Forensic Hydrology Reveals Why Groundwater Tables in The Province of Noord Brabant (The Netherlands) Dropped More Than Expected
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Approach
2.2. Changes in Land Use and Crop Yield
2.3. Estimating Changes in Annual Groundwater Recharge
2.3.1. Groundwater Recharge of Urban Area
2.3.2. Groundwater Recharge of Nature
2.3.3. Groundwater Recharge of Arable Land
2.4. Modelling the Effect on Groundwater Tables
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Annual Groundwater Recharge
3.2. Changes in Groundwater Tables
3.3. Effect of Land-Use and Crop Yield on Simulated Effects of Groundwater Abstraction
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations of Our Study
4.2. Comparison with Previous Work
4.3. General Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schewe, J.; Heinke, J.; Gerten, D.; Haddeland, I.; Arnell, N.W.; Clark, D.B.; Dankers, R.; Eisner, S.; Fekete, B.M.; Colón-González, F.J.; et al. Multimodel assessment of water scarcity under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3245–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitoun, M.; Warner, J. Hydro-hegemony–A framework for analysis of trans-boundary water conflicts. Water Policy 2006, 8, 435–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, R.W.; Van der Zee, S.E. Simulating the effect of capillary flux on the soil water balance in a stochastic ecohydrological framework. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W08425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. The Common Agricultural Policy—A Story to be Continued; European Union: Luxembourg, 2012; p. 20. ISBN 978-92-79-23265-7. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. The eu environmental implementation review country report—The Netherlands. Report of the staff of the Directorate—General for Environment, European Commision. Luxembourg, 2017. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/eir/pdf/report_nl_en.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Ten Berge, H.F.M.; Dalgaard, T.; Fraters, B.; Durand, P.; Hart, A.; Hofman, G.; Jacobsen, B.H.; Lalor, S.T.J.; Lesschen, J.P.; et al. Management, regulation and environmental impacts of nitrogen fertilization in northwestern europe under the nitrates directive; a benchmark study. Biogeoscience 2012, 9, 5143–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Tiktak, A.; Rougoor, C.W. Evaluation of the dutch implementation of the nitrates directive, the water framework directive and the national emission ceilings directive. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2016, 78, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runhaar, J.; Van Gool, C.; Groen, C. Impact of hydrological changes on nature conservation areas in the netherlands. Biol. Conserv. 1996, 76, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolf, H.L.M. Verlaging van de Grondwaterstanden in Nederland: Analyse Periode 1950–1986; Ministerie van Verkeer en Waterstaat: Den Haag, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhoud, B. From the publisher. Southwest Hydrol. 2007, 6, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Makkink, G.F. Testing the penman formula by means of lysimeters. J. Inst. Water Eng. 1957, 11, 277–288. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Hurk, B.; Siegmund, P.; Tank, A.K. Knmi’14: Climate Change Scenarios for the 21st Century—A Netherlands Perspective; KNMI: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, J.P.M.; Zaadnoordijk, W.J.; Cirkel, D.G.; Leunk, I.; Aarts, H.F.M. Grondwateraanvulling en Achtergrondverlaging in de Provincie Noord-Brabant; BTO 2015.015; KWR Watercycle Research Institute: Nieuwegein, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boheemen, P.J.M. Seizoen-en Piekbehoefte aan Kunstmatige Watervoorziening Bij gras-, Aardappelen en Tuinbouwgewassen; Instituut voor Cultuurtechniek en Waterhuishouding: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf, R.E.; Roeffen, B.; Den Ouden, T.; Souwer, B. Studie Naar de Huidige en Toekomstige Waterbehoefte van Stedelijke Gebieden; DeltaSync BV: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Geudens, P.J.J.G.; Van Grootveld, J. Dutch Drinking Water Statistics. From Source to Tap; VEWIN: Werkendam (NL), The Netherlands, 2017; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Van Thiel, L. Waterverbruik Thuis 2016; C8732; TNS Nipo: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Prestatievergelijking Drinkwaterbedrijven 2015; Inspectie Leefomgeving en Transport: Den-Haag, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Spieksma, J.F.M.; Dolman, A.J.; Schouwenaars, J.M. De verdamping van natuurterreinen. Stromingen 1997, 3, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dolman, H.; Moors, E.; Elbers, J.; Snijders, W.; Hamaker, P. Het Waterverbruik van Bossen in Nederland; Alterra: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Voortman, B.R.; Bartholomeus, R.P.; Van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Witte, J.P.M. Quantifying energy and water fluxes in dry dune ecosystems of the netherlands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3787–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, C.T. Transpiration and Crop Yields; Pudoc: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1958; p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- Aarts, H.F.M.; Degenhart, N. De Invloed van Ontwikkelingen in de Brabantse Landbouw op het Waterverbruik; Nota 44; AB-DLO: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Aarts, H.F.M. Resource Management in a ‘de marke’ Dairy Farming System; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, J.C.; Groenendijk, P.; Hendriks, R.F.A.; Kroes, J.G. Advances of modeling water flow in variably saturated soils with swap. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, F.; Van der Wal, B.J.; Moorman, J.; Westerhof, H.; Peerdeman, K.; Van Sijl, J. Ontwikkeling brabants grondwatermodel tot kennissysteem (“development of brabant groundwater modeling system”, in dutch). H2O-Online, 10 December 2014; 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Harbaugh, A.W.; Banta, E.R.; Hill, M.C.; McDonald, M.G. Modflow 2000, the U.S. Geological Survey Modular Ground Water Model User Guide to Modularization Concepts and the Ground Water Flow Process; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2000.
- Kroes, J.G.; Van Dam, J.C.; Groenendijk, P.; Hendriks, R.F.A.; Jacobs, C.M.J. Swap Version 3.4, Theory Description and User Manual; Alterra Report 1649; Wageningen University and Research Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zaadnoordijk, W.J. Simulating piecewise-linear surface water and ground water interactions with modflow. Groundwater 2009, 47, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, C.; Elbers, J.; Brolsma, R.; Hartogensis, O.; Moors, E.; Rodríguez-Carretero Márquez, M.T.; Van Hove, B. Assessment of evaporative water loss from dutch cities. Build. Environ. 2015, 83, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bakel, P.J.T.; De Wit, P.A.J.W. Zijn de toegenomen landbouwopbrengsten een der oorzaken van de verdroging in nederland? H2O 1995, 28, 771–773. [Google Scholar]
- Kabat, P.; Van den Broek, B.; Feddes, R. Swacrop: A water management and crop production simulation model. Icid Bull. 1992, 41, 61–84. [Google Scholar]

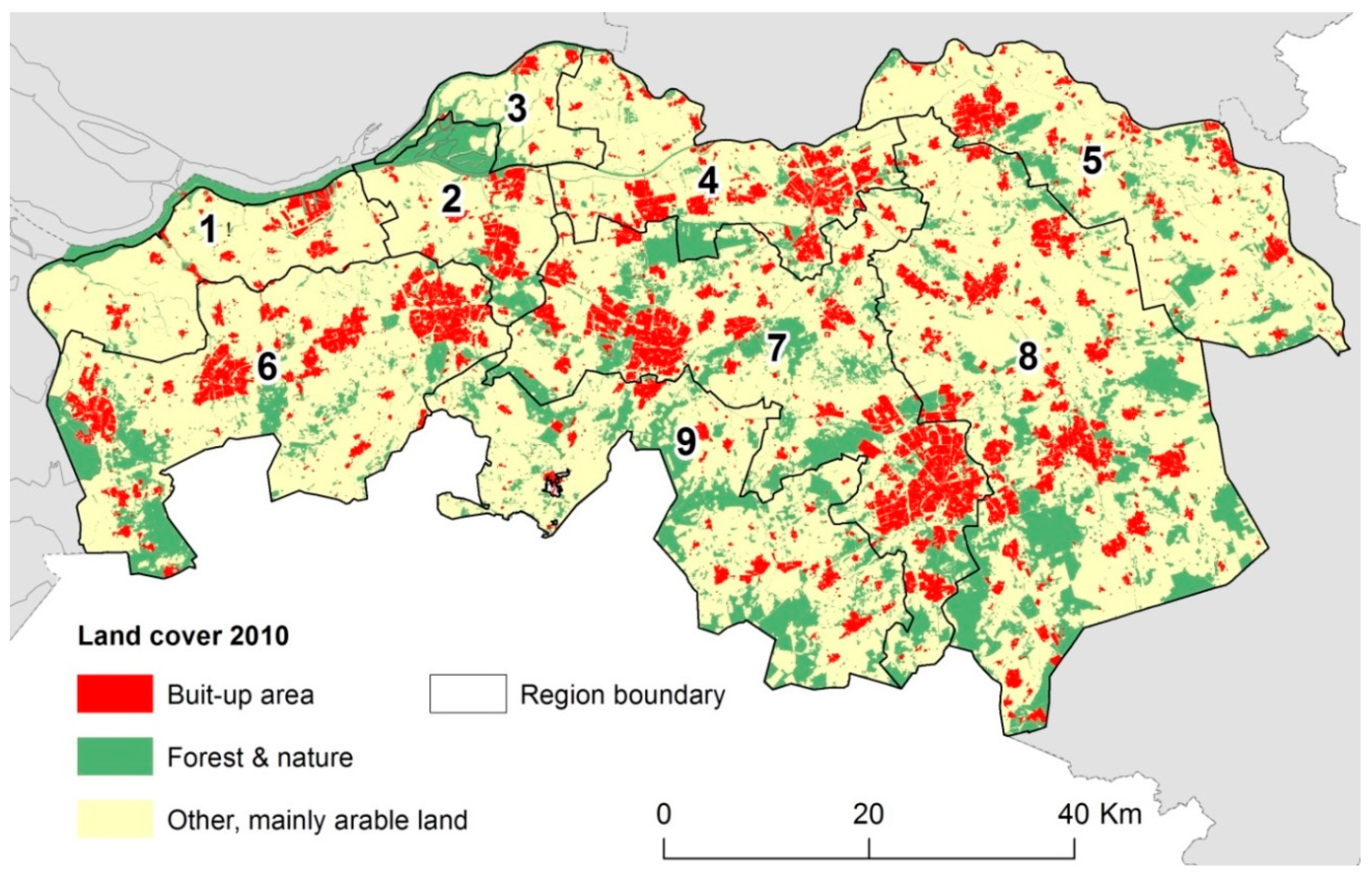
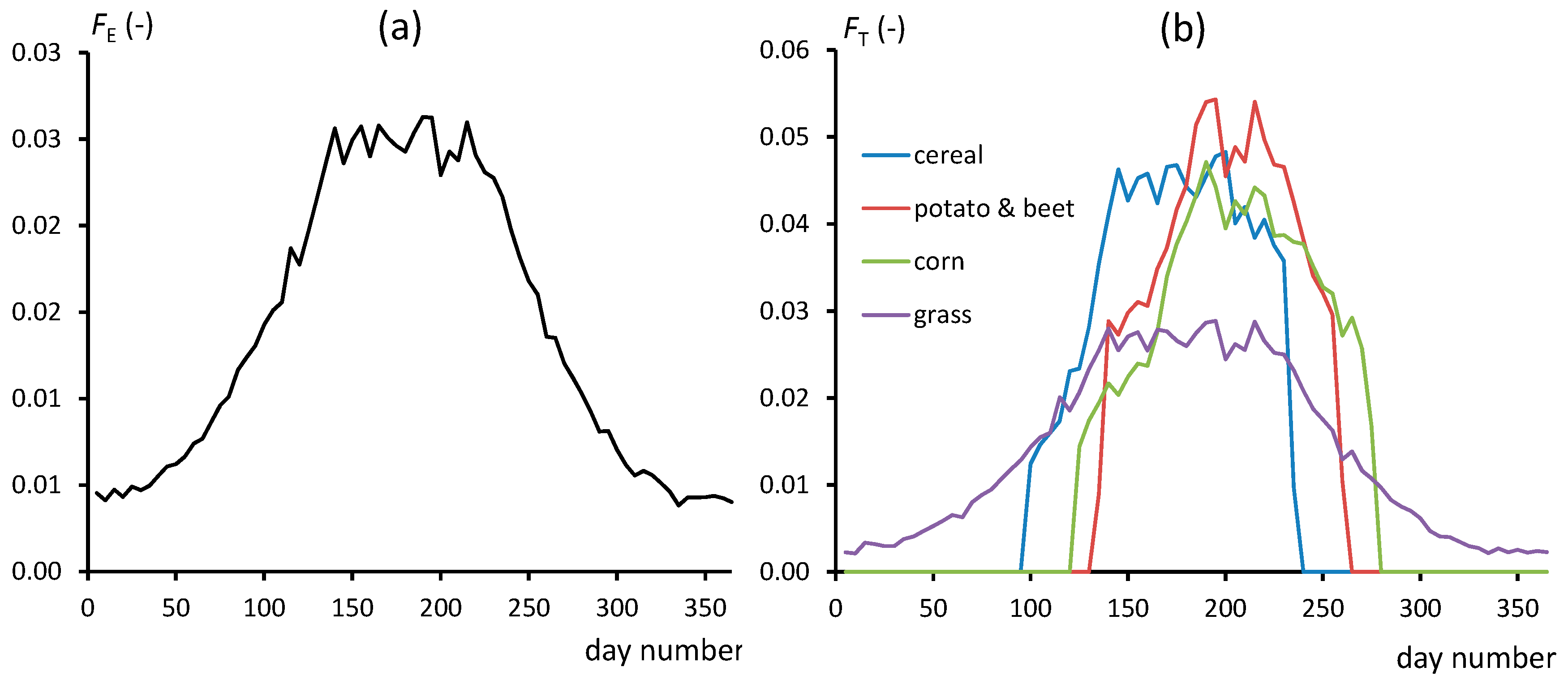
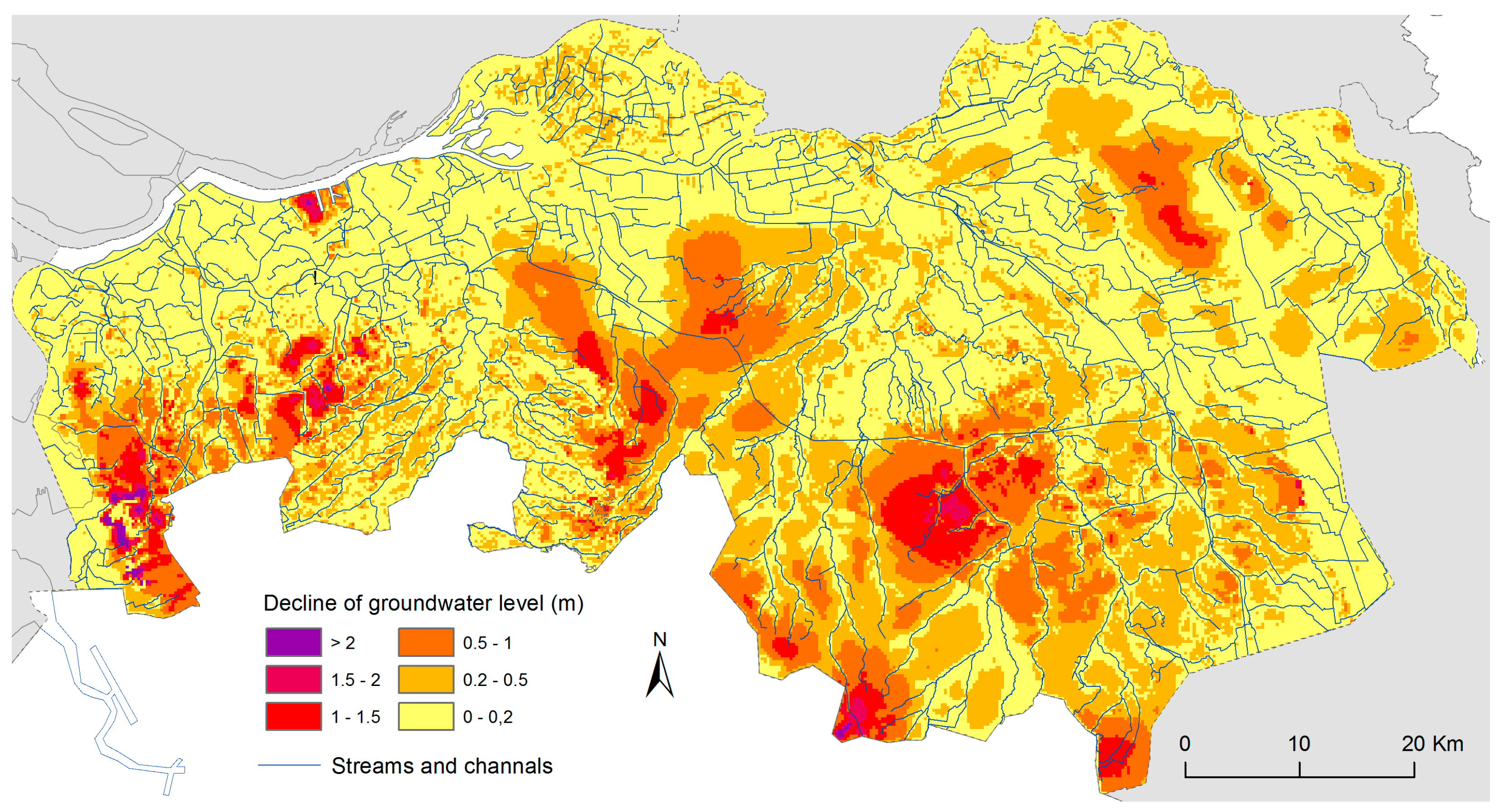
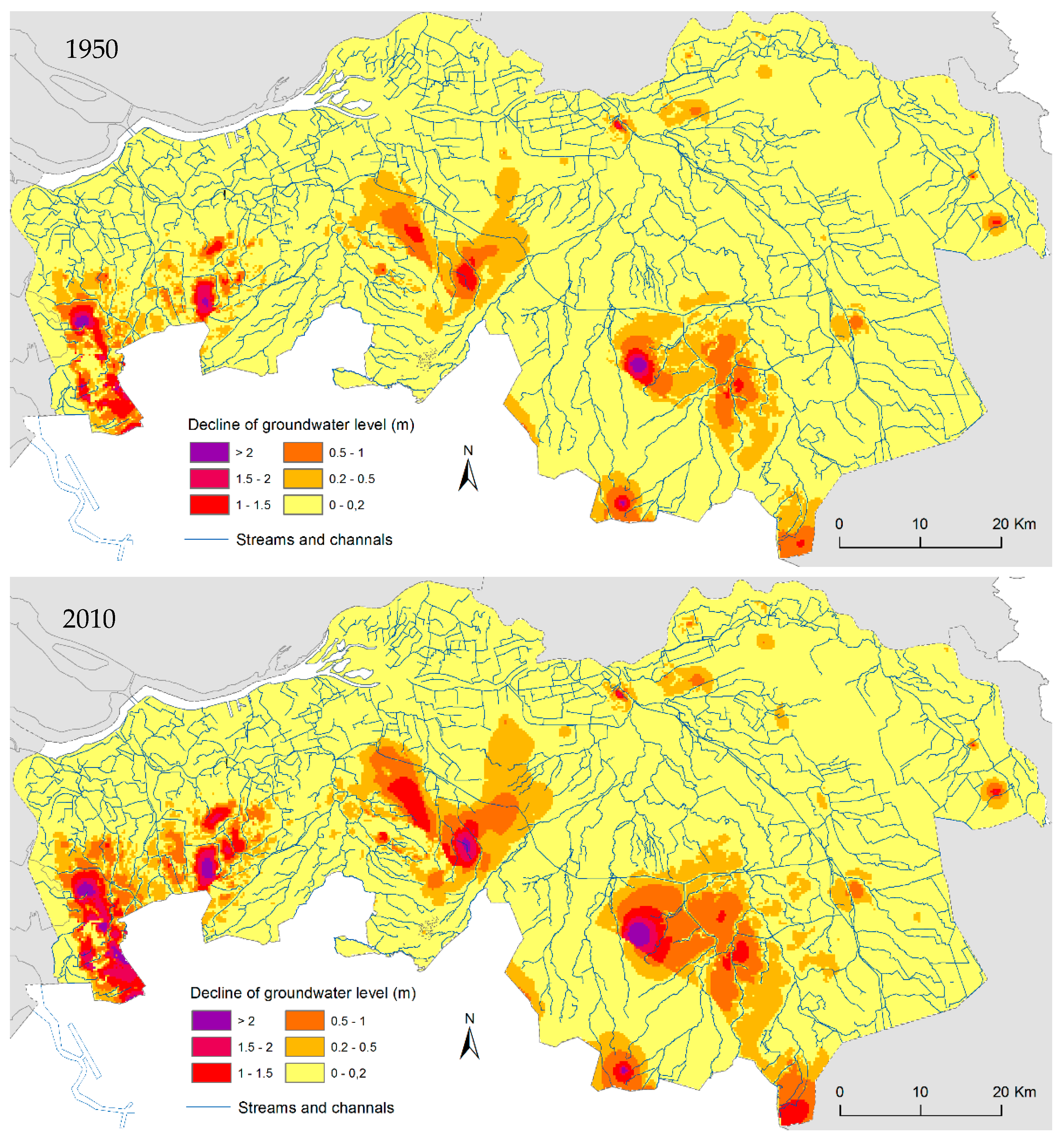
| Region | Area (ha) | Division (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable | Urban | Forest & Nature | Other | ||||||
| 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 | ||
| 1 | 31,299 | 80 | 70 | 2 | 11 | 4 | 4 | 14 | 15 |
| 2 | 22,213 | 74 | 62 | 6 | 17 | 15 | 14 | 6 | 7 |
| 3 | 12,191 | 56 | 51 | 3 | 8 | 11 | 10 | 30 | 32 |
| 4 | 37,900 | 74 | 61 | 9 | 25 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 6 |
| 5 | 58,087 | 74 | 75 | 4 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 9 | 1 |
| 6 | 73,774 | 65 | 55 | 6 | 19 | 16 | 15 | 13 | 11 |
| 7 | 85,178 | 68 | 50 | 9 | 26 | 23 | 21 | 0 | 3 |
| 8 | 119,630 | 74 | 59 | 4 | 15 | 21 | 20 | 0 | 6 |
| 9 | 64,935 | 68 | 67 | 3 | 8 | 26 | 25 | 3 | 0 |
| Total | 505,208 | 71 | 61 | 5 | 17 | 18 | 17 | 6 | 6 |
| Division (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 2010 | |
| Cereal | 33 | 11 |
| Potato | 7 | 8 |
| Beet | 7 | 4 |
| Corn | 1 | 27 |
| Grass | 51 | 49 |
| Cereal | Potato | Sugar Beet | Fodder Beat | Corn | Grass | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 | 1950 | 2010 |
| 1 | 3.4 | 9.1 | 24.0 | 49.0 | 42.3 | 81.7 | 57.0 | - | 9.0 | 17.1 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 2 | 2.8 | 9.4 | 23.0 | 50.6 | 39.2 | 82.0 | 54.8 | - | 9.0 | 18.1 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 3 | 3.2 | 9.3 | 23.1 | 50.7 | 41.4 | 79.0 | 55.8 | - | 9.0 | 17.3 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 4 | 2.5 | 8.2 | 21.5 | 50.3 | 35.8 | 81.3 | 53.6 | - | 9.0 | 16.7 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 5 | 2.4 | 6.4 | 22.0 | 52.2 | 32.9 | 74.5 | 53.0 | - | 9.0 | 17.1 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 6 | 2.4 | 8.5 | 21.4 | 46.7 | 34.0 | 74.6 | 49.6 | - | 9.0 | 16.5 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 7 | 2.5 | 6.1 | 22.2 | 49.5 | 30.2 | 74.9 | 52.1 | - | 9.0 | 16.2 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 8 | 2.2 | 6.3 | 1.9 | 53.9 | 29.9 | 73.5 | 50.9 | - | 9.0 | 15.9 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| 9 | 1.8 | 7.2 | 22.3 | 50.4 | 29.7 | 73.4 | 50.2 | - | 9.0 | 15.8 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| Average | 2.4 | 7.8 | 22.4 | 50.4 | 38.7 | 76.9 | 51.6 | - | 9.0 | 16.3 | 9.0 | 11.5 |
| CDM | CT | (Es + Ei) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (kg Dry Matter/kg Product) | (kg H2O/kg Dry Matter) | (mm·y−1) | |
| Cereal | 1.67 | 300 | 117 |
| Corn | 1.00 | 210 | 127 |
| Beet | 0.23 | 230 | 115 |
| Potato | 0.25 | 290 | 115 |
| Grass | 1.00 | 370 | 133 |
| R (mm·y−1) | Decline in R | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 2010 | mm·y−1 | % | |
| Urban area | 226 | 226 | 0 | 0 |
| Nature | 238 | 202 | 36 | 15 |
| Cereal | 594 | 321 | 273 | 46 |
| Corn | 515 | 361 | 154 | 30 |
| Beet | 511 | 309 | 202 | 40 |
| Potato | 554 | 350 | 203 | 37 |
| Grassland | 365 | 272 | 93 | 25 |
| Arable | 521 | 364 | 157 | 30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Witte, J.-P.M.; Zaadnoordijk, W.J.; Buyse, J.J. Forensic Hydrology Reveals Why Groundwater Tables in The Province of Noord Brabant (The Netherlands) Dropped More Than Expected. Water 2019, 11, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030478
Witte J-PM, Zaadnoordijk WJ, Buyse JJ. Forensic Hydrology Reveals Why Groundwater Tables in The Province of Noord Brabant (The Netherlands) Dropped More Than Expected. Water. 2019; 11(3):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030478
Chicago/Turabian StyleWitte, Jan-Philip M., Willem Jan Zaadnoordijk, and Jan Jaap Buyse. 2019. "Forensic Hydrology Reveals Why Groundwater Tables in The Province of Noord Brabant (The Netherlands) Dropped More Than Expected" Water 11, no. 3: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030478
APA StyleWitte, J.-P. M., Zaadnoordijk, W. J., & Buyse, J. J. (2019). Forensic Hydrology Reveals Why Groundwater Tables in The Province of Noord Brabant (The Netherlands) Dropped More Than Expected. Water, 11(3), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030478





