Ecotoxicological Analysis of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Discharges in the Coastal Zone of Cihuatlán (Jalisco, Mexico)
Abstract
1. Introduction
Ecotoxicology of Emerging Contaminants
2. Materials and Methods
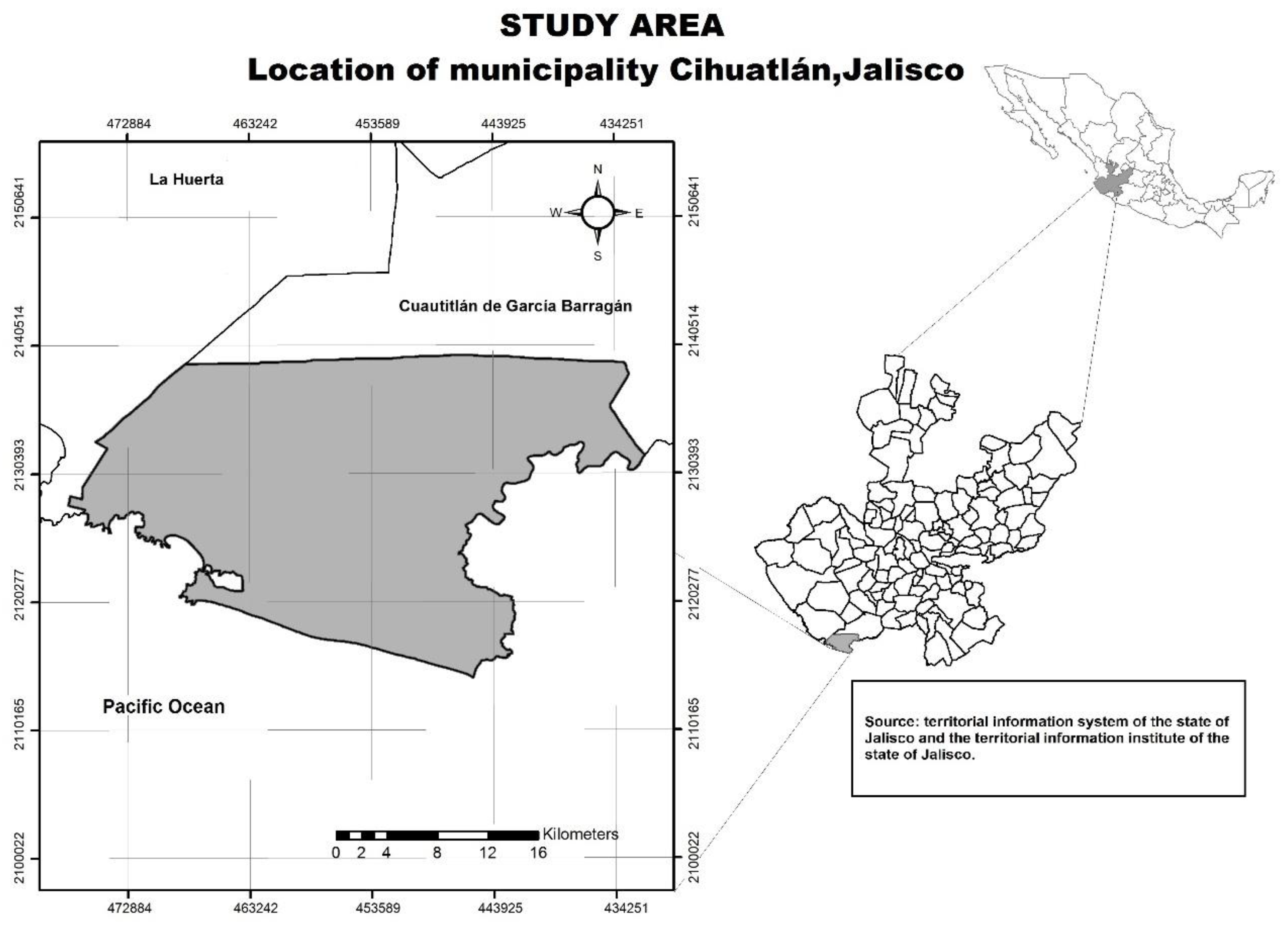
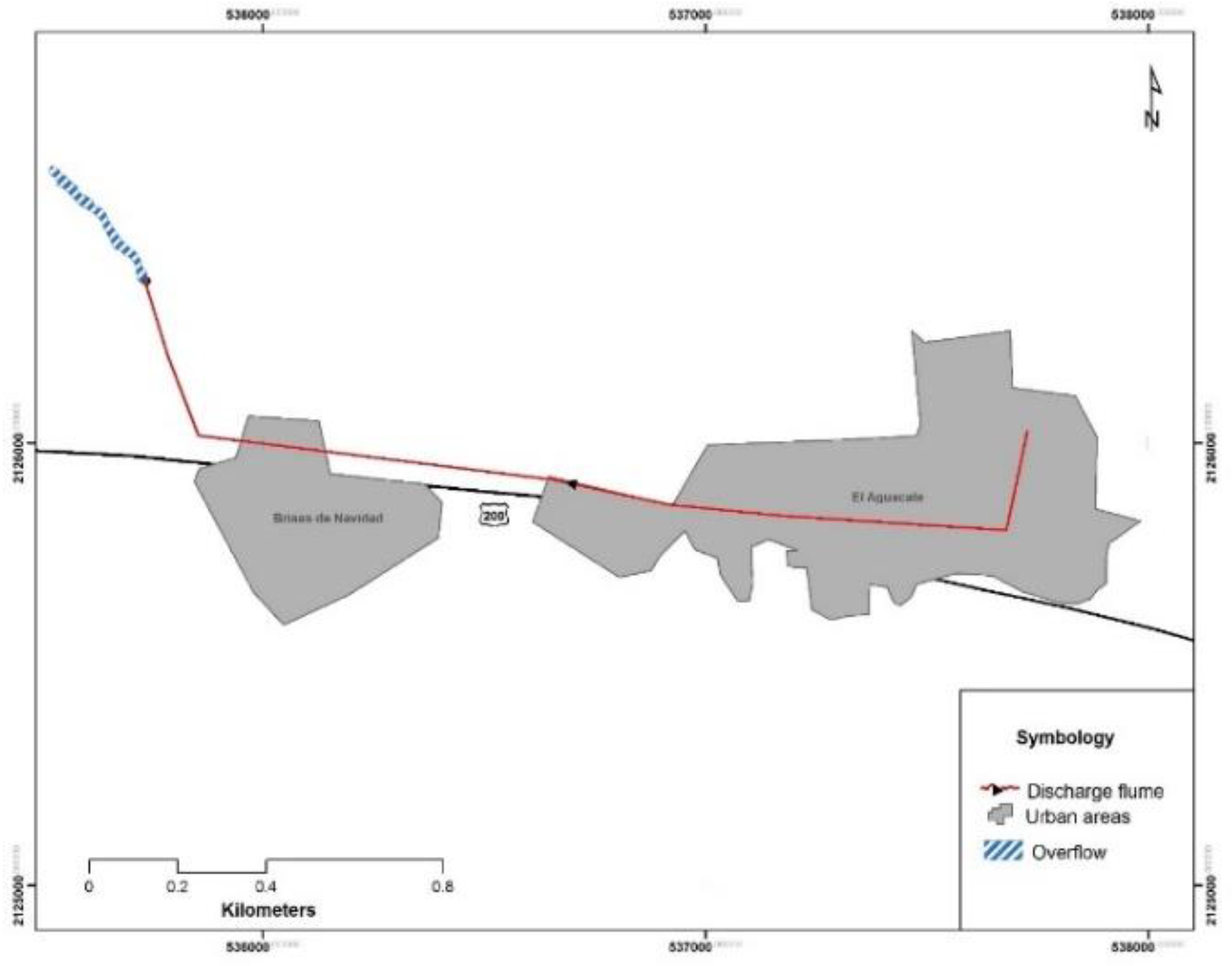
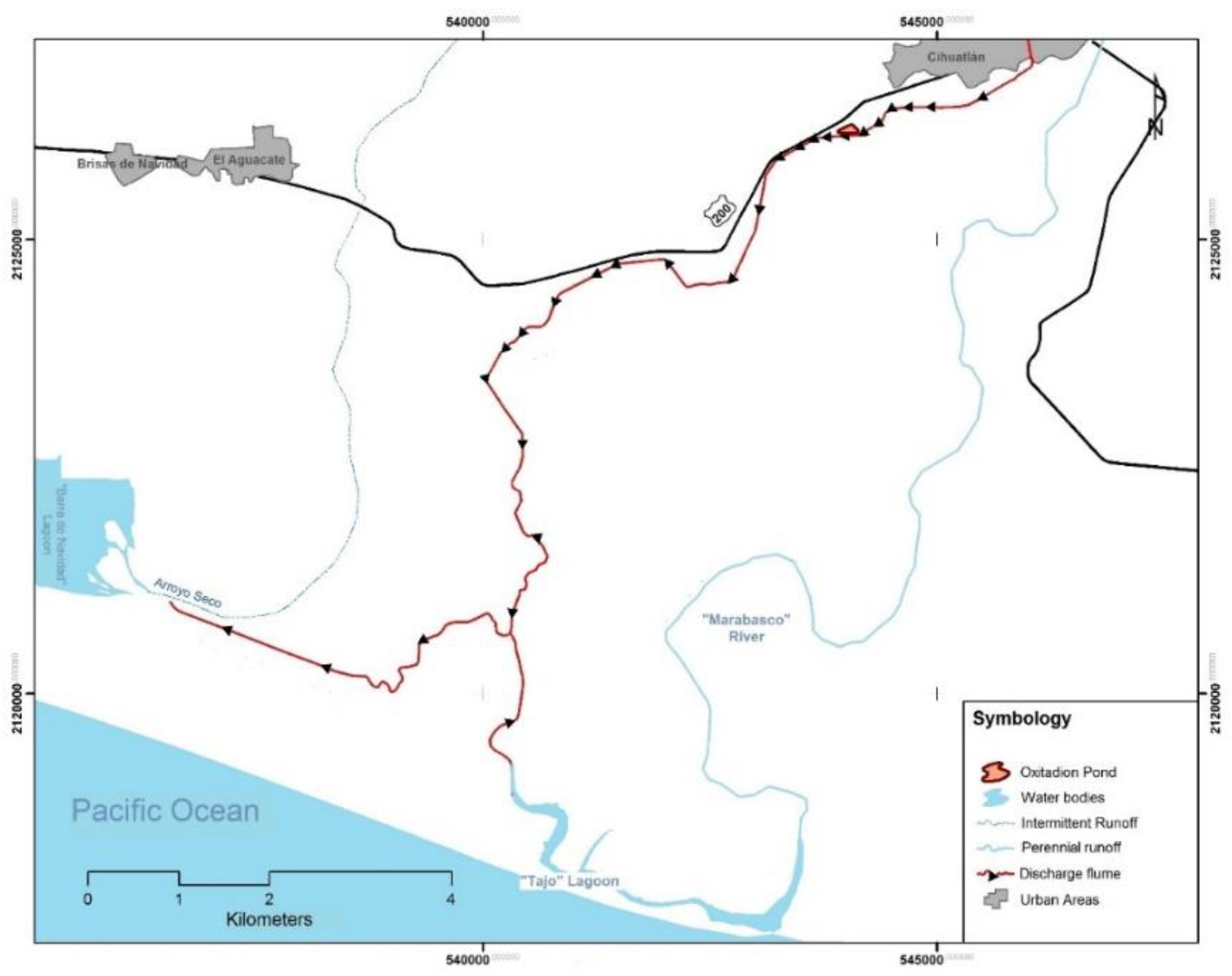
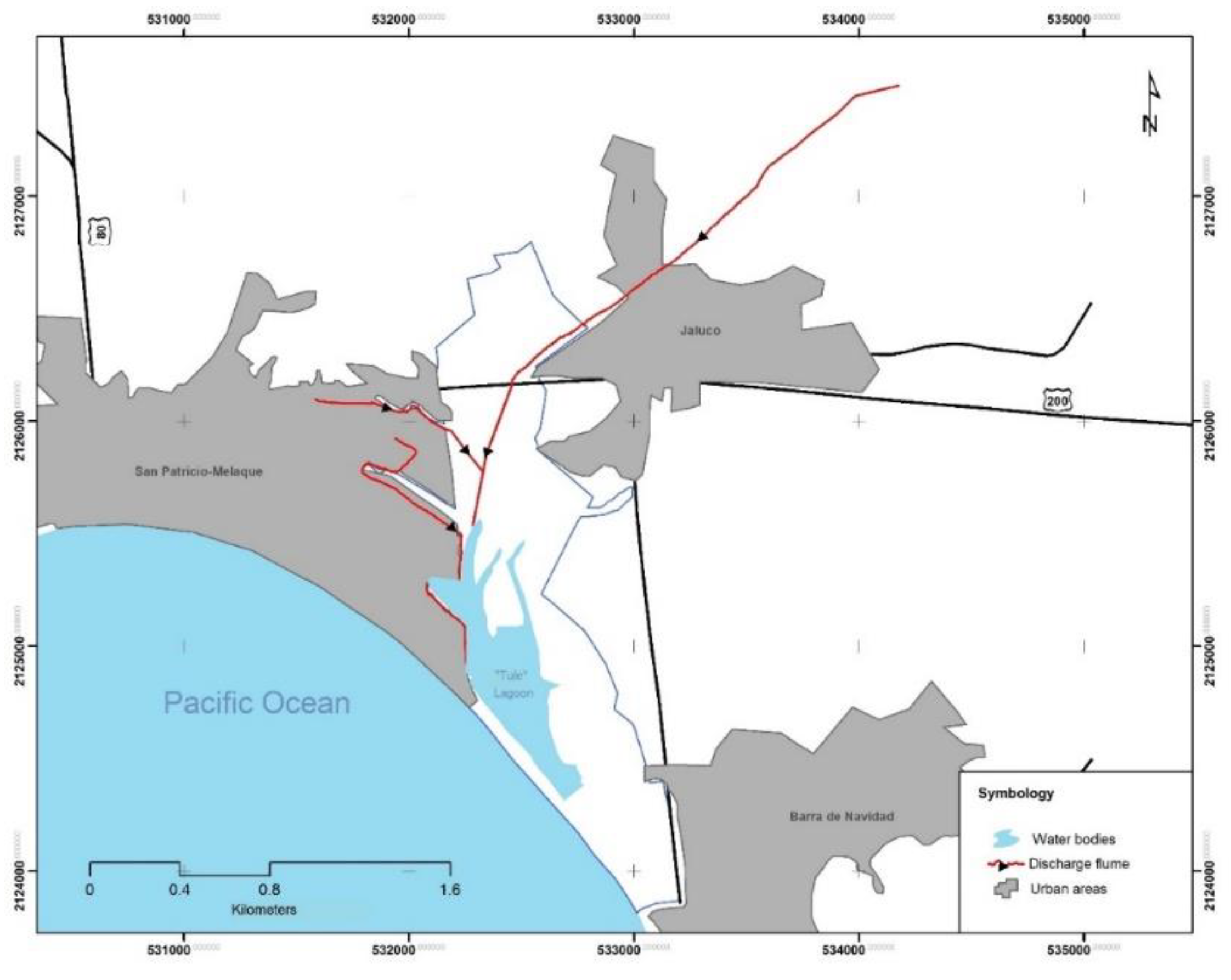
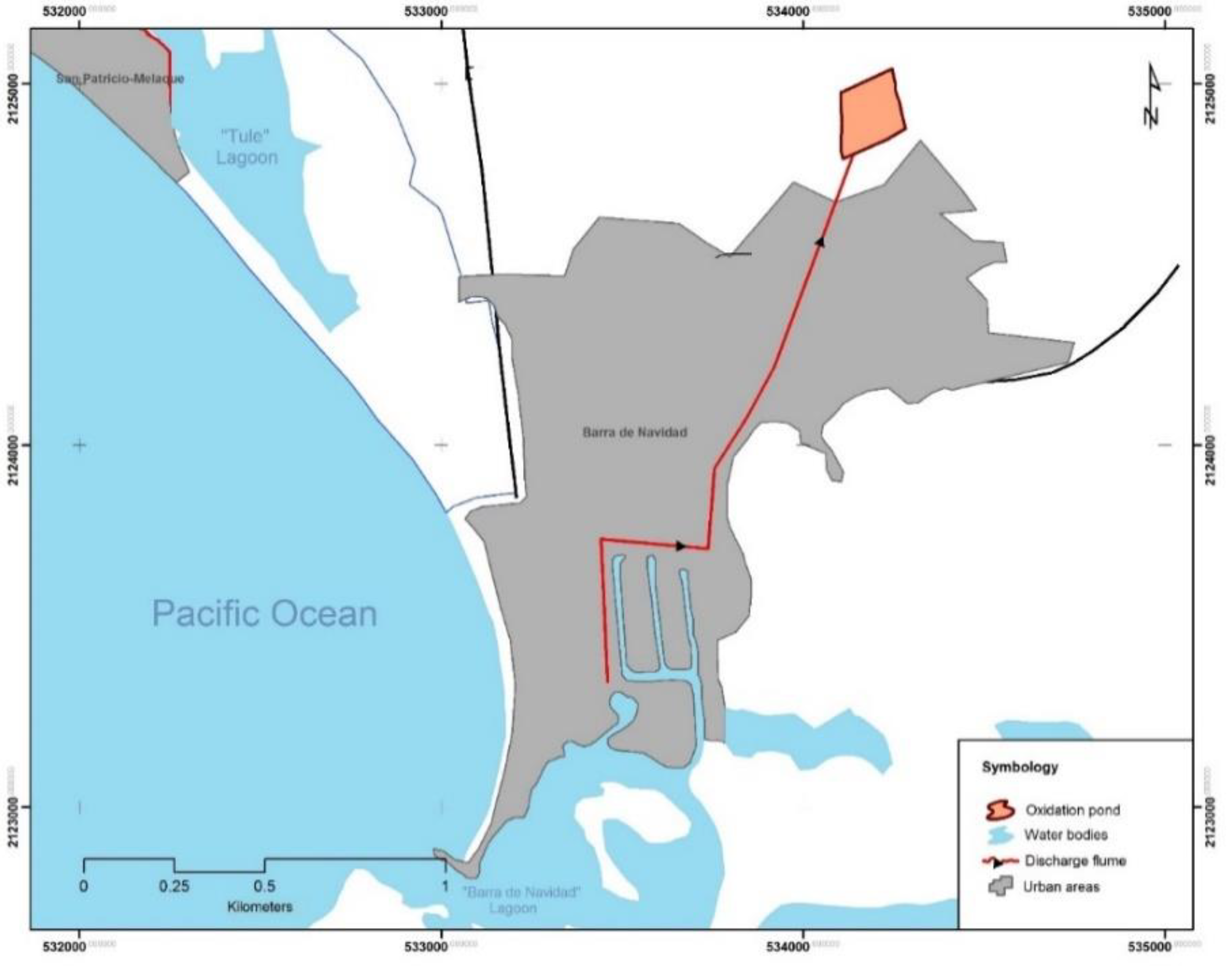
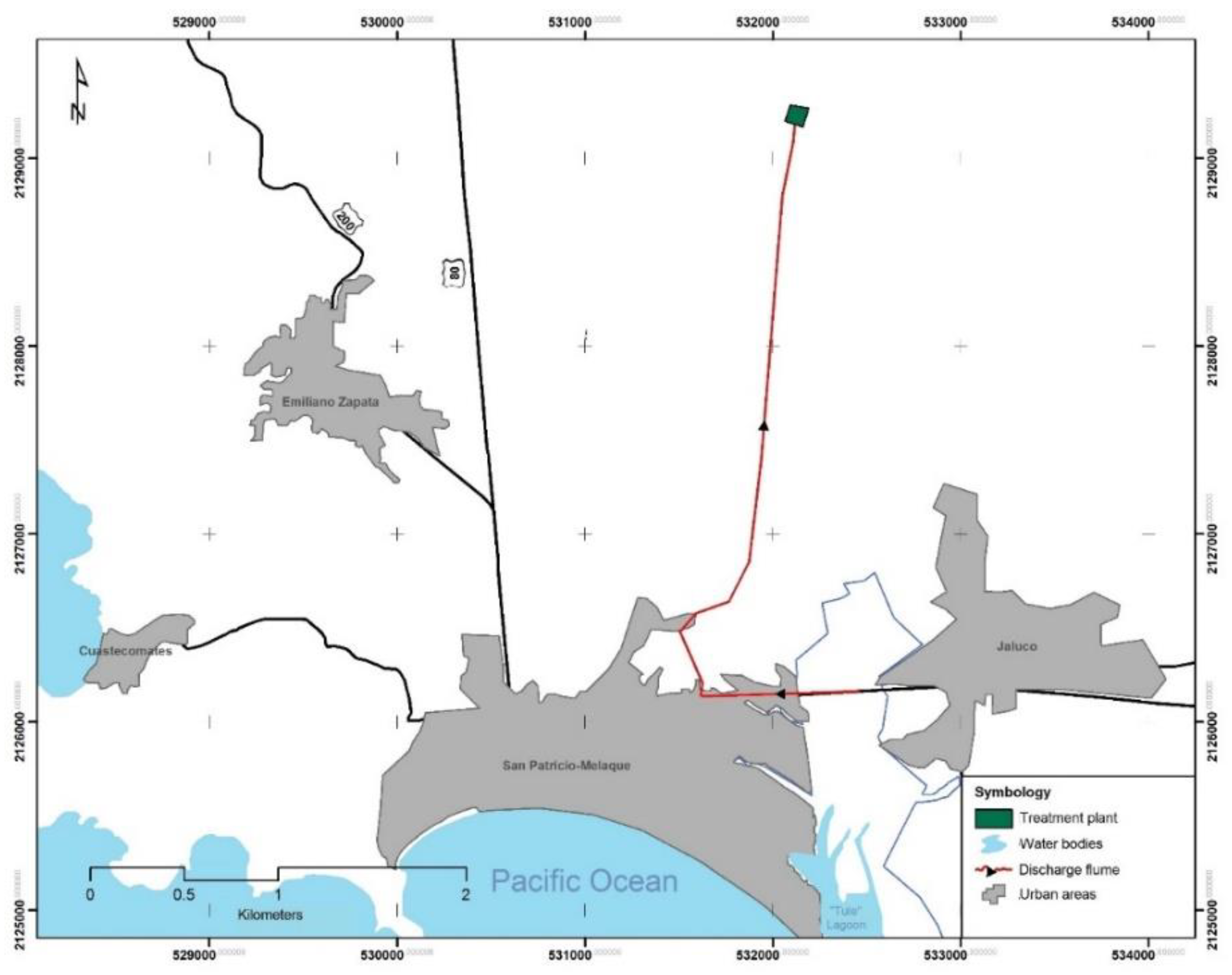
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Analysis of ECs
2.5. Quantitative Analysis of The Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) of ECs
2.6. Determination of Ecotoxicity of Emerging Contaminants
3. Results
4. Conclusions and Comments
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, E. Indicators of anthropogenic change and biological risk in coastal aquatic environments earth systems and environmental sciences. Encycl. Anthr. 2018, 3, 97–124. [Google Scholar]
- Omar TF, T.; Aris, A.Z.; Yusoff, F.M.; Mustafa, S. Occurrence, distribution, and sources of emerging organic contaminants in tropical coastal sediments of anthropogenically impacted Klang River estuary, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 131, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: Current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res. 2015, 1, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, M.; Lapworth, D. Emerging Organic Contaminants in Groundwater. Smart Sensors for Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 259–284. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, S.D.; Kimura, S.Y. Water analysis: Emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 546–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, J.P.R.; Lapworth, D.J.; Nkhuwa, D.C.; Stuart, M.E.; Gooddy, D.C.; Bell, R.A.; Chirwa, M.; Kabika, J.; Liemisa, M.; Chibesa, M.; et al. Emerging contaminants in urban groundwater sources in Africa. Water Res. 2015, 72, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, M.; Eljarrat, E.; Lopez de Alda, M.J.; Barceló, D. Endocrine disrupting compounds and other emerging contaminants in the environment: A survey on new monitoring strategies and occurrence data. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.; Holady, J.; Stanford, B.D.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in U.S. drinking water. Env. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bila, D.M.; Dezottii, M. Pharmaceutical drugs in the environment. Quím. Nova 2003, 26, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jondeau-Cabaton, A.; Soucasse, A.; Jamin, E.L.; Creusot, N.; Grimaldi, M.; Jouanin, I.; Aït-Aïssa, S.; Balaguer, P.; Debrauwer, L.; Zalko, D. Characterization of endocrine disruptors from a complex matrix using estrogen receptor affinity columns and high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Env. Sci. Poll. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 2705–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Matamoros, V.; Sidrach, R.; Villacorta, J. Comprehensive assessment of the design configuration of constructed wetlands for the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from urban wastewaters. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3669–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruya, K.A.; Dodder, N.G.; Tang, C.L.; Lao, W.; Tsukada, D. Which coastal and marine environmental contaminants are truly emerging? Env. Sci. Poll. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Pak, A.P. Acute and subchronic toxicity of the heavy metals copper, chromium, nickel, and zinc, individually and in mixture, to the freshwater copepod Mesocyclopspehpeiensis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 73, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Alvariño, C.; Espinosa, M.; Lloréns, M.; López, M.; Pellón, A. Waste in the pharmaceutical industry. Cenic Chem. Sci. 2006, 36, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.; Werner, I. Effect-based tools for monitoring and predicting the ecotoxicological effects of chemicals in the aquatic environment. Sensors 2012, 12, 12741–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Fanelli, R. Pharmaceuticals in the environment in Italy: Causes, occurrence, effects and control. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2006, 13, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, C.; Ottermanns, R.; Keiter, S.; Ait-Aissa, S.; Bluhm, K.; Brack, W. Bioassay battery interlaboratory investigation of emerging contaminants in spiked water extracts—Towards the implementation of bioanalytical monitoring tools in water quality assessment and monitoring. Water Res. 2016, 1, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernersson, A.S.; Carere, M.; Maggi, C.; Tusil, P.; Soldan, P.; James, A.; Sanchez, W.; Dulio, V.; Broeg, K. The European technical report on aquatic effect-based monitoring tools under the water framework directive. Env. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaGoy, P. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH). Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; vomSaal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangali-Quintanilla, V.; Sadmani, A.; McConville, M.; Kennedy, M.; Amy, G. A QSAR model for predicting rejection of emerging contaminants (pharmaceuticals, endocrine disruptors) by nanofiltration membranes. Water Res. 2010, 44, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U. Descriptors and their selection methods in QSAR analysis: Paradigm for drug design. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meffe, R.; De Bustamante, I. Emerging organic contaminants in surface water and groundwater: A first overview of the situation in Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INEGI. Census of Population and Housing 2010; National Institute of Statistic and Geography: Aguascalientes, Mexico, 2010; Available online: http://www.inegi.org.mx. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsar. Ramsar Sites List. Ramsar Convention. Available online: www.ramsar:document/the-list-of-wetlands-of-international-importance-the ramsar-list (accessed on 29 September 2018).
- SMN. Weather Normals Jalisco. National Meteorological Service, Mexico. Available online: https://smn.cna.gob.mx/es/informacion-climatologica-por-estado?estado=jal (accessed on 29 September 2018).
- Pérez-Parada, A.; Gómez-Ramos, M.; Martínez-Bueno, M.J.; Uclés, S.; Uclés, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Analytical improvements of hybrid LC-MS/MS techniques for the efficient evaluation of emerging contaminants in river waters: A case study of the Henares River (Madrid, Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, K.; De Brabander, H.; De Wulf, E.; Van Caeter, P.; Janssen, C.; Vanhaecke, L. Coupled chromatographic and mass-spectrometric techniques for the analysis of emerging pollutants in the aquatic environment. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 35, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.; Clausen, J.; Linkov, E.; Linkov, I. Predicting physical properties of emerging compounds with limited physical and chemical data: QSAR model uncertainty and applicability to military munitions. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Hoeschele, J.; Turner, J.; Jacobson, K.; Christie, N.; Paton, C.; Smith, L.; Witschi, H.; Lee, E. Chemical softness and acute metal toxicity in mice and drosophila. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1982, 63, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, G.; Konasewich, D. Structure-Activity Correlations in Studies of Toxicity and Bioconcentration with Aquatic Organisms; Great Lakes Advisory Board, International Joint Commission: Windsor, ON, Canada, 1983; pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Parrott, J.; Blunt, B. Life-cycle exposure of fathead minnows (Pimephalespromelas) to an ethinylestradiol concentration below 1 ng/L reduces egg fertilization success and demasculinizes males. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 23, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.P.; Kime, D.E.; Van der Ven, L.; Wester, P.; Brion, F.; Maack, G.; Tyler, C. Long-term exposure to environmental concentrations of the pharmaceutical ethynylestradiol causes reproductive failure in fish. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Terry, J.; Nestrick, A.; Savage, P. Microcontaminants in pentachlorophenol synthesis. 1. New bioassay for microcontaminant quantification industrial engineering. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 5199–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, S.; Van Aerle, R.; Tyler, C.; Braunbeck, T. Effects of 17a-ethinylestradiol in a fathead minnow (Pimephalespromelas) gonadal recrudescence assay. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger, B.; Van den Heuvel, M.R.; Hitzfeld, B.C.; Dietrich, D.R. Effects of treated sewage on immune function in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss). Aquatic Toxicol. 2004, 70, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Baddaloo, E.; Gerard, Y. Handbook of Chemical Toxicity Profiles of Biological Species; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; pp. 254–259. [Google Scholar]

| Contaminant | Molecular Formula | pKa | Solubility in Water (mg/L) | Bioassay | EC50 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diclofenac | C14H11NCl2O2 | 4.15 | 19.4 | Vibrio Fischeri 30 min | 13.5 |
| Daphnia Magna 48 h | 224.30 | ||||
| D: Subspicatus 3 d [32] | 72 | ||||
| Ibuprofen | C13H18O2 | 5.2 | 21 | Daphnia Magna 48 h | 9.06 |
| L. macrohiruz(fish) 48 h | 10 | ||||
| S.costatum 48 h [32] | 7.1 | ||||
| Ketorolac | C15H13NO3 | 3.84 | 15 | Rat 96 h [33] | 189 |
| PCP | C6Cl5OH | 4.74 | 20 | Palemonetes pugio 96 h | 0.515 |
| Pimephalespromelas 96 h | 0.19 | ||||
| Oncorhynchus mykiss 96 h [34] | 0.23 | ||||
| Estradiol | C18H24O2 | 10.33 | 3.6 | Fathead Minnows 3 d | 0.001 |
| Limneastagnalisa [35] | 0.004 |
| TEQ | Toxicity Classification |
|---|---|
| <1 | Low or no toxicity |
| 1–10 | Toxic |
| 11–100 | Very Toxic |
| >100 | Extremely toxic |
| Parameter | Effluent | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | D | J | L | S | |
| T (°C) | 28.9 ± 0.02 | 30.1 ± 0.5 | 29.9 ± 0.1 | 29.3 ± 0.1 | 31.2 ± 0.2 |
| pH | 5.9 ± 0.8 | 8.2 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.4 | 6.9 ± 0.7 | 7.56 ±0.5 |
| Conductivity (mS/cm3) | 1.215 ± 0.32 | 1.448 ± 0.86 | 1.325 ± 0.65 | 1.329 ± 0.76 | 1.775 ± 0.82 |
| TDS (g/L) | 0.527 ± 0.24 | 1.987 ± 0.32 | 0.882 ± 0.12 | 0.768 ± 0.11 | 1.072 ± 0.16 |
| % Salt | 0.79 ± 0.06 | 0.67 ± 0.13 | 0.72 ± 0.56 | 0.96 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.24 |
| DO (mg/L) | 0.82 ± 0.9 | 1.94 ± 0.8 | 1.26 ± 0.6 | 0.53 ± 0.4 | 0.68 ± 0.3 |
| P (mmHg) | 759.8 ± 0.2 | 757.8 ± 0.1 | 759.6 ± 0.4 | 759.3 ± 1.1 | 758.8 ± 1.2 |
| Q (L/min) | 62.5 ± 8.2 | 3333.33 ± 26.4 | 450.5 ± 38.2 | 1562.5 ± 124.3 | 328.12 ± 19.2 |
| Diclofenac (mg/min) | 0.335 ± 0.056 | 11.66 ± 0.32 | 0.43 ± 0.072 | 0 | 0.38 ± 0.023 |
| Ibuprofen (mg/min) | 0.345 ± 0.062 | 18.33 ± 0.56 | 0.76 ± 0.11 | 1.60 ± 0.35 | 0.46 ± 0.06 |
| Ketorolac (mg/min) | 0.270 ± 0.038 | 8.66 ± 0.67 | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 0.83 ± 0.032 | 0.31 ± 0.07 |
| PCP (mg/min) | 0.119 ± 0.024 | 6.23 ± 0.23 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Estradiol (mg/min) | 0.033 ± 0.018 | 2.13 ± 0.12 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Effluent | Emerging Contaminant | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diclofenac | Ibuprofen | Ketorolac | PCP | Estradiol | ||||||
| TEQ | Toxicity Class | TEQ | Toxicity Class | TEQ | Toxicity Class | TEQ | Toxicity Class | TEQ | Toxicity Class | |
| A | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | 4 | Toxic | 18 | Very Toxic |
| D | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | 4 | Toxic | 18 | Very Toxic |
| J | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | *Nd | - | *Nd | - |
| L | *Nd | - | 2 | Toxic | 2 | Toxic | *Nd | - | *Nd | - |
| S | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | 3 | Toxic | *Nd | - | *Nd | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arguello-Pérez, M.Á.; Mendoza-Pérez, J.A.; Tintos-Gómez, A.; Ramírez-Ayala, E.; Godínez-Domínguez, E.; Silva-Bátiz, F.d.A. Ecotoxicological Analysis of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Discharges in the Coastal Zone of Cihuatlán (Jalisco, Mexico). Water 2019, 11, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071386
Arguello-Pérez MÁ, Mendoza-Pérez JA, Tintos-Gómez A, Ramírez-Ayala E, Godínez-Domínguez E, Silva-Bátiz FdA. Ecotoxicological Analysis of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Discharges in the Coastal Zone of Cihuatlán (Jalisco, Mexico). Water. 2019; 11(7):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071386
Chicago/Turabian StyleArguello-Pérez, Miguel Ángel, Jorge Alberto Mendoza-Pérez, Adrián Tintos-Gómez, Eduardo Ramírez-Ayala, Enrique Godínez-Domínguez, and Francisco de Asís Silva-Bátiz. 2019. "Ecotoxicological Analysis of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Discharges in the Coastal Zone of Cihuatlán (Jalisco, Mexico)" Water 11, no. 7: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071386
APA StyleArguello-Pérez, M. Á., Mendoza-Pérez, J. A., Tintos-Gómez, A., Ramírez-Ayala, E., Godínez-Domínguez, E., & Silva-Bátiz, F. d. A. (2019). Ecotoxicological Analysis of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Discharges in the Coastal Zone of Cihuatlán (Jalisco, Mexico). Water, 11(7), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071386




