Evaluation of Fengyun-3C Soil Moisture Products Using In-Situ Data from the Chinese Automatic Soil Moisture Observation Stations: A Case Study in Henan Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
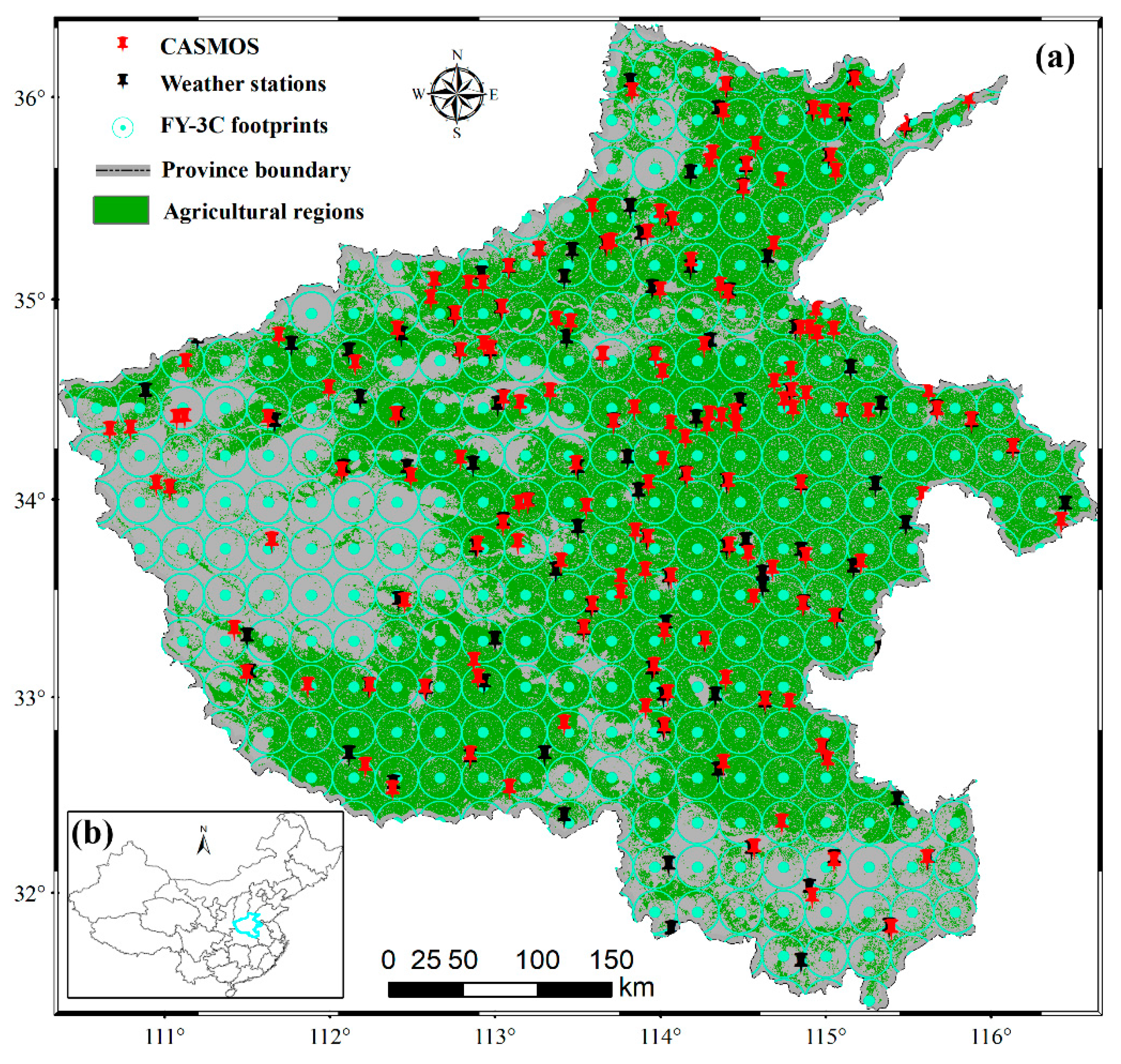
2.1. Study Area
2.2. FY-3C L2 Soil Moisture Product
2.3. AMSR2 and SMAP Soil Moisture Products
2.4. In Situ Soil Moisture Measurements
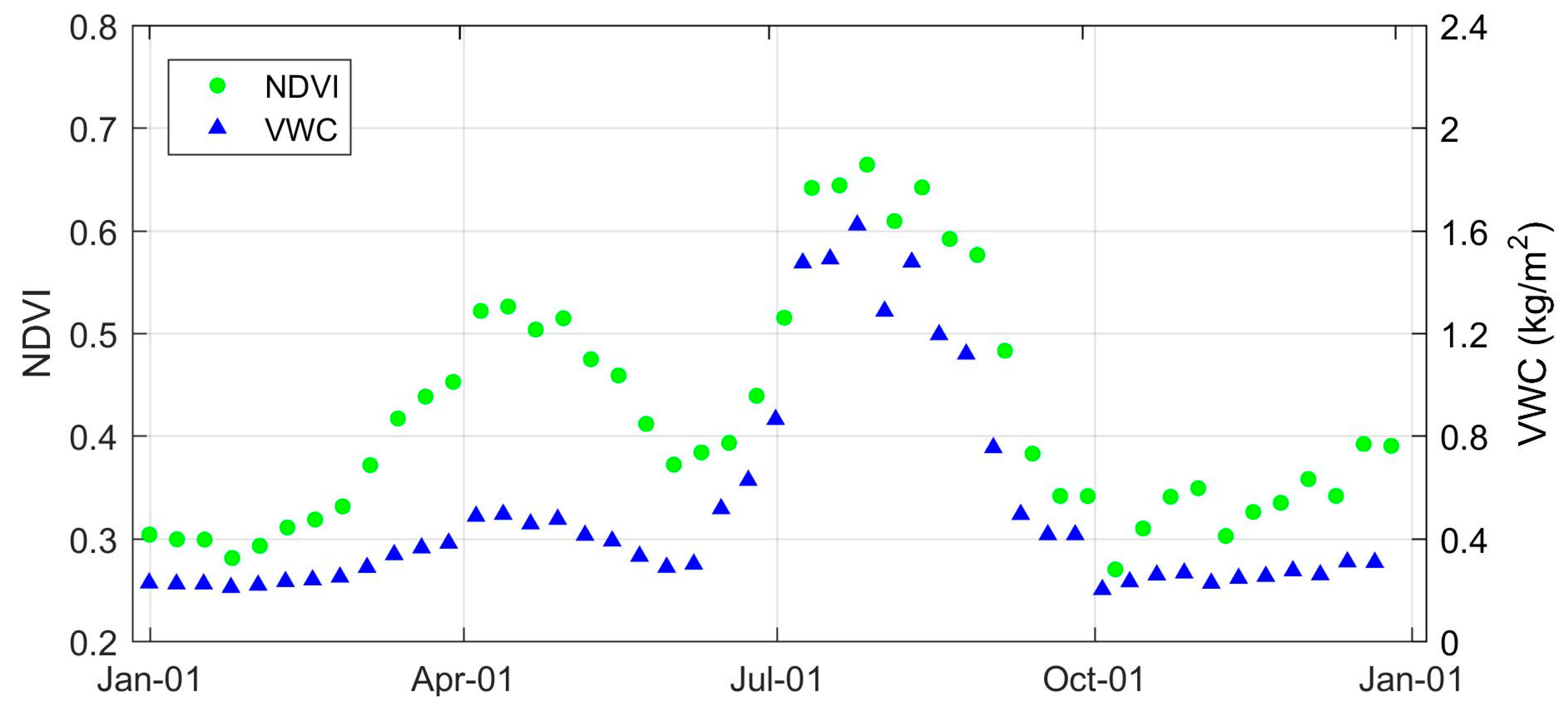
2.5. MODIS NDVI and Precipitation Data
3. Methodology
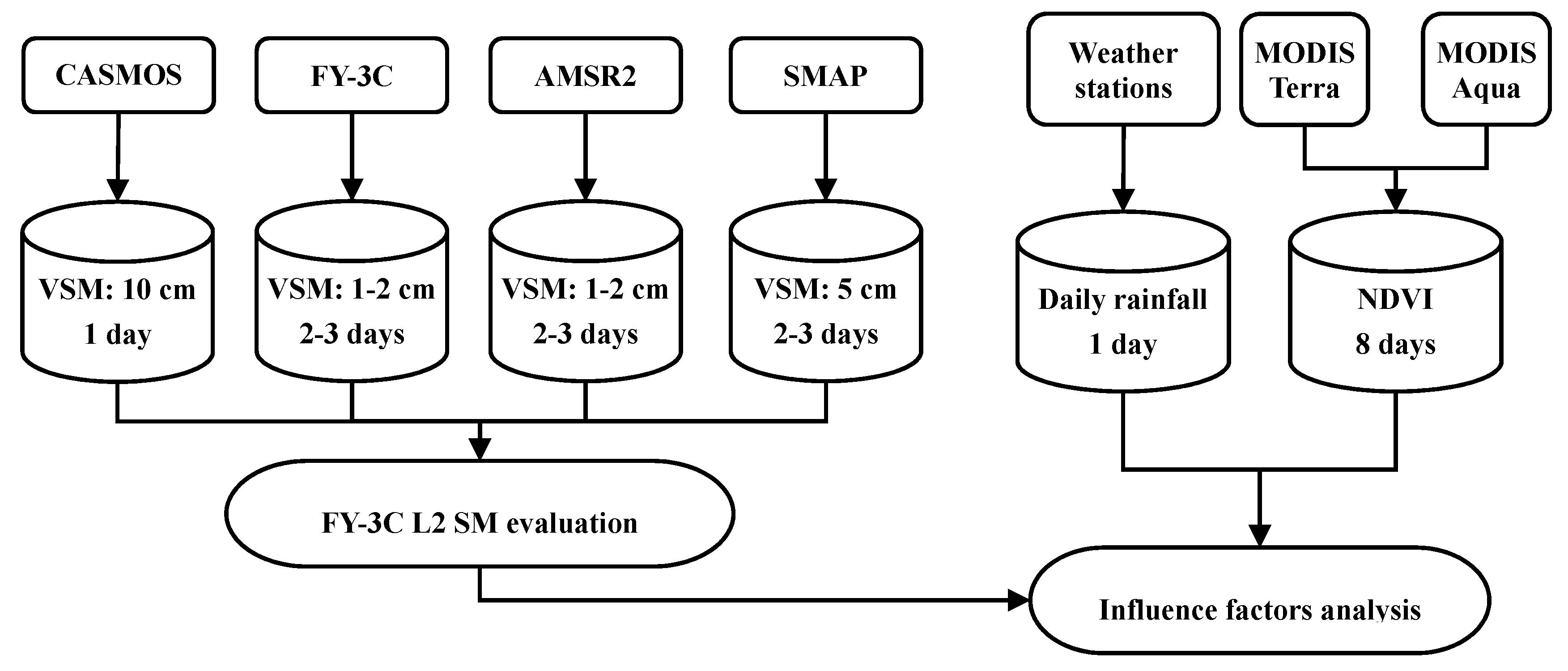
3.1. Study Framework and Data Integration
3.2. Four Statistical Indicators
4. Results
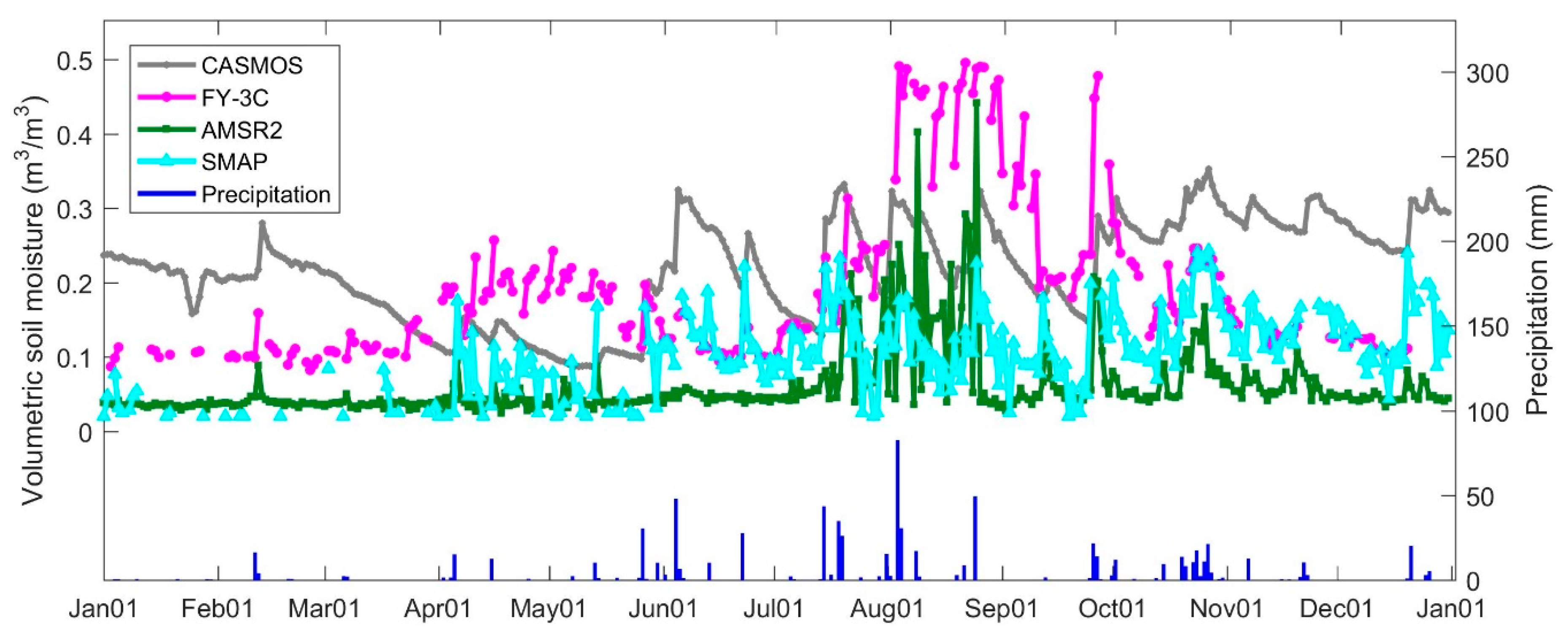
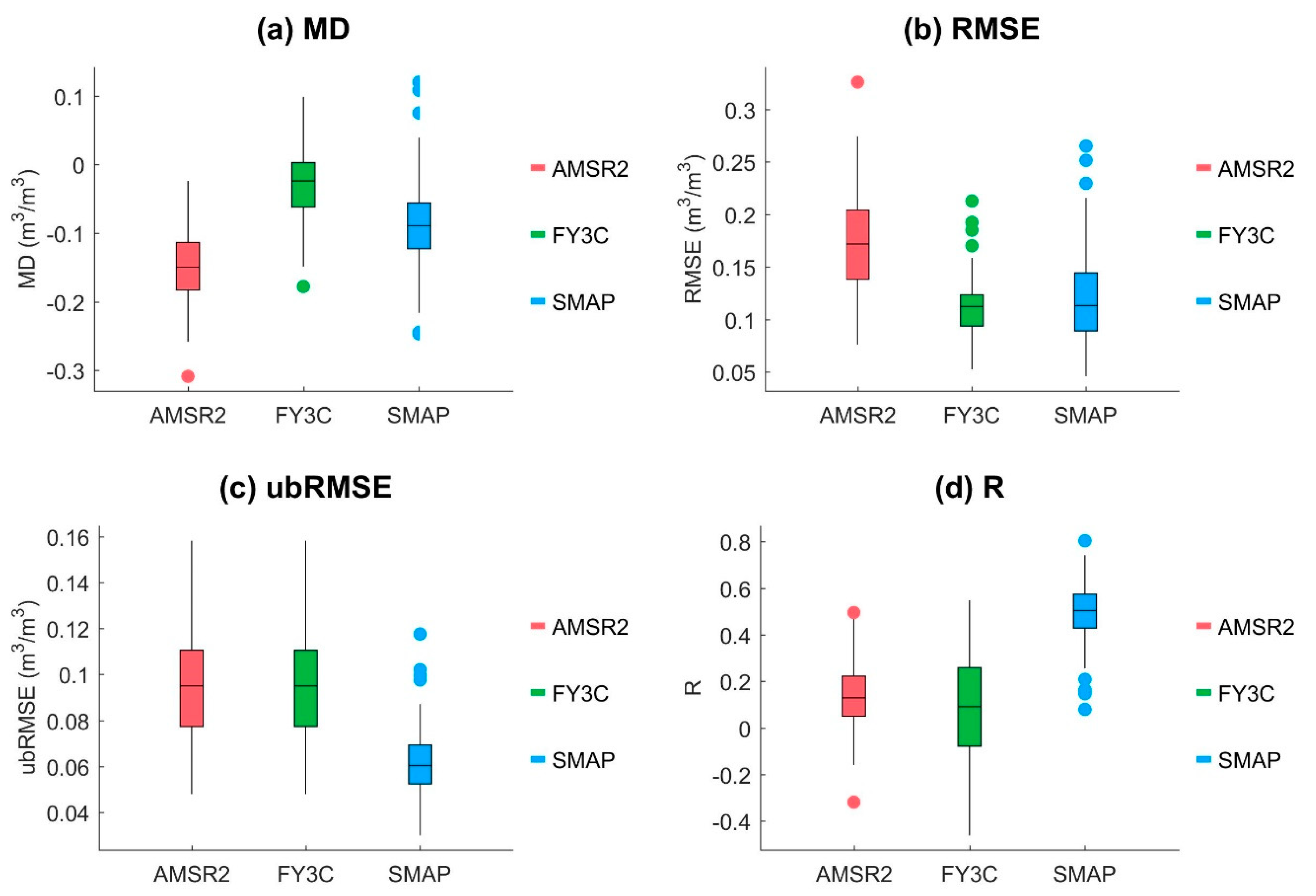
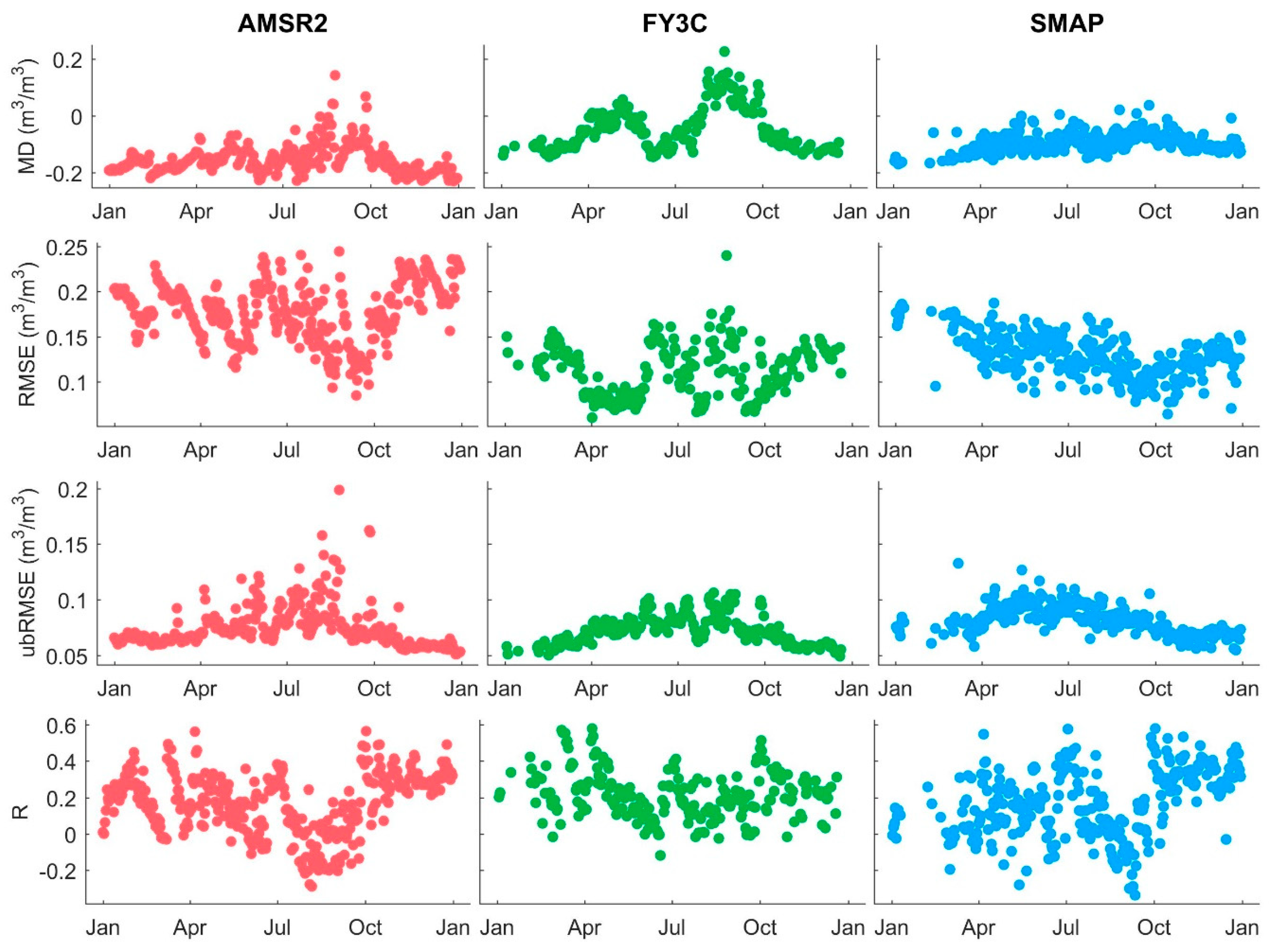
4.1. Temporal Performance for Different Footprints
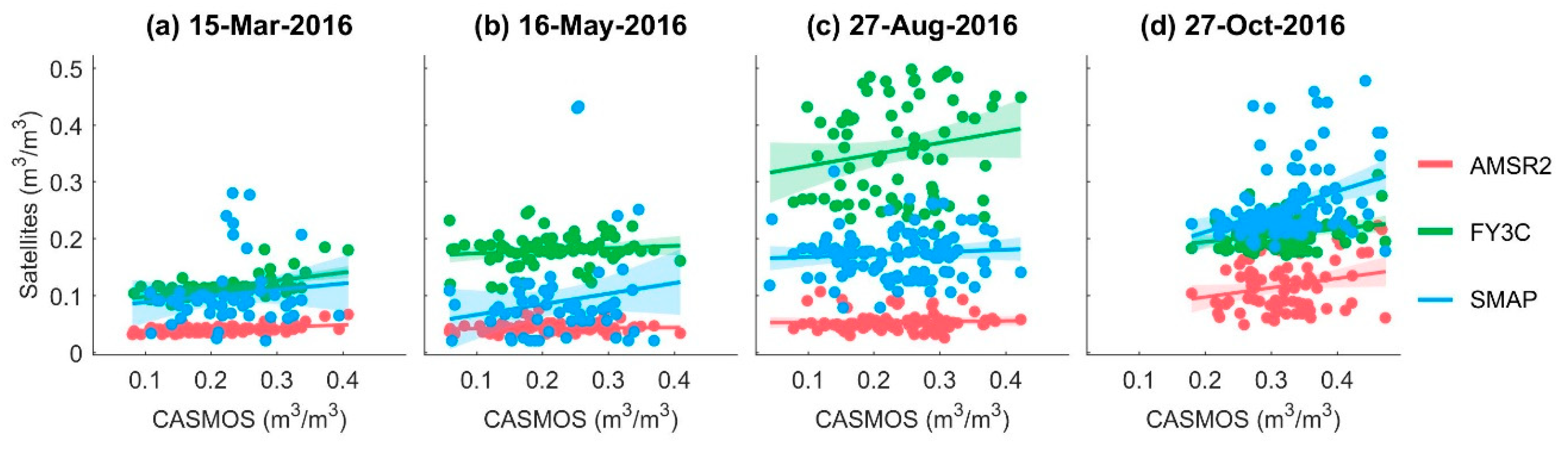
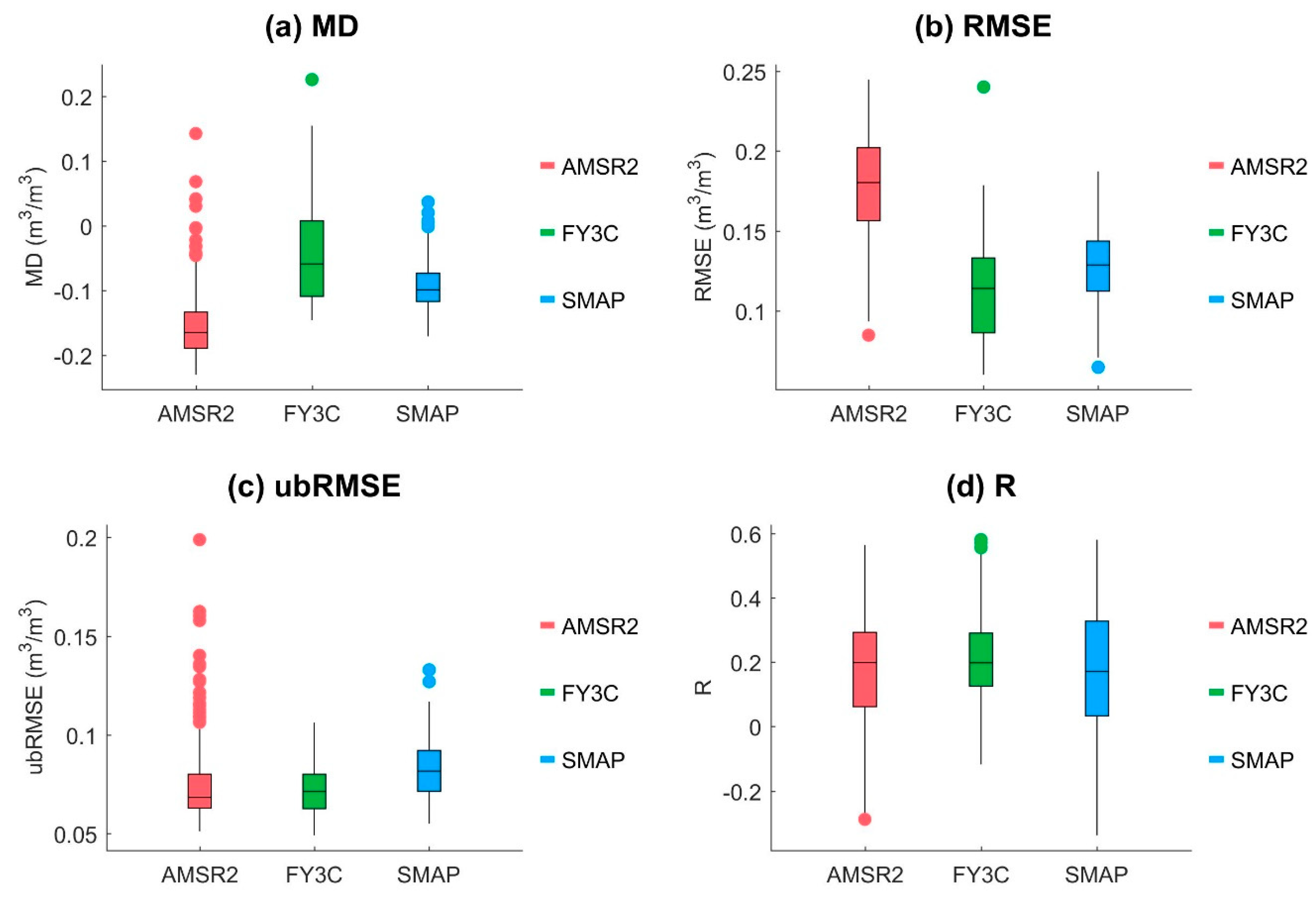
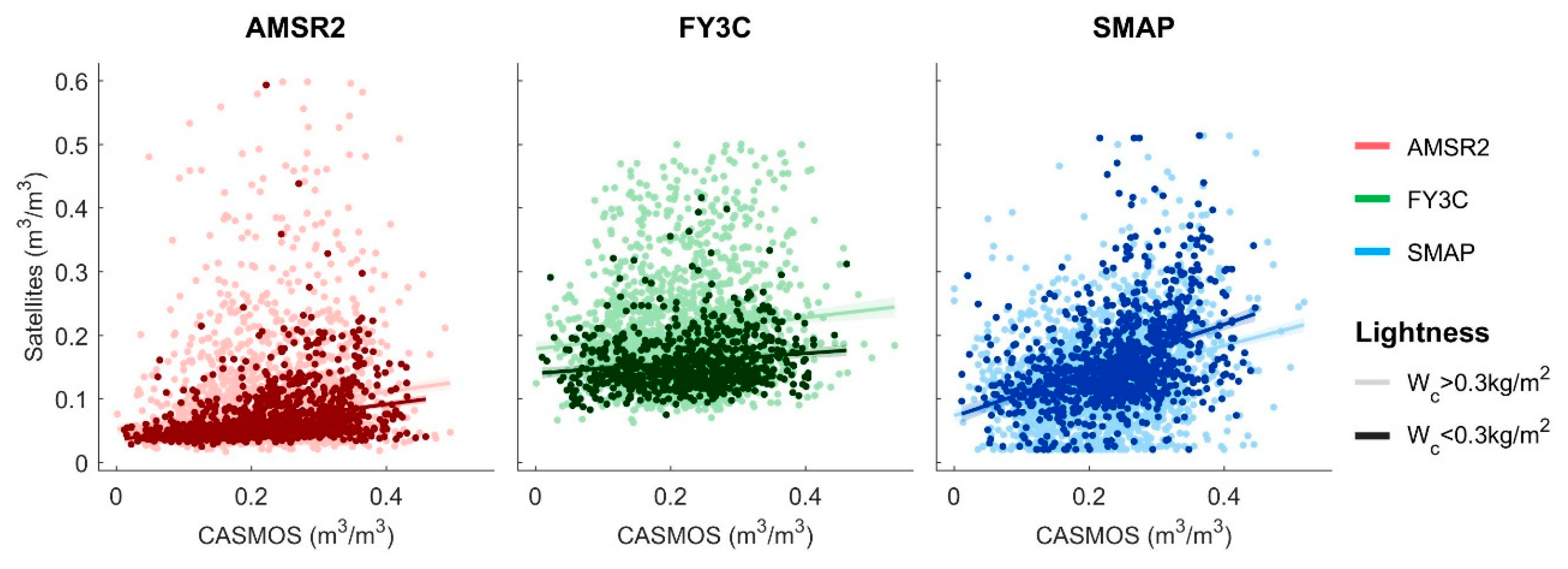
4.2. Spatial Performance At Different Times
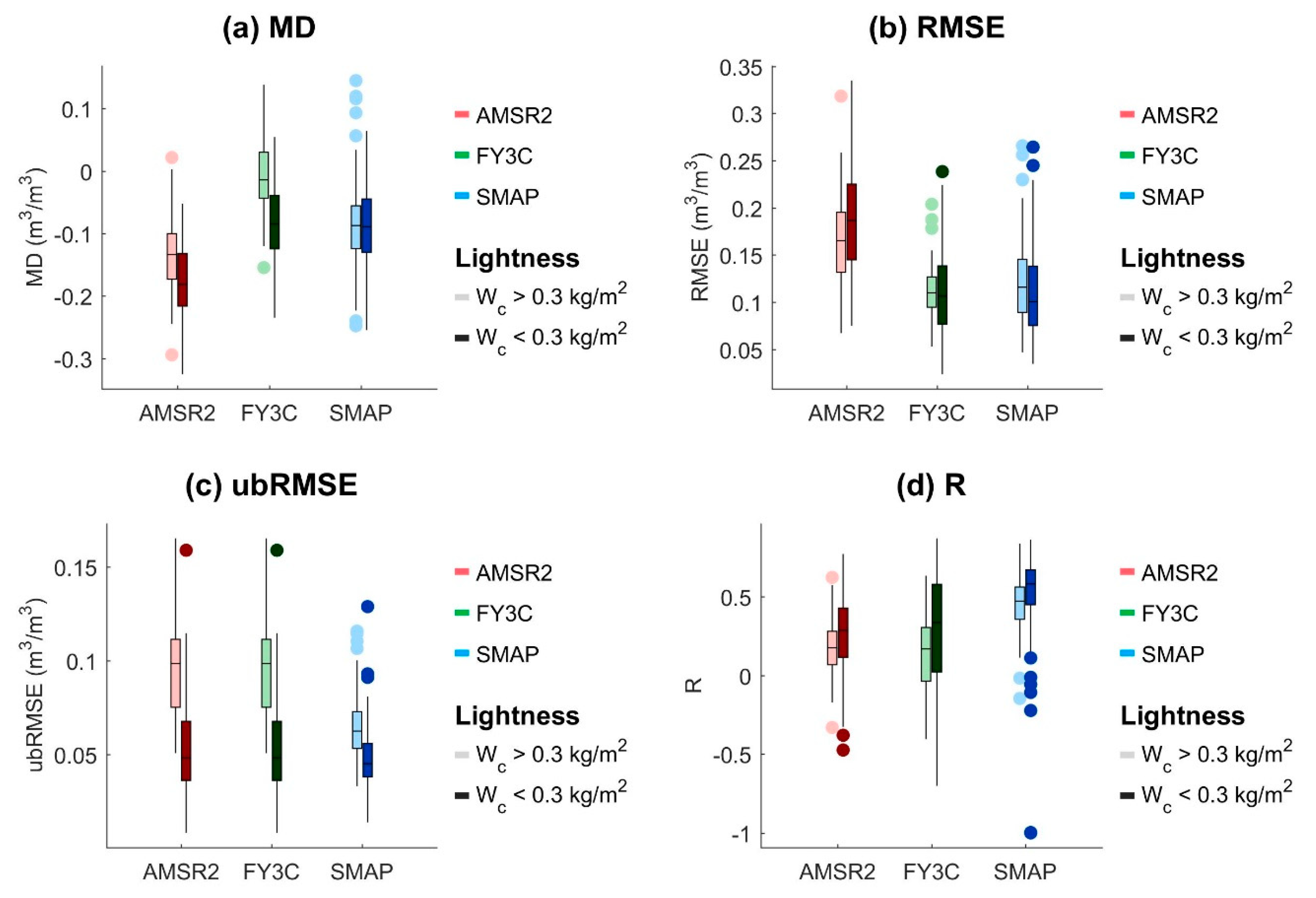
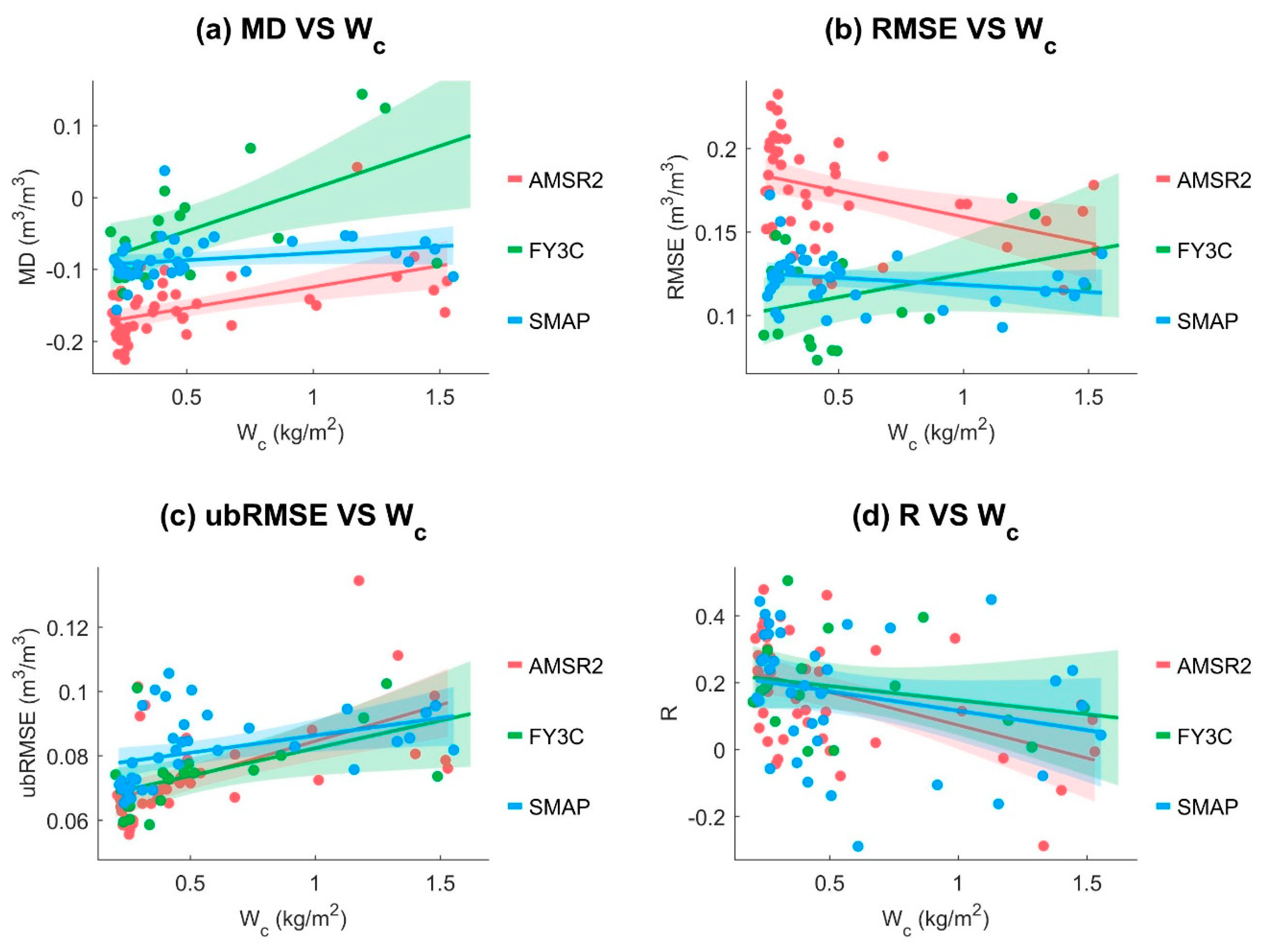
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makkeasorn, A.; Chang, N.B.; Beaman, M.; Wyatt, C.; Slater, C. Soil moisture estimation in a semiarid watershed using radarsat-1 satellite imagery and genetic programming. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W09401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, P.; Shao, Y.; Gao, S. Validation analysis of smap and amsr2 soil moisture products over the united states using ground-based measurements. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Deng, C. Evaluation of amsr2 soil moisture products over the contiguous united states using in situ data from the international soil moisture network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Pan, M.; Wanders, N.; Kumar, D.N.; Wood, E.F. Four decades of microwave satellite soil moisture observations: Part 1. A review of retrieval algorithms. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 109, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.S.; Kanniah, K.D.; Kerr, Y.H.; Cracknell, A.P. Analysis of in-situ soil moisture data and validation of smos soil moisture products at selected agricultural sites over a tropical region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3636–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Richaume, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mahmoodi, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Gruhier, C.; Juglea, S.E. The smos soil moisture retrieval algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1384–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J. The soil moisture active passive (smap) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, T.; Sezai, T.; Ito, Y.; Imaoka, K.; Takeshima, T.; Ishido, Y.; Shibata, A.; Miura, M.; Inahata, H.; Spencer, R.W. The advanced microwave scanning radiometer for the earth observing system (amsr-e), NASDA’S contribution to the eos for global energy and water cycle studies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.K.; Nghiem, S.V. Soil moisture retrieval from amsr-e. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaoka, K.; Kachi, M.; Kasahara, M.; Ito, N.; Nakagawa, K.; Oki, T. Instrument performance and calibration of amsr-e and amsr2. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, J.; Dong, C.; Lu, N.; Yang, Z.; Shi, J. General introduction on payloads, ground segment and data application of fengyun 3a. Front. Earth Sci. China 2009, 3, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, P.; Lu, N.; Yang, Z.; Shi, J.; Dong, C. Improvements on global meteorological observations from the current fengyun 3 satellites and beyond. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2012, 5, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinussa, R.; Wang, G.; Holmes, T.; Liu, Y.; Dolman, A.; De Jeu, R.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, P.; Shi, J. Global surface soil moisture from the microwave radiation imager onboard the fengyun-3b satellite. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 7007–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.A.; Scipal, K.; Parinussa, R.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wagner, W.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Naeimi, V. Error characterisation of global active and passive microwave soil moisture data sets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2010, 7, 5621–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Karssenberg, D.; Bierkens, M.; Parinussa, R.; de Jeu, R.; van Dam, J.; de Jong, S. Observation uncertainty of satellite soil moisture products determined with physically-based modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mo, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, Z.; Hu, S. Validation and trend analysis of ecv soil moisture data on cropland in north china plain during 1981–2010. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 48, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.P.; Ireland, G.; Srivastava, P.K.; Ioannou-Katidis, P. An appraisal of the accuracy of operational soil moisture estimates from smos miras using validated in situ observations acquired in a mediterranean environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5239–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Hasenauer, S.; Lacava, T.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Wagner, W.; Dorigo, W.; Matgen, P.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Llorens, P. Soil moisture estimation through ascat and amsr-e sensors: An intercomparison and validation study across europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3390–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, I.; Lakshmi, V.; Jackson, T.J.; Walker, J.P.; Merlin, O.; de Jeu, R.A. Validation of amsr-e soil moisture using l-band airborne radiometer data from national airborne field experiment 2006. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Cosh, M.H.; Zhao, T.; Starks, P.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Seyfried, M.; Moran, M.S.; Goodrich, D.C.; Kerr, Y.H. Validation of soil moisture and ocean salinity (smos) soil moisture over watershed networks in the us. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1530–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Ducharne, A.; Kerr, Y.; De Rosnay, P.; De Jeu, R.; Govind, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Albergel, C.; Munoz-Sabater, J. Global-scale evaluation of two satellite-based passive microwave soil moisture datasets (smos and amsr-e) with respect to land data assimilation system estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zou, X.; Yang, H.; Weng, F. Estimation and correction of geolocation errors in fengyun-3c microwave radiation imager data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zou, X.; Weng, F. Cloud and precipitation features of super typhoon neoguri revealed from dual oxygen absorption band sounding instruments on board fengyun-3c satellite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J., III. Measuring surface soil moisture using passive microwave remote sensing. Hydrol. Process. 1993, 7, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, K.-S.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Chanzy, A. A parameterized multifrequency-polarization surface emission model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, K.-S.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Chanzy, A.; Jackson, T.J. Physically based estimation of bare-surface soil moisture with the passive radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3145–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Cosh, M.H.; Bindlish, R.; Starks, P.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Seyfried, M.; Goodrich, D.C.; Moran, M.S.; Du, J. Validation of advanced microwave scanning radiometer soil moisture products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4256–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Xu, J.; Zeng, J.; Chen, K.-S.; Bai, X.; Lu, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, T. Soil moisture mapping from satellites: An intercomparison of smap, smos, fy3b, amsr2, and esa cci over two dense network regions at different spatial scales. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yu, D.; Warner, E.; Pan, X.; Petersen, G.; Gong, Z.; Weindorf, D. Soil database of 1: 1,000,000 digital soil survey and reference system of the chinese genetic soil classification system. Soil Horiz. 2004, 45, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, W.; Dai, Y.; Liu, B.; Ye, A.; Yuan, H. A soil particle-size distribution dataset for regional land and climate modelling in china. Geoderma 2012, 171, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.; Brodzik, M. An earth-gridded SSM/I data set for cryospheric studies and global change monitoring. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 16, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J. The application of fy3/mwri soil moisture product in the summer drought monitoring of middle China. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 2967–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.R.; Schmugge, T.J. An empirical model for the complex dielectric permittivity of soils as a function of water content. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1980, 18, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Koike, T.; Imaoka, K. Improvement of the amsr-e algorithm for soil moisture estimation by introducing a fractional vegetation coverage dataset derived from modis data. J. Remote Sens. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 29, 282–292. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.; Moon, H.; Choi, M. First assessment of the advanced microwave scanning radiometer 2 (amsr2) soil moisture contents in northeast asia. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2015, 93, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G. An algorithm for merging smap radiometer and radar data for high-resolution soil-moisture retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Das, N.; Kim, S.; Cosh, M.; Dunbar, R.; Dang, L.; Pashaian, L. Validation of smap surface soil moisture products with core validation sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD): L2/3_sm_p, nat. Aeronaut. Space Admin; Jet Propulsion Lab.: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Gao, T.; Xue, H. The study of quality control for observing data of automatic soil moisture. Hans J. Soil Sci. 2016, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liang, H.; Cao, T.; Yang, D.; Wei, Z.; Wu, X. Construction of operation monitoring system of automatic soil moisture observation network in china. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.Q.; Ye, L.M. Dzn2 automatic soil moisture observation system based on gprs transmission. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 341–342, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longqin, X.; Haibo, C.; Likui, S. Construction and operation management of automatic soil moisture observation station network in henan province. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 34, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; van Leeuwen, W.; Miura, T.; Glenn, E. Modis vegetation indices. In Land Remote Sensing and Global Environmental Change; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 579–602. [Google Scholar]
- Lunetta, R.S.; Knight, J.F.; Ediriwickrema, J.; Lyon, J.G.; Worthy, L.D. Land-cover change detection using multi-temporal modis ndvi data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the modis vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Walker, J.P.; Allahmoradi, M.; Monerris, A.; Ryu, D.; Jackson, T.J. Optical sensing of vegetation water content: A synthesis study. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, W.; Scipal, K.; Pathe, C.; Gerten, D.; Lucht, W.; Rudolf, B. Evaluation of the agreement between the first global remotely sensed soil moisture data with model and precipitation data. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Yueh, S.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Allen, A.; Bindlish, R.; Brown, M.; Chan, S.; Colliander, A.; Crow, W.T. Smap Handbook–Soil Moisture Active Passive: Mapping Soil Moisture and Freeze/Thaw from Space; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kaihotsu, I.; Fujii, H.; Koike, T. Preliminary Evaluation of AMSR2 l3 Soil Moisture Products Using In Situ Observation Data in Mongolia. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 Decembe 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Bi, H.; Qiu, J.; Zou, P. Evaluation of remotely sensed and reanalysis soil moisture products over the tibetan plateau using in-situ observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.S.; Walker, J.P.; Rüdiger, C.; Parinussa, R.M.; Koike, T.; Kerr, Y.H. A comparison of smos and amsr2 soil moisture using representative sites of the oznet monitoring network. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Yi, G.; Zhang, T.; Miao, J.; Li, J.; Bie, X. Temporal and spatial characteristics of evi and its response to climatic factors in recent 16 years based on grey relational analysis in inner mongolia autonomous region, china. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Hohensinn, R.; Hahn, S.; Paulik, C.; Xaver, A.; Gruber, A.; Drusch, M.; Mecklenburg, S.; van Oevelen, P. The international soil moisture network: A data hosting facility for global in situ soil moisture measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1675–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, T.; Choudhury, B.; Schmugge, T.; Wang, J.; Jackson, T. A model for microwave emission from vegetation-covered fields. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 11229–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Blöschl, G.; Pampaloni, P.; Calvet, J.-C.; Bizzarri, B.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Kerr, Y. Operational readiness of microwave remote sensing of soil moisture for hydrologic applications. Hydrol. Res. 2007, 38, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, J.-C.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Walker, J.; Karbou, F.; Chanzy, A.; Albergel, C. Sensitivity of passive microwave observations to soil moisture and vegetation water content: L-band to w-band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Tsutsui, H.; Koike, T. Ground truth of passive microwave radiative transfer on vegetated land surfaces. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
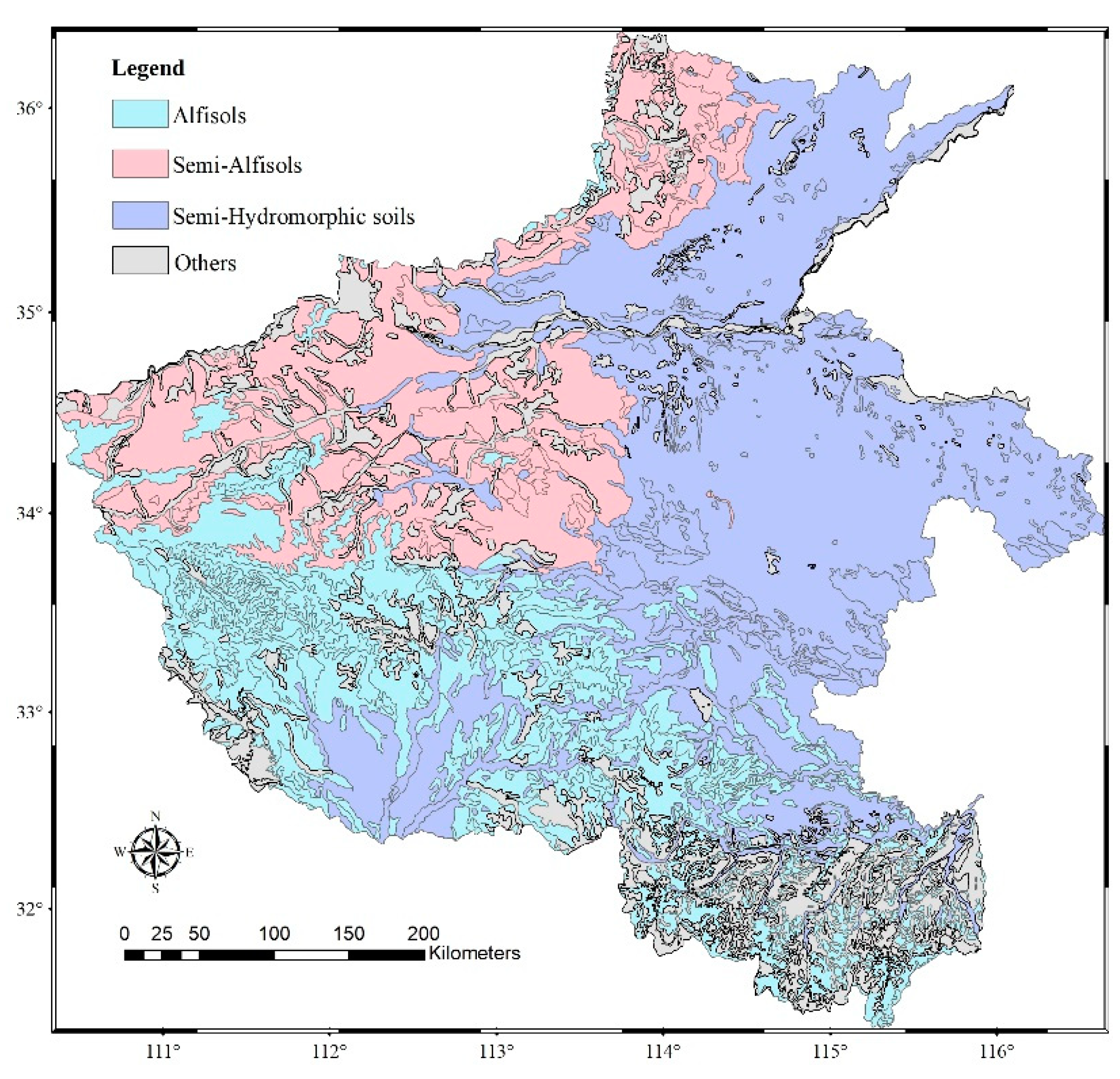

| Soil Type (Order) | Areal Fraction | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfisols | 23.4% | 10.8–19.4 | 18.5–32.6 | 34.0–60.2 |
| Semi-Alfisols | 18.0% | 16.7–25.3 | 25.4–36.6 | 37.2–65.6 |
| Semi-Hydromorphic soils | 41.6% | 25–35.4 | 20.0–37.6 | 35.4–54.0 |
| Others | 17.0% | - | - | - |
| Frequency (GHz) | Polarization | Bandwidth (MHz) | Sensitivity (K) | IFOV km × km | Pixel Size km × km |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.65 | V/H | 180 | 0.5 | 51 × 85 | 40 × 11.2 |
| 18.70 | V/H | 200 | 0.5 | 30 × 50 | 40 × 11.2 |
| 23.80 | V/H | 400 | 0.8 | 27 × 45 | 20 × 11.2 |
| 36.50 | V/H | 900 | 0.5 | 18 × 30 | 20 × 11.2 |
| 89.00 | V/H | 4600 | 1.0 | 9 × 15 | 10 × 11.2 |
| Parameters | FY3C MWRI SM Retrieval Algorithm |
|---|---|
| Soil and vegetation canopy physical temperatures | , linearly related with (36.5 GHz) |
| Surface roughness | (f) |
| Vegetation | b = 0.28–0.33, depending on the land type |
| Dielectric mixing model | Wang and Schmugge [33] |
| Products | MD | RMSE | ubRMSE | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMSR2 | −0.15 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.27 |
| FY-3C | −0.02 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.21 |
| SMAP | −0.12 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.63 |
| Products | MD | RMSE | ubRMSE | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMSR2 | −0.15 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| FY-3C | −0.03 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| SMAP | −0.09 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.49 |
| Products | MD | RMSE | ubRMSE | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMSR2 | −0.16 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.18 |
| FY-3C | −0.06 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.22 |
| SMAP | −0.10 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.16 |
| Indicators | Products | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | Jun. | Jul. | Aug. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | AMSR2 | −0.17 | −0.18 | −0.17 | −0.15 | −0.13 | −0.18 | −0.14 | −0.09 | −0.09 | −0.17 | −0.21 | −0.20 |
| FY3C | −0.12 | −0.12 | −0.09 | −0.02 | −0.01 | −0.11 | −0.05 | 0.11 | 0.05 | −0.08 | −0.12 | −0.12 | |
| SMAP | −0.16 | −0.14 | −0.13 | −0.11 | −0.08 | −0.10 | −0.08 | −0.09 | −0.06 | −0.08 | −0.10 | −0.11 | |
| RMSE | AMSR2 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| FY3C | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.13 | |
| SMAP | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.13 | |
| ubRMSE | AMSR2 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| FY3C | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| SMAP | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | |
| R | AMSR2 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.09 | -0.06 | 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.31 |
| FY3C | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.18 | |
| SMAP | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.31 |
| Products | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | RMSE | ubRMSE | R | MD | RMSE | ubRMSE | R | |
| AMSR2 | −0.17 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.26 | −0.14 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.18 |
| FY-3C | −0.08 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.29 | −0.01 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| SMAP | −0.09 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.53 | −0.09 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.45 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Pearson, S.; Wu, D.; Sun, R.; Johnson, S.; Wheeler, J.; Fang, S. Evaluation of Fengyun-3C Soil Moisture Products Using In-Situ Data from the Chinese Automatic Soil Moisture Observation Stations: A Case Study in Henan Province, China. Water 2019, 11, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020248
Zhu Y, Li X, Pearson S, Wu D, Sun R, Johnson S, Wheeler J, Fang S. Evaluation of Fengyun-3C Soil Moisture Products Using In-Situ Data from the Chinese Automatic Soil Moisture Observation Stations: A Case Study in Henan Province, China. Water. 2019; 11(2):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020248
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yongchao, Xuan Li, Simon Pearson, Dongli Wu, Ruijing Sun, Sarah Johnson, James Wheeler, and Shibo Fang. 2019. "Evaluation of Fengyun-3C Soil Moisture Products Using In-Situ Data from the Chinese Automatic Soil Moisture Observation Stations: A Case Study in Henan Province, China" Water 11, no. 2: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020248
APA StyleZhu, Y., Li, X., Pearson, S., Wu, D., Sun, R., Johnson, S., Wheeler, J., & Fang, S. (2019). Evaluation of Fengyun-3C Soil Moisture Products Using In-Situ Data from the Chinese Automatic Soil Moisture Observation Stations: A Case Study in Henan Province, China. Water, 11(2), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020248








