Implications of Water Scarcity for Water Productivity and Farm Labor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Irrigated Agriculture, Water Scarcity, and Water Productivity
2.2. Farm Labor Inputs
2.3. Farm Labor and Household Income
2.4. Farm Labor and Water Use: The Importance of Crop Types
3. Conceptual Frameworks
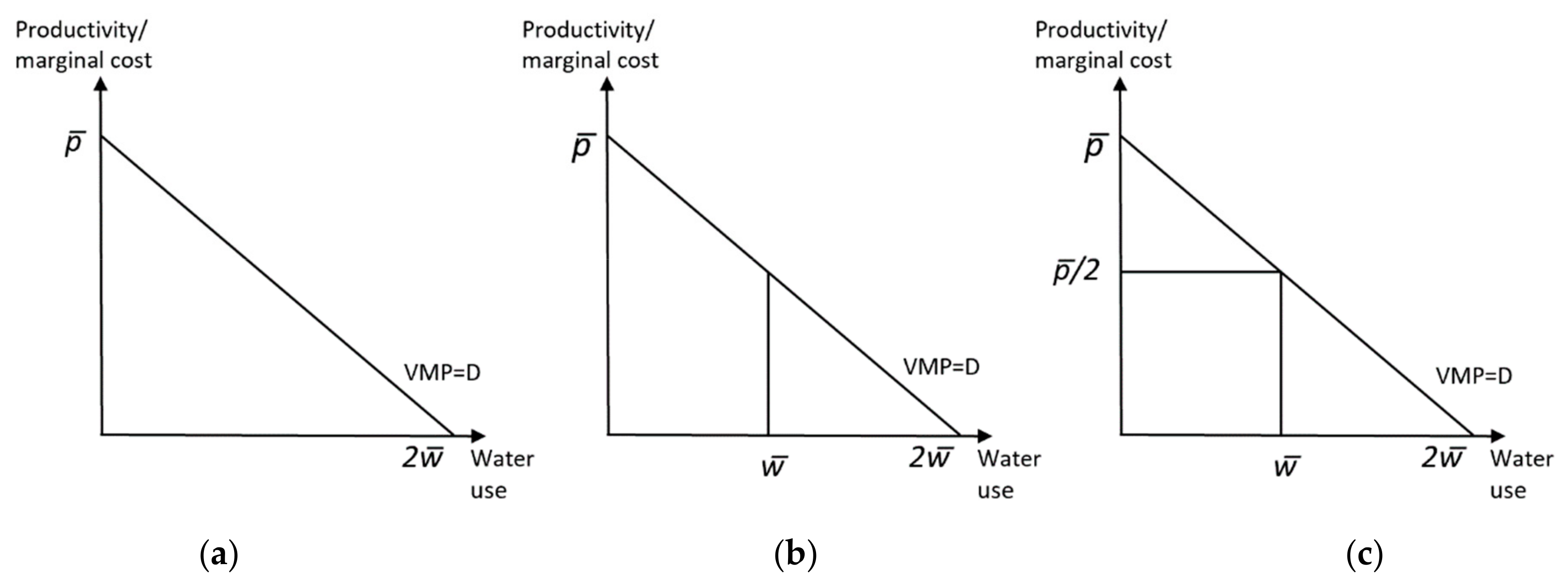
3.1. Water Productivity
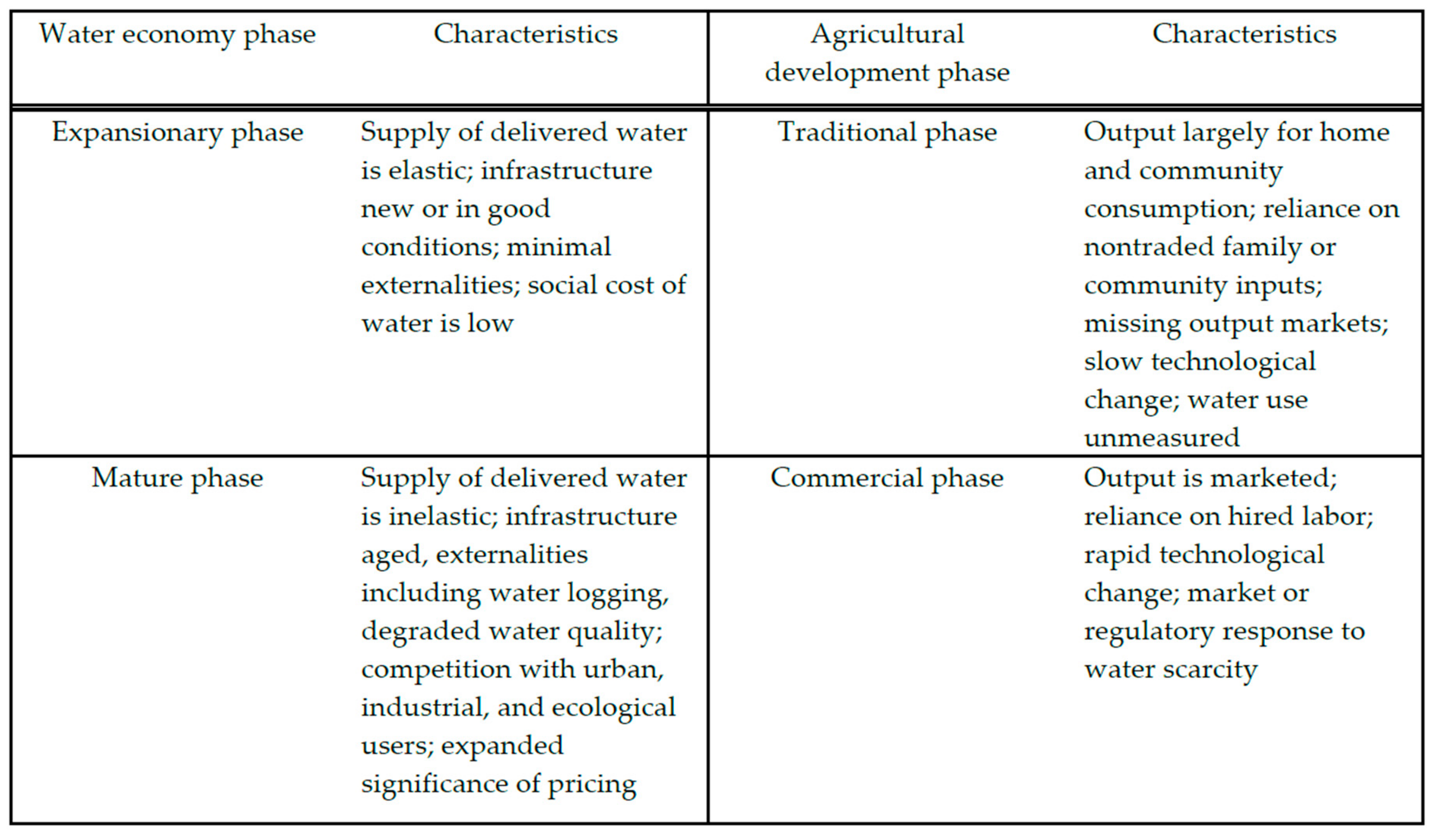
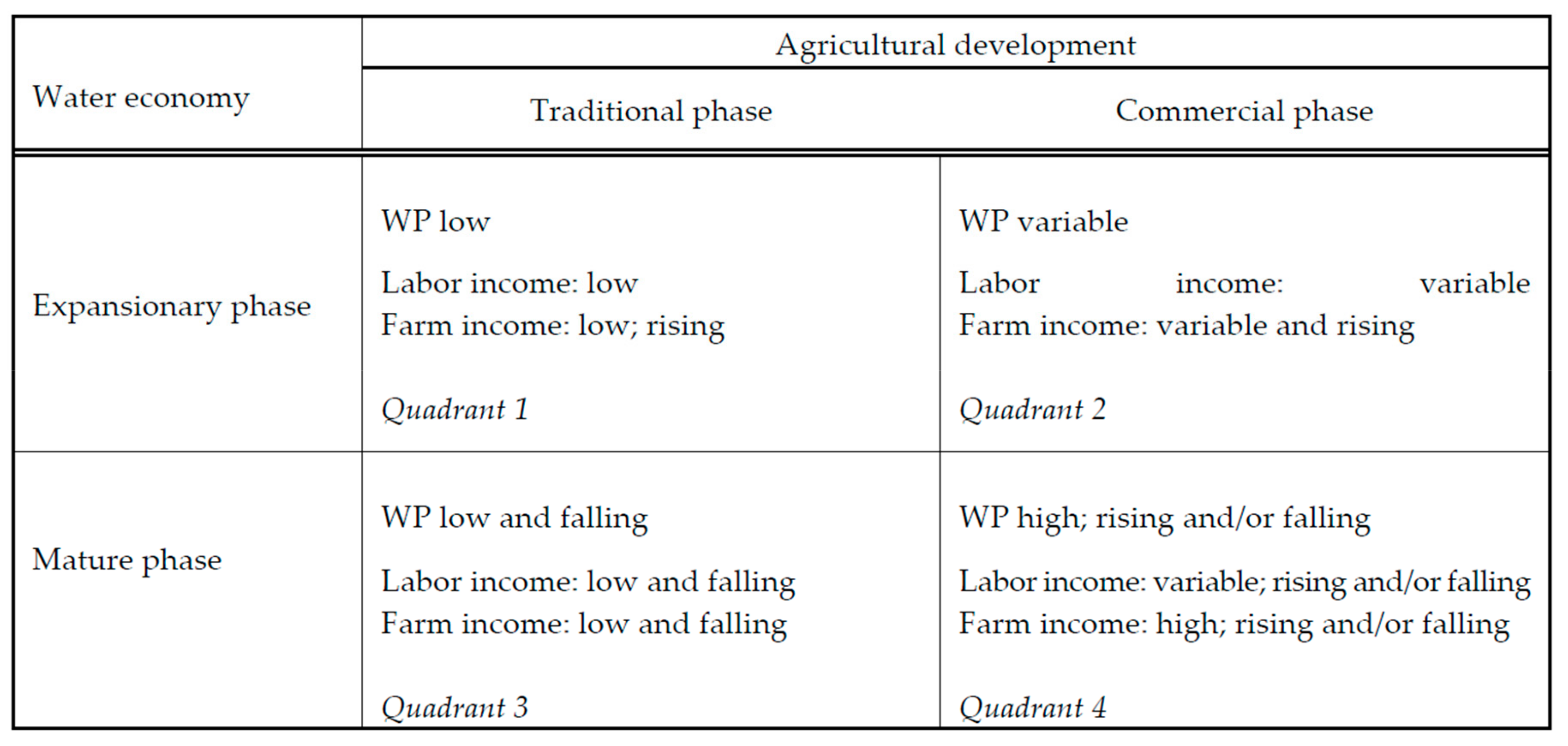
3.2. Water Economy and Irrigation Development Status
4. Case Study: Farm Labor and California Agriculture
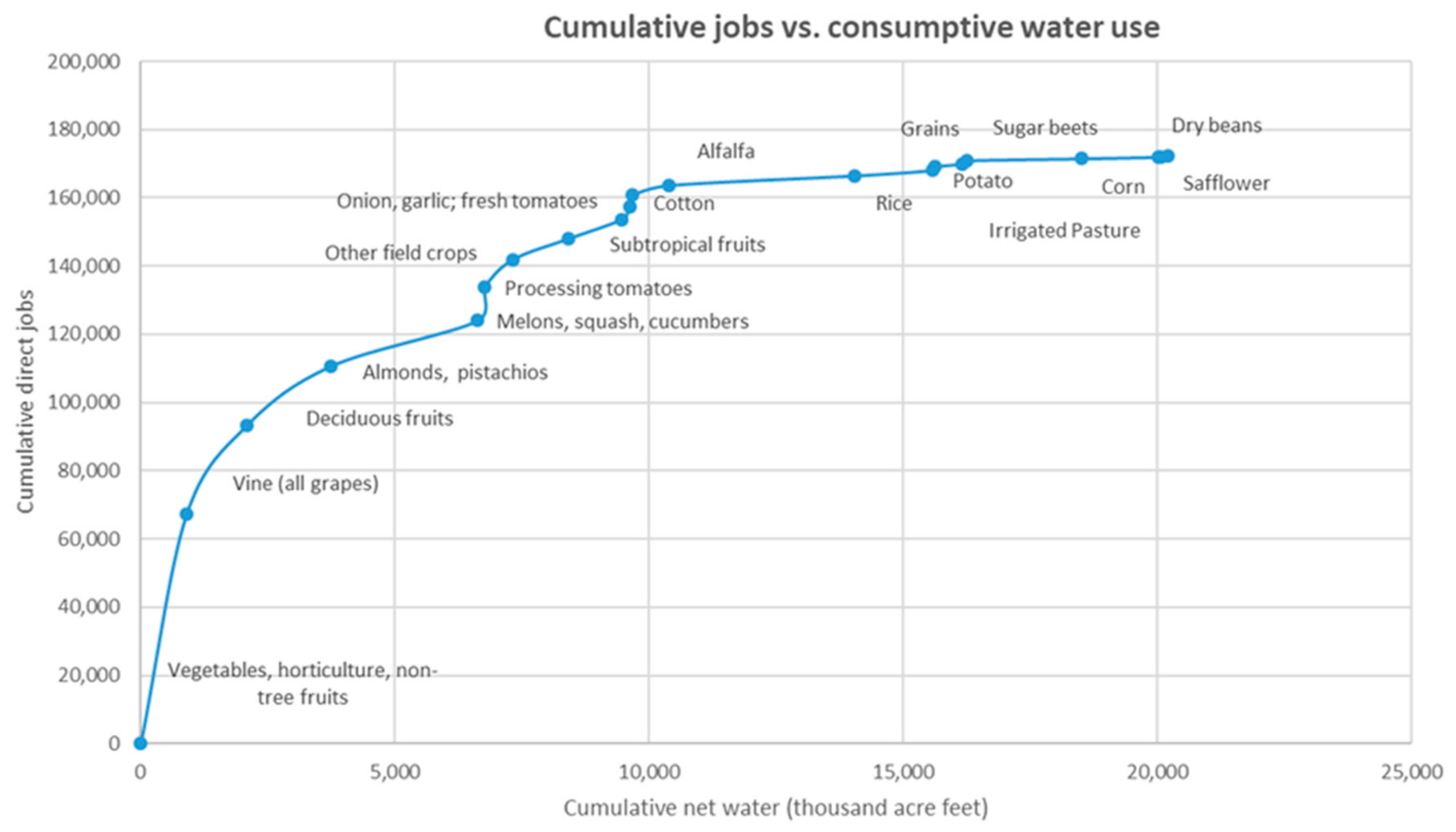
4.1. Water Productivity and Farm Labor
4.2. Crop Switching and Farm Labor
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallardo, R.K.; Sauer, J. Adoption of labor-saving technologies in agriculture. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2018, 10, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.E.; Charlton, D.; Yúnez-Naude, A. The end of farm labor abundance. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2012, 34, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahniser, S.; Taylor, J.E.; Hertz, T.; Charlton, D. Farm Labor Markets in the United States and Mexico Pose Challenges for U.S. Agriculture; EIB-201; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Gleick, P.H. Water management: Soft water paths. Nature 2002, 418, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.S.; Cordery, I.; Iacovides, I. Improved indicators of water use performance and productivity for sustainable water conservation and saving. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAO and the SDGs Indicators: Measuring up to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, M.P.; Gallardo, R.K.; Badruddozza, S.; Jiang, X. Regional equilibrium wage rate for hired farm workers in the tree fruit industry. West. Econ. Forum 2016, 15, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.E.; Martin, P.L. The immigrant subsidy in US agriculture: Farm employment, poverty, and welfare. Popul. Dev. Rev. 1997, 23, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, W.; Memon, F.A.; Savic, D.A. An integrated model to evaluate water-energy-food nexus at a household scale. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 93, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, R.; Medellin-Azuara, J.; MacEwan, D. Calculating California Cropping Patterns in 2050; University of California Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, E.M.; Bruce, E.; Boruff, B.; Duncan, J.M.; Horsley, J.; Pauli, N.; McNeill, K.; Neef, A.; Van Ogtrop, F.; Curnow, J.; et al. Sustainable development and the water–energy–food nexus: A perspective on livelihoods. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Azuara, J.; Lund, J.; Howitt, R. Jobs Per Drop Irrigating California Crops; California WaterBlog: Davis, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, M.; Turral, H.; Scheierling, S.M.; Tréguer, D.O.; McCornick, P.G. Beyond “More Crop Per Drop”: Evolving Thinking on Agricultural Water Productivity; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 169. [Google Scholar]
- Molden, D.; Oweis, T.; Steduto, P.; Bindraban, P.; Hanjra, M.A.; Kijne, J. Improving agricultural water productivity: Between optimism and caution. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheierling, S.; Treguer, D.O.; Booker, J.F. Water productivity in agriculture: Looking for water in the agricultural productivity and efficiency literature. Water Econ. Policy 2016, 2, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A. Determining the Economic Value of Water: Concepts and Methods, 1st ed.; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-1891853982. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, A. Property entitlements and pricing policies for a maturing water economy. Aust. J. Agric. Econ. 1981, 25, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp-Benedict, E.; Cook, S.; Allen, S.L.; Vosti, S.; Lemoalle, J.; Giordano, M.; Ward, J.; Kaczan, D. Connections between poverty, water and agriculture: Evidence from 10 river basins. Water Int. 2011, 36, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balana, B.B.; Bizimana, J.C.; Richardson, J.W.; Lefore, N.; Adimassu, Z.; Herbst, B.K. Economic and food security effects of small-scale irrigation technologies in northern Ghana. Water Resour. Econ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenmark, M.; Molden, D. Wake up to realities of river basin closure. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2008, 24, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey. Water Use Data for California. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/ca/nwis/water_use? (accessed on 2 January 2020).
- Hanak, E.; Escriva-Bou, A.; Gray, B.; Green, S.; Harter, T.; Jezdimirovic, J.; Lund, J.; Medellín-Azuara, J.; Moyle, P.; Seavy, N. Water and the Future of the San Joaquin Valley; Public Policy Institute of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlke, H.; Brown, A.; Orloff, S.; Putnam, D.; O’Geen, T. Managed winter flooding of alfalfa recharges groundwater with minimal crop damage. Calif. Agric. 2018, 72, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of California, Davis. Current Cost and Return Studies. Available online: https://coststudies.ucdavis.edu/en/current/ (accessed on 24 June 2019).
- Tindula, G.N.; Orang, M.N.; Snyder, R.L. Survey of irrigation methods in California in 2010. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedeling, E.; Zhang, M.; Girvetz, E.H. Climatic changes lead to declining winter chill for fruit and nut trees in California during 1950–2099. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, T.; Maskey, M.; Dahlberg, J.; Kearns, F.; Bali, K.; Zaccaria, D. Climate change trends and impacts on California agriculture: A detailed review. Agronomy 2018, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, A.; Dialesandro, J.; Steenwerth, K.; Lopez-Brody, N.; Elias, E. Vulnerability of California specialty crops to projected mid-century temperature changes. Clim. Chang. 2018, 148, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Azuara, J.; Howitt, R.E.; MacEwan, D.J.; Lund, J.R. Economic impacts of climate-related changes to California agriculture. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Crop with Specific Production Technologies | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation Technology | Almonds | Alfalfa | Black Eyed Beans | Grapes (Flame) | Peaches (Processing) | Tomatoes (Processing) |
| Drip | Sprinkler for Establishment, then Flood | Furrow; Double Cropped | Drip | Micro-Sprinkler | Sub-Surface Drip | |
| Costs ($/acre) | ||||||
| Total operating costs | 4027 | 1346 | 813 | 17,867 | 5550 | 3345 |
| Total labor cost | 345 | 74 | 70 | 10,641 | 251 | 396 |
| Irrigation labor cost (operating) | 124 | 42 | 20 | 124 | 41 | 85 |
| Total cost of irrigation water | 1144 | 693 | 432 | 432 | 210 | 625 |
| Total irrigation cost (total) | 1602 | 717 | 213 | 700 | 405 | 859 |
| Total operating and overhead costs | 6241 | 2409 | 1244 | 21,668 | 8825 | 4461 |
| Irrigation cost proportion (total) | 26% | 30% | 17% | 3% | 5% | 19% |
| Labor cost proportion (operating) | 3% | 3% | 2% | 1% | 1% | 3% |
| Irrigated Crop | 2015 FTE Jobs | Total Jobs | 2050 FTE Jobs | Total Jobs | 1991 FTE Jobs | Total Jobs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Jobs | Contract Labor | Direct Jobs | Contract Labor | Direct Jobs | Contract Labor | ||||
| Corn | 454 | 92 | 546 | 368 | 75 | 442 | 172 | 35 | 207 |
| Cotton | 2875 | 2891 | 5766 | 2606 | 2620 | 5226 | 11,133 | 11,195 | 22,328 |
| Dry beans | 119 | 24 | 143 | 107 | 22 | 129 | - | - | - |
| Grains | 928 | 189 | 1117 | 723 | 147 | 871 | 1049 | 214 | 1263 |
| Safflower | 126 | 25 | 151 | 120 | 24 | 144 | - | - | - |
| Sugar beets | 895 | 103 | 999 | 895 | 103 | 999 | 6910 | 795 | 7713 |
| Other field crops | 6114 | 5557 | 11,671 | 5003 | 4547 | 9550 | 3961 | 3600 | 7562 |
| Alfalfa | 2801 | 2546 | 5347 | 2,620 | 2381 | 5001 | 3056 | 2777 | 5833 |
| Irrigated Pasture | 588 | 534 | 1122 | 206 | 187 | 392 | 307 | 279 | 586 |
| Cucurbits | 9675 | 9136 | 18,811 | 10,291 | 9718 | 20,009 | - | - | - |
| Onion, garlic | 3647 | 3444 | 7092 | 3886 | 3670 | 7557 | - | - | - |
| Potato | 1011 | 954 | 1965 | 1073 | 1012 | 2085 | - | - | - |
| Fresh tomatoes | 3427 | 3236 | 6664 | 3647 | 3444 | 7092 | - | - | - |
| Processing tomatoes | 8214 | 7756 | 15,970 | 8652 | 8169 | 16,821 | 15,442 | 14,581 | 30,022 |
| Vegetables, horticulture, non-tree fruits | 67,227 | 63,484 | 130,711 | 71,563 | 67579 | 139,142 | 62,004 | 58,552 | 120,556 |
| Almonds, pistachios | 13,383 | 7006 | 20,389 | 13,498 | 7066 | 20,564 | - | - | - |
| Deciduous fruits | 17,383 | 20,315 | 37,699 | 17,538 | 20496 | 38,035 | 43,965 | 51,380 | 95,348 |
| Subtropical fruits | 5686 | 6645 | 12,331 | 5442 | 6360 | 11,802 | 8128 | 9499 | 17,628 |
| Vine (all grapes) | 26,008 | 30,395 | 56,404 | 26,965 | 31514 | 58,480 | 26,271 | 30,702 | 56,974 |
| Rice | 1573 | 320 | 1893 | 1566 | 319 | 1885 | 1499 | 305 | 1,803 |
| Total | 172,134 | 164,652 | 336,791 | 176,769 | 169,452 | 346,226 | 183,897 | 183,915 | 367,823 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Booker, J.F.; Trees, W.S. Implications of Water Scarcity for Water Productivity and Farm Labor. Water 2020, 12, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010308
Booker JF, Trees WS. Implications of Water Scarcity for Water Productivity and Farm Labor. Water. 2020; 12(1):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010308
Chicago/Turabian StyleBooker, James F., and W. Scott Trees. 2020. "Implications of Water Scarcity for Water Productivity and Farm Labor" Water 12, no. 1: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010308
APA StyleBooker, J. F., & Trees, W. S. (2020). Implications of Water Scarcity for Water Productivity and Farm Labor. Water, 12(1), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010308




