Evaluation of Gridded Precipitation Datasets over Arid Regions of Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
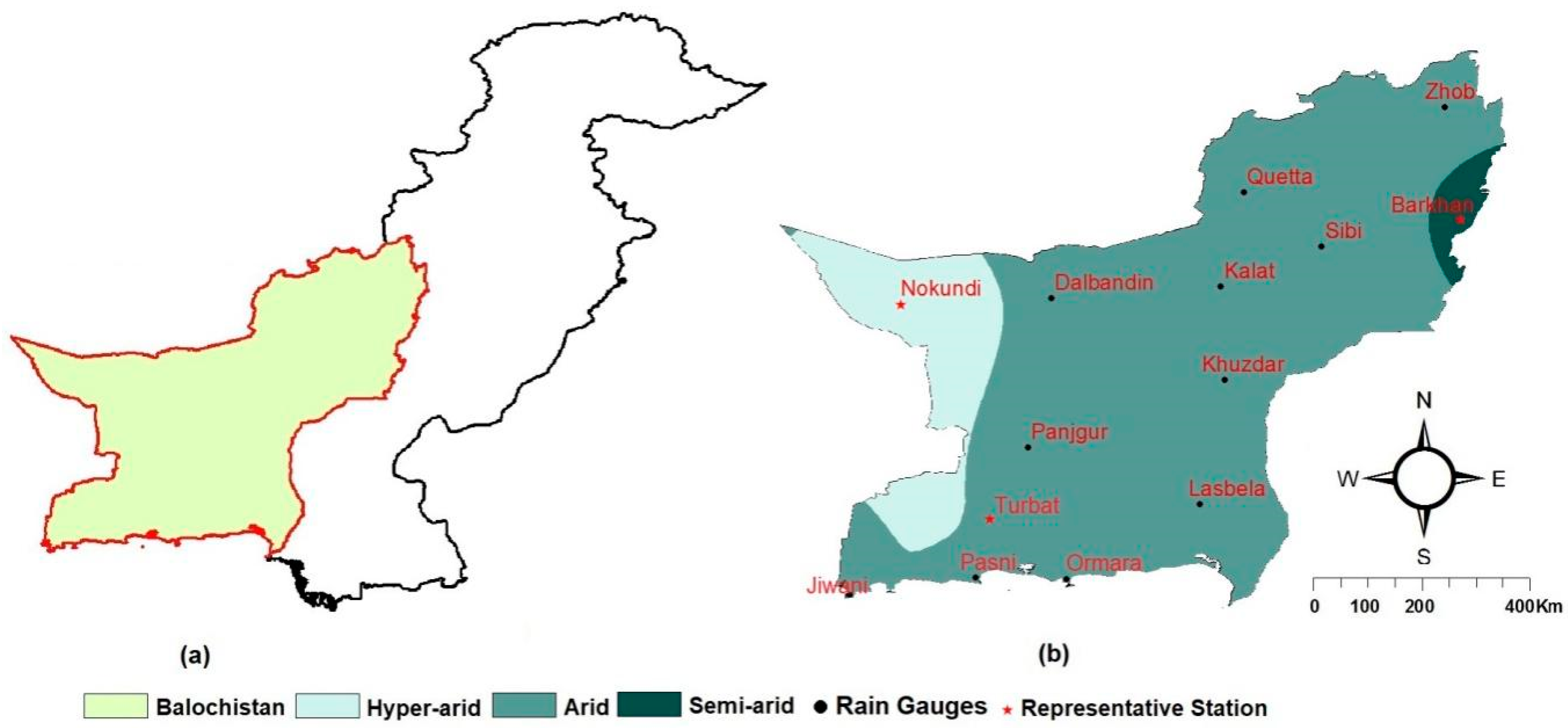
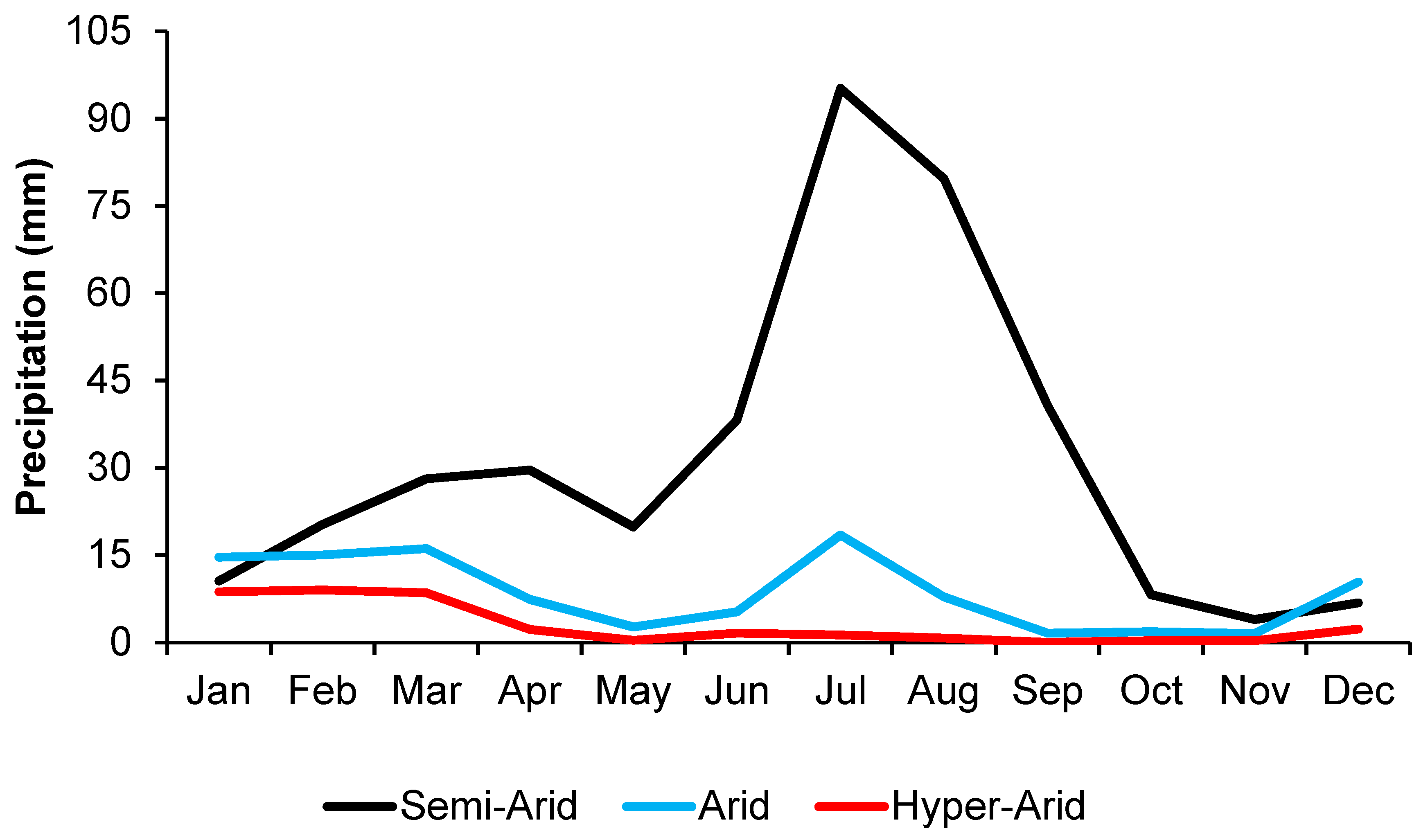
2. Study Area and Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. Mean Bias Errors (MBE)
3.2. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
3.3. Modified Index of Agreement
3.4. Distribution of Precipitation Data
4. Results
4.1. Homogeneity Test
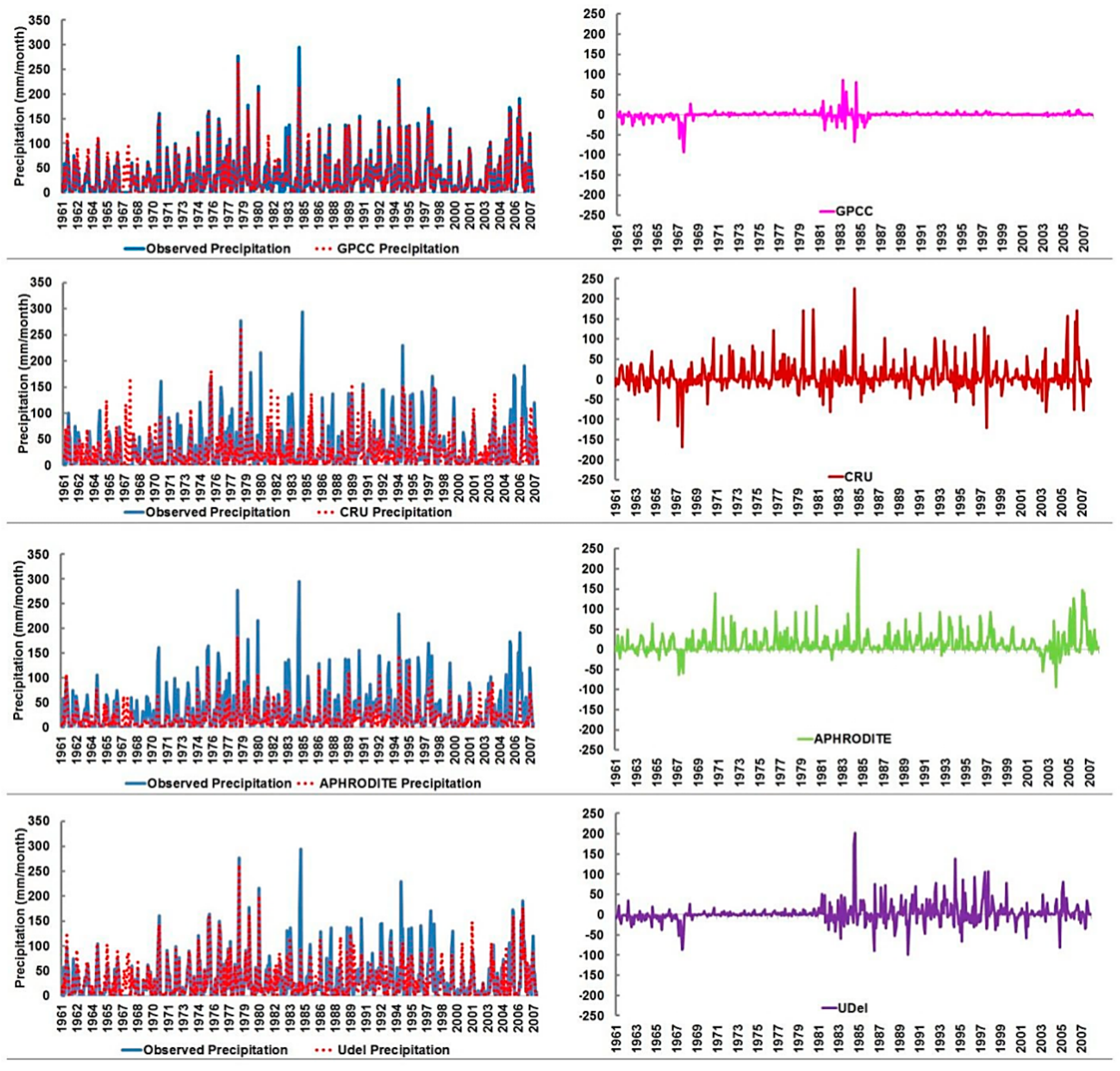
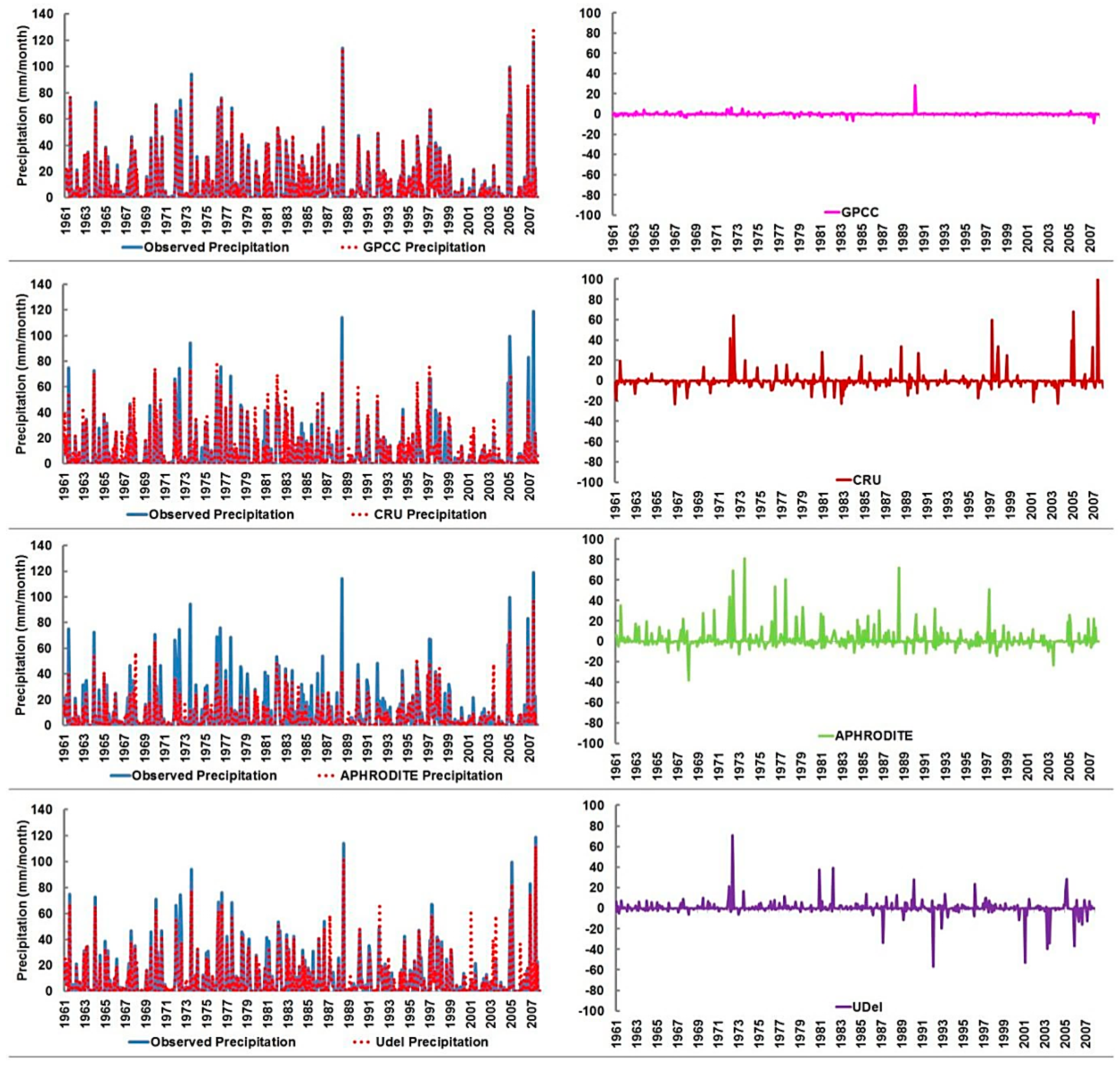
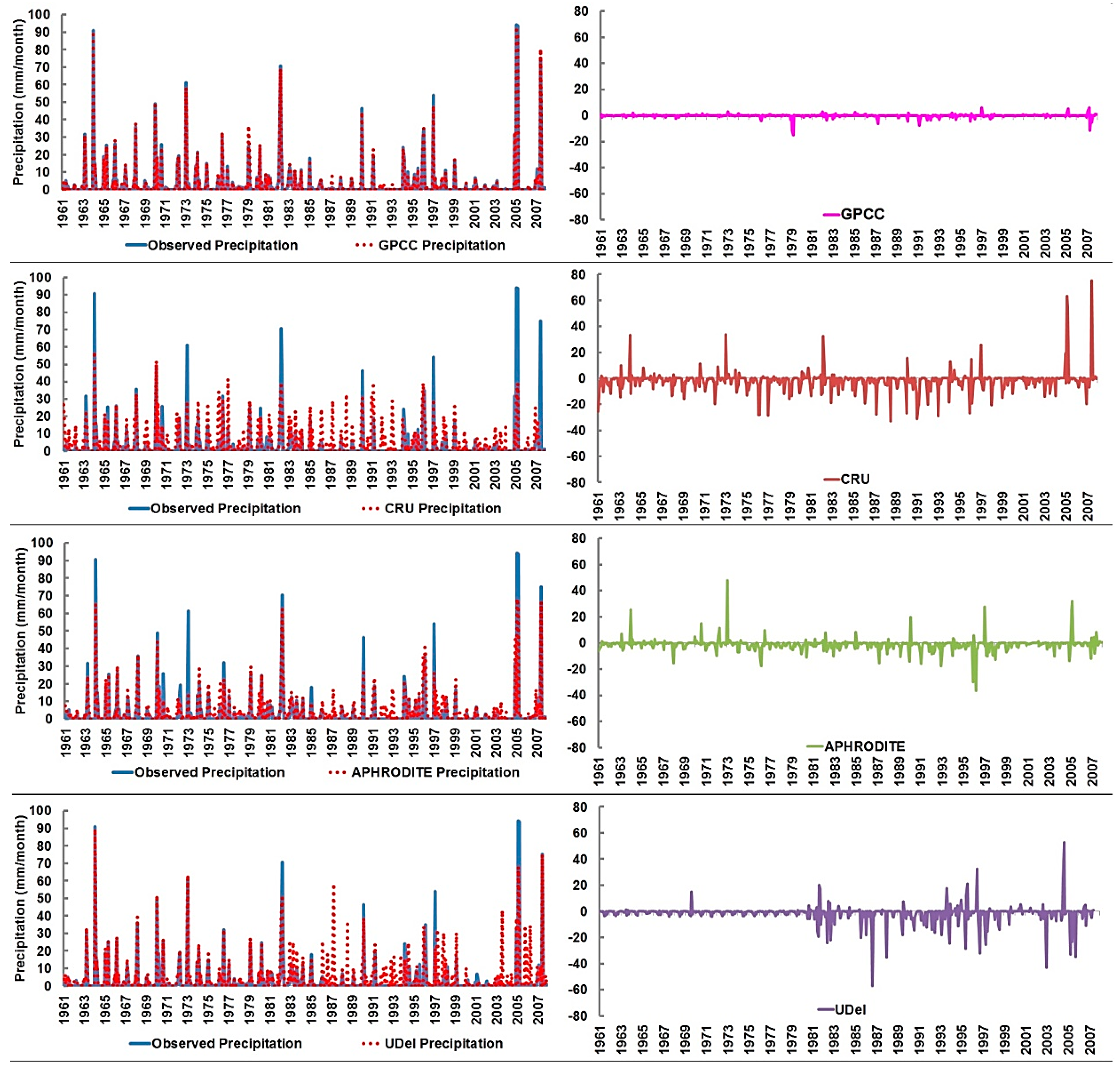
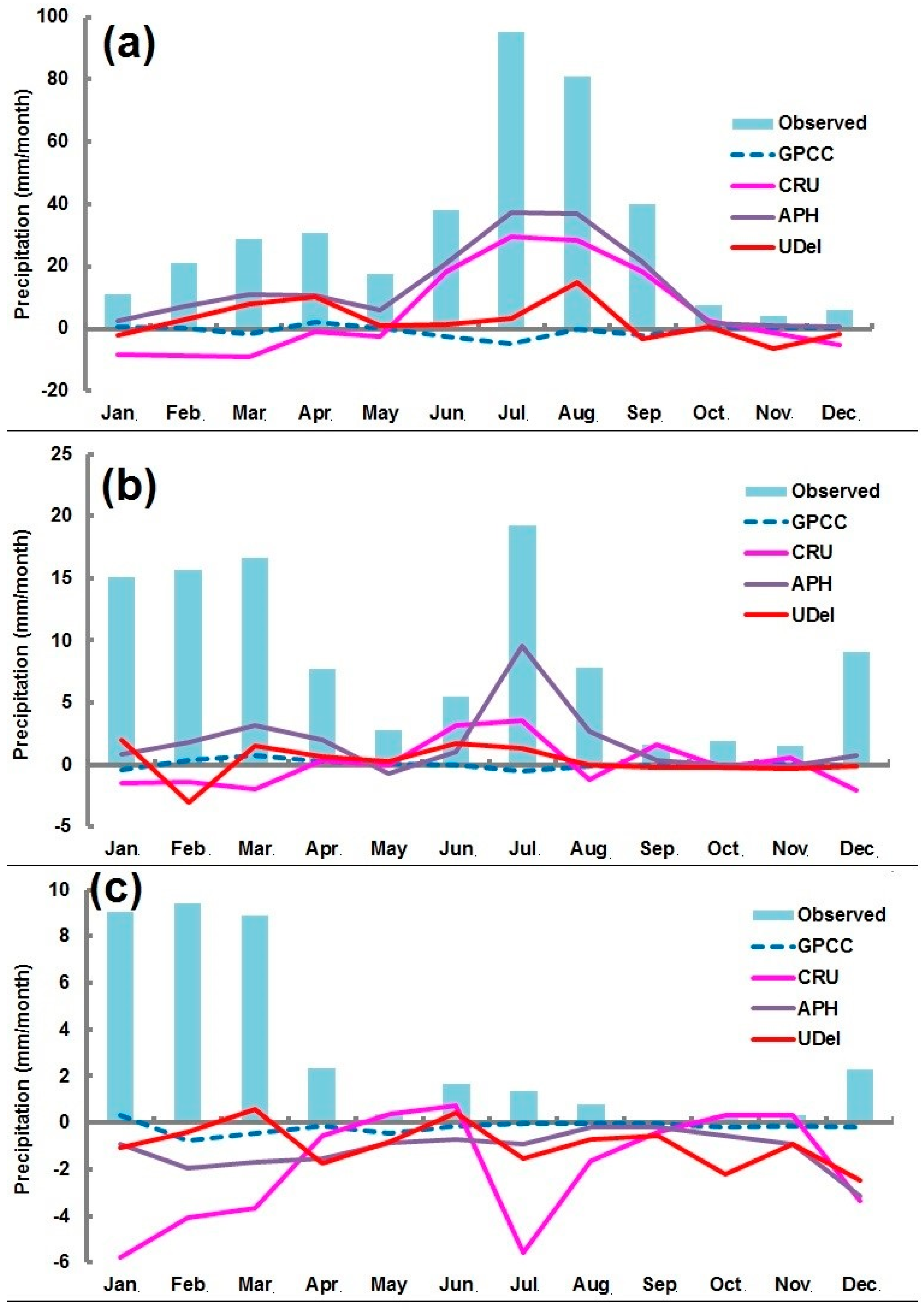
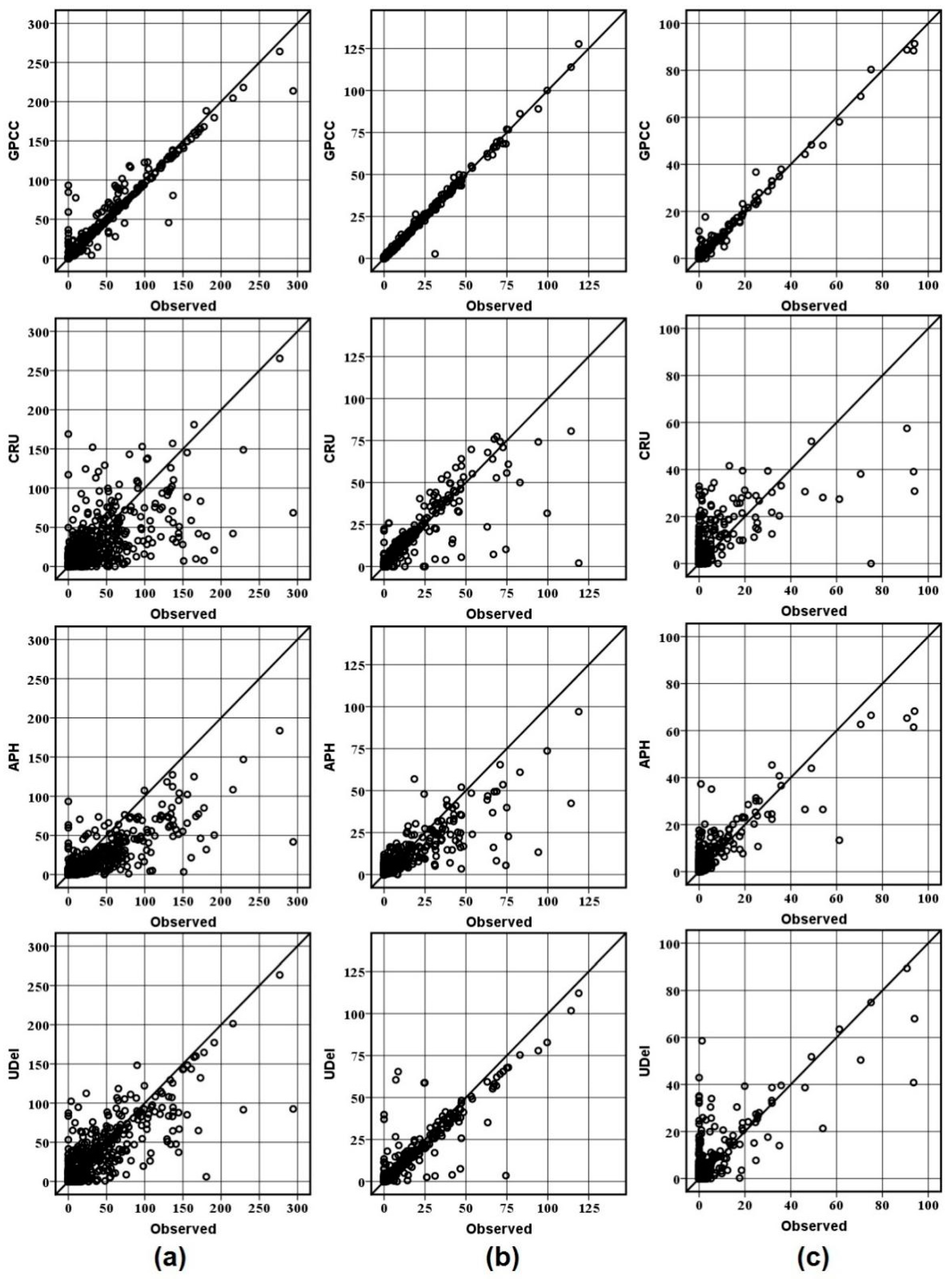
4.2. Performance of Gauge-Based Gridded Precipitation Data
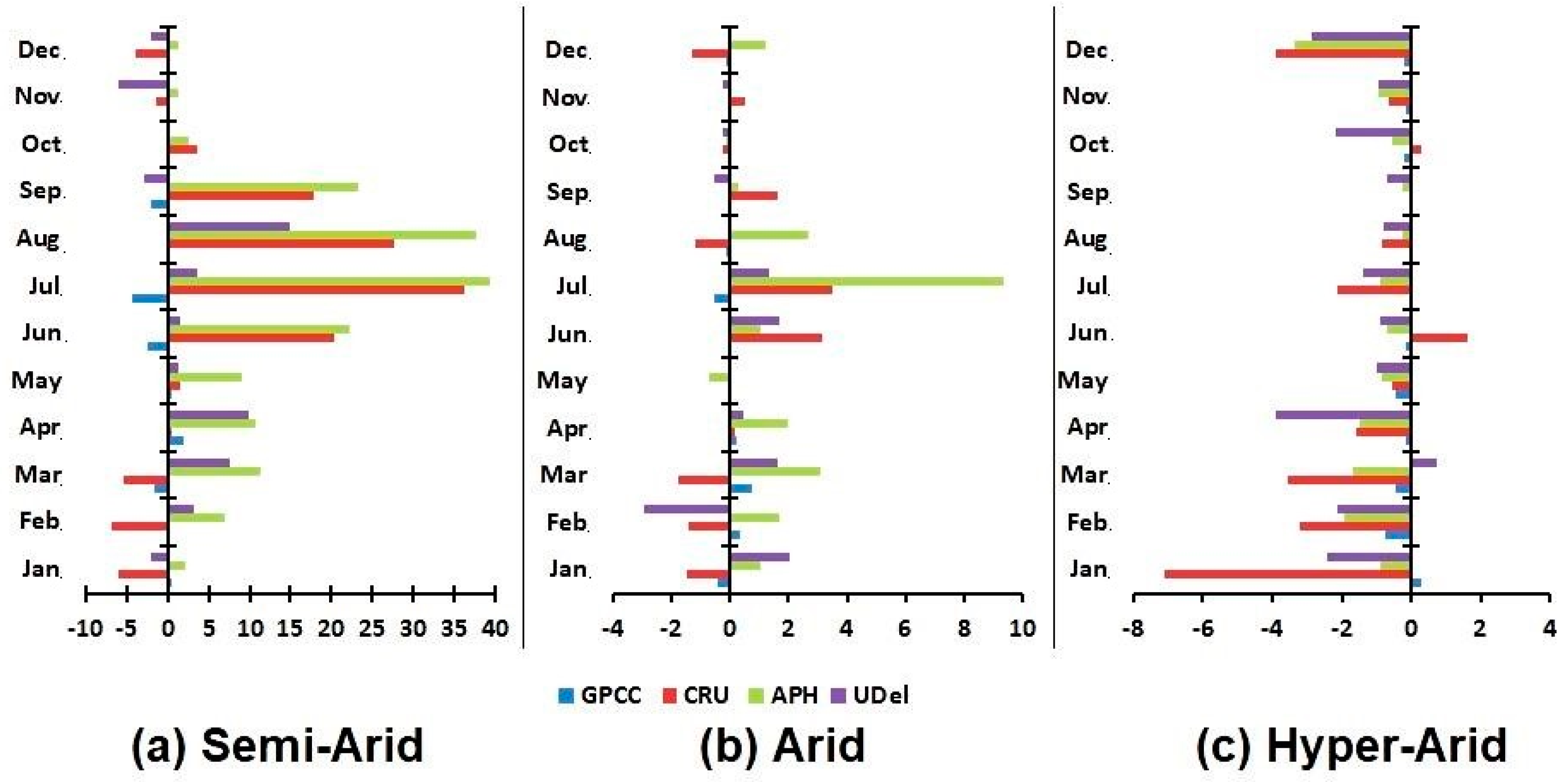
4.3. Mean Bias Error (MBE)
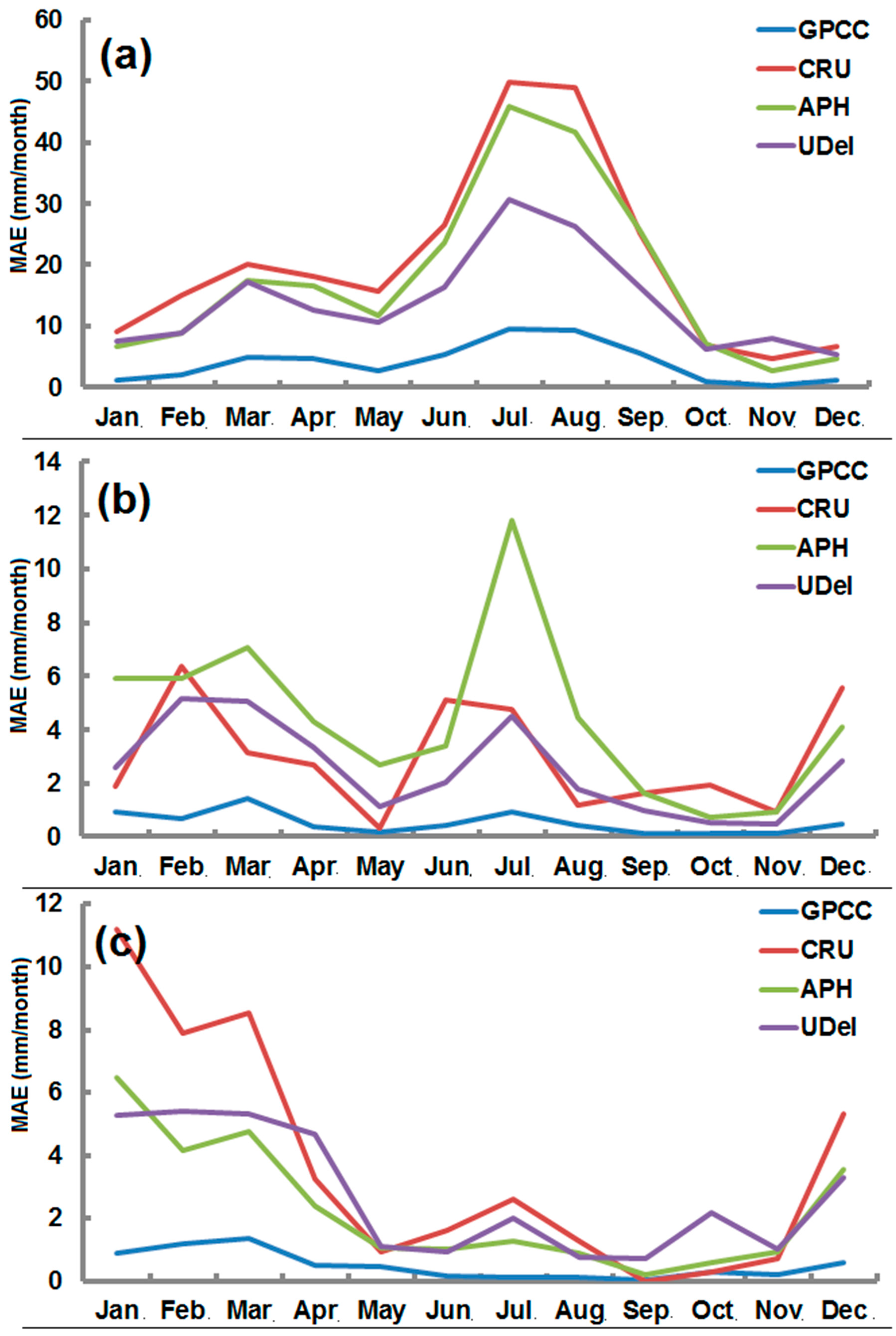
4.4. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
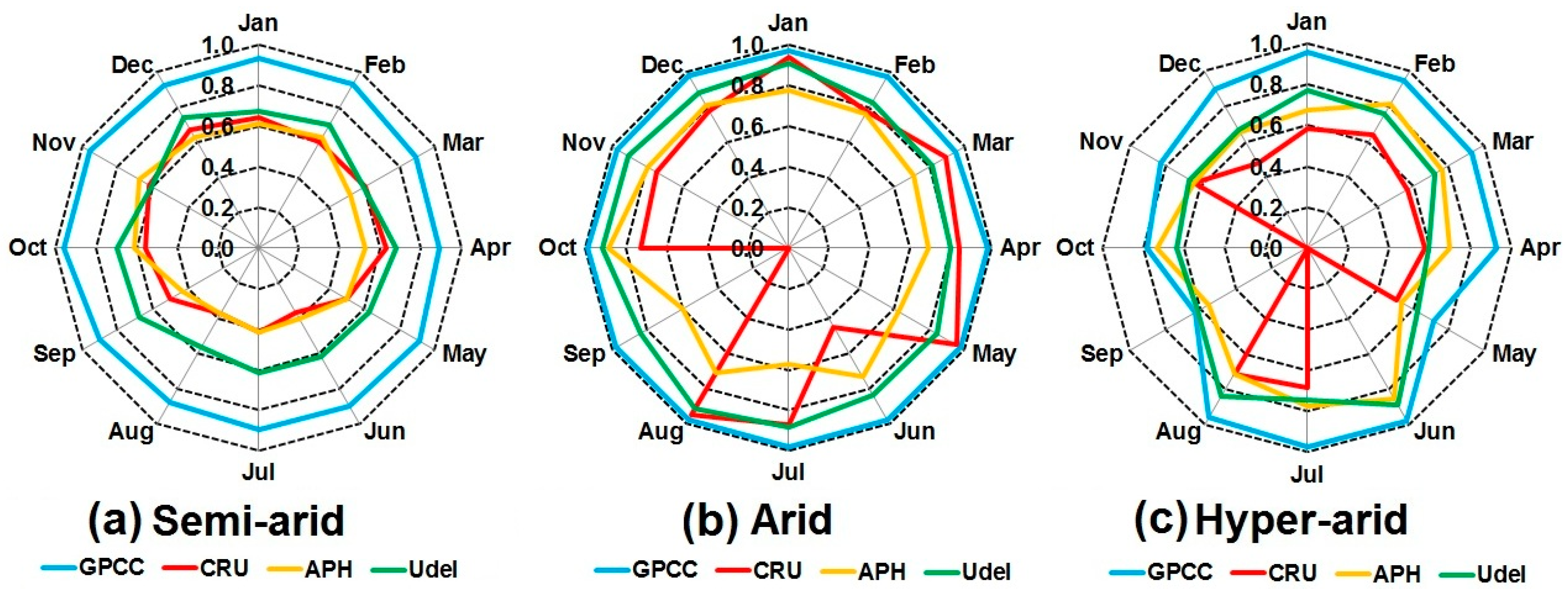
4.5. Modified Index of Agreement
4.6. Test of Similarity in Data Distribution
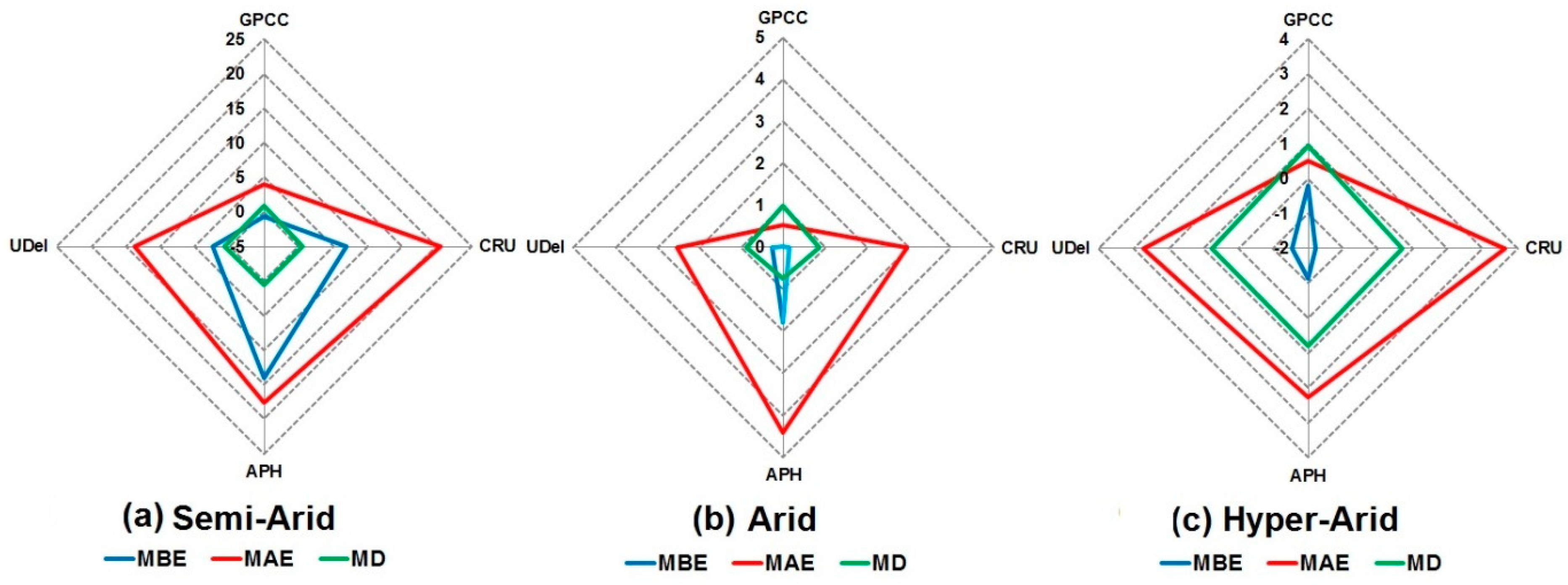
4.7. Multivariate Analysis
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trenberth, K.E. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekis, E.; Donaldson, N.; Reid, J.; Zucconi, A.; Hoover, J.; Li, Q.; Nitu, R.; Melo, S. An Overview of Surface-Based Precipitation Observations at Environment and Climate Change Canada. Atmos. Ocean. 2018, 56, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Min, J.; Zhang, W.; Pepin, N.; Kang, S. Comparison of multiple datasets with gridded precipitation observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 45, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Feng, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dan, L. Evaluating the performance of five twentieth-century reanalysis datasets in reproducing the severe drought in northern China during the 1920s–1930s. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hu, Q.; Qian, W. Quality control of daily meteorological data in China, 1951–2000: A new dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, A.; Simane, B.; Hassen, A.; Bantider, A. Variability and time series trend analysis of rainfall and temperature in northcentral Ethiopia: A case study in Woleka sub-basin. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2018, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Ali, R.O.; Harun, S.B.; Wang, X.-J. Evaluation of the performance of gridded precipitation products over Balochistan Province, Pakistan. Desalination 2017, 79, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z. Evaluation of Gridded Precipitation Data for Driving SWAT Model in Area Upstream of Three Gorges Reservoir. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Ahmed, K.; Nawaz, N. Trends in heat wave related indices in Pakistan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L. A review of global precipitation data sets: Data sources, estimation, and intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Nawaz, N.; Khan, N. Modeling climate change impacts on precipitation in arid regions of Pakistan: A non-local model output statistics downscaling approach. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haylock, M.; Hofstra, N.; Klein Tank, A.; Klok, E.; Jones, P.; New, M. A European daily high-resolution gridded data set of surface temperature and precipitation for 1950–2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, A.; Arakawa, O.; Kamiguchi, K.; Kawamoto, H.; Nodzu, M.I.; Hamada, A. A 44-year daily gridded precipitation dataset for Asia based on a dense network of rain gauges. Sola 2009, 5, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, E.P.; Wood, A.; Adam, J.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Nijssen, B. A long-term hydrologically based dataset of land surface fluxes and states for the conterminous United States. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 3237–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, B.; Allured, D. Daily precipitation grids for South America. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Ancell, R.; Pons, M.R.; Frías, M.D.; Fernández, J. Development and analysis of a 50-year high-resolution daily gridded precipitation dataset over Spain (Spain02). Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo-Pereira, M.; Dutra, E.; Viterbo, P. Evaluation of global precipitation data sets over the Iberian Peninsula. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemann, R.; Liniger, M.; Frei, C. Reduced space optimal interpolation of daily rain gauge precipitation in Switzerland. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vose, R.S.; Schmoyer, R.L.; Steurer, P.M.; Peterson, T.C.; Heim, R.; Karl, T.R.; Eischeid, J. The Global Historical Climatology Network: Long-Term Monthly Temperature, Precipitation, Sea Level Pressure, and Station Pressure Data; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1992; Volume 3912. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Xie, P.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A. Global Land Precipitation: A 50-yr Monthly Analysis Based on Gauge Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.D.; Osborn, T.J.; Lister, D.H. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations—The CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, K.; Willmott, C. Terrestrial Precipitation: 1900–2010 Gridded Monthly Time Series (1900–2010)(v 3.01 added 6/14/12). University of Delaware. 2012. Available online: http://climate.geog.udel.edu/~climate/html_pages/download.html (accessed on 15 April 2018).
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Ziese, M.; Rudolf, B. GPCC’s new land surface precipitation climatology based on quality-controlled in situ data and its role in quantifying the global water cycle. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, H.-I.; Dibike, Y.; Prowse, T.; Bonsal, B. Inter-comparison of high-resolution gridded climate data sets and their implication on hydrological model simulation over the Athabasca Watershed, Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4250–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Engelen, R.; Simmons, A.; Thépaut, J.-N. Toward a consistent reanalysis of the climate system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, T. An assessment of monsoon precipitation changes during 1901–2001. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunziker, S.; Gubler, S.; Calle, J.; Moreno, I.; Andrade, M.; Velarde, F.; Ticona, L.; Carrasco, G.; Castellón, Y.; Oria, C. Identifying, attributing, and overcoming common data quality issues of manned station observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4131–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairul, I.M.; Rasmy, M.; Koike, T.; Takeuchi, K. Inter-Comparison of Gauge-Corrected Global Satellite Rainfall Estimates and Their Applicability for Effective Water Resource Management in a Transboundary River Basin: The Case of the Meghna River Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Connor, S.J.; Ceccato, P.; Ropelewski, C.F. Comparison of global gridded precipitation products over a mountainous region of Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, G.; Dutra, E.; Barbosa, P.; Pappenberger, F.; Wetterhall, F.; Vogt, J.V. Comparison of drought indicators derived from multiple data sets over Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. On the use of dimensioned measures of error to evaluate the performance of spatial interpolators. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teegavarapu, R.S. Floods in a Changing Climate: Extreme Precipitation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cortesi, N.; Trigo, R.M.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C.; Ramos, A.M. Modelling monthly precipitation with circulation weather types for a dense network of stations over Iberia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J., Jr. Evaluating the use of” goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Robeson, S.M.; Matsuura, K. A refined index of model performance. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, B.; Takase, K. Effects of temporal resolution on hydrological model parameters and its impact on prediction of river discharge. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeniffer, K.; Su, Z.; Woldai, T.; Maathuis, B. Estimation of spatial–temporal rainfall distribution using remote sensing techniques: A case study of Makanya catchment, Tanzania. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12 (Suppl. 1), S90–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.B.; Wang, X.-J. Spatial distribution of unidirectional trends in temperature and temperature extremes in Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.-S.; Shahid, S.; Sung, J. Uncertainty in Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency Curves of Peninsular Malaysia under Changing Climate Scenarios. Water 2018, 10, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rudolf, B.; Schamm, K.; Schneider, U.; Ziese, M. A description of the global land-surface precipitation data products of the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre with sample applications including centennial (trend) analysis from 1901–present. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2013, 5, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Nemani, R. Evaluation of Multi-Satellite TRMM Derived Rainfall Estimates over a Western State of India. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayehu, G.T.; Tadesse, T.; Gessesse, B.; Dinku, T. Validation of new satellite rainfall products over the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, D.; Li, Z.; Mishra, A.K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Multi-scale evaluation of six high-resolution satellite monthly rainfall estimates over a humid region in China with dense rain gauges. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 1272–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Routray, J.K. Spatio-temporal characteristics of precipitation and drought in Balochistan Province, Pakistan. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Harun, S.B.; Wang, X.-J. Characterization of seasonal droughts in Balochistan Province, Pakistan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 30, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Nawaz, N. Impacts of climate variability and change on seasonal drought characteristics of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, S.; Ullah, K.; Shuanglin, L.; Gao, S.; Khan, A.H.; Mahmood, R. Comparison of various drought indices to monitor drought status in Pakistan. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Storch, H.; Navarra, A. Analysis of Climate Variability: Applications of Statistical Techniques; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Nawaz, N.; Wang, X.-J. Absolute homogeneity assessment of precipitation time series in an arid region of Pakistan. Atmosfera 2018, 31, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersson, H. A homogeneity test applied to precipitation data. J. Climatol. 1986, 6, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buishand, T.A. Some methods for testing the homogeneity of rainfall records. J. Hydrol. 1982, 58, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J. Distribution of the ratio of the mean square successive difference to the variance. Ann. Math. Stat. 1941, 12, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.C.; Greenslade, D.J. Indices for the objective assessment of tsunami forecast models. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2013, 170, 1601–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the evaluation of model performance in physical geography. In Spatial Statistics and Models; Springer Netherland: Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 443–460. [Google Scholar]
- Lovino, M.; García, N.O.; Baethgen, W. Spatiotemporal analysis of extreme precipitation events in the Northeast region of Argentina (NEA). J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2014, 2, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervais, M.; Tremblay, L.B.; Gyakum, J.R.; Atallah, E. Representing extremes in a daily gridded precipitation analysis over the United States: Impacts of station density, resolution, and gridding methods. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5201–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Donat, M.G.; Alexander, L.V.; Sun, Y. Multi-dataset comparison of gridded observed temperature and precipitation extremes over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2809–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Q. Evaluation of reanalysis, spatially interpolated and satellite remotely sensed precipitation data sets in central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5648–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Gairola, R.M.; Mitra, A.K. Comparison of large-scale global land precipitation from multisatellite and reanalysis products with gauge-based GPCC data sets. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 121, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushair, M.; Prakash, S.; Patel, S.; Gairola, R. Assessment of Kalpana-1 Rainfall Product over Indian Meteorological Sub-Divisions During the Summer Monsoon Season. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, A.L.; Zeng, X. Areal estimation of intensity and frequency of summertime precipitation over a midlatitude region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkiaka, E.; Nawaz, N.; Lovett, J. Evaluating global reanalysis precipitation datasets with rain gauge measurements in the Sudano-Sahel region: Case study of the Logone catchment, Lake Chad Basin. Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, S.M.; Ensor, L.A. Daily Precipitation Grids for South America. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 1095–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Maathuis, B.; Adem, A.A.; Demissie, S.S.; Langan, S.; Steenhuis, T.S. Comparison of rainfall estimations by TRMM 3B42, MPEG and CFSR with ground-observed data for the Lake Tana basin in Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4871–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Q.; Tian, H. Temperature changes in Central Asia from 1979 to 2011 based on multiple datasets. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1143–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Al-Abadi, A.M.; Wang, X.-J.; Chung, E.-S. Selection of gridded precipitation data for Iraq using compromise programming. Measurement 2018, 132, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xia, J.; Yuan, W.; Xu, B.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Assessment of multiple precipitation products over major river basins of China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Kong, D.; Ye, A.; Di, Z.; Gong, W. Would the ‘real’observed dataset stand up? A critical examination of eight observed gridded climate datasets for China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duethmann, D.; Zimmer, J.; Gafurov, A.; Güntner, A.; Kriegel, D.; Merz, B.; Vorogushyn, S. Evaluation of areal precipitation estimates based on downscaled reanalysis and station data by hydrological modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Lister, D.; Hulme, M.; Makin, I. A high-resolution data set of surface climate over global land areas. Clim. Res. 2002, 21, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, C.; Nicotina, L.; Parlange, M.B.; Berne, A.; Rinaldo, A. Improved interpolation of meteorological forcings for hydrologic applications in a Swiss Alpine region. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Rasul, G.; Mahmood, T.; Zaman, Q.; Cheema, S. Validation of APHRODITE precipitation data for humid and sub humid regions of Pakistan. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2012, 9, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Pour, S.H.; Harun, S.B.; Shahid, S. Genetic programming for the downscaling of extreme rainfall events on the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 914–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rustemeier, E.; Ziese, M.; Becker, A. Evaluating the hydrological cycle over land using the newly-corrected precipitation climatology from the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Station | Annual Precipitation (mm) | Standard Deviation | Missing Data (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barkhan | 389.32 | 158.64 | 1.02 |
| Dalbandin | 85.02 | 47.49 | 0.00 |
| Jiwani | 103.82 | 86.05 | 0.21 |
| Kalat | 161.12 | 118.54 | 8.74 |
| Khuzdar | 246.08 | 117.79 | 0.00 |
| Lasbela | 153.60 | 94.49 | 0.00 |
| Nokkundi | 36.10 | 38.36 | 0.61 |
| Ormara | 110.36 | 95.94 | 2.93 |
| Panjgur | 104.93 | 62.82 | 0.00 |
| Pasni | 99.80 | 73.31 | 7.73 |
| Quetta | 253.08 | 143.72 | 0.00 |
| Sibbi | 158.31 | 101.98 | 2.44 |
| Turbat | 98.85 | 87.93 | 2.24 |
| Zhob | 288.15 | 117.14 | 0.00 |
| Month | Semi-Arid | Arid | Hyper-Arid | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPCC | CRU | APH | UDel | GPCC | CRU | APH | UDel | GPCC | CRU | APH | UDel | |
| Jan. | 0.70 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.99 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Feb. | 0.72 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Mar. | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.29 | 1.00 | 0.07 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Apr. | 0.82 | 0.94 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.48 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| May | 0.52 | 0.94 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Jun. | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Jul. | 0.86 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.65 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.63 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Aug. | 0.85 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Sep. | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Oct. | 0.00 | 0.98 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Nov. | 0.00 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Dec. | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Month | 1961 | 1984 | 2007 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPCC | CRU | UDel | GPCC | CRU | UDel | GPCC | CRU | UDel | |
| Jan. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 7 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| Feb. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| Mar. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| Apr. | 12 | 5 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 7 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| May | 12 | 5 | 12 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 14 | 4 | 11 |
| Jun. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 14 | 0 | 11 |
| Jul. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| Aug. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| Sep. | 12 | 4 | 12 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 4 | 11 |
| Oct. | 12 | 5 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| Nov. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
| Dec. | 12 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 14 | 5 | 11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, N.; Khan, N. Evaluation of Gridded Precipitation Datasets over Arid Regions of Pakistan. Water 2019, 11, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020210
Ahmed K, Shahid S, Wang X, Nawaz N, Khan N. Evaluation of Gridded Precipitation Datasets over Arid Regions of Pakistan. Water. 2019; 11(2):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020210
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Kamal, Shamsuddin Shahid, Xiaojun Wang, Nadeem Nawaz, and Najeebullah Khan. 2019. "Evaluation of Gridded Precipitation Datasets over Arid Regions of Pakistan" Water 11, no. 2: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020210
APA StyleAhmed, K., Shahid, S., Wang, X., Nawaz, N., & Khan, N. (2019). Evaluation of Gridded Precipitation Datasets over Arid Regions of Pakistan. Water, 11(2), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020210







