A New Algorithm for Delineation of Surface Depressions and Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
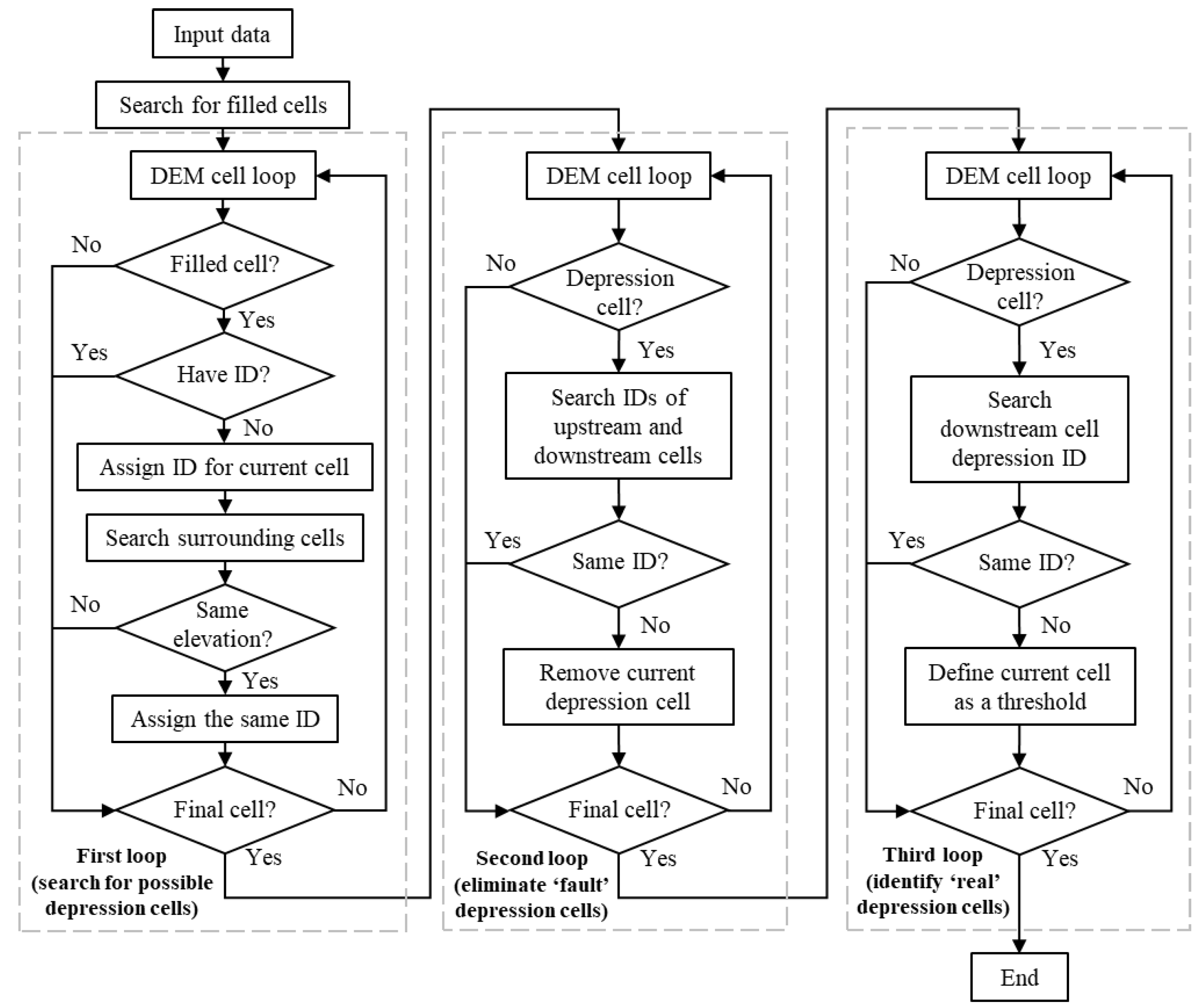
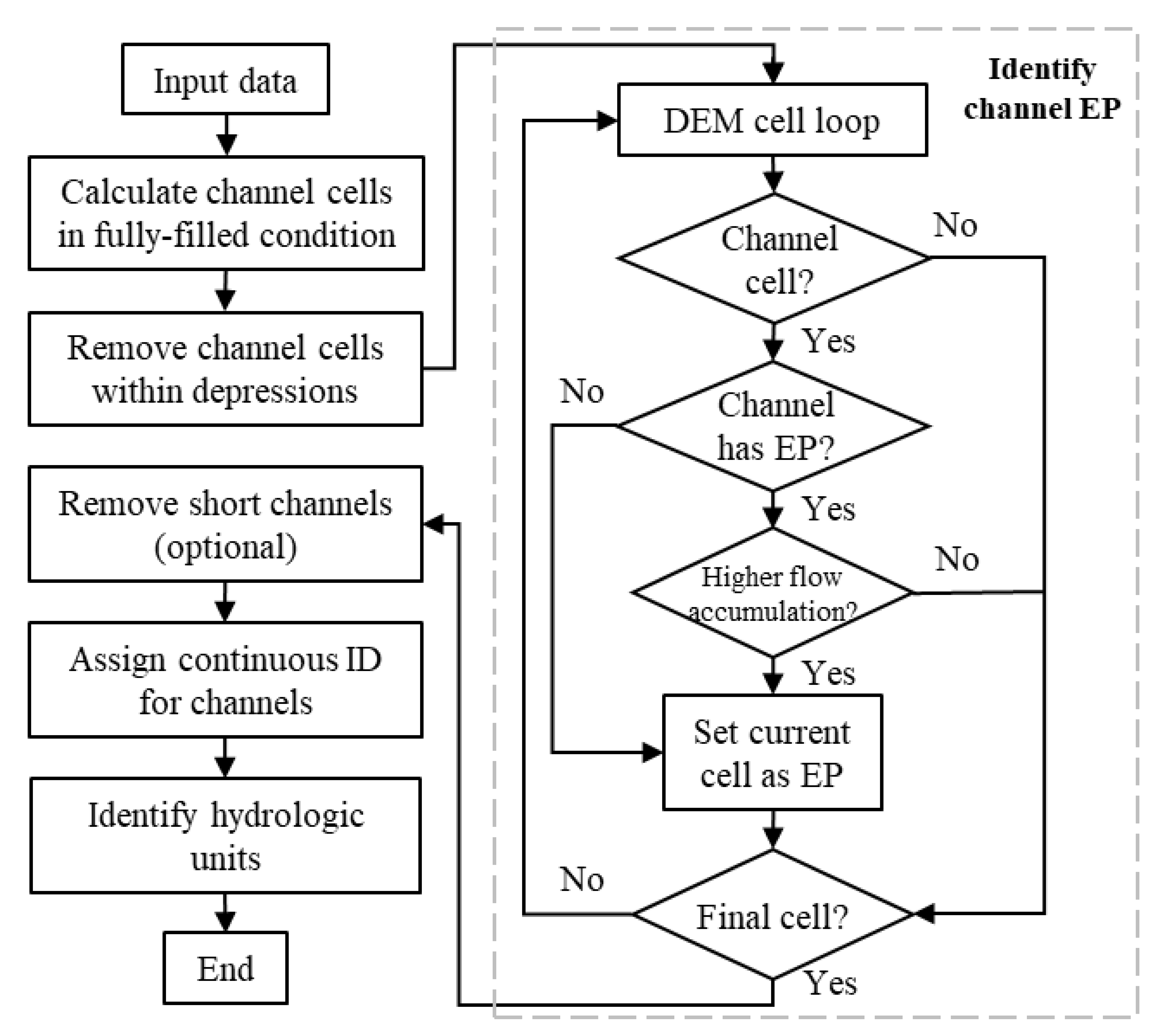
2.1. Development of HUD-DC
2.1.1. Identification of Depressions
2.1.2. Identification of Channels and Hydrologic Units
2.1.3. Output Data and Format
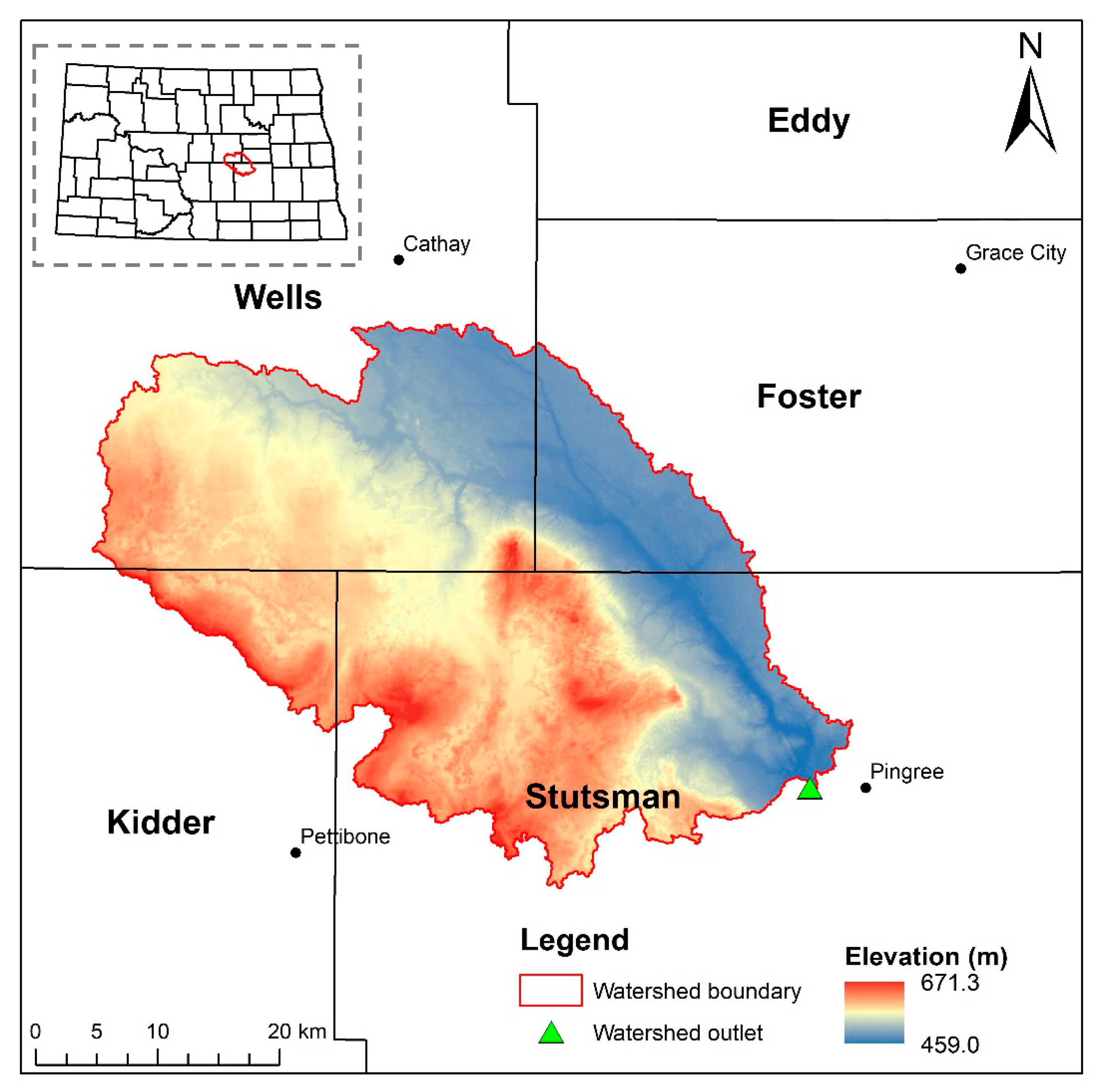
2.2. Study Area and Testing of HUD-DC
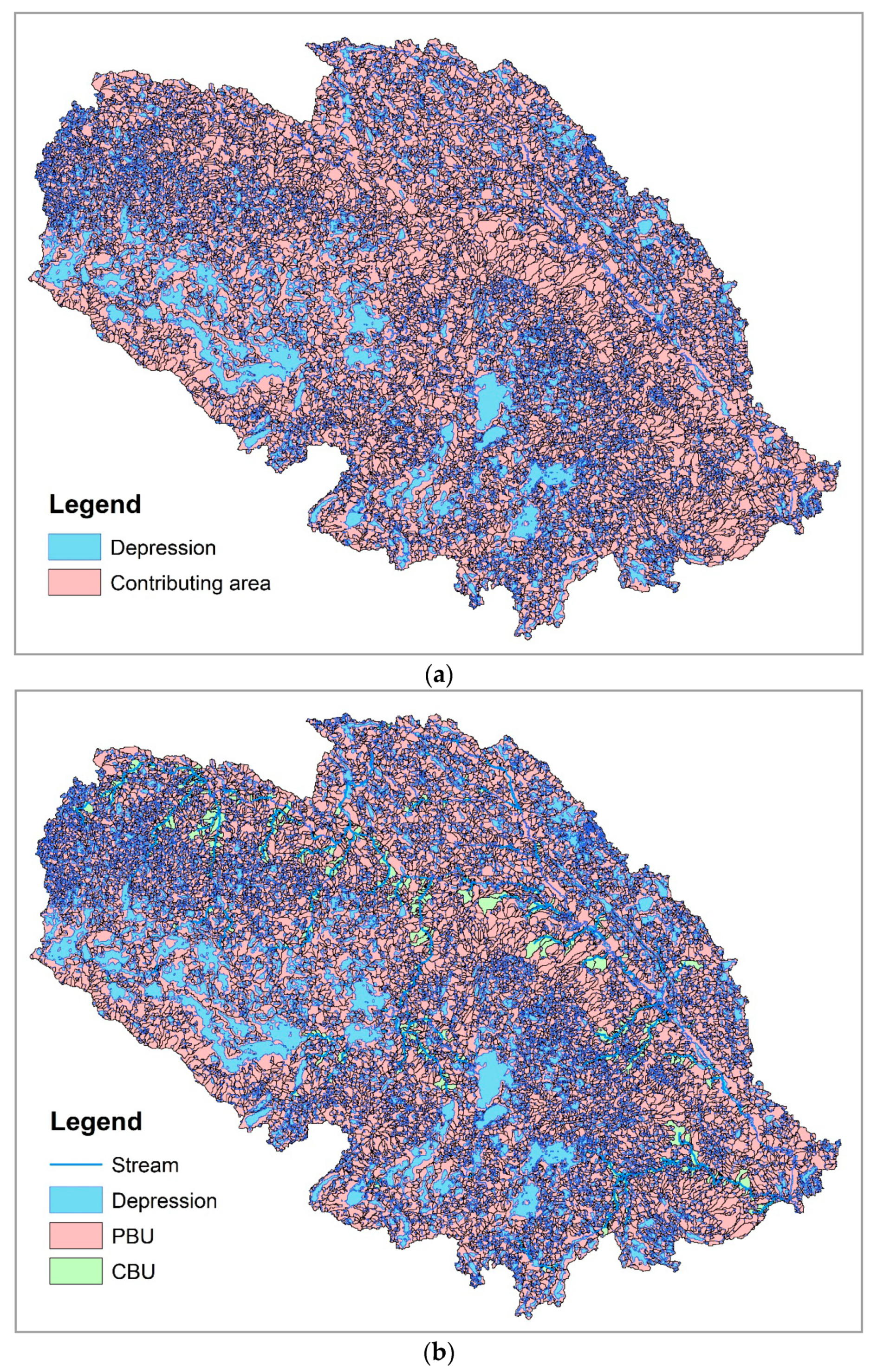
3. Results
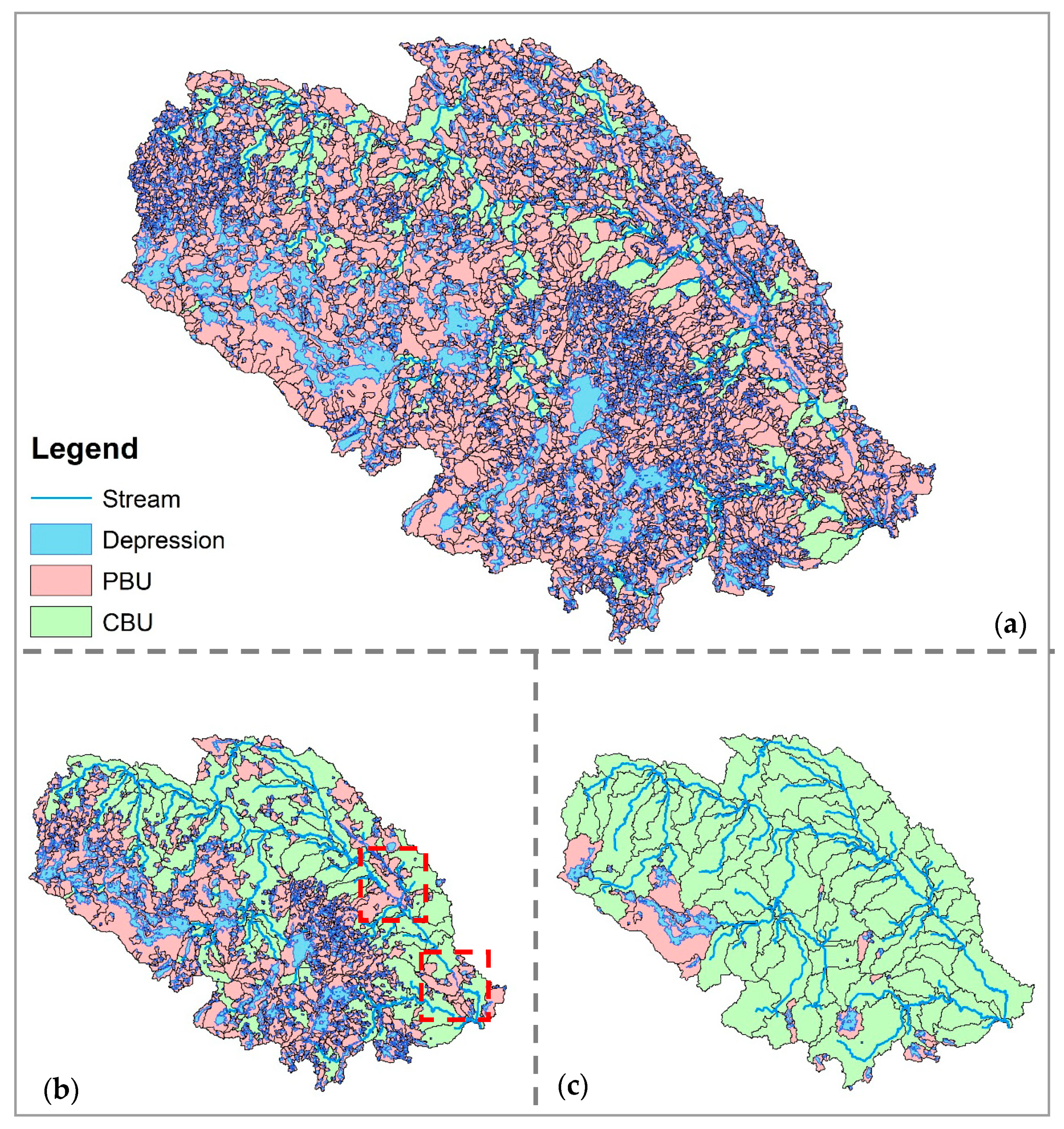
3.1. Watershed Delineation and Topographic Analysis
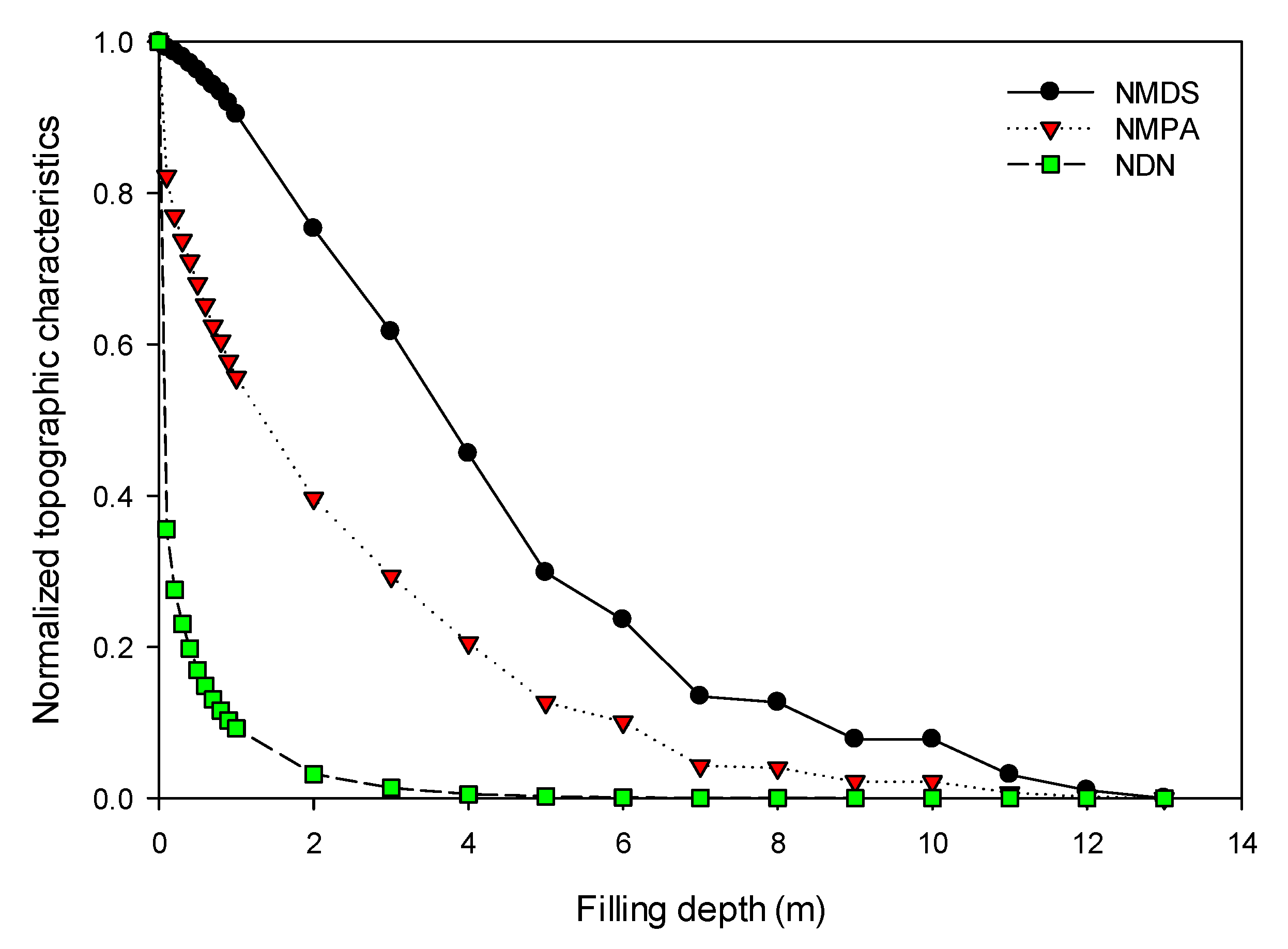
3.2. Identification of Filling Threshold for Removing Artifacts
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hay, L.; Norton, P.; Viger, R.; Markstrom, S.; Regan, R.S.; Vanderhoof, M. Modeling Surface-Water Depression Storage in a Prairie Depression Region. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 462–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhoof, M.K.; Alexander, L.C.; Todd, M.J. Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Wetland Extent Influence Variability of Surface Water Connectivity in the Prairie Pothole Region, United States. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbrecht, J.; Martz, L.W. TOPAZ: An Automated Digital Landscape Analysis Tool for Topographic Evaluation, Drainage Identification, Watershed Segmentation and Subcatchment Parameterization: TOPAZ User Manual; Grazinglands Research Laboratory, USDA Agricultural Research Services: El Reno, OK, USA, 1997.
- Jasiewicz, J.; Metz, M. A New GRASS GIS Toolkit for Hortonian Analysis of Drainage Networks. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 37, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenson, S.K.; Domingue, J.O. Extracting Topographic Structure from Digital Elevation Data for Geographic Information System Analysis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1988, 54, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Stuiver, H.J. Automated Delineation of Drainage Networks and Elementary Catchments from Digital Elevation Models. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 1998, 3, 198–208. [Google Scholar]
- O′Callaghan, J.F.; Mark, D.M. The Extraction of Drainage Networks from Digital Elevation Data. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1984, 28, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, N. A New Approach for Dealing with Depressions in Digital Elevation Models when Calculating Flow Accumulation Values. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 34, 781–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.A.; Pietroniro, A.; Martz, L.W. Topographic Analysis for the Prairie Pothole Region of Western Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3105–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, J.E.; Gahegan, M.N.; Roberts, S.A.; Hogg, J.; Hoyle, B.S. Feature-Based Derivation of Drainage Networks. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1993, 7, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, W. Automated River Line and Catchment Area Extraction from DEM Data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1993, 29, 642. [Google Scholar]
- Martz, L.W.; Garbrecht, J. The Treatment of Flat Areas and Depressions in Automated Drainage Analysis of Raster Digital Elevation Models. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soille, P. Optimal Removal of Spurious Pits in Grid Digital Elevation Models. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.C.; Lee, K.T. A Simple Depression-Filling Method for Raster and Irregular Elevation Datasets. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 124, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Yang, J.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, J. Dynamic Puddle Delineation and Modeling of Puddle-To-Puddle Filling-Spilling-Merging-Splitting Overland Flow Processes. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3825–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X. Delineation of Pothole-Dominated Wetlands and Modeling of Their Threshold Behaviors. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2017, 22, D5015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Chu, X. New Model for Simulating Hydrologic Processes Under Influence of Surface Depressions. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 04019008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, L.A.; Anteau, M.J. Generating Nested Wetland Catchments with Readily-Available Digital Elevation Data May Improve Evaluations of Land-Use Change on Wetlands. Wetlands 2014, 34, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, K.; Chu, X. Modeling of Spatiotemporal Variations in Runoff Contribution Areas and Analysis of Hydrologic Connectivity. Land. Degrad Dev. 2018, 29, 2629–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi Nasab, M.; Singh, V.; Chu, X. SWAT Modeling for Depression-Dominated Areas: How Do Depressions Manipulate Hydrologic Modeling? Water 2017, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temme, A.J.; Schoorl, J.M.; Veldkamp, A. Algorithm for Dealing with Depressions in Dynamic Landscape Evolution Models. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, D.R. ArcHydro: GIS for Water Resour; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, X.; Zhang, J.; Chi, Y.; Yang, J. An Improved Method for Watershed Delineation and Computation of Surface Depression Storage. In Watershed Management Conference 2010; Potter, K.W., Frevert, D.K., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 1113–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Chu, X. A New Modeling Approach for Simulating Microtopography-Dominated, Discontinuous Overland Flow on Infiltrating Surfaces. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 78, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi Nasab, M.; Zhang, J.; Chu, X. A New Depression-Dominated Delineation (D-Cubed) Method for Improved Watershed Modeling. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3364–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Shao, J.; Chu, X. An Automated Processing Algorithm for Flat Areas Resulting from DEM Filling and Interpolation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboton, D.G.; Bras, R.L.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. On the Extraction of Channel Networks from Digital Elevation Data. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
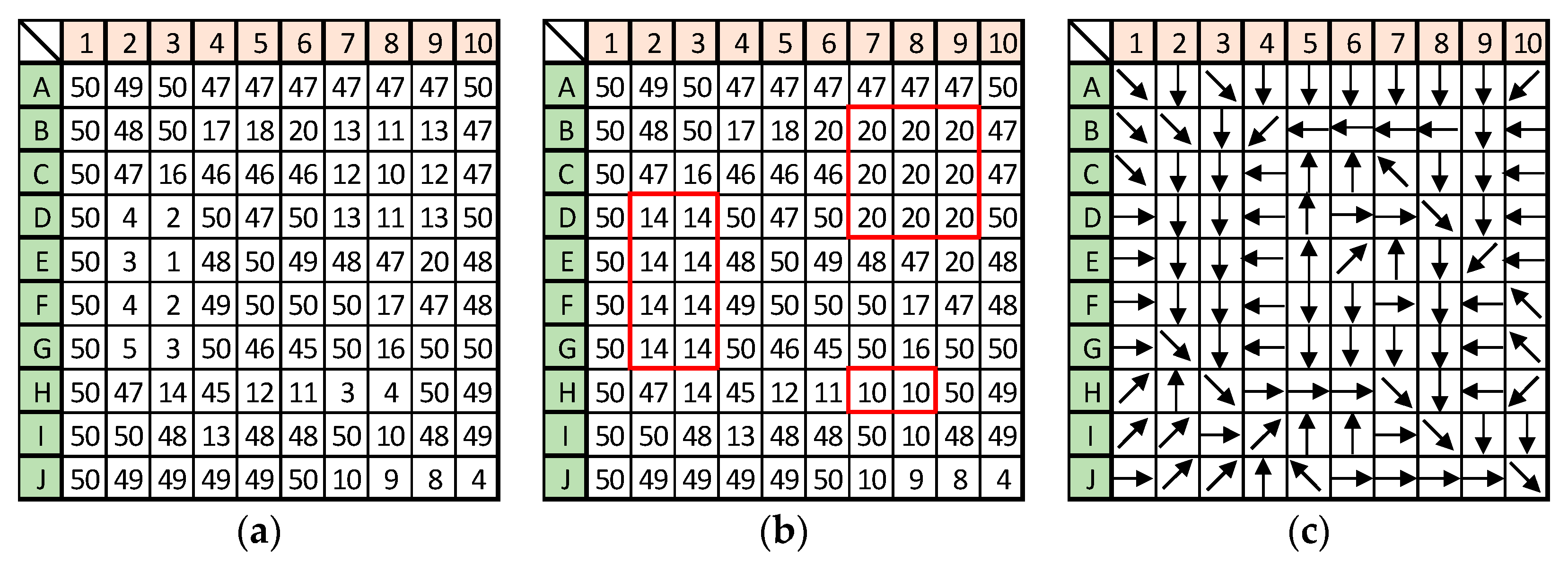
 Depression cell
Depression cell  Depression threshold.
Depression threshold.
 Depression cell
Depression cell  Depression threshold.
Depression threshold.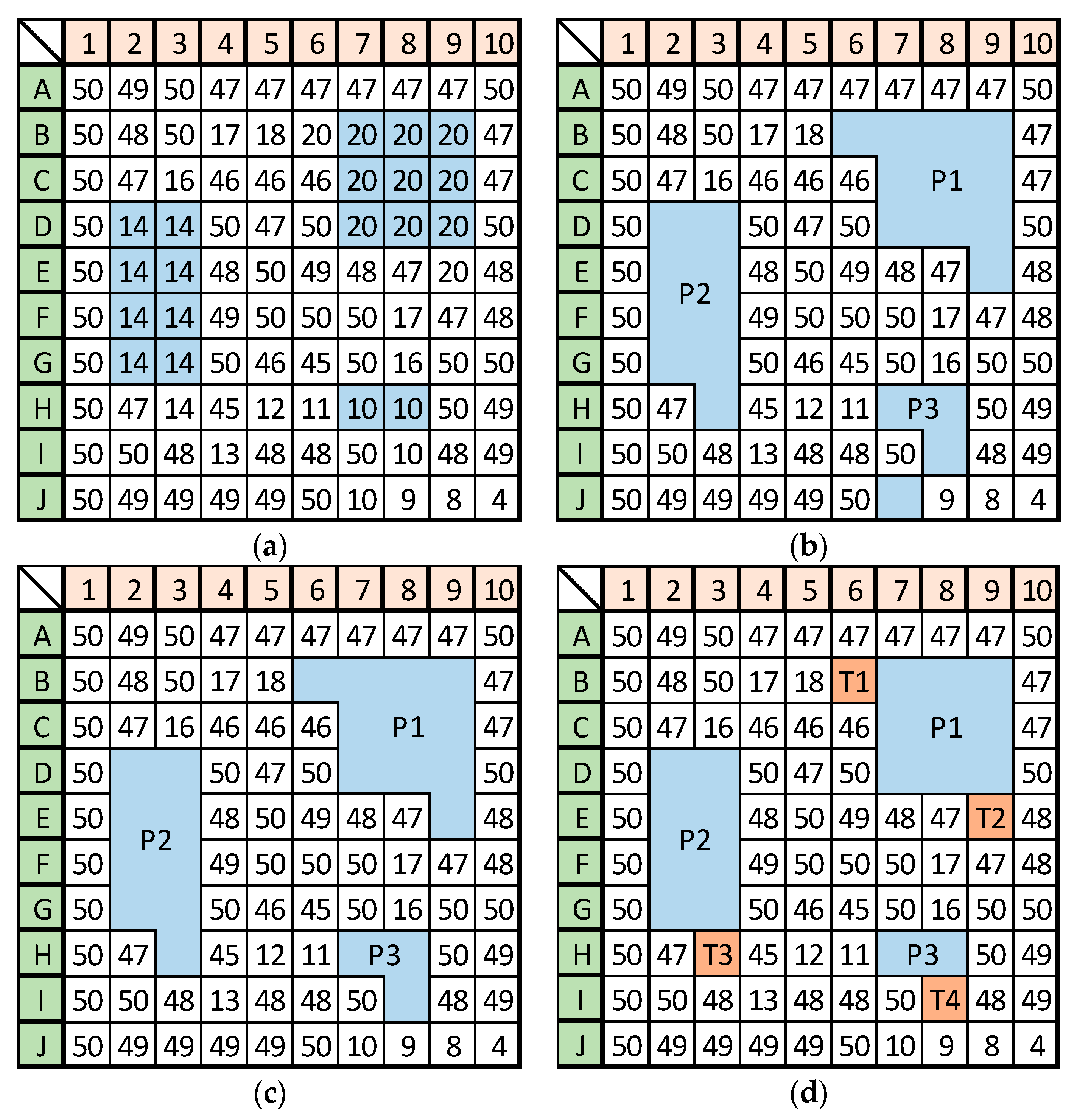
 Depression cell
Depression cell  Depression threshold
Depression threshold  Channel cell
Channel cell  Channel ending point
Channel ending point 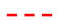 Hydrologic unit boundary.
Hydrologic unit boundary.
 Depression cell
Depression cell  Depression threshold
Depression threshold  Channel cell
Channel cell  Channel ending point
Channel ending point  Hydrologic unit boundary.
Hydrologic unit boundary.
| Method/Tool | Number of Depressions | MDS | MPA | PBU or DCA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (106 m3) | (km2) | (km2) | (%) | ||
| Arc Hydro | 18,190 | 404.33 | 267.47 | 1668.12 | 100.00 |
| HUD-DC | 17,827 | 404.33 | 292.04 | 1597.22 | 95.19 |
| Filling Depth | MDS | MPA | PBU | CBU | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (106 m3) | (km2) | (km2) | (%) | (km2) | (%) |
| 0.1 | 401.19 | 240.09 | 1449.51 | 86.90 | 218.61 | 13.10 |
| 1.0 | 365.55 | 162.47 | 912.26 | 54.69 | 755.86 | 45.31 |
| 5.0 | 120.56 | 36.97 | 161.82 | 9.70 | 1506.30 | 90.30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Chu, X. A New Algorithm for Delineation of Surface Depressions and Channels. Water 2020, 12, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010007
Wang N, Chu X. A New Algorithm for Delineation of Surface Depressions and Channels. Water. 2020; 12(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ning, and Xuefeng Chu. 2020. "A New Algorithm for Delineation of Surface Depressions and Channels" Water 12, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010007
APA StyleWang, N., & Chu, X. (2020). A New Algorithm for Delineation of Surface Depressions and Channels. Water, 12(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010007





