Behavioral Interactions and Trophic Overlap between Invasive Signal Crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Decapoda, Astacidae) and Native Fishes in Iberian Rivers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
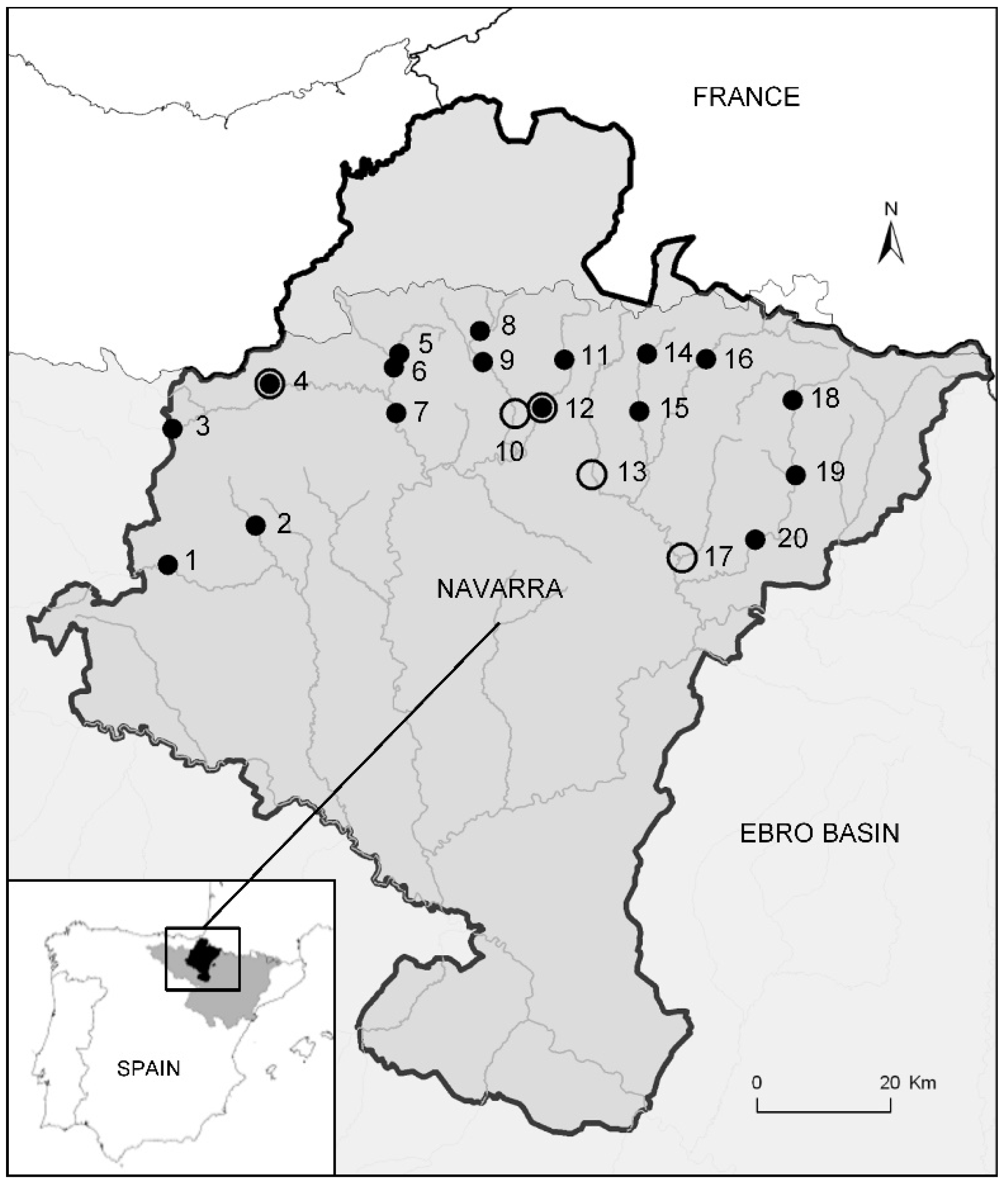
2.1. Study Area
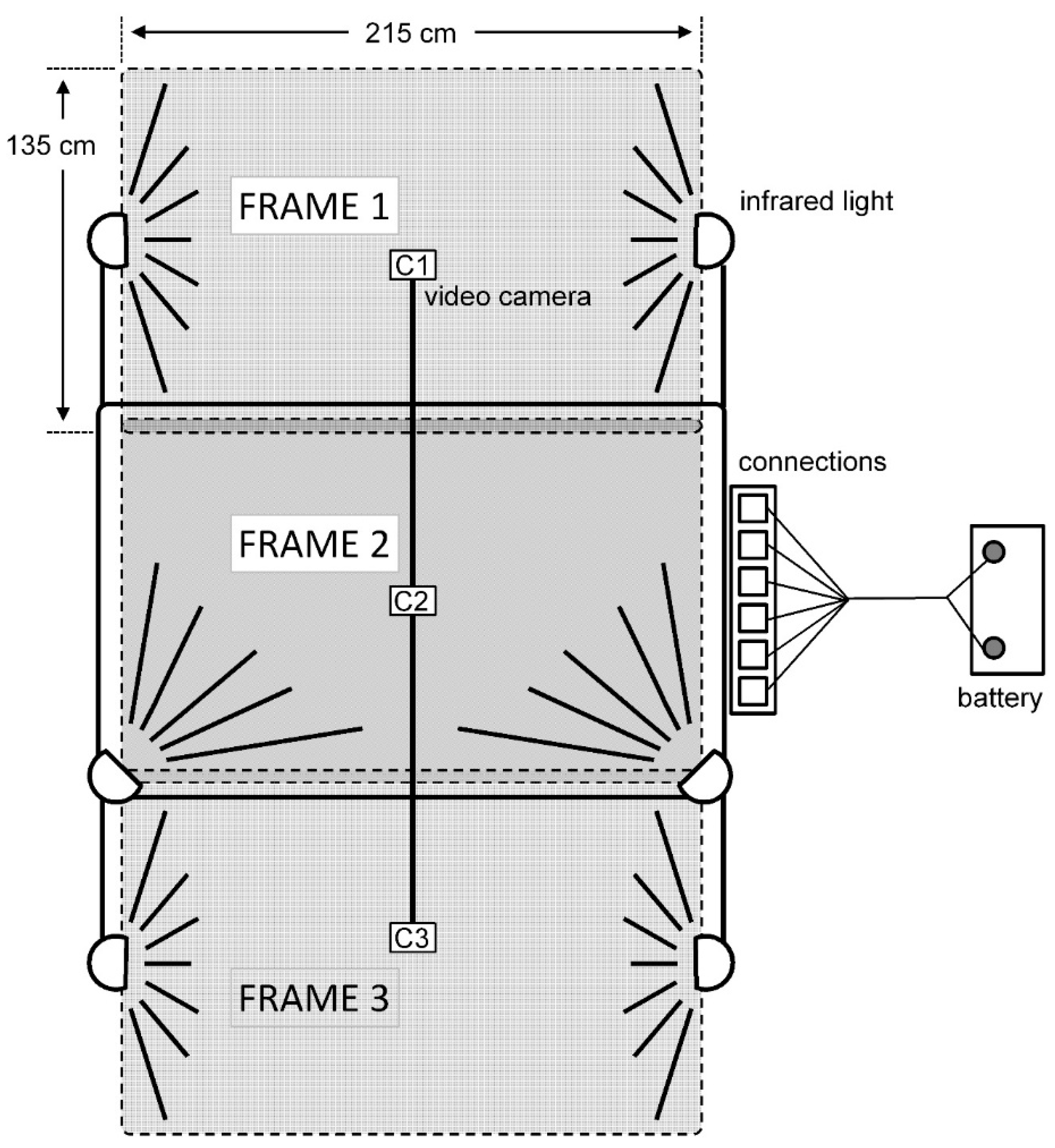
2.2. Behavioral Interactions
2.3. Trophic Overlap
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
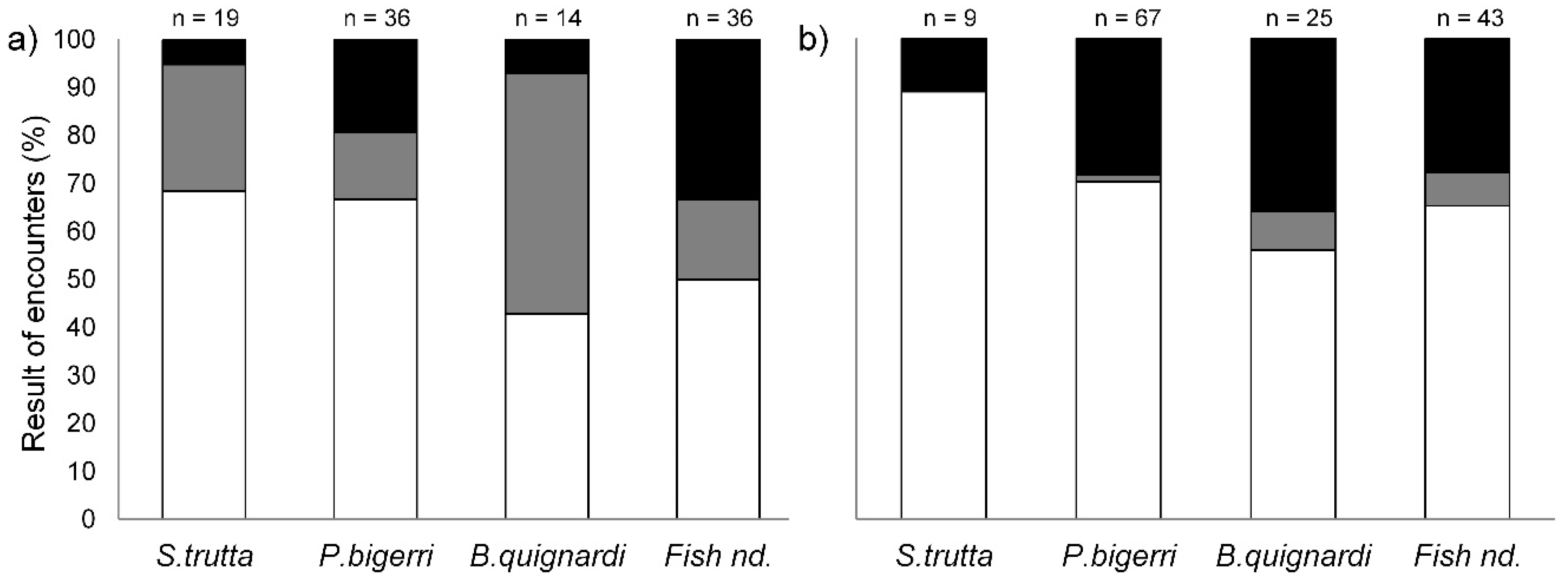
3.1. Behavioral Interactions
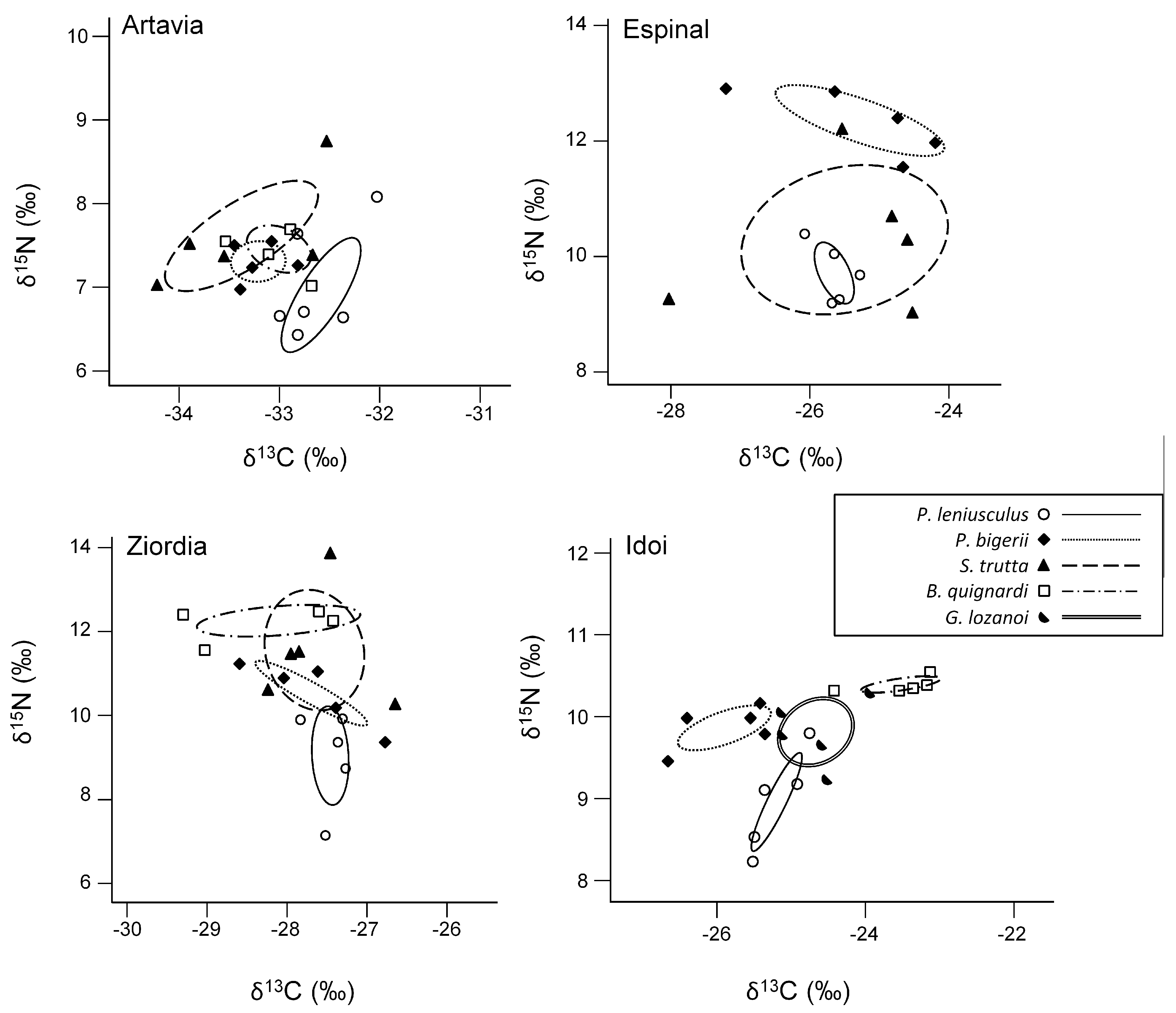
3.2. Trophic Overlap
4. Discussion
4.1. Behavioral Interactions
4.2. Trophic Overlap
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mooney, H.A.; Hobbs, R.J. Invasive Species in a Changing World; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Clavero, M.; García-Berthou, E. Invasive species are a leading cause of animal extinctions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchart, S.H.M.; Walpole, M.; Collen, B.; van Strien, A.; Scharlemann, J.P.W.; Almond, R.E.A.; Baillie, J.E.M.; Bomhard, B.; Brown, C.; Bruno, J.; et al. Global Biodiversity: Indicators of Recent Declines. Science 2010, 328, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, F. Biological invasions in inland waters: An overview. In Biological Invaders in Inland Waters: Profiles, Distribution, and Threats; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.G.; Darwall, W.R.T. The Status and Distribution of Freshwater Fish Endemic to the Mediterranean Basin; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Reyjol, Y.; Hugueny, B.; Pont, D.; Bianco, P.G.; Beier, U.; Caiola, N.; Casals, F.; Cowx, I.; Economou, A.; Ferreira, T.; et al. Patterns in species richness and endemism of European freshwater fish. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Ribeiro, F.; Leunda, P.M.; Vilizzi, L.; Copp, G.H. Effectiveness of FISK, an Invasiveness Screening Tool for Non-Native Freshwater Fishes, to Perform Risk Identification Assessments in the Iberian Peninsula. Risk Anal. 2013, 33, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedia, I.; Miranda, R. Review of the state of knowledge of crayfish species in the Iberian Peninsula. Limnetica 2013, 32, 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, W.; Alcorlo, P.; Baltanás, A.; Montes, C. Impact of an introduced crustacean on the trophic webs of Mediterranean wetlands. Biol. Invasions 2005, 7, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.D. A review of ecological interactions between crayfish and fish, indigenous and introduced. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2011, 401, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.Z.; Wiles, P.R. Ecological impact of introduced crayfish on benthic fishes in a British Lowland River. Conserv. Biol. 1997, 11, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peay, S.; Guthrie, N.; Spees, J.; Nilsson, E.; Bradley, P. The impact of signal crayfish (Pacifastacus leniusculus) on the recruitment of salmonid fish in a headwater stream in Yorkshire, England. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2009, 12, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, D.H.; O’Malley, O.J.; Gooderham, A.C.; Lucas, M.C. Relative impacts of native and non-native crayfish on shelter use by an indigenous benthic fish. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2009, 19, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.W.; Collen, P.; Armstrong, J.D. Competition for shelter among over-wintering signal crayfish and juvenile Atlantic salmon. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 65, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glon, M.G.; Larson, E.R.; Pangle, K.L. Connecting laboratory behavior to field function through stable isotope analysis. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, D.A.; Moore, P.A. Field observations of intraspecific agonistic behavior of two crayfish species, Orconectes rusticus and Orconectes virilis, in different habitats. Biol. Bull. 2003, 205, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crandall, K.A.; De Grave, S. An updated classification of the freshwater crayfishes (Decapoda: Astacidea) of the world, with a complete species list. J. Crustac. Biol. 2017, 37, 615–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Merino-Aguirre, R.; Vilizzi, L.; Copp, G.H. Interspecific Aggressive Behaviour of Invasive Pumpkinseed Lepomis gibbosus in Iberian Fresh Waters. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bearhop, S.; Adams, C.E.; Waldron, S.; Fuller, R.A.; MacLeod, H. Determining trophic niche width: A novel approach using stable isotope analysis. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Fry, B. Stable Isotopes in Ecosystem Studies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Montaña, C.G.; Post, D.M. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 2007, 88, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caut, S.; Angulo, E.; Courchamp, F. Variation in discrimination factors (Δ15N and Δ13C): The effect of diet isotopic values and applications for diet reconstruction. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, F.; Ruokonen, T.J.; Hämäläinen, H.; Jones, R.I. Does the introduced signal crayfish occupy an equivalent trophic niche to the lost native noble crayfish in boreal lakes? Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 2025–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C.; Evangelista, C.; Zhao, T.; Lecerf, A.; Britton, J.R.; Cucherousset, J. Between-lake variation in the trophic ecology of an invasive crayfish. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, M.D.; Marchamalo, M.; de Jalón, D.G.; del Tánago, M.G. Flow regime patterns and their controlling factors in the Ebro basin (Spain). J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leunda, P.; Miranda, R.; Oscoz, J. Occurrence and conservation of the threatened endemic cobitid, Cobitis calderoni, in the Erro River (Ebro Basin, Spain). Cybium 2007, 31, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Leunda, P.M.; Sistiaga, M.; Oscoz, J.; Miranda, R. Ichthyofauna of a near-natural Pyrenean river: Spatio-temporal variability and reach-scale habitat. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2012, 11, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodóvar, A.; Nicola, G.G.; Elvira, B.; García-Marín, J.L. Introgression variability among Iberian brown trout Evolutionary Significant Units: The influence of local management and environmental features. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, D.H.; Thom, T.J.; Lucas, M.C. Movement and dispersal of the invasive signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus in upland rivers. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Huber, R. Activity patterns, behavioural repertoires, and agonistic interactions of crayfish: A non-manipulative field study. Behaviour 2007, 144, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavey, C.R.; Fielder, D.R. The influence of size differential on agonistic behaviour in the freshwater crayfish, Cherax cuspidatus (Decapoda: Parastacidae). J. Zool. 1996, 238, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.H.; Saltzman, L.; Buckholt, M.A.; Mathews, L.M. Agonistic Interactions Differ by Sex and Season in the Crayfish Orconectes quinebaugensis. J. Crustac. Biol. 2009, 29, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.D.; O’Connor, W.; O’Keeffe, C.; Lynn, D. A Technical Manual for Monitoring White-Clawed Crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes in Irish Lakes; Irish Wildlife Manuals: Dublin, Ireland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nahon, S.; Séité, S.; Kolasinski, J.; Aguirre, P.; Geurden, I. Effects of euthanasia methods on stable carbon (δ13 C value) and nitrogen (δ15 N value) isotopic compositions of fry and juvenile rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscoz, J.; Galicia, D.; Miranda, R. Identification Guide of Freshwater Macroinvertebrates of Spain; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tronquart, N.H.; Mazeas, L.; Reuilly-Manenti, L.; Zahm, A.; Belliard, J. Fish fins as non-lethal surrogates for muscle tissues in freshwater food web studies using stable isotopes. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H.; Tamaki, A.; Harada, K.; Shimoda, K.; Koyama, K.; Ishihi, Y. Variability of diet-tissue isotopic fractionation in estuarine macrobenthos. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 296, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Eldridge, P.M. Estimating the timing of diet shifts using stable isotopes. Oecologia 2006, 147, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenroth, P.; Holmqvist, N.; Nyström, P.; Berglund, O.; Larsson, P.; Granéli, W. Stable isotopes as indicator of diet in omnivorous crayfish (Pacifastacus leniusculus): The influence of tissue, sample treatment, and season. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agresti, A. An Introduction to Categorical Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Oscoz, J.; Escala, M.C.; Campos, F. La alimentación de la trucha común (Salmo trutta L., 1758) en un río de Navarra (N. España). Limnetica 2000, 18, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Oscoz, J.; Campos, F.; Escala, M.C. Alimentación del piscardo (Phoxinus phoxinus) en un río del norte de España. Ecología 2001, 15, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Oscoz, J.; Campos, F.; Escala, M.C. Alimentación del gobio (Gobio gobio (L., 1758)) en el río Larraun (Navarra, N. España). Limnetica 2003, 22, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Oscoz, J.; Campos, F.; Escala, M.C. Notas sobre la alimentación del lobo de río (Barbatula barbatula) en Navarra. Lucas Mallada 2004, 11, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Oscoz, J.; Leunda, P.M.; Campos, F.; Escala, M.C.; Miranda, R. Diet of 0+ brown trout (Salmo trutta L., 1758) from the river Erro (Navarra, north of Spain). Limnetica 2005, 24, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Oscoz, J.; Leunda, P.M.; Escala, M.C.; Miranda, R. Summer feeding relationships of the co-occurring hatchling brown trout Salmo trutta and Gobio lozanoi (Cyprinidae) in an Iberian river. Acta Zool. Sin. 2006, 54, 418–432. [Google Scholar]
- Oscoz, J.; Mellado, A.; Miranda, R. Red biológica del Ebro: Análisis de Macroinvertebrados en las Redes de Vigilancia, Control Operativo y Referencia (Report); Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro: Zaragoza, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schoener, T.W. Nonsynchronous spatial overlap of lizards in patchy habitats. Ecology 1970, 51, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.K. An assessment of diet-overlap indexes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1981, 110, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Light, T. Behavioral effects of invaders: Alien crayfish and native sculpin in a California stream. Biol. Invasions 2005, 7, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A. Agonistic behavior in freshwater crayfish. In Evolutionary Ecology of Social and Sexual Systems; Duffy, J.E., Thiel, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 90–114. [Google Scholar]
- Degerman, E.; Nilsson, P.A.; Nyström, P.; Nilsson, E.; Olsson, K. Are fish populations in temperate streams affected by crayfish?—A field survey and prospects. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2007, 78, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahel, F.J.; Stein, R.A. Complex predator-prey interactions and predator intimidation among crayfish, piscivorous fish, and small benthic fish. Oecologia 1988, 75, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.E.; Mitchell, J. The response of a grey heron Ardea cinerea breeding colony to rapid change in prey species. Bird Study 1995, 42, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.; Persson, A. Do instream habitat variables and the abundance of brown trout Salmo trutta (L.) affect the distribution and growth of stone loach, Barbatula barbatula (L.)? Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2005, 14, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remonti, L.; Prigioni, C.; Balestrieri, A.; Sgrosso, S.; Priore, G. Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) prey selection in response to a variation of fish abundance. Ital. J. Zool. 2010, 77, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty-Bone, T.M.; Dunn, A.M.; Liddell, C.; Brown, L.E. Transformation of detritus by a European native and two invasive alien freshwater decapods. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, K.L.; Rice, S.P.; Wood, P.J. Temporal variability in lotic macroinvertebrate communities associated with invasive signal crayfish (Pacifastacus leniusculus) activity levels and substrate character. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. Streams in Mediterranean Climate Regions: Abiotic Influences and Biotic Responses to Predictable Seasonal Events. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1999, 30, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, A.; Dingsør, G.E.; Huse, G.; Vinther, M.; Floeter, J.; Temming, A. The importance of predator-prey overlap: Predicting North Sea cod recovery with a multispecies assessment model. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosewarne, P.J.; Mortimer, R.J.G.; Newton, R.J.; Grocock, C.; Wing, C.D.; Dunn, A.M. Feeding behaviour, predatory functional responses and trophic interactions of the invasive Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) and signal crayfish (Pacifastacus leniusculus). Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, A.K.; Allendorf, F.W.; Holt, J.S.; Lodge, D.M.; Molofsky, J.; With, K.A.; Baughman, S.; Cabin, R.J.; Cohen, J.E.; Ellstrand, N.C.; et al. The Population Biology of Invasive Species. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondar, C.A.; Bottriel, K.; Zeron, K.; Richardson, J.S. Does trophic position of the omnivorous signal crayfish (Pacifastacus leniusculus) in a stream food web vary with life history stage or density? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 2632–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanden, M.J.V.; Casselman, J.M.; Rasmussen, J.B. Stable isotope evidence for the food web consequences of species invasions in lakes. Nature 1999, 401, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milardi, M.; Thomas, S.M.; Kahilainen, K.K. Reliance of brown trout on terrestrial prey varies with season but not fish density. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanbäck, R.; Persson, L. Individual diet specialization, niche width and population dynamics: Implications for trophic polymorphisms. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedia, I.; Galicia, D.; Baquero, E.; Oscoz, J.; Miranda, R. Environmental factors influencing the distribution and abundance of the introduced signal crayfish in the north of Iberian Peninsula. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.D. On the Relation between Niche Overlap and Competition: The Effect of Incommensurable Niche Dimensions. Oikos 1987, 48, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, A.J. Cobitis calderoni. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2006, e.T5027A11108148. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2006.RLTS.T5027A11108148.en (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Fausch, K.D.; Torgersen, C.E.; Baxter, C.V.; Li, H.W. Landscapes to Riverscapes: Bridging the Gap between Research and Conservation of Stream Fishes. BioScience 2002, 52, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Prey category | % occurrence | % abundance | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL | BQ | ST | GL | PB | PL | BQ | ST | GL | PB | |
| Turbellaria | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | <1 | – | – |
| Nematoda | – | – | 39 | 7 | 2 | – | – | 7 | 1 | <1 |
| Oligochaeta | – | – | 8 | – | – | – | – | <1 | – | – |
| Gastropoda | 4 | – | 8 | 7 | 6 | 1 | – | <1 | <1 | 2 |
| Hydracarina | 9 | – | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | – | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Crustacea 1 | 12 | 32 | 39 | 35 | 10 | 6 | 6 | 46 | 17 | 2 |
| Crayfish | – | – | 1 | 8 | – | – | – | <1 | <1 | – |
| Ephemeroptera 2 | 27 | 64 | 71 | 15 | 23 | 13 | 10 | 26 | <1 | 5 |
| Plecoptera 2 | 1 | 4 | 13 | 2 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Heteroptera adults | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | <1 | – | – |
| Megaloptera larvae | – | – | 1 | – | – | – | – | <1 | – | – |
| Trichoptera larvae | 29 | 56 | 39 | 48 | 45 | 22 | 6 | 15 | 7 | 28 |
| Diptera larvae | 30 | 84 | 24 | 98 | 70 | 53 | 76 | 2 | 66 | 51 |
| Coleoptera larvae | 2 | – | 4 | 2 | 2 | <1 | – | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Terrestrial Arthropoda 3 | 8 | 16 | 22 | 63 | 35 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 9 |
| Fish | – | – | 2 | – | – | – | – | <1 | – | – |
| Schoener Index | – | 0.77 | 0.39 | 0.69 | 0.84 | |||||
| Town | River | Species | n | δ13C | δ15N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zuñiga (1) | Ega | P. leniusculus | 5 | −28.9 ± 0.3 | 9.9 ± 0.6 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −29.7 ± 0.3 * | 10.5 ± 0.5 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −29.7 ± 0.7 | 11.5 ± 0.7 * | ||
| G. lozanoi | 5 | −28.9 ± 0.7 | 11.1 ± 0.2 * | ||
| Artavia (2) | Urederra | P. leniusculus | 5 | −32.6 ± 0.4 | 6.9 ± 0.7 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −33.2 ± 0.3 * | 7.3 ± 0.2 | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −33.4 ± 0.7 | 7.6 ± 0.7 | ||
| B. quignardi | 5 | −33.0 ± 0.3 | 7.5 ± 0.3 | ||
| Ziordia (3) | Ega | P. leniusculus | 5 | −27.5 ± 0.2 | 9.0 ± 1.1 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −27.7 ± 0.7 | 10.5 ± 0.8 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −27.6 ± 0.6 | 11.5 ± 1.4 * | ||
| B. quignardi | 5 | −28.1 ± 1.0 | 12.2 ± 0.4 * | ||
| Lizarragabengoa (4) | Lizarrusti | P. leniusculus | 5 | −26.6 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 1.0 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −27.4 ± 0.8 | 6.0 ± 1.4 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −29.2 ± 0.7 * | 5.4 ± 0.5 * | ||
| Udabe (5) | Basaburua | P. leniusculus | 5 | −26.6 ± 0.5 | 7.5 ± 0.5 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −27.9 ± 0.7 * | 8.7 ± 0.5 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −27.9 ± 0.6 * | 8.8 ± 0.5 * | ||
| Latasa (6) | Larraun | P. leniusculus | 5 | −26.0 ± 0.1 | 9.8 ± 0.5 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −26.2 ± 0.6 | 10.8 ± 0.4 * | ||
| G. lozanoi | 5 | −25.6 ± 0.5 | 10.4 ± 0.1 | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −26.3 ± 0.5 | 10.6 ± 0.2 * | ||
| P. miegii | 5 | −24.8 ± 0.5 * | 9.4 ± 0.1 | ||
| Oskia (7) | Arakil | P. leniusculus | 5 | −26.8 ± 0.3 | 12.0 ± 0.7 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −28.2 ± 0.9 * | 13.9 ± 0.7 * | ||
| P. miegii | 5 | −26.7 ± 1.1 | 13.2 ± 0.3 * | ||
| Iraizoz (8) | Ulzama | P. leniusculus | 5 | −24.0 ± 0.3 | 8.0 ± 0.4 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −24.0 ± 0.6 | 10.4 ± 0.4 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −23.7 ± 0.5 | 10.4 ± 0.7 * | ||
| Latasa (9) | Ulzama | P. leniusculus | 5 | −25.0 ± 0.1 | 10.6 ± 0.5 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −25.2 ± 0.4 | 13.8 ± 1.6 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −25.7 ± 0.3 * | 10.7 ± 1.0 | ||
| Urtasun (11) | Arga | P. leniusculus | 5 | −27.8 ± 0.4 | 7.1 ± 1.0 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −23.9 ± 0.3 * | 8.1 ± 0.3 | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −24.8 ± 1.7 * | 7.5 ± 0.2 | ||
| Idoi (12) | Arga | P. leniusculus | 5 | −25.2 ± 0.3 | 8.9 ± 0.6 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −25.9 ± 0.6 | 9.8 ± 0.3 * | ||
| G. lozanoi | 5 | −24.7 ± 0.5 | 9.8 ± 0.4 | ||
| B. quignardi | 5 | −23.5 ± 0.5 * | 10.4 ± 0.1 * | ||
| Espinal (14) | Urrobi | P. leniusculus | 5 | −25.7 ± 0.3 | 9.7 ± 0.5 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −25.3 ± 1.2 | 12.3 ± 0.6 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −25.5 ± 1.5 | 10.3 ± 1.3 | ||
| Uriz (15) | Urrobi | P. leniusculus | 5 | −25.2 ± 0.6 | 6.9 ± 0.4 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −23.8 ± 1.1 * | 10.3 ± 0.7 * | ||
| Aribe (16) | Irati | P. leniusculus | 5 | −25.6 ± 0.3 | 5.6 ± 0.5 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −25.3 ± 1.0 | 6.8 ± 0.3 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −27.4 ± 1.3 * | 6.3 ± 0.5 | ||
| B. quignardi | 5 | −26.5 ± 0.5 * | 6.5 ± 0.4 * | ||
| Ezcaroz (18) | Salazar | P. leniusculus | 5 | −25.8 ± 0.2 | 8.5 ± 0.4 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −26.5 ± 0.7 | 10.8 ± 0.3 * | ||
| S. trutta | 5 | −26.9 ± 0.7 * | 10.8 ± 1.0 * | ||
| Guesa (19) | Salazar | P. leniusculus | 5 | −26.3 ± 0.7 | 9.0 ± 0.8 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −27.5 ± 0.7 | 10.2 ± 0.5 * | ||
| G. lozanoi | 5 | −25.9 ± 0.8 | 10.7 ± 0.4 * | ||
| Aspurz (20) | Salazar | P. leniusculus | 5 | −28.4 ± 1.0 | 8.2 ± 0.8 |
| P. bigerri | 5 | −28.3 ± 0.5 | 9.4 ± 0.4 * | ||
| G. lozanoi | 5 | −27.3 ± 0.5 | 9.6 ± 0.4 * |
| Species | SEAc (‰2) | Area of Overlap (‰2) |
|---|---|---|
| P. leniusculus | 0.80 ± 0.49 | – |
| B. quignardi | 0.68 ± 0.55 | (2.7 ± 5.4) × 10−4 |
| G. lozanoi | 0.62 ± 0.25 | (1.3 ± 2.6) × 10−2 |
| P. bigerri | 1.05 ± 0.67 | (2.8 ± 3.2) × 10−18 |
| P. miegii | 0.55 ± 0.65 | (4.8 ± 6.7) × 10−18 |
| S. trutta | 2.01 ± 2.00 | 0.1 ± 0.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vedia, I.; Almeida, D.; Rodeles, A.A.; Leunda, P.M.; Baquero, E.; Galicia, D.; Oscoz, J.; Elustondo, D.; Santamaría, J.M.; Miranda, R. Behavioral Interactions and Trophic Overlap between Invasive Signal Crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Decapoda, Astacidae) and Native Fishes in Iberian Rivers. Water 2019, 11, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030459
Vedia I, Almeida D, Rodeles AA, Leunda PM, Baquero E, Galicia D, Oscoz J, Elustondo D, Santamaría JM, Miranda R. Behavioral Interactions and Trophic Overlap between Invasive Signal Crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Decapoda, Astacidae) and Native Fishes in Iberian Rivers. Water. 2019; 11(3):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030459
Chicago/Turabian StyleVedia, Iván, David Almeida, Amaia A. Rodeles, Pedro M. Leunda, Enrique Baquero, David Galicia, Javier Oscoz, David Elustondo, Jesús M. Santamaría, and Rafael Miranda. 2019. "Behavioral Interactions and Trophic Overlap between Invasive Signal Crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Decapoda, Astacidae) and Native Fishes in Iberian Rivers" Water 11, no. 3: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030459
APA StyleVedia, I., Almeida, D., Rodeles, A. A., Leunda, P. M., Baquero, E., Galicia, D., Oscoz, J., Elustondo, D., Santamaría, J. M., & Miranda, R. (2019). Behavioral Interactions and Trophic Overlap between Invasive Signal Crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Decapoda, Astacidae) and Native Fishes in Iberian Rivers. Water, 11(3), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030459







