Testing the Prediction Ability of LEM-Derived Sedimentary Budget in an Upland Catchment of the Southern Apennines, Italy: A Source to Sink Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
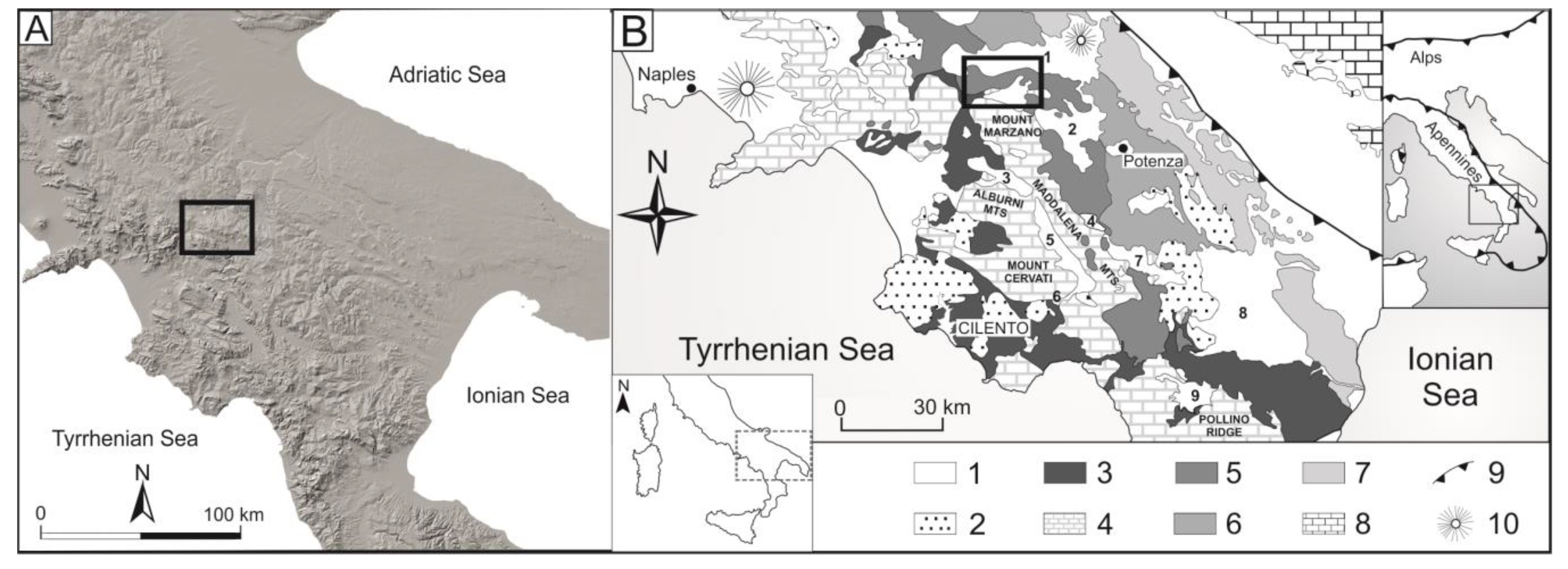
2. Regional and Local Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
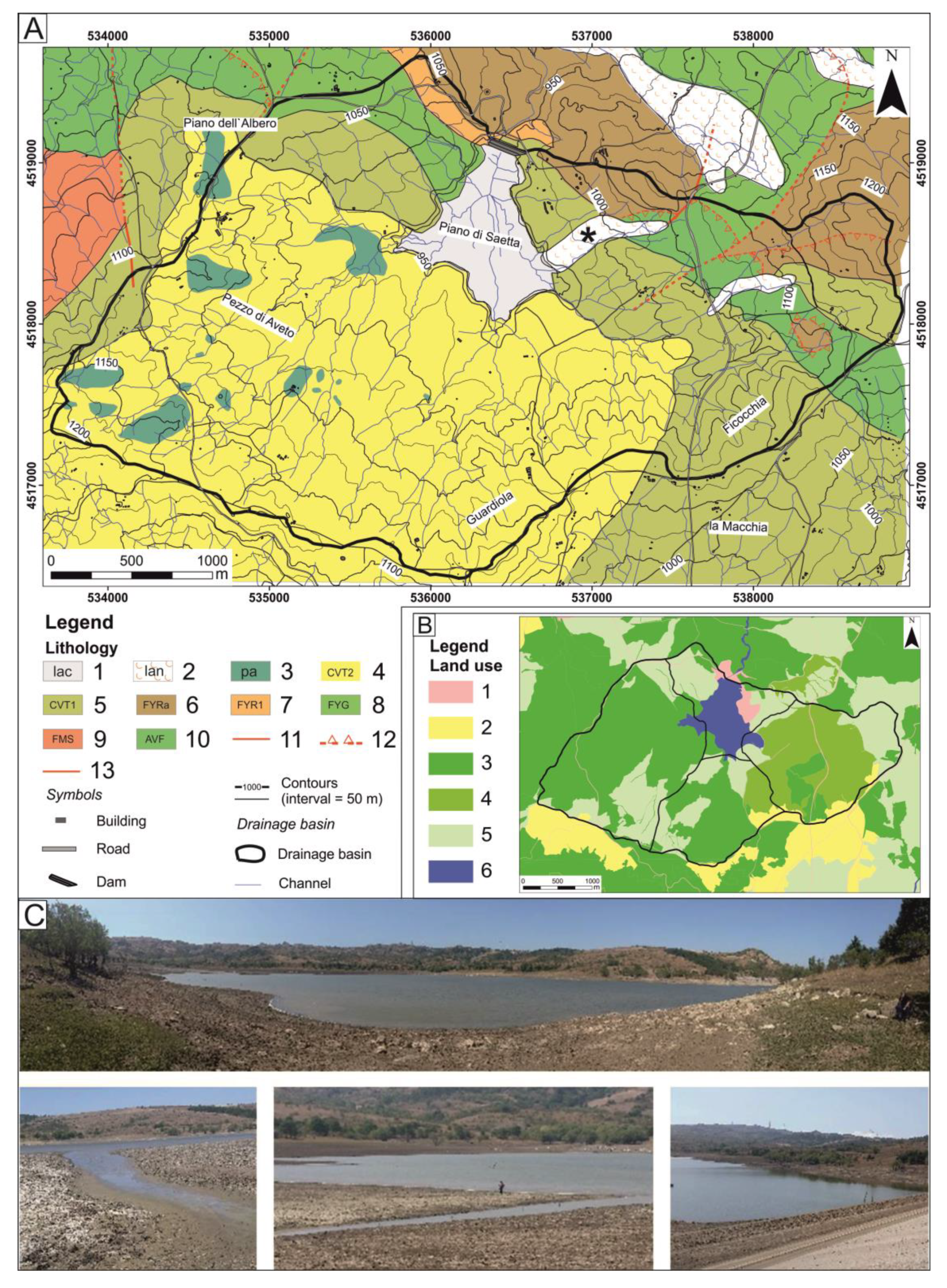
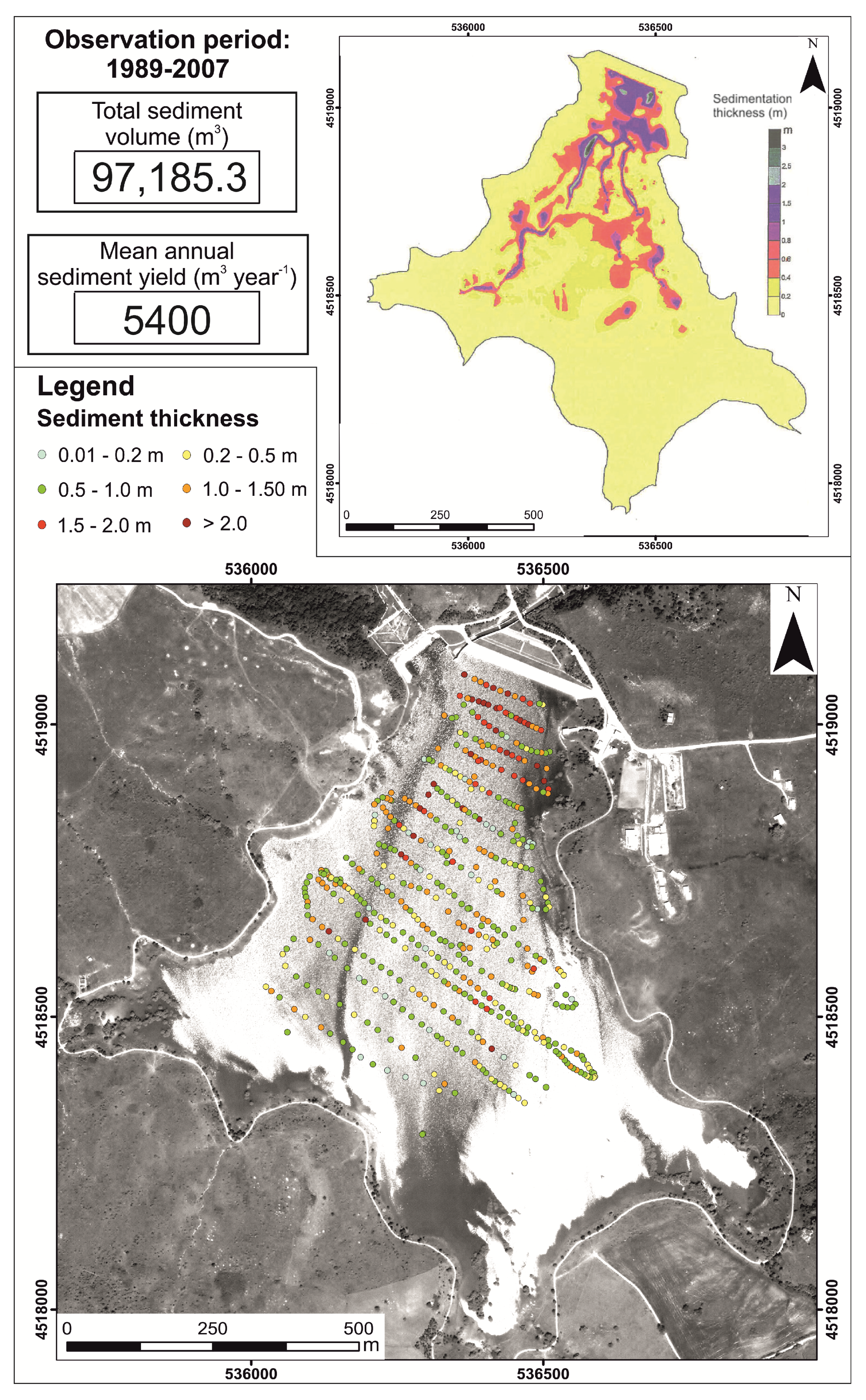
3.1. Sediment Storage in the Artificial Reservoir
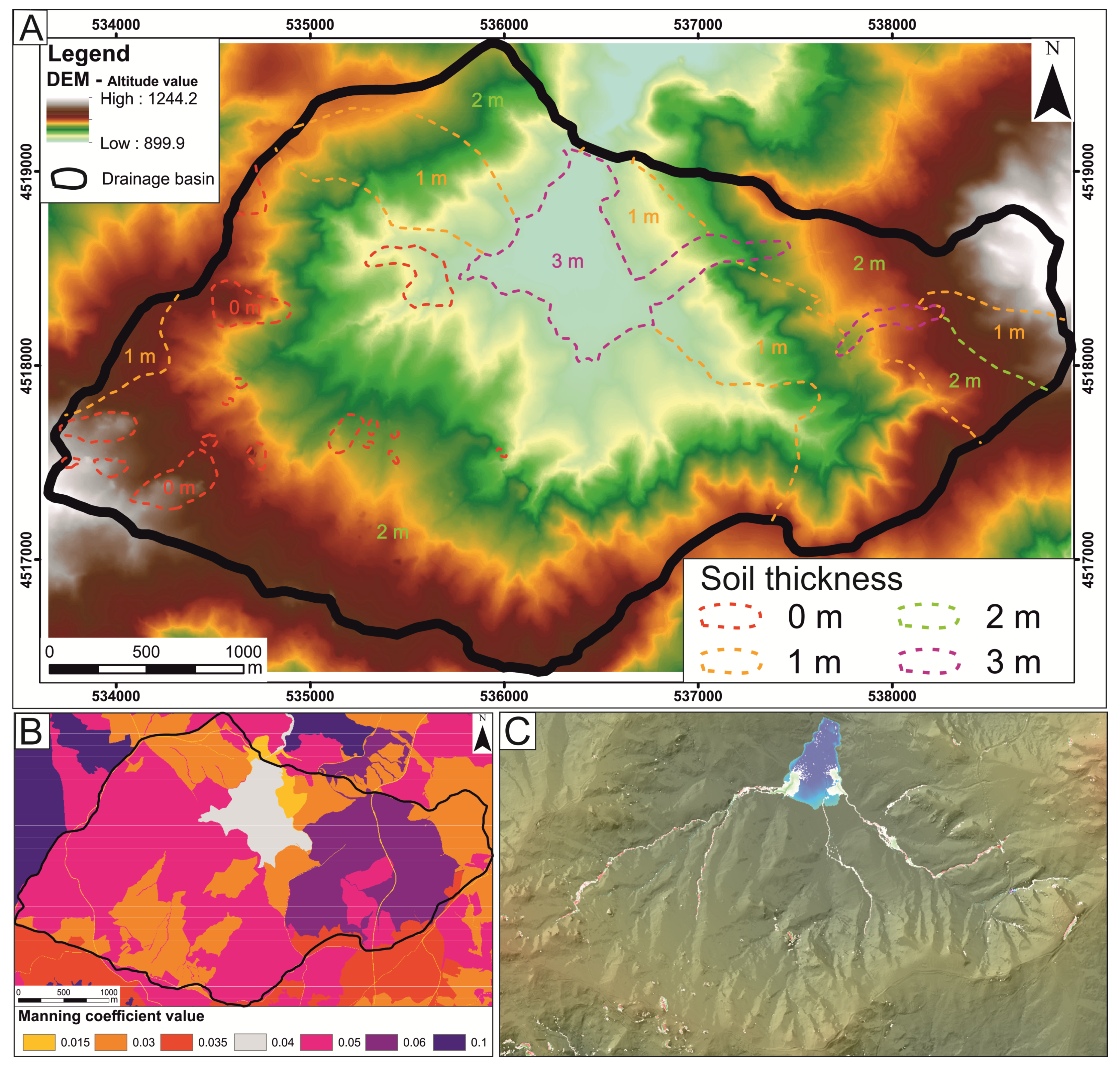
3.2. Caesar-Lisflood Landscape Evolution Model (LEM): Model Description and Parameterization
4. Results
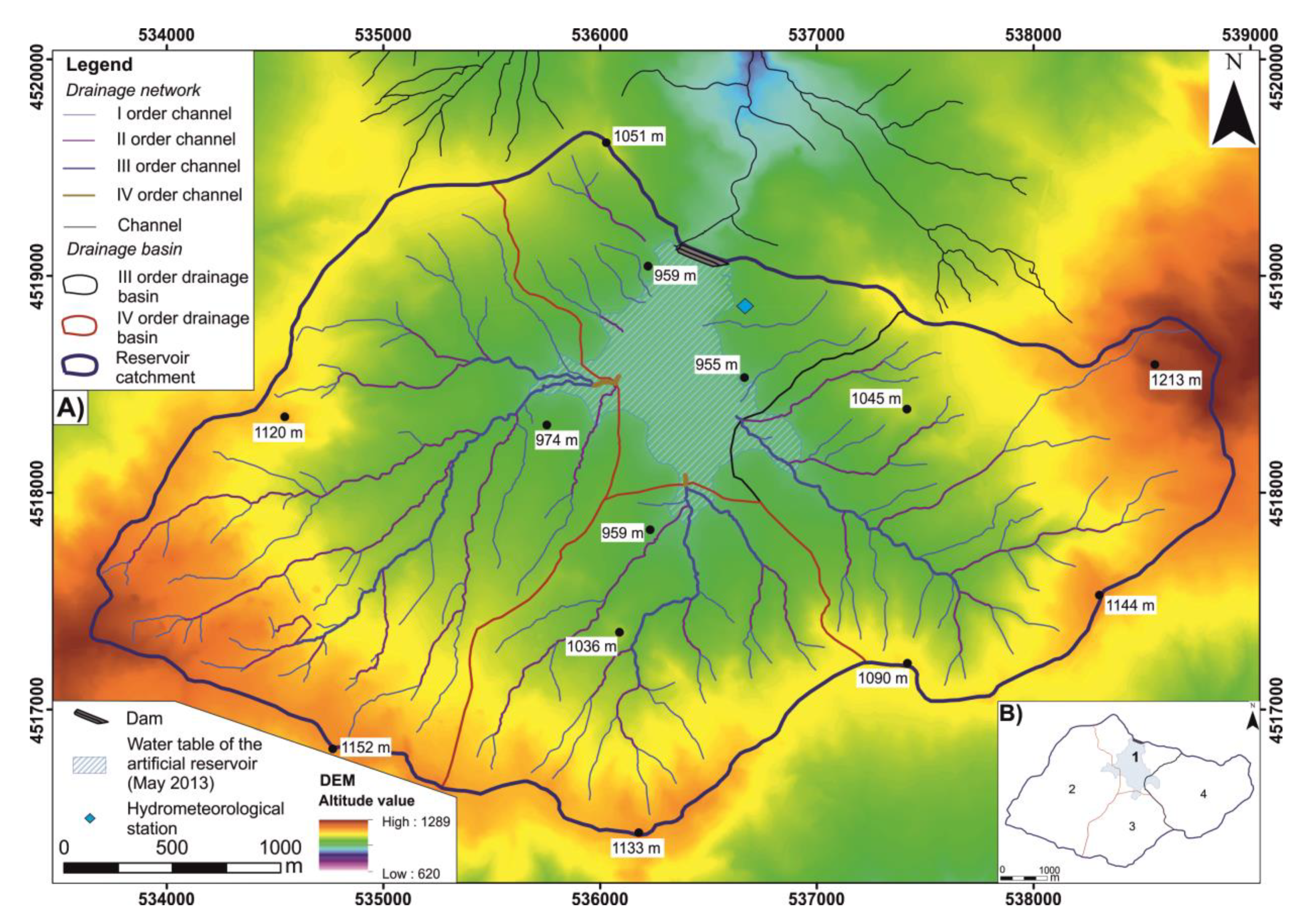
4.1. Geomorphological Features
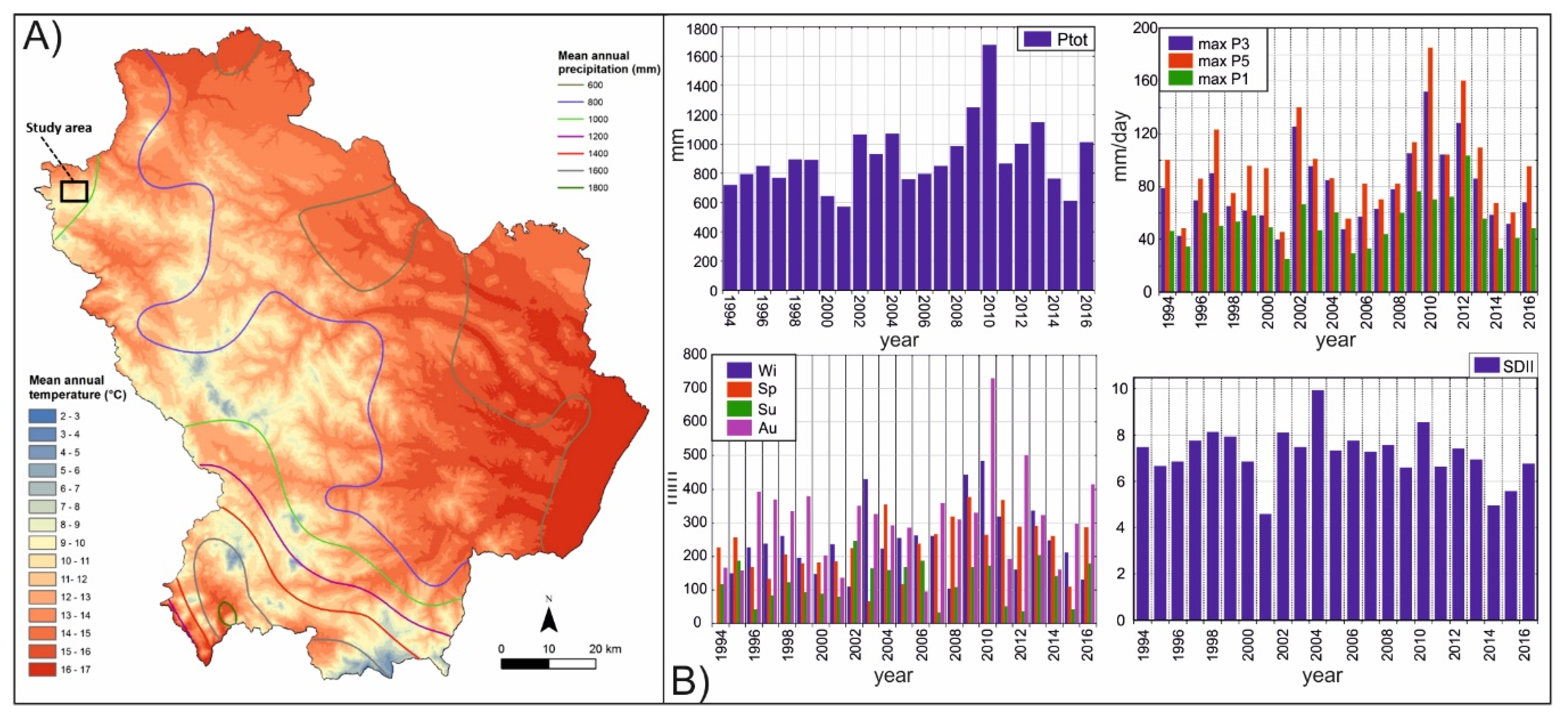
4.2. Regional Climate Setting and Local Rainfall Distribution
4.3. Reservoir Sediment Storage
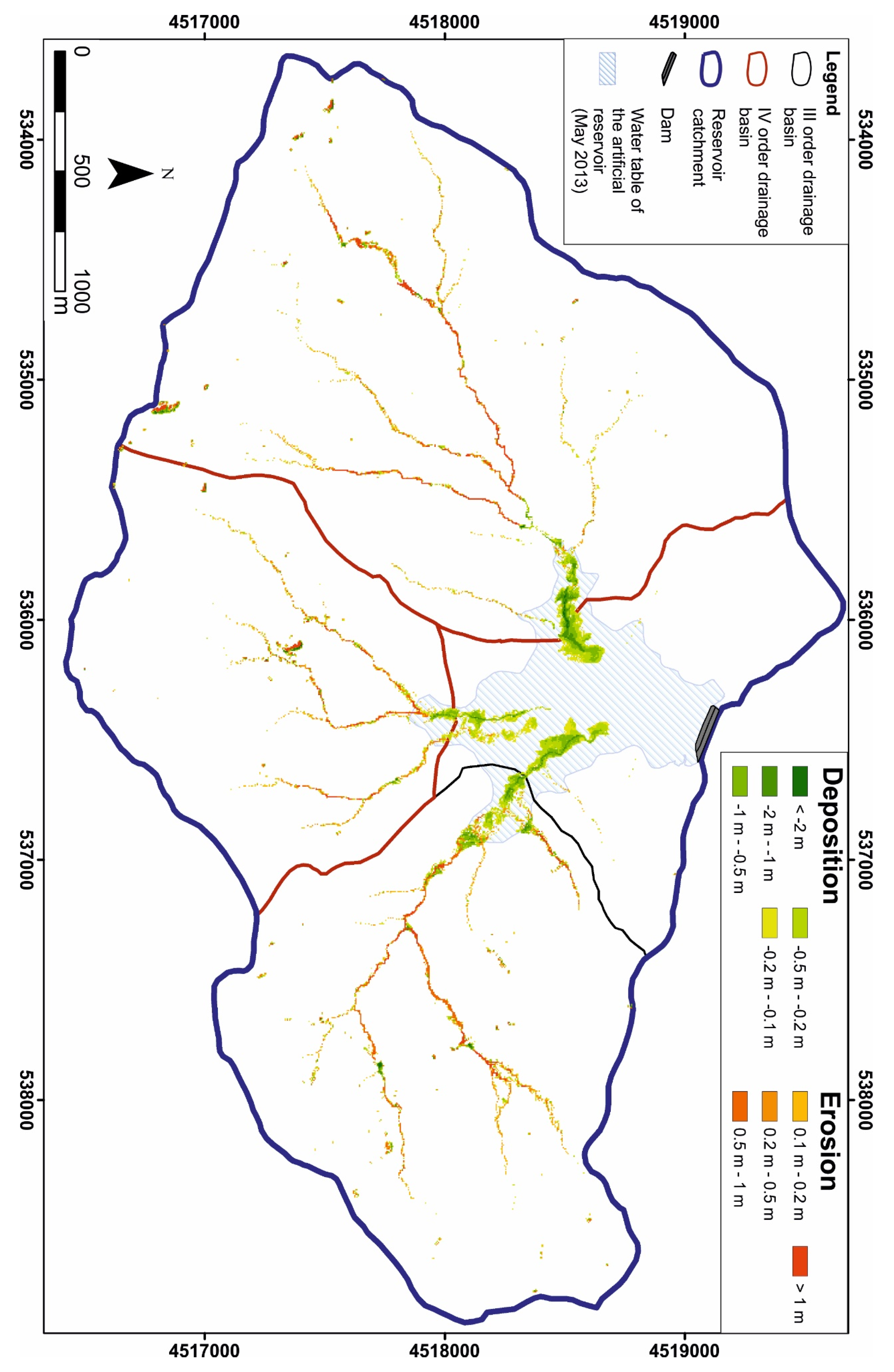
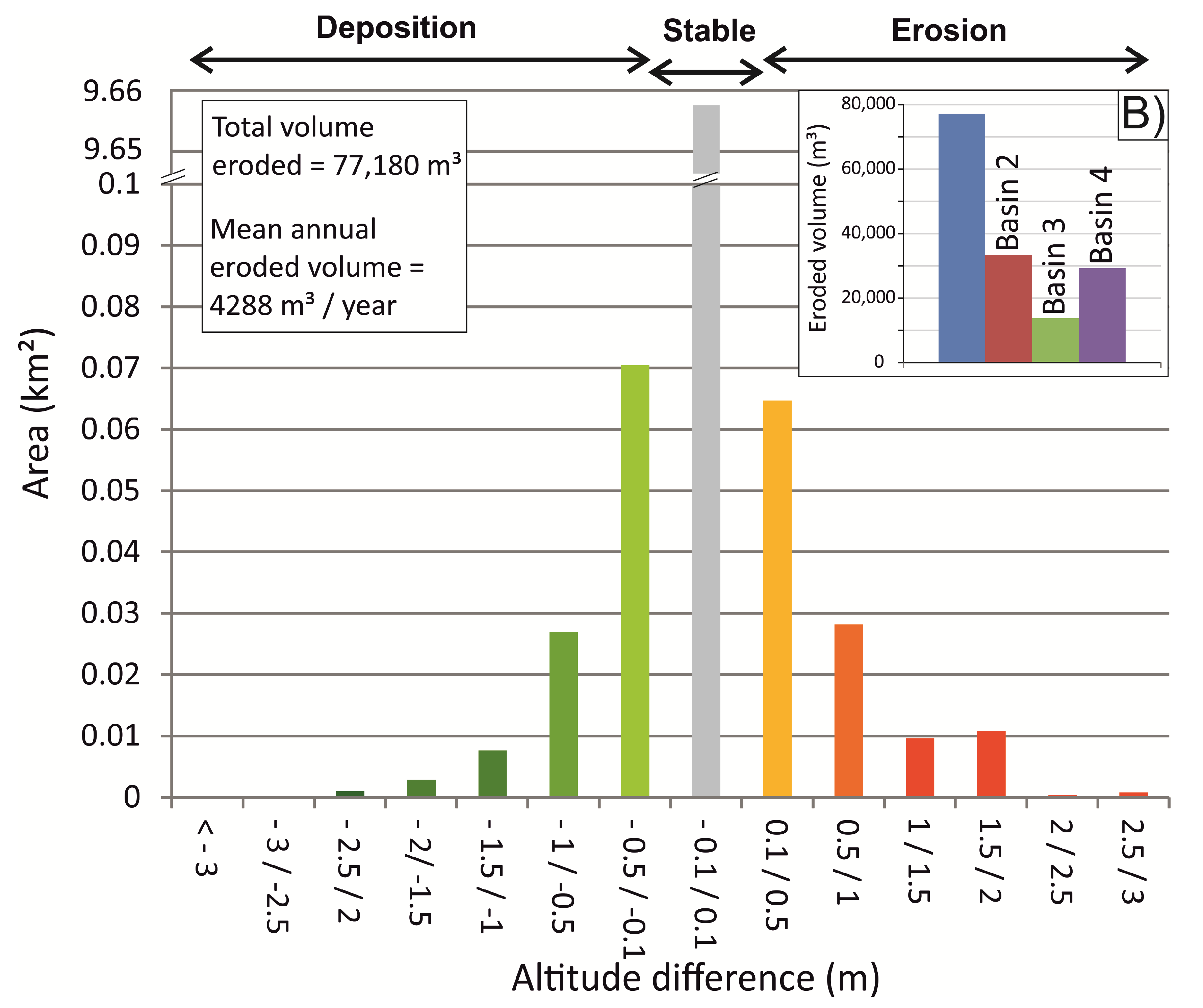
4.4. Caesar–Lisflood LEM
5. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazzari, M.; Gioia, D.; Piccarreta, M.; Danese, M.; Lanorte, A. Sediment yield and erosion rate estimation in the mountain catchments of the Camastra artificial reservoir (Southern Italy): A comparison between different empirical methods. CATENA 2015, 127, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Märker, M.; Panagos, P.; Schütt, B. Modeling soil erosion and river sediment yield for an intermountain drainage basin of the Central Apennines, Italy. CATENA 2014, 114, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oleire-Oltmanns, S.; Marzolff, I.; Peter, K.D.; Ries, J.B. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for monitoring soil erosion in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3390–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vente, J.; Poesen, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Van Rompaey, A.; Govers, G. Spatially distributed modelling of soil erosion and sediment yield at regional scales in Spain. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 60, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolongo, D.; Pennetta, L.; Piccarreta, M.; Fallacara, G.; Boenzi, F. Spatial and temporal variations in soil erosion and deposition due to land-levelling in a semi-arid area of Basilicata (Southern Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amore, E.; Modica, C.; Nearing, M.A.; Santoro, V.C. Scale effect in USLE and WEPP application for soil erosion computation from three Sicilian basins. J. Hydrol. 2004, 293, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, W.S.; Letcher, R.A.; Jakeman, A.J. A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 761–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyaş, H.; Kolat, Ç.; Süzen, M.L. A new approach to estimate cover-management factor of RUSLE and validation of RUSLE model in the watershed of Kartalkaya Dam. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Vega, J.A. Evaluation of the rusle and disturbed wepp erosion models for predicting soil loss in the first year after wildfire in NW Spain. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Adamo, M.; Canora, F. Remote sensing and GIS to assess soil erosion with RUSLE3D and USPED at river basin scale in southern Italy. CATENA 2015, 131, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onori, F.; de Bonis, P.; Grauso, S. Soil erosion prediction at the basin scale using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in a catchment of Sicily (southern Italy). Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.G.; Carey, C.; Erkens, G.; Fuchs, M.; Hoffmann, T.; Macaire, J.-J.; Moldenhauer, K.-M.; Walling, D.E. From sedimentary records to sediment budgets: Multiple approaches to catchment sediment flux. Geomorphology 2009, 108, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Schkade, U.; Kirchner, G. Estimating short-term soil erosion rates after single and multiple rainfall events by modelling the vertical distribution of cosmogenic 7Be in soils. Geoderma 2015, 243–244, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.O.; Nearing, M.A.; Stone, J.J.; Holifield Collins, C.D.; Nichols, M.H. Quantifying decadal-scale erosion rates and their short-term variability on ecological sites in a semi-arid environment. CATENA 2016, 137, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabit, L.; Benmansour, M.; Walling, D.E. Comparative advantages and limitations of the fallout radionuclides 137Cs, 210Pbex and 7Be for assessing soil erosion and sedimentation. J. Environ. Radioact. 2008, 99, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.R.; Lowry, J.B.C.; Coulthard, T.J.; Evans, K.G.; Moliere, D.R. A catchment scale evaluation of the SIBERIA and CAESAR landscape evolution models. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, P.; Walling, D.E. Using 137Cs and Pbex measurements to document erosion rates for different time windows in a small catchment in southern Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Porto, P.; Walling, D.E. Use of caesium-137 measurements and long-term records of sediment load to calibrate the sediment delivery component of the SEDD model and explore scale effect: Examples from southern Italy. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Changing ideas in hydrology—The case of physically-based models. J. Hydrol. 1989, 105, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Monte, M.; Vergari, F.; Brandolini, P.; Capolongo, D.; Cevasco, A.; Ciccacci, S.; Conoscenti, C.; Fredi, P.; Melelli, L.; Rotigliano, E.; et al. Multi-method evaluation of denudation rates in small mediterranean catchments. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory—Volume 1: Climate Change and Engineering Geology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 563–567. [Google Scholar]
- Ciccacci, S.; Fredi, F.; Palmieri, E.L.; Pugliese, F. Contributo dell’analisi geomorfica quantitativa alla valutazione dell’entita dell’erosione nei bacini fluviali. Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1980, 99, 455–516. [Google Scholar]
- Gioia, D.; Martino, C.; Schiattarella, M. Long- to short-term denudation rates in the southern Apennines: Geomorphological markers and chronological constraints. Geol. Carpathica 2011, 62, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauso, S.; Pasanisi, F.; Tebano, C.; Grillini, M.; Peloso, A. Investigating the Sediment Yield Predictability in Some Italian Rivers by Means of Hydro-Geomorphometric Variables. Geosciences 2018, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vente, J.; Poesen, J.; Bazzoffi, P.; Van Rompaey, A.; Verstraeten, G. Predicting catchment sediment yield in Mediterranean environments: The importance of sediment sources and connectivity in Italian drainage basins. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 1017–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, T.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Climatic and morphologic relationships of rivers: Implications of sea-level fluctuations on river loads. J. Geol. 1996, 104, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change: Importance and research needs. CATENA 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, L.; Bittelli, M.; Wu, J.Q.; Dun, S.; Flanagan, D.C.; Pisa, P.R.; Ventura, F.; Salvatorelli, F. Using the Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) model to simulate field-observed runoff and erosion in the Apennines mountain range, Italy. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terranova, O.; Antronico, L.; Coscarelli, R.; Iaquinta, P. Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: An application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 2009, 112, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingaro, M.; Refice, A.; Giachetta, E.; D‘Addabbo, A.; Lovergine, F.; De Pasquale, V.; Pepe, G.; Brandolini, P.; Cevasco, A.; Capolongo, D. Sediment mobility and connectivity in a catchment: A new mapping approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappadonia, C.; Coco, L.; Buccolini, M.; Rotigliano, E. From Slope Morphometry to Morphogenetic Processes: An Integrated Approach of Field Survey, Geographic Information System Morphometric Analysis and Statistics in Italian Badlands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, P.; Pepe, G.; Capolongo, D.; Cappadonia, C.; Cevasco, A.; Conoscenti, C.; Marsico, A.; Vergari, F.; Del Monte, M. Hillslope degradation in representative Italian areas: Just soil erosion risk or opportunity for development? Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3050–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucelli, P.P.C.; Conforti, M.; Della Seta, M.; Del Monte, M.; D’Uva, L.; Rosskopf, C.M.; Vergari, F. Multi-temporal Digital Photogrammetric Analysis for Quantitative Assessment of Soil Erosion Rates in the Landola Catchment of the Upper Orcia Valley (Tuscany, Italy). Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1075–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, T.; Galli, A.; Marsala, V.; Miccadei, E. Analysis of soil erosion induced by heavy rainfall: A case study from the NE Abruzzo Hills Area in Central Italy. Water (Switzerland) 2018, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, T.J.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D.; Ramirez, J.; de Almeida, G.A.M.; Hancock, G.R. Integrating the LISFLOOD-FP 2D hydrodynamic model with the CAESAR model: Implications for modelling landscape evolution. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, T.J.; Hancock, G.R.; Lowry, J.B.C. Modelling soil erosion with a downscaled landscape evolution model. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, T.J.; van de Wiel, M.J. Modelling long term basin scale sediment connectivity, driven by spatial land use changes. Geomorphology 2017, 277, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.R.; Coulthard, T.J.; Martinez, C.; Kalma, J.D. An evaluation of landscape evolution models to simulate decadal and centennial scale soil erosion in grassland catchments. J. Hydrol. 2011, 398, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, C.J.; Coulthard, T.J.; Schwanghart, W.; Van De Wiel, M.J.; Hancock, G. Global sensitivity analysis of parameter uncertainty in landscape evolution models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 4873–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescatore, T.; Renda, P.; Schiattarella, M.; Tramutoli, M. Stratigraphic and structural relationships between Meso-Cenozoic Lagonegro basin and coeval carbonate platforms in southern Apennines, Italy. Tectonophysics 1999, 315, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, A.M.; Rea, G. Deep structure of the Campanian-Lucanian Arc (Southern Apennine, Italy). Tectonophysics 2000, 324, 239–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patacca, E.; Scandone, P. Geology of the Southern Apennines. Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. Suppl. 2007, 7, 75–119. [Google Scholar]
- Malinverno, A.; Ryan, W.B.F. Extension in the Tyrrhenian Sea and shortening in the Apennines as result of arc migration driven by sinking of the lithosphere. Tectonics 1986, 5, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinque, A.; Patacca, E.; Scandone, P.; Tozzi, M. Quaternary kinematic evolution of the southern Apennines. Relationships between surface geological features and deep lithospheric structures. Ann. Geophys. 1993, 36, 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Schiattarella, M.; Giano, S.I.; Gioia, D. Long-term geomorphological evolution of the axial zone of the Campania-Lucania Apennine, southern Italy: A review. Geol. Carpathica 2017, 68, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giano, S.I.; Gioia, D.; Schiattarella, M. Morphotectonic evolution of connected intermontane basins from the southern Apennines, Italy: The legacy of the pre-existing structurally controlled landscape. Rend. Lincei 2014, 25, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, D.; Schiattarella, M.; Mattei, M.; Nico, G. Quantitative morphotectonics of the Pliocene to Quaternary Auletta basin, southern Italy. Geomorphology 2011, 134, 326–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiattarella, M.; Romeo, M.; Marino, M.; Giannandrea, P. Pliocene to Quaternary evolution of the Ofanto Basin in southern Italy: An approach based on the unconformity-bounded stratigraphic units. Ital. J. Geosci. 2014, 133, 27–44. [Google Scholar]
- Casciello, E.; Esestime, P.; Cesarano, M.; Pappone, G.; Snidero, M.; Verges, J. Lower plate geometry controlling the development of a thrust-top basin: The tectonosedimentary evolution of the Ofanto basin (Southern Apennines). J. Geol. Soc. 2013, 170, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labella, R.; Capolongo, D.; Giannandrea, P.; Giano, S.I.; Schiattarella, M. Morphometric analysis of fluvial network and age constraints of terraced surfaces of the Ofanto basin, Southern Italy. Rend. Lincei 2014, 25, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzoffi, P. Progetto REL: Attività tecnico-scientifiche “Assistenza tecnica e supporto agli enti concessionari nel settore dell’uso irriguo delle risorse idriche”, Rilievi batimetrici e sedimentologici dell’invaso Saetta; Centro per l’Agrobiologia e la Pedologia, CREA: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Coulthard, T.J.; van de Wiel, M.J. Climate, tectonics or morphology: What signals can we see in drainage basin sediment yields? Earth Surf. Dyn. 2013, 1, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, H.A. The Bed-Load Function for Sediment Transportation in Open Channel Flows. Soil Conserv. Serv. 1950, 1026, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, R.W.; Joanna, C.C. Surface-based Transport Model for Mixed-Size Sediment. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2003, 129, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Jia, Y.; Sam, S.Y.W. Identification of Manning’s Roughness Coefficients in Shallow Water Flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.V.; Tadayon, S. Selection of Manning’s Roughness Coefficient for Natural and Constructed Vegetated and Non-Vegetated Channels, and Vegetation Maintenance Plan Guidelines for Vegetated Channels in Central Arizona; Report 2006-5108; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2006.
- Büttner, G. CORINE Land Cover and Land Cover Change Products. In Land Use and Land Cover Mapping in Europe: Practices & Trends; Manakos, I., Braun, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Piccarreta, M.; Lazzari, M.; Pasini, A. Trends in daily temperature extremes over the Basilicata region (southern Italy) from 1951 to 2010 in a Mediterranean climatic context. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1964–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccarreta, M.; Pasini, A.; Capolongo, D.; Lazzari, M. Changes in daily precipitation extremes in the Mediterranean from 1951 to 2010: The Basilicata region, southern Italy. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 3229–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, M.; Gioia, D. Regional-scale landslide inventory, central-western sector of the Basilicata region (Southern Apennines, Italy). J. Maps 2016, 12, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, M.; Gioia, D.; Anzidei, B. Landslide inventory of the Basilicata region (Southern Italy). J. Maps 2018, 14, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.L.; Rendell, H.M. Hindcasting extreme events: The occurrence and expression of damaging floods and landslides in Southern Italy. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Calculation of Monthly and Annual 30-Year Standard Normals; WCDP No. 10, WMO-TD/No. 341; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hoober, D.; Svoray, T.; Cohen, S. Using a landform evolution model to study ephemeral gullying in agricultural fields: The effects of rainfall patterns on ephemeral gully dynamics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | Caesar–Lisflood Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grainsizes (m) | 0.0005, 0.001, 0.002, 0.004, 0.008, 0.016, 0.032, 0.064, 0.128 |
| 2 | Grainsize proportions (total 1) | 0.20, 0.18, 0.12, 0.06, 0.03, 0.03, 0.1, 0.25 |
| 3 | Rainfall timestep | hourly |
| 4 | Sediment transport law | Einstein |
| 5 | Max erode limit (m) | 0.01 |
| 6 | Active layer thickness (m) | 0.1 |
| 7 | Lateral edge smoothing passes | 40 |
| 8 | Manning coefficient | 0.015–0.1—Land-use map |
| 9 | Soil creep/diffusion value | 0.0025 |
| 10 | Slope failure threshold | 40 |
| 11 | Vegetation critical stress | 100 |
| Number | Land-Use Cover | Manning Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anthropic surfaces and roads | 0.015 |
| 2 | Arable lands | 0.035 |
| 3 | Sclerophyllous vegetation | 0.05 |
| 4 | Broad-leaved and mixed forests | 0.1 |
| 5 | Natural grasslands | 0.03 |
| 6 | Water courses and water bodies | 0.04 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gioia, D.; Lazzari, M. Testing the Prediction Ability of LEM-Derived Sedimentary Budget in an Upland Catchment of the Southern Apennines, Italy: A Source to Sink Approach. Water 2019, 11, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050911
Gioia D, Lazzari M. Testing the Prediction Ability of LEM-Derived Sedimentary Budget in an Upland Catchment of the Southern Apennines, Italy: A Source to Sink Approach. Water. 2019; 11(5):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050911
Chicago/Turabian StyleGioia, Dario, and Maurizio Lazzari. 2019. "Testing the Prediction Ability of LEM-Derived Sedimentary Budget in an Upland Catchment of the Southern Apennines, Italy: A Source to Sink Approach" Water 11, no. 5: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050911
APA StyleGioia, D., & Lazzari, M. (2019). Testing the Prediction Ability of LEM-Derived Sedimentary Budget in an Upland Catchment of the Southern Apennines, Italy: A Source to Sink Approach. Water, 11(5), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050911






