Aquifer Response to Estuarine Stream Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
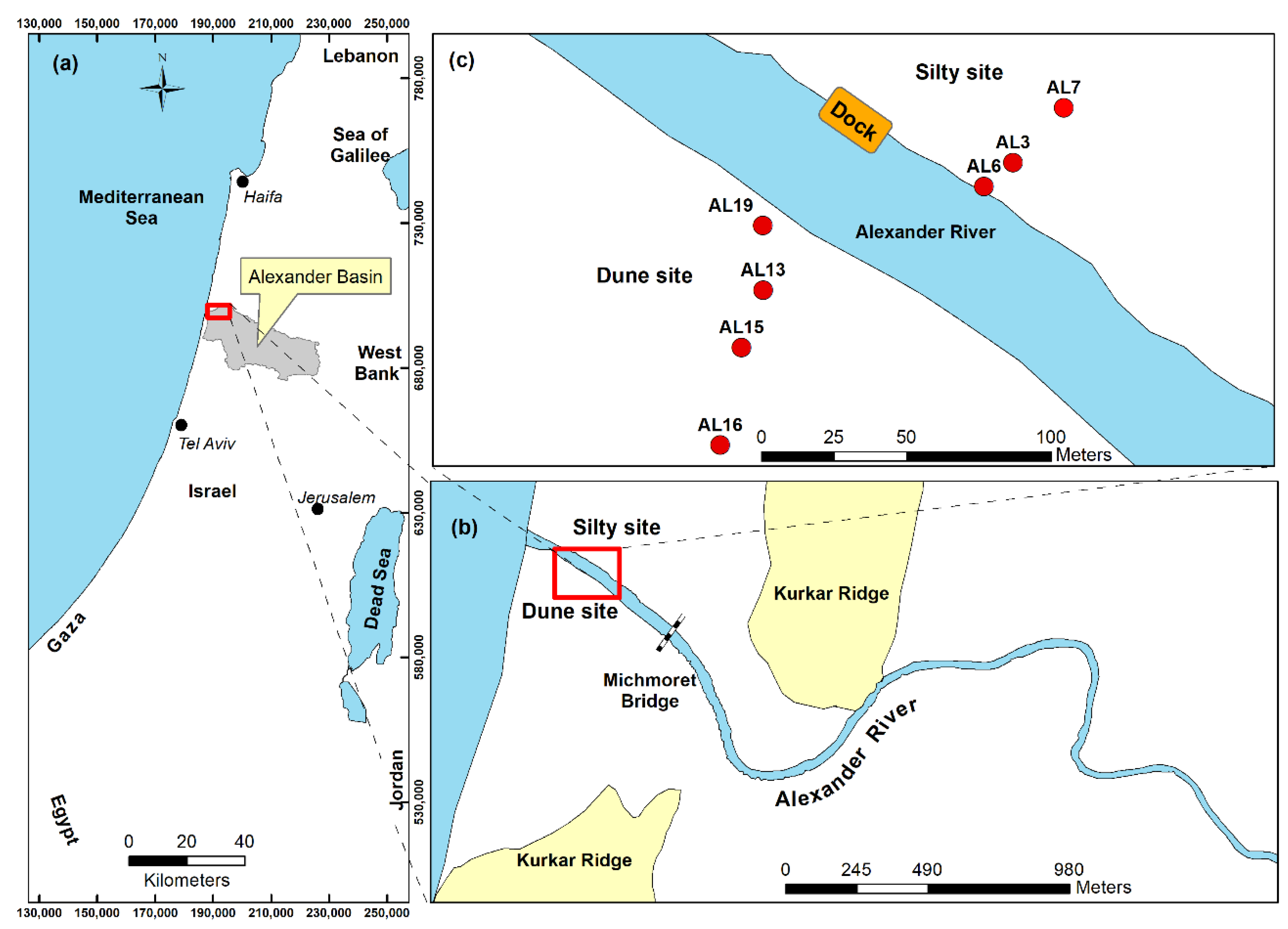
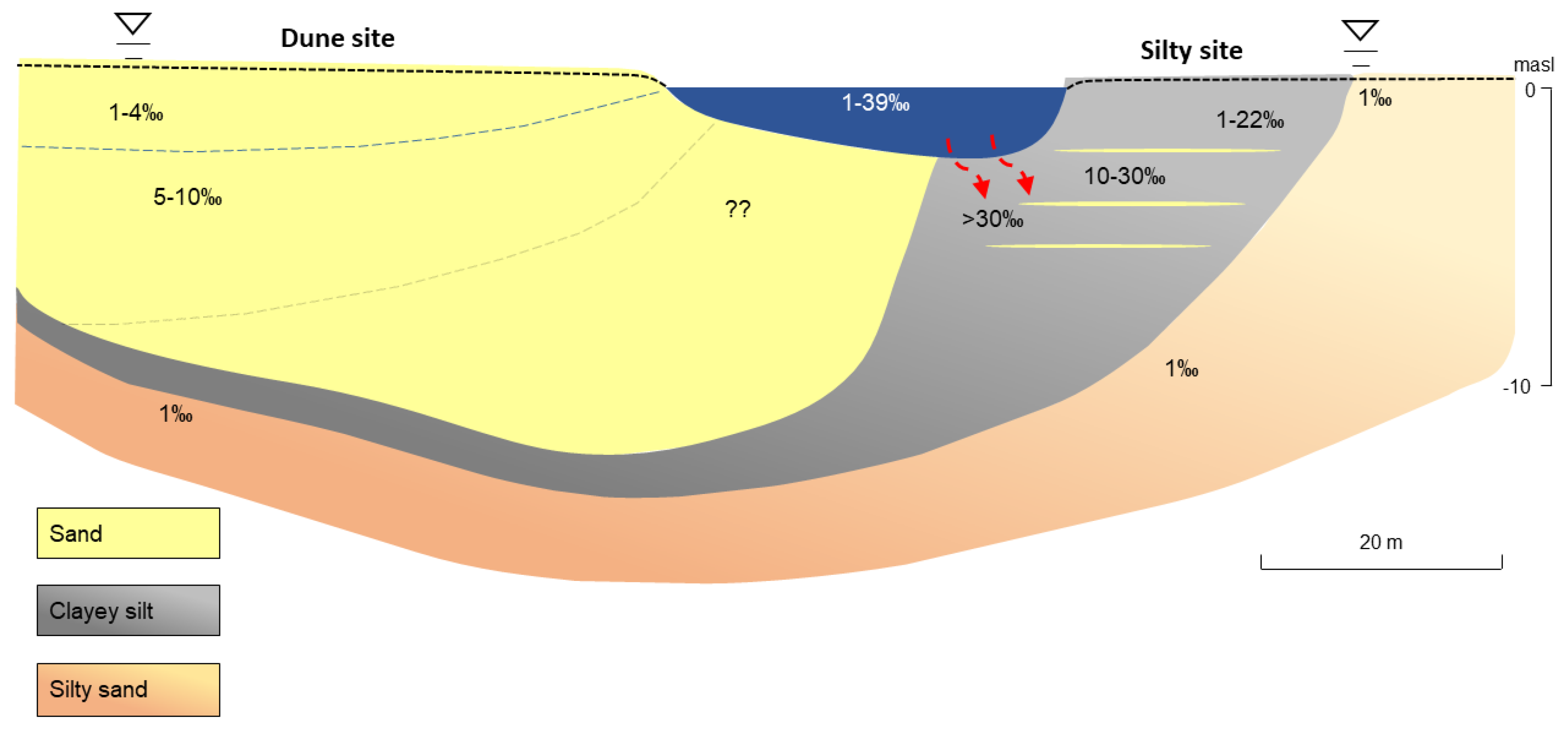
The Study Area
2. Methods
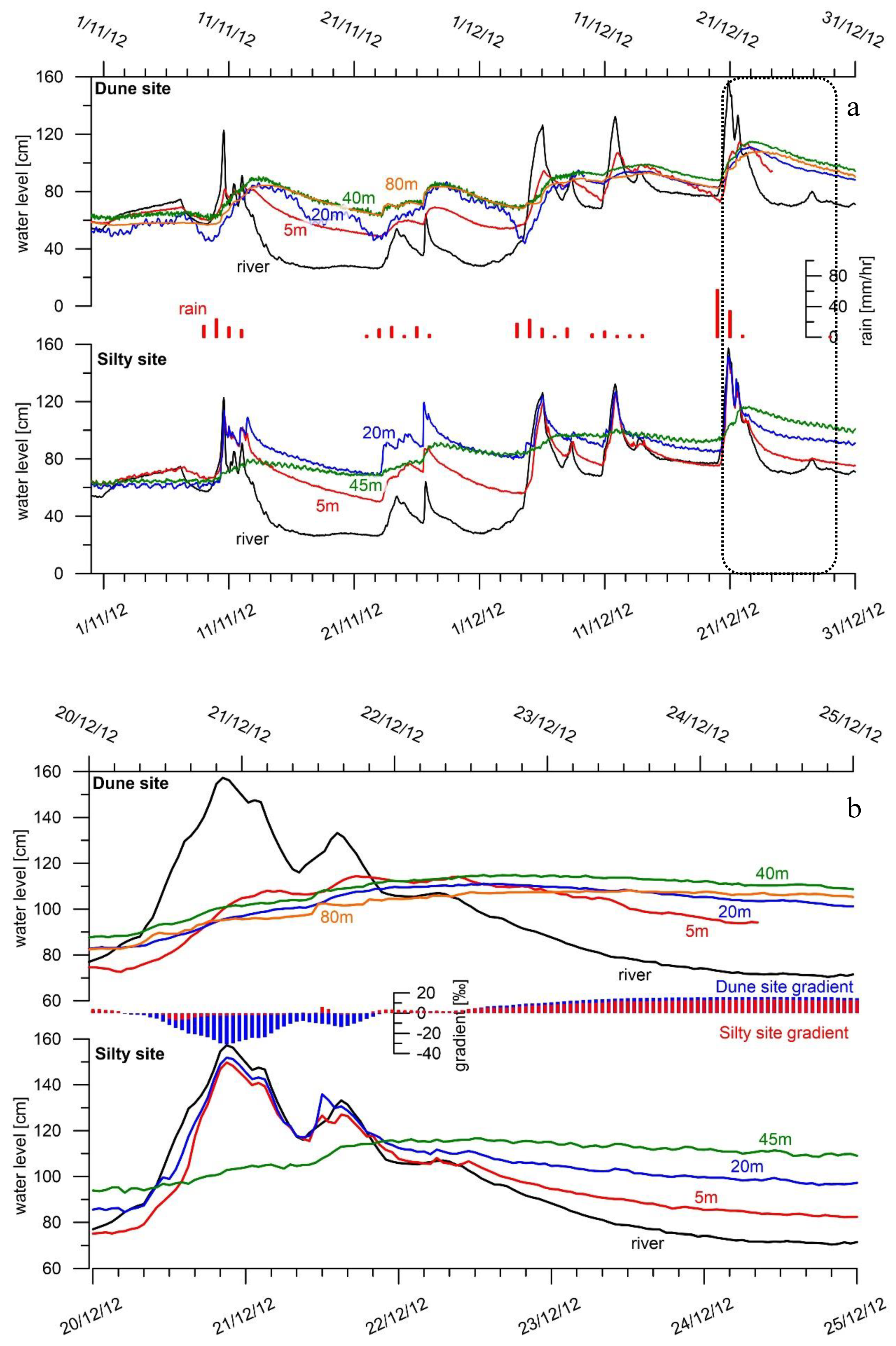
3. Results
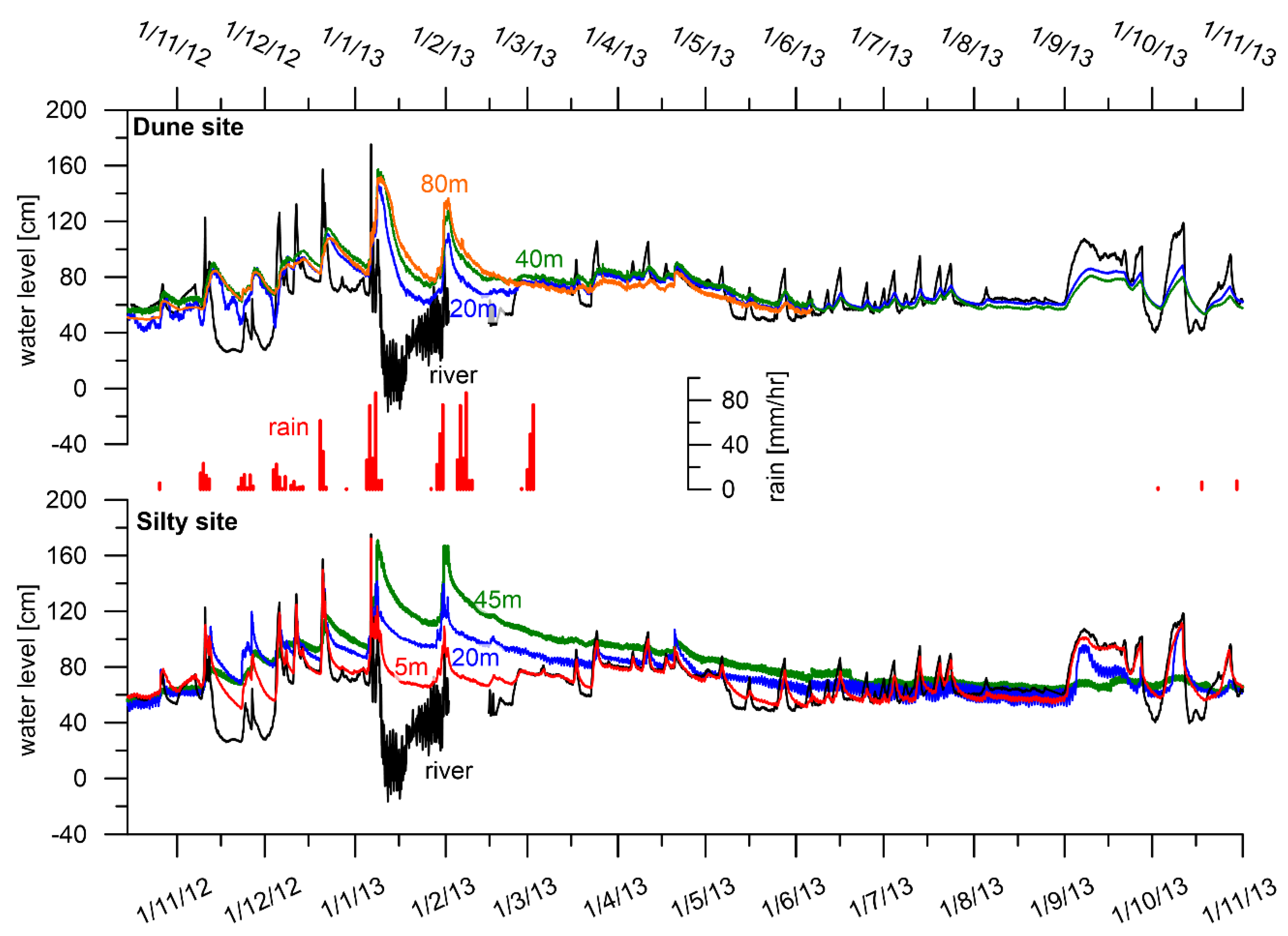
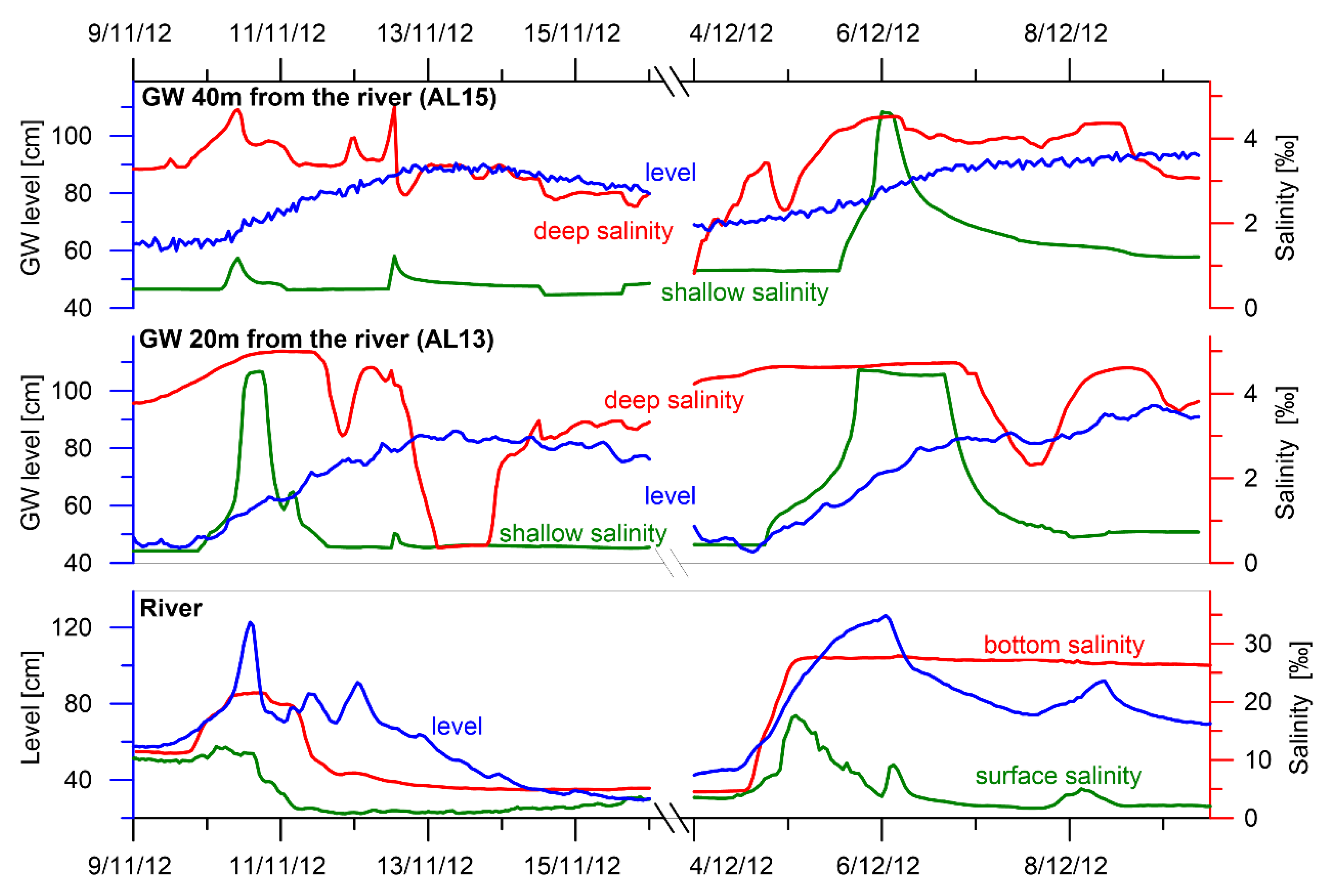
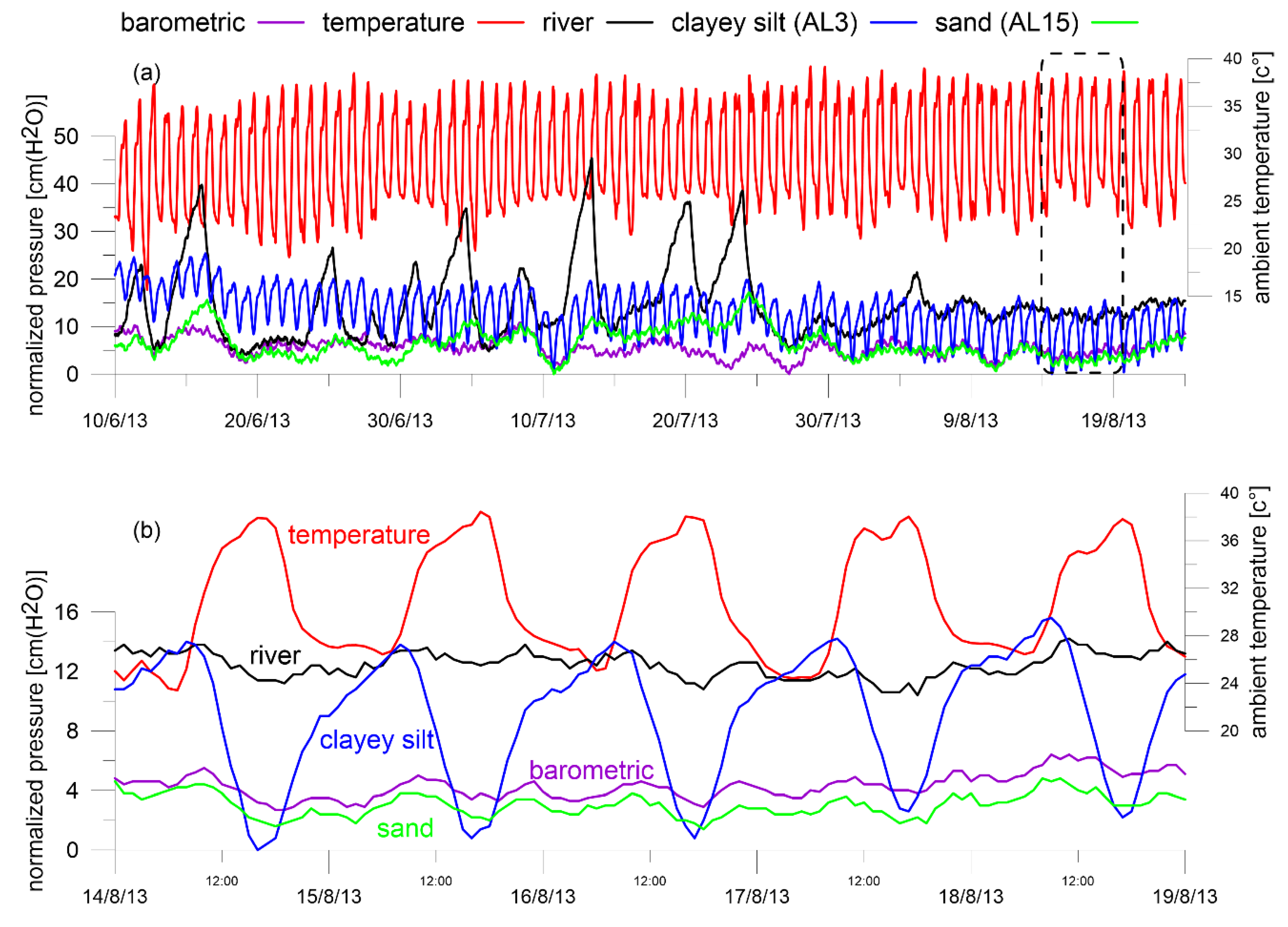
3.1. River Level and Salinity Dynamics
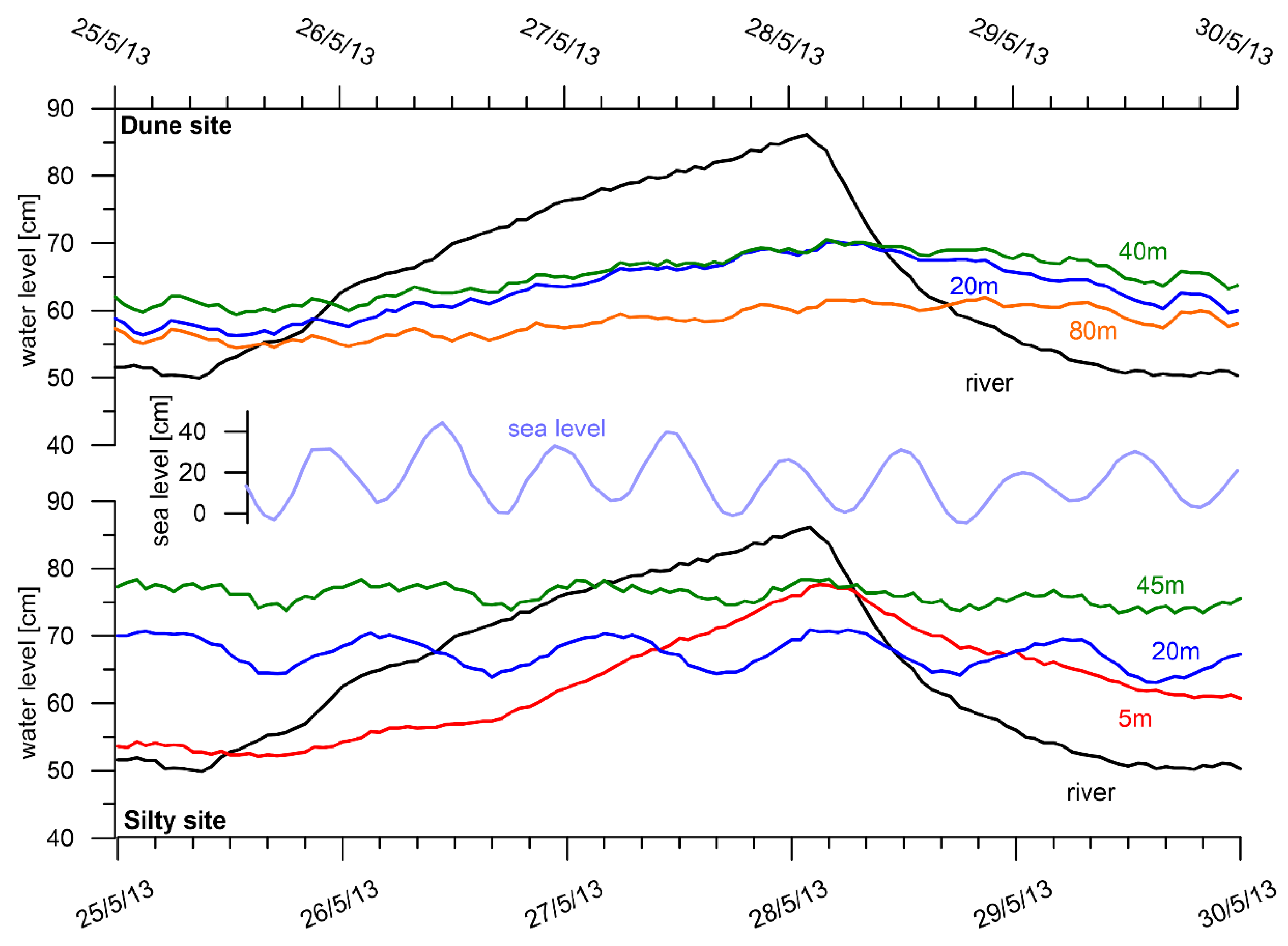
3.2. Groundwater Dynamics
3.2.1. Groundwater Levels
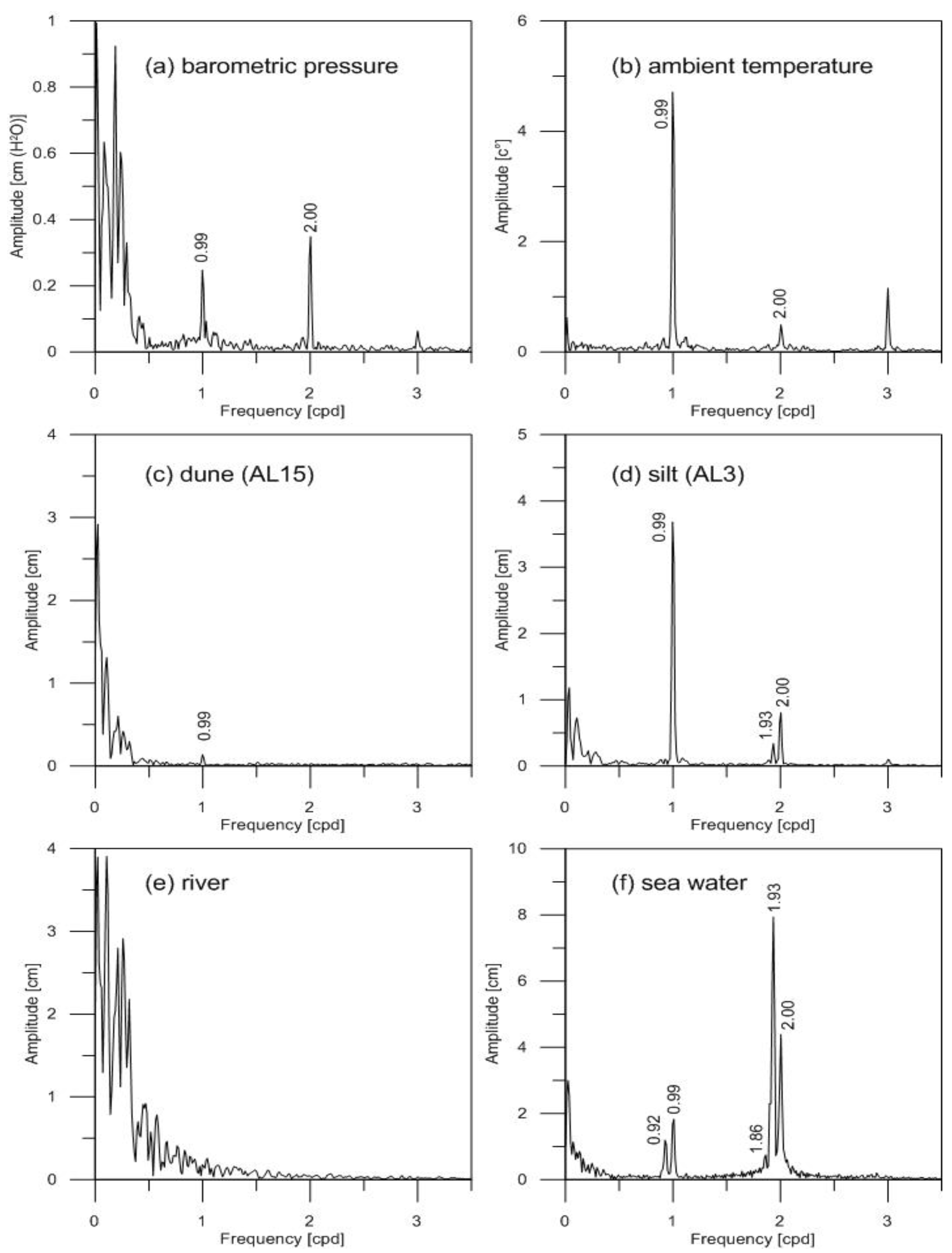
Diurnal Level Fluctuations
3.2.2. Groundwater Salinity
Salinity in the Sandy Dune Site
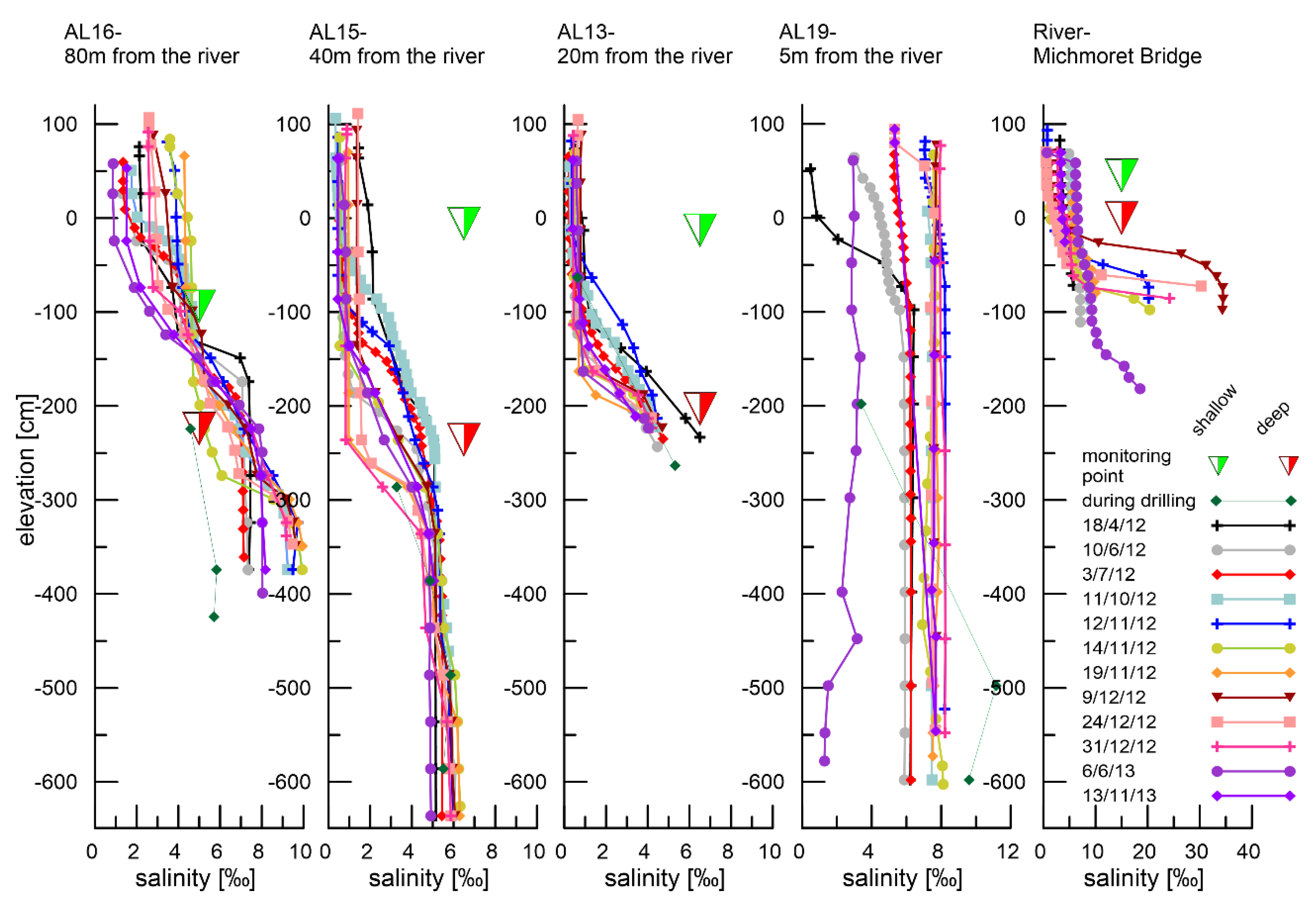
Salinities at the Silty Site
4. Discussion
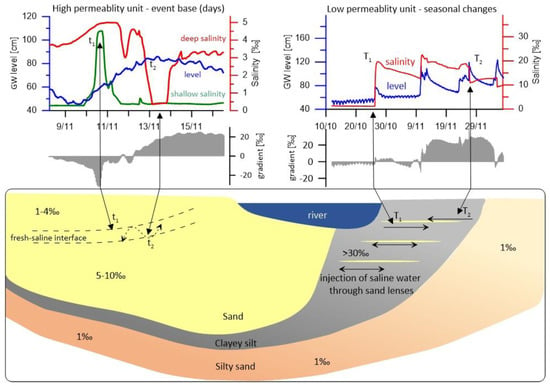
4.1. Salinization Patterns in a Sandy Bank
4.2. Controls on Salinization in the Silty Bank
Tidal Signals in Groundwater
4.3. Conclusions
- The interaction of an estuarine river with a high-permeability aquifer, such as at the Dune site, is similar to common coastal settings, including the formation of a quasi-steady-state FSI.
- Low-permeability aquifer units may store high-salinity water, remnants of past seawater encroachment in the river channel.
- The sharp fluctuations in salinity, observed in the Alexander River Silty site in relation to river events are due to (1) the occurrence of saline water bodies in this unit, (2) changes in river water levels, and (3) the existence of high-permeability lenses with low storativity within the silt.
- The low-permeability unit is efficiently blocking the saline water from reaching the regional sandy aquifer, even at a short distance from the river.
- Daily fluctuations in the Silty unit, which negatively correlate with solar radiation, are probably due to a photosynthetic pump.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conrads, P.; Roehl, E.; Daamen, R.; Cook, J.; Sexton, C.T.; Water, B.J.; Authority, S.; Tufford, D.L.; Carbone, G.J.; Dow, K. Estimating salinity intrusion effects due to climate change on the lower savannah river estuary. In Proceedings of the South Carolina Environmental Conference, Myrle Beach, SC, USA, 10–13 March 2019; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Demirel, Z. The history and evaluation of saltwater intrusion into a coastal aquifer in Mersin, Turkey. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 70, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.R.; Taniguchi, M.; Kooi, H.; Gurdak, J.J.; Allen, D.M.; Hiscock, K.M.; Treidel, H.; Aureli, A. Beneath the surface of global change: Impacts of climate change on groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 532–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kåss, A.; Gavrieli, I.; Yechieli, Y.; Vengosh, A.; Starinsky, A. The impact of freshwater and wastewater irrigation on the chemistry of shallow groundwater: A case study from the Israeli Coastal Aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2005, 300, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.M.; Singh, V.P. Effect of climate change on sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acworth, R.I.; Rau, G.C.; McCallum, A.M.; Andersen, M.S.; Cuthbert, M.O. Understanding connected surface-water/groundwater systems using Fourier analysis of daily and sub-daily head fluctuations. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 23, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.H. A hypothesis concerning the dynamic balance of fresh water and salt water in a coastal aquifer. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1959, 64, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments. Nature 1996, 380, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, Y.; Burnett, W.C.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Shalem, Y.; Yechieli, Y.; Herut, B. Role of aquifer heterogeneity in fresh groundwater discharge and seawater recycling: An example from the Carmel coast, Israel. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, C12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.; Cheng, A.H.D.; Sorek, S.; Ouazar, D.; Herrera, I. Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: Concepts, Methods, and Practices; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 1999; p. 627. [Google Scholar]
- Oz, I.; Shalev, E.; Gvirtzman, H.; Yechieli, Y.; Gavrieli, I. Groundwater flow patterns adjacent to a long-term stratified (meromictic) lake. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.E.A. Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: Is our technology ready for the problems ahead? Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, J.C. Exploitation, Restoration and Management. In Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers—Concepts, Methods and Practices; Bear, J., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 1999; pp. 73–125. [Google Scholar]
- Acworth, R.I.; Dasey, G.R. Mapping of the hyporheic zone around a tidal creek using a combination of borehole logging, borehole electrical tomography and cross-creek electrical imaging, New South Wales, Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linderfelt, W.R.; Turner, J.V. Interaction between shallow groundwater, saline surface water and nutrient discharge in a seasonal estuary: The Swan-Canning system. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 2631–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalem, Y.; Weinstein, Y.; Levi, E.; Herut, B.; Goldman, M.; Yechieli, Y. The extent of aquifer salinization next to an estuarine river: An example from the eastern Mediterranean. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 23, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, O.; Yechieli, Y.; Herut, B.; Lazar, B. Geochemical evolution and timescale of seawater intrusion into the coastal aquifer of Israel. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Rosenthal, E. Saline groundwater in Israel: Its bearing on the water crisis in the country. J. Hydrol. 1994, 156, 389–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Volker, R.; Lockington, D. Tidal effects on sea water intrusion in unconfined aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1999, 216, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloul, A.J.; Zeitoun, D.G. A Semi-Empirical Approach to Intrusion Monitoring in Israeli Coastal Aquifer. In Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: Concepts, Methods and Practices; Bear, J., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 1999; pp. 543–558. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.; Gibbes, B.; Carey, H.; Li, L. Salt-freshwater dynamics in a subterranean estuary over a spring-neap tidal cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Erler, D.V.; Santos, I.; Lockington, D. Effects of beach slope breaks on nearshore groundwater dynamics. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 2530–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.; Gilad, D.; Ronen, A.; Melloul, A. Mapping of seawater intrusion into the coastal aquifer of Israel by the time domain electromagnetic method. Geoexploration 1991, 28, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarzenski, P.W.; Burnett, W.C.; Greenwood, W.J.; Herut, B.; Peterson, R.; Dimova, N.; Shalem, Y.; Yechieli, Y.; Weinstein, Y. Combined time-series resistivity and geochemical tracer techniques to examine submarine groundwater discharge at Dor Beach, Israel. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979; p. 604. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, H.A.; Mulligan, A.E.; Harvey, C.F. Seasonal oscillations in water exchange between aquifers and the coastal ocean. Nature 2005, 436, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faye, S.; Maloszewski, P.; Stichler, W.; Trimborn, P.; Cissé Faye, S.; Bécaye Gaye, C. Groundwater salinization in the Saloum (Senegal) delta aquifer: Minor elements and isotopic indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 343, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgulet, D.; Tick, G. The extent of saltwater intrusion in Southern Baldwin County, Alabama. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngom, F.; Tweed, S.; Bader, J.-C.; Saos, J.-L.; Malou, R.; LeDuc, C.; Leblanc, M. Rapid evolution of water resources in the Senegal delta. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 144, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navoy, A.S.; Voronin, L.M.; Modica, E. Vulnerability of Production Wells in the Potomac-Raritan-Magothy Aquifer System to Saltwater Intrusion from the Delaware River in Camden, Gloucester, and Salem Counties, New Jersey; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Leston, VA, USA, 2005.
- Smith, A.J.; Turner, J.V. Density-dependent surface water-groundwater interaction and nutrient discharge in the Swan-Canning Estuary. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 2595–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, S. Importance of surface-subsurface exchange in stream ecosystems: The hyporheic zone. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Rosenberry, D.O. Effects of Ground Water Exchange on the Hydrology and Ecology of Surface Water. Ground Water 2002, 40, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.D. Nutrient and flow vector dynamics at the hyporheic/groundwater interface and their effects on the interstitial fauna. Hydrobiologia 1993, 251, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Glover, R.E. The pattern of fresh-water flow in a coastal aquifer. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1959, 64, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenkopane, M.; Werner, A.D.; Lockington, D.A.; Li, L. Influence of variable salinity conditions in a tidal creek on riparian groundwater flow and salinity dynamics. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, T.E.; Goodman, A.S. Quantitative analysis of saltwater-freshwater relationships in groundwater systems—A historical perspective. J. Hydrol. 1985, 80, 125–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Lockington, D.A. Tidal impacts on riparian salinities near estuaries. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trefry, M.; Svensson, T.; Davis, G. Hypoaigic influences on groundwater flux to a seasonally saline river. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarig, G. The Suspected Influence of Seawater Drainage from Sea Turtle Rescue Center on the Ecological System of the Alexander Estuary; Rupin Academic Center: Michmoret, Israel, 2008; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Gvirtzman, G.; Wieder, M. Climate of the last 53,000 Years in the eastern Mediterranean, based on soil-sequence Stratigraphy in the coastal plain of Israel. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2001, 20, 1827–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichter, M. The Dynamic Morphology of River Mouths along the Mediterranean Coast of Israel; Haifa University: Haifa, Israel, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lichter, M.; Klein, M.; Zviely, D. Dynamic morphology of small south-eastern Mediterranean river mouths: A conceptual model. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.L. The practical salinity scale of 1978 and its antecedents. Mar. Geodesy 1982, 5, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Camp, M.; Vauterin, P. Tsoft: Graphical and interactive software for the analysis of time series and Earth tides. Comput. Geosci. 2005, 31, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvirtzman, H.; Magaritz, M. Investigation of Water Movement in the Unsaturated Zone Under an Irrigated Area Using Environmental Tritium. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, D.; Magaritz, M.; Paldor, N.; Bachmat, Y. The Behavior of Groundwater in the Vicinity of the Water Table Evidenced by Specific Discharge Profiles. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, H.; Lenkopane, M.K.; Werner, A.D.; Li, L.; Lockington, D.A.; Werner, A. Tidal controls on coastal groundwater conditions: Field investigation of a macrotidal system. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 56, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.; DeSimone, L.; Moench, A. Aquifer response to stream-stage and recharge variations. II. Convolution method and applications. J. Hydrol. 2000, 230, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moench, A.F.; Barlow, P.M. Aquifer response to stream-stage and recharge variations. I. Analytical step-response functions. J. Hydrol. 2000, 230, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Kong, J.; Li, L.; Barry, D.; Barry, D. Effects of soil stratigraphy on pore-water flow in a creek-marsh system. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanon, E.; Yechieli, Y.; Shalev, E.; Friedman, V.; Gvirtzman, H. Reliable Monitoring of the Transition Zone Between Fresh and Saline Waters in Coastal Aquifers. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2013, 33, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalev, E.; Lazar, A.; Wollman, S.; Kington, S.; Yechieli, Y.; Gvirtzman, H. Biased Monitoring of Fresh Water-Salt Water Mixing Zone in Coastal Aquifers. Ground Water 2009, 47, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.J.; Kluitenberg, G.J.; Whittemore, D.O.; Loheide, S.P.; Jin, W.; Billinger, M.A.; Zhan, X. A field investigation of phreatophyte-induced fluctuations in the water table. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W02404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribovszki, Z.; Szilágyi, J.; Kalicz, P. Diurnal fluctuations in shallow groundwater levels and streamflow rates and their interpretation—A review. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal-Larsen, J.H. Fluctuations in the level of the phreatic surface with an atmospheric deposit in the form of dew. Bodenkd. Forsch. 1935, 4, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Cayan, D.R.; Lundquist, J.D. Seasonal and Spatial Patterns in Diurnal Cycles in Streamflow in the Western United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 591–603. [Google Scholar]
- Wain, A. Diurnal River Flow Variations and Development Planning in the Tropics. Geogr. J. 1994, 160, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Malama, B.; Barrash, W.; Flores, A.N. Recognizing and modeling variable drawdown due to evapotranspiration in a semiarid riparian zone considering local differences in vegetation and distance from a river source. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Site | Lithology | Borehole | Depth (m) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Hydraulic Conductivities (m/day) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silty | Clayey silt | AL6 | 2–3 | 37.0 | 49.0 | 14.0 | 1 |
| Dune | Sand | AL13 | 3–4 | 94.5 | 5.0 | 0.5 | 13 |
| Dune | Sand | AL15 | 6–7 | 94 | 5.5 | 0.5 | 15 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shalem, Y.; Yechieli, Y.; Herut, B.; Weinstein, Y. Aquifer Response to Estuarine Stream Dynamics. Water 2019, 11, 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081678
Shalem Y, Yechieli Y, Herut B, Weinstein Y. Aquifer Response to Estuarine Stream Dynamics. Water. 2019; 11(8):1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081678
Chicago/Turabian StyleShalem, Yehuda, Yoseph Yechieli, Barak Herut, and Yishai Weinstein. 2019. "Aquifer Response to Estuarine Stream Dynamics" Water 11, no. 8: 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081678
APA StyleShalem, Y., Yechieli, Y., Herut, B., & Weinstein, Y. (2019). Aquifer Response to Estuarine Stream Dynamics. Water, 11(8), 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081678