Evaluation of GloFAS-Seasonal Forecasts for Cascade Reservoir Impoundment Operation in the Upper Yangtze River
Abstract
1. Introduction
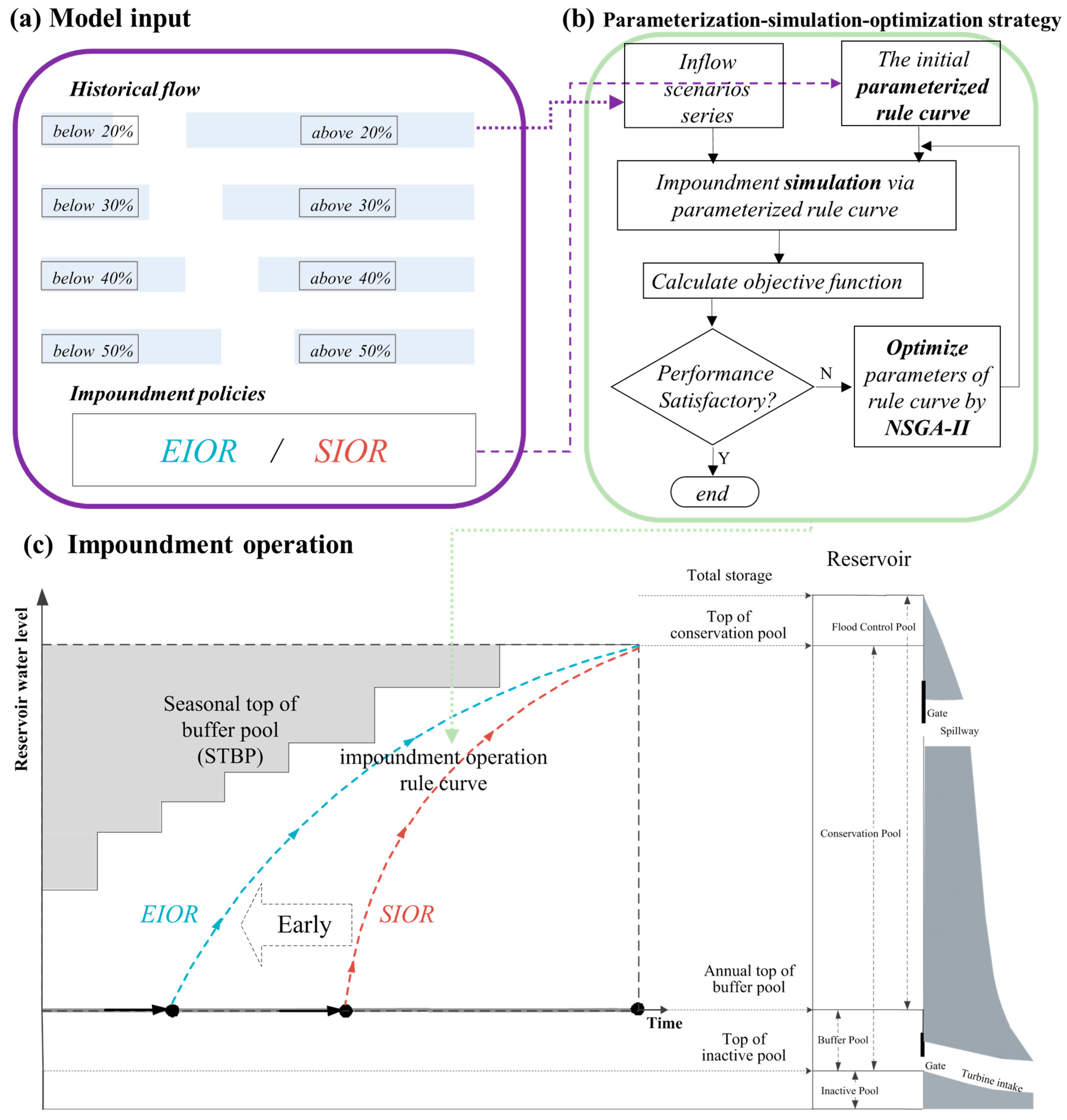
2. Cascade Reservoir Impoundment Model
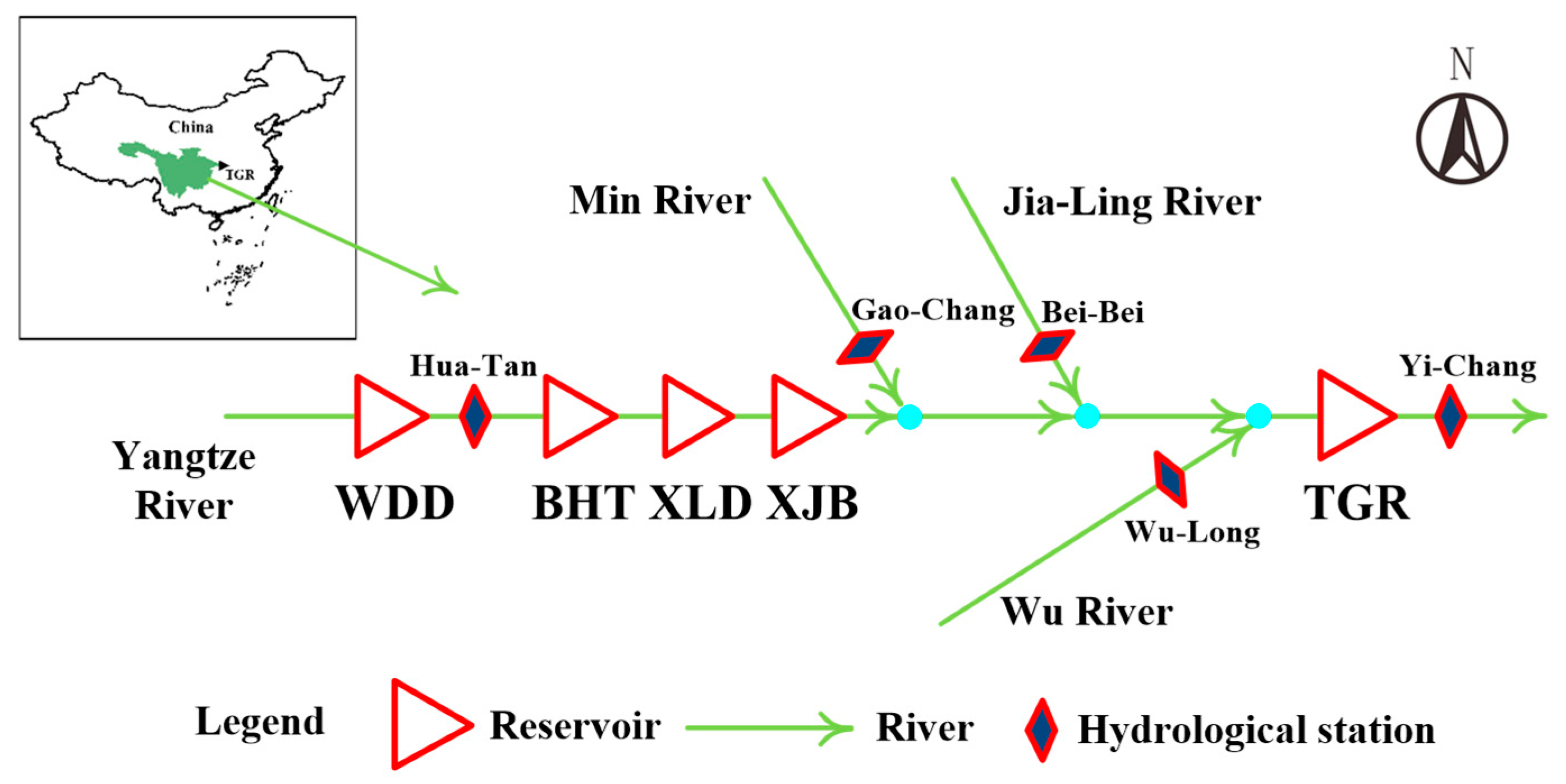
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Impoundment Operation Rules for Cascade Reservoirs
2.3. Objective Functions and Constrains
2.3.1. Objective Functions
| M | the number of reservoirs; |
| N | the number of years for hydrological time series; |
| HGi,k | hydropower generation of the kth reservoir in the ith simulated year, kW·h |
| αk | the weight for fullness storage rate of the kth reservoir, calculated by the ratio about the total storage capacity of M reservoirs; |
| FSRi,k | fullness storage rate of the kth reservoir in the ith simulated year; |
| the storage capacity corresponding to the annual top of buffer pool of the kth reservoir, m3; | |
| the storage capacity corresponding to the top of conservation pool of the kth reservoir, m3; | |
| the highest storage during impoundment operation of the kth reservoir in the ith simulated year, m3; | |
| Rk | flood control risk of the kth reservoir; |
| Nrisk,k | the number of years when the water level exceeds STBP of the kth reservoir. |
2.3.2. Operation Constraints
| N | the number of years for hydrological time series; |
| T | total number of days during impoundment operation in the ith simulated year; |
| the kth reservoir storage at the beginning of the jth day in the ith simulated year, m3; | |
| the kth reservoir inflow on the jth day in the ith simulated year, m3/s; | |
| the water discharge of kth reservoir on the jth day in the ith simulated year, m3/s; | |
| the water discharge for hydropower generation of the kth reservoir on the jth day in the ith simulated year, m3/s; | |
| the spilled water discharge of the kth reservoir on the jth day in the ith simulated year, m3/s; | |
| Ak | the hydropower generation efficiency of the kth reservoir; |
| the average hydropower head of the kth reservoir on the jth day in the ith simulated year, m; | |
| the minimum power limits of the kth hydropower plant, kW; | |
| the maximum power limits of the kth hydropower plant, kW; | |
| the minimum water discharge for downstream of the kth reservoir, m3/s; | |
| the maximum water discharge for flood control safety in downstream of the kth reservoir, m3/s; | |
| ΔQk | the maximum water discharge fluctuation of the kth reservoir, m3/s; |
| the minimum water level at downstream of the kth dam site, m; | |
| the maximum water level at downstream of the kth dam site, m; | |
| the water level at downstream of kth dam site on the jth day in the ith simulated year, m; | |
| f(⋅) | the function provided by reservoir managers expressing the relationship between reservoir discharge and downstream water level. |
2.4. NSGA-II Optimization Algorithm
3. Evaluation of GloFAS-Seasonal Forecasts
3.1. Discrimination
3.2. Skill
3.3. Reliability, Resolution, and Sharpness
4. Results and Discussion
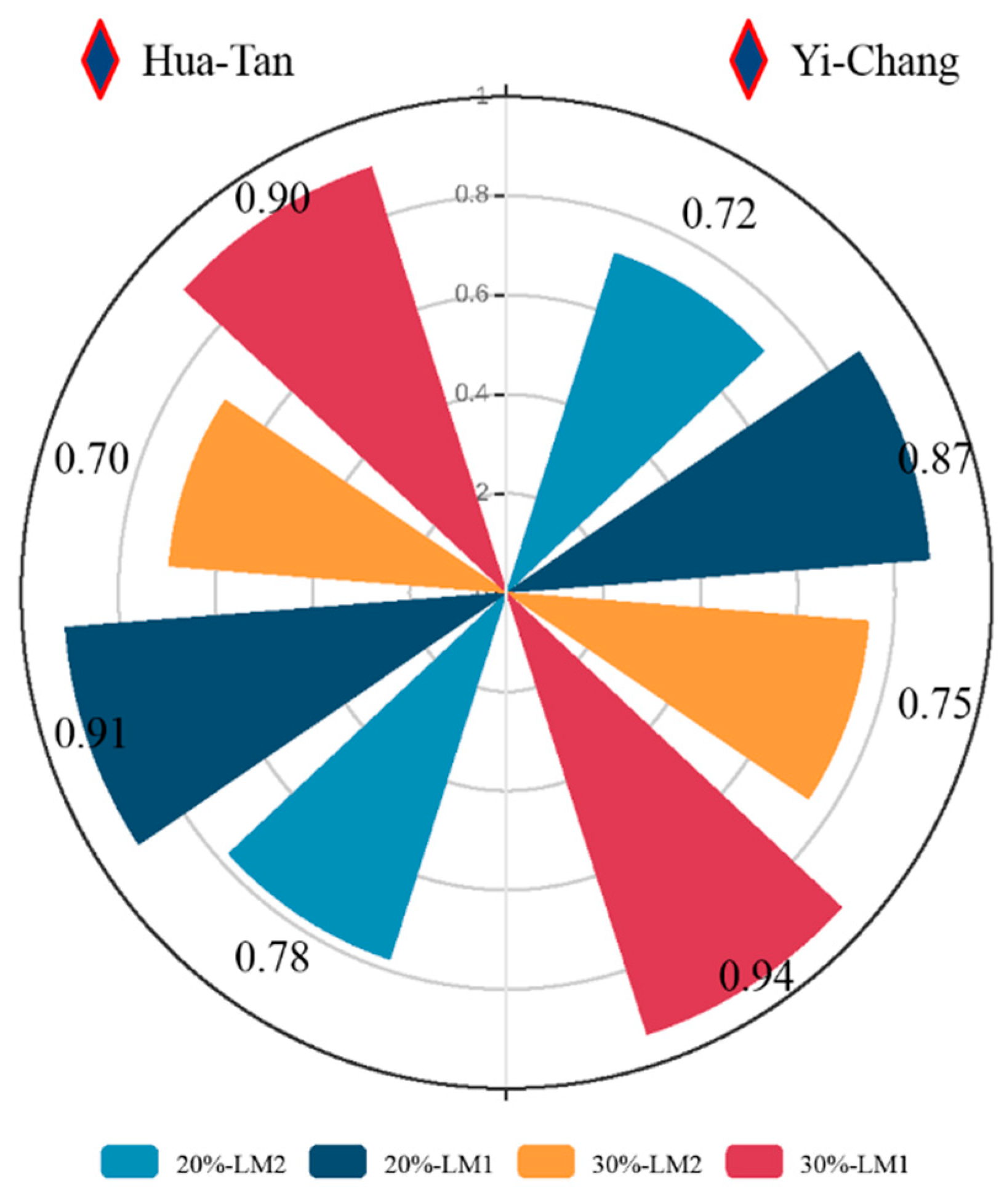
4.1. The Selected Thresholds
4.2. Evaluation of GloFAS-Seasonal Reforecasts
4.2.1. AUC Values
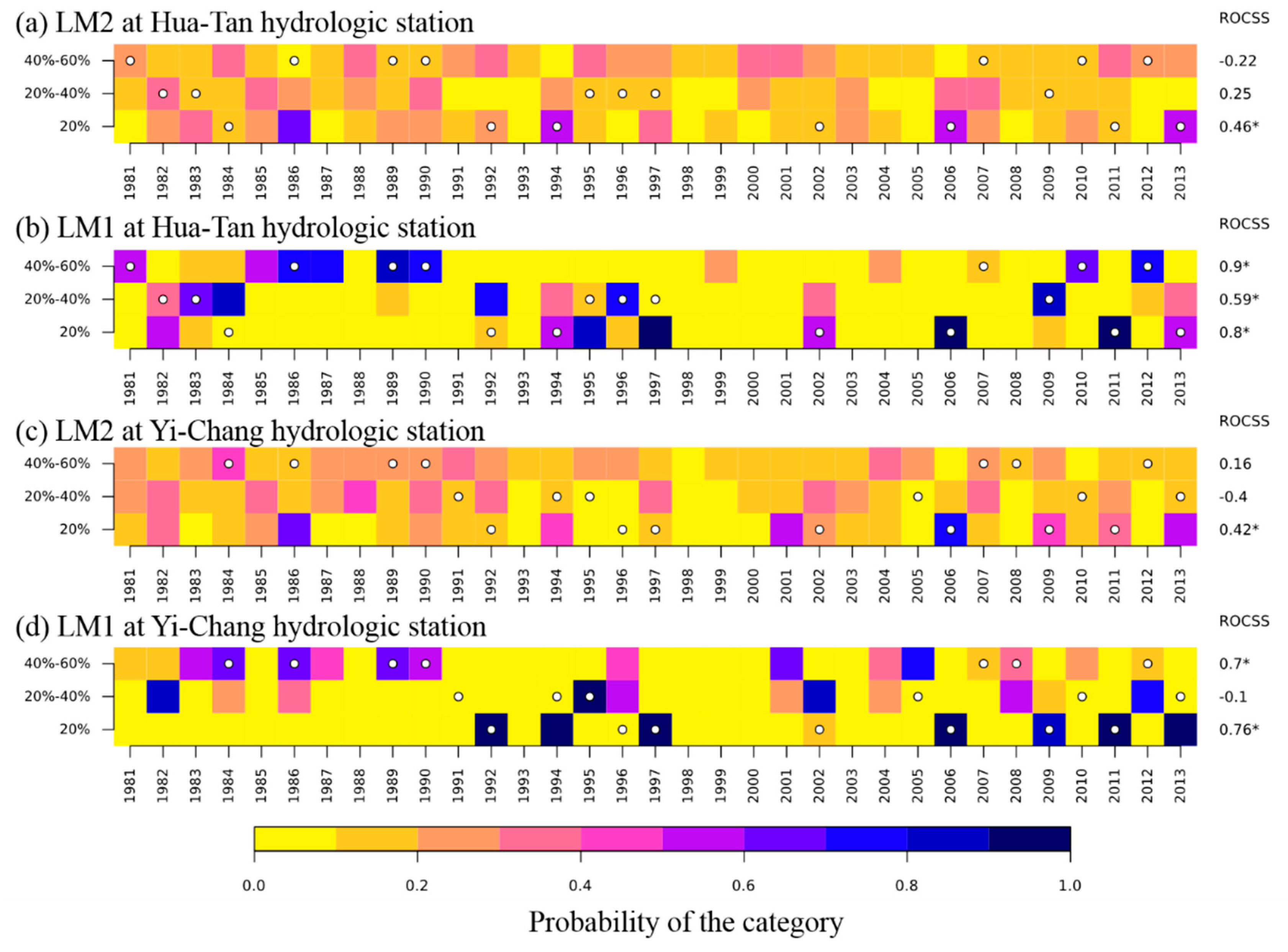
4.2.2. ROCSS Values
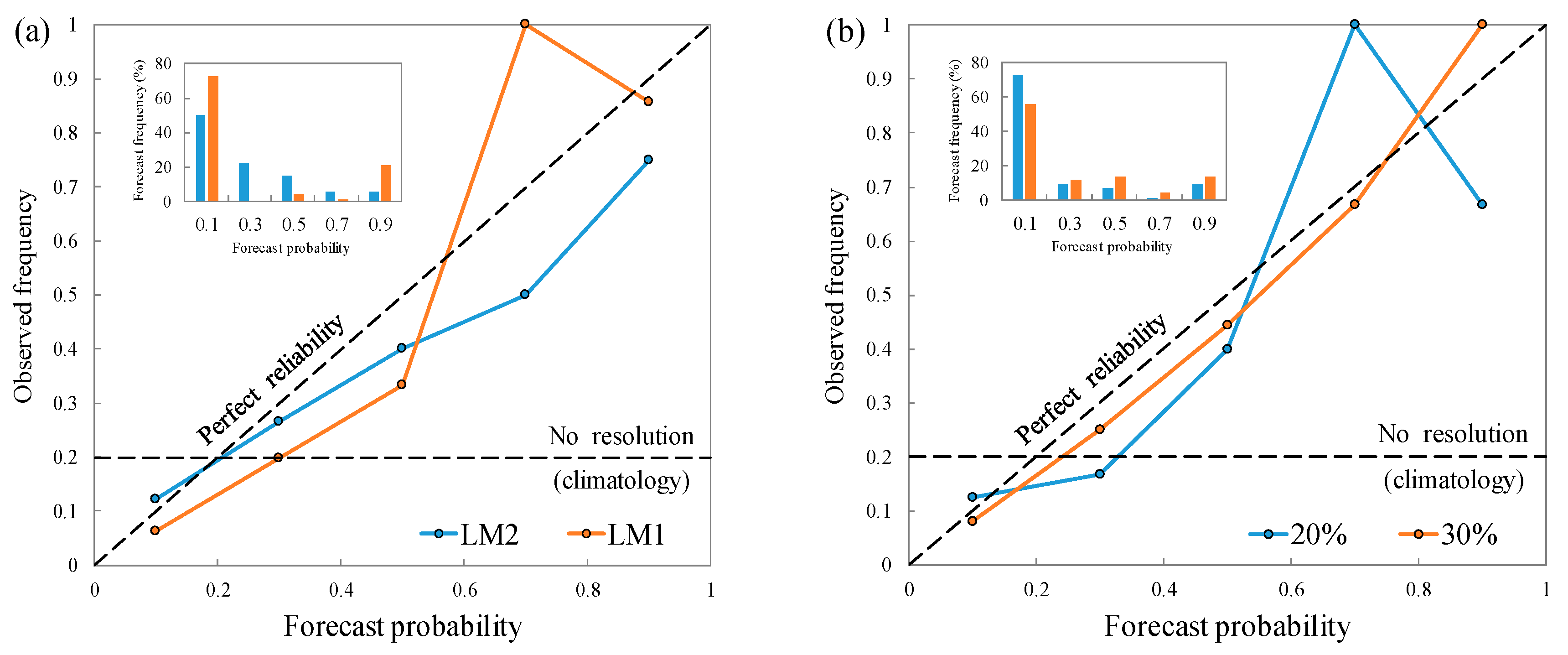
4.2.3. Reliability Diagram
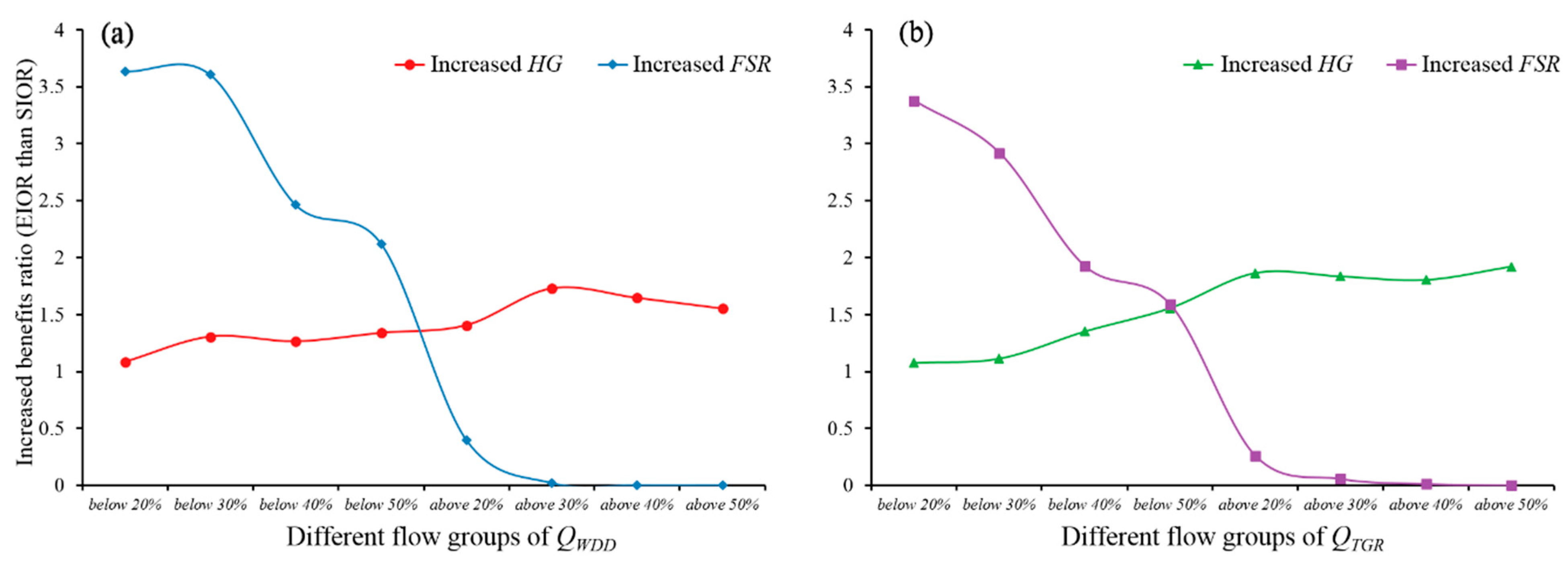
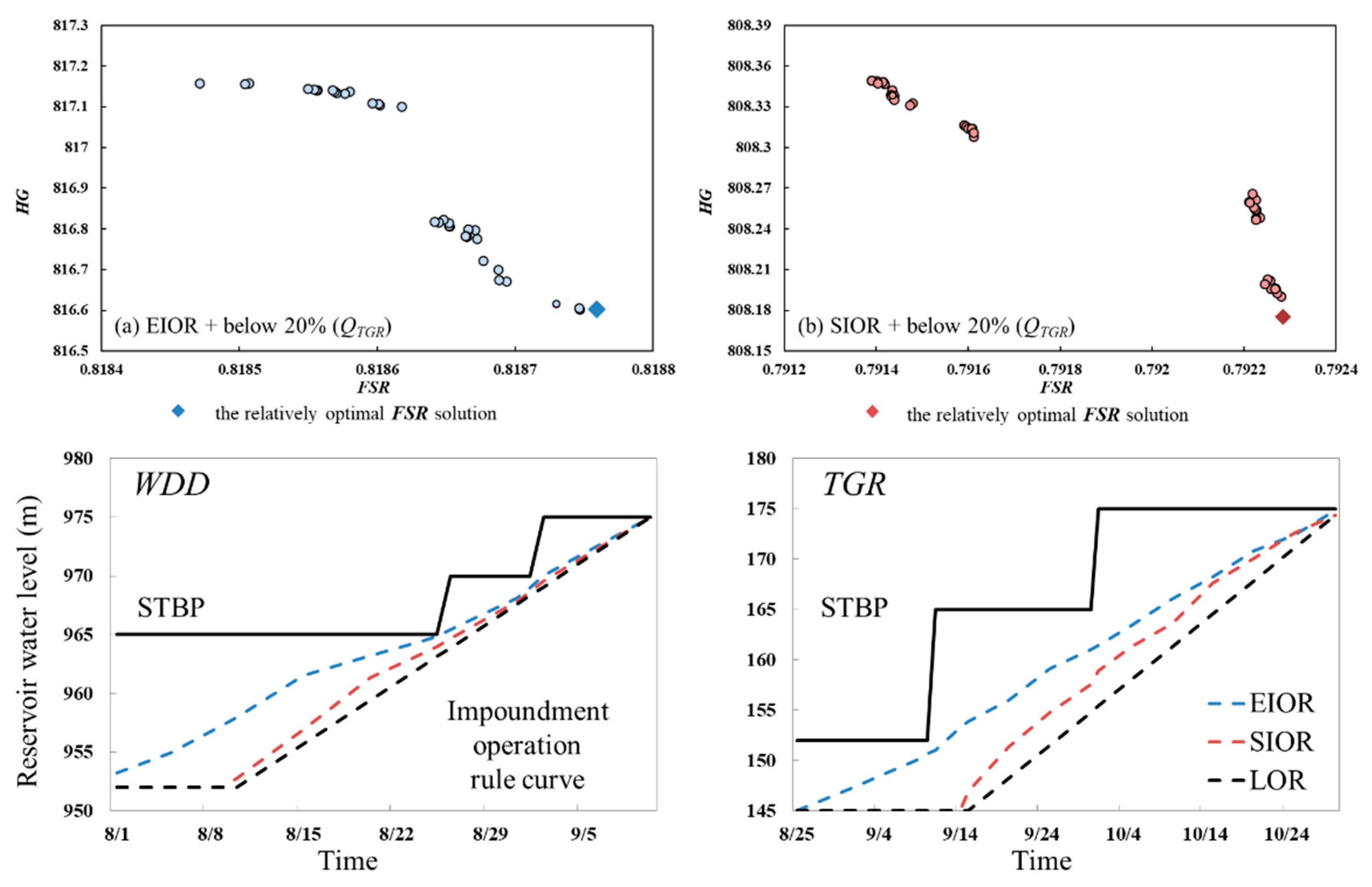
4.3. Specific Analysis and Benefits of the EIOR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Labadie, J.W. Optimal operation of multireservoir systems: State-of-the-art review. J. Water Res. Plan. Man. 2004, 130, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Zhang, H.G.; Chen, H.; Peng, D.Z.; Liu, P.; Pang, B. A reservoir flood forecasting and control system for China. Hydrolog. Sci. J. 2004, 49, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, A.; Mazdiyasni, O.; AghaKouchak, A. A hybrid framework for assessing socioeconomic drought: Linking climate variability, local resilience, and demand. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7520–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnamay Naeini, M. A Framework for Optimization and Simulation of Reservoir Systems Using Advanced Optimization and Data Mining Tools. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Sun, N.; Chen, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, J.Z.; Zha, G.; Luo, G.L.; Dai, L.; Yang, X. Optimal Operation of Cascade Reservoirs for Flood Control of Multiple Areas Downstream: A Case Study in the Upper Yangtze River Basin. Water 2018, 10, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.S.; Zhou, J.Z.; Huang, K.D.; Dai, L.; Zha, G.; Chen, L.; Qin, H. Risk Assessment and Decision-Making Based on Mean-CVaR-Entropy for Flood Control Operation of Large Scale Reservoirs. Water 2019, 11, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Guo, S.L.; Xu, C.Y.; Liu, P.; Qin, H. Deriving joint optimal refill rules for cascade reservoirs with multi-objective evaluation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, P.; Guo, S.L.; Ming, B.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, Y.L. Hybrid Two-Stage Stochastic Methods Using Scenario-Based Forecasts for Reservoir Refill Operations. J. Water Res. Plan. Man. 2018, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.K.; Guo, S.L.; Chen, K.B.; Deng, L.L.; Liao, Z.; Xiong, F.; Yin, J.B. Optimal impoundment operation for cascade reservoirs coupling parallel dynamic programming with importance sampling and successive approximation. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 131, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla, R.J.; Gomez, C.M.; Kondolf, G.M. Reservoir-induced hydrological changes in the Ebro River basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2004, 290, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, E.J. Impounding reservoirs. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1956, 48, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, J.R. Developing Seasonal and Long-Term Reservoir System Operation Plans Using HEC-PRM; Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, J.R.; Guzman, J. Derived operating rules for reservoirs in series or in parallel. J. Water Res. Plan. Man. 1999, 125, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Guo, S.L.; Xiong, L.H.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.G. Deriving reservoir refill operating rules by using the proposed DPNS model. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Guo, S.L.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Li, X.A. Deriving Optimal Refill Rules for Multi-Purpose Reservoir Operation. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, S.L.; Quo, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.Y.; Chen, J.H. Deriving the optimal refill rule for multi-purpose reservoir considering flood control risk. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhou, J.Z.; Ouyang, S.; Li, C.L. Research on Joint Impoundment Dispatching Model for Cascade Reservoir. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 5527–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Guo, S.L.; Chang, F.J.; Xu, C.Y. Boosting hydropower output of mega cascade reservoirs using an evolutionary algorithm with successive approximation. Appl. Energ. 2018, 228, 1726–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasperse, J.; Ralph, M.; Anderson, M.; Brekke, L.D.; Dillabough, M.; Dettinger, M.D.; Haynes, A.; Hartman, R.; Jones, C.; Forbis, J. Preliminary Viability Assessment of Lake Mendocino Forecast Informed Reservoir Operations; Center For Western Weather and Water Extremes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.L.; Xiao, C.; Du, L.M.; Zhang, P.Q.; Wang, G.F. Extended-Range Runoff Forecasting Using a One-Way Coupled Climate-Hydrological Model: Case Studies of the Yiluo and Beijiang Rivers in China. Water 2019, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagoulia, D. Impacts of Giss-Modeled Climate Changes on Catchment Hydrology. Hydrolog. Sci. J. 1992, 37, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wood, E.F.; Ma, Z.G. A review on climate-model-based seasonal hydrologic forecasting: Physical understanding and system development. Wires Water 2015, 2, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagoulia, D.; Dimou, G. Sensitivity of flood events to global climate change. J. Hydrol. 1997, 191, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhou, T. Understanding and seasonal forecasting of hydrological drought in the Anthropocene. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5477–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnal, L.; Cloke, H.L.; Stephens, E.; Wetterhall, F.; Prudhomme, C.; Neumann, J.; Krzeminski, B.; Pappenberger, F. Skilful seasonal forecasts of streamflow over Europe? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2057–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.C.; Wang, Q.J.; Robertson, D.E.; Schepen, A.; Li, M.; Michael, K. Assessment of an ensemble seasonal streamflow forecasting system for Australia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6007–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demargne, J.; Wu, L.M.; Regonda, S.K.; Brown, J.D.; Lee, H.; He, M.X.; Seo, D.J.; Hartman, R.; Herr, H.D.; Fresch, M.; et al. The Science of NOAA’s Operational Hydrologic Ensemble Forecast Service. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, P. Tailoring seasonal climate forecasts for hydropower operations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorit, J.; Ortuya, E.C.G.; Block, P. Evaluation of model-based seasonal streamflow and water allocation forecasts for the Elqui Valley, Chile. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4711–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.A.; Wood, A.W.; Rajagopalan, B. Developing Subseasonal to Seasonal Climate Forecast Products for Hydrology and Water Management. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 55, 1024–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.B.; Guo, S.L.; He, S.K.; Xu, T.; Zhong, Y.X.; Sun, S.R. The Value of Hydrologic Information in Reservoir Outflow Decision-Making. Water 2018, 10, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.Z.; Ye, L.; Meng, C.Q. Streamflow estimation by support vector machine coupled with different methods of time series decomposition in the upper reaches of Yangtze River, China. Environ. Earth 2016, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.R.; Chen, Y.F.; Huang, Q.; Yu, S.N.; Hou, Y. Evaluation of ocean-atmospheric indices as predictors for summer streamflow of the Yangtze River based on ROC analysis. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 1903–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.F.; Lei, X.H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wen, X.; Ji, Y.; Kang, A.Q. An adaptive middle and long-term runoff forecast model using EEMD-ANN hybrid approach. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerton, R.; Zsoter, E.; Arnal, L.; Cloke, H.L.; Muraro, D.; Prudhomme, C.; Stephens, E.M.; Salamon, P.; Pappenberger, F. Developing a global operational seasonal hydro-meteorological forecasting system: G1oFAS-Seasonal v1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 3327–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.W.G. Reservoir Management and Operations Models - a State-of-the-Art Review. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 1797–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.H.; Zhang, J.W.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.N.; Khu, S.T.; Li, Z.J.; Tan, Q.F. Deriving mixed reservoir operating rules for flood control based on weighted non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeste, A.B.; Billib, M. Evaluation of stochastic reservoir operation optimization models. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.T.G.; Zhao, J.S. Optimizing Operation of Water Supply Reservoir: The Role of Constraints. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, M.R.; Yang, T.T.; Sadegh, M.; AghaKouchak, A.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Duan, Q.Y.; Lei, X.H. Shuffled Complex-Self Adaptive Hybrid EvoLution (SC-SAHEL) optimization framework. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2018, 104, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Chang, F.J. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for operating parallel reservoir system. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.P.; Chang, F.J.; Chang, L.C.; Herricks, E.E. AI techniques for optimizing multi-objective reservoir operation upon human and riverine ecosystem demands. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uen, T.S.; Chang, F.J.; Zhou, Y.L.; Tsai, W.P. Exploring synergistic benefits of Water-Food-Energy Nexus through multi-objective reservoir optimization schemes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chang, F.J. Evolutionary artificial neural networks for hydrological systems forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, G.; Pappenberger, F.; Dutra, E.; Viterbo, P.; van den Hurk, B. A revised land hydrology in the ECMWF model: A step towards daily water flux prediction in a fully-closed water cycle. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landman, W.A.; Beraki, A. Multi-model forecast skill for mid-summer rainfall over southern Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundel, F.; Jorg-Hess, S.; Zappa, M. Monthly hydrometeorological ensemble prediction of streamflow droughts and corresponding drought indices. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanas, R.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Bhend, J.; Hemri, S.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Torralba, V.; Penabad, E.; Brookshaw, A. Bias adjustment and ensemble recalibration methods for seasonal forecasting: A comprehensive intercomparison using the C3S dataset. Clim. Dynam. 2019, 53, 1287–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.J.; Graham, N.E. Conditional probabilities, relative operating characteristics, and relative operating levels. Weather Forecast. 1999, 14, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappenberger, F.; Ramos, M.H.; Cloke, H.L.; Wetterhall, F.; Alfieri, L.; Bogner, K.; Mueller, A.; Salamon, P. How do I know if my forecasts are better? Using benchmarks in hydrological ensemble prediction. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogutu, G.E.O.; Franssen, W.H.P.; Supit, I.; Omondi, P.; Hutjes, R.W.A. Skill of ECMWF system-4 ensemble seasonal climate forecasts for East Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2734–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, E.; Orfila, B.; Frias, M.D.; Fernandez, J.; Cofino, A.S.; Gutierrez, J.M. Downscaling ECMWF seasonal precipitation forecasts in Europe using the RCA model. Tellus A 2011, 63, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Stephenson, D.B. Forecast Verification: A Practitioner’s Guide in Atmospheric Science; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, S.J.; Stephenson, D.B. How do we know whether seasonal climate forecasts are any good? In Seasonal Climate: Forecasting and Managing Risk; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 259–289. [Google Scholar]
| Reservoir | Basin Area (Thousand km2) | Annual Top of Buffer Pool (m) | Top of Conservation Pool (m) | Total Storage Capacity (Billion m3) | Storage for Flood Control (Billion m3) | Installed Hydropower Capacity (GW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WDD | 406.1 | 952 | 975 | 3.94 | 2.44 | 10.20 |
| BHT | 430.3 | 785 | 825 | 20.60 | 7.50 | 16.00 |
| XLD | 454.4 | 560 | 600 | 12.67 | 4.65 | 13.86 |
| XJB | 458.8 | 370 | 380 | 5.16 | 0.90 | 7.75 |
| TGR | 1000 | 145 | 175 | 45.07 | 22.15 | 22.50 |
| Reservoir | Initial Impoundment Time | Final Impoundment Time (SIOR, EIOR) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (SIOR) | (EIOR) | ||
| WDD | Aug. 10th | Aug.1st | Sep. 10th |
| BHT | Aug. 10th | Aug.1st | Sep. 30th |
| XLD | Sep. 10st | Aug. 25th | Sep. 30th |
| XJB | Sep. 10st | Aug. 25th | Sep. 30th |
| TGR | Sep. 15th | Aug. 25th | Oct. 31st |
| Reservoir | Seasonal Top of Buffer Pool (m) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug.15th | Aug.25th | Sep.1st | Sep.10th | Sep.30th | Oct.31st | |
| WDD | 965 | 965 | 970 | 975 | 975 | 975 |
| BHT | 800 | 810 | 810 | 810 | 825 | 825 |
| XLD | 560 | 565 | 575 | 575 | 600 | 600 |
| XJB | 370 | 372 | 375 | 375 | 380 | 380 |
| TGR | 145 | 145 | 152 | 152 | 165 | 175 |
| Flow Group | EIOR | SIOR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG (108 kW·h) | FSR (%) | R (%) | HG (108 kW·h) | FSR (%) | R (%) | ||
| QWDD | below 20% | 813.784 | 82.68% | 0 | 805.070 | 79.78% | 0 |
| below 30% | 845.857 | 85.43% | 0 | 834.963 | 82.45% | 0 | |
| below 40% | 868.680 | 89.40% | 0 | 857.848 | 87.25% | 0 | |
| below 50% | 895.822 | 91.72% | 0 | 884.002 | 89.81% | 0 | |
| above 20% | 1025.617 | 99.25% | 1.802% | 1011.410 | 98.86% | 2.229% | |
| above 30% | 1040.072 | 99.98% | 2.035% | 1022.395 | 99.96% | 2.123% | |
| above 40% | 1060.128 | 100.00% | 2.924% | 1042.975 | 100.00% | 2.284% | |
| above 50% | 1074.293 | 100.00% | 3.730% | 1057.887 | 100.00% | 2.842% | |
| QTGR | below 20% | 816.973 | 81.86% | 0 | 808.284 | 79.18% | 0 |
| below 30% | 838.596 | 86.20% | 0 | 829.380 | 83.76% | 0 | |
| below 40% | 876.391 | 89.49% | 0 | 864.720 | 87.80% | 0 | |
| below 50% | 895.437 | 91.56% | 2.055% | 881.728 | 90.13% | 0 | |
| above 20% | 1024.592 | 99.23% | 2.217% | 1005.852 | 98.97% | 2.742% | |
| above 30% | 1042.250 | 99.70% | 2.313% | 1023.483 | 99.65% | 2.098% | |
| above 40% | 1048.775 | 99.88% | 2.237% | 1030.204 | 99.87% | 2.902% | |
| above 50% | 1072.242 | 99.96% | 2.263% | 1052.043 | 99.96% | 3.043% | |
| Flow Group | Rule Curve in Figure 7 | Benefit and Risk | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG (108 kW·h) | FSR (%) | R (%) | |||
| QTGR | below 20% | LOR | 785.042 | 77.512% | 0 |
| EIOR | 816.601 | 81.876% | 0 | ||
| Increased ratio | 4.02% | 5.63% | 0 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Qin, P.; He, S.; Sun, S.; Naeini, M.R. Evaluation of GloFAS-Seasonal Forecasts for Cascade Reservoir Impoundment Operation in the Upper Yangtze River. Water 2019, 11, 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122539
Chen K, Guo S, Wang J, Qin P, He S, Sun S, Naeini MR. Evaluation of GloFAS-Seasonal Forecasts for Cascade Reservoir Impoundment Operation in the Upper Yangtze River. Water. 2019; 11(12):2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122539
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kebing, Shenglian Guo, Jun Wang, Pengcheng Qin, Shaokun He, Sirui Sun, and Matin Rahnamay Naeini. 2019. "Evaluation of GloFAS-Seasonal Forecasts for Cascade Reservoir Impoundment Operation in the Upper Yangtze River" Water 11, no. 12: 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122539
APA StyleChen, K., Guo, S., Wang, J., Qin, P., He, S., Sun, S., & Naeini, M. R. (2019). Evaluation of GloFAS-Seasonal Forecasts for Cascade Reservoir Impoundment Operation in the Upper Yangtze River. Water, 11(12), 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122539






