Spectral Decomposition and a Waveform Cluster to Characterize Strongly Heterogeneous Paleokarst Reservoirs in the Tarim Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
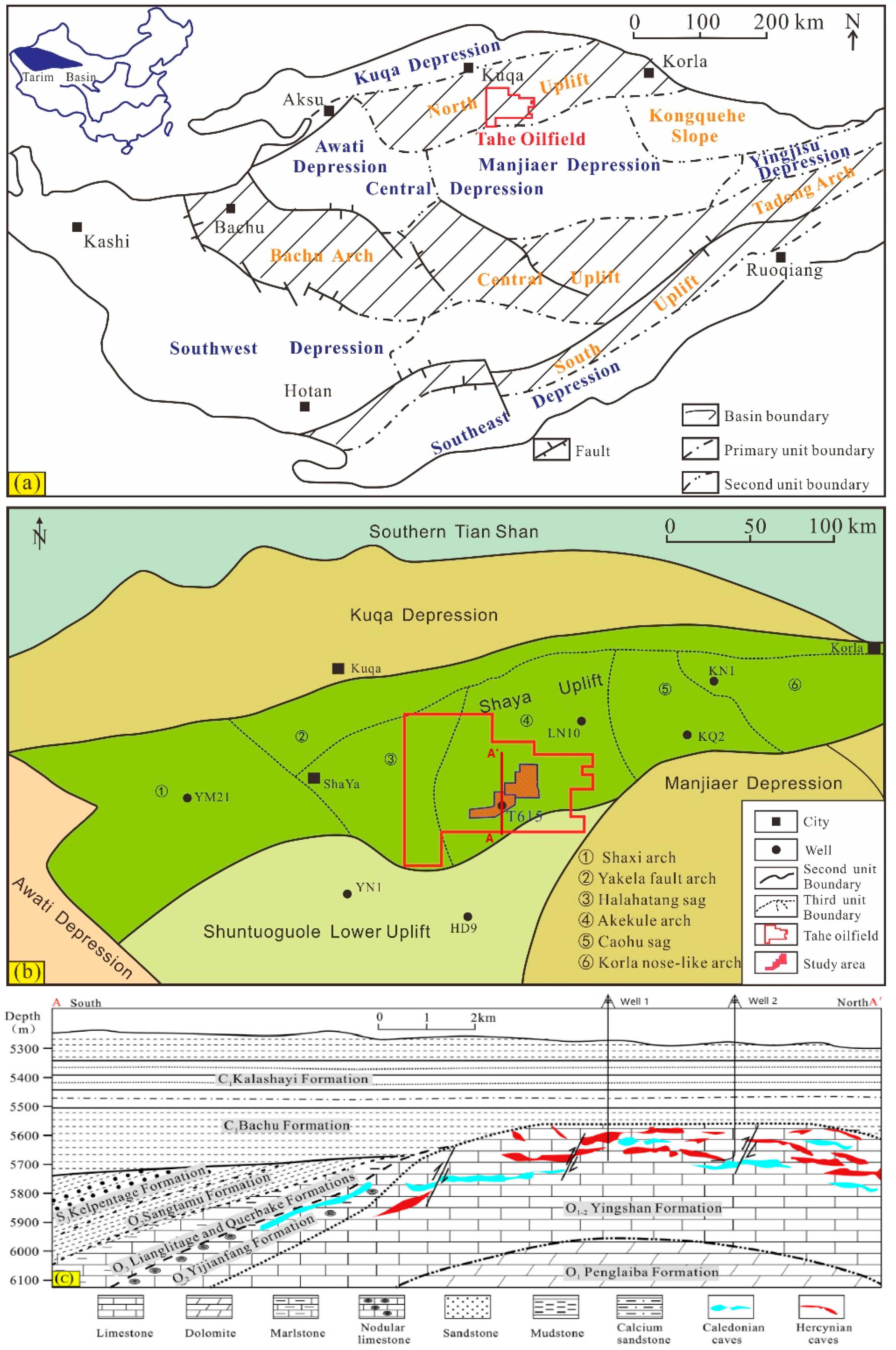
2. Geological Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Spectral Decomposition
3.1.1. Continuous Wavelet Transform
3.1.2. S-Transform
3.1.3. Matching Pursuit
- (1)
- Set the time of the maximum envelope of the complex trace to be the time delay , the instantaneous frequency to be the center frequency , and the instantaneous phase to be the phase .
- (2)
- Then, use Equation (7) to search for the optimal parameter over a group of preselected, uniformly distributed values with fixed values.where denotes the inner product of functions and , and .
- (3)
- Update these four parameters for an optimal wavelet by searching within a range D using Equation (8). The searching range around a parameter is ; for instance, is the time-sampling interval.
- (4)
- After 3, the amplitude of the optimal wavelet is
3.2. Waveform Cluster
- (1)
- Select the time window to extract the waveforms, where is the th waveform in the time window, is the time sampling number, and is the number of waveforms;
- (2)
- Select appropriate values for and and a small positive number . Initialize the prototype matrix M randomly and set the step variable t = 0.
- (3)
- Calculate (at t = 0) or update (at t > 0) the membership matrix by:
- (4)
- Update the prototype matrix M by:
- (5)
- Repeat steps 2–3 until . The th waveform is assigned to the th cluster if is the maximum of all
4. Results and Discussions
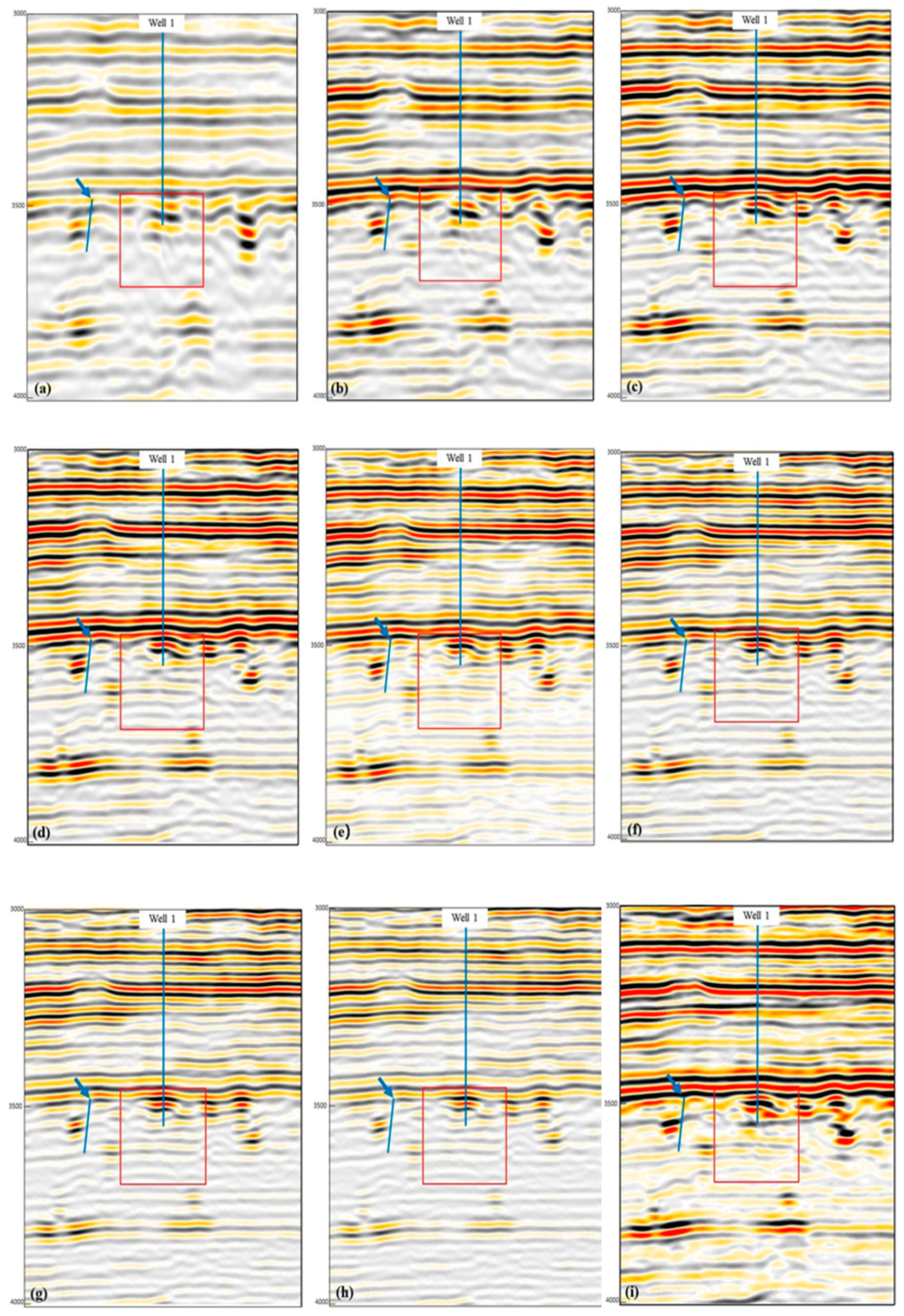
4.1. Choose the Reservoir-Sensitive Single-Frequency Data
- (1)
- The signal-to-noise ratio is significantly improved;
- (2)
- The recognition of small-scale caves and fractures is obviously improved, the energy is more concentrated, and the cave’s edge is much clearer (shown in the red box in Figure 5e);
- (3)
- Small fractures, such as the one marked by the blue arrow in Figure 5e, are clearer; and
- (4)
- The continuity of strata around the fracture-cavity reservoir is greatly increased.
4.2. Verification of the Sensitive Single-Frequency Data
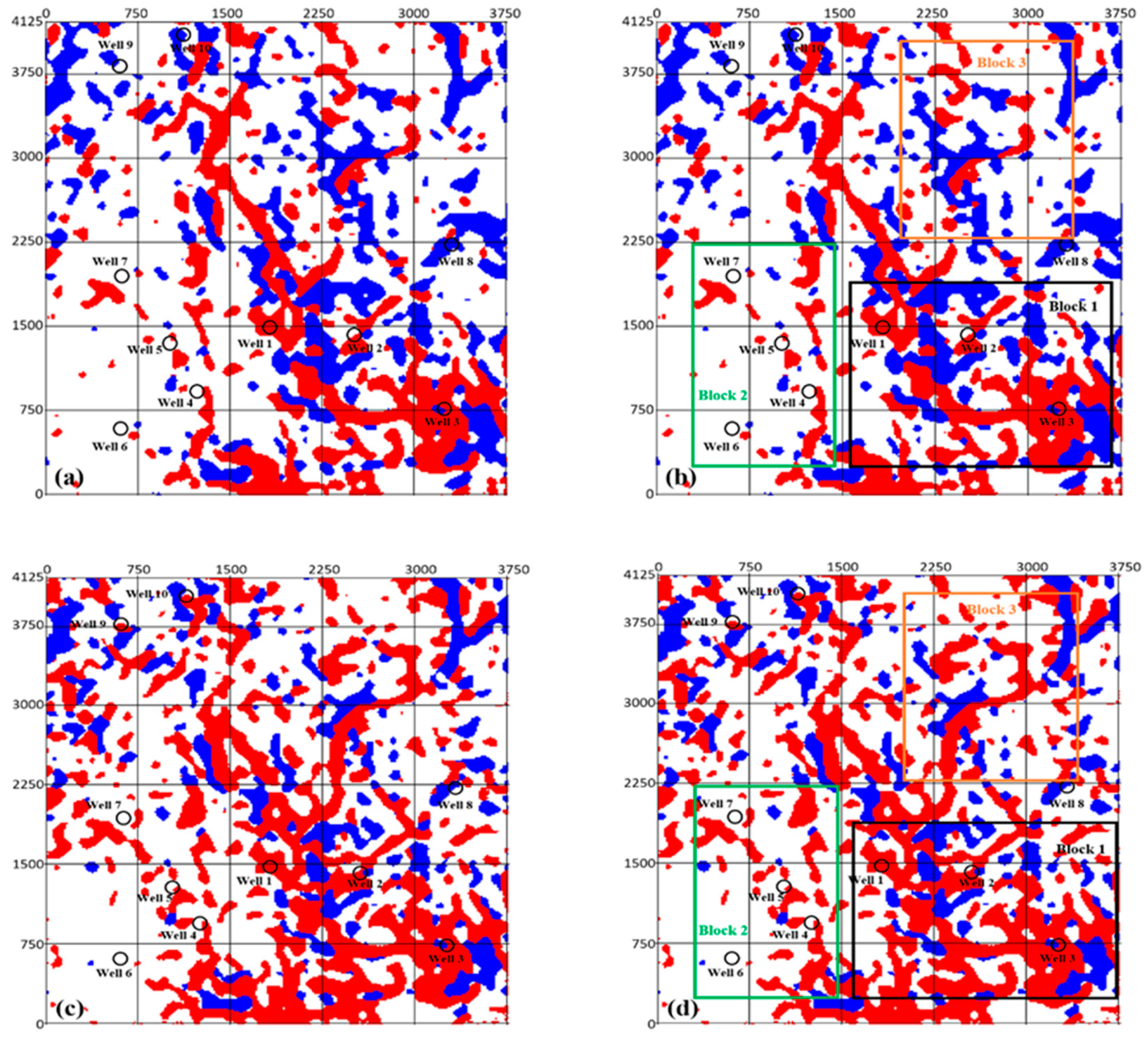
4.3. Characterization of the Reservoir Distribution by a Waveform Cluster
- (1)
- The connectivity between wells is much better, such as the connection between Well 1, Well 2, and Well 3 in Block 1, and Well 4, Well 5, and Well 6 in Block 2. The river connectivity in Block 3 is significantly improved and the river width is widened. Previous studies on the karst development [2,3,14,46,88] and the actual drilling process show that Well 1 and Well 2 have a certain degree of connectivity (Figure 7d), which is not shown in the clustering results of the full-band data (Figure 7b). The near-shore karst platform and gentle karst slopes of the ancient channel were formed by strong hydrodynamic erosion, which can easily form a pipeline system “crossing the mountain”. The pipeline system is less damaged by the filling in the later stage, and the formed oil and gas reservoirs are larger. An increase in the connectivity of the paleo-channel may indicate a corresponding increase in reservoir connectivity.
- (2)
- The portrayed trend in channels is more obvious. Well 4, Well 5, and Well 7 in Block 2 of Figure 7b are randomly distributed, which suggests that there is no connection between them. The connectivity in Block 2 of Figure 7d is better and the trend in channels is more obvious, which indicate that a small channel branch may have formed. This provides a new perspective for understanding the crack caves in the Tahe Oilfield.
4.4. Geological and Geophysical Interpretation of the Reservoir
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Su, J.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Y. Secondary alteration to ancient oil reservoirs by late gas filling in the Tazhong area, Tarim Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 122, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Jin, Q.; Lu, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, H.; Rong, Y.; Liu, N. Multi-layered ordovician paleokarst reservoir detection and spatial delineation: A case study in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, Western China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 69, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Lu, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, H.; Rong, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, N. Structure and filling characteristics of paleokarst reservoirs in the Northern Tarim basin, revealed by outcrop, core and borehole images. Open Geosci. 2017, 9, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Classification and characteristics of karst reservoirs in china and related theories. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2009, 36, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xue, F.; Pan, W.; Chen, L.; Yang, P.; Tong, Y. Seismic description of karst topography and caves of Ordovician carbonate reservoirs, Lungu area, Tarim Basin, West China. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstract 2010; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010; pp. 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Loucks, R.; Janson, X.; Wang, G.; Xia, Y.; Yuan, B.; Xu, L. Three-dimensional seismic geomorphology and analysis of the Ordovician paleokarst drainage system in the central Taber Uplift, northern Tarim Basin, western China. AAPG Bull. 2011, 95, 2061–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Sun, Y.; Sullivan, C.; Guo, H. Paleokarst system development in the san andres formation, permian basin, revealed by seismic characterization. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y. High-frequency anomalies in carbonate reservoir characterization using spectral decomposition. Geophysics 2011, 76, v47–v57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdangkoo, R.; Abdideh, M. Application of wavelet transform to detect fractured zones using conventional well logs data (Case study: Southwest of Iran). Int. J. Pet. Eng. 2016, 2, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lu, W. Coherence attribute at different spectral scales. Interpretation 2014, 2, SA99–SA106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Identification of small-scale carbonate reservoir. In Proceedings of the CPS/SEG Beijing International Geophysical Conference, Beijing, China, 21–24 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Parchkoohi, M.H.; Farajkhah, N.K.; Delshad, M.S. Automatic detection of karstic sinkholes in seismic 3d images using circular hough transform. J. Geophys. Eng. 2015, 12, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Case History Seismic characterization of a carbonate reservoir in Tarim Basin. Geophysics 2017, 82, b177–b188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, F.; Li, X.; Yang, D.; Li, T.; Lv, Y.; He, X. New insights into the carbonate karstic fault system and reservoir formation in the Southern Tahe area of the Tarim Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 86, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdangkoo, R.; Abdideh, M. Fracture density estimation from well logs data using regression analysis: Validation based on image logs (Case study: South West Iran). Int. J. Pet. Eng. 2016, 2, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, X. Characterization of architectural elements of ordovician fractured-cavernous carbonate reservoirs, Tahe Oilfield, China. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 91, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, X.B. A study of the genetics of karst-type subtle reservoir in Tahe oilfield. Petrol. Sci. 2004, 2, 99–104, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.L.; Peng, S.T.; Zhang, T. Controlling factors and genetic pattern of the Ordovician reservoirs in the Tahe area, Tarim Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2010, 31, 743–752, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W. Evaluating the impaction of coal mining on Ordovician KarstWater through statistical methods. Water 2018, 10, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, S.; Su, J.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, L. Alteration and multi-stage accumulation of oil and gas in the Ordovician of the Tabei Uplift, Tarim Basin, NW China: Implications for genetic origin of the diverse hydrocarbons. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 48, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.L. Description and reserves calculation of fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2014, 36, 9–15, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.; Fan, T.; Yin, S.; Gao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yu, C.; Jiang, L. Characterization of carbonate microfacies and reservoir pore types based on formation microImager logging: A case study from the Ordovician in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, China. Interpretation 2017, 6, T71–T82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Di, Q.; Jin, Q.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Niu, C.; Li, Y. Multiscale Geological-Geophysical Characterization of the Epigenic Origin and Deeply Buried Paleokarst System in Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 102, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Deng, Y.; Xu, B.; Dong, J. Bottom water breakthrough prediction in fractured-vuggy reservoirs with bottom water-an example from the well s48 in block 4 of Tahe oilfield. Oil Gas Geol. 2012, 33, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; He, D. Paleozoic fault systems of the Tazhong uplift, Tarim basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 39, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, L.; Cao, Z. Hydrocarbon enrichment pattern and exploration potential of the ordovician in Shunnan area, Tarim basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2014, 35, 788–797, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.X.; Gu, H.; Li, Z.M.; Lu, X.B. Theoretical discussion on resolution of maximum height of cavity in the Tahe oil field based on seismic amplitude. Prog. Geophys. 2008, 23, 1499–1506, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.Z.; Zhou, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z. Fractured reservoir modeling by discrete fracture network and seismic modeling in the Tarim basin, China. Pet. Sci. 2011, 8, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Tian, F. Investigation of fracture-cavity constructions of Ordovician karst reservoirs in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, Western China. J. China Univ. Pet. 2013, 37, 15–21, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.; Xie, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z. Application of water injection curves for the dynamic analysis of fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2018, 169, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Cai, C.; Cai, L.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, L. Origin of sulfides in the middle and lower ordovician carbonates in Tahe oilfield, Tarim basin. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerans, C. Karst-controlled reservoir heterogeneity in Ellenburger group carbonates of west Texas. AAPG Bull. 1988, 72, 1160–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Pang, X. Research processes and main development directions of deep hydrocarbon geological theories. Acta Pet. Sin. 2015, 36, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, L.; Guo, J.; Huang, T. Forming mechanism of hydrocarbon reservoirs in Yingshan Formation of Yuqi block in Akekule arch, Tarim Basin. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2008, 15, 244–250, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.B. Burial dissolution of Ordovician granule limestone in the Tahe Oilfield of the Tarim Basin, NW China, and its geological significance. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2008, 82, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlet, J.; Arens, G.; Fourgeau, E.; Giard, D. Wave propagation and sampling theory—Part II: Sampling theory and complex waves. Geophysics 1982, 47, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partyka, G.; Gridley, J.; Lopez, J. Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Marfurt, K.J. Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-56080-141-2. [Google Scholar]
- Meza, R.; Sierra, A.; Castaqna, J.; Barbato, U. Joint time-variant spectral analysis, part II: A case study. Interpretation 2018, 6, T985–T999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Okaya, D. Frequency-time decomposition of seismic data using wavelet-based methods. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, J.; Oyem, A.; Portniaguine, O.; Aikulola, U. Phase decomposition. Interpretation 2016, 4, SN1–SN10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Qi, J.; Bai, B. Seismic time-frequency decomposition by using a hybrid basis-matching pursuit technique. Interpretation 2016, 4, T239–T248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, F. Seismic spectral decomposition using deconvolutive short-time Fourier transform spectrogram. Geophysics 2013, 78, V43–V51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Routh, P.S.; Anno, P.D.; Castagna, J.P. Spectral decomposition of seismic data with continuous-wavelet transform. Geophysics 2005, 70, P19–P25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.C.; Davogustto, O.; Zhang, K.; Marfurt, K.J. Detecting stratigraphic discontinuities using time-frequency seismic phase residues. Geophysics 2011, 76, P1–P10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, E.; Gao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Generalized S transform and its applications for analysis of seismic thin beds. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstract 2002; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2002; pp. 2217–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthner, M.P.; Oliveira, A.S. Application of S transform in the spectral decomposition of seismic data. In Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society & EXPOGEF, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil, 11–14 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Castagna, J. S-transform and Fourier transform frequency spectra of broadband seismic signals. Geophysics 2017, 82, O71–O81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, J.P.; Sun, S.; Siegfried, R.W. Instantaneous spectral analysis: Detection of low-frequency shadows associated with hydrocarbons. Lead. Edge 2003, 22, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puryear, C.I.; Portniaguine, O.N.; Cobos, C.M.; Castagna, J.P. Constrained least-squares spectral analysis: Application to seismic data. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstract 2012; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyton, L.; Bottjer, R.; Partyka, G. Interpretation of incised valleys using new 3-D seismic techniques: A case history using spectral decomposition and coherency. Lead. Edge 1998, 17, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, K.J.; Kirlin, R.L. Narrow-band spectral analysis and thin-bed tuning. Geophysics 1999, 66, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Seismic time-frequency spectral decomposition by matching pursuit. Geophysics 2007, 72, v13–v20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing, Third Edition: The Sparse Way, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN1 0123743702. ISBN2 9780123743701. [Google Scholar]
- Rioul, O.; Vetterli, M. Wavelets and Signal Processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1991, 8, 14–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlawatsch, F.; Boudreauxbartels, G.F. Linear and quadratic time-frequency signal representations. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1992, 9, 21–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abry, P.; Gonçalvès, P.; Flandrin, P. Wavelet-based spectral analysis of 1/f processes. In Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 27–30 April 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell, R.G.; Mansinha, L.; Lowe, R.P. Localization of the complex spectrum: The S transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 44, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G.; Zhang, Z. Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 1993, 41, 3397–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, N.; Davis, T.L. Spectral Decomposition applied to time-lapse seismic interpretation, Rulison Field, Colorado. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstract 2009; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2009; pp. 3845–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Chen, D. Signal representation using adaptive normalized gaussian functions. Signal Process. 1994, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Neira, L.; Lowe, D. Optimized orthogonal matching pursuit approach. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, E. Independent multiresolution component analysis and matching pursuit. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2003, 42, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrle, M.; Rebollo-Neira, L. A swapping-based refinement of orthogonal matching pursuit strategies. Signal Process. 2006, 86, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrle, M.; Rebollo-Neira, L.; Sagianos, E. Backward-Optimized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Approach. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2004, 11, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, J.P.; Sun, S. Comparison of spectral decomposition methods. First Break 2006, 24, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Djeffal, A. Enhancement of Margrave Deconvolution and Qestimation in Highly Attenuating Media Using the Modified S-Transform. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pinnegar, C.R.; Mansinha, L. The S-transform with windows of arbitrary and varying shape. Geophysics 2003, 68, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnegar, C.R.; Eaton, D.W. Application of the s transform to prestack noise attenuation filtering. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2422–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Castagna, J. Matching Pursuit of Two Dimensional Seismic Data and Its Filtering Application. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstract 2000; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2000; pp. 2067–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Time-Frequency decomposition based on Ricker wavelet. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstract 2004; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2004; pp. 1937–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Marfurt, K.J. Matching pursuit decomposition using Morlet wavelets. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstract 2005; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2005; pp. 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Marfurt, K.J. Instantaneous spectral attributes to detect channels. Geophysics 2007, 72, p23–p31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Multichannel matching pursuit for seismic trace decomposition. Geophysics 2010, 75, V61–V66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, B.; Pennington, W.; He, Z. Relative P-impedance estimation using a dipole-based matching pursuit decomposition strategy. Interpretation 2015, 3, T197–T206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshin, B.M.; Ghazali, A.R.; Amin, Y.K.; Barnes, A.E. Hybrid Waveform Classification Applied to Delineate Compartments in a Complex Reservoir in the Malay Basin. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 10–12 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Basman, Y.V. Seismic waveform classification renewing the interest in Barrolka field, SW Queensland, Cooper Basin. In Proceedings of the ASEG Extended Abstracts 2015: 24th International Geophysical Conference and Exhibition, Perth, Australia, 15–18 February 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- John, A.K.; Lake, L.W.; Torresverdin, C.; Srinivasan, S. Seismic facies identification and classification using simple statistics. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2008, 11, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Matos, M.; Marfurt, K.J. Automatic Seismic Facies Classification with Kohonen Self Organizing Maps—A Tutorial. Geohorizons J. Soc. Pet. Geophys. 2010, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H. Seismic geomorphology-based facies classification. Lead. Edge 2004, 23, 644–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.P.; Cole, D.M. A Comparison of Popular Neural Network Facies-Classification Schemes. Lead. Edge 2017, 36, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-Y.; Weng, L.-S.; University, N.C.T.; Shen, L.-C. Well Log Data Inversion Using Radial Basis Function Network. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; She, B.; Liu, Z.; Su, M.; Hu, G. Supervised Seismic Facies Analysis Using Discrimination Dictionary. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Anaheim, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1585–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-H. Cellular Neural Network for Seismic-Pattern Recognition. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Anaheim, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 2221–2225. [Google Scholar]
- Taherdangkoo, R.; Taherdangkoo, M. Modified Stem Cells Algorithm-Based Neural Network Applied to Bottom Hole Circulating Pressure in Underbalanced Drilling. Int. J. Pet. Eng. 2015, 1, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkidi, M.; Batistakis, Y.; Vazirgiannis, M. On clustering validation techniques. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2001, 17, 107–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wunsch, D. Survey of Clustering Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2005, 16, 645–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W. Integrated Geological-Geophysical Characterizations of Deeply Buried Fractured-Vuggy Carbonate Reservoirs in Ordovician Strata, Tarim Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 99, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Qin, X.; Shan, X.; Yao, X. FDOM conversion in karst watersheds expressed by three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy. Water 2018, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.N. Origin and Morphology of Limestone Caves. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1991, 103, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebreen, H.; Banning, A.; Wohnlich, S.; Niedermayr, A.; Ghanem, M.; Wisotzky, F. The Influence of Karst Aquifer Mineralogy and Geochemistry on Groundwater Characteristics: West Bank, Palestine. Water 2018, 10, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenica, L.; Gotovac, H.; Kamber, G.; Simunovic, S.; Allu, S.; Divic, V. Groundwater Flow Modeling in Karst Aquifers: Coupling 3D Matrix and 1D Conduit Flow via Control Volume Isogeometric Analysis—Experimental Verification with a 3D Physical Model. Water 2018, 10, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Qu, S.; Huang, Q.; Liu, S.; Xu, Q.; Ni, L. A New Perspective to Explore the Hydraulic Connectivity of Karst Aquifer System in Jinan Spring Catchment, China. Water 2018, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Fang, Z.; Yang, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Bu, L.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X. Experimental Study of Influence of Karst Aquifer on the Law of Water Inrush in Tunnels. Water 2018, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D. Characteristics of Dissolutional Cave Systems in Carbonate Rocks. In Paleokarst; James, N.P., Choquette, P.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 25–57. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, T.J. Instantaneous Frequency Spectra. Lead. Edge 2015, 34, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, X.; Tian, F.; Cheng, F.; Yang, C.; Xin, W. Spectral Decomposition and a Waveform Cluster to Characterize Strongly Heterogeneous Paleokarst Reservoirs in the Tarim Basin, China. Water 2019, 11, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020256
Shan X, Tian F, Cheng F, Yang C, Xin W. Spectral Decomposition and a Waveform Cluster to Characterize Strongly Heterogeneous Paleokarst Reservoirs in the Tarim Basin, China. Water. 2019; 11(2):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020256
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Xiaocai, Fei Tian, Fuqi Cheng, Changchun Yang, and Wei Xin. 2019. "Spectral Decomposition and a Waveform Cluster to Characterize Strongly Heterogeneous Paleokarst Reservoirs in the Tarim Basin, China" Water 11, no. 2: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020256
APA StyleShan, X., Tian, F., Cheng, F., Yang, C., & Xin, W. (2019). Spectral Decomposition and a Waveform Cluster to Characterize Strongly Heterogeneous Paleokarst Reservoirs in the Tarim Basin, China. Water, 11(2), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020256





