Water Lifting Water: A Comprehensive Spatiotemporal Review on the Hydro-Powered Water Pumping Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
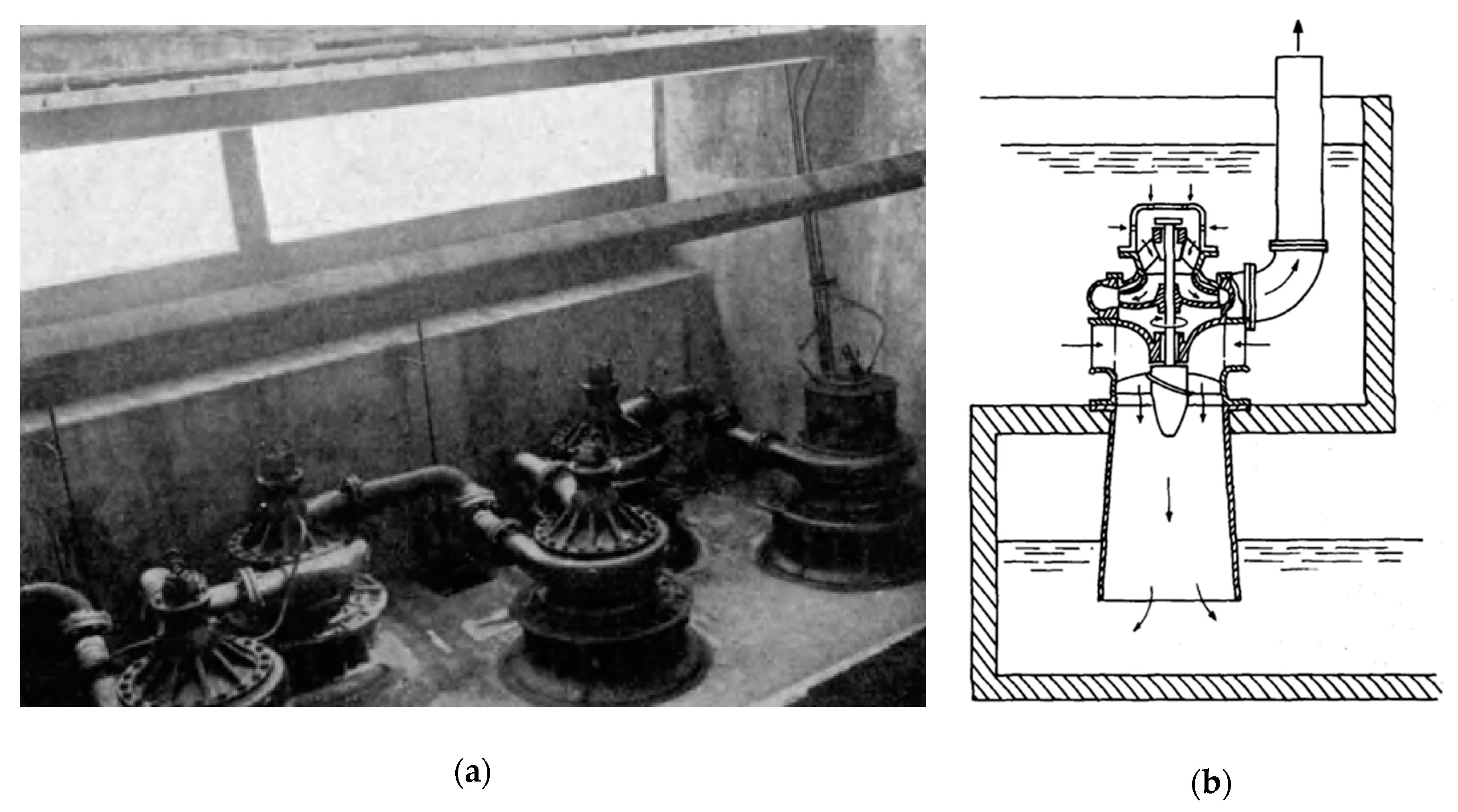
- To summarize and classify the HPP technologies researched, applied, and eventually commercialized globally over time;
- To define their state-of-the-art by synthesizing their respective storylines and highlighting the highest level of their developments;
- To identify global spatial and temporal patterns on the (re)invention, application, and spread of HPP technologies.
2. Methods
2.1. Selection Criteria for HPP Technologies
- Exclusively driven by the kinetic and/or potential energy of water;
- Rely exclusively on hydro-mechanical energy, hence not relying whatsoever on electro/electrochemical conversion processes;
- Work by building up pressure (i.e., must not be a direct lift technology);
- Pose any form of actual or potential use for supplying water, preferably to agricultural activities and human consumption, thus must ensure a relatively constant and reliable flow. As a consequence, devices such as the superhydrophobic pump [33] were neglected;
2.2. Sources of Information
- Peer-reviewed literature, from online academic databases through Google Scholar search engine (https://scholar.google.com/) and Google Books digital library service (https://books.google.com/);
- Peer-reviewed and grey literature (i.e., non-peer-reviewed), retrieved from online databases, accessed through Google search engine (https://www.google.com/);
- Documents bibliographically referenced in the two previous sources (particularly old ones)—yet not indexed in the previous search engines—from different academic databases and libraries worldwide (through TU Delft library services);
- Personal communication from other authors.
2.3. Literature Screening
2.3.1. Keywords and Terms
2.3.2. Selection of Results
2.3.3. Data Classification and Processing
3. Main Findings
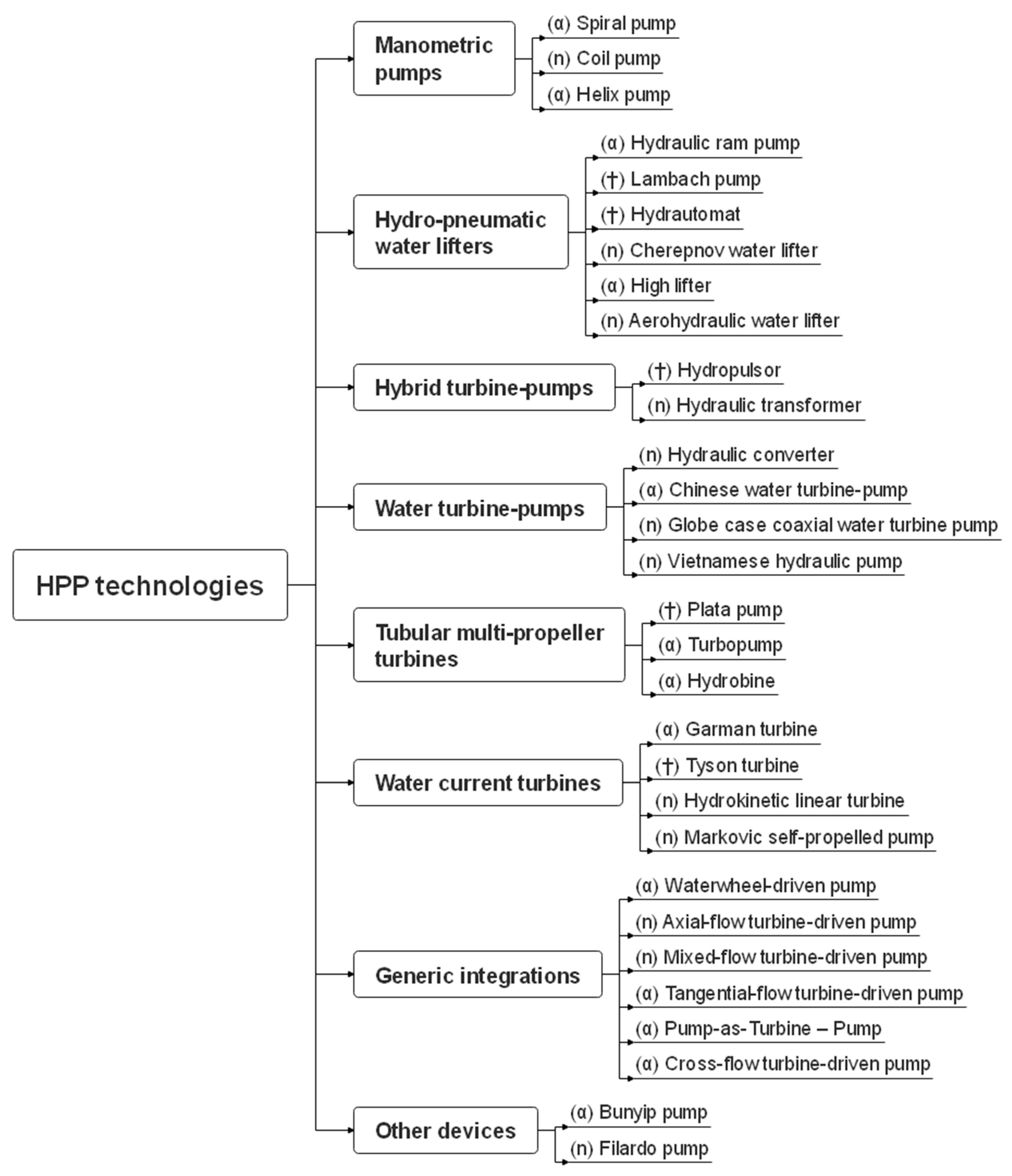
3.1. HPP Technologies
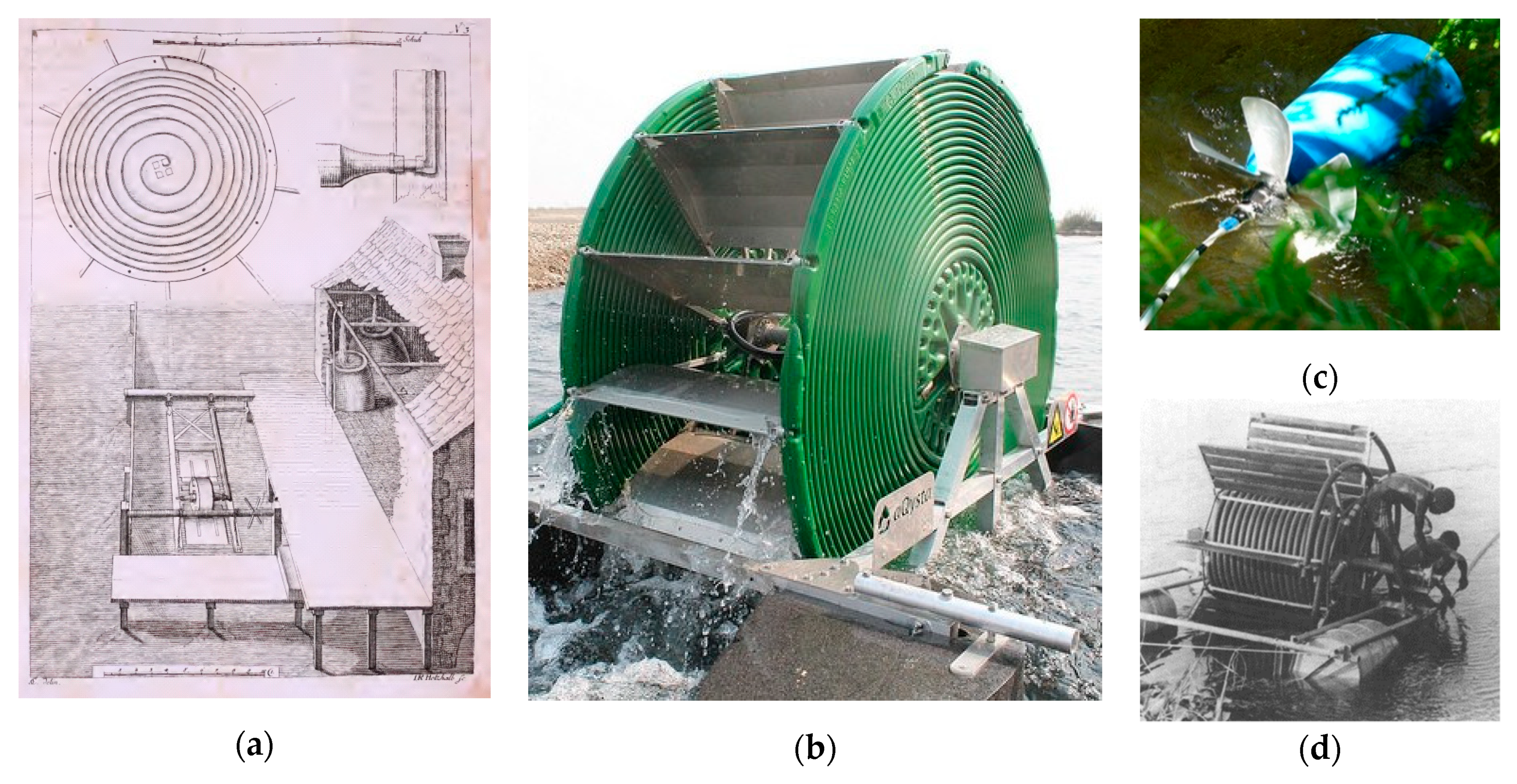
3.1.1. Manometric Pumps
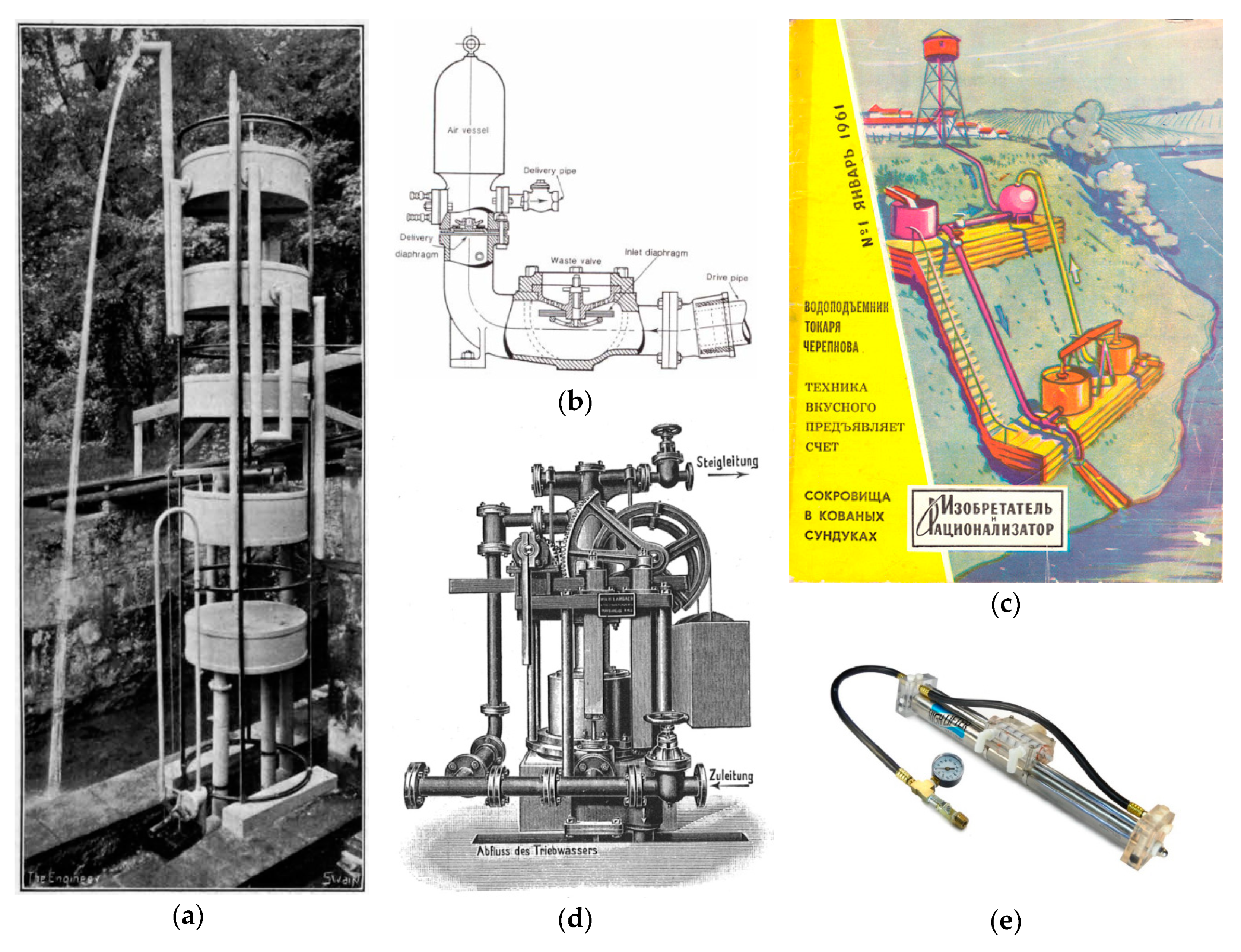
3.1.2. Hydro-Pneumatic Water Lifters
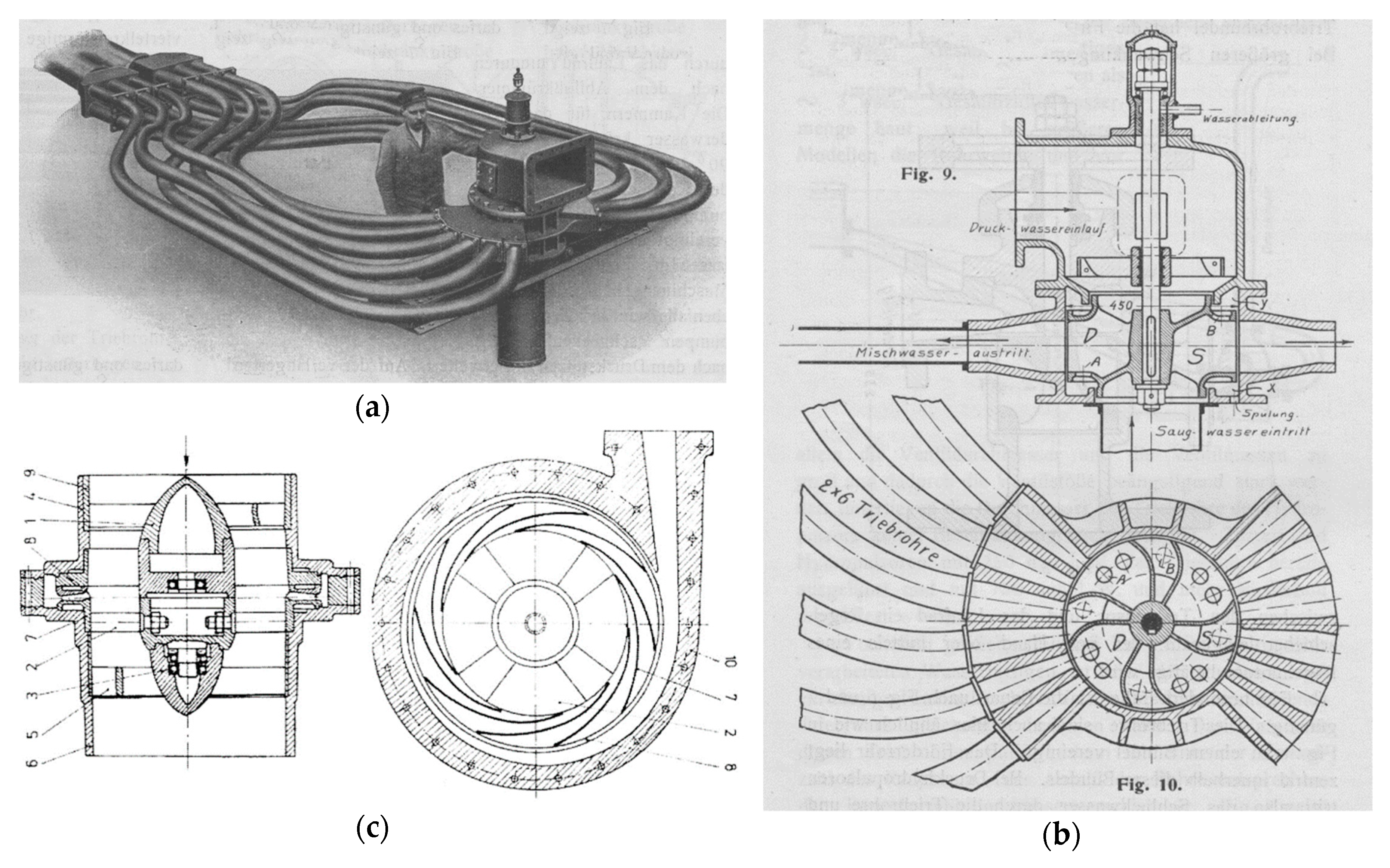
3.1.3. Hybrid Turbine-Pumps
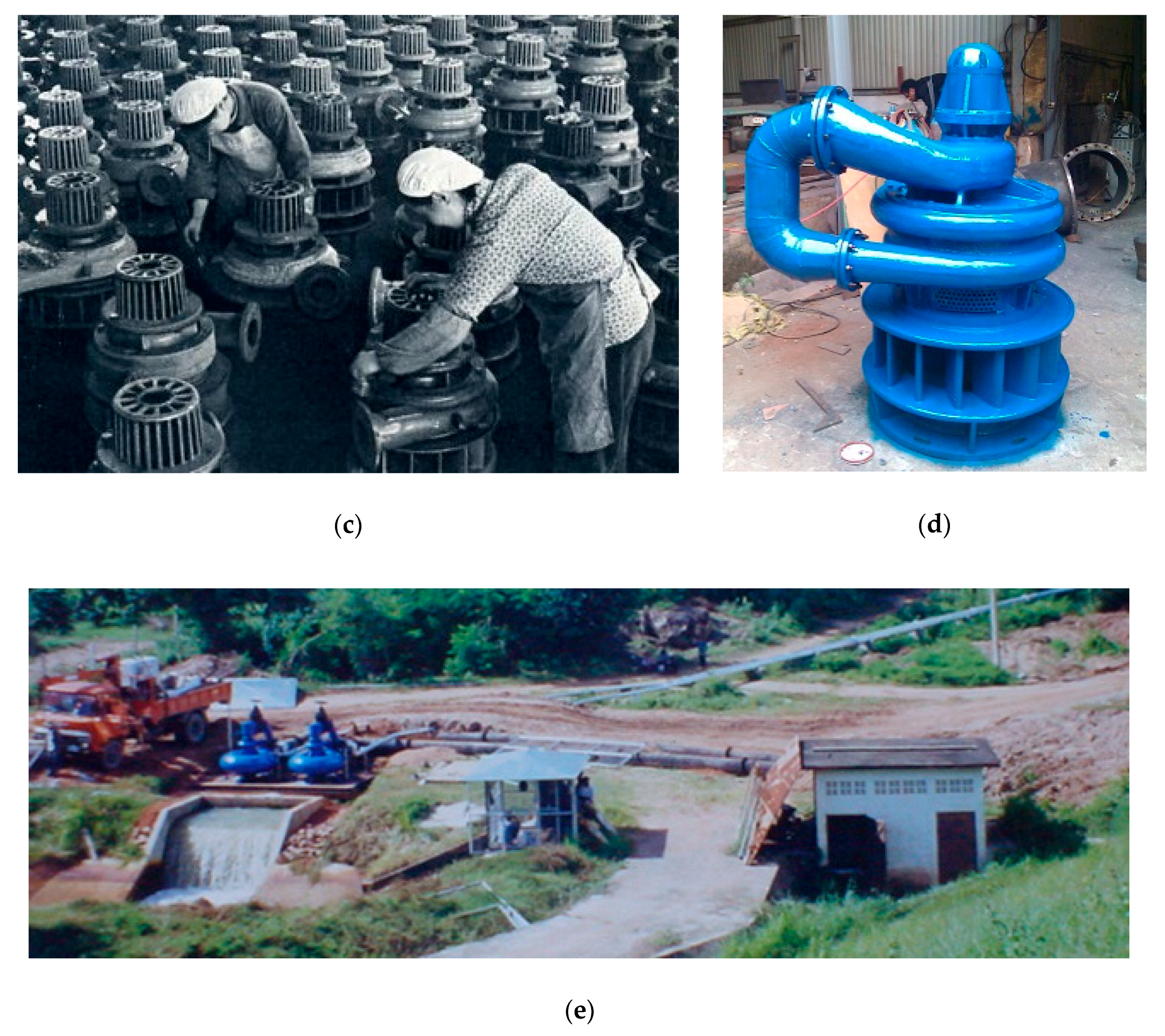
3.1.4. Water Turbine-Pumps
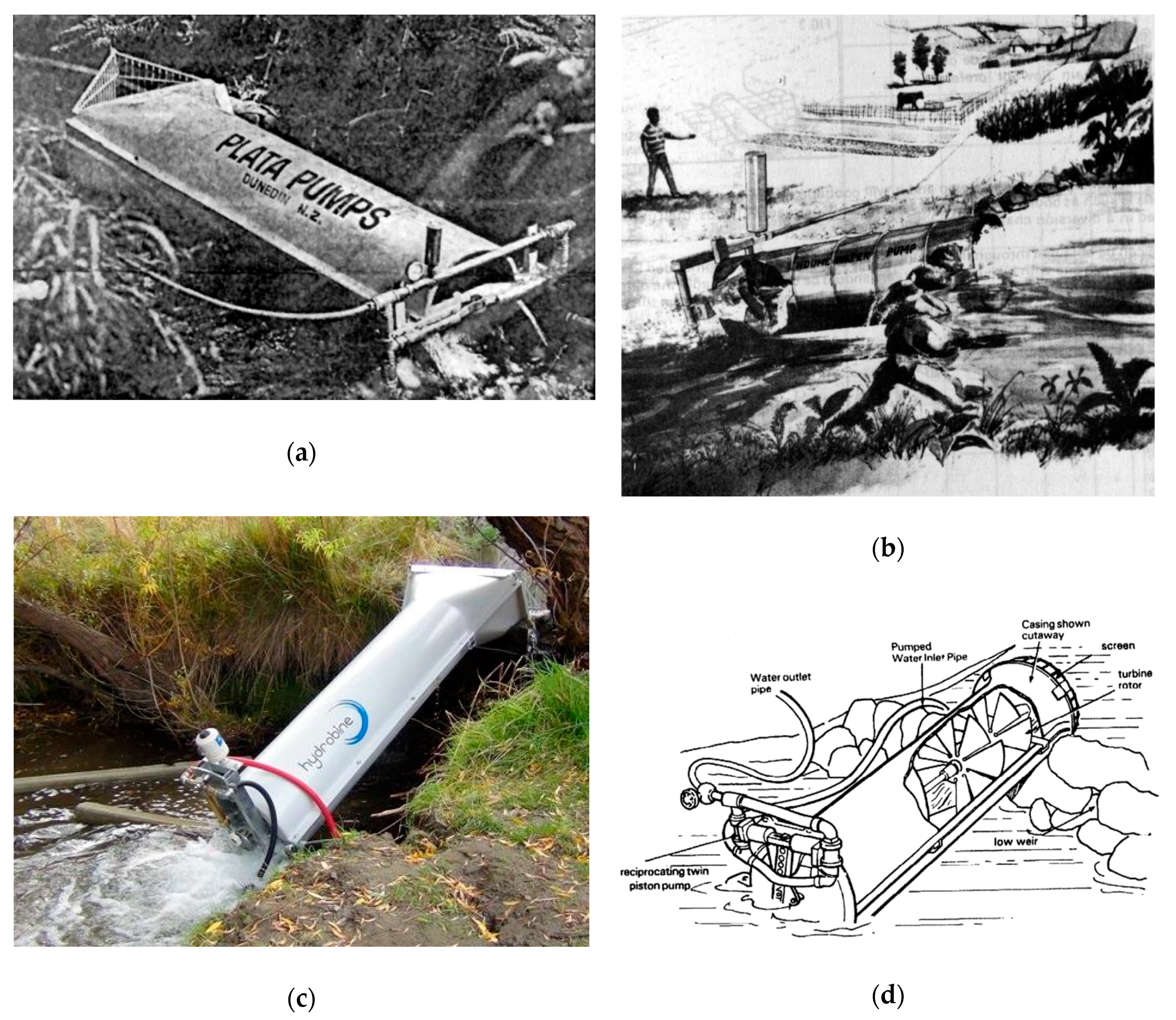
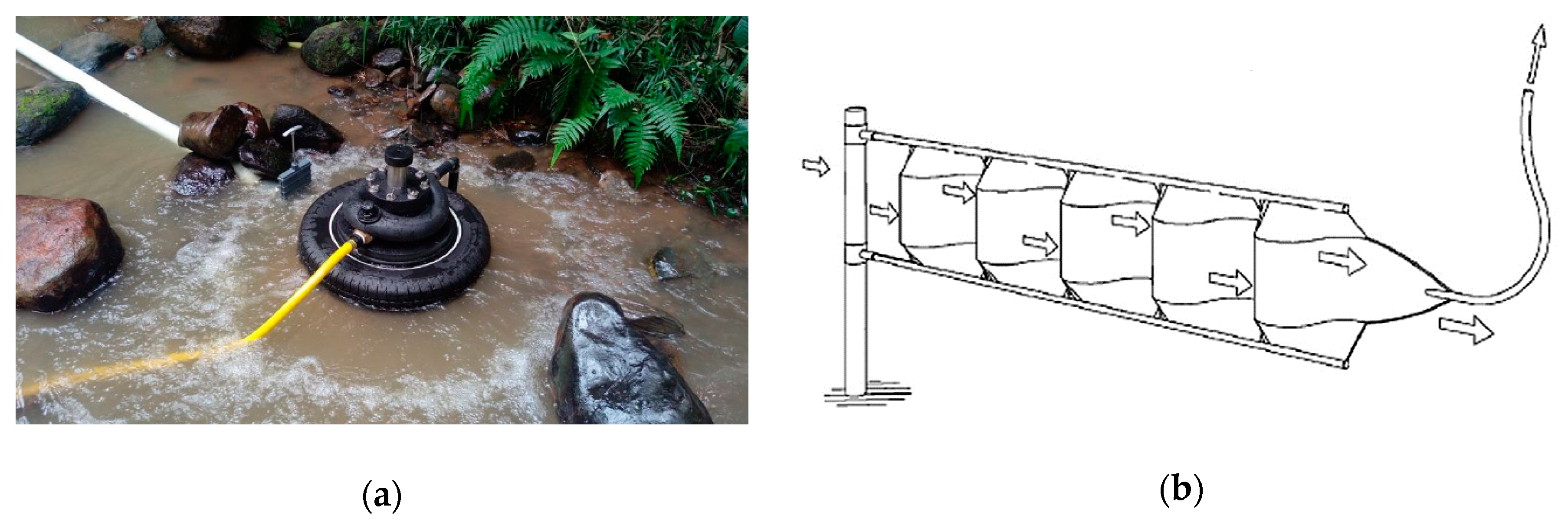
3.1.5. Tubular Multi-Propeller Turbines
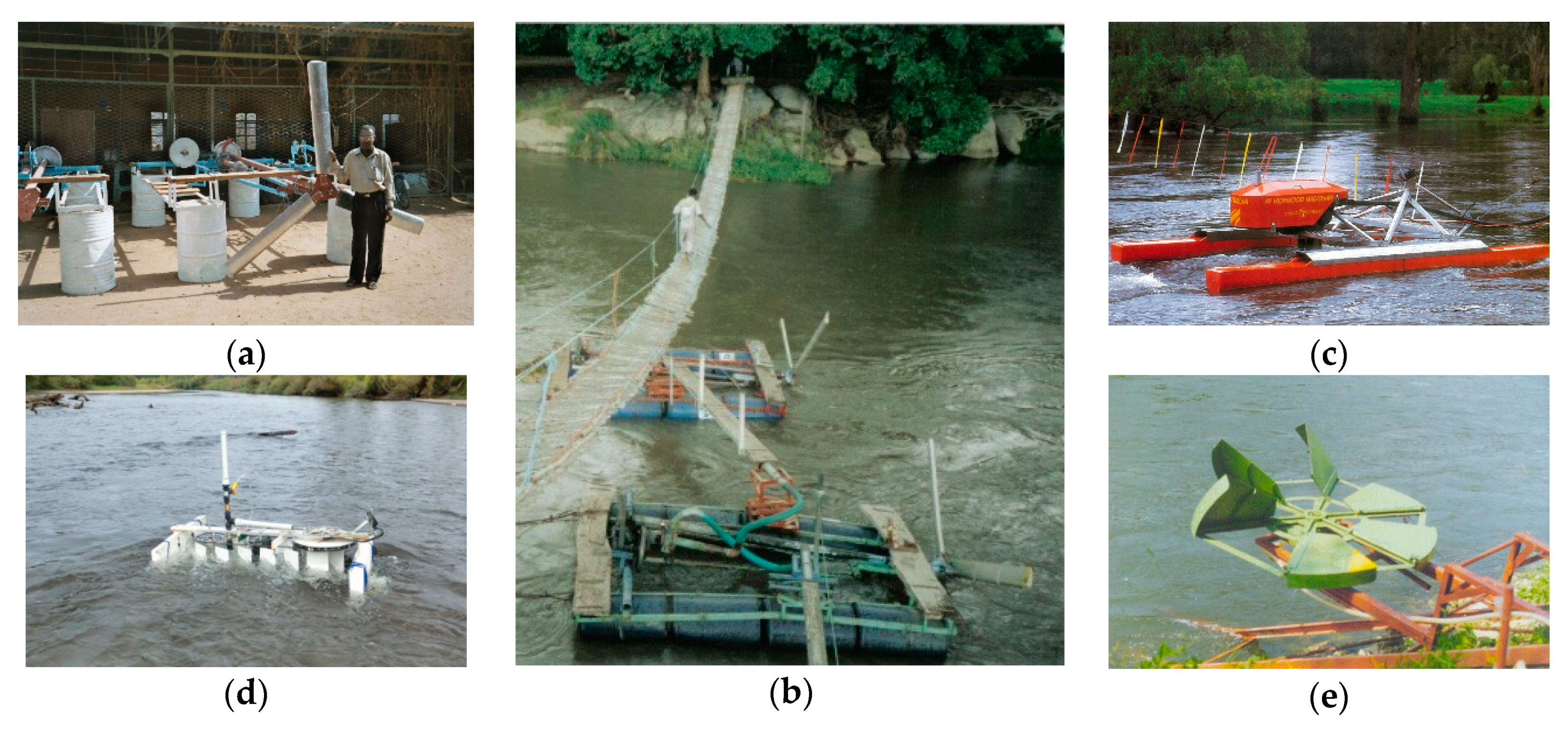
3.1.6. Water Current Turbines
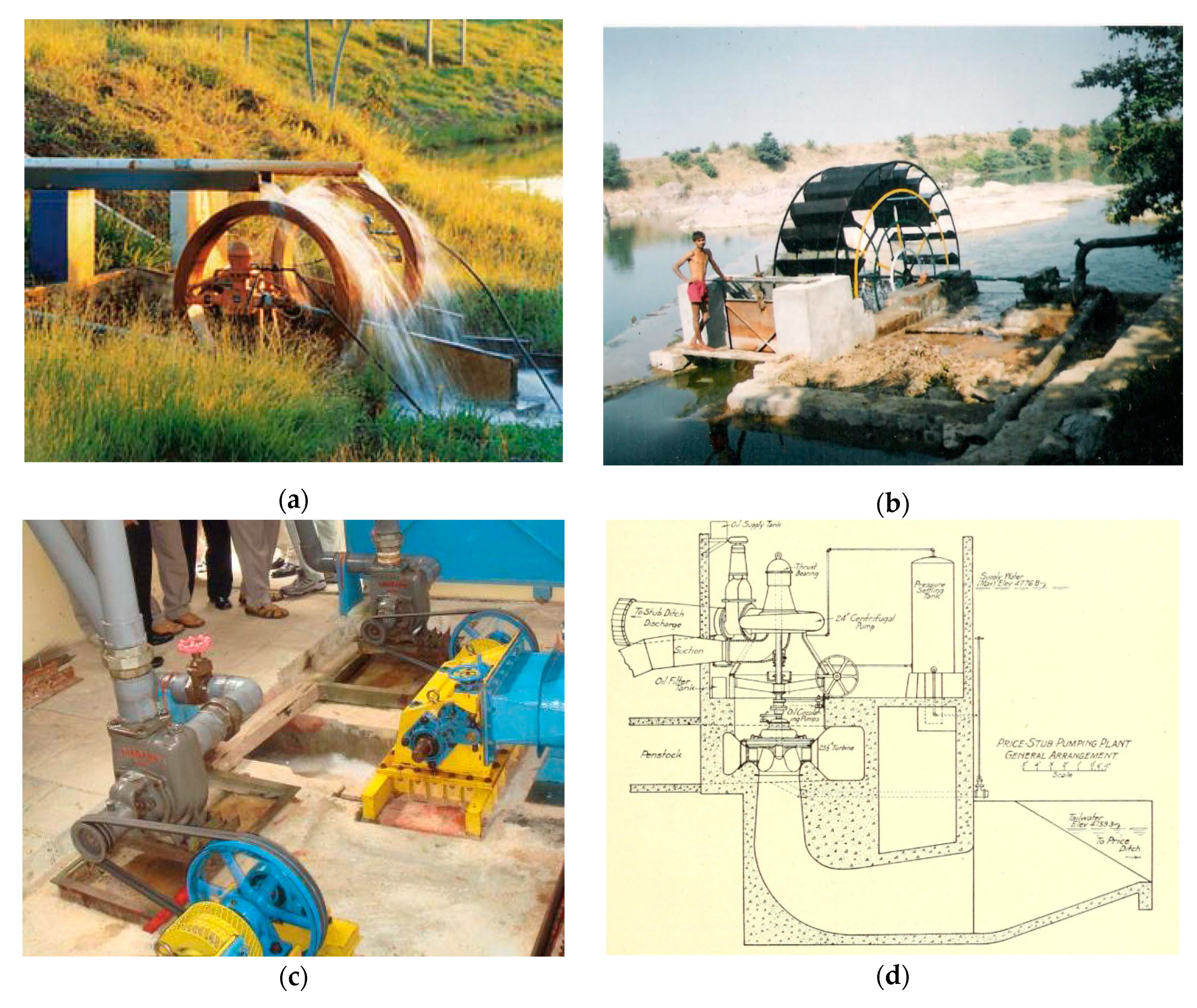
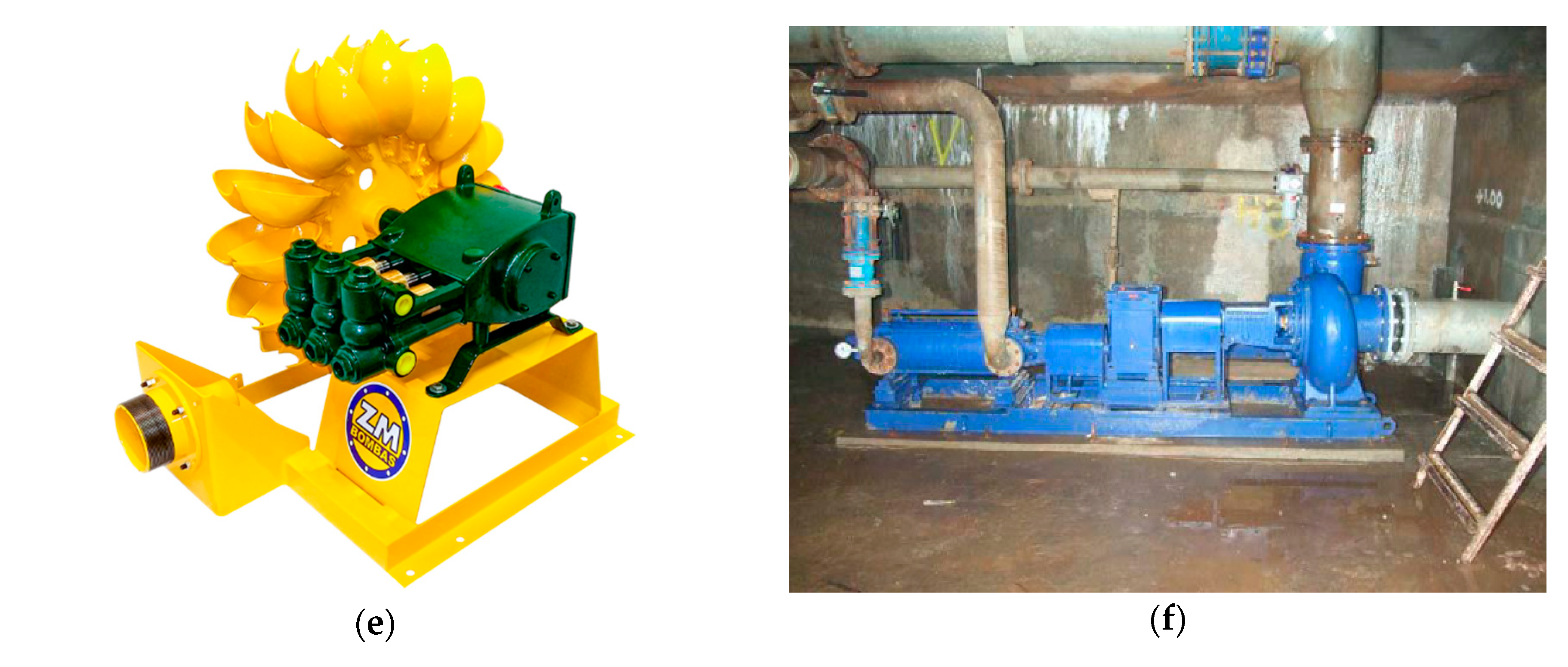
3.1.7. Generic Integrations
3.1.8. Other Devices
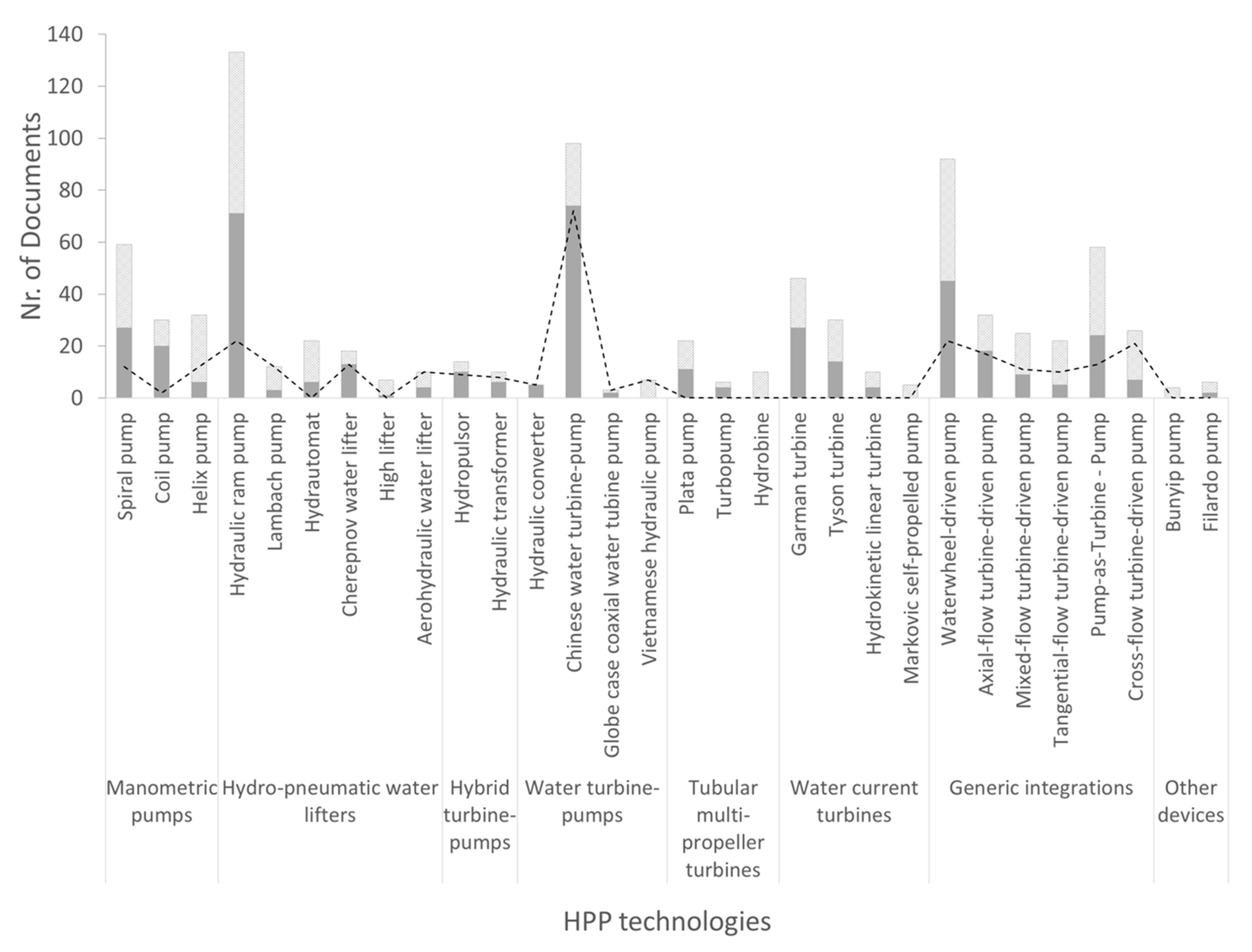
3.2. Literature Analysis
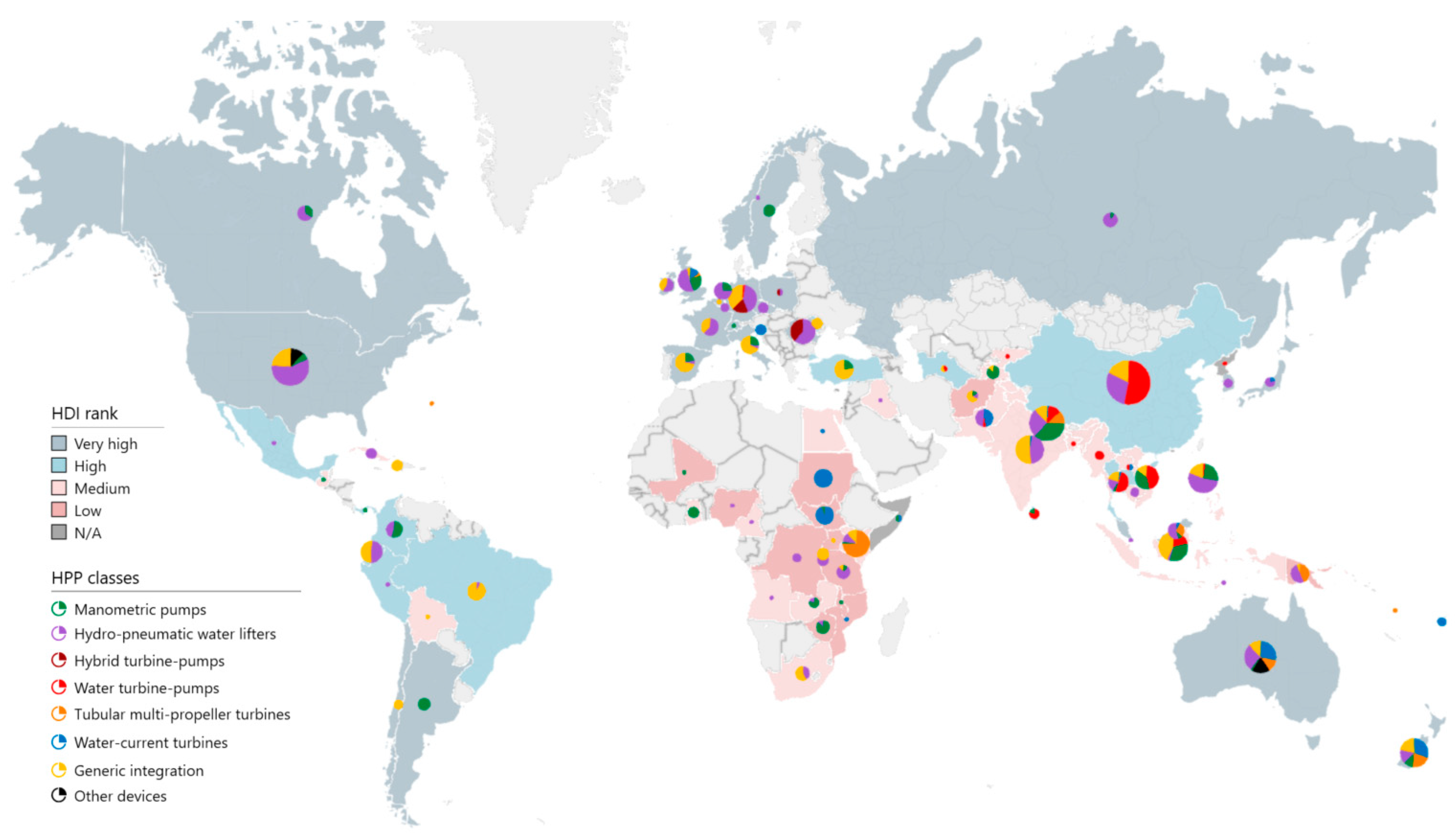
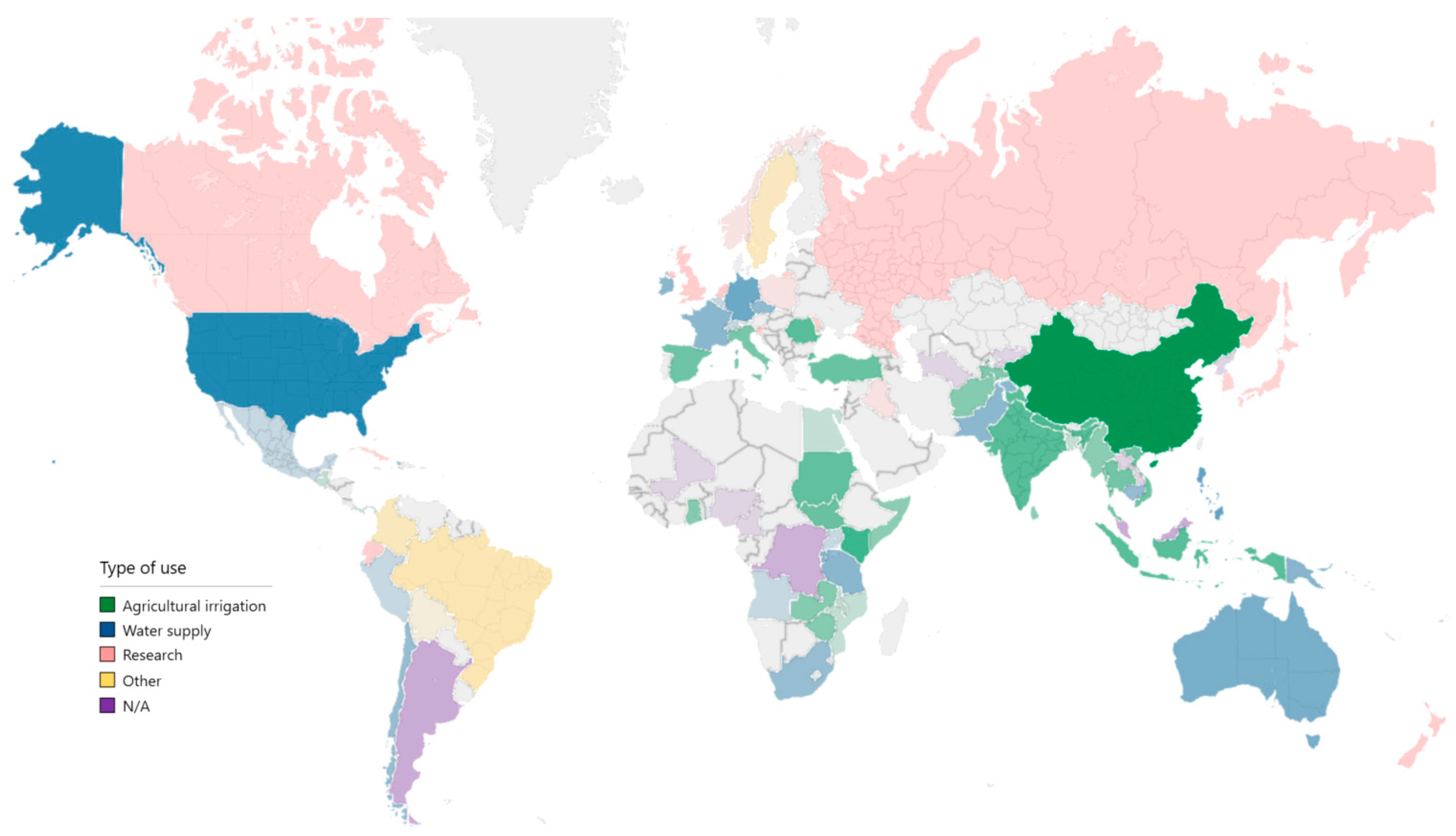
3.3. Spatial Analysis
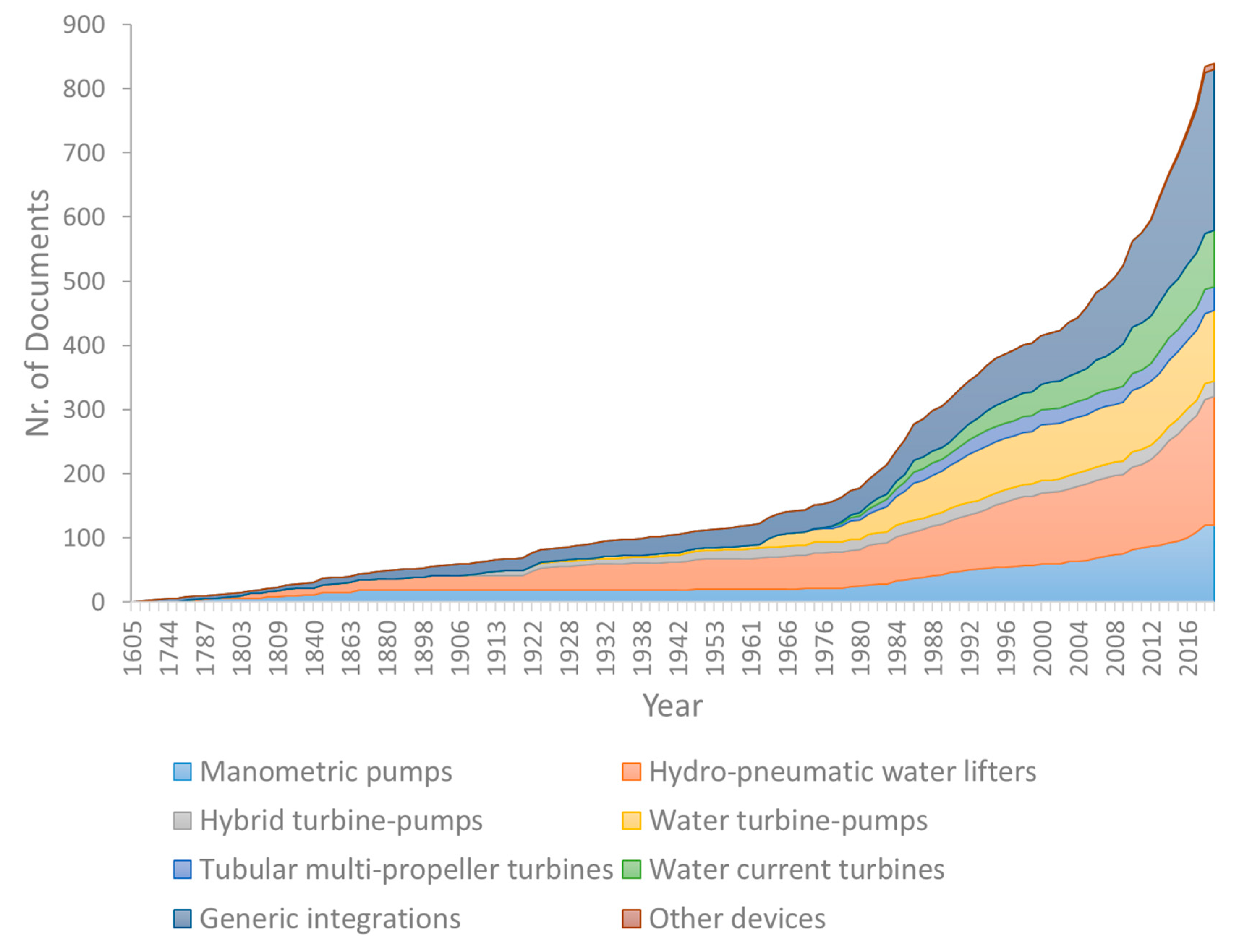
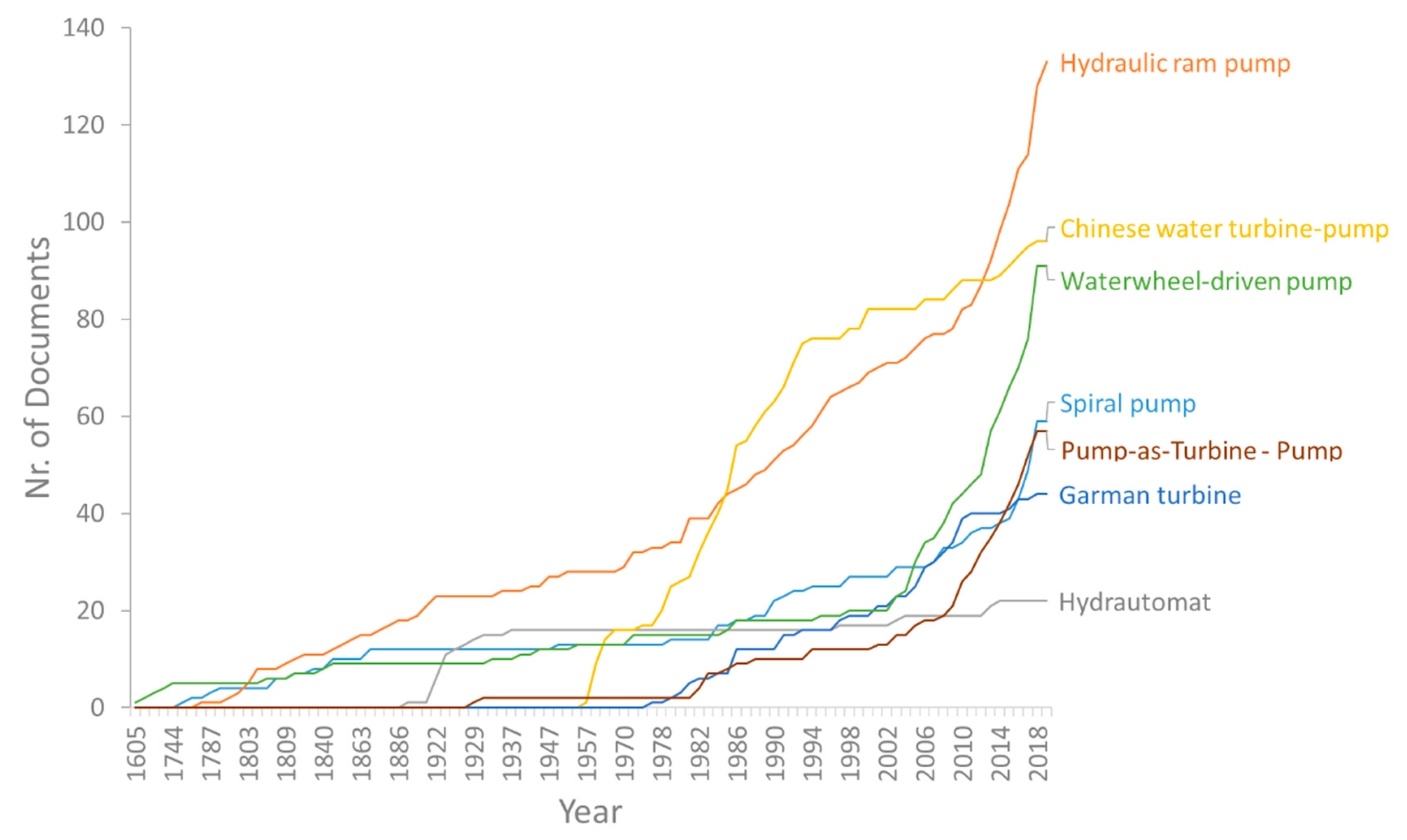
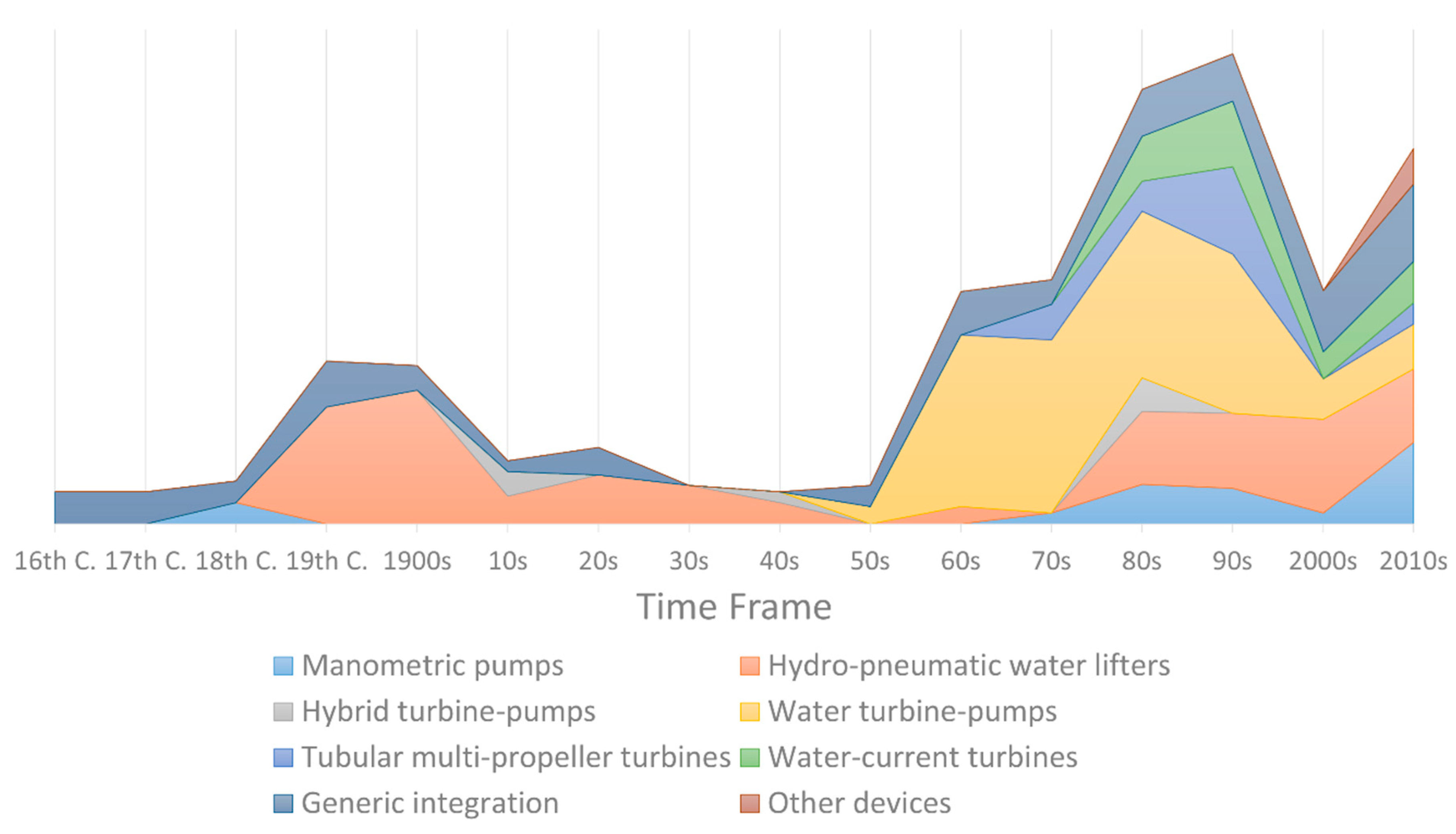
3.4. Temporal Analysis
4. Conclusions
- The concept of pumping water by only relying in hydro-mechanical power–at least due to the amount of readily available “westernized” literature–is something seemingly reserved for few well-known technologies like the HRP, WDP, CWTP, GT, and HSP. Nevertheless, after an exhaustive and systematic search process, up to 30 HPP technologies were screened and analyzed. However, due to the wide range of features and applicability, their classification became eventually a main challenge for the present study. It is so that eight classes were defined, not based on one single property on the technologies, but on the combination of several of them (i.e., working principle, pumping principle, prime mover, pumping device, integration of the parts).
- HPP technologies are not currently the main protagonists globally in water lifting. Some of them, however, mainly off-the-shelf devices within the class of generic integrations (i.e., CDP, PAT-P, TDP, WDP) applied in low-income countries, keep being the standard-bearers of their development, commercialization, and application. Moreover, and despite their more than two century-long existence, both HRP and HSP pose a sustained interest from manufacturers and researchers, who persistently find in them low-cost, robust, and environmentally sound means of delivering water to new heights.
- Individual HPP technologies do not present any apparent global spatial and temporal patterns. However, their aggregated analysis does say much more, not only on what has been done before, but on the current, as well as possible future, directions of research, application, and commercialization. For instance, nowadays, many South American countries show an incipient, yet growing interest in working with these technologies in both academia and industry. On the other hand, Sub-Saharan Africa remains a region where HPPs have the potential to create a higher social impact by improving livelihoods through sustained water supply. Last, yet not least, the baggage of expertise on design and manufacturing, as well as a higher capacity of adoption and use of HPPs in other regions (i.e., Europe, South and Southeast Asia), will be always a valuable capital for academics and manufacturers while exploring new insights in their respective domains.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms
| RE | Renewable energy |
| HPP | Hydro-powered pumping |
| HSP | Hydro-powered spiral pump |
| HCP | Hydro-powered coil pump |
| HHP | Hydro-powered helix pump |
| HRP | Hydraulic ram pump |
| LP | Lambach pump |
| CWL | Cherepnov water lifter |
| HT | Hydraulic transformer |
| WTP | Water turbine pump |
| CWTP | Chinese water turbine pump |
| TMPT | Tubular multi-propeller turbine |
| WCT | Water current turbine |
| GT | Garman turbine |
| TT | Tyson turbine |
| WDP | Waterwheel-driven pump |
| ADP | Axial-flow turbine-driven pump |
| MDP | Mixed-flow turbine-driven pump |
| TDP | Tangential-flow turbine-driven pump |
| PAT-P | Pump-as-Turbine – Pump |
| CDP | Cross-flow turbine-driven pump |
| H-HDI | Very High and High-human development index |
| L-LDI | Medium and Low-human development index |
References
- Lowder, S.K.; Skoet, J.; Raney, T. The Number, Size, and Distribution of Farms, Smallholder Farms, and Family Farms Worldwide. World Dev. 2016, 87, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Clough, Y.; Wanger, T.C.; Jackson, L.; Motzke, I.; Perfecto, I.; VanderMeer, J.; Whitbread, A. Global food security, biodiversity conservation and the future of agricultural intensification. Boil. Conserv. 2012, 151, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, J.A.; Naylor, R.L. Smallholder Irrigation as a Poverty Alleviation Tool in Sub-Saharan Africa. World Dev. 2012, 40, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, M.; Hassan, G.; Said, S.A.; Siddiqui, M.U.; Alawami, A.T.; Elamin, I.M. A review of solar-powered water pumping systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 87, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, S.; Naik, M.N.; Chandel, R. Review of solar photovoltaic water pumping system technology for irrigation and community drinking water supplies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 1084–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, C.; Mohanraj, M.; Chandramohan, P.; Chandrasekar, P. Renewable energy source water pumping systems—A literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Russo, F.; Russo, F. Ancient Engineers’ Inventions. Precursors of the Present; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, S.I.; Lyberatos, G.; Theodossiou, N.; Li, W.; Valipour, M.; Tamburrino, A.; Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of Water Lifting Devices (Pumps) over the Centuries Worldwide. Water 2015, 7, 5031–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jazarī, I.A.-R. Pump driven by a water-wheel. In The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1974; pp. 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista Paz, E.; Ceccarelli, M.; Echávarri Otero, J.; Muñoz Sanz, J.L. A Brief Illustrated History of Machines and Mechanisms; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agricola, G. De re Metallica; Dover Publications, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Ramelli, A. Le Diverse et Artificiose Machine del Capitano Agostino Ramelli [The Various and Ingenious Machines of Captain Agostino Ramelli]; Casa Del’autore: Paris, France, 1588. [Google Scholar]
- Shulman, J.-C. A Tale of Three Thirsty Cities: The Innovative Water Supply Systems of Toledo, London and Paris in the Second Half of the Sixteenth Century; Koninklijke Brill NV: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraenkel, P. Water Pumping Devices: A Handbook for Users and Choosers; Intermediate Technology Publications: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Meah, K.; Ula, S.; Barrett, S. Solar photovoltaic water pumping—Opportunities and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1162–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, P. Financial evaluation of renewable energy technologies for irrigation water pumping in India. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 3134–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, P.; Kandpal, T.C. Renewable energy technologies for irrigation water pumping in India: Projected levels of dissemination, energy delivery and investment requirements using available diffusion models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2005, 9, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kandpal, T. Renewable energy technologies for irrigation water pumping in India: A preliminary attempt towards potential estimation. Energy 2007, 32, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B. Comparative assessment of the feasibility for solar irrigation pumps in Sudan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, N.; Foster, R.; Ellis, A. Renewable Energy for Water Pumping Applications in Rural Villages; Period of Performance: April 1, 2001–September 1, 2001; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Jia, Y.L. A Bibliometric Analysis of Publications on Solar Pumping Irrigation. Sustain. Dev. Water Resour. Hydraul. Eng. China Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becenen, İ.; Eker, B. Powering of Water Pumps by Alternative Energy Sources in Thrace Region. Trakia J. Sci. 2005, 3, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed Wazed, S.; Hughes, B.R.; O’Connor, D.; Kaiser Calautit, J. A review of sustainable solar irrigation systems for Sub-Saharan Africa. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1206–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemersma, J.J.; Heeren, N.A. Small Scale Hydropower Technologies: An Overall View of Hydropower Technologies for Small Scale Appliances; Stichting TOOL: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kristoferson, L.A.; Bokalders, V. Renewable Energy Technologies: Their Applications in Developing Countries, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofkes, E.H.; Visscher, J.T. Renewable Energy Sources for Rural Water Supply; IRC: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1986; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Collett, J. Hydro powered water lifting devices for irrigation. In FAO/DANIDA Work. Water Lifting Devices Asia near East; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Bangkok, Thailand, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, S.; Nilsson, R. Renewable Energy Sources in Small-Scale Water Pumping Systems; Allmänna Ingenjörsbyrån AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel, P. The Power Guide. A Catalogue of Small Power Equipment; Intermediate Technology Publications: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, A.D.; Ruff, J.F.; Richardson, E.V. Pumps and Water Lifters for Rural Development; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, A.D. Water Lifters and Pumps for the Developing World; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Intriago, J.C.; Ertsen, M.; Diehl, J.-C.; Michavila, J.; Arenas, E. Co-creation of affordable irrigation technology: The DARE-TU project. In Proceedings of the International Conference Water Science for Impact, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 16–18 October 2018; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Li, K.; Dong, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, S.; Song, C.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic “Pump”: Continuous and Spontaneous Antigravity Water Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J. Research on low-level water supply techniques. Fire Sci. Technol. 2007, 26, 658–660. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Yuan, Y.; Xue, L. Research on Design of High-Efficiency Fire Turbopump Supplying Water from Low-Level Water Resources. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 697, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozier, J.; Oklejas, E.; Silbernagel, M. The hydraulic turbocharger™: A new type of device for the reduction of feed pump energy consumption in reverse osmosis systems. Desalination 1989, 75, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahood, Q.; Van Eerd, D.; Irvin, E. Searching for grey literature for systematic reviews: Challenges and benefits. Res. Synth. Methods 2014, 5, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Collins, A.M.; Coughlin, D.; Kirk, S. The Role of Google Scholar in Evidence Reviews and Its Applicability to Grey Literature Searching. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intriago Zambrano, J.C. Results of Systematic Literature Review on Hydro-Powered Water Pump, as Part of the DARE-TU PhD Project. DataverseNL, V1. 2019. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10411/5RSELQ (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Young, T. A Course of Lectures on Natural Philosophy and the Mechanical Arts; Joseph Johnson: London, UK, 1807; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Stuckey, A.T.; Wilson, E.M. The stream-powered manometric pump. Appropr. Technol. Civ. Eng. 1981, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer, G.H. The Coil Pumps; Loughborough University of Technology: Loughborough, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer, G.H.; Annable, R. The Coil Pump—Theory and Practice. J. Hydraul. Res. 1984, 22, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annable, R.J. Analysis and Development of a Stream-Powered Coil Pump; Loughborough University of Technology: Loughborough, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Encyclopædia Perthensis. Sect. VII. Of the famous Hydraulic Engines erected at Zurich, and Florence. In The New Encyclopædia; or, Universal Dictionary Ofarts and Sciences; Vernor, Hood & Sharpe: London, UK, 1807; Volume XXIII, pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, O. A Treatise of Mechanics, Theoretical, Practical and Descriptive; Thomas Davison: London, UK, 1826; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ewbank, T. A Descriptive and Historical Account of Hydraulic and Other Machines for Raising Water; D. Appleton and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1842. [Google Scholar]
- Eytelwein, J.A. Von der Spiralpumpe [On the Spiral Pump]. In Handbuch der Mechanik fester Körper und der Hydraulik [Manual of Solid Body Mechanics and Hydraulics]; Friedrich Fleischer: Leipzig, Germany, 1842; p. 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernoulli, D. Expositio theoretica singularis machinae hydraulicae, tiguri Helvetiorum exstructae. [Theoretical explanation of the unique hydraulic machine built in Zurich, Switzerland]. In Novi Commentarii Academiae Scientiarum Imperialis Petropolitanae; Petropoli: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1772; pp. 251–271, 795. [Google Scholar]
- Naegel, L.C.A. The Hydrostatic Spiral Pump: Design, Construction and Field Tests of Locally-Developed Spiral Pumps; Jaspers Verslag: Munich, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, M. The stream-driven coil pump. Waterlines 1985, 4, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.H. Vorläufige Anzeige eines neuen Schöpfrades [Preliminary display of a new bucket wheel]. Treatises Nat. Res. Soc. Zur. 1766, 3, 431–463. [Google Scholar]
- Securing Water for Food. Hydro-Powered Pump Offers Eco-Friendly Irrigation Solution. 2016. Available online: https://securingwaterforfood.org/innovator-news/hydro-powered-pump-offers-eco-friendly-irrigation-solution (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- RIFE. Pumps. RIFE Hydraul Engine Mfg Co. Available online: https://www.riferam.com/pumps.html (accessed on 10 August 2018).
- Morgan, P. A new water pump: Spiral tube. Zimb. Rhod. Sci. News 1979, 13, 179–180. [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta, E.; Michavila, J. Sustainable Irrigation with Hydro-Powered Pumps. Hydrolink 2018, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, P. Spiral Pump Using Water Current of Shire River at Zalewa, Malawi; Uniterra: Blantyre, Malawi, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kassab, S.Z.; Abdel Naby, A.A.; Abdel Basier, E.S.I. Performance of Multi-layers Coil Pump. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt, 23–25 March 2006; pp. 431–445. [Google Scholar]
- Aronovich, G.V.; Shtaerman, E.Y. On the theory of the Cherepnov water lifter. Fluid Dyn. 1966, 1, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fessehaye, M.; Geekie, R. The Cherepnov Water Lifter. In Applying Research to Hydraulic Practice; Smith, P.E., Ed.; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Cherepnov, L. Безмоторная автоматическая водоподъемная установка [Motorless automatic water-lifting system]. Technol. Agric. 1964, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Meixner, H. Die Wasserversorgung des Georgsschutzhauses am Hochschar durch eine Lambach-Pumpe [The water supply of the Georgsschutzhauses on the Hochschar by a Lambach pump]. HDI Releases 1926, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Krol, J. The Automatic Hydraulic Ram. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1951, 165, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, K. Water-powered pumping. Soft Technol. 1995, 53, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson, I. The rebirth of the hydraulic ram pump. Waterlines 1993, 12, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Some Novel Hydro-Pneumatic Pumping Plants. The Engineer. 16 October 1925. Available online: https://www.gracesguide.co.uk/The_Engineer_1925/10/16 (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Boving, J.O. New Developments in Hydraulic Pneumatic Engineering. J. R. Soc. Arts 1929, 78, 58–88. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M. Investigating the Pulser Pump; Loughborough University: Loughborough, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrovskiy, N.V. Система технологических и технических решений для рационального использования водных ресурсов и повышения эффективности орошения при возделывании риса [System of Technological and Technical Solutions for the Rational Use of Water Resources]; Kuban State Agrarian University: Krasnodar, Russia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- High Lifter. Welcome to High Lifter. 2016. Available online: http://high-lifter.com/ (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Maschinenfabrik Wilh. Lambach. Die Lambach-Pumpe [The Lambach Pump]; Maschinenfabrik Wilh. Lambach: Marienheide-Rheinland, Germany, 1950; Available online: http://www.oberwipper.de/oberwipper_cont/oberwipper/LambachProsp/LambachProspekt1950a.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Wagner, P. Lambach-Pumpen: Legendäre Technik aus Marienheide [Lambach Pumps: Legendary Technology from Marienheide]. OberwipperDe. 2014. Available online: http://www.oberwipper.de/oberwipper_cont/oberwipper/LambachPumpen.html (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Papa Pump. Papa Pump: The Pump That Uses No Fuel. 2018. Available online: https://papapump.com/ (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Watt, S.B. A Manual on the Hydraulic Ram for Pumping Water; Intermediate Technology Publications: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Musin, E. Так просто! Водоподъемник токаря Черепнова [So simple! Cherepnov water lifter]. Invent. Innov. 1961, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Water Powered Technologies. Venturo: Zero Energy Large Scale Water Transfer. 2018. Available online: https://www.waterpoweredtechnologies.com/venturo/ (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- The Hydrautomat. The Engineer. 7 July 1922. Available online: https://www.gracesguide.co.uk/The_Engineer_1922/07/07 (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Milln, J. Hydraulic Rams. Industrial. Archaeology. News, Summer 1995. Available online: https://industrial-archaeology.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/AIA-News-93-Summer-1995.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Inventor and Innovator. Умолк рупор творчества [The Shout of Creativity]. Available online: http://i-r.ru/article/2254/ (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Horner, T. Welcome. 2014. Available online: http://www.humboldtsolarwaterpump.com/ (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Lawaczeck, F. Turbinen und Pumpen: Theorie und Praxis [Turbines and Pumps: Theory and Practice]; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărglăzan, A.N. Transformatorul Hidraulic, Studiu Teoretic și Experimental [Hydraulic Transformer, Theoretical and Experimental Study]; Scoala Politehnica din Timisoara: Tameshburg, Romania, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Wehry, A.; Guler, S.P. Microstaţii de Pompare Pentru Irigaţii Folosind Energie Neconvenţională [Micro-Pumping Stations for Irrigation Using Non-Conventional Energy]; Timişoara Editura Orizonturi Universitare: Timisoara, Romania, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Prometheus. Der Hydropulsor, eine neue hydraulische Schöpfmaschine [The Hydropulsor, a new hydraulic scooping machine]. Prometh. Illus. Wkly. Mag. Adv. Commer. Ind. Sci. 1911, 23, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Preger, E. Der hydropulsor, eine neue wasserfördermaschine [The hydropulsor, a new water supply machine]. Dinglers Polytech. J. 1912, 327, 737–741, 759–762. [Google Scholar]
- Bărglăzan, A.N. Transformatorul hidraulic [Hydraulic transformer]. Sci. Bull. Politeh. Univ. Timis. 1941, 10, 273–330. [Google Scholar]
- Pavel, D. Utilizarea transformatoarelor hidraulice [Use of hydraulic transformers]. Energ. Hidroteh. 1955, 3, 434–437. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, I.; Cozma, M.; Gyulai, F.; Wehry, A.; Tămaş, M. Transformatorul hidraulic tip “BARGLAZAN” utilizat în amenajări de irigaţii locale [The “BARGLAZAN” hydraulic transformer used in local irrigation facilities]. Hidrotehnica 1990, 35, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Man, T.E.; Constantinescu, L.; Blenesi, D.A. Water energy in hydroameliorative systems using the hydraulic transformer type A. Barglazan and the hydraulic hammer (hydraulic pump). Ann. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 11, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lunzhang, S. The Chinese water turbine pump. Waterlines 1987, 5, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunzhang, S. The Turbine Pump: A Specific Solution to a General Problem. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Small Hydropower, Hangzhou, China, 1–4 April 1986; pp. 610–626. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, A. 水轮泵原理,结构及设计 [The principle, structure and design of the water turbine pump]. Water-Turbine Pump 1989, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui, H. Water Lifting Devices with Renewable Energy for Agriculture in Asian Developing Countries —With emphasis on the Chinese experience. J. Irrig. Eng. Rural Plan. 1989, 1989, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. A water turbine pump. World Pumps 1984, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, A. Understanding the water-turbine pump. World Pumps 1986, 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Yang, S. Water powered water lifting devices in China—The water-turbine pump. In Proceedings of the Vth World Congress on Water Resources, Brussels, Belgium, 9–15 June 1985; pp. 1189–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Weng, A. An introduction to the water-turbine pump. In FAO/UNDP/China Work. Water Lifting Devices Water Management; FAO, Ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Fuzhou, China, 1982; pp. 62–79. [Google Scholar]
- Charoenchan, S.; Chittaladakon, S. Water using project by globe case coaxial water turbine pump at Mae Pum water reservoirs, Phayao province, Thailand. Kasetsart Eng. J. 2000, 14, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Volunteers in Technical Assistance. China’s turbine-pump lifts water to new heights. VITA News 1982, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvani, P. (Ed.) Tools for Agriculture: A Buyer’s Guide to Appropriate Equipment; Intermediate Technology Development Group: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Zhang, F. 介绍福建省应用水轮泵的情况和经验 [Introduce the situation and experience of applying the water turbine pump in Fujian Province]. Water Resour. Hydropower Technol. 1964, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Yang, D. 水轮泵站的枢纽布置与水工结构(二) [Hub arrangement and hydraulic structure of water pumping station (2)]. Farml. Water Conserv. Soil Water Conserv. 1964, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, S. 介绍几种水轮泵 [Introducing multistage water turbine pumps]. Agric. Mach. 1979, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.; Liang, J.; Jiang, X. 40—10水轮泵水力模型设计研究报告 [Research report on hydraulic model design of 40-10 water turbine pump]. Water-Turbine Pump 1988, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S. “三用”水轮泵的调查报告 [Investigation report of “three-purpose” water turbine pump]. Water-Turbine Pump 1990, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S. 一座大型河床式“三用”水轮泵站——浙江省义乌塔下“水轮泵、水电、电灌”三用站建成投产 [A large riverbed “three-purpose” turbine water pump station]. Water Resour. Hydropower Technol. 1979, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G. Water-turbine pump engineering. In FAO/UNDP/China Work. Water Lifting Devices Water Management; FAO, Ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Fuzhou, China, 1982; pp. 92–103. [Google Scholar]
- Collett, J. Chinese Water-lifting Devices. Appropr. Technol. 1982, 9, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G. 修筑水轮泵拦河坝的经验介绍 [Experience in building a water wheel pump to block a river dam]. Guangxi Agric. Sci. 1964, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Z.; Xiao, G. Tidal water-turbine pump stations (in China). In FAO/UNDP/China Work. Water Lifting Devices Water Management; FAO, Ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Fuzhou, China, 1982; pp. 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Padelletti, G. This “underwater windmill” makes rivers lift themselves. CERES 1993, 26, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. 我国水轮泵工程的现状、特点及展望——纪念水轮泵情报网建网15周年 [Current Status, Characteristics and Prospects of China’s Water Turbine Pump Project—Commemorating the 15th Anniversary of Hydrofoil Pump Information Network Construction]. Water-Turbine Pump 1992, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Cai, L. 十五”期间水轮泵行业的发展与展望 [Development and Prospect of the Water Turbine Pump Industry during the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period]. Water-Turbine Pump 2000, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, A. 水轮泵的技术发展 [Technical development of the water turbine pump]. Water-Turbine Pump 1994, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wuhan Jiuhong Pump. 福建一企业研制出国内最大水轮泵 [Fujian Company Developed the Largest Domestic Water Pump]. 2015. Available online: http://www.pump027.com/newsshow.asp?id=1290 (accessed on 17 August 2018).
- Vietnam Academy for Water Resources. Công Nghệ Bơm Thủy Luân, Bơm Nước tự Động Phục vụ Nông Nghiệp Miền Núi và Trung du [Hydraulic Pump Technology, Automatic Water Pumps for Agriculture in Mountainous and Mid-Lands]. Available online: http://www.vawr.org.vn/index.aspx?aac=CLICK&aid=ARTICLE_DETAIL&ari=2314&lang=1&menu=&mid=-138&pid=1&title=cong-nghe-bom-thuy-luan-bom-nuoc-tu-dong-phuc-vu-nong-nghiep-mien-nui-va-trung-du (accessed on 19 September 2018).
- Charoenchan, S. Water Energy Pumping System Research and Development in Royal Irrigation Department. Chonlasarn Res. J. Irrig. Manag. 2014, 2, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Muckle, T. The NDUME turbo-pump—A user experience. Waterlines 1992, 10, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soft Technology. A Plata Pump…. Soft Technology, Aug/Oct 1983. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/softtechaltetech.13.18 (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Beyond the Bale. Pump it up! Beyond the Bale. September 2014. Available online: https://www.wool.com/globalassets/start/about-awi/publications/btb_60_september_2014_web.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Perkinz. Hydrobine. 2017. Available online: http://www.hydrobine.co.nz/ (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- White, S.C. Notes on Small Scale Irrigation in Lower Embu and Meru Districts of Kenya; Land Resources Development Centre: Surrey, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrobine. Facebook. 2018. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/Hydrobine/ (accessed on 13 September 2018).
- Garman, P. Water Current Turbines: A Fieldworker’s Guide; Practical Action Publishing: Warwickshire, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, D. Power from natural flow at zero static head. Int. Power Gener. 1995, 18, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, K.; Service, J. Theoretical conditions related to an open channel flow linear turbine. In Small Hydro Power Fluid Machinery 1984; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, C.M. Tyson turbine. Indian J. Power River Val. Dev. 1994, 44, 369, 392–395. [Google Scholar]
- Soft Technology. The Tyson Turbine: Power from River Flow. Soft Technol. 1991, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tuapeka Turbines. Tuapeka Turbines Clean Sustain Energy. 2018. Available online: http://tuapeka-turbines.com/ (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Markovic, V. Energy as enemy. Available online: http://izumi.si/doc/ENERGY_AS_ENEMY.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Kamal, S. The Renewable Revolution: How We Can Fight Climate Change, Prevent Energy Wars, Revitalize the Economy and Transition to a Sustainable Future; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D. Water pumping and electricity from a river flow turbine. SunWorld 1994, 18, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D. The Tyson Turbine, Another Remote Area Water Supply. Sol. Prog. 1995, 16, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- CADDET. Water Current Turbines Pump Drinking Water; CADDET Renew Energy: Oxfordshire, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Anyi, M.; Kirke, B. Evaluation of small axial flow hydrokinetic turbines for remote communities. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2010, 14, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyi, M. Water Current Energy for Remote Community: Design and Testing of a Clog-free Horizontal Axis Hydrokinetic Turbine System; University of South Australia: Adelaide, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Garman, P. The Development of a Turbine for Tapping River Current Energy. Appropr. Technol. 1981, 8, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Swenson, W.J. The evaluation of an axial flow, lift type turbine for harnessing the kinetic energy in a tidal flow. In Proceedings of the Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference AUPEC, Darwin, Australia, 26–29 September 1999; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Tuckey, A.M.; Patterson, D.J.; Swenson, J. A kinetic energy tidal generator in the Northern Territory-results. In Proceedings of the IECON’97 23rd International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control, and Instrumentation (Cat. No.97CH36066), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 1997; Volume 2, pp. 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garman, P.G.; Sexon, B.A. Water current turbines for pumping and electricity generation. In First International Conference Renewable Energy-Small Hydro; Varma, C.V.J., Rao, A.R.G., Eds.; Oxford & IBH Pub. Co.: Hyderabad, India, 1997; pp. 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Thropton Energy Services. Water Current Turbine Case Study: Supply of Irrigation Water for 12 Acre Date Farm. 2016. Available online: http://www.throptonenergy.co.uk/casestudy.html (accessed on 31 August 2018).
- Petchers, N. Combined Heating, Cooling & Power Handbook: Technologies & Applications: An Integrated Approach to Energy Resource Optimization; The Fairmont Press, Inc.: Lilburn, GA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Verdant Power. Technology Evaluation of Existing and Emerging Technologies: Water Current Turbines for River Applications; Natural Resources Canada: St. Catharines, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Bhuyan, G.; Iqbal, M.; Quaicoe, J. Hydrokinetic energy conversion systems and assessment of horizontal and vertical axis turbines for river and tidal applications: A technology status review. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Iqbal, M.; Quaicoe, J. River current energy conversion systems: Progress, prospects and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2177–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, I.; Gheorghe, A.; Dulgheru, V.; Sobor, I.; Bostan, V.; Sochirean, A. Kinetical Energy of River Running Water. Resilient Energy System—Renewables Wind, Solar, Hydro; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 165–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewa, V.M.; Mhlanga, S.; Maphosa, N.; Phuthi, N. Design of a Flood Water Powered Water Pump. In First International Conference Appropriate Technology; Mhlanga, S., Trimble, J., Eds.; National University of Science and Technology: Bulawayo, Zimbabwe, 2004; pp. 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- PowerSpout. Pelton Pump (PHP). 2015. Available online: https://www.powerspout.com/collections/php-pelton-3 (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- Betta Hidroturbinas. Turbo Roda Betta. Betta Hidroturbinas A Força Da Água 2017. Available online: http://www.bettahidroturbinas.com.br/bombeamento/tuboroda-betta (accessed on 4 December 2018).
- Pallabazzer, R.; Sebbit, A. A micro-hydro pilot plant for mechanical pumping. In Hydropower in the New Millennium, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference Hydropower, Bergen, Norway, 20–22 June 2001; Honningsvag, B., Midttomme, G.H., Repp, K., Vaskinn, K., Westeren, T., Eds.; Swets & Zeitlinger Publishers: Lisse, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, R.; Arancibia, G. Ahora tenemos agua de sobra y no gastamos un centavo. GEA y la turbobomba de Polcura [Now we have plenty of water and we do not spend a penny. GEA and the Polcura Turbo pump]. LEISA Rev. Agroecol. 2005, 21, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, S.; Guder, W. Pump as Turbines. Techno Dig 2005, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Duymuş, E.; Ertöz, A.Ö. Mini ve mikro düzeyde hidrolik enerjiden yararlanma yollari [Routes of hydraulic energy in mini and micro level]. 2011. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20111125055823/http://vansan.com.tr/docs/hidrolik.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Zhou, G.; Dai, H. 青山水轮泵站的改造 [Reconstruction of Qingshan Water Turbine Pumping Station]. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2014, 20, 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, S.O. The Price-Stub Pumping Plant. Reclam. Rec. 1920, 11, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Uyan, A. Lamas Çayı Üzerinde İçme Ve Sulama Amaçlı Su Kullanım Sistemlerinin Değerlendirilmesi [Evaluation of Water Use Systems for Drinking and Irrigation on Lamas Stream]; Çukurova University: Adana, Turkey, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oberle, P.; Stoffel, D.; Walter, D.; Kahles, G.; Riester, K.; Nestmann, F. Implementierung innovativer Wasserförder- und -verteilkonzepte in einer Gebirgsregion im Norden Vietnams [Implementation of innovative water supply and distribution concepts in a mountainous region in northern Vietnam]. Wasserwirtschaft 2018, 108, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberle, P.; Ikhwan, M.; Stoffel, D.; Nestmann, F. Adapted hydropower-driven water supply system: Assessment of an underground application in an Indonesian karst area. Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 6, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A. Pumps as Turbines: A User’s Guide; ITDG Publishing: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Idrovo, I. Obras civiles del proyecto de turbobombeo Chingazo-Pungal [Civil works of the turbo-pumping project Chingazo-Pungal]. In Seminario Internacional sobre turbobombeo con fines de riego. Memoria [International seminar on turbo-pumping for irrigation. Report]; CESA: Quito, Ecuador, 1985; pp. 65–85. [Google Scholar]
- Poças, M. A Roda de Água [The waterwheel]. AGROTEC, 2.° Trimestre 2013. Available online: https://dl.uc.pt/bitstream/10316.2/29970/1/Agrotec7_artigo35.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Dogra, B. How a Bundelkhand Farmer’s Engineering Innovation Was Ignored. The Wire, 8 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Isnugroho. Pompa Air Mikro Hidro, Alternatif Menghadapi Krisis Energi [Micro Hydro Water Pump, an Alternative to Overcome the Energy Crisis]. Din. Tek. Sipil 2012, 12, 230–238. [Google Scholar]
- Nestmann, F.; Oberle, P.; Ikhwan, M.; Stoffel, D. Solichin Development of Underground Water Extraction System for Karst Regions with Adapted Technologies and Operating System—Pilot Plant in Java, Indonesia. Procedia Eng. 2013, 54, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta’s Affordable Pumps. Facebook. 2018. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/portasaffordablepumps/ (accessed on 17 December 2018).
- Muriel, D.; Tinoco, R.; Filardo, B.; Cowen, E.; Filardo, B. Development of a novel, robust, sustainable and low cost self-powered water pump for use in free-flowing liquid streams. Renew. Energy 2016, 91, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, A.C., Jr. The Introduction of the American Water Ram, CA. 1843–1850. Bull. Assoc. Preserv. Technol. 1975, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; Derakhshan Houreh, S.; Ramos, H.M. Pumps as Turbines: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laux, C.H. Reverse-running Standard Pumps as Energy Recovery Turbines. Sulzer. Tech. Rev. 1982, 62, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, E.J. Proceedings of a Workshop on Hydraulic Ram Pump (HYDRAM) Technology; Ottawa IDRC: Arusha, Tanzania, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Noguera, J. Oil prices: Breaks and trends. Energy Econ. 2013, 37, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboredo, J.C. Is there dependence and systemic risk between oil and renewable energy stock prices? Energy Econ. 2015, 48, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, T.D.; Thomas, T.H.; Smith, A.V.; Glover, P.B.; Fountain, P.D. Hydraulic Ram Pumps: A Guide to Ram Pump Water Supply Systems; Practical Action Publishing: Warwickshire, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, M. Use of Hydraulic Rams in Nepal: A Guide to Manufacturing and Installation; UNICEF: Kathmandu, Nepal, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Peace Corps. A Training Manual in Conducting a Workshop in the Design, Construction, Operation, Maintenance and Repair of Hydrams; Humanity Development Library: Washington, DC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kindel, E.W. A Hydraulic Ram for Village Use; Volunteers in Technical Assistance: Pierce, WA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, U. Local Experience with Micro-Hydro Technology; SKAT: St. Gallen, Switzerland, 1981; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Roßmann, G. Diseño técnico de las turbinas [Technical design of the turbines]. In Seminario Internacional sobre turbobombeo con fines de riego. Memoria [International seminar on turbo-pumping for irrigation. Report]; CESA: Quito, Ecuador, 1985; pp. 31–54. [Google Scholar]

| Class | Technology | First Record | Last Record | Reported Devices | Nr. of Countries | Prime Mover | Pumping Device | Pumping Principle | Integration | Required Head | Location in Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manometric pumps | Spiral pump | 1746 | 2018 | 192 | 19 | Waterwheel | Spiral pipe | PD | DA, CS | ZH | SS |
| Coil pump | 1778 | 1997 | 14 | 8 | Waterwheel | Coil pipe | PD | DA | ZH | SS | |
| Helix pump | 1987 | 2017 | 27 | 12 | Axial-flow propeller | Helix pipe | PD | DA | ZH | SS | |
| Hydro-pneumatic water lifters | Hydraulic ram pump | 1796 | 2017 | ~6840 | 42 | Compressed air | HT, SARP | PD | VS, Diaphragm | LH | OS, SS, SU |
| Lambach pump | 1880s | 1961 | 35 | 3 | Compressed air | SARP, DARP | PD | PS | LH | OS | |
| Hydrautomat | 1920s | 2013 | 13 | 6 | Compressed air | HT | PD | VS | LH | SU | |
| Cherepnov water lifter | 1960 | 1996 | 6 | 5 | Compressed air | HT | PD | VS | LH | OS | |
| High lifter | 1984 | 2016 | 4 | 1 | Compressed air | SARP | PD | PS | LH | OS | |
| Aerohydraulic water lifter | 1998 | 1998 | 4 | 1 | Compressed air | HT | PD | VS | LH | SS | |
| Hybrid turbine-pumps | Hydropulsor | 1909 | 1912 | 5 | 2 | Turbine-pump impeller | Turbine-pump impeller | VH | Integrated impeller | LH | OS |
| Hydraulic transformer | 1940 | 1999 | 12 | 1 | Turbine-pump impeller | Turbine-pump impeller | VH | Integrated impeller | LH | OS | |
| Water turbine-pumps | Hydraulic converter | 1921 | 1921 | 1 | 1 | Axial turbine | CP | VH | CS | LH | SU |
| Chinese water turbine-pump | 1954 | 2007 | ~81500 | 15 | Kaplan turbine | CP | VH | CS, TS | LH, MH | SU | |
| Globe case coaxial water turbine pump | 1999 | 2014 | 4 | 1 | Kaplan turbine | CP | VH | CS | LH | OS | |
| Vietnamese hydraulic pump | 2009 | 2014 | 9 | 1 | Kaplan turbine | CP | VH | CS | LH | SU | |
| Tubular multi-propeller turbines | Plata pump | 1972 | 1990 | 17 | 8 | Multi-propeller turbine | SARP | PD | TS | ULH | SS |
| Turbopump | 1983 | 1992 | ~300 | 1 | Multi-propeller turbine | SARP | PD | TS | ULH | SS | |
| Hydrobine | 1998 | 2014 | 7 | 4 | Multi-propeller turbine | SARP | PD | TS | ULH | SS | |
| Water current turbines | Garman turbine | 1976 | 2018 | 69 | 6 | 3-bladed propeller turbine | CP | VH | TS | ZH | SS |
| Tyson turbine | 1982 | 2009 | 28 | 9 | 7-bladed turbine | DARP | PD | TS | ZH | SS | |
| Hydrokinetic linear turbine | 1984 | 2017 | 13 | 4 | Linear turbine | SARP | PD | Slider-crank | ZH | SS | |
| Markovic self-propelled pump | 1993 | 2009 | 3 | 1 | Mixed flow propeller turbine | SARP | PD | Slider-crank | ZH | SU | |
| Generic integrations | Waterwheel-driven pump | 1528 | 2018 | 139 | 19 | Waterwheel | SARP, DARP, DP, CP | PD, VH | TS | ZH, LH | OS, SS |
| Axial-flow turbine-driven pump | 1851 | 2011 | 88 | 9 | Axial-flow turbines (Kaplan, Tubular, Bulb, S-shape, Jonval, Girard) | DARP, CP, DP | PD, VH | CS, TS | LH | SS, SU | |
| Mixed-flow turbine-driven pump | 1897 | 2005 | 18 | 4 | Mixed-flow turbines (Francis, Samson, S. Morgan Smith, Leffel) | CP, DARP | PD, VH | CS, TS | LH | SS | |
| Tangential-flow turbine-driven pump | 1900 | 2018 | 17 | 7 | Tengential-flow turbines (Pelton, Turgo, Ghatta) | CP, Plunger pump, Progressive cavity pump, DP, SARP, DARP | PD, VH | CS, TS | HH | OS | |
| Pump-as-Turbine - Pump | 1952 | 2018 | 47 | 10 | Pump working in reverse | CP, DP | PD, VH | CS, TS | LH | OS | |
| Cross-flow turbine-driven pump | 1979 | 2018 | 26 | 10 | Cross-flow turbine (Michell – Banki, Ossberger, BYS) | CP, DP | PD, VH | CS, TS | LH | OS | |
| Other devices | Bunyip pump | 2006 | 2018 | 6 | 1 | Rubber tire | SARP | PD | DA | LH | OS |
| Filardo pump | 2012 | 2013 | 5 | 1 | Ribbon frond mechanism | Peristaltic pumping pipes | PD | DA | ZH | SU |
| Ranking | Density of Technologies | Concentration of Diverse Technologies | Nr. of Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China (CWTP) | USA (11) | UK (8) |
| 2 | USA (HRP) | Australia (9) | China, USA (7) |
| 3 | Kenya (Turbopump) | New Zealand (8) | Brazil, New Zealand (6) |
| 4 | Nepal (HSP) | Indonesia, Nepal, Thailand (7) | Australia (5) |
| 5 | Philippines (HRP) | Germany, Kenya, UK (6) | Colombia, Nepal (4) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Intriago Zambrano, J.C.; Michavila, J.; Arenas Pinilla, E.; Diehl, J.C.; Ertsen, M.W. Water Lifting Water: A Comprehensive Spatiotemporal Review on the Hydro-Powered Water Pumping Technologies. Water 2019, 11, 1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081677
Intriago Zambrano JC, Michavila J, Arenas Pinilla E, Diehl JC, Ertsen MW. Water Lifting Water: A Comprehensive Spatiotemporal Review on the Hydro-Powered Water Pumping Technologies. Water. 2019; 11(8):1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081677
Chicago/Turabian StyleIntriago Zambrano, Juan Carlo, Jaime Michavila, Eva Arenas Pinilla, Jan Carel Diehl, and Maurits W. Ertsen. 2019. "Water Lifting Water: A Comprehensive Spatiotemporal Review on the Hydro-Powered Water Pumping Technologies" Water 11, no. 8: 1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081677
APA StyleIntriago Zambrano, J. C., Michavila, J., Arenas Pinilla, E., Diehl, J. C., & Ertsen, M. W. (2019). Water Lifting Water: A Comprehensive Spatiotemporal Review on the Hydro-Powered Water Pumping Technologies. Water, 11(8), 1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081677





