Effect of Physical Factors on the Growth of Chlorella Vulgaris on Enriched Media Using the Methods of Orthogonal Analysis and Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. The Process of Comprehensive Experiment
2.2. Experimental Sediments
2.3. The Cultivation of C. Vulgaris
2.4. Instruments and Tests
2.5. Design of Orthogonal Experiment
2.6. Establishment of RSM
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Results of Biomass and pH in the Comprehensive Experiment
3.2. The Classical Orthogonal Distribution
3.3. Range Analysis of the Orthogonal Experiment
3.4. Factor Effects and Variance (ANOVA) of the Orthogonal Experiment
3.5. Box-Behnken Design of RSM
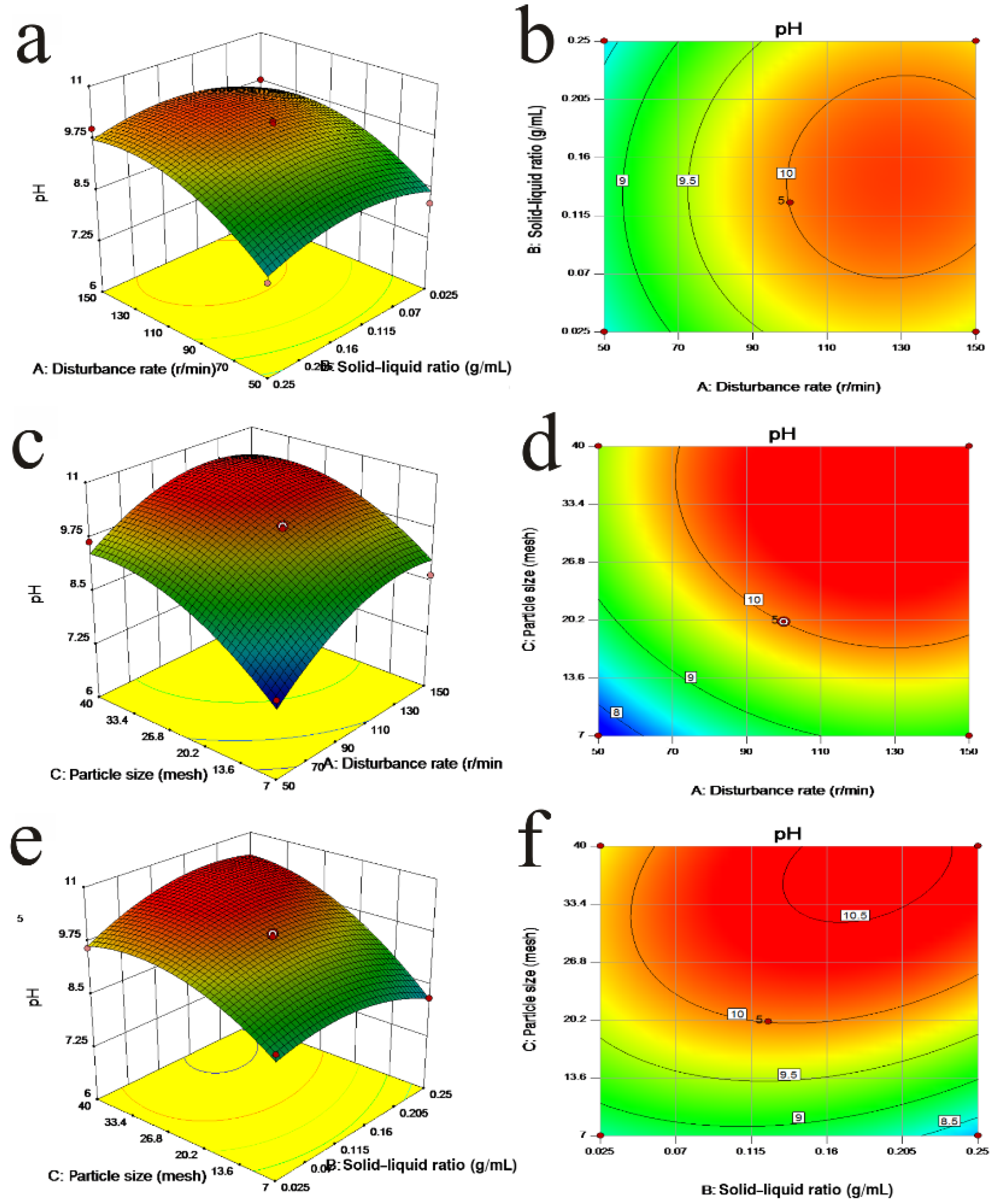
3.6. Interaction Effect of Three Factors on Biomass and pH
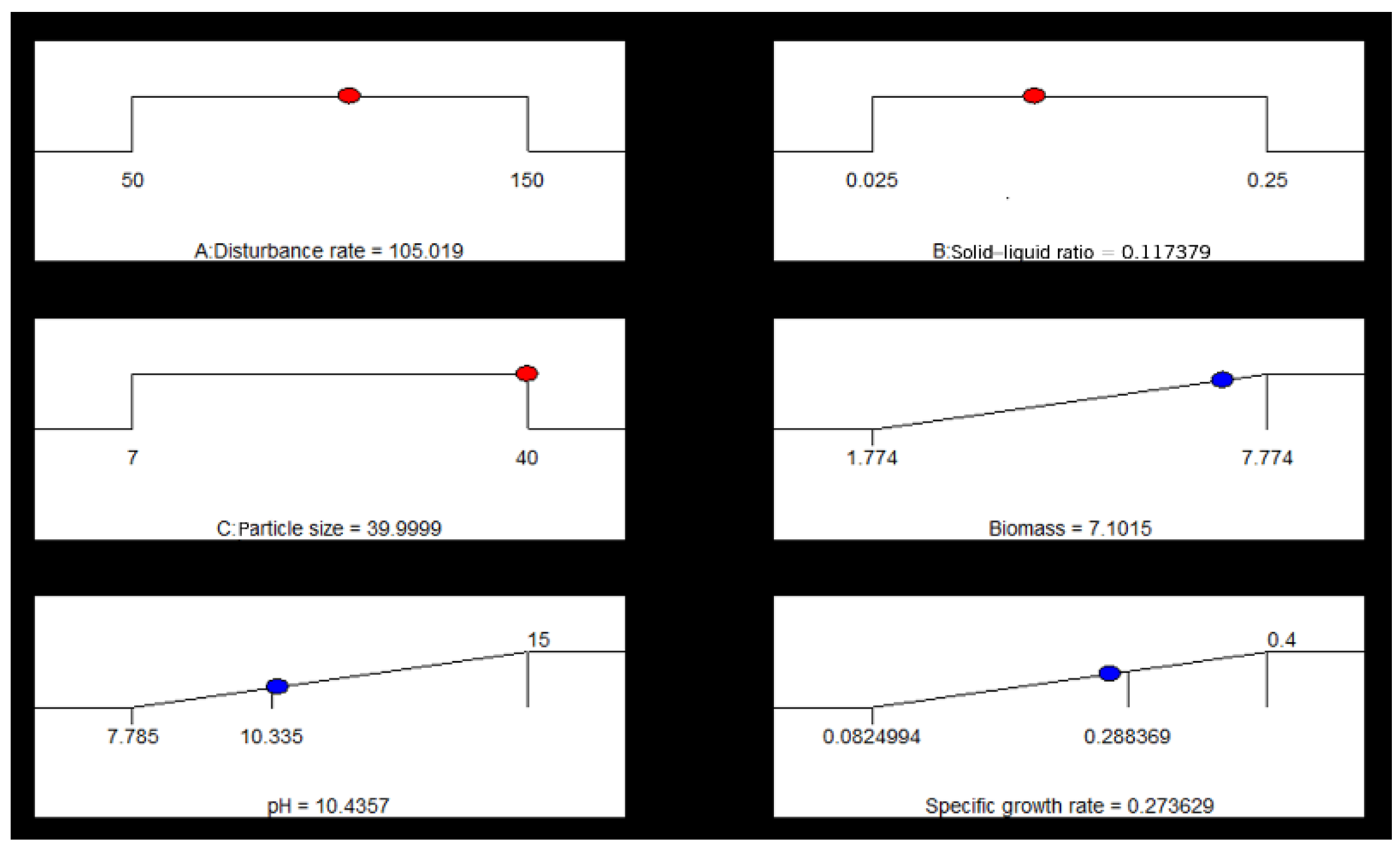
3.7. Optimization of Biomass
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Song, S.; Wen, Y. Reduction of Cr (VI) into Cr (III) by organelles of Chlorella vulgaris in aqueous solution: An organelle-level attempt. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 572, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhouyang, S.; Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal coupled with carbohydrate production by five microalgae cultures cultivated in biogas slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.T.; Vu, N.D.; Matsukawa, M.; Okajima, M.; Kaneko, T.; Ohki, K.; Yoshikawa, S. Heavy metal biosorption from aqueous solutions by algae inhabiting rice paddies in Vietnam. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalhmunsiama; Gupta, P.L.; Jung, H.; Tiwari, D.; Kong, S.-H.; Lee, S.-M. Insight into the mechanism of Cd(II) and Pb(II) removal by sustainable magnetic biosorbent precursor to Chlorella vulgaris. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 71, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhan, J.; He, C.; Wang, Q. Algal biofuel production coupled bioremediation of biomass power plant wastes based on Chlorella sp C2 cultivation. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, R.; Rajor, A.; Kundu, K.; Kumar, N. Production of biodiesel from unused algal biomass in Punjab, India. Pet. Sci. 2018, 15, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnour, S.A.; Sheiha, A.M.; Taha, A.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Alarifi, S.; Alkahtani, S.; Ali, D.; AlBasher, G.; Almeer, R.; Falodah, F.; et al. Impacts of Enriching Growing Rabbit Diets with Chlorella vulgaris Microalgae on Growth, Blood Variables, Carcass Traits, Immunological and Antioxidant Indices. Animals 2019, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, K.; Roostaei, J.; Zhang, Y. Mixed culture of Chlorella sp. and wastewater wild algae for enhanced biomass and lipid accumulation in artificial wastewater medium. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Lu, H.; Liu, Z.; Duan, N.; Dong, T.; Xiao, H.; Li, B.; Xu, P. Microalgae cultivation and culture medium recycling by a two-stage cultivation system. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.W. Mechanism of the influence of hydrodynamics on Microcystis aeruginosa, a dominant bloom species in reservoirs. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 636, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J. Effect of Small-Scale Turbulence on the Physiology and Morphology of Two Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; de Giesen, N.; Zhu, D. The Influence of a Eutrophic Lake to the River Downstream: Spatiotemporal Algal Composition Changes and the Driving Factors. Water 2015, 7, 2184–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.-Y.; Wu, L.; Meng, G.-H.; Guo, W.-H. Numerical simulation for impacts of hydrodynamic conditions on algae growth in Chongqing Section of Jialing River, China. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.; Newton, A.; Tett, P.; Fernandes, T.F. Sediment and water nutrients and microalgae in a coastal shallow lagoon, Ria Formosa (Portugal): Implications for the Water Framework Directive. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.F.; Shen, Q.S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.X.; Zhong, J.C.; Yan, S.H. [Environment effects of algae-caused black spots: Driving effects on the N, P changes in the water-sediment interface]. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2010, 31, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; He, Q.; Safar, Z.; Chassagne, C. The role of algae in fine sediment flocculation: In-situ and laboratory measurements. Mar. Geol. 2019, 413, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Holbach, A.; Wilhelms, A.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zou, H.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Norra, S. Highly time-resolved analysis of seasonal water dynamics and algal kinetics based on in-situ multi-sensor-system monitoring data in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 660, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, Q.; Ji, F. Factors influencing phosphorus adsorption onto sediment in a dynamic environment. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayers, J.J.; Flynn, K.J.; Shields, R.J. Influence of the N:P supply ratio on biomass productivity and time-resolved changes in elemental and bulk biochemical composition of Nannochloropsis sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, C.; Zebib, B.; Merah, O.; Pontalier, P.-Y.; Vaca-Garcia, C. Morphology, composition, production, processing and applications of Chlorella vulgaris: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Arya, S.K. Hydrogen from algal biomass: A review of production process. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J.; Esquivel-Elizondo, S.; Wu, Y. Microorganisms-based methods for harmful algal blooms control: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman Shayan, S.; Agblevor, F.A.; Bertin, L.; Sims, R.C. Hydraulic retention time effects on wastewater nutrient removal and bioproduct production via rotating algal biofilm reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A. Evaluation of flocculation induced by pH increase for harvesting microalgae and reuse of flocculated medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyabyev, A.; Andreyeva, I.; Rachimova, G. Influence of pH shift and salting on the energetics of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella maritima. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, Z.I.; Asker, M.M.S.; El-Sayed, S.; Kobbia, I.A. Effect of pH on growth and biochemical responses of Dunaliella bardawil and Chlorella ellipsoidea. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashok, K.S.; Yadav, S.; Saminathan, K.R.; Monisha, N.; Malarvizhi, J.; Ganesan, M.; Mantri, V.A. An orthogonal design to optimize seed production, out-planting, and cultivation of the industrially overexploited red alga Gracilaria edulis (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.D.; Gude, V.G.; Mannarswamy, A.; Cooke, P.; Munson-McGee, S.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Lammers, P.; Deng, S. Optimization of microwave-assisted transesterification of dry algal biomass using response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Hong, C.-H.; Choi, Y.-E. Efficient algal biodiesel production with an optimal harvest condition obtained via response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Ge, F.; Liu, N.; Wong, M.H. A pH-dependent enhancement effect of co-cultured Bacillus licheniformis on nutrient removal by Chlorella vulgaris. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.F.; Xiang, W.Z.; Fan, J.W.; Wu, H.L.; Li, T.; Long, L.J. High pH-induced flocculation of marine Chlorella sp for biofuel production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.T.; Feng, Y.Z.; Kang, L.G.; Luo, M.Y.; Yang, J.H. Effects of light and pH on cell density of Chlorella vulgaris. Energy Procedia 2014, 61, 2012–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
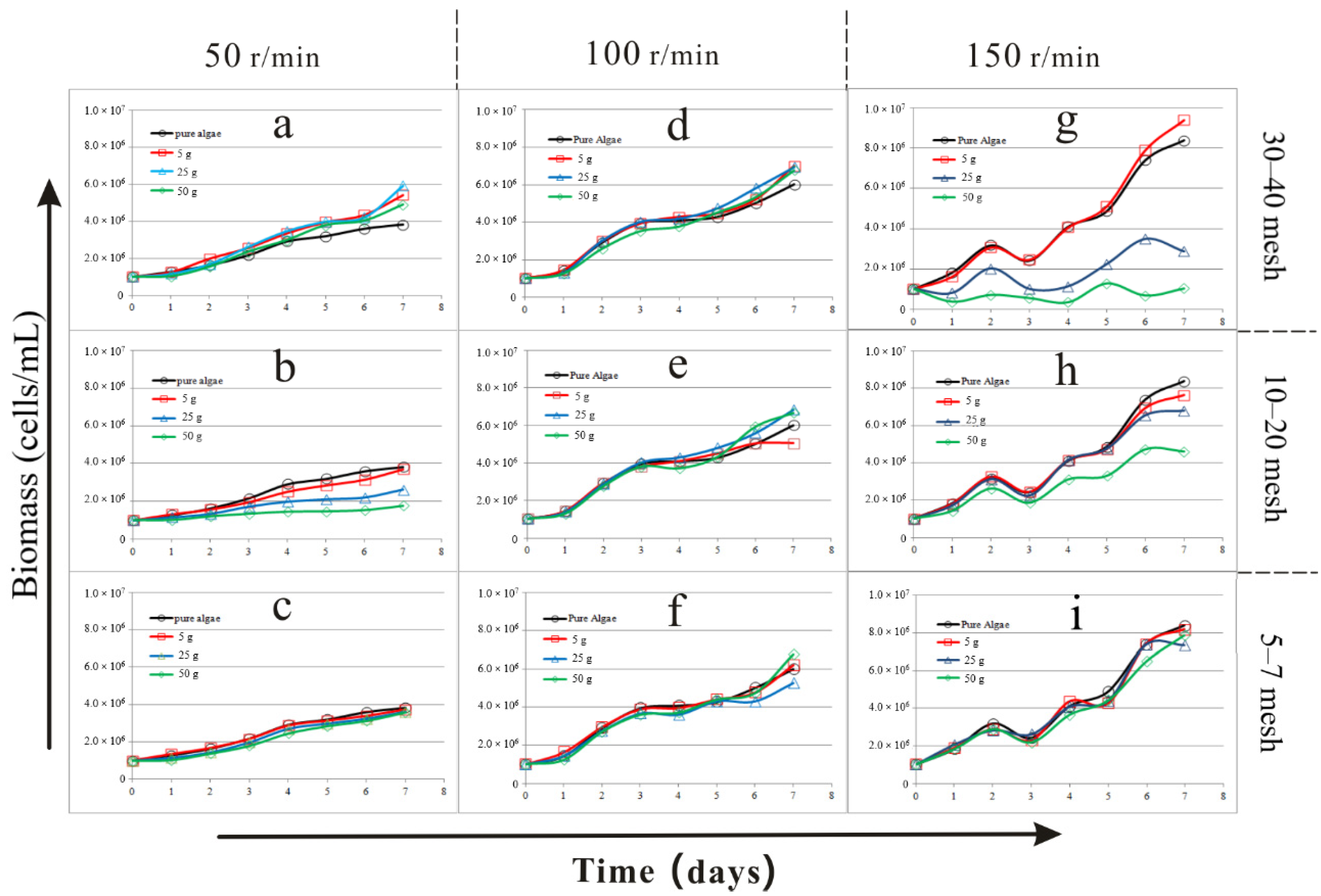
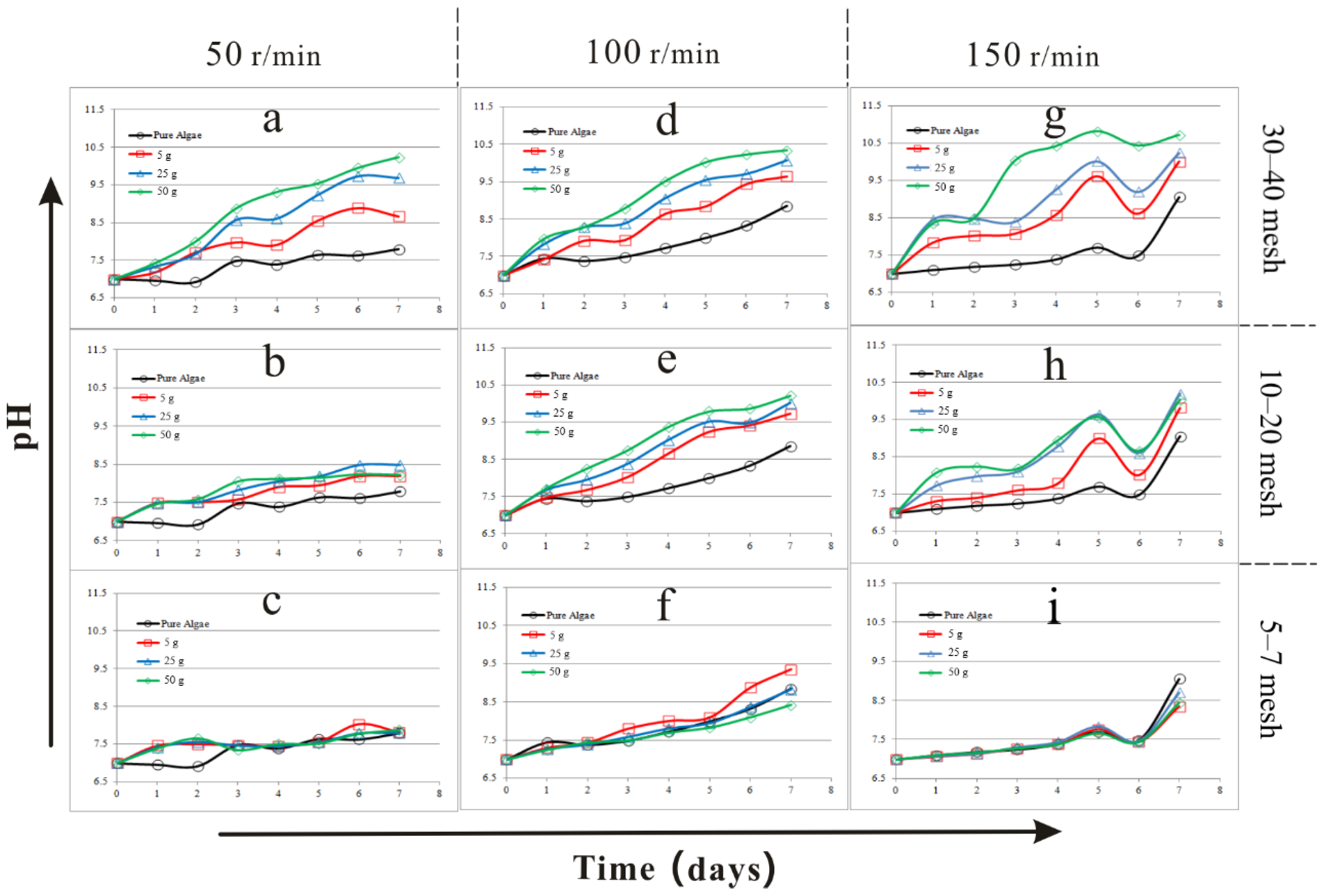
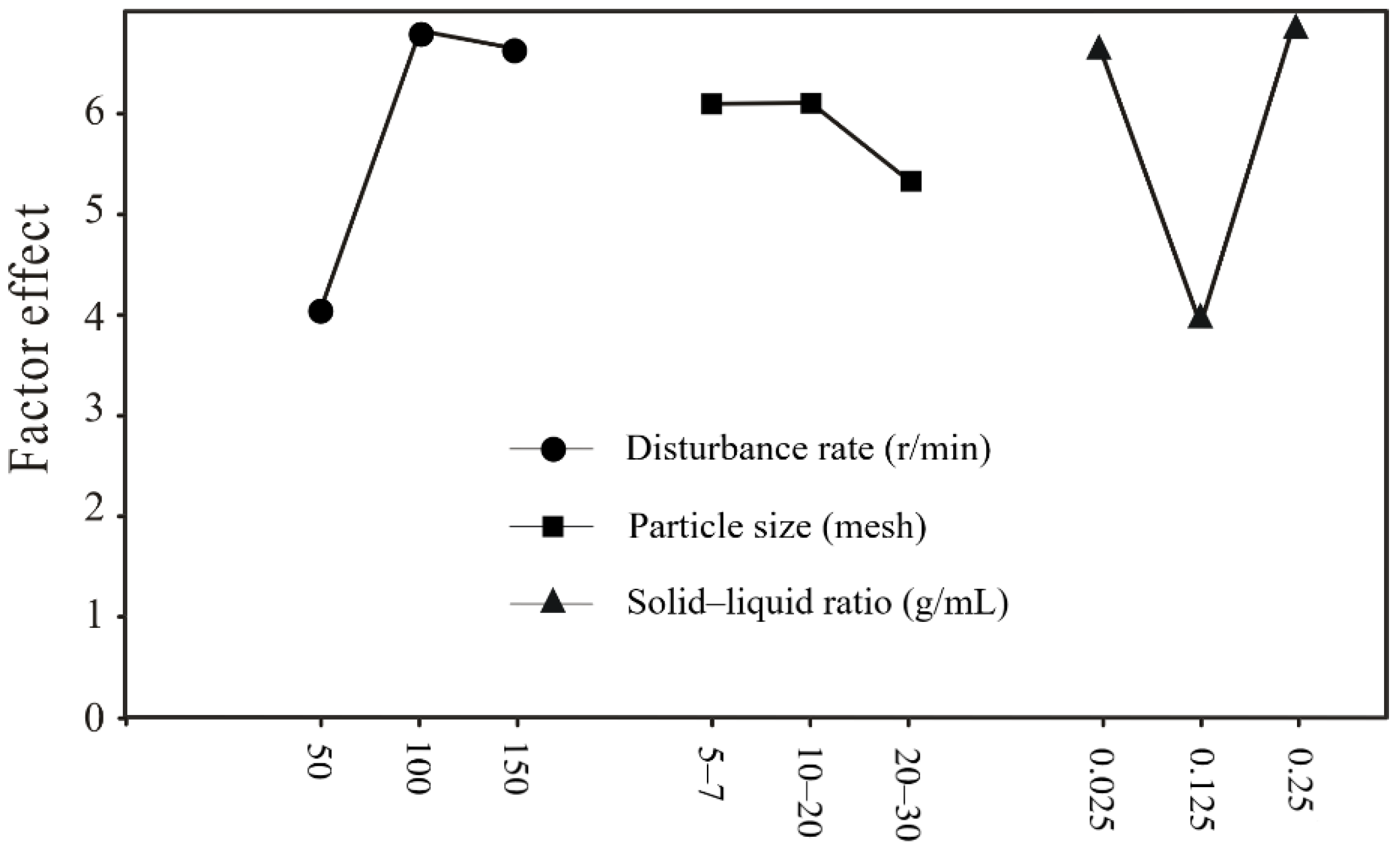
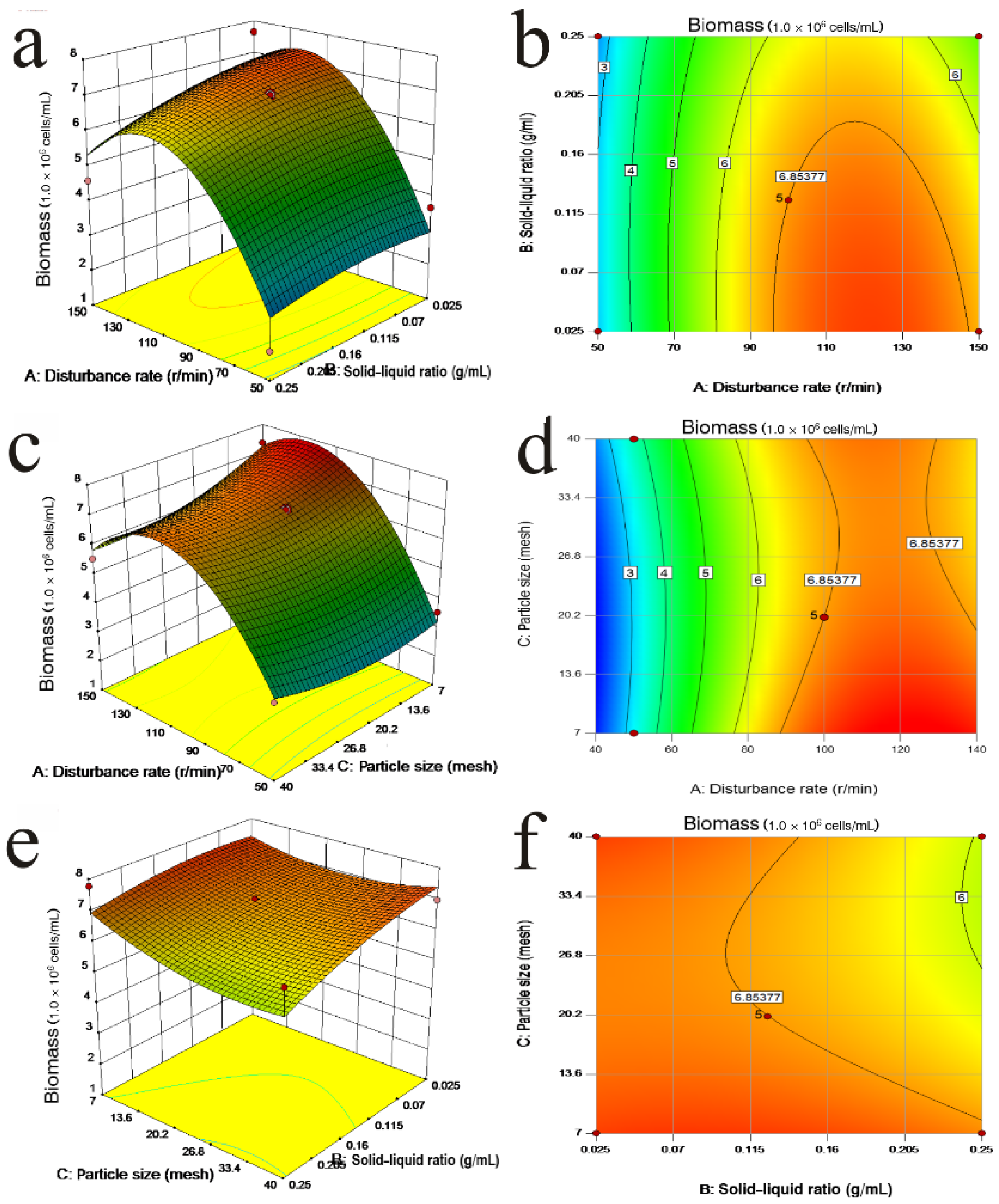
| Factors | Biomass (1.0 × 107 cells/mL) | pH | Specific Growth Rate (d−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| K1 | 3.74 | 5.62 | 6.12 | 8.845 | 9.178 | 8.62 | 0.185 | 0.245 | 0.227 |
| K2 | 6.31 | 5.64 | 3.58 | 9.712 | 9.087 | 9.413 | 0.258 | 0.223 | 0.242 |
| K3 | 6.14 | 4.92 | 6.48 | 9.577 | 9.868 | 10.1 | 0.273 | 0.239 | 0.247 |
| Rank | KA2 > KA3 > KA1 | KA2 > KA3 > KA1 | KB3 > KB1 > KB2 | ||||||
| KB2 > KB1 > KB3 | KB3 > KB1 > KB2 | KB1 > KB3 > KB2 | |||||||
| KC3 > KC1 > KC2 | KB3 > KB1 > KB2 | KC3 > KC2 > KC1 | |||||||
| Range (R) | 2.90 | 0.72 | 2.57 | 0.867 | 0.781 | 1.48 | 0.088 | 0.013 | 0.02 |
| Ring | A > C > B | A > B > C | A > C > B | ||||||
| Factor | Square Sum of the Deviation | Degree of Freedom | F Ratio | Critical Value of F | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.86 * 1013 | 2 | 31.33 | 9 | * |
| B | 5.92 * 1011 | 2 | 2.0 | 9 | |
| C | 1.36 * 1013 | 2 | 23.02 | 9 | * |
| Error | 5.9 * 1011 | 2 |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Response 1 | Response 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | A: Disturbance Rate (r/min) | B: Solid–Liquid Ratio (g/mL) | C: Particle Size (mesh) | Biomass (1 × 106 cell/mL) | pH |
| 1 | 150 | 0.25 | 20–30 | 4.63 | 10.03 |
| 2 | 150 | 0.125 | 30–40 | 2.87563 | 10.24 |
| 3 | 50 | 0.025 | 20–30 | 3.70375 | 8.18 |
| 4 | 50 | 0.125 | 5–7 | 3.6025 | 7.79 |
| 5 | 100 | 0.125 | 20–30 | 6.665 | 9.94 |
| 6 | 50 | 0.25 | 20–30 | 1.774 | 8.22 |
| 7 | 100 | 0.125 | 20–30 | 7.0025 | 10.09 |
| 8 | 50 | 0.125 | 30–40 | 5.93563 | 9.69 |
| 9 | 100 | 0.25 | 5–7 | 6.77375 | 8.24 |
| 10 | 100 | 0.25 | 30–40 | 6.78125 | 10.34 |
| 11 | 100 | 0.125 | 20–30 | 6.98956 | 10.08 |
| 12 | 150 | 0.025 | 20–30 | 7.65375 | 9.81 |
| 13 | 100 | 0.025 | 30–40 | 6.9925 | 9.64 |
| 14 | 100 | 0.125 | 20–30 | 6.8956 | 9.9 |
| 15 | 100 | 0.125 | 20–30 | 6.7432 | 10.02 |
| 16 | 100 | 0.025 | 5–7 | 6.1875 | 8.83 |
| 17 | 150 | 0.125 | 5–7 | 7.35938 | 8.71 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Q. Effect of Physical Factors on the Growth of Chlorella Vulgaris on Enriched Media Using the Methods of Orthogonal Analysis and Response Surface Methodology. Water 2020, 12, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010034
He L, Chen Y, Wu X, Chen S, Liu J, Li Q. Effect of Physical Factors on the Growth of Chlorella Vulgaris on Enriched Media Using the Methods of Orthogonal Analysis and Response Surface Methodology. Water. 2020; 12(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Lile, Yongcan Chen, Xuefei Wu, Shu Chen, Jing Liu, and Qiongfang Li. 2020. "Effect of Physical Factors on the Growth of Chlorella Vulgaris on Enriched Media Using the Methods of Orthogonal Analysis and Response Surface Methodology" Water 12, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010034
APA StyleHe, L., Chen, Y., Wu, X., Chen, S., Liu, J., & Li, Q. (2020). Effect of Physical Factors on the Growth of Chlorella Vulgaris on Enriched Media Using the Methods of Orthogonal Analysis and Response Surface Methodology. Water, 12(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010034





