Transient Hydraulic Tomography Analysis of Fourteen Pumping Tests at a Highly Heterogeneous Multiple Aquifer–Aquitard System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
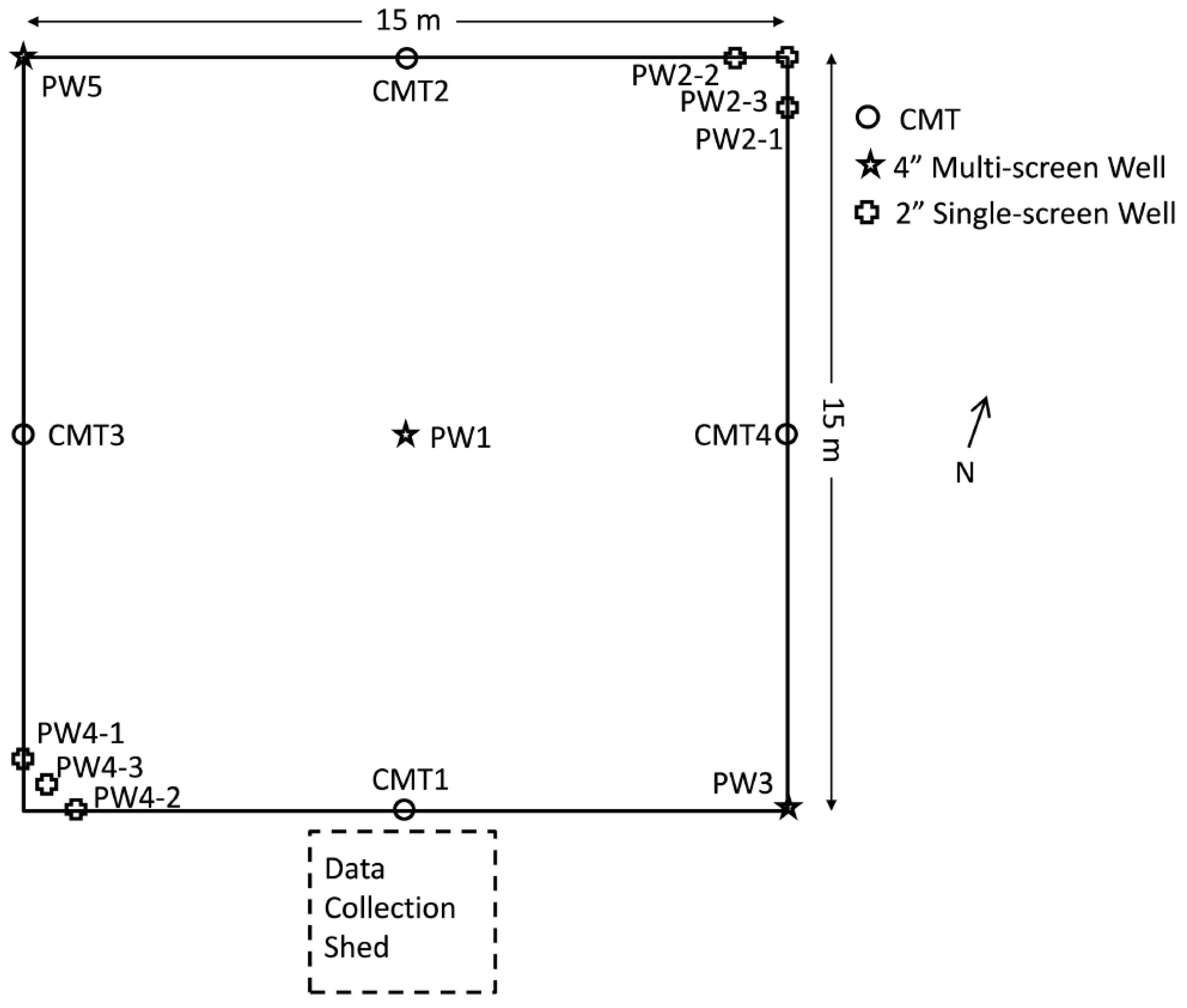
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sensors and Data Collection
2.3. Pumping Test Description and Data Selection
3. Inverse Modeling
3.1. Inverse Modeling Approach
3.2. Inverse Model Setup
4. Results
4.1. K and Ss Tomograms
4.2. Model Calibration
4.3. Comparison of the THT Results to Permeameter Test K
4.4. Model Validation
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Results to Those from Berg and Illman [18]
5.2. Advantages and Limitations of the Technology
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sudicky, E.A. A natural gradient experiment on solute transport in a sand aquifer: Spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity and its role in the dispersion process. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 2069–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Berg, S.J.; Illman, W.A. Field Study of Hydrogeologic Characterization Methods in a Heterogeneous Aquifer. Groundwater 2011, 49, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.J., Jr.; Dietrich, P.; Wittig, V.; Christy, T. Characterizing Hydraulic Conductivity with the Direct-Push Permeameter. Groundwater 2007, 45, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.C.; Liu, S. Hydraulic tomography: Development of a new aquifer test method. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Gardiner, R. Effectiveness of hydraulic tomography: Sandbox experiments. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, J.; Dietrich, P. Identification of the permeability distribution in soil by hydraulic tomography. Inverse Probl. 1995, 11, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, M.; Barrash, W.; Kitanidis, P.K.; Malama, B.; Revil, A.; Straface, S.; Rizzo, E. A potential-based inversion of unconfined steady-state hydraulic tomography. Groundwater 2009, 47, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Brauchler, R.; Herold, M.; Bayer, P. Hydraulic tomography analog outcrop study: Combining travel time and steady shape inversion. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Brauchler, R.; Bayer, P. A new sequential procedure for hydraulic tomographic inversion. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 62, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soueid Ahmed, A.; Jardani, A.; Revil, A.; Dupont, J.P. Specific storage and hydraulic conductivity tomography through the joint inversion of hydraulic heads and self-potential data. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 89, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soueid Ahmed, A.; Zhou, J.; Jardani, A.; Revil, A.; Dupont, J.P. Image-guided inversion in steady-state hydraulic tomography. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 82, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A.; Liu, X.; Craig, A. Steady-state hydraulic tomography in a laboratory aquifer with deterministic heterogeneity: Multi-method and multiscale validation of hydraulic conductivity tomograms. J. Hydrol. 2007, 341, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauchler, R.; Böhm, G.; Leven, C.; Dietrich, P.; Sauter, M. A laboratory study of tracer tomography. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Illman, W.A.; Berg, S.J. On the importance of geological data for hydraulic tomography analysis: Laboratory sandbox study. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straface, S.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Zhu, J.; Troisi, S.; Lee, C.H. Sequential aquifer tests at a well field, Montalto Uffugo Scalo, Italy. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohling, G.C.; Butler, J.J.; Zhan, X.; Knoll, M.D. A field assessment of the value of steady shape hydraulic tomography for characterization of aquifer heterogeneities. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Englert, A.; Cirpka, O.A.; Vereecken, H. Three-dimensional geostatistical inversion of flowmeter and pumping test data. Groundwater 2008, 46, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, S.J.; Illman, W.A. Three-dimensional transient hydraulic tomography in a highly heterogeneous glaciofluvial aquifer-aquitard system. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstetler, D.L.; Barrash, W.; Leven, C.; Cardiff, M.; Chidichimo, F.; Kitanidis, P.K. Hydraulic Tomography: Continuity and Discontinuity of High-K and Low-K Zones. Groundwater 2016, 54, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Yeh, T.-C.J.; Wen, J.-C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zha, Y.; Tsai, J.-P.; Hao, Y.; Liang, Y. Characterizing subsurface hydraulic heterogeneity of alluvial fan using riverstage fluctuations. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A.; Liu, X.; Takeuchi, S.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Ando, K.; Saegusa, H. Hydraulic tomography in fractured granite: Mizunami Underground Research site, Japan. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yeh, T.C.J. Characterization of aquifer heterogeneity using transient hydraulic tomography. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Yeh, T.-C.J.; Illman, W.A.; Tanaka, T.; Bruines, P.; Onoe, H.; Saegusa, H.; Mao, D.; Takeuchi, S.; Wen, J.-C. An Application of Hydraulic Tomography to a Large-Scale Fractured Granite Site, Mizunami, Japan. Groundwater 2016, 54, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, S.J.; Illman, W.A. Comparison of Hydraulic Tomography with Traditional Methods at a Highly Heterogeneous Site. Groundwater 2015, 53, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illman, W.A.; Zhu, J.; Craig, A.J.; Yin, D. Comparison of aquifer characterization approaches through steady state groundwater model validation: A controlled laboratory sandbox study. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, S.J.; Illman, W.A. Capturing aquifer heterogeneity: Comparison of approaches through controlled sandbox experiments. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Illman, W.A. On the importance of geological data for three-dimensional steady-state hydraulic tomography analysis at a highly heterogeneous aquifer-aquitard system. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 640–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.J.; Frind, E.G. Modeling a Complex Multi-Aquifer System: The Waterloo Moraine. Ground Water. 1998, 36, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verruijt, A. Elastic Storage of Aquifers, Flow through Porous Media; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 331–376. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, P.A. Deformation-Induced Changes in Hydraulic Head During Ground-Water Withdrawal. Groundwater 1996, 34, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Wen, J.C. A simultaneous successive linear estimator and a guide for hydraulic tomography analysis. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Jin, M.; Hanna, S. An Iterative Stochastic Inverse Method: Conditional Effective Transmissivity and Hydraulic Head Fields. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Srivastava, R.; Guzman, A.; Harter, T. A Numerical Model for Water Flow and Chemical Transport in Variably Saturated Porous Media. Groundwater 1993, 31, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Zhu, J.; Tim, H.L.; Hsu, N.S.; Chen, C.H.; Sancho, A.F. Traditional analysis of aquifer tests: Comparing apples to oranges? Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Well Location | Pumping/Injection Rate (L/min) c | Duration (hour) | Maximum Pressure Head Change (m) | Port of Maximum Pressure Head Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW1-1 b | −1.89 | 4.5 | 0.55 | CMT2-2 |
| PW1–3 a | 10.50 | 6 | 1.10 | CMT4-3 |
| PW1–4 a | 6.30 | 8.5 | 0.98 | CMT2-4 |
| PW1–5 a | 4.40 | 22.5 | 0.18 | CMT2-4 |
| PW1-6 b | 0.95 | 6.5 | 0.74 | CMT3-6 |
| PW1-7 b | 1.05 | 26.5 | 0.42 | CMT3-6 |
| PW2-3 b | 1.91 | 7 | 0.30 | CMT4-3 |
| PW3-1 b | −0.94 | 4.4 | 0.21 | CMT1-2 |
| PW3–3 a | 2.10 | 22 | 0.57 | CMT1-3 |
| PW3–4 a | 1.50 | 22 | 0.08 | CMT1-5 |
| PW4–3 a | 30.20 | 22.5 | 0.88 | CMT3-4 |
| PW5-1 b | −0.85 | 4.52 | 0.12 | CMT2-1 |
| PW5–3 a | 7.80 | 22 | 0.92 | CMT2-3 |
| PW5–4 a | 7.80 | 8.5 | 0.45 | CMT2-4 |
| PW5–5 a | 8.10 | 22 | 0.32 | CMT2-3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Illman, W.A.; Zha, Y.; Yeh, T.-C.J.; Mok, C.M.B.; Berg, S.J.; Han, D. Transient Hydraulic Tomography Analysis of Fourteen Pumping Tests at a Highly Heterogeneous Multiple Aquifer–Aquitard System. Water 2019, 11, 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091864
Zhao Z, Illman WA, Zha Y, Yeh T-CJ, Mok CMB, Berg SJ, Han D. Transient Hydraulic Tomography Analysis of Fourteen Pumping Tests at a Highly Heterogeneous Multiple Aquifer–Aquitard System. Water. 2019; 11(9):1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091864
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhanfeng, Walter A. Illman, Yuanyuan Zha, Tian-Chyi Jim Yeh, Chin Man Bill Mok, Steven J. Berg, and Dongmei Han. 2019. "Transient Hydraulic Tomography Analysis of Fourteen Pumping Tests at a Highly Heterogeneous Multiple Aquifer–Aquitard System" Water 11, no. 9: 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091864
APA StyleZhao, Z., Illman, W. A., Zha, Y., Yeh, T.-C. J., Mok, C. M. B., Berg, S. J., & Han, D. (2019). Transient Hydraulic Tomography Analysis of Fourteen Pumping Tests at a Highly Heterogeneous Multiple Aquifer–Aquitard System. Water, 11(9), 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091864







