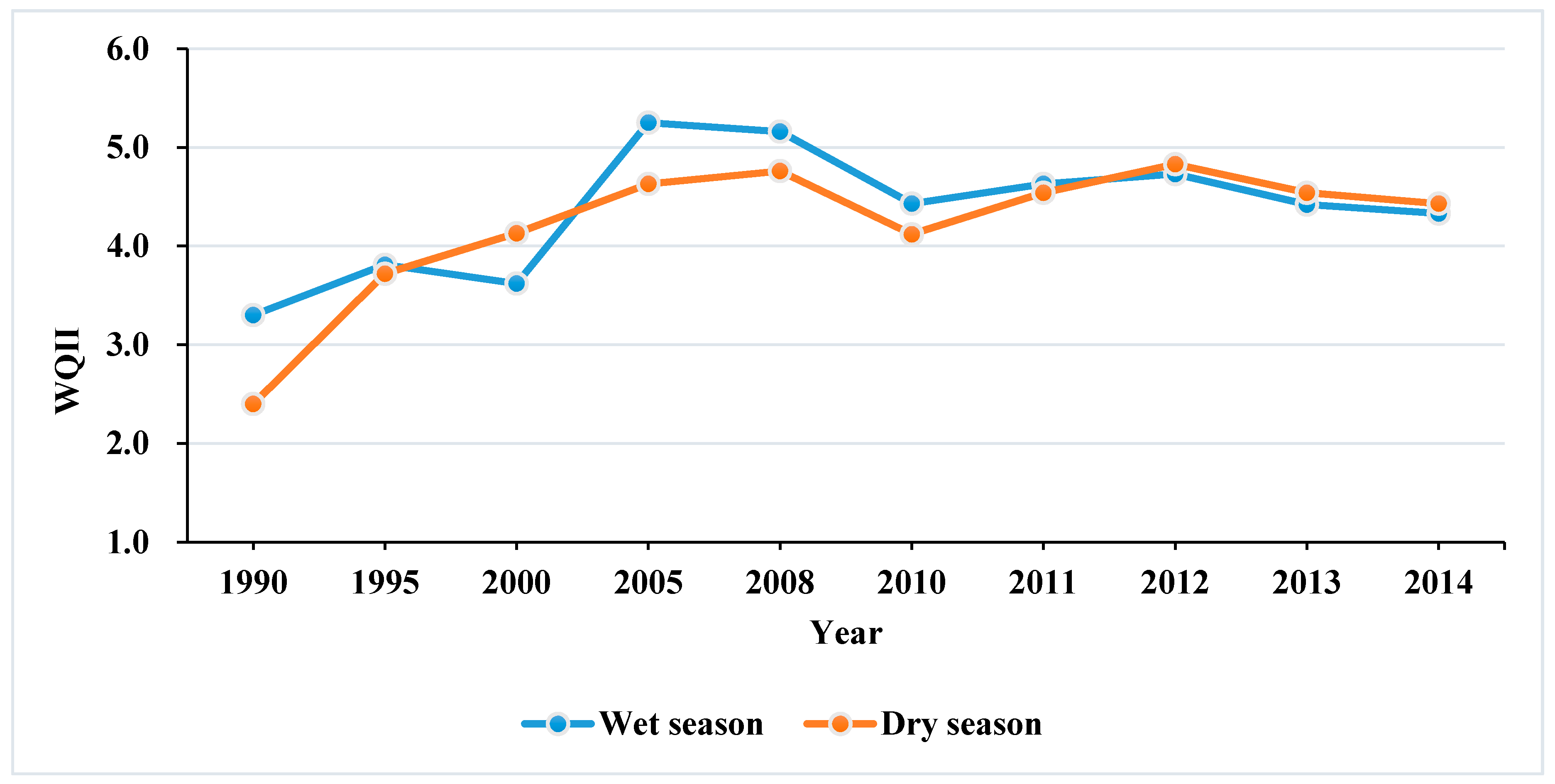
| Sub-Basin | River Grade | Sampling Site |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Qinhuai River sub-basin | Main river | Shangfangmen Bridge—QM1, Dongshan Bridge—QM2, Caihong Bridge—QM3, Qinhuaixin River (Caocun Bridge—QM4), Xinhefanshui station—QM5, Yang Bridge—QM6 |
| Secondary river | Niushoushan River (Yinxiang Bridge—QS1),Yuntaishan River (Xinhe Bridge—QS2), Pangjia Bridge—QS3, Qingtian Village—QS4 | |
| Jurong River sub-basin | Main river | Qianhan Village—JM1, Longdu Bridge—JM2, Hushu Bridge—JM3, Zhaojia Village Bridge—JM4 |
| Secondary river | Ge Bridge—JS1, Tongjin Bridge—JS2, Liangtai Bridge—JS3, Shuimen Bridge—JS4) | |
| Lishui River sub-basin | Main river | Wusha Bridge—LM1 |
| Secondary river | Ergan River (Changle Bridge—LS1, Kaitai Bridge—LS6), Yigan River (Shahe Bridge—LS2, Zhenzhu Bridge—LS3, Chenjiaba Bridge—LS4), Sangan River (Shijiazhuang Station—LS5), Hengxi River (Hengxihe Bridge—LS7) |
| Analysis Method | Instrument and Equipment | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water (Class) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |||||||
| T (°C) | Thermometer Method | Thermometer (0–50 °C) | 2.0 | 34.60 | 17.83 | 8.85 | Increase (Decrease) in weekly average maximum temperature ≤ 1 (≤2) | ||||
| pH | Glass electrode method | pH meter (PHS-3C) | 5.41 | 8.92 | 7.78 | 0.36 | 6–9 | ||||
| Zn (mg/L) | Atomic absorption spectrometry | Atomic absorption spectrophotometer (SOLAAR-M6) | 0.00 | 1.57 | 0.05 | 0.10 | ≤0.05 | (0.05,1] | (0.05,1] | (1,2] | (1,2] |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry | UV-VIS Spectrophotometer (TU-1901) | 0.05 | 18.20 | 1.89 | 2.23 | ≤0.15 | (0.15,0.5] | (0.5,1] | (1,1.5] | (1.5,2] |
| TN (mg/L) | Alkaline potassium persulfate digestion UV spectrophotometric method | UV-VIS spectrophotometer (TU-1900) | 0.49 | 30.33 | 3.24 | 3.64 | ≤0.2 | (0.2,0.5] | (0.5,1] | (1,1.5] | (1.5,2] |
| TP (mg/L) | Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometric method | UV-VIS spectrophotometer (TU-1900) | 0.01 | 5.67 | 0.34 | 0.48 | ≤0.02 | (0.02,0.1] | (0.1,0.2] | (0.2,0.3] | (0.3,0.4] |
| DO (mg/L) | Electrochemical probe method | Portable dissolved oxygen determining meter (S9-Field Kit) | 0.80 | 10.90 | 5.98 | 1.66 | ≥7.5 | (6,7.5] | (5,6] | (3,5] | (2,3] |
| F− (mg/L) | Fluorine reagent spectrophotometry | UV-VIS spectrophotometer (TU-1900) | 0.07 | 1.63 | 0.35 | 0.17 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | (1,1.5] | (1,1.5] |
| TS (m) | Disc method | Secchi disc | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.06 | No | ||||
| CODcr (mg/L) | Small-scale sealed tube method | COD digestion instrument (DRB200) | 10.20 | 82.2 | 24.81 | 8.12 | ≤15 | ≤15 | (15,20] | (20,30] | (30,40] |
| CODMn (mg/L) | Acid potassium permanganate method | —— | 2.80 | 28.6 | 6.71 | 2.13 | ≤2 | (2,4] | (4,6] | (6,10] | (10,15] |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | Dilution and seeding method | Biochemical incubator (BSP-250) | 1.00 | 20.20 | 3.85 | 1.58 | ≤3 | ≤3 | (3,4) | (4,6] | (6,10] |
| Judging Standard | Comprehensive Water Quality Grade | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 ≤ X.Y < 2 | I | Excellent |
| 2 ≤ X.Y < 3 | II | Clean |
| 3 ≤ X.Y < 4 | III | Slightly polluted |
| 4 ≤ X.Y < 5 | IV | Moderately polluted |
| 5 ≤ X.Y < 6 | V | Highly polluted |
| 6 ≤ X.Y < 7 | Inferior V not malodorous and black | Seriously polluted |
| X. Y > 7 | Inferior V and malodorous and black | Malodorous and black |
| Parameters | Wet Season | Dry Season | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| T | 0.23 | −0.20 | 0.83 | 0.02 | 0.85 | −0.26 |
| pH | −0.11 | −0.49 | 0.78 | −0.34 | 0.90 | −0.12 |
| DO | −0.06 | −0.74 | 0.49 | −0.83 | 0.18 | 0.002 |
| CODMn | 0.97 | 0.13 | −0.04 | 0.41 | −0.14 | 0.83 |
| CODcr | 0.95 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.54 | −0.17 | 0.76 |
| BOD5 | 0.90 | 0.15 | −0.25 | 0.47 | −0.05 | 0.82 |
| NH4+ −N | 0.38 | 0.86 | −0.10 | 0.85 | 0.05 | 0.41 |
| Zn | 0.17 | 0.24 | −0.62 | −0.24 | −0.48 | 0.66 |
| F− | −0.22 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 0.12 |
| TS | −0.25 | 0.06 | 0.85 | −0.22 | 0.68 | −0.30 |
| TN | 0.15 | 0.79 | −0.23 | 0.75 | −0.14 | 0.18 |
| TP | 0.56 | 0.76 | −0.21 | 0.75 | −0.05 | 0.38 |
| Variability (%) | 44.81 | 20.13 | 16.20 | 47.05 | 21.02 | 10.35 |
| Cumulative (%) | 44.81 | 64.93 | 81.14 | 47.05 | 68.07 | 78.42 |
| Rainfall (mm) | Total Discharge (108 m3) | Floodgate Open Time (Days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Open (Days) | Flood Discharge (Days) | Water Diversion (Days) | |||
| 2008 | 995 | 1.14 | 7 | 7 | 0 |
| 2009 | 1442 | 5.21 | 29 | 29 | 0 |
| 2010 | 1231 | 5.77 | 93 | 51 | 42 |
| 2011 | 1037 | 3.14 | 35 | 35 | 0 |
| 2012 | 983 | 2.42 | 53 | 10 | 43 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Li, N.; Gong, C. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and the Water Quality Identification Index for the Qinhuai River Basin, East China. Water 2020, 12, 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102764
Ma X, Wang L, Yang H, Li N, Gong C. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and the Water Quality Identification Index for the Qinhuai River Basin, East China. Water. 2020; 12(10):2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102764
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiaoxue, Lachun Wang, Hong Yang, Na Li, and Chang Gong. 2020. "Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and the Water Quality Identification Index for the Qinhuai River Basin, East China" Water 12, no. 10: 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102764
APA StyleMa, X., Wang, L., Yang, H., Li, N., & Gong, C. (2020). Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and the Water Quality Identification Index for the Qinhuai River Basin, East China. Water, 12(10), 2764. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102764






