Water-Exchange Response of Downstream River–Lake System to the Flow Regulation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
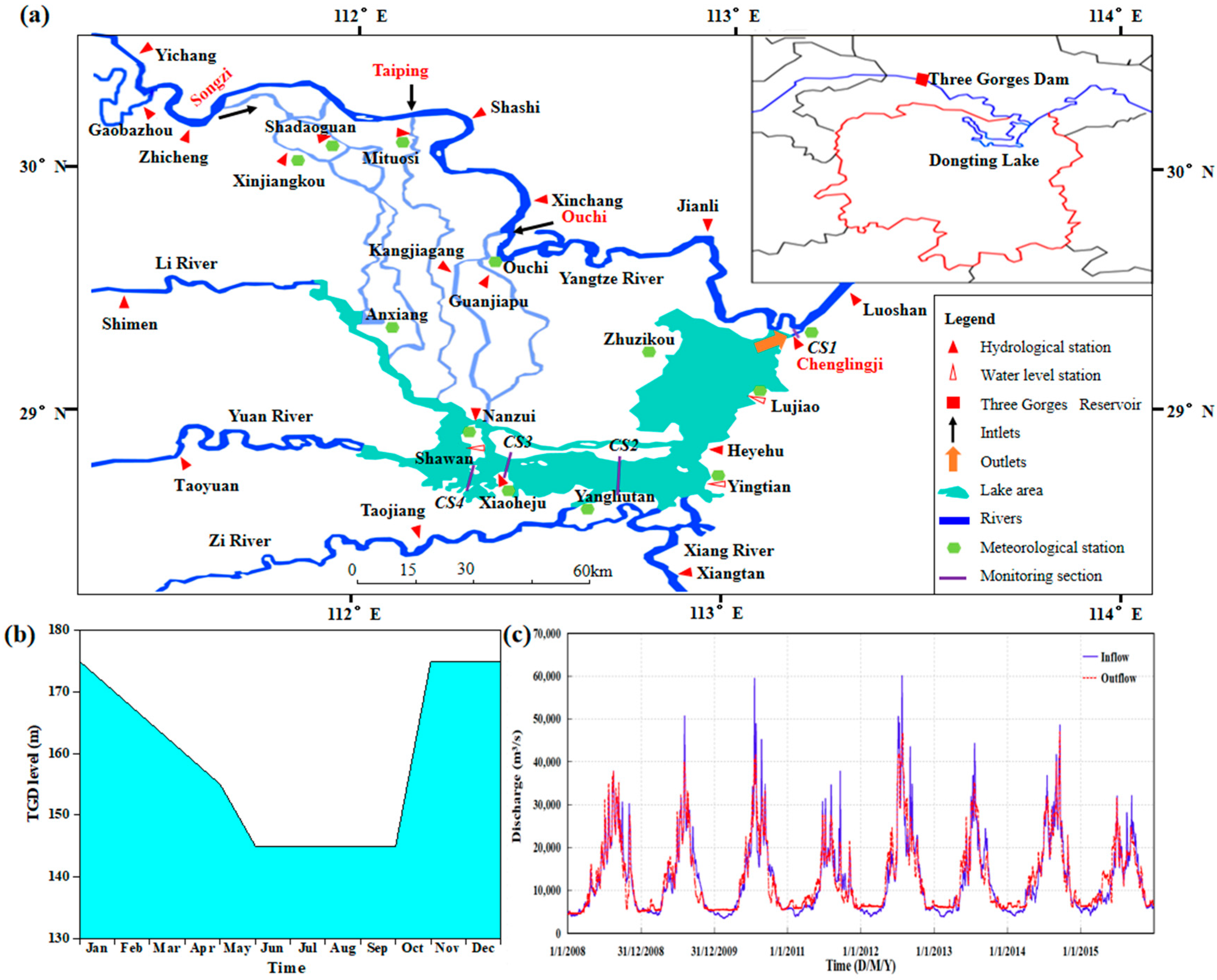
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. 1D/2D Coupled Hydrodynamic Model
2.3. Hydrologic Residence
2.4. Evaluation of Hydrologic Regime Changes during the Impounding Periods
3. Results
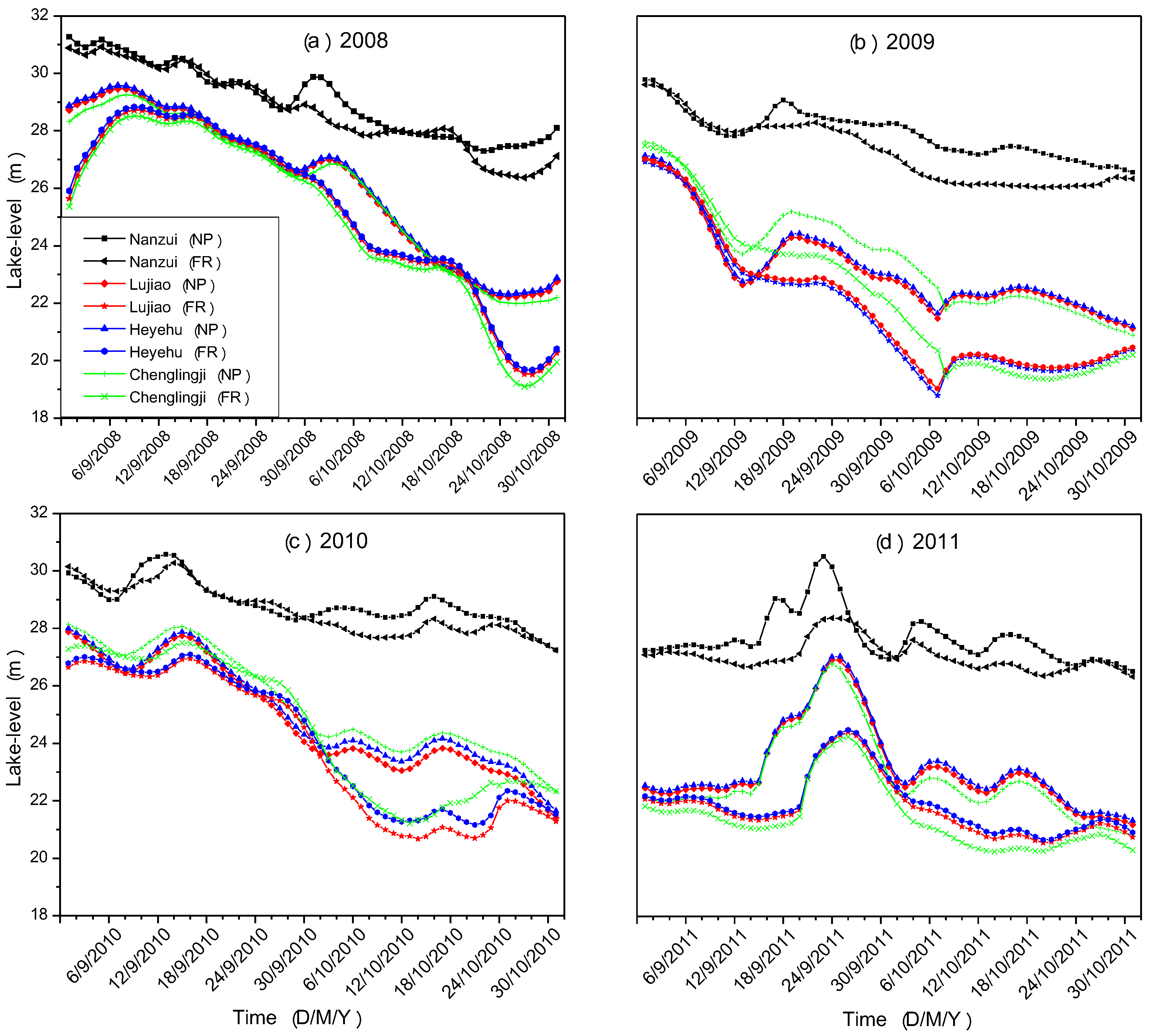
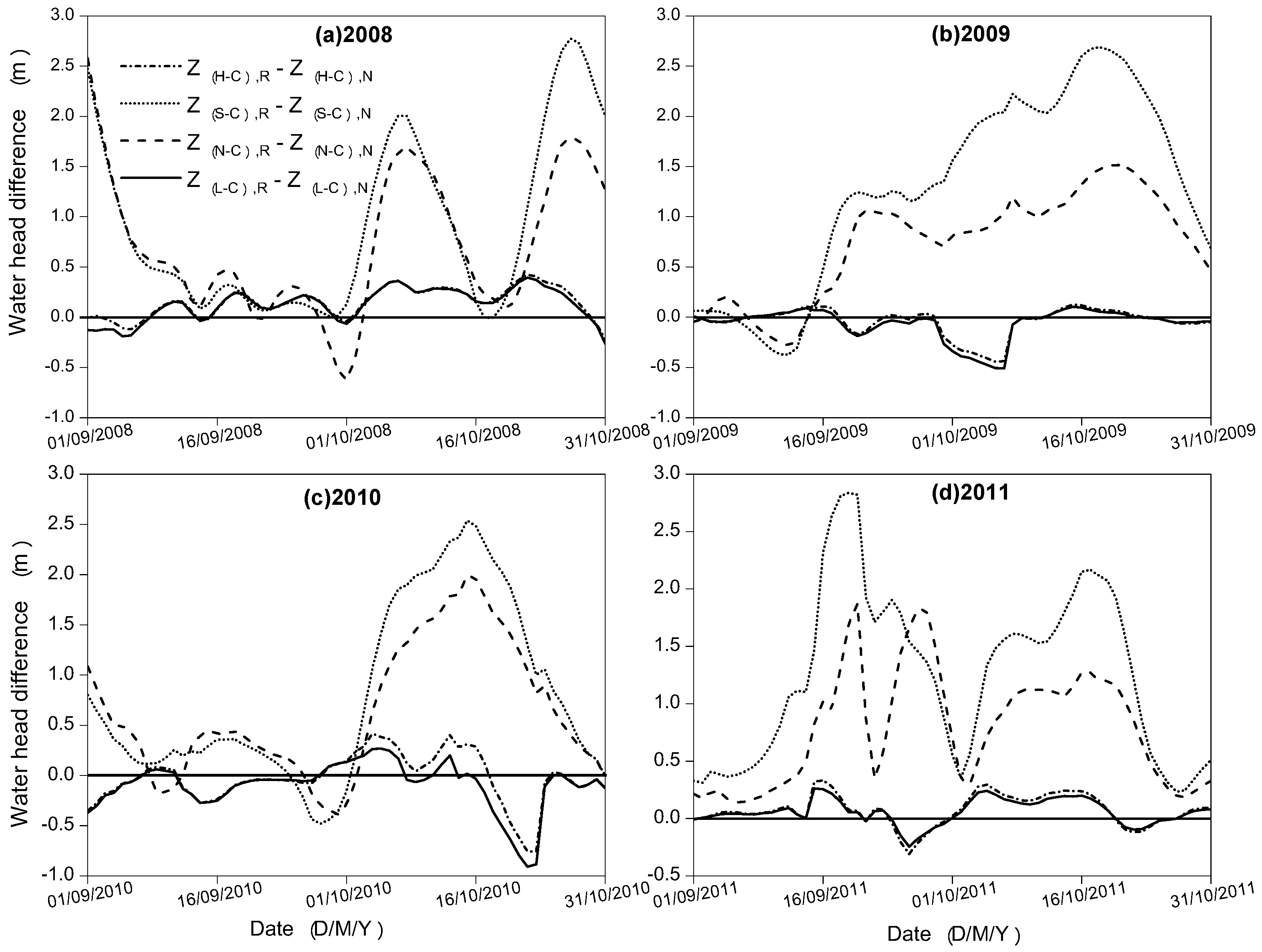
3.1. Water Exchange between the Dongting Lake and the Yangtze River
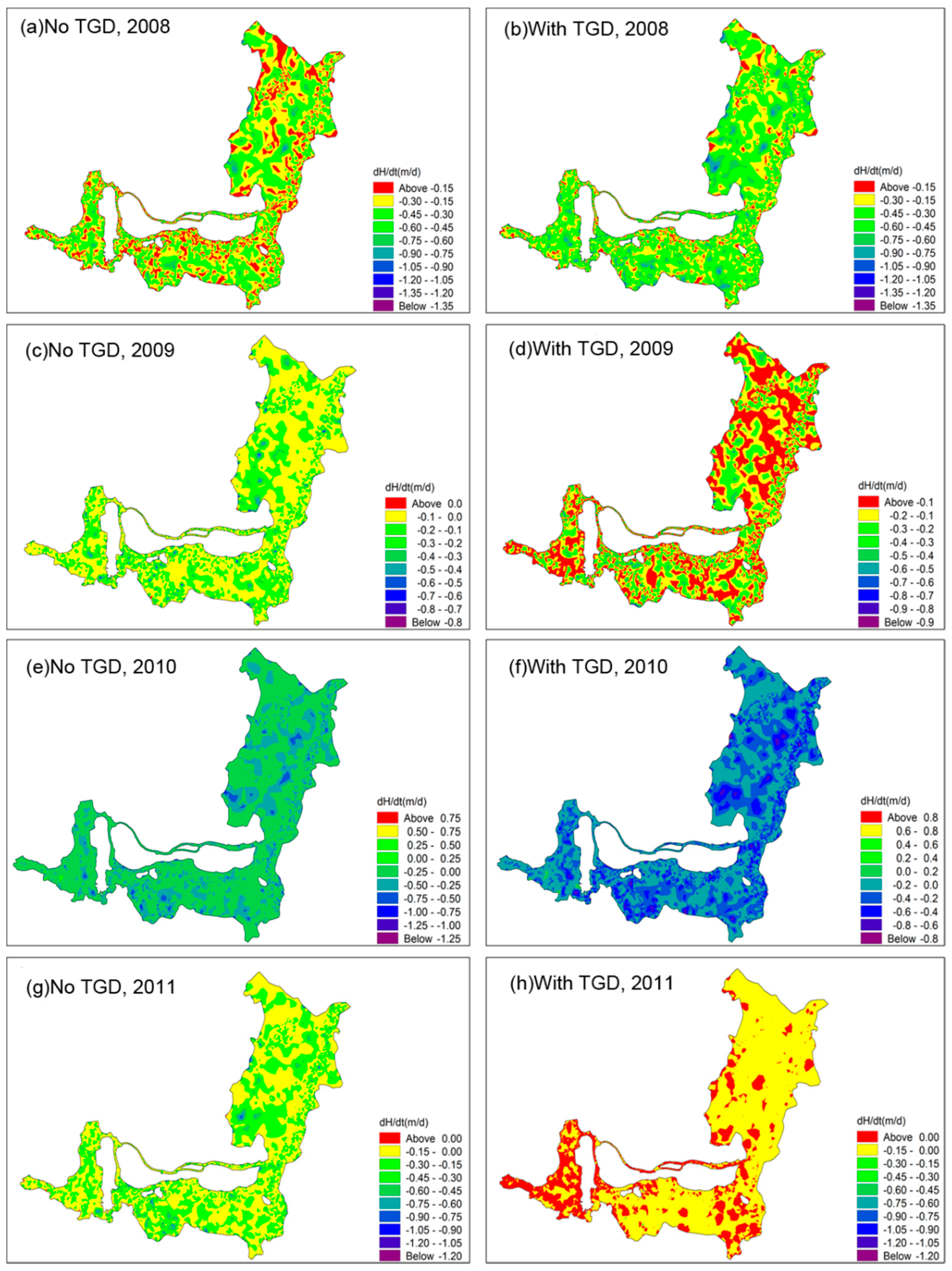
3.2. Changes in the Hydrological Regime of the Dongting Lake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daneshvar, A.; Svanfelt, J.; Kronberg, L.; Prévost, M.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A. Seasonal variations in the occurrence and fate of basic and neutral pharmaceuticals in a Swedish river–lake system. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, J.; Hoeg, S. Phytoplankton selection in a river—Lake system during two decades of changing nutrient supply. In The Trophic Spectrum Revisited. Developments in Hydrobiology; Reynolds, C.S., Dokulil, M., Padisák, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 150, pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.B.; Carpenter, S.R.; Dahm, C.N.; McKnight, D.M.; Naiman, R.J.; Postel, S.L.; Running, S.W. Water in a changing world. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1027–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karels, A.; Niemi, A. Fish community responses to pulp and paper mill effluents at the southern Lake Saimaa, Finland. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 116, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberts, D. The Tonle Sap Lake as a productive ecosystem. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2006, 22, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prowse, T.; Beltaos, S.; Gardner, J.; Gibson, J.; Granger, R.; Leconte, R.; Peters, D.; Pietroniro, A.; Romolo, L.; Toth, B. Climate change, flow regulation and land-use effects on the hydrology of the Peace-Athabasca-Slave system; Findings from the Northern Rivers Ecosystem Initiative. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 113, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdendorf, C.; HBkanson, L.; Jude, D.; Sly, P. A review of the physical and chemical components of the Great Lakes: A basis for classification and inventory of aquatic habitats. In The Development of an Aquatic Habitat Classification System for Lakes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 121–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ravikumar, B.; Bai, G.; Li, X. Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S. Measure of Correlation between River Flows Using the Copula-Entropy Method. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Noges, T.; Noges, P.; Attayde, J.L.; Zohary, T.; Coppens, J. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Huang, K. Bayesian Technique for the Selection of Probability Distributions for Frequency Analyses of Hydrometeorological Extremes. Entropy 2018, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Huang, X.; Mu, H.; Yin, W. Impacts of land-use changes on the lakes across the Yangtze floodplain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, Y.; Burbano, M.; Roush, J.; Kang, H.; Sridhar, V.; Hyndman, D.W. A Review of the Integrated Effects of Changing Climate, Land Use, and Dams on Mekong River Hydrology. Water 2018, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Xiong, F. An Entropy-Based Generalized Gamma Distribution for Flood Frequency Analysis. Entropy 2017, 19, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. The effect of cyanobacterial blooms in the Siemianówka Dam Reservoir on the phytoplankton structure in the Narew River. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2011, 40, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Zulkafli, Z.; Grainger, S.; Acosta, L.; Alemie, T.C.; Bastiaensen, J.; De Bièvre, B.; Bhusal, J.; Clark, J.; Dewulf, A. Citizen science in hydrology and water resources: Opportunities for knowledge generation, ecosystem service management, and sustainable development. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, N. Ecological and socio-economic utilization of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes Mart Solms). J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2010, 14, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.T. Water management in Bangladesh: An analytical review. Water Policy 2010, 12, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Fang, C. Water resources flows related to urbanization in China: Challenges and perspectives for water management and urban development. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P. An objective method for partitioning the entire flood season into multiple sub-seasons. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strehmel, A.; Schmalz, B.; Fohrer, N. Evaluation of land use, land management and soil conservation strategies to reduce non-point source pollution loads in the three gorges region, China. Environ. Manag. 2016, 58, 906–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, M.; Deng, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, X. Runoff and Sediment Response to Cascade Hydropower Exploitation in the Middle and Lower Han River, China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 8785236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, K.; Wang, Q.; Zha, G. Flood-risk analysis based on a stochastic differential equation method. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12 (Suppl. 1), e12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, H. Flow regime of the three outlets on the south bank of Jingjiang River, China: An impact assessment of the Three Gorges Reservoir for 2003–2010. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, J.; Singh, V.P.; Zhou, J.; Huang, K. Copula-based method for stochastic daily streamflow simulation considering lag-2 autocorrelation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Murakami, S.; Xu, K.; Watanabe, M.; Xu, B. Daily runoff simulation by an integrated catchment model in the middle and lower regions of the Changjiang basin, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Xiong, L. Rainfall-runoff simulation in karst dominated areas based on a coupled conceptual hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Jiang, J.; Yang, G.; Lu, X. Should the Three Gorges Dam be blamed for the extremely low water levels in the middle–lower Yangtze River? Hydrol. Processes 2014, 28, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wada, Y. Little impact of the Three Gorges Dam on recent decadal lake decline across China’s Yangtze Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 3854–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Lai, X.; Huang, Q. The characteristics of flood responses to the restoration of polders on Dongting Lake, China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 671–685. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, D.; Zhu, X.; Lu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, C. The hydrological effect between Jingjiang River and Dongting Lake during the initial period of Three Gorges Project operation. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.D.; Huang, Q.; Opp, C.; Hennig, T.; Marold, U. Impacts and Implications of Major Changes Caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Wu, G.P.; Guo, R.F.; Wan, R.R. Changing landscapes by damming: The Three Gorges Dam causes downstream lake shrinkage and severe droughts. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, X.L.; Zhao, X. Dramatic Inundation Changes of China’s Two Largest Freshwater Lakes Linked to the Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9628–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Qu, G.; Guo, X. Multi-objective reservoir operation during flood season considering spillway optimization. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Dai, M.; Xu, W.; Yan, T. Water compensation and its implication of the Three Gorges Reservoir for the river-lake system in the middle Yangtze River, China. Water 2018, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, S.; Chatterjee, C.; Mohanty, S.; Singh, R.; Raghuwanshi, N. Flood inundation modeling using MIKE FLOOD and remote sensing data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2009, 37, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderkimpen, P.; Melger, E.; Peeters, P. Flood modeling for risk evaluation: A MIKE FLOOD vs. SOBEK 1D/2D benchmark study. In Flood Risk Management: Research and Practice; Samuels, P., Huntington, S., Allsop, W., Harrop, J., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2008; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kadam, P.; Sen, D. Flood inundation simulation in Ajoy River using MIKE-FLOOD. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 18, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI). Hydrodynamic Module, User Guide; DHI Water & Environment: Horsholm, Demark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI). MIKE 11 Flow Model: Hydrodynamic Module User Guide; DHI Water and Environment: Horsholm, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI). MIKE 21 Flow Model: Hydrodynamic Module User Guide; DHI Water and Environment: Horsholm, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, X.; Jiang, J.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Q. Large-scale hydrodynamic modeling of the middle Yangtze River Basin with complex river–lake interactions. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lou, L.; Cui, X.; Tang, J.; Li, P.; Cao, R. Significance of biological effects on phosphorus transformation processes at the water–sediment interface under different environmental conditions. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Time | Without TGD | TGD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WRR | MRT (Day) | WRR | MRT (Day) | |
| 2008 | −0.234 | 18 | −0.242 | 17 |
| 2009 | −0.285 | 12 | −0.351 | 10 |
| 2010 | −0.191 | 16 | −0.198 | 15 |
| 2011 | −0.038 | 25 | −0.05 | 23 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Feng, L.; Yang, Y. Water-Exchange Response of Downstream River–Lake System to the Flow Regulation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water 2019, 11, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112394
Zhang J, Huang T, Chen L, Liu X, Zhu L, Feng L, Yang Y. Water-Exchange Response of Downstream River–Lake System to the Flow Regulation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water. 2019; 11(11):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112394
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junhong, Tao Huang, Lu Chen, Xiaofang Liu, Lingling Zhu, Luojie Feng, and Yunping Yang. 2019. "Water-Exchange Response of Downstream River–Lake System to the Flow Regulation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China" Water 11, no. 11: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112394
APA StyleZhang, J., Huang, T., Chen, L., Liu, X., Zhu, L., Feng, L., & Yang, Y. (2019). Water-Exchange Response of Downstream River–Lake System to the Flow Regulation of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water, 11(11), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112394








