Abstract
The addition of substrates to small instream obstacles, like low-head ramped weirs, has been considered a useful management solution to retrofit those structures and enhance fish passage. Substrate dimensions and spatial arrangement, together with discharge, and consequently water depths, appear as important factors for the creation of hydrodynamic conditions that may facilitate the successful passage of fish, though related studies are scarce to support decision-making. This study assessed the influence of discharge (Q) and different retrofitting designs (RD) on the upstream passage performance of a potamodromous cyprinid, the Iberian barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei). Different substrates (small boulders, large boulders, cobbles) and spatial arrangements (aligned, offset) were tested. Numerical modelling was performed to characterize the hydrodynamics. Results indicate that Q and RD influenced the upstream negotiation of ramped weirs. Cobbles randomly distributed along the ramp (Nature design) was the most successful configuration, recording the highest number of upstream passages. Low velocities along the ramp, and low turbulence downstream, were registered in this configuration, indicating that the use of natural substrate may help to increase the permeability of ramped weirs to fish movements. The outcomes from this work can help engineers and biologists to design more appropriate passage structures for low-head instream obstacles.
1. Introduction
Freshwater fish are among the most threatened species, especially because of the flow modification and habitat destruction or degradation [1,2,3]. The presence of small engineered structures (e.g., low-head weirs, culverts) has been considered one of the main causes to habitat fragmentation on rivers worldwide. Recent studies have pointed the fact that, because of the high abundance of these small obstacles, which are far more numerous than large dams [4], their cumulative impact on fish populations may be greater than estimated [5,6,7].
More than 8000 small weirs (height < 5 m) have been located in Portuguese rivers [8]. The small broad-crested weirs, which have a vertical downstream face [5,9], and especially low-head ramped weirs, with inclined faces that fish may be able to negotiate by swimming [5,10], are the two most common designs [6]. In fact, in order to enhance fish passability, some old broad-crested weirs which, after assessment, could not be removed, have undergone rehabilitation works to include ramps in their designs (e.g., [11,12]). This design reconfiguration enables water to pass over the ramp, not generating a waterfall [5,10], a condition that may afford a more holistic negotiation by fish [5,13]. Nevertheless, fish swimming abilities, which are closely related to fish guilds and body size [14,15,16,17], and hydrodynamic conditions, such as water depth, discharge, and turbulence present over the ramp and in the vicinity of the structure [5,18,19,20], are key factors that influence the permeability of such structures to fish movements.
The addition of substrates to instream obstacles and fish transposition devices, commonly referred to as retrofitting, has been considered a useful management solution to enhance upstream fish passage [5,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. The placement of substrates in culverts to mimic natural stream conditions and facilitate fish passage has been successfully implemented since the early 1970s [29]. In low-head ramped weirs, natural substrates like pebbles, cobbles, or boulders, are frequently used as retrofitting solutions to increase the bed roughness, and consequently promote energy dissipation, creating localized zones of low-velocity and turbulence [23,24,25,30] that may be used by fish as resting areas during the upstream negotiation of ramps [20,27,31,32,33]. These low velocities may be especially important to species of weaker swimming capabilities, such as potamodromous cyprinids [5,21,22]. Substrate dimensions and spatial arrangement, together with discharge, and consequently water depths, appear therefore as important factors for the creation of suitable hydrodynamic conditions that may facilitate the successful upstream passage of fish [20,23,28]. Nonetheless, the effectiveness and efficiency of most retrofitting solutions remains poorly understood, particularly for potamodromous cyprinids, which are an important component of Mediterranean fish assemblages [34,35,36].
This study aims to assess the influence of discharge (Q) and different retrofitting designs (RD) to improve upstream passage performance of the Iberian barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei). A total of six configurations were tested, contemplating: four configurations of Boulders placed on the sloped face of an experimental ramped weir, varying on size (Small vs. Large) and arrangement (Aligned vs. Offset); a nature-like design, hereafter referred to as Nature, consisting of cobbles randomly distributed along the ramp, as another potential improvement for fish passage [37]; and a Control configuration (smooth bottom, no substrate), as the reference situation to assess potential improvements on fish passage. These six configurations were tested under two different Q: 55 and 110 L·s−1. Additionally, numerical modelling was performed to characterize the hydrodynamics of all the configurations tested, using the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) commercial software FLOW-3D®. Iberian barbel was selected as the target species, since it is considered representative of a few species of medium-sized benthic potamodromous cyprinids commonly present in Iberian and Western European rivers [22,38,39]. It was expected that: (i) passage performance of fish, considering attraction as well as successful upstream movements, will be influenced by both factors Q and RD; (ii) attraction efficiency would increase with increasing Q, and with RD that provide higher velocity magnitudes; and (iii) successful passages, and consequently passage efficiency, would decrease with increasing Q and with RD presenting high turbulence and high velocity magnitude.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Facility
Experiments were performed in an indoor ecohydraulic flume installed at the Hydraulics and Environment Department of the National Laboratory for Civil Engineering (LNEC), in Lisbon. The rectangular steel frame flume (Figure 1A), 10.00 m long × 0.60 m wide × 1.20 m high, comprises an upstream and a downstream tank, from where the water enters the flume and is recirculated, that are separated from the main channel by mesh panels. The sidewalls of the main channel are glass-viewing panels that allow a direct, and unobtrusive, observation of fish behavior throughout the experiments. In order to represent the average slope of central and southern Iberian small size watercourses, the channel was set at a 3% slope (Catchment Characterization and Modelling, version 2 (CCM2); [40]).
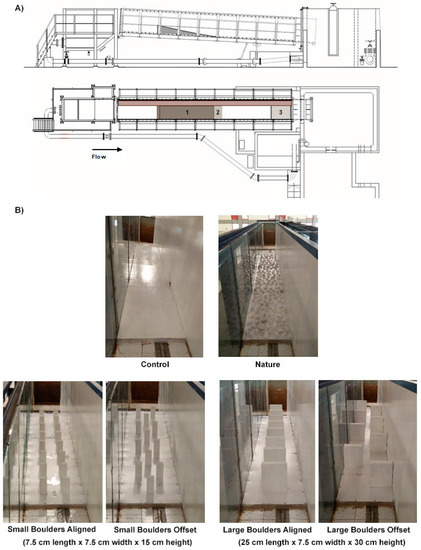
Figure 1.
(A) Scheme of the experimental flume, representing a side view of the channel on a slope of 3% (above), and a top view (below) with the location of (1) the experimental low-head ramped weir (ramp 3.00 m long on a slope of 10%, with a 0.20 m weir crest, located 2.50 m upstream the acclimation area), (2) the approach area (the 0.30 m2 shaded area immediately downstream of the ramp toe), and (3) the acclimation area (the 0.60 m2 shaded area between the two removable fine mesh panels located downstream); (B) Images of the six configurations tested, contemplating the Control ramp (without substrates) and the retrofitted designs selected: Nature (ramp with cobbles randomly distributed), Small Boulders Aligned and Offset (boulder dimensions 7.5 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 15 cm high), and Large Boulders Aligned and Offset (boulder dimensions 25 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 30 cm high).
The experimental low-head ramped weir used in this study, with a length of 3.00 m and a slope of 10%, was selected based on the results of a previous study by Amaral et al. [41], in which it was found that this combination of ramp length and slope may have adversely affected the successful negotiations for the same species. As in Amaral et al. [41], the experimental ramped weir, made of maritime plywood, was fixed in the flume (Figure 1A) at 2.50 m upstream of the acclimation area, a 0.60 m2 area created by two mesh panels in the downstream zone of the flume, and immediately downstream of the ramp toe, a 0.50 m long zone was established as the approach area. Six different configurations (Figure 1B) were tested, considering a Control ramp, without substrates, and five retrofitted designs contemplating: a Nature design, where cobbles of 10 to 30 cm were randomly distributed along the ramp; Small Boulders Aligned and Small Boulders Offset, using boulders 7.5 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 15 cm high, spatially aligned and alternating respectively; and Large Boulders Aligned and Large Boulders Offset, where larger boulders (25 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 30 cm high) were set in an aligned and alternating design respectively. Figure 2 illustrates the spatial arrangement of substrates on the retrofitted designs tested. Furthermore, to assess the influence of Q on the passage performance of fish, the six configurations were tested under two different discharges—55 and 110 L·s−1. The lower discharge (Q = 55 L·s−1) was selected considering the recommendations by Baudoin et al. [5] that suggests that the minimum water column over the ramp, referred to as non-limiting for the successful upstream passage of fish, should be between one and two times the body depth of the fish. Regarding the higher discharge (Q = 110 L·s−1; double the lower Q), which was previously tested by Amaral et al. [41], it was selected to test the effect that higher water velocities and turbulence may have on hydrodynamics of different RD and, consequently, on the passage performance of fish. Discharge was measured by a flow meter installed in the supply pipe.
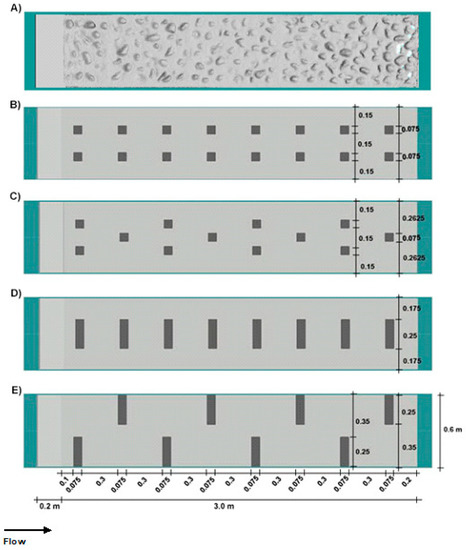
Figure 2.
Scheme of the substrates arrangement for the retrofitted designs (RD), showing flow direction and the 0.2 m weir crest: (A) Nature (the mapping of cobbles along the ramp was done using a Kinect Sensor); (B) Small Boulders Aligned; (C) Small Boulders Offset; (D) Large Boulders Aligned; (E) Large Boulders Offset. Substrates dimensions: Cobbles—10 to 30 cm; Small Boulders—7.5 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 15 cm high; Large Boulders—25 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 30 cm high.
2.2. Fish Capture and Holding
Adult Iberian barbel used in the experiments (n = 240; mean total length (TL) ± standard deviation (SD) = 17.4 ± 2 cm; maximum body depth (H) ± SD = 3 ± 0.3 cm; body width (W) ± SD = 1.9 ± 0.3 cm) were captured by wadeable electrofishing (Hans Grassl IG-200) in the Lisandro River, a small Atlantic coastal river near Lisbon. A total of six electrofishing episodes were performed (one episode per week, collecting 40 fish per episode) according to the protocol adopted by the European Committee for Standardization [42]. Only adult fish were selected to avoid bias in swimming performance. Fish were transported to the laboratory facilities at LNEC in a fish transport box (Hans Grassl, Schönau am Königssee, Germnay, 190 L) with portable external aeration (ELITE, Germany), and were maintained for a maximum period of 6 days in filtered and aerated acclimation tanks (700 L tanks; Fluval Canister Filter FX5), each featured with two U-shape ceramic roof tiles (45 cm long × 25 cm wide × 10 cm high) to provide shelter [43]. Water quality of the tanks was monitored daily (temperature = 22 ± 1 °C, pH = 7.7 ± 0.3, and conductivity = 180 ± 15 μs.cm−1), using a multiparametric probe (HANNA, HI 9812-5, Wensojit, RI, USA), and high-quality levels (i.e., active fish, no mortality) were ensured by the mechanical and biological filtration system, with a turnover rate of 2300 L·h−1. Fish were only tested after an acclimation period of 48 h from the holding conditions in the laboratory. During that period, fish were fed with Tetra Pond sticks up to 24–48 h before the experiments. No fish were sacrificed during the experiments, and efforts were made to minimize stress.
2.3. Fish Experiments
Fish experiments were conducted in strict accordance with ethical provisions on the welfare of experimental animals enforced by the European Union and were coordinated by J.M. Santos, who holds FELASA level C certification (www.felasa.eu) to direct animal experiments. Fish capture, handling, transportation, and holding permits were issued by the Institute for Conservation of Nature and Forests (ICNF) (permit numbers 40/2017 and 222/2017/CAPT; 41/2017 and 223/2017/CAPT; 42/2017 and 224/2017/CAPT). Fish experiments and maintenance in the LNEC facility were authorized by the Department for Health and Animal Protection (Direcção de Serviços de Saúde e Protecção Animal) in accordance with the recommendations of the “protection of animal use for experimental and scientific work.”
Experiments were performed during late spring-early summer, reported by some authors as the main reproductive season for this species [5,44,45], following the previous findings by Amaral et al. [41]. Four replicates were carried out for each configuration tested (6 configurations × 2 discharges × 4 replicates = 48 trials) using schools of 5 fish (20 fish tested per configuration) with similar size, which were not individualized. Fish were randomly selected from the acclimation tanks and were used only once. Each replicate started with an acclimation period of 15 min, for fish to adapt to the flume conditions. After that time, the upstream mesh panel of the acclimation area was removed, and fish were able to explore the channel for 60 min. Both upstream and downstream passages were allowed, so fish could approach, attempt to pass, and successfully negotiate the ramp multiple times.
Fish movements, specifically the number of fish that entered the approach area (Ap), the number of fish that entered into the ramp and actively tried to negotiate it (At), and the number of fish that navigated the entire ramp reaching the upstream part of the flume—complete successful passages (S), were monitored by direct observation, and also recorded (top view) by a video camera (GoPro HERO5, San Mateo, CA, USA). The metrics of passage performance—percentage of attraction efficiency (AE; %) and percentage of passage efficiency (PE; %), were also calculated from Equations (1) and (2).
AE (%) = 100 × At/Ap
PE (%) = 100 × S/At
The influence of factors RD and Q, as well as their interaction on the passage performance of Iberian barbel considering the movements of Ap and At, as well as S was analyzed performing a PERMANOVA test, using the package PERMANOVA for PRIMER +v6.0 [46]. This statistical test was selected for being a robust non-parametric method based on the permutations tests that directly partitions the variation in a distance matrix according to Euclidean distances or non-Euclidean-embeddable dissimilarity measures [47,48]. In this analysis, the Euclidean distance was applied to compute the distance matrix due to the presence, and relevance, of zeros in the assessed data [46].
2.4. Hydrodynamic Modelling
The hydrodynamics of the tested configurations were characterized by numerical modelling using FLOW-3D®, a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) commercial software. FLOW-3D® uses the finite volume method to solve the governing equations of fluid motion, by subdividing the computational domain into a structured mesh grid of variable-sized hexahedral cells, using a volume of fluid (VOF) method to track the free surface [49,50]. The fractional area/volume obstacle representation [51], named FAVORTM method, is one of the major features of FLOW-3D®. This method is used to represent obstacles through fractional areas and volumes in the fixed orthogonal grid. Flow Science [50] presents additional details regarding the theoretical and numerical fundamentals of FLOW-3D®, which has been used in recent years to characterize flow hydrodynamics in ecohydraulics and fishway research (e.g., [52,53,54]).
The computational domain was discretized using two grid blocks: one, with a uniform mesh size of 0.01 m that contained the entire flume geometry, and one nested block with half the grid spacing (0.005 m) from the upstream face of the weir to 0.5 m downstream the ramp. Data on spatial arrangement of the tested configurations—Control, Small Boulders Aligned, Small Boulders Offset, Large Boulders Aligned, and Large Boulders Offset, was generated using AutoCAD and was imported into the model as stereolithography (STL) files. For the Nature design, the 3D-bottom bathymetric data was measured using Kinect TM (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, EUA), an input device designed for the Microsoft® Xbox 360® [55]. The upstream boundary was specified as a constant volume flow rate with the initial inlet water level defined as the water depth observed in the experimental flume, and the downstream boundary was specified as a pressure boundary condition, based on the water depth observed in the trials. The side walls and the bottom were modelled as smooth no-slip boundaries, and, at the top, a symmetry boundary condition (zero value for normal velocity, zero gradients for the other quantities) was applied. The initial pressure was set to the atmospheric pressure. A second order monotonicity preserving method and the large-eddy simulation (LES) model was employed for the momentum advection equations and the turbulence modelling and an implicit generalized minimum residual method solver (GMRES) was used [50]. The simulations were performed for a number of time steps enough to achieve a statistically stationary solution and obtain converged time-averaged values.
Model performance was validated with values of water depth and velocity magnitude measured during experiments in 27 sampling points (Figure 3), located along the ramped weir and both up and downstream (more details in Amaral et al. [41]). Velocity magnitude was measured with a flow probe (model FP 101, Global Water Instrumentation Inc., College Station, TX, USA), since water column was not deep, and there was excessive aeration and turbulence in most of the configurations tested, conditions that narrow the use of a 3D acoustic doppler velocimeter. To check the influence of the grid resolution on the results, a coarser mesh (2.5 million cells), which doubled the size of the mesh cells (by halving the number of cells in each direction), was tested for the Control configuration. The LES index of resolution quality (LES IQ), proposed by Celik et al. [56], and mean absolute differences (MAD) were computed in the 27 sampling points, where water depth and velocity magnitude were measured, to verify the numerical model quality.
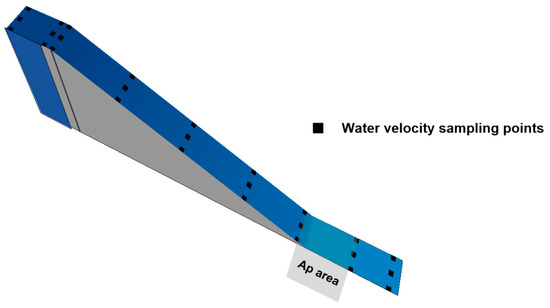
Figure 3.
Location of the water velocity sampling points. Measurements were taken along 3 longitudinal planes—at the center of the ramp, and 2 lateral planes spaced 0.05 m from the walls. Points were distanced 0.75 m along the ramp, and 0.50 m upstream and downstream (0.50 m and 1.00 m) of the ramped weir. Water velocity at the middle of the weir crest was also measured.
Finally, to illustrate the hydrodynamic conditions formed in each configuration tested (e.g., areas of high velocity and turbulence gradients that might have affected fish movements), 3D contour maps, representing the mean velocity magnitudes (; m·s−1) and turbulent kinetic energy per unit mass (TKE; m2·s−2), calculated from Equations (3) and (4) respectively, were plotted using the post-processing tool FlowSight. Mean water depths over the ramp (; cm) were also calculated.
3. Results
3.1. Fish Movements
Numerous movements of approach and attempts to negotiate the experimental ramps, as well as upstream successful passages were registered in all configurations tested. However, results from the different RD and Q tested (Table 1) were considerably different.

Table 1.
Total number of attempts (At), approaches (Ap), upstream successful passages (S), as well as attraction efficiency (AE%; ratio of the number of attempts per number of approaches × 100) and passage efficiency (PE%; ratio of successful upstream passages per number of attempts × 100) for the control low-head ramped weir and the retrofitting designs (RD) selected, considering the tested discharges (Q) of 55 L·s−1 (first rows) and 110 L·s−1 (second rows).
In general, more movements of Ap (n = 3010) and At (n = 437) were observed with Q = 55 L·s−1, relative to 110 L·s−1 (1385 and 200, respectively). Regarding S, more successes (n = 50) were also registered with Q = 55 L·s−1 when compared to 110 L·s−1 (n = 36), except for the two designs using the small boulders, in which only one successful passage was registered in the configuration Small Boulders Aligned, and no successes were attained in the Small Boulders Offset configuration. Concerning Q = 110 L·s−1, the poorest results were registered for the configurations Large Boulders Aligned and Control, with only three successes, and the total number of Ap (22 and 28 total approaches, respectively) and At (10 and 20 attempts to negotiate the ramp, respectively) observed in these configurations were also the lowest. For both discharges tested, the Nature design was the most successful configuration in terms of S, achieving 23 and 12 upstream passages for Q = 55 and 110 L·s−1, respectively. Regarding the metrics of passage performance, although Q = 55 L·s−1 registered an overall high number of fish movements, as mentioned above, AE (average of 46%) and PE (average of 4%) were lower than those recorded with Q = 110 L·s−1 (average of 50% and 24%, respectively). The Nature design was, in general, the configuration most efficient, registering values of AE = 75% and PE = 8%, for Q = 55 L·s−1, and PE = 48%, for Q = 110 L·s−1. However, for Q = 110 L·s−1, this configuration was the least attractive, registering the lowest value of AE (26%). In terms of PE, the poorest results were registered in the configurations Small Boulders Aligned (0% and 9%, for Q = 55 and 110 L·s−1, respectively) and Small Boulders Offset (0% and 11%, for Q = 55 and 110 L·s−1, respectively), for both discharges tested.
Results of the PERMANOVA analysis indicated that the number of Ap and At were significantly influenced by RD (Ap: F = 2.99; p = 0.03; and At: F = 2.84; p = 0.03) and by Q (Ap: F = 74.13; p < 0.01; At: F = 122.18; p < 0.01), but the combination of these factors (RD × Q) was not influencing fish movements (Ap: F = 1.41; p = 0.24; At: F = 2.01; p > 0.05). Concerning the influence on S, results reveal that successes were significantly influenced by RD (F = 6.55; p < 0.01) and by the combination RD × Q (F = 2.82; p = 0.02), but the influence of Q per se was not confirmed (F = 1.86; p > 0.05). Results of the pairwise comparisons (Table 2), performed after the main PERMANOVA test, showed that configurations had no differences in terms of S, except for Control vs. Small Boulders Offset, and especially for the Nature design, which registered more upstream successful passages when compared with all other configurations tested.

Table 2.
Results of the pairwise comparisons, performed after the main test PERMANOVA, on the number of successful upstream passages (S) for the factor retrofitting design (RD). Bold values highlight significant differences (α = 0.05).
3.2. Hydrodynamics
Results from the LES IQ quality index show that the finer mesh has an average value of 0.86, for Q = 55 L·s−1, and 0.89, for Q = 110 L·s−1. According to Pope [57], a good LES should have an LES IQ higher than 0.80, which means that 80% of the TKE was resolved. Thus, the values obtained for the finer mesh indicate that sufficient grid resolution was used. Regarding the results from MAD, computed from observed and modelled values, they ranged from 0.01 to 0.02 m for , registering a coefficient of determination (R2) between 0.96 and 0.99. When comparing observed and modelled , MAD ranged from 0.2 to 0.3 m·s−1, registering an R2 between 0.75 and 0.90. Therefore, the numerical model accurately reproduced the laboratory experiments.
Three-dimensional contour maps, showing the variation of (Figure 4) and TKE per unit mass (Figure 5) for the tested configurations, indicate that both hydraulic parameters increased with discharge. Moreover, Small Boulders Aligned, Small Boulders Offset, Large Boulders Aligned, and Large Boulders Offset, were configurations especially turbulent, registering values of TKE per unit mass above 0.4 m2·s−2, even with Q = 55 L·s−1. As for the configurations Control and Nature, lower values of TKE per unit mass (Control: <0.3 m2·s−2, and Nature: <0.25 m2·s−2) were registered, for both Q tested. However, in terms of , in both discharges tested, higher magnitudes were registered, as expected, in the Control configuration (max mean magnitude of 2.6 m·s−1 for Q = 55 L·s−1, and 3.4 m·s−1 for Q = 110 L·s−1), along with the Nature design (max mean magnitude of 2.5 m.s−1 for Q = 55 L·s−1, and 2.7 m·s−1 for Q = 110 L·s−1). As for the other RD, values of were lower, registering overall max mean magnitudes of 2.2 m·s−1 for Q = 55 L·s−1, and 2.5 m·s−1 for Q = 110 L·s−1. Nevertheless, for configurations Large Boulders Aligned and Large Boulders Offset, 3D-contour maps showed localized zones of low-velocity (< 0.5 m·s−1) between boulders.
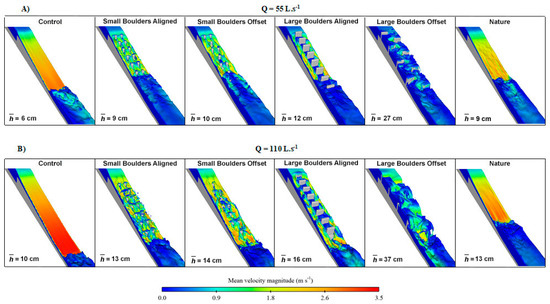
Figure 4.
Characterization of the mean water velocity magnitude (; m·s−1) for each configuration tested, using the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) commercial software FLOW-3D®, considering the discharges of: (A) 55 L·s−1, and (B) 110 L·s−1. Mean water depths over the ramp (; cm) is also presented for each configuration.
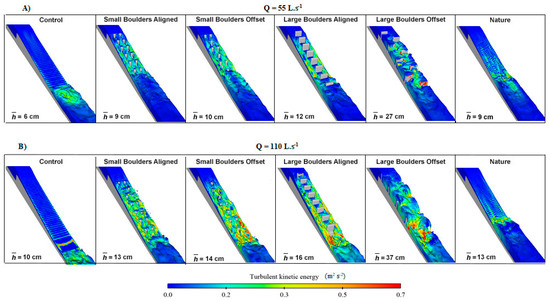
Figure 5.
Characterization of the turbulent kinetic energy per unit mass (; m2·s−2) for each configuration tested, using the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) commercial software FLOW-3D®, considering the discharges of: (A) 55 L·s−1, and (B) 110 L·s−1. Mean water depths over the ramp (; cm) is also presented for each configuration.
Regarding (Figure 4 and Figure 5), mean depths varied according to Q and the RD tested. Higher depths were registered, as expected, with Q = 110 L·s−1 (>4 cm, on average, except for the configuration Large Boulders Offset that registered a variation of 10 cm), and in the configurations with the larger boulders, especially in the Large Boulders Offset ( = 27 cm, for Q = 55 L·s−1, and 37 cm, for Q = 110 L·s−1). Shallower water depths were observed in the configurations Control ( = 6 cm, for Q = 55 L·s−1, and 10 cm, for Q = 110 L·s−1) and Nature ( = 9 cm, for Q = 55 L·s−1, and 13 cm, for Q = 110 L·s−1).
4. Discussion
The present study focused on the influence of RD and Q, as well as their interaction, on the passage performance of Iberian barbel negotiating low-head ramped weirs. The high number of observed movements (approaches, attempts to negotiate the ramp, and successful upstream passages) show that Iberian barbel were stimulated to move upstream and negotiate the ramped weirs. However, passage successes and efficiencies of designs varied among configurations tested, indicating that some substrates and spatial arrangements, along with discharge, provided more favorable hydrodynamic conditions for successful upstream passages of fish. Thus, to assess the effects of hydrodynamics on the fish behavior, numerical modelling (the 3D CFD model FLOW-3D®) was used in this study to characterize influential hydrodynamic variables, such as velocity magnitude, TKE, and water depths, present in each configuration tested, in order to identify areas of high velocity and turbulence gradients that might have affected the fish movements. Over the last few years, 3D CFD models have proved to be a practical and robust tool to characterize hydrodynamics on several hydraulic structures, being widely used for the assessment of fish passages (e.g., studies on functioning over a wide range of discharges, prediction of suitable conditions for fish), optimization of designs, and evaluation of different retrofitting solutions [52,53,54,58,59,60,61,62,63,64]. However, given that uncertainty in CFD modelling for environmental fluid mechanics in complex flow fields, like the flow field in the vicinity of a macro-scale roughness (e.g., wake region), can arise from a very wide range of sources, care should be taken when performing a numerical model study [65]. In the present study, a careful verification and validation of the numerical model was done, to ensure that a substantial reduction in the uncertainty of the results was achieved, by carefully following CFD best practice guidelines [65].
Like in other studies [9,23,25,66], Q, associated with velocity magnitude and turbulence, proved to be an important variable on the negotiation of the experimental low-head ramped weirs. In general, more approaches and attempts were registered with the lowest Q tested (55 L·s−1), which had almost seven times more records when compared to Q = 110 L·s−1. Nevertheless, for both Q, it was observed that, of the total number of fish approaches, only less than half resulted in effective attempts to negotiate the ramped weir, suggesting that many non-oriented Ap occurred, especially with 55 L·s−1. Consequently, lower values of AE (%) were registered with 55 L·s−1, as initially envisaged, except for the Nature design that achieved the highest value (75%). These results generally agree with previous studies on negotiation of low-head obstacles (e.g., [9,66,67]), and may indicate that, except for the Nature design, velocity magnitude (0.5–1.0 m·s−1) and TKE per unit mass (0.2–0.3 m2·s−2) occurring close to the ramps, which are parameters directly related with Q and influenced by RD [5,30], were not the most suitable to create attractive paths for fish to attempt to negotiate the obstacle and successfully pass it [32,68,69].
In addition to hydrodynamics though, biological factors beyond swimming ability may affect attraction and passage efficiency, as the following field assessment indicates. Landsman et al. [33] evaluated a nature-like fishway, for passage of Rainbow Smelt (Osmerus mordax) and Brook Trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). In each of the two study years, AE at the fishway for Rainbow Smelt was almost the same, 30.1% (2014; mean TL = 17 cm, range 15–24 cm) and 30.4% (2016; Mean TL = 15.9 cm, range 14–26 cm), while PE was 26.5% and 28.6%, respectively (not significantly different). In contrast, although AE for Brook Trout was only 9.2% in 2016 (Mean TL = 28.1 cm, range 16–52 cm), PE was 91.7%. The rather low but close AE and PE values for the shorter Rainbow Smelt, compared to the very high PE, despite the very low AE for the longer Brook Trout, implies that biological factors beyond length and corresponding swimming performance may contribute to successful passage effectiveness. Moreover, as Plesiński et al. [70] mentions, although for successful upstream passages fish may only need one usable path, for approaching the obstacle accurately and successfully attempt to negotiate it, fish primarily need to be able to detect the most functional paths when confronted with varied hydrodynamic conditions. Thus, metrics of attraction such as AE, which are directly dependent on the movements of Ap and At, vary substantially depending on the type of obstacle, its design and specificities (e.g., different retrofitting solutions, as tested in this study), and the consequently surrounding hydrodynamic conditions [5,71,72,73]. Therefore, future studies should focus on the quantification of the attraction in further subcomponents [74], such as guidance (i.e., arrival at the entrance) in response to hydrodynamic cues, and entry (i.e., decision to enter), using, for example, biotelemetry techniques to monitor fine-scale behavior [75,76].
Regarding S, as initially expected, the number of successes decreased with the increase of Q, except for the two RD using small boulders (Small Boulders Aligned and Small Boulders Offset). However, in terms of PE, higher values were unexpectedly achieved in all the configurations with Q = 110 L·s−1. Nevertheless, in both Q tested, configurations Small Boulders Aligned and Small Boulders Offset registered the lowest values of PE (0% for both configurations with 55 L·s−1; 9 and 11% with 110 L·s−1). In these two configurations, high values of velocity (2.0–3.0 m·s−1) and TKE per unit mass (0.3–0.5 m2·s−2) were registered and, especially, unpredictable fluctuations in both hydraulic parameters occurred along the ramp and at its toe, as shown in the CFD 3D-contour maps (Figure 4 and Figure 5). These conditions, together with the chaotic and small water depths over the ramp (ranging from 7–8 cm and 13–14 cm, for 55 L·s−1 and 110 L·s−1, respectively), may have influenced the fish passage because, as mentioned by Plesiński et al. [25], Liao [31], and Elder and Coombs [32], fish tend to avoid unexpected fluctuations of velocity, chaotic flows, and other flow conditions that may interfere with their swimming trajectories (e.g., vortex systems with diameters similar or greater than the fish body length; [77]). Moreover, the size of the boulders used in these configurations (7.5 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 15 cm high) may have been unsuitable to provide sizeable low-velocity zones, which could have been used by fish as resting areas, to recover energy and prepare for the successful upstream passage [20,23,25,27,31]. As for the two configurations using larger boulders (25 cm long × 7.5 cm wide × 30 cm high), Large Boulders Aligned and Large Boulders Offset, CFD 3D-contour maps showed localized zones of low-velocity (<0.5 m·s−1) between boulders, which could have provided conditions for fish to shelter and rest, as observed during the trials. Nevertheless, despite the occurrence of lower velocities and higher water depths (12–16 cm with 55 L·s−1, and 27–37 cm with 110 L·s−1, for Large Boulders Aligned and Large Boulders Offset, respectively), these two configurations were also not the most successful. The high TKE per unit mass (above 0.4 m2·s−2) present along the ramp, and especially at its toe, resulting from the combination of RD and Q, should have been the main condition that hampered the fish upstream movements. As referred by Knapp et al. [20], although localized low-velocity areas displaying high turbulence may provide resting conditions for fish, in the upstream negotiation of obstacles this turbulence per se may be limiting on the fish swimming ability. Finally, concerning the best results, the configuration Nature was, overall, the best RD tested. Comparing with the Control configuration, velocity magnitudes along the ramp (Control: 2.6–3.4 m·s−1, and Nature: 2.5–2.7 m·s−1), and especially TKE per unit mass registered downstream (Control: <0.3 m2·s−2, and Nature: <0.25 m2·s−2), were lower for both Q tested. Therefore, the random placement of natural cobbles on ramped weirs, as in this study, may generate an effective energy dissipation, reducing velocity and turbulence along the ramp, and especially downstream [5,23,24,26,73]. Consequently, more suitable conditions for fish to approach and successfully negotiate ramped weirs may be promoted upon retrofitting these structures with natural cobble substrate, as it may provide important “flow refugia,” creating homogeneous areas, with reduced velocity and turbulence, that fish may use to rest during the upstream negotiation of the ramp [28]. Future studies, contemplating distinct fish species with different ecological traits (e.g., small-bodied fish that utilize the upper portion of the water column), additional biological groups (e.g., macroinvertebrates), and a different range of discharges should be considered to enhance the knowledge on species passage effectiveness. Improved biological and hydrodynamic conditions at low-head ramped weirs are needed to help engineers and biologists to design more holistic structures, or retrofitting solutions, for low-head instream obstacles.
5. Conclusions
This study highlighted the importance of RD and Q, and especially of hydrodynamics resulting from the combination of these two factors, on the passage performance of the Iberian barbel, a medium-sized potamodromous cyprinid, negotiating low-head ramped weirs. The fact that experiments were carried out under laboratory conditions allowed the detailed observation of fish behavior (e.g., fish approaching the ramp, attempts to pass, successful upstream passages), as well as the control and the analysis of all the physical and hydraulic factors (e.g., substrate arrangements, discharges) considered preponderant in the successful passage of fish. Moreover, by using the 3D CFD model FLOW-3D® to characterize the hydrodynamics in each configuration tested, it was possible to identify areas of high velocity and turbulence gradients that might have affected fish movements.
Overall, results showed that the type of substrate, especially the size and the spatial arrangement selected to retrofit this type of low-head obstacles, together with discharge, played an important role in the creation of suitable hydrodynamics for the upstream successful negotiation of ramped weirs. As observed in other studies [22,23,24,26,28,33,78], the use of natural substrate may help to increase the permeability of these structures to fish movements, by providing an effective energy dissipation along the obstacle. That energy dissipation, together with the occurrence of low-velocity areas and small turbulence intensities, and the essential prevalence of spatial and temporal predictable flows, have proved to be key factors to consider in planning these type of retrofitting solutions [5,20,25,26]. Moreover, as mentioned by Knapp et al. [20] and Katopodis et al. [69], in addition to hydrodynamics, it is also crucial to analyze fish swimming behavior and passage performance in order to establish more applicable design guidelines. Thus, the outcomes from the present work, complemented with further research on hydrodynamics of low-head ramped weirs and fish passage performance, engaging laboratory experiments and in situ studies [18], may significantly contribute to help engineers and biologists to design more appropriate passage structures for low-head instream obstacles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D.A., P.B., and J.M.S.; methodology, S.D.A., A.L.Q., and J.M.S.; formal analysis, S.D.A. and A.L.Q.; investigation, S.D.A., F.R., P.B., and J.M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.D.A., A.L.Q., P.B., and J.M.S.; writing—review and editing, F.R., C.K., M.T.F., and A.N.P.; supervision, J.M.S.
Funding
Forest Research Centre (CEF) is a research unit funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. (FCT), Portugal (UID/AGR/00239/2019). Susana D. Amaral was funded by a PhD grant from University of Lisbon/Santander Totta (SantTotta/BD/RG2/SA/2011), and by FCT (SFRH/BD/110562/2015). José M. Santos has been a recipient of a FCT researcher contract (IF/00020/2015), and Paulo Branco is financed by national funds via FCT, under “Norma Transitória – DL57/2016/CP1382/CT0020”.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank to the staff of the National Laboratory for Civil Engineering (LNEC), especially to João Manuel Pereira and Ricardo Jónatas, for the support during the experiments and for collecting the 3D-bottom bathymetric data with the KinectTM, respectively. Electrofishing and fish holding permits were issued by the Institute for Conservation of Nature and Forests (ICNF) (permit numbers 40/2017 and 222/2017/CAPT; 41/2017 and 223/2017/CAPT; 42/2017 and 224/2017/CAPT).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozlan, R.E.; Karimov, B.K.; Zadereev, E.; Kuznetsova, D.; Brucet, S. Status, trends, and future dynamics of freshwater ecosystems in Europe and Central Asia. Inland Waters 2019, 9, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, M.C.; Bubb, D.H.; Jang, M.; Ha, K.; Masters, J.E.G. Availability of and access to critical habitats in regulated rivers: Effects of low-head barriers on threatened lampreys. Freshwater Biol. 2009, 54, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudoin, J.M.; Burgun, V.; Chanseau, M.; Larinier, M.; Ovidio, M.; Sremski, W.; Steinbach, P.; Voegtle, B. Assessing the Passage of Obstacles by Fish. Concepts, Design and Application; Onema: Paris, France, 2014; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Branco, P.; Amaral, S.D.; Ferreira, M.T.; Santos, J.M. Do small barriers affect the movement of freshwater fish by increasing residency? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie-Gauvin, K.; Franklin, P.; Wilkes, M.; Aarestrup, K. Moving beyond fitting fish into equations: Progressing the fish passage debate in the Anthropocene. Aquat. Conserv. 2019, 29, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordeix, M.; González, G.; Sanz-Ronda, F.J.; Santos, J.M. Restoring fish migration in the rivers of the Iberian Peninsula. In From Sea to Source 2.0. Protection and Restoration of Fish Migration in Rivers Worldwide; Brink, K., Gough, P., Royte, J., Schollema, P.P., Wanningen, H., Eds.; World Fish Migration Foundation: Groningen, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, S.D.; Branco, P.; Silva, A.T.; Katopodis, C.; Viseu, T.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Santos, J.M. Upstream passage of potamodromous cyprinids over small weirs: The influence of key-hydraulic parameters. J. Ecohydraulics 2016, 1, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà, C.; Ordeix, M.; Pou-Rovira, Q.; Sellarès, N.; Queralt, A.; Bardina, M.; Casamitjana, A.; Munné, A. Longitudinal connectivity in hydromorphological quality assessments of rivers. The ICF index: A river connectivity index and its application to Catalan rivers. Limnetica 2011, 30, 273–292. [Google Scholar]
- [FAO] Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Deutscher Verband für Wasserwirtschaft und Kulturbau e.V. Fish Passes—Design, Dimensions and Monitoring; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2002; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Habitat Restoration for Diadromous Fish in River Mondego, Portugal. Available online: http://www.rhpdm.uevora.pt/index.html (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Baker, C.F. Effect of ramp length and slope on the efficacy of a baffled fish pass. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, P.S.; O’Hanley, J.R. Procedures for evaluating and prioritising the removal of fish passage barriers: A synthesis. Fisheries Manag. Ecol. 2010, 17, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Ronda, F.J.; Ruiz-Legazpi, J.; Bravo-Córdoba, F.J.; Makrakis, S.; Castro-Santos, T. Sprinting performance of two Iberian fish: Luciobarbus bocagei and Pseudochondrostoma duriense in an open channel flume. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katopodis, C.; Gervais, R. Fish Swimming Performance Database and Analyses; Fisheries and Oceans Canada Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2016; p. 550. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, M.; Dodd, J.A.; Barry, J.; Boylan, P.; Adams, C.E. The impact of a small-scale riverine obstacle on the upstream migration of Atlantic Salmon. Hydrobiologia 2018, 806, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovidio, M.; Capra, H.; Philippart, J.C. Field protocol for assessing small obstacles to migration of brown trout Salmo trutta, and European grayling Thymallus thymallus: A contribution to the management of free movement in rivers. Fisheries Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.H.; Kingsford, R.T.; Peirson, W.; Baumgartner, L.J. Mitigating the effects of barriers to freshwater fish migrations: The Australian experience. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2016, 68, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Montgomery, J.; Whittaker, C.; Franklin, P.; Baker, C.; Friedrich, H. Fish passage hydrodynamics: Insights into overcoming migration challenges for small-bodied fish. J. Ecohydraulics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Branco, P.J.; Silva, A.T.; Katopodis, C.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Viseu, T.; Ferreira, M.T. Effect of two flow regimes on the upstream movements of the Iberian barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei) in an experimental pool-type fishway. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 29, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Branco, P.; Katopodis, C.; Ferreira, T.; Pinheiro, A. Retrofitting pool-and-weir fishways to improve passage performance of benthic fishes: Effect of boulder density and fishway discharge. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, K.; Nakanishi, S.; Kayaba, Y. Boulder arrangement on a rocky ramp fishway based on the swimming behavior of fish. Limnologica 2017, 62, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, E.M.; Heaslip, B.M.; Cramp, R.L.; Riches, M.; Gordos, M.A.; Franklin, C.E. Substrate roughening improves swimming performance in two small-bodied riverine fishes: Implications for culvert remediation and design. Conserv. Physiol. 2017, 5, cox034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesiński, K.; Bylak, A.; Radecki-Pawlik, A.; Mikołajczyk, T.; Kukuła, K. Possibilities of fish passage through the block ramp: Model-based estimation of permeability. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, H.R.; Watson, J.R.; Cramp, R.L.; Gordos, M.A.; Franklin, C.E. Making culverts great again. Efficacy of a common culvert remediation strategy across sympatric fish species. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 116, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chanson, H. Modelling upstream fish passage in standard box culverts: Interplay between turbulence, fish kinematics, and energetics. River Res. Appl. 2018, 34, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; Wait, L.E.; Monk, S.K.; Rader, R.; Hotchkiss, R.H.; Belk, M.C. Effects of substrate on movement patterns and behavior of stream fish through culverts: An experimental approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katopodis, C.; Aadland, L.P. Effective dam removal and river channel restoration approaches. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2006, 4, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towler, B.; Mulligan, K.; Haro, A. Derivation and application of the energy dissipation factor in the design of fishways. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.C. A review of fish swimming mechanics and behavior in altered flows. Philos. T. Roy. Soc. B 2007, 362, 1973–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, J.; Coombs, S. The influence of turbulence on the sensory basis of rheotaxis. J. Com. Physiol. A 2015, 201, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsman, S.J.; McLellan, N.; Platts, J.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Nonsalmonid versus salmonid passage at nature-like and pool-and-weir fishways in Atlantic Canada, with special attention to Rainbow smelt. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.J.; Santos, J.; Ferreira, T.; Mendes, A. Evaluating the response of biological assemblages as potential indicators for restoration measures in an intermittent Mediterranean river. Environ. Manag. 2010, 46, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Reino, L.; Porto, M.; Oliveira, J.; Pinheiro, P.; Almeida, P.R.; Cortes, R.; Ferreira, M.T. Complex size-dependent habitat associations in potamodromous fish species. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, J.P.; Matondo, B.N.; Dierckx, A.; Ovidio, M. An overview of potamodromous fish upstream movements in medium-sized rivers, by means of fish passes monitoring. Aquat. Ecol. 2015, 49, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katopodis, C.; Williams, J.G. The development of fish passage research in a historical context. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 28, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Boavida, I.; Almeida, V.; Cooke, S.J.; Pinheiro, A.N. Do artificial velocity refuges mitigate the physiological and behavioural consequences of hydropeaking on a freshwater Iberian cyprinid? Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, F.; Branco, P.; Quaresma, A.L.; Amaral, S.D.; Pinheiro, A.N. Effectiveness of a multi-slot vertical slot fishway versus a standard vertical slot fishway for potamodromous cyprinids. Hydrobiologia 2018, 816, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, J.; Soille, P.; De Jager, A.; Rimaviciute, E.; Mehl, W.; Foisneau, S.; Bodis, K.; Dusart, J.; Paracchini, M.L.; Haastrup, P.; et al. A Pan-European River and Catchment Database; European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability: Ispra, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, S.D.; Branco, P.; Katopodis, C.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Santos, J.M. Passage Performance of Potamodromous Cyprinids over an Experimental Low-Head Ramped Weir: The Effect of Ramp Length and Slope. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [CEN] European Committee for Standardization. Water Quality: Sampling of Fish with Electricity; The European Standard EN 14011; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Stammler, K.L.; Corkum, L.D. Assessment of fish size on shelter choice and intraspecific interactions by round gobies Neogobius melanostomus. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2005, 73, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Godinho, F.N.; Bochechas, J. Efficacy of a nature-like bypass channel in a Portuguese lowland river. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, F.; Santos, J.M.; Katopodis, C.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Branco, P. How Does Season Affect Passage Performance and Fatigue of Potamodromous Cyprinids? An Experimental Approach in a Vertical Slot Fishway. Water 2018, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ For PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). Wiley StatsRef Stat. Ref. Online 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, C.W.; Nichols, B.D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 1981, 39, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flow-3D Version 11.2; User Manual; Flow Science Inc.: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2016.
- Hirt, C.W.; Sicilian, J.M. A porosity technique for the definition of obstacles in rectangular cell meshes. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Numerical Ship Hydrodynamics, Washington, DC, USA, 24–27 September 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Duguay, J.M.; Lacey, R.W. Numerical study of an innovative fish ladder design for perched culverts. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2016, 43, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolden, E.; Fox, B.D.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Kondratieff, M.C. Modelling whitewater park hydraulics and fish habitat in Colorado. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, A.L.; Romão, F.; Branco, P.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A.N. Multi slot versus single slot pool-type fishways: A modelling approach to compare hydrodynamics. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 122, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankoff, K.D.; Russo, T.A. The Kinect: A low-cost, high-resolution, short range 3D camera. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2013, 38, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.B.; Cehreli, Z.N.; Yavuz, I. Index of Resolution Quality for Large Eddy Simulations. J. Fluid. Eng. 2005, 127, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Heimerl, S.; Hagmeyer, M.; Echteler, C. Numerical flow simulation of pool-type fishways: New ways with well-known tools. Hydrobiologia 2008, 609, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, E.; Katopodis, C.; Revelli, R.; Comoglio, C. Turbulent flow field comparison and related suitability for fish passage of a standard and a simplified low gradient vertical slot fishway. River Res. Appl. 2017, 33, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, E.; Katopodis, C.; Comoglio, C. Effects of bed slope on the flow field of vertical slot fishways. River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanagiotto, D.G.; Rossi, J.B.; Bravo, J.M. Applications of computational fluid dynamics in the design and rehabilitation of nonstandard vertical slot fishways. Water 2019, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feurich, R.; Boubée, J.; Olsen, N.R.B. Improvement of fish passage in culverts using CFD. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baki, A.B.; Zhu, D.Z.; Rajaratnam, N. Flow simulation in a Rock-Ramp Fish Pass. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Pérez, J.F.; Silva, A.T.; Tuhtan, J.A.; García-Vega, A.; Carbonell-Baeza, R.; Musall, M.; Kruusmaa, M. 3D modelling of non-uniform and turbulent flow in vertical slot fishways. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2018, 99, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B.; Gualtieri, C. Ten iterative steps for model development and evaluation applied to Computational Fluid Dynamics for Environmental Fluid Mechanics. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2012, 3, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.D.; Branco, P.; Katopodis, C.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Santos, J.M. To swim or to jump? Passage behaviour of a potamodromous cyprinid over an experimental broad-crested weir. River Res. Appl. 2018, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerig, E.; Castro-Santos, T. Is motivation important to brook trout passage through culverts? Can. J. Fish. Aquatic Sci. 2017, 74, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, D.S.; Lupandin, A.I.; Skorobogatov, M.A. The effects of flow turbulence on the behavior and distribution of fish. J. Ichthyol. 2000, 40, S232–S261. [Google Scholar]
- Katopodis, C.; Cai, L.; Johnson, D. Sturgeon survival: The role of swimming performance and fish passage research. Fish. Res. 2019, 212, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesiński, K.; Gibbins, C.N.; Radecki-Pawlik, A. Effects of interlocked carpet ramps on upstream movement of brown trout Salmo trutta in an upland stream. J. Ecohydraul. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, C.M.; Katopodis, C.; McKinley, R.S. Attraction and passage efficiency of white suckers and small mouth bass by two Denil fishways. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1999, 19, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calles, O.; Greenberg, L. Connectivity is a two-way street—The need for a holistic approach to fish passage problems in regulated rivers. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 1268–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, C.M.; Castro-Santos, T.; Haro, A. Reinforcement and Validation of the Analyses and Conclusions Related to Fishway Evaluation Data from Bunt et al.: ‘Performance of Fish Passage Structures at Upstream Barriers to Migration’. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, D.W.; Hinch, S.G. Effectiveness monitoring of fish passage facilities: Historical trends, geographic patterns and future directions. Fish Fish. 2010, 11, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Hinch, S.G.; Wikelski, M.; Andrews, R.D.; Kuchel, L.J.; Wolcott, T.G.; Butler, P.J. Biotelemetry: A mechanistic approach to ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Hinch, S.G. Improving the reliability of fishway attraction and passage efficiency estimates to inform fishway engineering, science, and practice. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 58, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.; Katopodis, C.; Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A.N. Cyprinid swimming behaviour in response to turbulent flow. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.; Boavida, I.; Santos, J.M.; Pinheiro, A.; Ferreira, M.T. Boulders as building blocks: Improving habitat and river connectivity for stream fish. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).