The Characterization of Microbial Communities Response to Shallow Groundwater Contamination in Typical Piedmont Region of Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
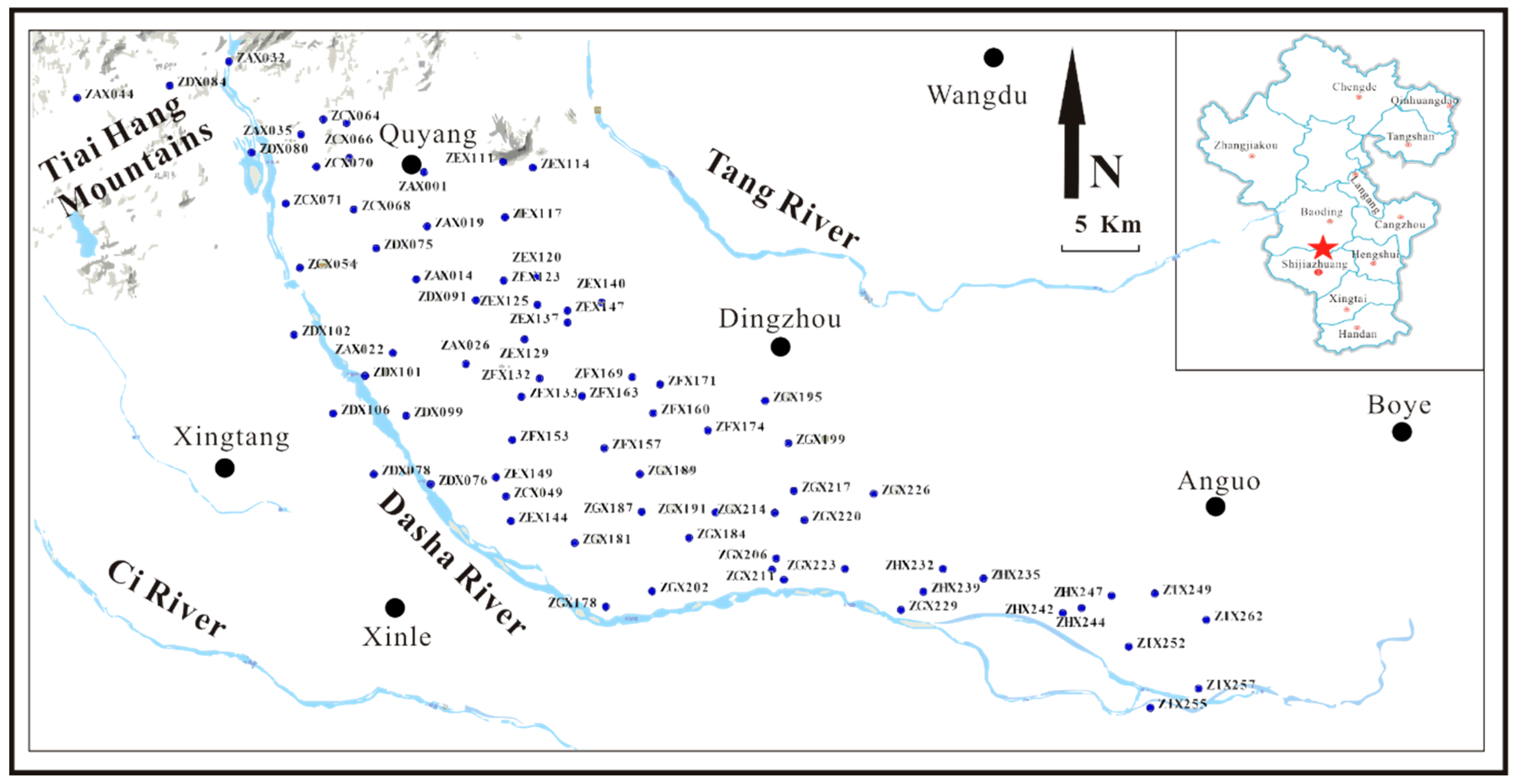
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Procedure
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing and Chemical Analyses
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
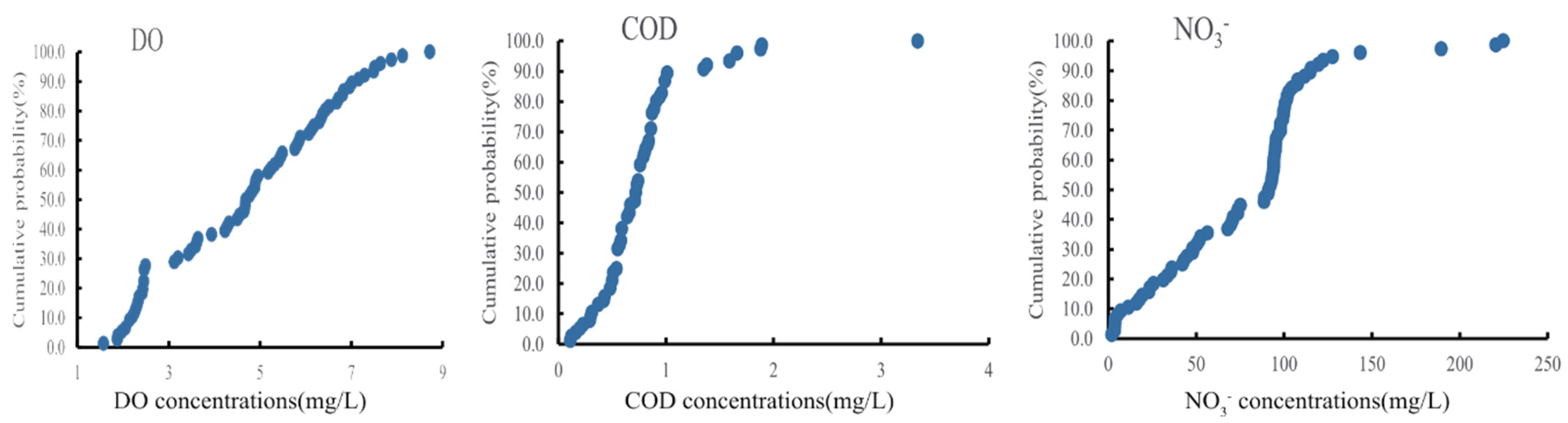
3.1. Grouping Scheme of Different Contamination
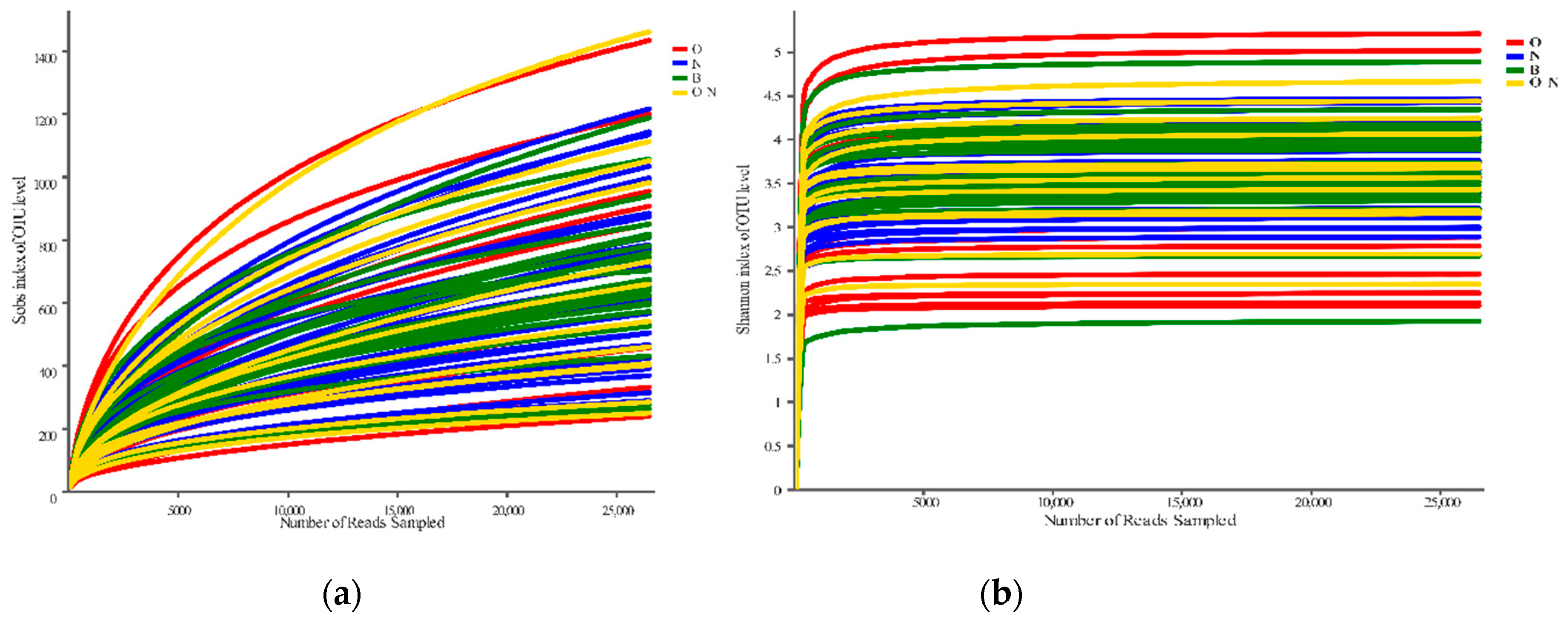
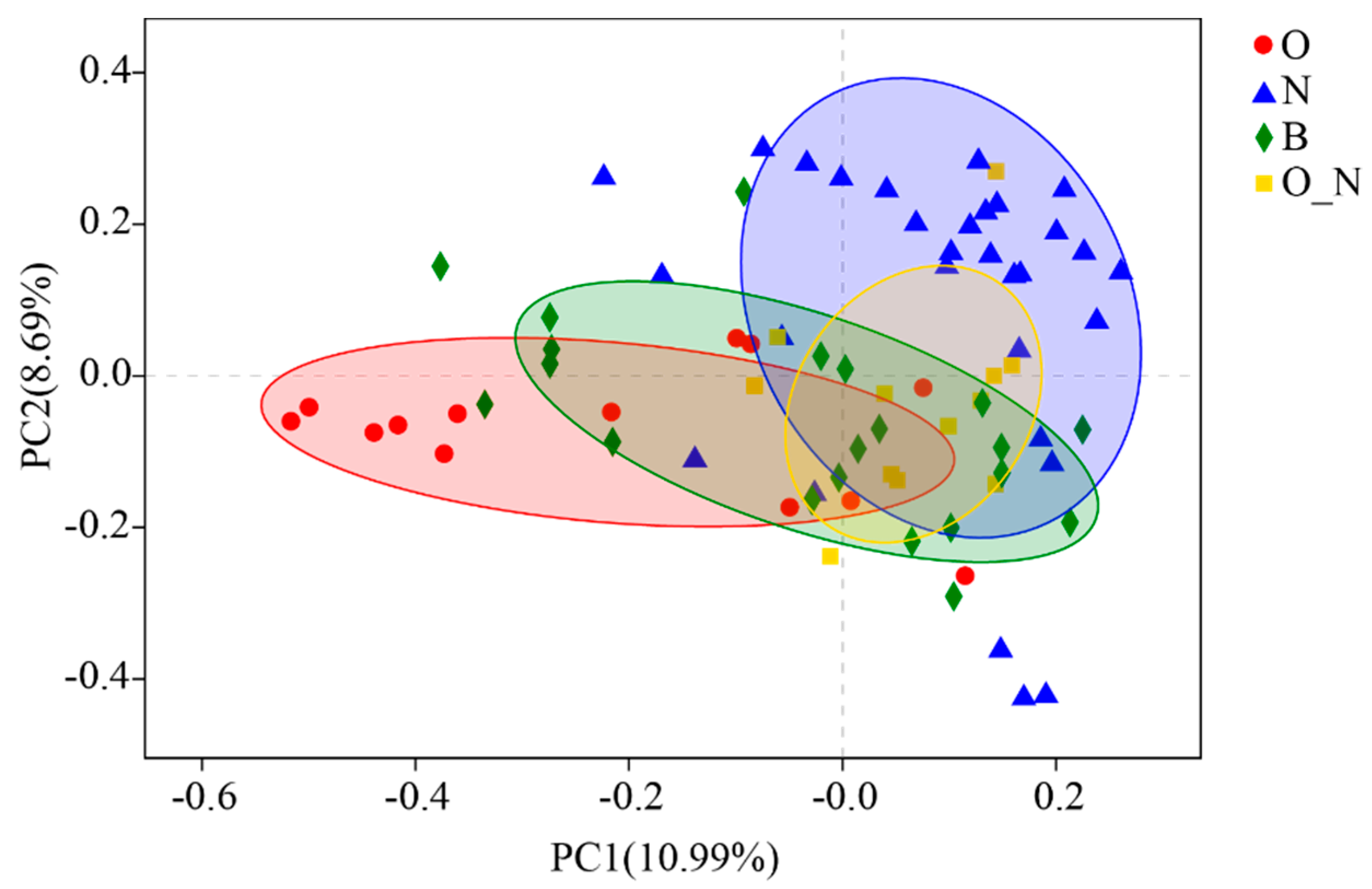
3.2. Reliability Test of Sequencing Results and Grouping Scheme
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Microbial Diversity and Community Structure
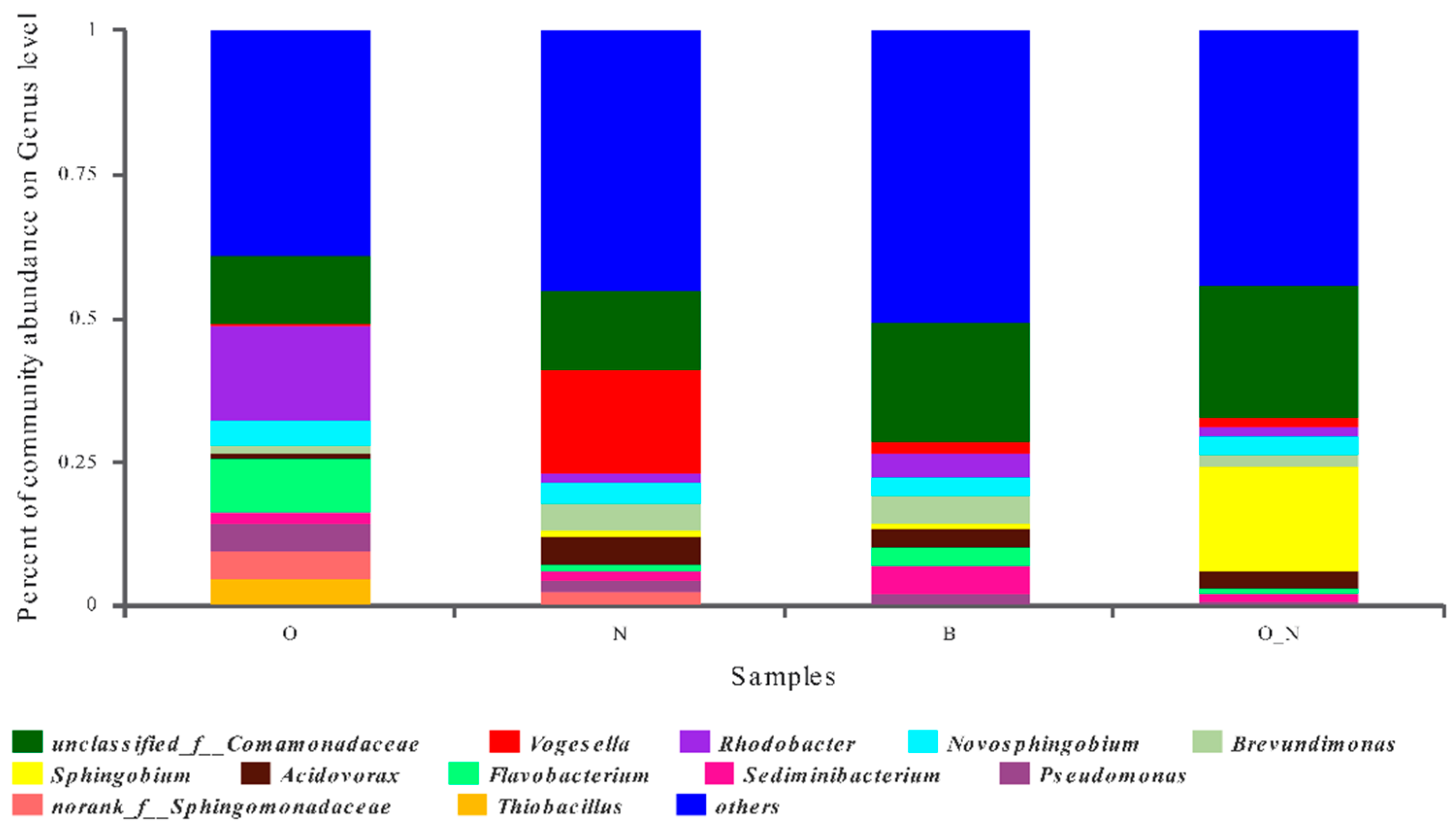
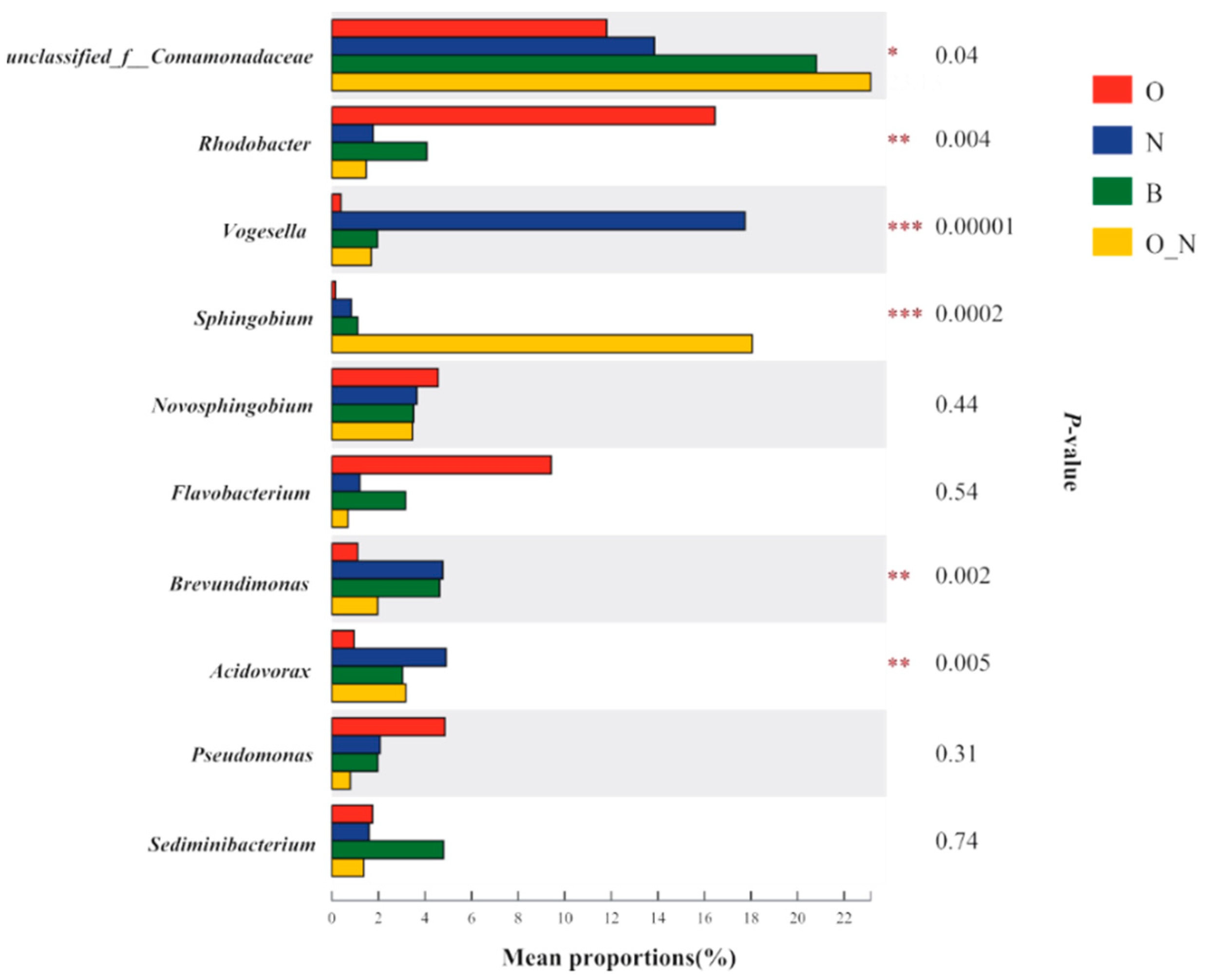
4.2. Microbial Indicators Related to Contamination
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steube, C.; Richter, S.; Griebler, C. First attempts towards an integrative concept for the ecological assessment of groundwater ecosystems. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struckmeier, W.; Rubin, Y.; Jones, J. Groundwater-Reservoir for a Thirsty Planet? Earth Sciences for Society; a Prospectus for a Key Theme of the International Year of Planet Earth; IUGS International Union of Geological Sciences Secretariat, Geological Survey of Norway: Trondheim, Norway, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Chen, D.; White, R.E. Spatial variability of shallow groundwater level, electrical conductivity and nitrate concentration, and risk assessment of nitrate contamination in North China Plain. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Kendy, E. Groundwater Exploitation and Its Impact on the Environment in the North China Plain. Water Int. 2001, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Hao, Q.; Liu, H.; Hao, Z.; Meng, G.; Pei, Q.; Yan, H. Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater in a long-term reclaimed water irrigation area, North China Plain. Water 2018, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Yasong, L.I.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J. Preliminary analysis on the organic contamination of groundwater in the North China Plain. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 20, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W. Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the alluvial fans of the Taihang Mts and Yanshan Mts. IAHS Publ. 2008, 43, 579–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmer, B.G.; Ernst, B.; Simon, J.; Kuefer, R.; Bartsch, G.; Bach, D.; Gschwend, J.E. Influence of nitrate levels in drinking water on urological malignancies: A community-based cohort study. Br. J. Urol. Int. 2015, 95, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, M.; Vachelard, C.; Duchez, D.; Larroche, C. In situ bioremediation of monoaromatic pollutants in groundwater: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5296–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.T.; Lovley, D.R. Ecology and Biogeochemistry of in Situ Groundwater Bioremediation; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 289–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaei, K.; Nassery, H.R.; Asadi, M.M.; Mohammadzadeh, H.; Mahmoodlu, M.G. BTEX biodegradation in contaminated groundwater using a novel strain (Pseudomonas sp. BTEX-30). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 116, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J.A.; Rahme, H.; Hopkins, G.D.; Lebron, C.; Reinhard, M. Enhanced in situ bioremediation of BTEX-contaminated groundwater by combined injection of nitrate and sulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Specification for Regional Groundwater Contamination Survey and Evaluation. In DZT0288-2015; Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Heide, S.; Claudia, K.; Schmidt, S.I.; Heike, B.; Christian, S.; Berkhoff, S.E.; Andreas, F.; Hans Jürgen, H.; Barbara, T.; Christian, G. The potential use of fauna and bacteria as ecological indicators for the assessment of groundwater quality. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Zhang, M.; He, Z.; Cai, P.; Guo, C.; Wang, P. Spatial Pattern of Bacterial Community Diversity Formed in Different Groundwater Field Corresponding to Electron Donors and Acceptors Distributions at a Petroleum-Contaminated Site. Water 2018, 10, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Kirchner, V.; Bernard, W.; Ulrich, N.; McLimans, C.; Campa, M.F.; Hazen, T.; Macbeth, T.; Marabello, D.; McDermott, J. Bacterial Community Dynamics in Dichloromethane-Contaminated Groundwater Undergoing Natural Attenuation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, L.; Rocha, A.M.; Tu, Q.; Shi, Z.; Wu, B.; Qin, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, Q. Microbial functional gene diversity predicts groundwater contamination and ecosystem functioning. mBio 2018, 9, e02435-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Tom, F.; Delong, E.F. The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haack, S.K.; Fogarty, L.R.; West, T.G.; Alm, E.W.; Mcguire, J.T.; Long, D.T.; Hyndman, D.W.; Forney, L.J. Spatial and temporal changes in microbial community structure associated with recharge-influenced chemical gradients in a contaminated aquifer. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.-M.; Liao, H.-Y.; Chien, C.-C.; Tseng, Y.-K.; Tang, P.; Lin, C.-E.; Chen, S.-C. The change of microbial community from chlorinated solvent-contaminated groundwater after biostimulation using the metagenome analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinshuang, M.; Shengyong, L.; Mingliang, L.; Yinguo, R. Research of Groundwater Prediction Model in Shallow Groundwater Over-Exploitation Zone in the Northern Area. South-to-North Water Divers. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 9, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.E.; Chen, J. Transport and sorption of organic contaminants during infiltration from Cihe River to groundwater. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Water Resource & Environmental Protection, Xi’an, China, 20–22 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; Mcdonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G. A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeltier, C. A simplified statistical treatment of geochemical data by graphical representation. Econ. Geol. 1969, 64, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matschullat, J.; Ottenstein, R.; Reimann, C. Geochemical background–can we calculate it? Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for groundwater quality. In GB/T 14848-2017; National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Teh, B.S.; Sun, C.; Hu, S.; Lu, X.; Boland, W.; Shao, Y. Biodiversity and Activity of the Gut Microbiota across the Life History of the Insect Herbivore Spodoptera littoralis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Joseph, S.D.; Ji, M.; Nielsen, S.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Donne, S.; Horvat, J.; Wang, J.; Munroe, P.; Thomas, T. Chemolithotrophic processes in the bacterial communities on the surface of mineral-enriched biochars. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Xue, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F.; Chen, D. Effects of Water Diversion from Yangtze River to Lake Taihu on the Phytoplankton Habitat of the Wangyu River Channel. Water 2018, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, A.F.L.; Brinkhurst, R.O. Using the Bootstrap to Assess Statistical Significance in the Cluster. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Huang, T.; Gong, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Dou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ma, W. In Situ Water Quality Improvement Mechanism (Nitrogen Removal) by Water-Lifting Aerators in a Drinking Water Reservoir. Water 2018, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Jiang, Z.; Sinkkonen, A.; Wang, S.; Tu, J.; Wei, D.; Dong, H.; Wang, Y. Microbial Community of High Arsenic Groundwater in Agricultural Irrigation Area of Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Jin, C. The Performance and Microbial Community Identification in Mesophilic and Atmospheric Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Associated with Different Hydraulic Retention Times. Water 2019, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walega, A.; Młyński, D.; Bogdał, A.; Kowalik, T. Analysis of the course and frequency of high water stages in selected catchments of the upper Vistula basin in the south of Poland. Water 2016, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zi, X.; Wang, Q. Bacterial community diversity of oil-contaminated soils assessed by high throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA genes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12002–12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanghai Majorbio. I-sanger Cloud Platform Home Page. Available online: http://www.i-sanger.com (accessed on 6 February 2018).
- Jiao, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Bai, Z.; Huang, Z. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil by Rhodobacter sphaeroides biofertilizer and plants. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 28, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Ying, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Simulation Study of Atrazine-contaminated Soil Biodegradation by Strain W16. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 11, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grimes, D.J.; Woese, C.R.; Macdonell, M.T.; Colwell, R.R. Systematic study of the genus Vogesella gen. nov. and its type species, Vogesella indigofera comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.J.; Chou, J.H.; Lin, M.C.; Arun, A.B.; Young, C.C.; Chen, W.M. Vogesella perlucida sp. nov., a non-pigmented bacterium isolated from spring water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Michael, C.; Kertesz, M.A. Effect of Sphingobium yanoikuyae B1 inoculation on bacterial community dynamics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in aged and freshly PAH-contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanfeng, L.; Gareth, L.J. Sphingobium scionense sp. nov., an aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from contaminated sawmill soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rup, L.; Mandeep, D.; Kirti, K.; Pooja, S.; Ajaib, S.; Hansi, K.; Simran, J.; Sanjay Kumar, G.; Aeshna, N.; Devi, L. Pseudomonas sp. to Sphingobium indicum: A journey of microbial degradation and bioremediation of Hexachlorocyclohexane. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Influence of microbial community structure of seed sludge on the properties of aerobic nitrifying granules. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavić, A.; Stanković, S.; Marjanović, Ž. Biochemical characterization of a sphingomonad isolate from the ascocarp of white truffle (Tuber magnatum Pico). Arch. Biol. Sci. 2011, 63, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| COD > 1.0 | COD < 1.0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO > 3.0 | DO < 3.0 | DO > 3.0 | DO < 3.0 | |
| NO3− < 88.57 | B | O | O | O |
| NO3− > 88.57 | N | O_N | O_N | O_N |
| Groups | Coverage | Chao | ACE | Sobs | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 0.990 ± 0.004 | 1054 ± 352 | 1261 ± 472 | 682 ± 224 | 3.70 ± 0.63 | 0.087 ± 0.10 |
| O | 0.990 ± 0.004 | 1044 ± 488 | 1197 ± 476 | 662 ± 369 | 3.16 ± 1.05 | 0.16 ± 0.093 |
| N | 0.989 ± 0.004 | 1113 ± 386 | 1359 ± 483 | 687 ± 253 | 3.67 ± 0.52 | 0.084 ± 0.046 |
| O_N | 0.989 ± 0.005 | 1077 ± 534 | 1294 ± 588 | 687 ± 380 | 3.60 ± 0.69 | 0.085 ± 0.050 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Ning, Z.; Yang, M.; Huang, G.; Cui, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, J. The Characterization of Microbial Communities Response to Shallow Groundwater Contamination in Typical Piedmont Region of Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain. Water 2019, 11, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040736
He Z, Ning Z, Yang M, Huang G, Cui H, Wang H, Sun J. The Characterization of Microbial Communities Response to Shallow Groundwater Contamination in Typical Piedmont Region of Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain. Water. 2019; 11(4):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040736
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Ze, Zhuo Ning, Mingnan Yang, Guanxing Huang, Haiwei Cui, Huiwei Wang, and Jichao Sun. 2019. "The Characterization of Microbial Communities Response to Shallow Groundwater Contamination in Typical Piedmont Region of Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain" Water 11, no. 4: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040736
APA StyleHe, Z., Ning, Z., Yang, M., Huang, G., Cui, H., Wang, H., & Sun, J. (2019). The Characterization of Microbial Communities Response to Shallow Groundwater Contamination in Typical Piedmont Region of Taihang Mountains in the North China Plain. Water, 11(4), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040736





