Dynamics of Runoff and Soil Erosion on Abandoned Steep Vineyards in the Mosel Area, Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
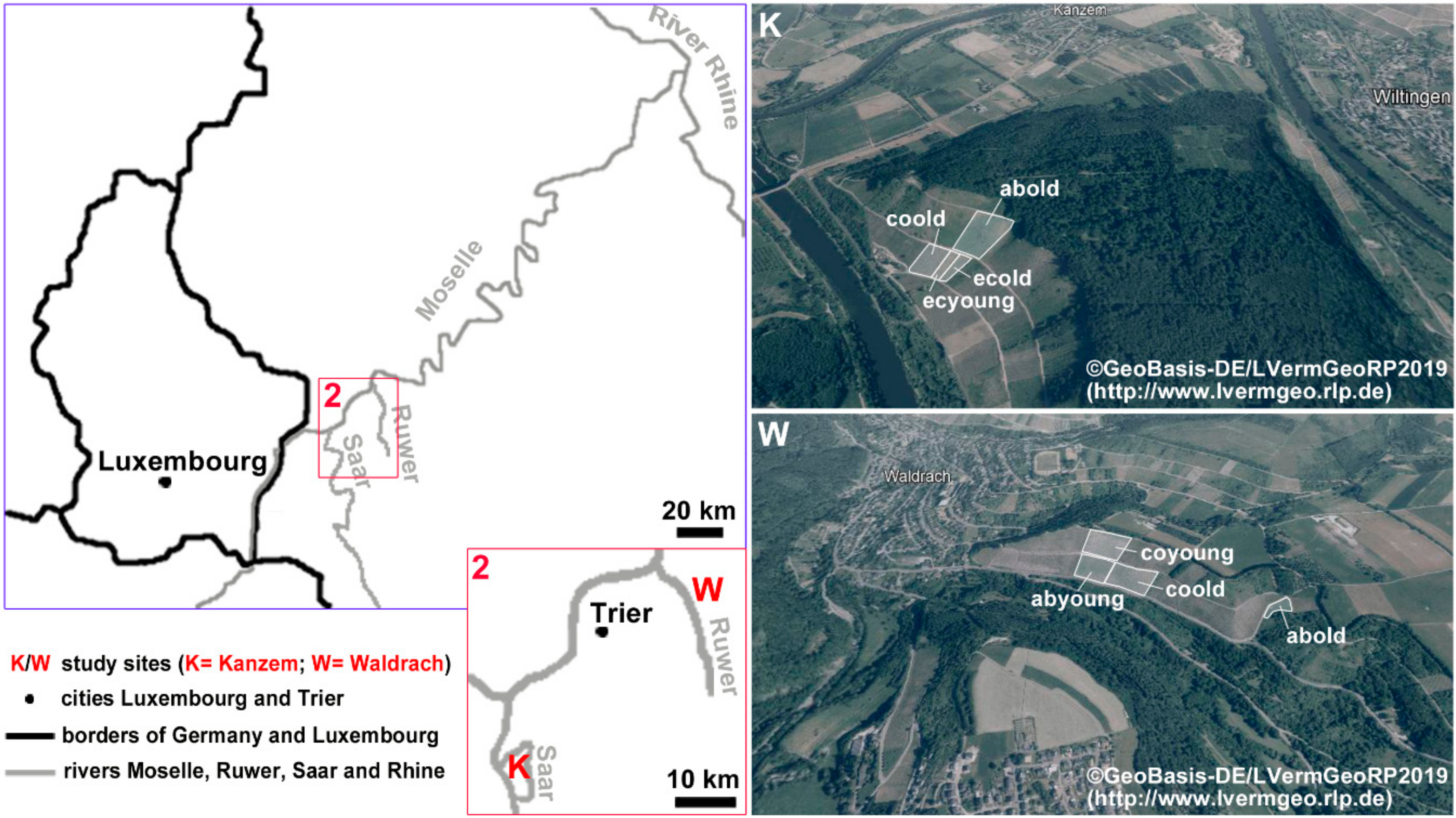
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Methods
2.3. Rainfall Simulation Experiments
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evolution of Wine-Growing Surface
3.2. Surface Dynamics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bork, H.-R.; Beckedahl, H.R.; Dahlke, C.; Geldmacher, K.; Mieth, A.; Li, Y. The world-wide explosion of soil erosion rates in the 20th century: The global soil erosion drama—Are we losing our food production base? Petermanns Geographische Mitteilungen 2003, 147, 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bork, H.R. Bodenerosion und Umwelt: Verlauf, Ursachen und Folgen der mittelalterlichen und neuzeitlichen Bodenerosion, Bodenerosionsprozesse, Modelle und Simulationen; Landschaftsgenese und Landschaftsökologie; Abt. für Physische Geographie und Landschaftsökologie und für Physische Geographie und Hydrologie der Techn. University Selbstverl: Braunschweig, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, A.; Dotterweich, M.; Schmidtchen, G.; Bork, H.-R. Vineyards, hopgardens and recent afforestation: Effects of late Holocene land use change on soil erosion in northern Bavaria, Germany. Catena 2003, 51, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiß, S.; Dreibrodt, S.; Lubos, C.C.M.; Bork, H.-R. Land use history and historical soil erosion at Albersdorf (northern Germany)—Ceased agricultural land use after the pre-historical period. Catena 2009, 77, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkelboom, F.; Poesen, J.; Trébuil, G. The multiple land degradation effects caused by land-use intensification in tropical steeplands: A catchment study from northern Thailand. Catena 2008, 75, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, J.L.; Echeverria, M.T.; Julián, A.; Chueca, J. Processus d´accumulation et d´incision pendant l´Antiquité Classique dans la vallée de la Huerva (Bassin de l´Ebre, Espagne). In Geoarchaeology of the Landscapes of Classical Antiquity; Babesch Supplementa; Peeters: Leuven, Belgium, 2000; pp. 151–159. ISBN 978-90-429-0928-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sancho, C.; Gutierrez-Elorza, M.; Peña-Monné, J.L. Erosion and sedimentation during the Upper Holocene in the Ebro Depression: quantification and environmental significance. Soil Eros. Stud. Spain 1991, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; van Doorn, A.; Quetier, F.; Chouvardas, D.; Rounsevell, M. The response of soil erosion and sediment export to land-use change in four areas of Europe: The importance of landscape pattern. Geomorphology 2008, 98, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.; Bork, H.-R.; Mäckel, R.; Preston, N.; Wunderlich, J.; Dikau, R. Changes in sediment flux and storage within a fluvial system: Some examples from the Rhine catchment. Hydrol. Processes 2003, 17, 3321–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinillo, M.; Lasanta, T.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Managing mountainous degraded landscapes after farmland abandonment in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. Environ. Manag. 1997, 2, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Ruiz, J.M.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Martí, C.; Ortigosa, L.; Gonzáles, C. Soil erosion and desertification as a consequence of farmland abandonment in mountain areas. Desertif. Control Bull. 1994, 25, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Lasanta, T.; Marti, C.; Gonzales, C.; White, S.; Ortigosa, L.; Ruiz Flano, P. Changes in runoff and erosion as a consequence of land-use changes in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. Physics Chem. Earth 1995, 20, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, P.; Queralt, L.; Plana, F.; Gallart, F. Studying solute and particulate sediment transfer in a small mediterranean mountainous catchment subject to land abandonment. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 1997, 22, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Vaezi, A.R.; Pulido, M.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Keesstra, S.D. Long-term impact of rainfed agricultural land abandonment on soil erosion in the Western Mediterranean basin. Progress Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2018, 42, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal-Romero, E.; Lasanta, T.; Regüés, D.; Lana-Renault, N.; Cerdà, A. Hydrological response and sediment production under different land cover in abandoned farmland fields in a mediterranean mountain environment. Boletin de la Asociacion de Geografos Espanoles 2011, 55, 303–323, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Lasanta, T.; Perez-Rontome, C.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Machin, J.; Navas, A. Hydrological problems resulting from farmland abandonment in semi-arid environments: The central Ebro depression. Physics Chem. Earth 1995, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.B. Geomorphodynamics on fallow land and abandoned fields in the Ebro Basin and the Pyrenees—Monitoring of processes and development. Z. Geomorph. N.F. 2002, 127, 21–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ries, J.B.; Marzolff, I.; Seeger, M. Influence of grazing on vegetation cover and geomorphodynamics. Einfluss der Beweidung auf Vegetationsbedeckung und Geomorphodynamik Zwischen Ebrobecken und Pyrenäen 2003, 55, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Seeger, M. Uncertainty of factors determining runoff and erosion processes as quantified by rainfall simulations. Catena 2007, 71, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Díaz, A.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Robledano-Aymerich, F.; Brevik, E.C.; Cerdà, A. Ecosystem responses to land abandonment in Western Mediterranean Mountains. Catena 2017, 149, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Nadal-Romero, E.; Cammeraat, E.L.H. Hydrological Connectivity Does Change Over 70 Years of Abandonment and Afforestation in the Spanish Pyrenees. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Gabarrón Galeote, M.A.; Martinez Murillo, J.F.; Garcia Marín, R. Vegetation strategies for soil water consumption along a pluviometric gradient in southern Spain. Catena 2011, 84, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienes, R.; Marques, M.J.; Sastre, B.; García-Díaz, A.; Ruiz-Colmenero, M. Eleven years after shrub revegetation in semiarid eroded soils. Influence in soil properties. Geoderma 2016, 273, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Preti, F.; Romano, N. Terraced landscapes: From an old best practice to a potential hazard for soil degradation due to land abandonment. Anthropocene 2014, 6, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, P.; Cevasco, A.; Capolongo, D.; Pepe, G.; Lovergine, F.; Del Monte, M. Response of Terraced Slopes to a Very Intense Rainfall Event and Relationships with Land Abandonment: A Case Study from Cinque Terre (Italy). Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunjó, G.; Pardini, G.; Gispert, M. Land use change effects on abandoned terraced soils in a Mediterranean catchment, NE Spain. Catena 2003, 52, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, K.; Fiener, P.; Dikau, R. Rates of sheet and rill erosion in Germany—A meta-analysis. Geomorphology 2009, 111, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdan, O.; Govers, G.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Van Oost, K.; Poesen, J.; Saby, N.; Gobin, A.; Vacca, A.; Quinton, J.; Auerswald, K.; et al. Rates and spatial variations of soil erosion in Europe: A study based on erosion plot data. Geomorphology 2010, 122, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, G. Bodenerosion in Rebanlagen des Moselgebietes. Ergebnisse Quantitativer Untersuchungen 1974–1977; Forschungsstelle Bodenerosion d. University Trier: Mertesdorf, Germany, 1979; Volume 3, p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, G. On the soil erosion problem in the temperate humid area of Central Europe. GeoJournal 1980, 4, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoglu, S. Determination of soil erosion in a steep hill slope with different land-use types: a case study in Mertesdorf (Ruwertal/Germany). J. Environ. Biol. 2007, 28, 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Stehling, E.; Schmidt, R.G. Das Datenarchiv der Forschungsstelle Bodenerosion in Mertesdorf (Ruwertal); Forschungsstelle Bodenerosion d. University Trier: Trier, Germany, 2017; Volume 16, p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer-Bower, T.A.S.; Burt, T.P. Rainfall simulators for investigating soil response to rainfall. Soil Technol. 1989, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer-Bower, T.A.S.; Bryan, R.B. Rill initiation: concepts and experimental evaluation on badland slopes. Zeitschrift fur Geomorphologie, Supplementband 1986, 60, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Iserloh, T.; Fister, W.; Seeger, M.; Willger, H.; Ries, J.B. A small portable rainfall simulator for reproducible experiments on soil erosion. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M. Experiments as tools in geomorphology. Cuadernos de Investigación Geográfica 2017, 43, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jenkins, M.B.; Truman, C.C.; Siragusa, G.; Line, E.; Bailey, J.S.; Frye, J.; Endale, D.M.; Franklin, D.H.; Schomberg, H.H.; Fisher, D.S.; et al. Rainfall and tillage effects on transport of fecal bacteria and sex hormones 17β-estradiol and testosterone from broiler litter applications to a Georgia Piedmont Ultisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 403, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coles, A.E.; Wetzel, C.E.; Martínez-Carreras, N.; Ector, L.; McDonnell, J.J.; Frentress, J.; Klaus, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Diatoms as a tracer of hydrological connectivity: are they supply limited? Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, R.J. Using rainfall simulation to guide planning and management of rehabilitated areas: Part I. Experimental methods and results from a study at the northparkes mine, Australia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2000, 11, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, R.J.; Connolly, R.D.; Littleboy, M. Using rainfall simulation to guide planning and management of rehabilitated areas: Part II. computer simulations using parameters from rainfall simulation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2000, 11, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindewolf, M.; Schmidt, J. Parameterization of the EROSION 2D/3D soil erosion model using a small-scale rainfall simulator and upstream runoff simulation. Catena 2012, 91, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hümann, M.; Schüler, G.; Müller, C.; Schneider, R.; Johst, M.; Caspari, T. Identification of runoff processes – The impact of different forest types and soil properties on runoff formation and floods. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butzen, V.; Seeger, M.; Marruedo, A.; de Jonge, L.; Wengel, R.; Ries, J.B.; Casper, M.C. Water repellency under coniferous and deciduous forest—Experimental assessment and impact on overland flow. Catena 2015, 133, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemke, J.J. Runoff and Soil Erosion Assessment on Forest Roads Using a Small Scale Rainfall Simulator. Hydrology 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Neugirg, F.; Schindewolf, M.; Haas, F.; Schmidt, J. Simulation of rainfall effects on sediment transport on steep slopes in an Alpine catchment. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 367, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hänsel, P.; Schindewolf, M.; Eltner, A.; Kaiser, A.; Schmidt, J. Feasibility of High-Resolution Soil Erosion Measurements by Means of Rainfall Simulations and SfM Photogrammetry. Hydrology 2016, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler Wildhaber, Y.; Bänninger, D.; Burri, K.; Alewell, C. Evaluation and application of a portable rainfall simulator on subalpine grassland. Catena 2012, 91, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Putte, A.; Govers, G.; Leys, A.; Langhans, C.; Clymans, W.; Diels, J. Estimating the parameters of the Green–Ampt infiltration equation from rainfall simulation data: Why simpler is better. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, C.; Govers, G.; Diels, J.; Clymans, W.; Van den Putte, A. Dependence of effective hydraulic conductivity on rainfall intensity: Loamy agricultural soils. Hydrol. Proc. 2010, 24, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, C.; Govers, G.; Diels, J.; Leys, A.; Clymans, W.; Putte, A.V.D.; Valckx, J. Experimental rainfall-runoff data: Reconsidering the concept of infiltration capacity. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, U.; Zeiger, M.; Fohrer, N. Soil structure and herbicide transport on soil surfaces during intermittent artificial rainfall. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, Supplementary Issues 2013, 57, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, M.; Fohrer, N. Impact of organic farming systems on runoff formation processes—A long-term sequential rainfall experiment. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 102, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguería, S.; López Moreno, J.I.; Lorente, A.; Seeger, M.; Garcia Ruiz, J.M. Assessing the Effect of Climate Oscillations and Land-use Changes on Streamflow in the Central Spanish Pyrenees. Ambio 2003, 32, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, H.; Murphy, A. Germany’s Mosel Valley: Can Tourism Help Preserve Its Cultural Heritage? Tour. Rev. Int. 2006, 9, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forneck, A.; Eder, J.; Schmid, J. Reblaus - Neue Gefahr: Blattgallen. Der Deutsche Weinbau 2017, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Molitor, D.; Baus, O.; Berkelmann-Löhnertz, B. Schwarzfäule—Was gibt es Neues? Das Deutsche Weinmagazin 2010, 26, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Redl, H. Verwilderte Weingärten und Stilllegungsflächen mit hohem Gefahrenpotenzial. Der Winzer 2006, 62, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; ISBN 978-92-5-108370-3. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Brings, C.; Lassu, T.; Iserloh, T.; Senciales, J.M.; Martínez Murillo, J.F.; Ruiz Sinoga, J.D.; Seeger, M.; Ries, J.B. Rainfall and human activity impacts on soil losses and rill erosion in vineyards (Ruwer Valley, Germany). Solid Earth 2015, 6, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.B.; Marzen, M.; Iserloh, T.; Fister, W. Soil erosion in Mediterranean landscapes–Experimental investigation on crusted surfaces by means of the Portable Wind and Rainfall Simulator. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 100–101, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS 26 Statistics for Windows; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, S.; Strub, L. Winzergenossenschaften: Bewirtschaftung von Steillagen. Wein + Markt 2017, 28, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, S.; Pabst, E. Strukturelle Unterschiede: Sebstvermarkter. Der Deutsche Weinbau 2018, 23, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gutzler, M. Preissteigerungen im Weingut umsetzen: Analyse von Preislisten. Das Deutsche Weinmagazin 2016, 20, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.V.; White, M.A.; Cooper, O.R.; Storchmann, K. Climate Change and Global Wine Quality. Clim. Change 2005, 73, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenfelter, O.; Storchmann, K. Using Hedonic Models of Solar Radiation and Weather to Assess the Economic Effect of Climate Change: The Case of Mosel Valley Vineyards. Rev. Econom. Stat. 2010, 92, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levers, C.; Schneider, M.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Estel, S.; Kuemmerle, T. Spatial variation in determinants of agricultural land abandonment in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M.; Ries, J.B. Soil degradation and soil surface process intensities on abandoned fields in Mediterranean mountain environments. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. The effect of season and parent material on water erosion on highly eroded soils in eastern Spain. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 52, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, K.D.; d’Oleire-Oltmanns, S.; Ries, J.B.; Marzolff, I.; Ait Hssaine, A. Soil erosion in gully catchments affected by land-levelling measures in the Souss Basin, Morocco, analysed by rainfall simulation and UAV remote sensing data. Catena 2014, 113, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelder, D.J.; Bryan, R.B. The use of rainfall simulation tests to assess the influence of vegetation density on soil loss on degraded rangelands in the Baringo District, Kenya. Catena 1995, 25, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Seeger, M.; Ries, J.B. Soil erosion in sloping vineyards under conventional and organic land use managements (Saar-Mosel Valley, Germany). Cuadernos de Investigación Geográfica 2017, 43, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Brings, C.; Iserloh, T.; Casper, M.C.; Seeger, M.; Senciales, J.M.; Brevik, E.C.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. Temporal changes in soil water erosion on sloping vineyards in the Ruwer-Mosel Valley. The impact of age and plantation works in young and old vines. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2017, 65, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butzen, V.; Seeger, M.; Wirtz, S.; Huemann, M.; Mueller, C.; Casper, M.; Ries, J.B. Quantification of Hortonian overland flow generation and soil erosion in a Central European low mountain range using rainfall experiments. Catena 2014, 113, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morvan, X.; Naisse, C.; Malam Issa, O.; Desprats, J.F.; Combaud, A.; Cerdan, O. Effect of ground-cover type on surface runoff and subsequent soil erosion in Champagne vineyards in France. Soil Manag. 2014, 30, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Ackermann, O.; Terol, E.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Impact of Farmland Abandonment on Water Resources and Soil Conservation in Citrus Plantations in Eastern Spain. Water 2019, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, J.R.; Bogunovic, I.; Mohajerani, H.; Pereira, P.; Cerdà, A.; Ruiz Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. The Impact of Vineyard Abandonment on Soil Properties and Hydrological Processes. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, T.J.; Incze, J.; Spohn, M.; Glina, B.; Giani, L. Soil and vegetation transformation in abandoned vineyards of the Tokaj Nagy-Hill, Hungary. Catena 2014, 123, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaez, J.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Ortigosa, L. Factors affecting runoff and erosion under simulated rainfall in Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Iserloh, T.; Morvan, X.; Malam Issa, O.; Naisse, C.; Keesstra, S.D.; Cerdà, A.; Prosdocimi, M.; Arnáez, J.; Lasanta, T. Soil erosion processes in European vineyards: a qualitative comparison of rainfall simulation measurements in Germany, Spain and France. Hydrology 2016, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnáez, J.; Larrea, V.; Ortigosa, L. Surface runoff and soil erosion on unpaved forest roads from rainfall simulation tests in northeastern Spain. Catena 2004, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, K.; Schwab, A. Erosion risk (C factor) of different viticultural practices. Die Wein-Wissenschaft Viticult. Enolog. Sci. 1999, 54, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Iserloh, T.; Lassu, T.; Cerdà, A.; Keestra, S.D.; Prosdocimi, M.; Brings, C.; Marzen, M.; Ramos, M.C.; Senciales, J.M. Quantitative comparison of initial soil erosion processes and runoff generation in Spanish and German vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Saladino, S.S.; Santoro, A.; Cerdà, A. Soil erosion assessment on tillage and alternative soil managements in a Sicilian vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The immediate effectiveness of barley straw mulch in reducing soil erodibility and surface runoff generation in Mediterranean vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U.; Rickson, R.J.; Auerswald, K. Soil erosion protection measures in Europe. In Proceedings of the European Community workshop, Freising, Germany, 24–26 May 1988; Schweizerbart Science Publishers: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Emde, K. Erosion exposure of the Hessen winegrowing regions, Germany. Recommendations for protection measures with view to climatic conditions. In Proceedings of the Foerderungsdienst, Wien; Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft; Wien: Vienna, Austria, 1994; Volume Sonderausgabe, pp. 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer, W. Cultivation of steeply sloping vineyards. Rebe Wein 1976, 29, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Joerger, V.; Stoermann-Belting, J.; Zipf, S. Results for 1992 of the pilot project environment-friendly viticulture. Der Badische Winzer 1993, 18, 276–281. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, H.; Steinberg, B.; Kiefer, W. Root observations on grapevine dependent on different soil management systems. Die Wein-Wissenschaft Viticult. Enolog. Sci. 1994, 49, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Götzke, A. Entwicklung einer Naturschutzkonzeption in Weinbaugebieten auf der Grundlage einer Vergleichenden Untersuchung Faunistischer und Betriebswirtschaftlicher Parameter Praxisüblich und Ökologisch Erzeugender Weinbaubetriebe; Bayerische Julius-Maximilians-Universität: Würzburg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]


| Site | Management Group | RS Experiments |
|---|---|---|
| Kanzem | abold | 14 |
| coold | 11 | |
| ecold | 11 | |
| ecyoung | 9 | |
| Waldrach | abold | 13 |
| abyoung | 9 | |
| coold | 9 | |
| coyoung | 6 |
| Variables | Area | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kanzem | Waldrach | t-Test | |||||||
| avg | stddev | min | max | avg | stddev | min | max | Sig. (2-tailed) | |
| spQ | 2.3 | 3.9 | 0 | 16.9 | 3.4 | 5.3 | 0 | 25.9 | 0.29 |
| RC | 11.6 | 19.2 | 0 | 82.8 | 17.2 | 23.5 | 0 | 88.9 | 0.24 |
| spSY | 10.1 | 21.5 | 0 | 95.9 | 23.3 | 66.6 | 0 | 373.2 | 0.21 |
| SSC | 1.6 | 2.9 | 0 | 10.9 | 2.9 | 5.5 | 0 | 25.2 | 0.17 |
| des. par. | spQ | RC | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abold | abyoung | coold | coyoung | ecold | ecyoung | abold | abyoung | coold | coyoung | ecold | ecyoung | |
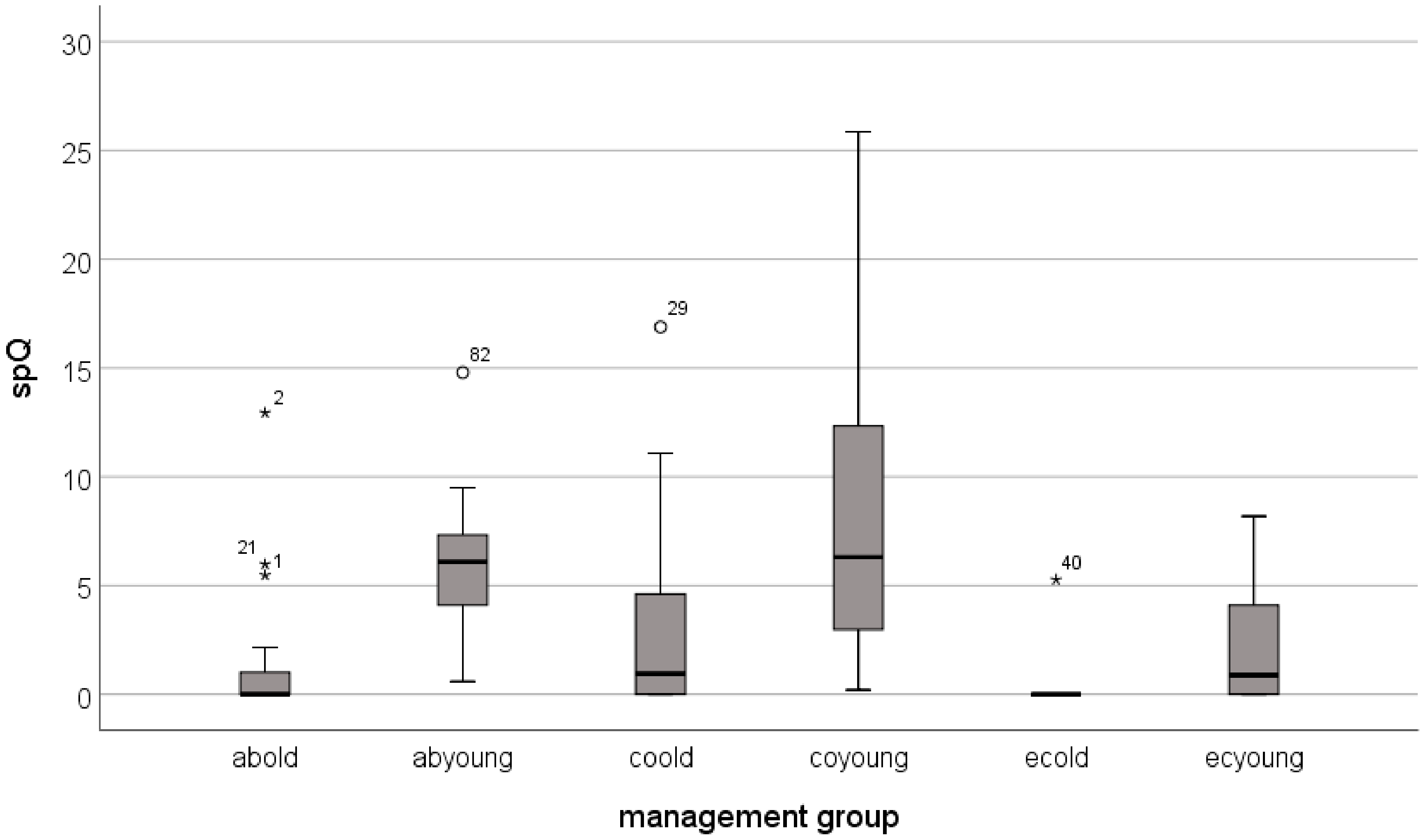
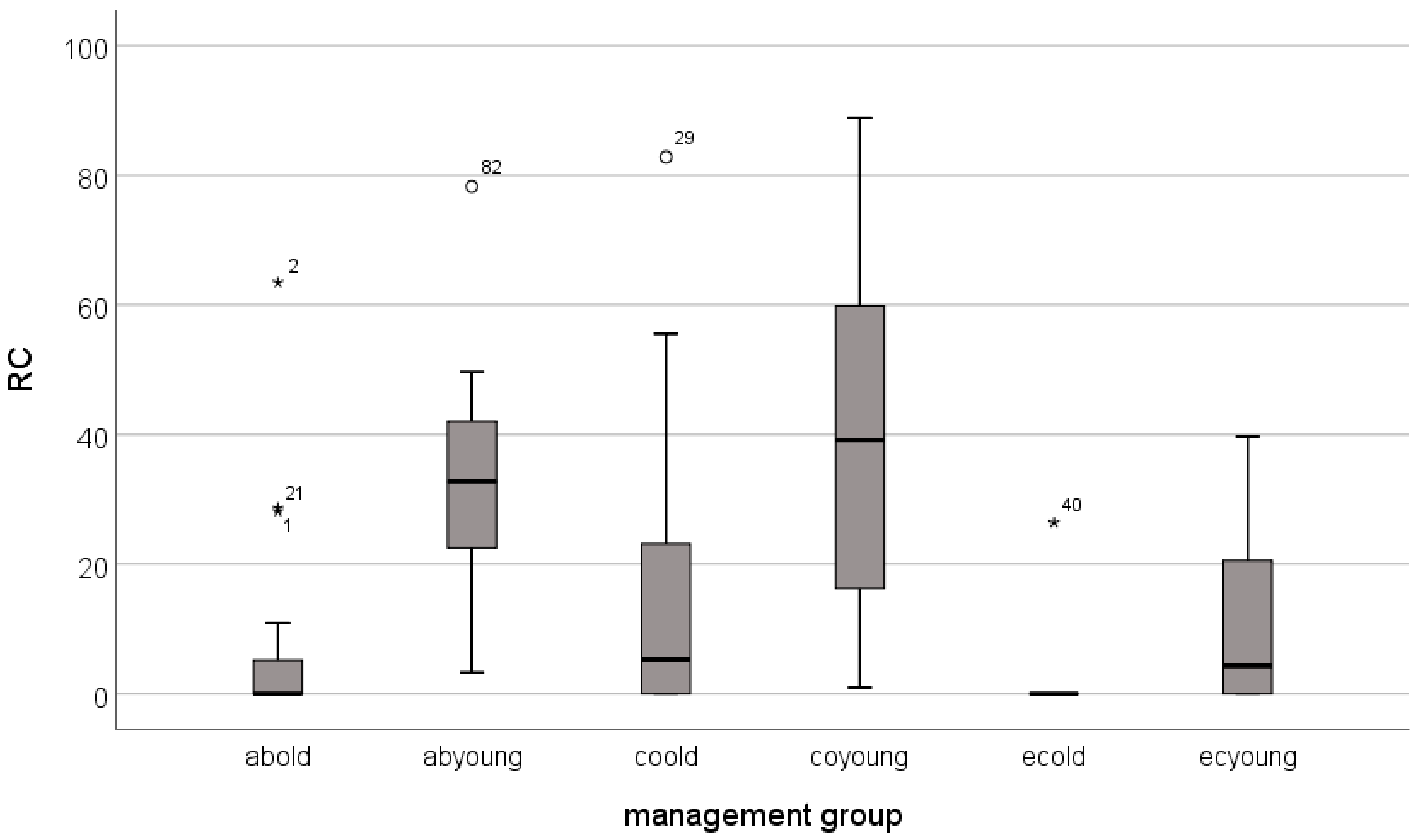
| avg | 1.2 | 6.4 | 3.1 | 9.0 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 5.9 | 35.2 | 15.3 | 40.7 | 2.4 | 11.8 |
| median | 0.0 | 6.1 | 0.9 | 6.3 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 32.7 | 5.3 | 39.1 | 0.0 | 4.3 |
| stdev | 2.8 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 9.2 | 1.6 | 3.0 | 13.9 | 21.2 | 22.1 | 31.2 | 8.0 | 14.7 |
| min | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.3 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| max | 12.9 | 14.8 | 16.9 | 25.9 | 5.3 | 8.2 | 63.5 | 78.3 | 82.8 | 88.9 | 26.4 | 39.7 |
| des. par. | spSY | SSC | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abold | abyoung | coold | coyoung | ecold | ecyoung | abold | abyoung | coold | coyoung | ecold | ecyoung | |
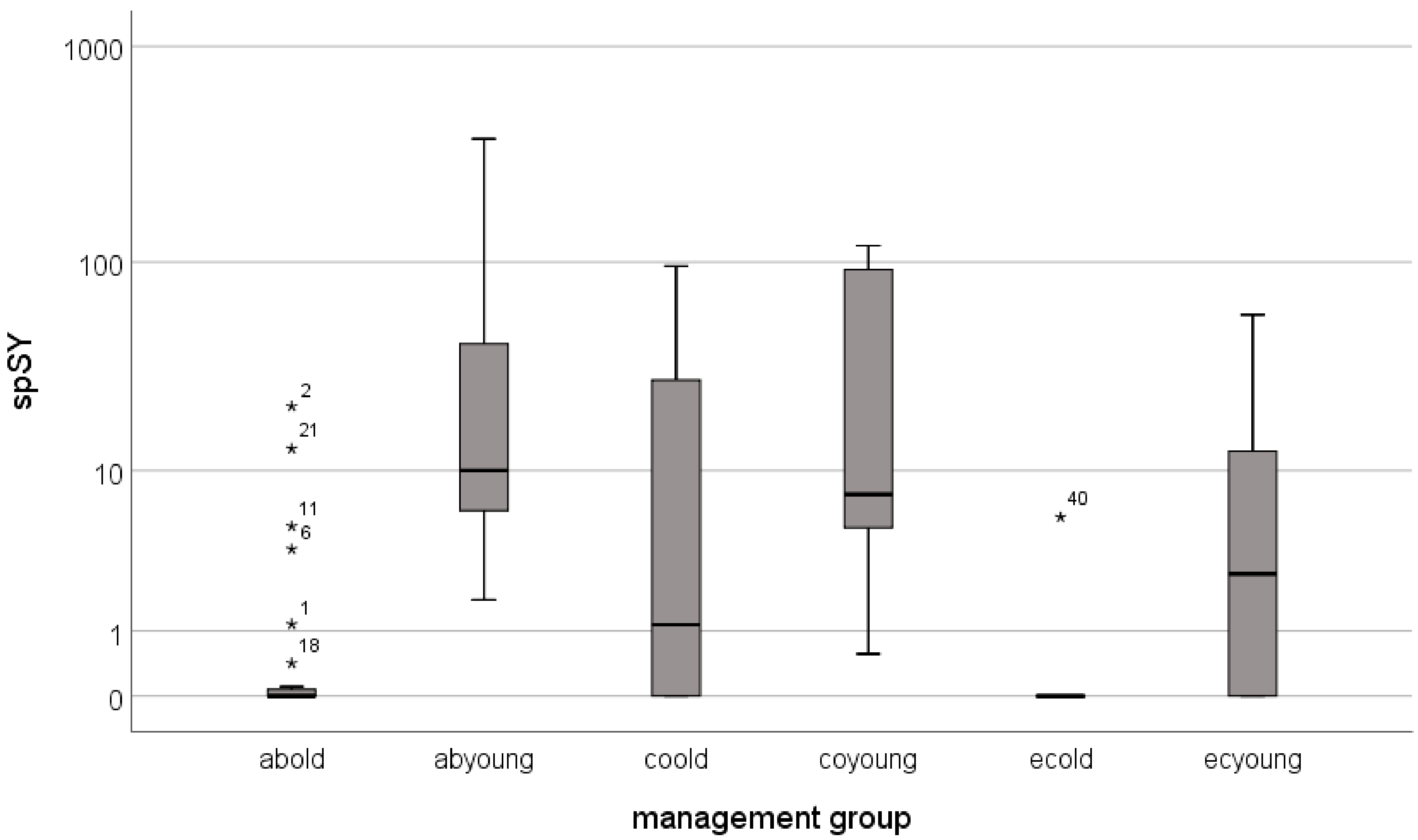
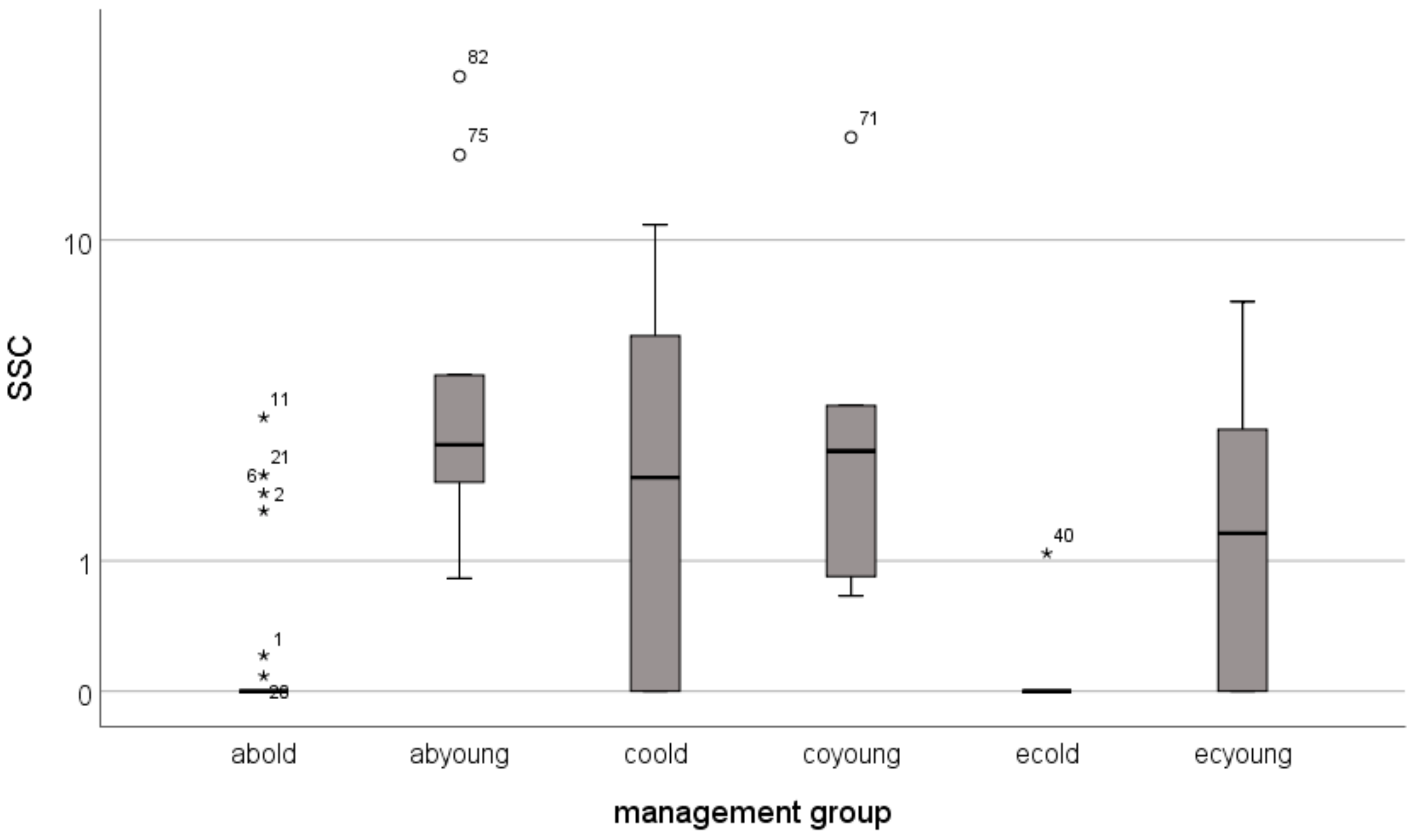
| Avg | 1.6 | 64.7 | 17.8 | 38.7 | 0.5 | 10.3 | 0.3 | 6.5 | 3.2 | 4.7 | 0.1 | 2.1 |
| median | 0.0 | 10.0 | 1.3 | 7.6 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| stdev | 4.7 | 121.5 | 28.1 | 52.7 | 1.7 | 18.3 | 0.8 | 8.5 | 3.7 | 6.6 | 0.3 | 2.6 |
| min | 0.0 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| max | 20.8 | 373.2 | 95.9 | 119.3 | 5.7 | 56.7 | 3.3 | 25.2 | 10.9 | 18.0 | 1.1 | 6.9 |
| Group Pairs | spQ | RC | spSY | SSC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | corr. p | p | corr. p | p | corr. p | p | corr. p | |
| ecold-abold | 0.382 | 1.000 | 0.380 | 1.000 | 0.457 | 1.000 | 0.572 | 1.000 |
| ecold-ecyoung | 0.071 | 1.000 | 0.078 | 1.000 | 0.046 | 0.968 | 0.035 | 0.731 |
| ecold-coold | 0.018 | 0.378 | 0.021 | 0.437 | 0.006 | 0.135 | 0.002 | 0.047 |
| ecold-abyoung | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.020 |
| ecold-coyoung | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| abold-ecyoung | 0.195 | 1.000 | 0.215 | 1.000 | 0.102 | 1.000 | 0.052 | 1.000 |
| abold-coold | 0.051 | 1.000 | 0.061 | 1.000 | 0.010 | 0.217 | 0.001 | 0.029 |
| abold-abyoung | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.023 |
| abold-coyoung | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| ecyoung-coold | 0.848 | 1.000 | 0.849 | 1.000 | 0.753 | 1.000 | 0.622 | 1.000 |
| ecyoung-abyoung | 0.026 | 0.552 | 0.020 | 0.419 | 0.097 | 1.000 | 0.167 | 1.000 |
| ecyoung-coyoung | 0.046 | 0.963 | 0.034 | 0.715 | 0.041 | 0.864 | 0.074 | 1.000 |
| coold-abyoung | 0.016 | 0.328 | 0.011 | 0.231 | 0.108 | 1.000 | 0.254 | 1.000 |
| coold-coyoung | 0.036 | 0.758 | 0.025 | 0.533 | 0.037 | 0.782 | 0.108 | 1.000 |
| abyoung-coyoung | 0.992 | 1.000 | 0.970 | 1.000 | 0.868 | 1.000 | 0.830 | 1.000 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seeger, M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Iserloh, T.; Brings, C.; Ries, J.B. Dynamics of Runoff and Soil Erosion on Abandoned Steep Vineyards in the Mosel Area, Germany. Water 2019, 11, 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122596
Seeger M, Rodrigo-Comino J, Iserloh T, Brings C, Ries JB. Dynamics of Runoff and Soil Erosion on Abandoned Steep Vineyards in the Mosel Area, Germany. Water. 2019; 11(12):2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122596
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeeger, Manuel, Jesús Rodrigo-Comino, Thomas Iserloh, Christine Brings, and Johannes B. Ries. 2019. "Dynamics of Runoff and Soil Erosion on Abandoned Steep Vineyards in the Mosel Area, Germany" Water 11, no. 12: 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122596
APA StyleSeeger, M., Rodrigo-Comino, J., Iserloh, T., Brings, C., & Ries, J. B. (2019). Dynamics of Runoff and Soil Erosion on Abandoned Steep Vineyards in the Mosel Area, Germany. Water, 11(12), 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122596






