Identification of Factors Affecting Bacterial Abundance and Community Structures in a Full-Scale Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
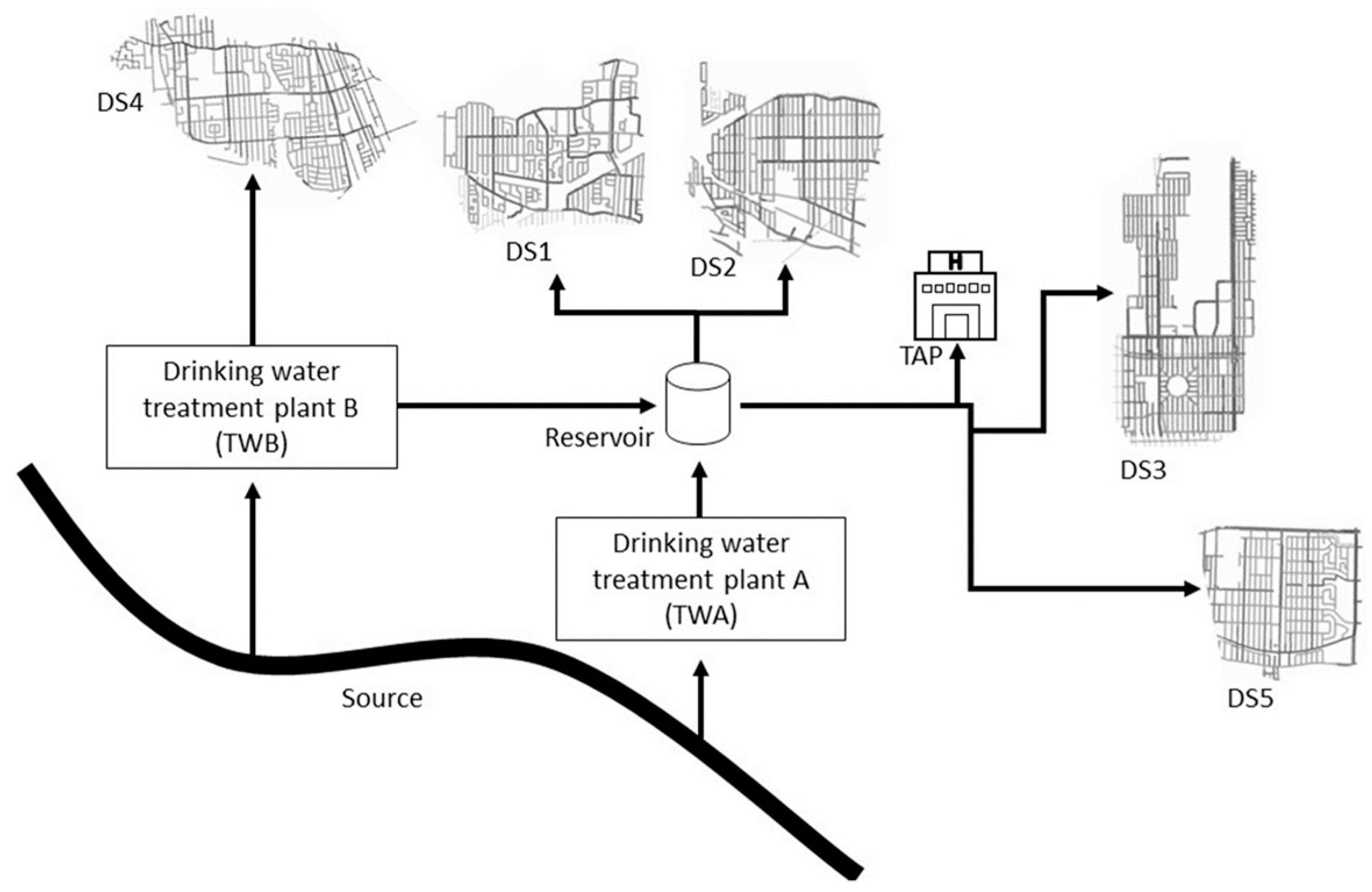
2.1. Water Sampling
2.2. Water Quality Analysis
2.3. Filtration and DNA Extraction
2.4. Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene PCR-Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Raw High-Throughput Sequencing Data Accession Number
3. Results
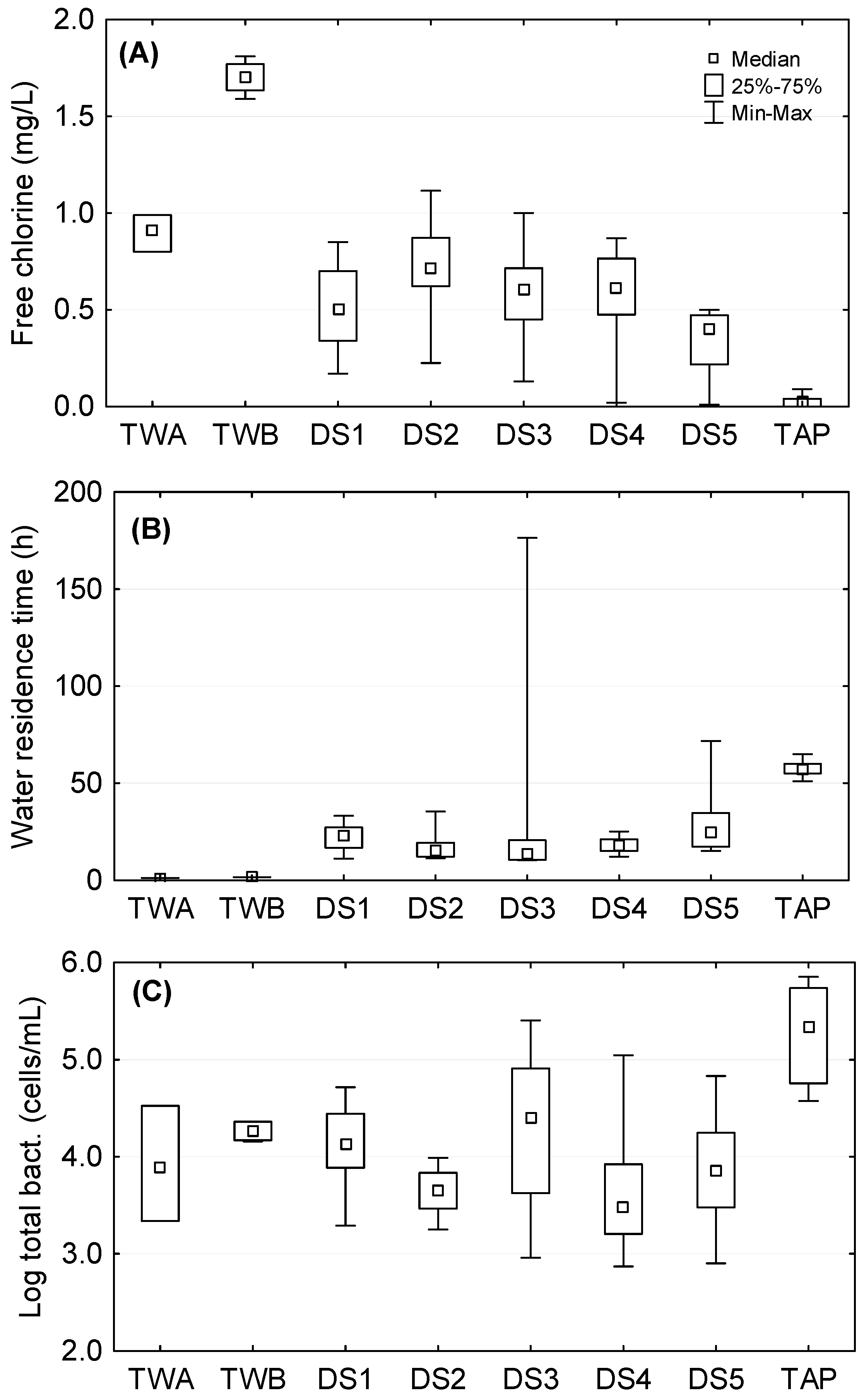
3.1. Amplification of Total Bacterial Counts and Decrease in Disinfectant Residual Concentration through the DWDS
3.2. Bacterial Community Diversity and Composition
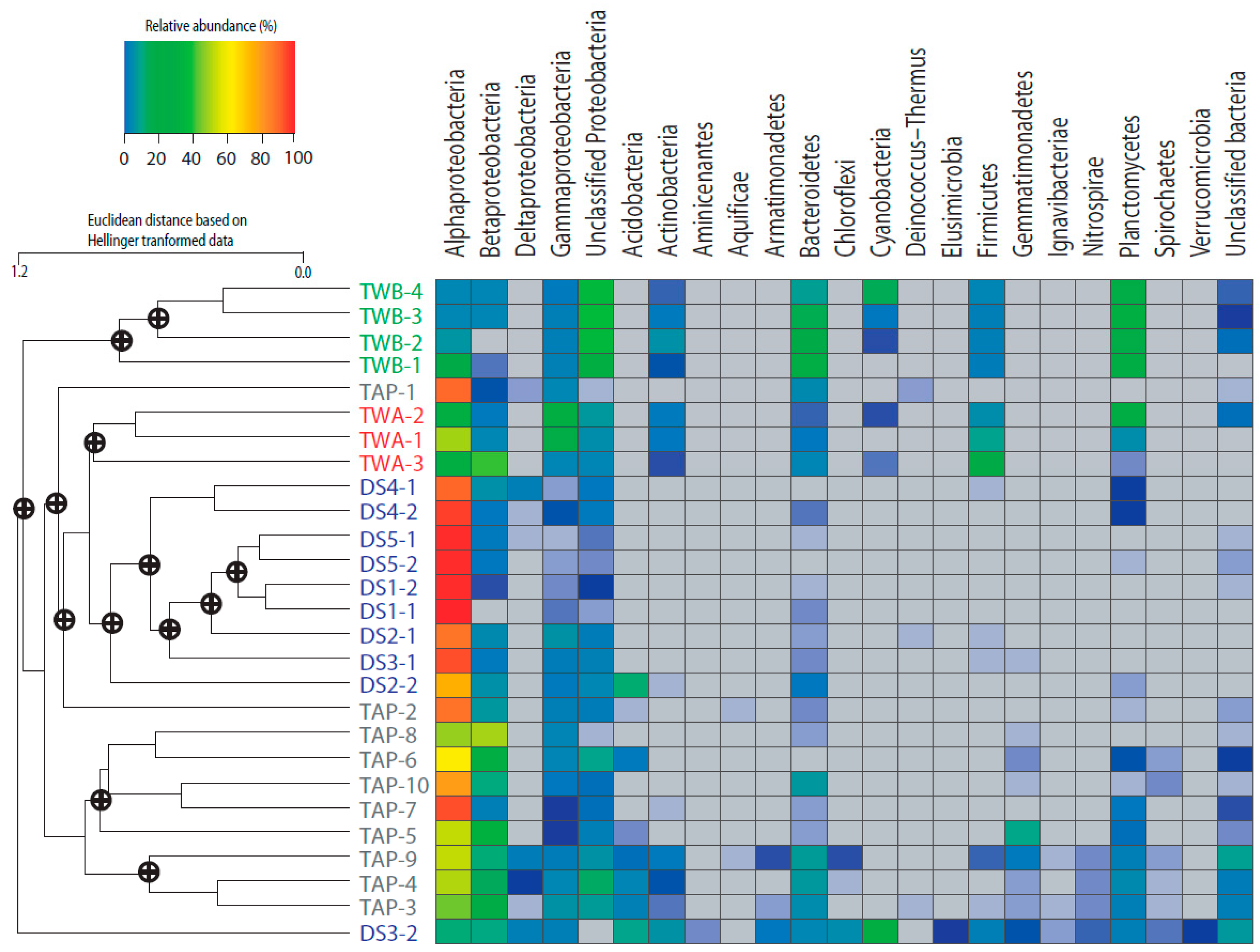
3.3. Differences between Bacterial Communities over Time
3.4. Distribution of OTUs across the Subsystems and Their Relationship with Water Quality Parameters and Estimators of Diversity and Richness
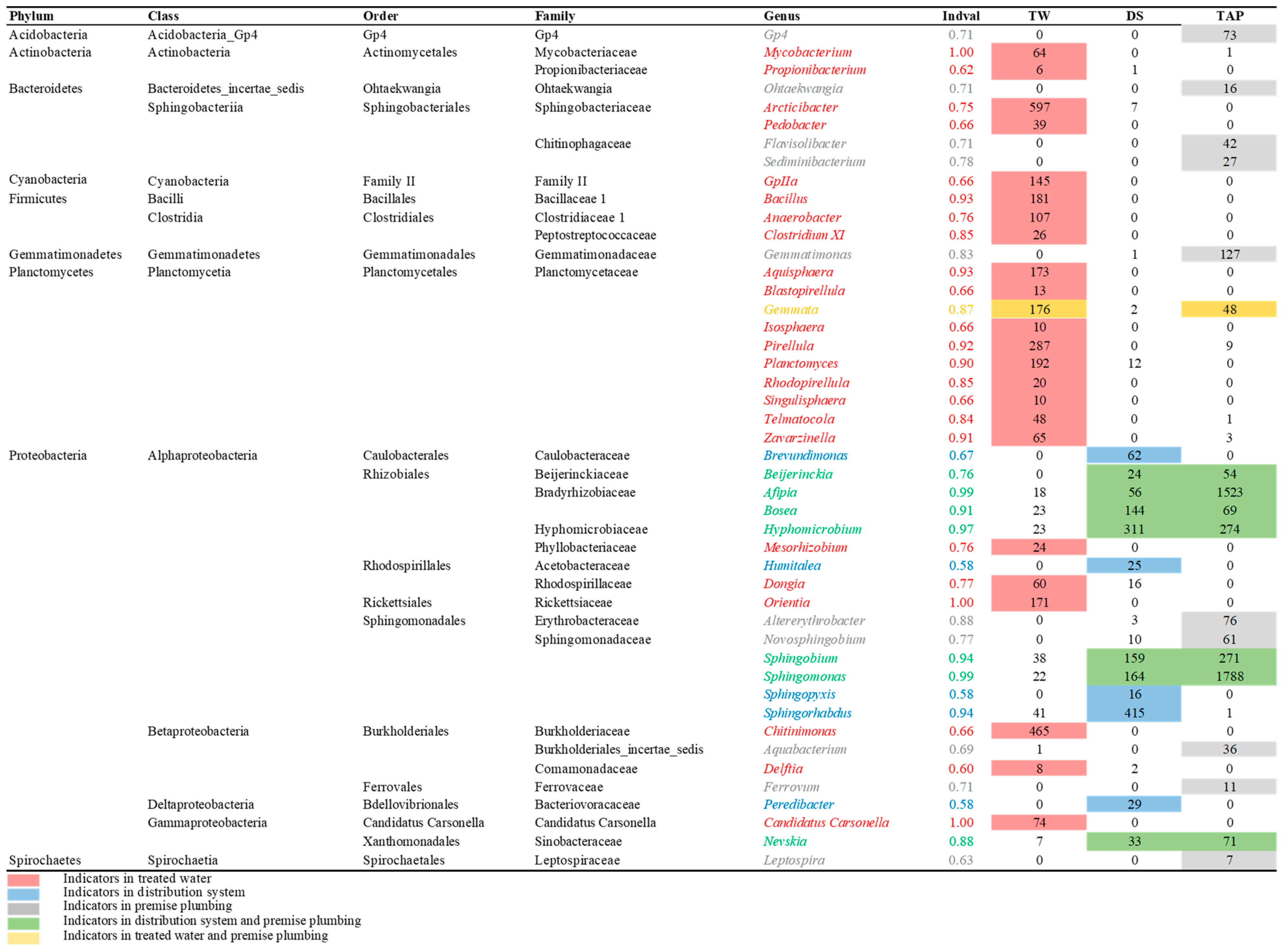
3.5. Detection of Potential Opportunistic Pathogens, Cosmopolitan, and Endemic Species across the Specific Subsystems
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.D.; DiGiano, F.A. Comparison of bacterial regrowth in distribution systems using free chlorine and chloramine: A statistical study of causative factors. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1469–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Xi, C.; Raskin, L. Microbial ecology of drinking water distribution systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Verberk, J.Q.; Van Dijk, J.C. Bacteriology of drinking water distribution systems: An integral and multidimensional review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9265–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, C.M.; Nunes, O.C.; Melo, L.F. Unsteady state flow and stagnation in distribution systems affect the biological stability of drinking water. Biofouling 2010, 26, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prévost, M.; Besner, M.-C.; Laurent, P.; Servais, P. Emerging issues of biological stability in drinking water distribution systems (chapter 10). In Microbial Growth in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Problems, Causes, Prevention and Research Needs; van der Kooij, D., van der Wielen, P.W., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 261–290. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, C.R.; Hammes, F. Drinking water microbiology-from measurement to management. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard, E.; Laferrière, C.; Déziel, E.; Prévost, M. Impact of stagnation and sampling volume on water microbial quality monitoring in large buildings. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.; Reses, H.; Vigar, M.; Roth, D.M.; Roberts, V.A.; Mattioli, M.; Cooley, L.A.; Hilborn, E.D.; Wade, T.J.; Fullerton, K.; et al. Surveillance for waterborne disease outbreaks associated with drinking water—United States, 2013–2014. Weeky 2017, 66, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkinham, J.O.; Hilborn, E.D.; Arduino, M.J.; Pruden, A.; Edwards, M.A. Epidemiology and ecology of opportunistic premise plumbing pathogens: Legionella pneumophila, mycobacterium avium, and pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perola, O.; Nousiainen, T.; Suomalainen, S.; Aukee, S.; Karkkainen, U.M.; Kauppinen, J.; Ojanen, T.; Katila, M.L. Recurrent sphingomonas paucimobilisbacteraemia associated with a multi-bacterial water-borne epidemic among neutropenic patients. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 50, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, C.A.; Cohen, A.L.; Trevino, I.; Rupp, A.H.; Harris, M.; Forkan-Kelly, S.; Noble-Wang, J.; Jensen, B.; Shams, A.; Arduino, M.J.; et al. Outbreak of burkholderia cepacia complex among ventilated pediatric patients linked to hospital sinks. Am. J. Infect. Control 2011, 39, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.M.; Armbruster, C.R.; Arduino, M.J. Plumbing of hospital premises is a reservoir for opportunistically pathogenic microorganisms: A review. Biofouling J. Bioadhes. Biofilm Res. 2013, 29, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.; Ling, F.; Andersen, G.L.; LeChevallier, M.W.; Liu, W.T. Microbial community dynamics of an urban drinking water distribution system subjected to phases of chloramination and chlorination treatments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7856–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.J.; Xi, C.; Raskin, L. Bacterial community structure in the drinking water microbiome is governed by filtration processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8851–8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, K.; Hwang, C.; Liu, W.-T.; Boon, N.; Köster, O.; Vrouwenvelder, H.; Egli, T.; Hammes, F. A microbiology-based multi-parametric approach towards assessing biological stability in drinking water distribution networks. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holinger, E.P.; Ross, K.A.; Robertson, C.E.; Stevens, M.J.; Harris, J.K.; Pace, N.R. Molecular analysis of point-of-use municipal drinking water microbiology. Water Res. 2014, 49, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prest, E.I.; El-Chakhtoura, J.; Hammes, F.; Saikaly, P.E.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Combining flow cytometry and 16s rRNA gene pyrosequencing: A promising approach for drinking water monitoring and characterization. Water Res. 2014, 63, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Chakhtoura, J.; Prest, E.; Saikaly, P.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Hammes, F.; Vrouwenvelder, H. Dynamics of bacterial communities before and after distribution in a full-scale drinking water network. Water Res. 2015, 74, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeselers, G.; Coolen, J.; van der Wielen, P.W.J.J.; Jaspers, M.C.; Atsma, A.; de Graaf, B.; Schuren, F. Microbial biogeography of drinking water: Patterns in phylogenetic diversity across space and time. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2505–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-de los Santos, Q.M.; Schroeder, J.L.; Sevillano-Rivera, M.C.; Sungthong, R.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Sloan, W.T.; Pinto, A.J. Emerging investigators series: Microbial communities in full-scale drinking water distribution systems—A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Chakhtoura, J.; Saikaly, P.E.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Impact of distribution and network flushing on the drinking water microbiome. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Parks, J.; Edwards, M.A.; Pruden, A. Impact of water chemistry, pipe material and stagnation on the building plumbing microbiome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, F.; Whitaker, R.; LeChevallier, M.W.; Liu, W.-T. Drinking water microbiome assembly induced by water stagnation. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; van der Mark, E.; Magic-Knezev, A.; Pinto, A.; van den Bogert, B.; Liu, W.; van der Meer, W.; Medema, G. Assessing the origin of bacteria in tap water and distribution system in an unchlorinated drinking water system by sourcetracker using microbial community fingerprints. Water Res. 2018, 138, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz-Moreira, I.; Egas, C.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Bacterial diversity from the source to the tap: A comparative study based on 16s rRNA gene-DGGE and culture-dependent methods. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 200.8—Determination of Trace Elements in Waters and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma—Mass Spectrometry (Revision 5.4—EMMC Version); Office of Research and Development: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1994; p. 57.
- Wang, Y.; Hammes, F.; Düggelin, M.; Egli, T. Influence of size, shape, and flexibility on bacterial passage through micropore membrane filters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6749–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Mohn, W.W. Killing two birds with one stone: Simultaneous extraction of DNA and RNA from activated sludge biomass. Can. J. Microbiol. 1999, 45, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntyre, D.A.; Chandiramani, M.; Lee, Y.S.; Kindinger, L.; Smith, A.; Angelopoulos, N.; Lehne, B.; Arulkumaran, S.; Brown, R.; Teoh, T.G.; et al. The vaginal microbiome during pregnancy and the postpartum period in a European population. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. ‘vegan’. Community Ecology Package. R package. 2016. Available online: http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=vegan (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Gorley, R.N. Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: Similarity profiles and biota-environment linkage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrêne, M.; Legendre, P. Species assemblages and indicator species: The need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévost, M.; Laurent, P.; Servais, P.; Joret, J.-C. Biodegradable Organic Matter in Drinking Water Treatment and Distribution, 1st ed.; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2005; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Pruden, A.; Edwards, M.; Falkinham, J.O., III; Arduino, M. State of the Science and Research Needs for Opportunistic Pathogens in Premise Plumbing; Water Research Foundation (WRF): Denver, CO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Potgieter, S.; Pinto, A.; Sigudu, M.; du Preez, H.; Ncube, E.; Venter, S. Long-term spatial and temporal microbial community dynamics in a large-scale drinking water distribution system with multiple disinfectant regimes. Water Res. 2018, 139, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, S.T.; VanBriesen, J.M. Temporal variability of bacterial diversity in a chlorinated drinking water distribution system. J. Environ. Eng. ASCE 2012, 138, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douterelo, I.; Sharpe, R.L.; Boxall, J.B. Influence of hydraulic regimes on bacterial community structure and composition in an experimental drinking water distribution system. Water Res. 2013, 47, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xie, S. Phylogenetic diversity of microbial communities in real drinking water distribution systems. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2013, 18, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, Y.; Bouchon, D.; Delafont, V.; Moulin, L.; Hechard, Y. Microbiome of drinking water: A full-scale spatio-temporal study to monitor water quality in the Paris distribution system. Water Res. 2018, 149, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaerewijck, M.J.M.; Huys, G.; Palomino, J.C.; Swings, J.; Portaels, F. Mycobacteria in drinking water distribution systems: Ecology and significance for human health. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Scola, B.; Barrassi, L.; Raoult, D. Isolation of new fastidious α Proteobacteria and Afipia felis from hospital water supplies by direct plating and amoebal co-culture procedures. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2000, 34, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-N.; Lai, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-L.; Huang, C.-K.; Chen, W.-F.; Wang, J.-L.; Chung, H.-C.; Liang, S.-H.; Lin, H.-H. Sphingomonas paucimobilis bacteremia in humans: 16 case reports and a literature review. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2010, 43, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Adley, C.C. Sphingomonas paucimobilis: A persistent gram-negative nosocomial infectious organism. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 75, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Nie, X.; Li, C.; Gu, J.; Zhang, C. Molecular analysis of bacterial communities in biofilms of a drinking water clearwell. Microbes Environ. 2012, 27, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz-Moreira, I.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Diversity and antibiotic resistance patterns of sphingomonadaceae isolates from drinking water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5697–56706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavissich, J.P.; Vargas, I.T.; González, B.; Pastén, P.A.; Pizarro, G.E. Culture dependent and independent analyses of bacterial communities involved in copper plumbing corrosion. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bakker, G.L.; Li, S.; Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Verberk, J.Q.J.C.; Medema, G.J.; Liu, W.T.; Van Dijk, J.C. Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial communities in unchlorinated drinking water distribution system: An integral study of bulk water, suspended solids, loose deposits, and pipe wall biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5467–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. Afipia felis in hospital water supply in association with free-living amoebae. Lancet 1999, 353, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousbia, S.; Papazian, L.; Saux, P.; Forel, J.M.; Auffray, J.P.; Martin, C.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Serologic prevalence of amoeba-associated microorganisms in intensive care unit pneumonia patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghnatios, R.; Drancourt, M. Colonization of hospital water networks by gemmata massiliana, a new planctomycetes bacterium. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subsystem | Coverage a | Shannon | Ace | Chao | Evenness b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 3.21 ± 0.26 | 105 ± 28 | 106 ± 28 | 0.72 ± 0.03 |
| DS | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 2.21 ± 1.18 | 138 ± 51 | 108 ± 30 | 0.51 ± 0.23 |
| TAP | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 2.64 ± 0.91 | 115 ± 50 | 101 ± 54 | 0.62 ± 0.14 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, V.C.F.; Durand, A.-A.; Constant, P.; Prévost, M.; Bédard, E. Identification of Factors Affecting Bacterial Abundance and Community Structures in a Full-Scale Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System. Water 2019, 11, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030627
Dias VCF, Durand A-A, Constant P, Prévost M, Bédard E. Identification of Factors Affecting Bacterial Abundance and Community Structures in a Full-Scale Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System. Water. 2019; 11(3):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030627
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Vanessa C. F., Audrey-Anne Durand, Philippe Constant, Michèle Prévost, and Emilie Bédard. 2019. "Identification of Factors Affecting Bacterial Abundance and Community Structures in a Full-Scale Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System" Water 11, no. 3: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030627
APA StyleDias, V. C. F., Durand, A.-A., Constant, P., Prévost, M., & Bédard, E. (2019). Identification of Factors Affecting Bacterial Abundance and Community Structures in a Full-Scale Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution System. Water, 11(3), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030627





