Community Assembly Mechanisms Underlying the Core and Random Bacterioplankton and Microeukaryotes in a River–Reservoir System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
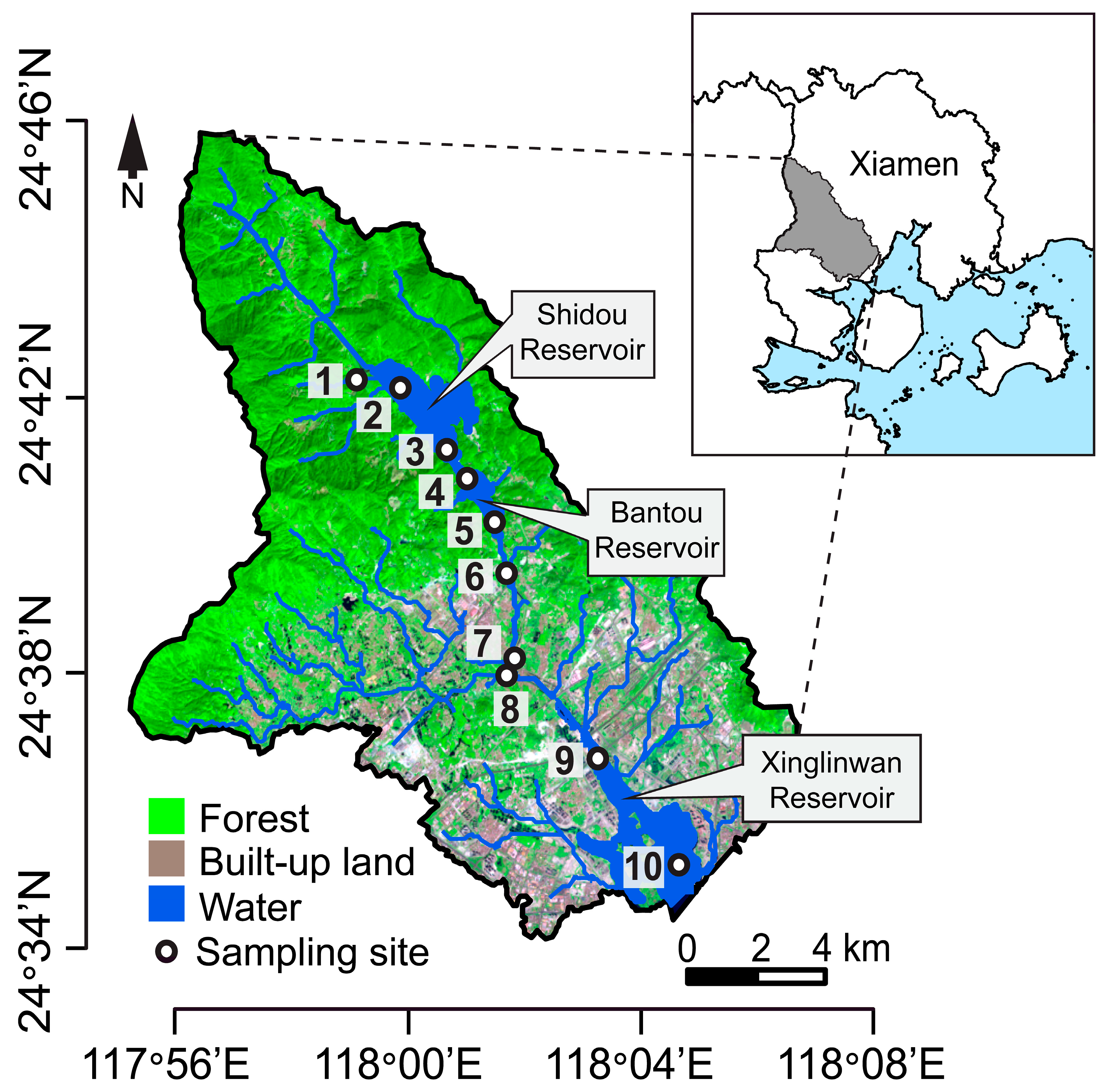
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Environmental Variables
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Illumina Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.6. Modelling Spatial Abundance Distributions (SpADs)
2.7. Multivariate Analyses
2.8. Neutral Community Model
2.9. Phylogenetic Null Model Analysis
2.10. Quantifying Environmental Synchrony
3. Results
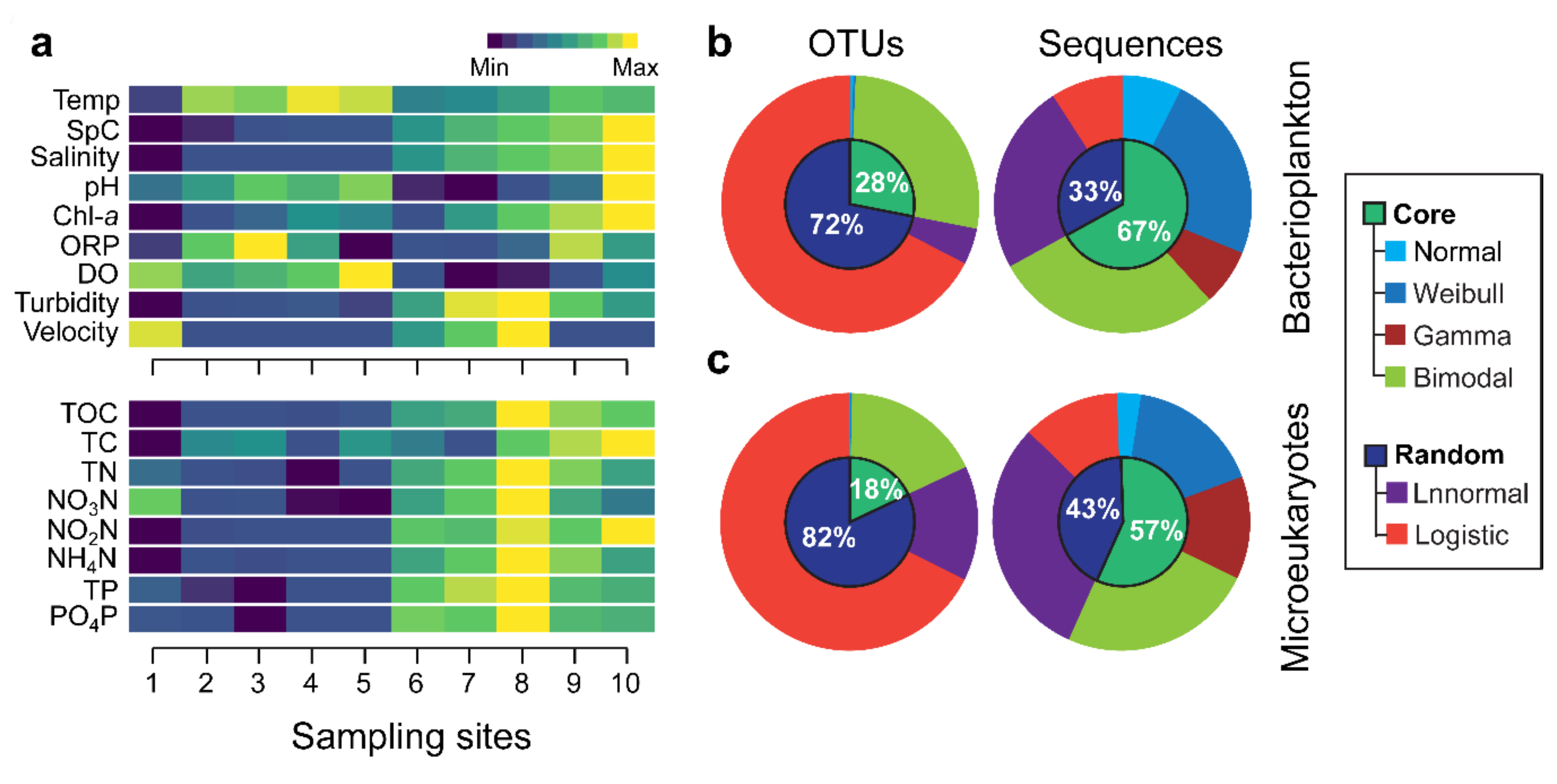
3.1. Environmental Variation and Spacies Abundance Distributions (SpADs)
3.2. Distribution Patterns of the Core and Random Plankton
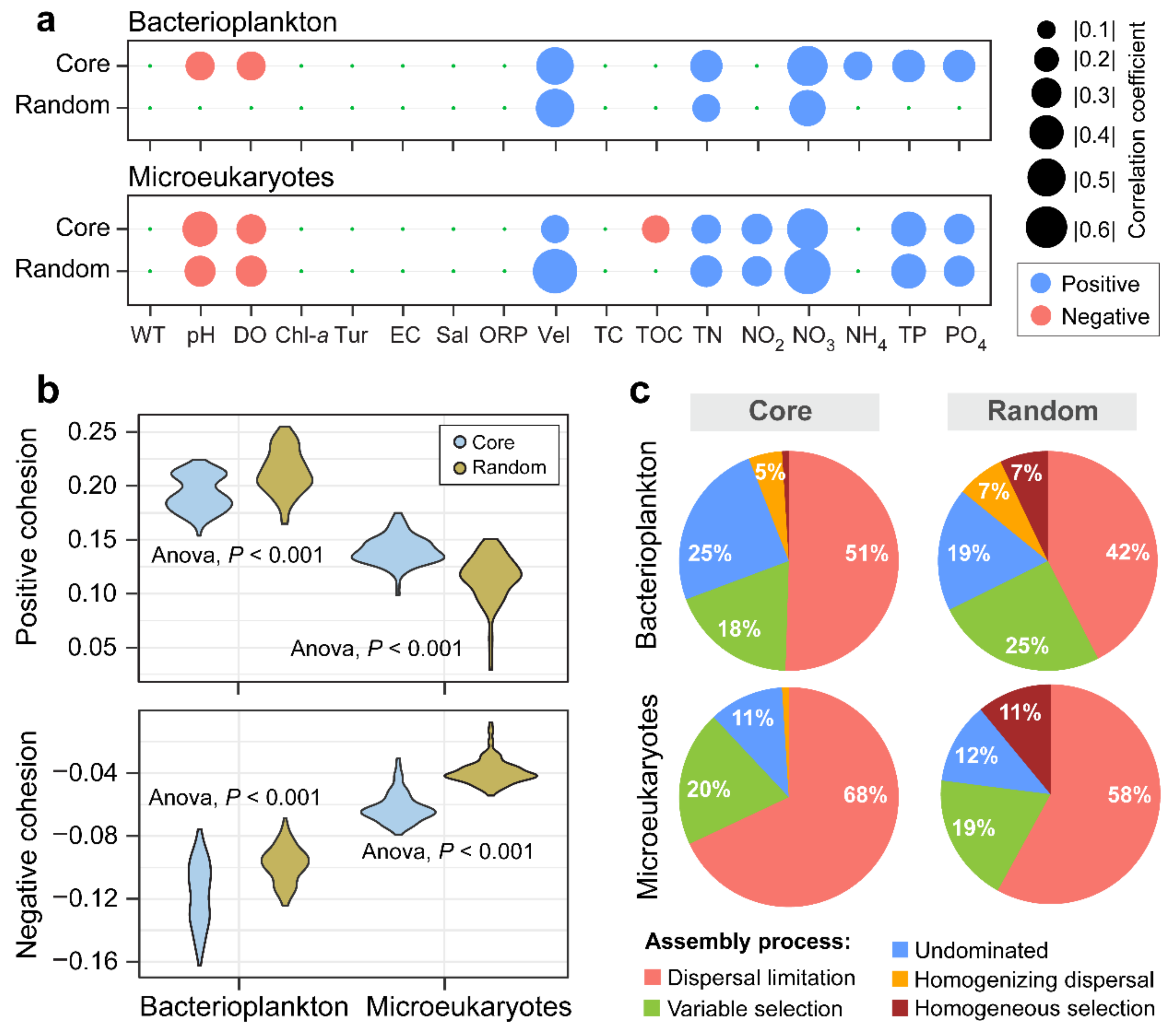
3.3. Environmental Synchrony Among the Core and Random Plankton Communities
3.4. Ecological Processes Underlying the Core and Random Plankton Communities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, J.A.; Dubilier, N.; Rudgers, J.A. Nature’s microbiome: Introduction. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locey, K.J.; Lennon, J.T. Scaling laws predict global microbial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5970–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogin, M.L.; Morrison, H.G.; Huber, J.A.; Mark Welch, D.; Huse, S.M.; Neal, P.R.; Arrieta, J.M.; Herndl, G.J. Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12115–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemergut, D.R.; Schmidt, S.K.; Fukami, T.; O’Neill, S.P.; Bilinski, T.M.; Stanish, L.F.; Knelman, J.E.; Darcy, J.L.; Lynch, R.C.; Wickey, P. Patterns and processes of microbial community assembly. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, A.; Dunn, R.R.; Blowes, S.A.; Keil, P.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Herrmann, M.; Kusel, K.; Lennon, J.T.; Sanders, N.J.; Storch, D.; et al. Macroecology to unite all life, large and small. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savio, D.; Sinclair, L.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Parajka, J.; Reischer, G.H.; Stadler, P.; Blaschke, A.P.; Bloschl, G.; Mach, R.L.; Kirschner, A.K.T.; et al. Bacterial diversity along a 2600 km river continuum. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4994–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeglin, L.H. Stream microbial diversity in response to environmental changes: Review and synthesis of existing research. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isabwe, A.; Yang, J.R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Community assembly processes underlying phytoplankton and bacterioplankton across a hydrologic change in a human-impacted river. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, A.N.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, S.F.; Jiang, X.T.; Dang, C.Y.; Ma, T.; Liu, S.T.; Chen, Q.; Xie, S.G.; et al. Integrated biogeography of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial communities in the Yangtze River. Microbiome 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, D.S.; Gweon, H.S.; Bowes, M.J.; Newbold, L.K.; Field, D.; Bailey, M.J.; Griffiths, R.I. Catchment-scale biogeography of riverine bacterioplankton. ISME J. 2015, 9, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenopoulos, M.A.; Downing, J.A.; Kumar, M.D.; Menden-Deuer, S.; Voss, M. Headwaters to oceans: Ecological and biogeochemical contrasts across the aquatic continuum. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño-García, J.P.; Ruiz-González, C.; Del Giorgio, P.A. Interactions between hydrology and water chemistry shape bacterioplankton biogeography across boreal freshwater networks. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Lin, Y.; Yu, Z.; Lin, S. Biogeographic patterns of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in three subtropical bays resulting from selective and neutral processes. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P.; Borda-De-Agua, L. The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography: Reply. Ecology 2004, 85, 3175–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellend, M. Conceptual synthesis in community ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 2010, 85, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Stegen, J.C.; Yu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Nearly a decade-long repeatable seasonal diversity patterns of bacterioplankton communities in the eutrophic Lake Donghu (Wuhan, China). Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 3839–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danczak, R.E.; Johnston, M.D.; Kenah, C.; Slattery, M.; Wilkins, M.J. Microbial community cohesion mediates community turnover in unperturbed aquifers. mSystems 2018, 3, e00066-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R.; Tesson, V.M.S.; Canbäck, B.; Pontarp, K.M.; Hedlund, R.K. Contrasting prevalence of selection and drift in the community structuring of bacteria and microbial eukaryotes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massana, R.; Logares, R. Eukaryotic versus prokaryotic marine picoplankton ecology. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.X.; Lu, H.P.; Sastri, A.; Yeh, Y.C.; Gong, G.C.; Chou, W.C.; Hsieh, C.H. Contrasting the relative importance of species sorting and dispersal limitation in shaping marine bacterial versus protist communities. ISME J. 2018, 12, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrós-Alió, C. The rare bacterial biosphere. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vargas, C.; Audic, S.; Henry, N.; Decelle, J.; Mahe, F.; Logares, R.; Lara, E.; Berney, C.; Le Bescot, N.; Probert, I.; et al. Ocean plankton. Eukaryotic plankton diversity in the sunlit ocean. Science 2015, 348, 1261605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.D.J.; Neufeld, J.D. Ecology and exploration of the rare biosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño-García, J.P.; Ruiz-González, C.; Del Giorgio, P.A. Landscape-scale spatial abundance distributions discriminate core from random components of boreal lake bacterioplankton. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Salles, J.F. Community assembly processes of the microbial rare biosphere. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-González, C.; Niño-García, J.P.; Kembel, S.W.; del Giorgio, P.A. Identifying the core seed bank of a complex boreal bacterial metacommunity. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, A.; Jones, S.E.; Caporaso, J.G.; Handelsman, J.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N.; Gilbert, J.A. Conditionally rare taxa disproportionately contribute to temporal changes in microbial diversity. mBio 2014, 5, e01371-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Xue, Y.; Huang, B.; Yang, J. Community dynamics of free-living and particle-attached bacteria following a reservoir Microcystis bloom. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, T.J.; Whittaker, R.J. Neutral theory and the species abundance distribution: Recent developments and prospects for unifying niche and neutral perspectives. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Gao, X.F.; Peng, F.; Chen, H.H.; Tang, L.N.; Yang, J. Relationship between water quality and landscape characteristics of Houxi River watershed in Xiamen city along a rural-urban gradient. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 2021–2033. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F.; Isabwe, A.; Guo, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. An extensively shared antibiotic resistome among four seasons suggests management prioritization in a subtropical riverine ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, X.Q.; Liu, L.M.; Zhang, W.J.; Guo, P.Y. Algae community and trophic state of subtropical reservoirs in southeast Fujian, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J.; et al. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maechler, M. Diptest: Hartigan’s Dip Test Statistic for Unimodality-Corrected. R Package Version 0.75-7. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=diptest (accessed on 17 December 2018).
- Delignette-Muller, M.L.; Dutang, C. Fitdistrplus: An R package for fitting distributions. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 64, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Matesanz, S.; Gimeno, T.E.; de la Cruz, M.; Escudero, A.; Valladares, F. Competition may explain the fine-scale spatial patterns and genetic structure of two co-occurring plant congeners. J. Ecol. 2011, 99, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Woodcock, S.; Lunn, M.; Head, I.M.; and Curtis, T.P. Modeling taxa-abundance distributions in microbial communities using environmental sequence data. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 53, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography (MPB-32); Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, C.M.; McMahon, K.D. Cohesion: A method for quantifying the connectivity of microbial communities. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Martiny, J.B.H. Beyond biogeographic patterns: Processes shaping the microbial landscape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.M.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wilkinson, D.M. The biogeography of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in the lakes and reservoirs of China. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.B.; Stegen, J.C. Dispersal-based microbial community assembly decreases biogeochemical function. Processes 2017, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C. At the nexus of history, ecology, and hydrobiogeochemistry: Improved predictions across scales through integration. mSystems 2018, 3, e00167-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.Q.; Cao, X.F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J.H.; Jiang, D.L.; Huang, Y. Similar community assembly mechanisms underlie similar biogeography of rare and abundant bacteria in lakes on Yungui Plateau, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, M.C.; Huang, Y. The importance of neutral and niche processes for bacterial community assembly differs between habitat generalists and specialists. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.X.; Liu, H.B. Disentangling protist communities identified from DNA and RNA surveys in the Pearl River-South China Sea Continuum during the wet and dry seasons. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 4627–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, I.; Heppell, C.M.; Ryo, M.; Rillig, M.C. Application of the microbial community coalescence concept to riverine networks. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 1832–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibold, M.A.; Urban, M.C.; De Meester, L.; Klausmeier, C.A.; Vanoverbeke, J. Regional neutrality evolves through local adaptive niche evolution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2612–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Luo, Z.; Rashid, A.; Chen, S.; Huang, W.; Yu, C.-P. Prokaryotic footprints in urban water ecosystems: A case study of urban landscape ponds in a coastal city, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottos, E.M.; Kennedy, D.W.; Romero, E.B.; Fansler, S.J.; Brown, J.M.; Bramer, L.M.; Chu, R.K.; Tfaily, M.M.; Jansson, J.K.; Stegen, J.C. Dispersal limitation and thermodynamic constraints govern spatial structure of permafrost microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, T.; Neurath, R.; Perera, A.; Chu-Jacoby, I.; Ning, D.; Zhou, J.; Nico, P.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Firestone, M. Microbial community assembly differs across minerals in a rhizosphere microcosm. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 4444–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Bao, F.; Xiong, S.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D. Microeukaryotic biogeography in the typical subtropical coastal waters with multiple environmental gradients. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenchel, T.; Finlay, B.J. The ubiquity of small species: Patterns of local and global diversity. Bioscience 2004, 54, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.R.; Karunaratne, S.; Campbell, C.D.; Yao, H.Y.; Robinson, L.; Singh, B.K. Deterministic processes vary during community assembly for ecologically dissimilar taxa. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewson, I.; Fuhrman, J.A. Richness and diversity of bacterioplankton species along an estuarine gradient in Moreton Bay, Australia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3425–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | Bacterioplankton | Microeukaryotes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | m | R2 | m | |
| All | 0.62 | 0.19 | 0.56 | 0.04 |
| Core | 0.45 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.06 |
| Random | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.41 | 0.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isabwe, A.; Ren, K.; Wang, Y.; Peng, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Community Assembly Mechanisms Underlying the Core and Random Bacterioplankton and Microeukaryotes in a River–Reservoir System. Water 2019, 11, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061127
Isabwe A, Ren K, Wang Y, Peng F, Chen H, Yang J. Community Assembly Mechanisms Underlying the Core and Random Bacterioplankton and Microeukaryotes in a River–Reservoir System. Water. 2019; 11(6):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061127
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsabwe, Alain, Kexin Ren, Yongming Wang, Feng Peng, Huihuang Chen, and Jun Yang. 2019. "Community Assembly Mechanisms Underlying the Core and Random Bacterioplankton and Microeukaryotes in a River–Reservoir System" Water 11, no. 6: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061127
APA StyleIsabwe, A., Ren, K., Wang, Y., Peng, F., Chen, H., & Yang, J. (2019). Community Assembly Mechanisms Underlying the Core and Random Bacterioplankton and Microeukaryotes in a River–Reservoir System. Water, 11(6), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061127






