Assessment of Lake Water Quality and Eutrophication Risk in an Agricultural Irrigation Area: A Case Study of the Chagan Lake in Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
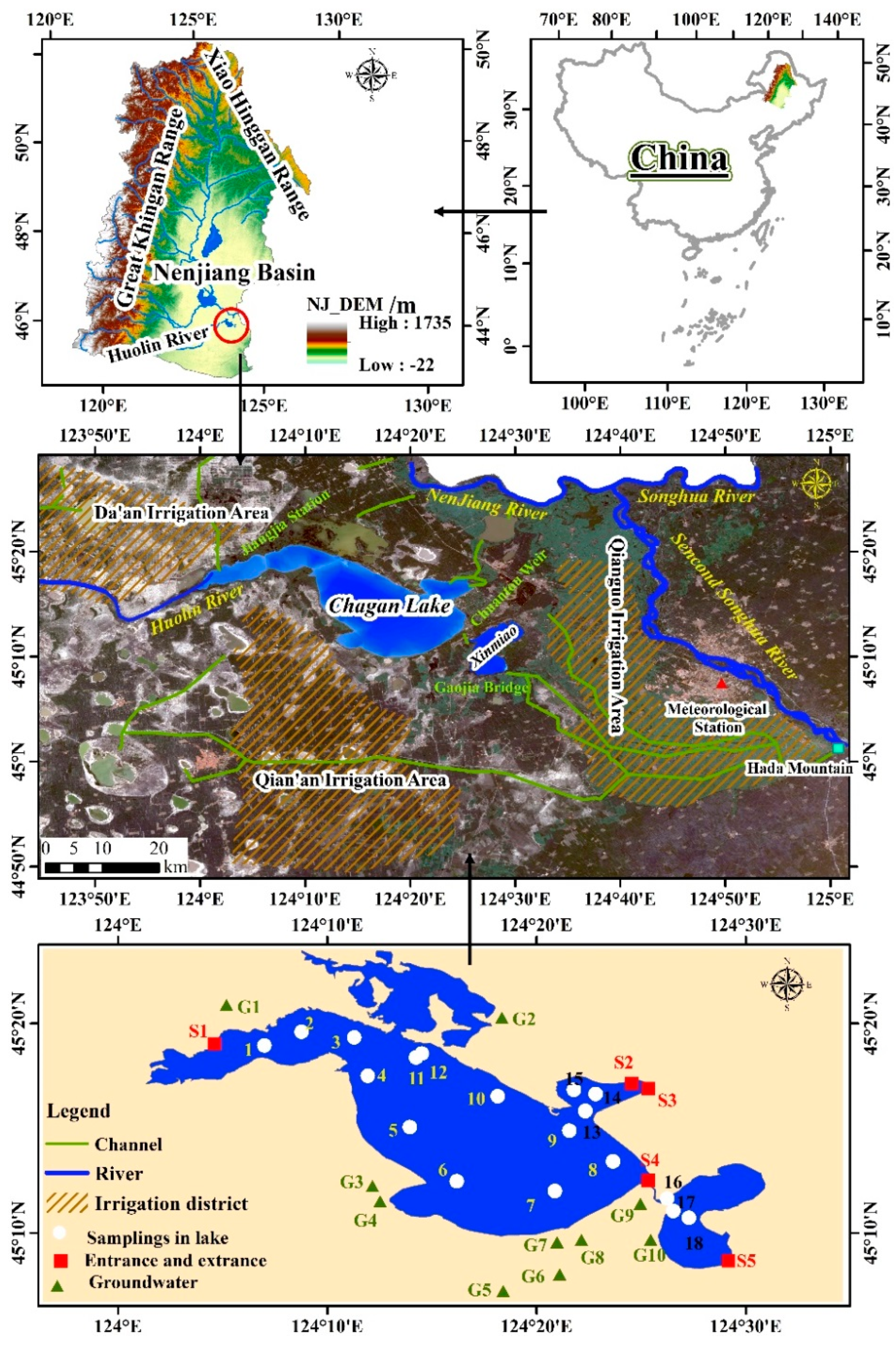
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sample Collection
2.3. Water Sample Analysis
2.4. Calculations of Eutrophication Indices
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydro-Chemical Properties of the Lake Water
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Variation of N and P Concentrations
3.2.1. Monthly Variations
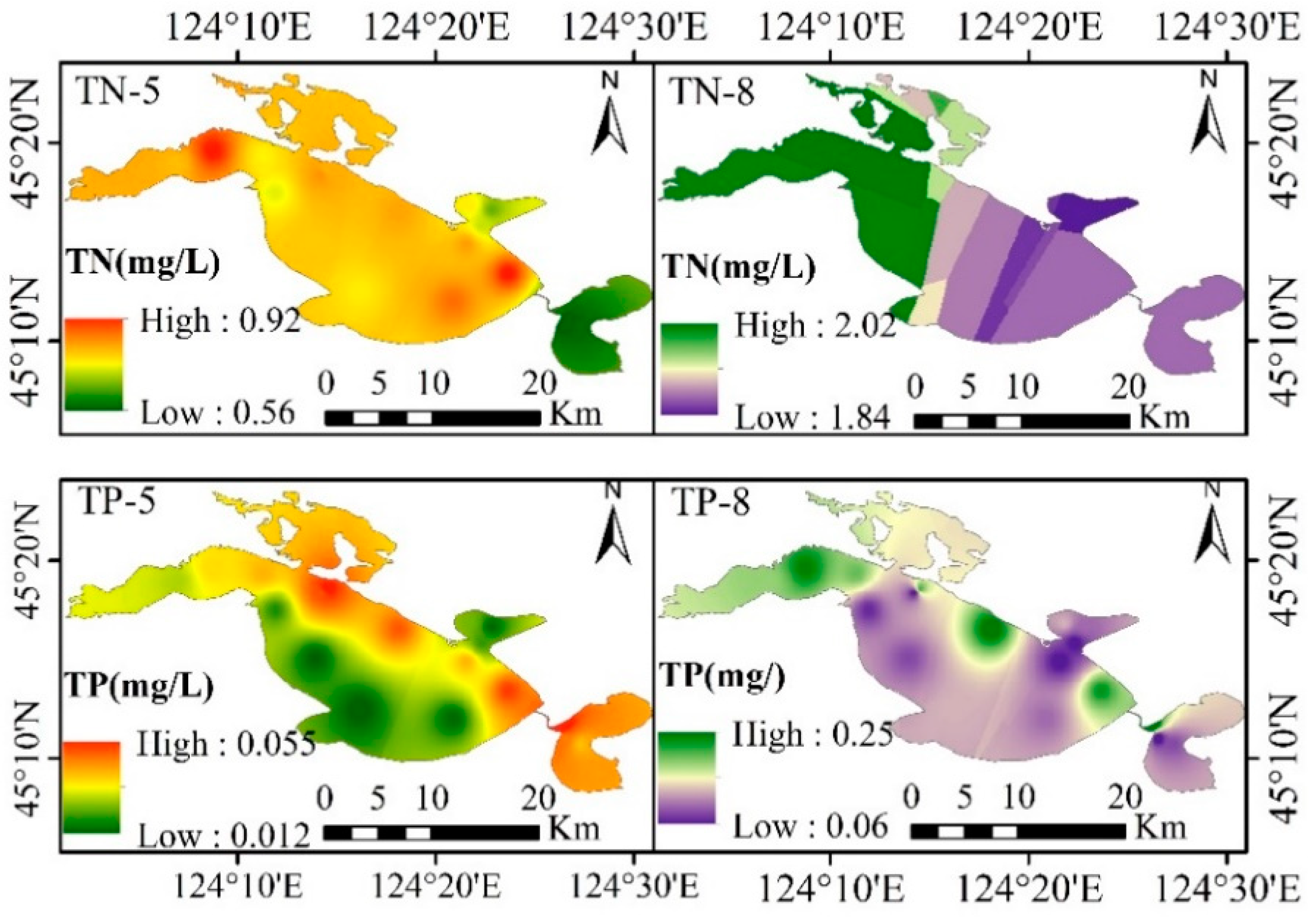
3.2.2. Variations of TN and TP in Different Locations
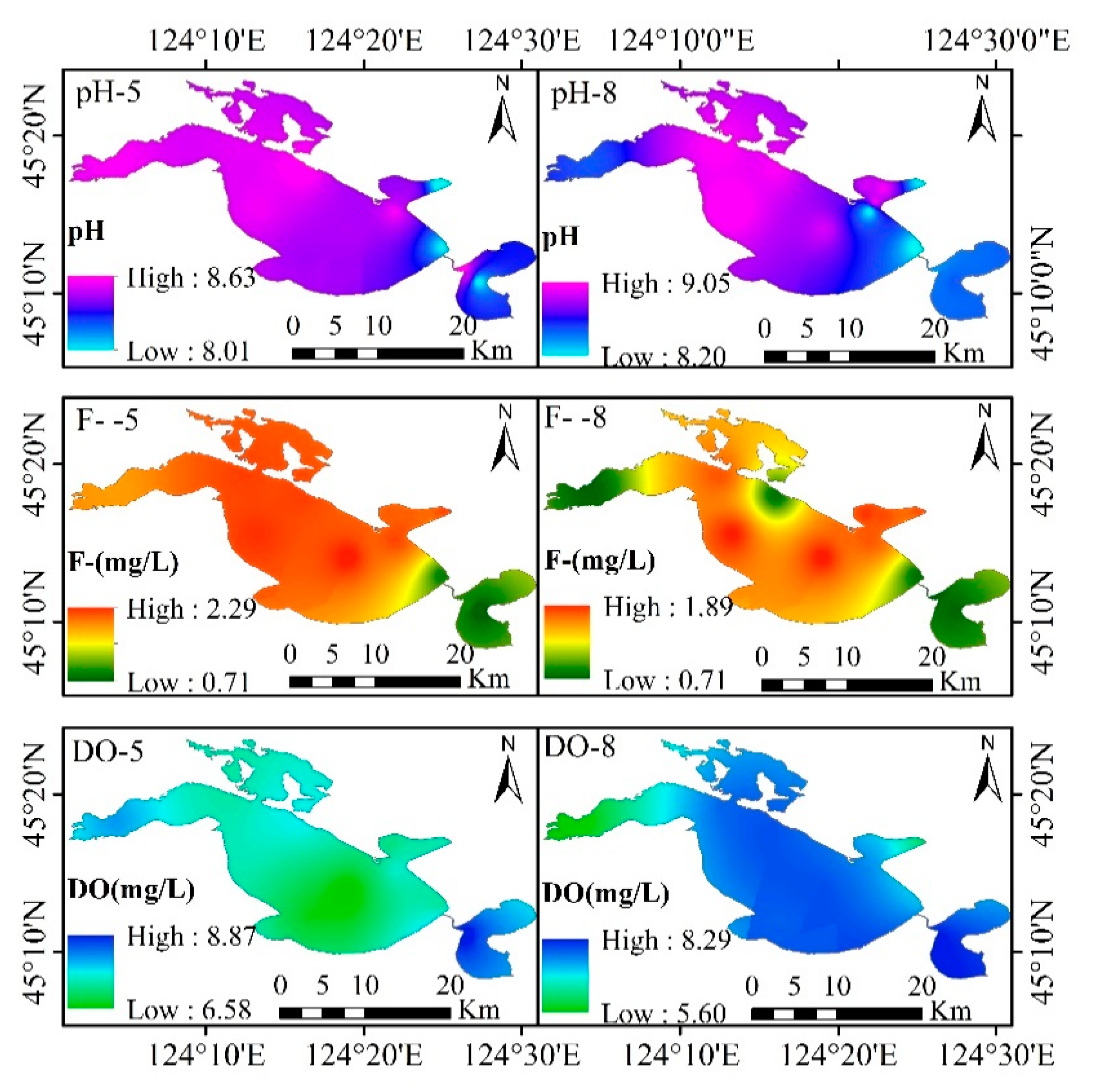
3.2.3. Variations of pH, F−, and Dissolved Oxygen in Different Locations
3.3. Eutrophication Indices
3.4. Statistical Analysis Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W. The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes. P. Roy. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4322–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapra, S.C.; Hecky, R.E.; Orihel, D.M. Reducing phosphorus to curb lake eutrophication is a success. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8923–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication and recovery in experimental lakes: Implications for lake management. Science 1974, 184, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, W.K. Eutrophication and trophic state in rivers and streams. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, H.A.; Ivanova, D.; Stadler, K.; Merciai, S.; Schmidt, J.; Van Zelm, R.; Wood, R. Trade and the role of non-food commodities for global eutrophication. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T. Eutrophication’s neglected drivers. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, P.; Willern, S.; Bo, B.J. Diffusive boundary layers of the colony-forming plankton alga Phaeocystis sp. –Implications for nutrient uptake and cellular grouth. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Smith, V.H. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, A.F. Accelerated eutrophication of lakes in the United States: Ecological response to human activities. Environ. Pollut. 1970, 1, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, M.J.; Temte, J. Seasonal patterns of grazing and nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in a eutrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, M.S.; Smol, J.P.; Savelle, J.M.; Blais, J.M. Prehistoric Inuit whalers affected Arctic freshwater ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, H.S.; Andersen, F.O. Importance of temperature, nitrate, and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.; Kosten, S.; Meerhoff, M.; Battarbee, R.W.; Jeppesen, E.; Mazzeo, N.; Paerl, H. Allied attack: Climate change and eutrophication. Inland waters 2011, 1, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Cabana, G. δ15N in riverine food webs: Effects of N inputs from agricultural watersheds. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, Z.E.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Quantifying relationships among phosphorus, agriculture, and lake depth at an inter-regional scale. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sith, R.; Watanabe, A.; Nakamura, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Nadaoka, K. Assessment of water quality and evaluation of best management practices in a small agricultural watershed adjacent to Coral Reef area in Japan. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; Findlay, D.L.; Stainton, M.P.; Parker, B.R.; Paterson, M.J.; Kasian, S.E.M. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater–marine continuum: Dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuaries Coasts 2009, 32, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fastner, J.; Abella, S.; Litt, A.; Morabito, G.; Vörös, L.; Pálffy, K.; Chorus, I. Combating cyanobacterial proliferation by avoiding or treating inflows with high P load—Experiences from eight case studies. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sharp, R.P.; Weil, C.; Bennett, E.M.; Pascual, U.; Arkema, K.K.; Brauman, K.A.; Bryant, B.P.; Guerry, A.D.; Haddad, N.M.; et al. Global modeling of nature’s contributions to people. Science 2019, 366, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.W.W. Use of hypolimnetic oxygen depletion rate as a trophic state index for lakes. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. Expanding the Trophic State Concept to Identify Non-Nutrient Limited Lakes and Reservoirs. Enhancing States’s Lake Manag. Programs. 1991, pp. 59–71. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/246134025 (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Matthews, R.; Hilles, M.; Pelletier, G. Determining trophic state in Lake Whatcom, Washington (USA), a soft water lake exhibiting seasonal nitrogen limitation. Hydrobiologia 2002, 468, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovich, B.V.; Medvinsky, A.B.; Nikitina, L.V.; Radchikova, N.P.; Mikheyeva, T.M.; Kovalevskaya, R.Z.; Zhukova, T.V. Relations between variations in the lake bacterioplankton abundance and the lake trophic state: Evidence from the 20-year monitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 97, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ni, W.; Luo, Y.; Stevenson, R.J.; Qi, J. Response of freshwater algae to water quality in Qinshan Lake within Taihu Watershed, China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Ma, C.; Xi, B.; Su, J.; Zan, F.; Ji, D.; He, Z. Establishing eutrophication assessment standards for four lake regions, China. J. Environ. Sci. Chin. 2013, 25, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Song, K.; Wang, Z. Assessment of chlorophyll-a concentration and trophic state for Lake Chagan using Landsat TM and field spectral data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 129, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Nover, D.; Yang, G.; Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Liu, C. Water quality assessment and pollution source identification of the eastern Poyang Lake Basin using multivariate statistical methods. Sustainability 2016, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, L. Satellite data regarding the eutrophication response to human activities in the plateau lake Dianchi in China from 1974 to 2009. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Deng, J.; Zhou, Y. Aquatic vegetation in response to increased eutrophication and degraded light climate in Eastern Lake Taihu: Implications for lake ecological restoration. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 23867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Qiao, H.; Liu, F. Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, X.; Liu, D.; Lang, C.; Shan, B. Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen and phosphorus and eutrophication assessment for a typical arid river—Fuyang River in northern China. J. Environ. Sci. Chin. 2017, 55, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, X. The features and development trend of the water quality and eutrophication of Cagan Lake. Jilin Water Resour. 2007, 10, 3–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Guo, C. A universal index formula for eutrophic evaluation using a logarithmic power function. Acta Sci. Circumst 2010, 30, 664–672. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, X. Present situation and tendency of saline-alkali soil in west Jilin Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2001, 11, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Xu, C.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Wang, X.C.; Ren, P.A. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournebize, J.; Chaumont, C.; Mander, Ü. Implications for constructed wetlands to mitigate nitrate and pesticide pollution in agricultural drained watersheds. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 103, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Yang, W.N.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Jin, P.K.; Dzakpasu, M.; Ao, D. Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Environ Int. 2016, 92, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, A.E.; Pearsons, T.N.; Zendt, J.S.; Mesa, M.G.; Johnson, C.L.; Connolly, P.J. Nutrient enrichment with salmon carcass analogs in the Columbia River basin, USA: A stream food web analysis. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2012, 141, 802–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reitan, K.I.; Rainuzzo, J.R.; Øie, G.; Olsen, Y. A review of the nutritional effects of algae in marine fish larvae. Aquaculture 1997, 155, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinikmann, K.; Hupfer, M.; Lewandowski, J. Phosphorus in groundwater discharge—A potential source for lake eutrophication. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Wood, S.A.; McBride, C.G.; Atalah, J.; Hamilton, D.P.; Abell, J. Phosphorus and nitrogen loading restraints are essential for successful eutrophication control of Lake Rotorua, New Zealand. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowmer, K.H. Nutrient removal from effluents by an artificial wetland: Influence of rhizosphere aeration and preferential flow studied using bromide and dye tracers. Water Res. 1987, 21, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.L.; Tu, Y.T.; Chiang, P.C.; Chen, S.H.; Kao, C.M. Using aerated gravel-packed contact bed and constructed wetland system for polluted river water purification: A case study in Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Sun, G.Z. Simulation and evaluation of the water purification function of Zhalong Wetland based on a combined water quantity-quality model. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, J.J.; Puntoriero, M.L.; Troncoso, J.J.; Volpedo, A.V.; Fernández Cirelli, A. Occurrence of fluoride in arsenic-rich surface waters: A case study in the Pampa Plain, Argentina. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 87, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, T.; Yu, C.; Drake, H.; Peltola, P.; Svensson, D.; Åström, M.E. Fluorine geochemistry of quaternary deposits in a nemo-boreal catchment with elevated dissolved fluoride in surface waters and groundwater. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 170, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.F.; Hansen, P.J. Effects of high pH on the growth and survival of six marine heterotrophic protists. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 260, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, D.L. Dissolved oxygen and fish behavior. Environ. Boil. Fish. 1987, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianmin, B.; Yu, W.; Juan, Z. Arsenic and fluorine in groundwater in western Jilin Province, China: Occurrence and health risk assessment. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Schäfer, A.I. Factors affecting fluoride and natural organic matter (NOM) removal from natural waters in Tanzania by nanofiltration/reverse osmosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.; Mathurin, F.A.; Drake, H.; Åström, M.E. Fluoride abundance and controls in fresh groundwater in Quaternary deposits and bedrock fractures in an area with fluorine-rich granitoid rocks. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Venkatesh, A.S.; Singh, R.; Udayabhanu, G.; Saha, D. Geochemical signatures and isotopic systematics constraining dynamics of fluoride contamination in groundwater across Jamui district, Indo-Gangetic alluvial plains, India. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Sankar, K.; Dar, I.A. Fluorine contamination in groundwater: A major challenge. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasfar, S.; Monette, F.; Millette, L.; Azzouz, A. Intrinsic growth rate: A new approach to evaluate the effects of temperature, photoperiod and phosphorus–nitrogen concentration on duckweed growth under controlled eutrophication. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, M.E.; Berge, D.; Eggestad, H.O.; Vandsemb, S.M. Phosphorus transfer from agricultural areas and its impact on the eutrophication of lakes—Two long-term integrated studies from Norway. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.; Neal, C.; Jarvie, H.; Doody, D. Agriculture and eutrophication: Where do we go from here? Sustainability 2014, 6, 5853–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, D.; An, S. Decreasing but still significant facilitation effect of cold-season macrophytes on wetlands purification function during cold winter. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 27011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J. Occurrence and distribution of endocrine-disrupting compounds in the Honghu Lake and East Dongting Lake along the Central Yangtze River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2015, 22, 17644–17652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, L.M. Drought impacts on the water quality of freshwater systems; review and integration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 140, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Xue, L. A selective overview of sparse principal component analysis. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, G.; Rogora, M.; Austoni, M.; Ciampittiello, M. Could the extreme meteorological events in Lake Maggiore watershed determine a climate-driven eutrophication process? Hydrobiologia 2018, 824, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Esbensen, K.; Geladi, P. Principal component analysis. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 1987, 2, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wo, F.; Chen, C.; Fang, K. Seasonal changes in the concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus in farmland drainage and groundwater of the Taihu Lake region of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 169, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giblin, A.E.; Weston, N.B.; Banta, G.T.; Tucker, J.; Hopkinson, C.S. The effects of salinity on nitrogen losses from an oligohaline estuarine sediment. Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoumans, O.F.; Chardon, W.J.; Bechmann, M.E.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Hofman, G.; Kronvang, B.; Dorioz, J.M. Mitigation options to reduce phosphorus losses from the agricultural sector and improve surface water quality: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Grades | TN mg/L | TP μg/L | Chl-a μg/L | TLI | TSI | EI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oligotrophic | 0.08 | <12 | <7.3 | <30 | <40 | <20 |
| Mesotrophic | 0.31 | 12–24 | 2.6–7.3 | 30–50 | 40–50 | 20–39.42 |
| Eutrophic | 1.2 | 24–96 | 7.3–56 | 50–60 | 50–70 | 39.42–61.29 |
| Hyper eutrophic | 2.3 | 96–192 | 56–155 | 60–70 | 70–80 | 61.29–76.28 |
| Extreme eutrophication | 9.1 | 192–384 | >155 | >70 | >80 | 76.28–99.77 |
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | G9 | G10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (ms/cm) | 0.65 | 1.07 | 0.64 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.83 |
| TDS (ppt) | 0.33 | 0.55 | 0.33 | 1.39 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.42 |
| Tw (°C) | 12.9 | 11.3 | 14.2 | 13.3 | 11.1 | 12.5 | 13.4 | 20.4 | 13.0 | 12.5 |
| May | June | July | August | September | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | III | IV | IV | V | IV |
| TP | III | V | IV | V | V |
| TP | TN | NH4-N | NO3-N | CODmn | Chla | SD | pH | EC | TDS | Tw | F- | DO | BOD5 | P | E | T | Rh | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TN | 0.43 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NH4-N | 0.31 * | 0.26 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NO3-N | 0.25 | 0.88 ** | 0.04 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CODmn | 0.48 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.12 | 0.59 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Chla | 0.43 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.17 | 0.53 ** | 0.46 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SD | −0.06 | 0.27 | −0.01 | 0.39 ** | 0.09 | −0.06 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| pH | 0.05 | 0.19 | −0.24 | 0.38 ** | 0.32 * | −0.13 | 0.10 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| EC | −0.17 | −0.41 ** | −0.01 | −0.36 * | −0.22 | −0.37 * | 0.01 | 0.33 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TDS | −0.18 | −0.41 ** | −0.02 | −0.35 ** | −0.22 | −0.37 * | 0.02 | 0.33 ** | 0.99 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Tw | 0.34 * | 0.72 ** | 0.34 * | 0.70 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.35 * | 0.03 | 0.54 ** | −0.07 | -0.07 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| F− | −0.28 | −0.50 ** | −0.07 | −0.44 ** | −0.24 | −0.45 ** | 0.01 | 0.37 ** | 0.90 ** | 0.89 ** | -0.17 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| DO | 0.20 | 0.34 * | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.52 ** | 0.24 | −0.14 | 0.57 ** | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.62 ** | 0.12 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| BOD5 | 0.72 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.75 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.51 ** | 0.14 | -0.17 | −0.16 | −0.16 | 0.62 ** | −0.28 | 0.27 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| P | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.16 | −0.01 | -0.20 | −0.14 | −0.13 | 0.04 | −0.12 | −0.10 | 0.36 * | 1 | - | - | - |
| E | −0.03 | 0.34 * | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.25 | −0.07 | -0.04 | −0.31 * | −0.32 * | 0.33 * | −0.33 * | 0.25 | 0.12 | −0.09 | 1 | - | - |
| T | 0.28 | 0.41 ** | 0.22 | 0.40 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.31 * | 0.09 | 0.45 ** | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.59 ** | −0.06 | 0.47 ** | 0.36 * | −0.11 | 0.21 | 1 | - |
| Rh | 0.30 * | 0.61 ** | 0.19 | 0.61 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.02 | 0.27 | −0.25 | −0.24 | 0.65 ** | −0.35 * | 0.29 | 0.43 * | 0.43 * | 0.14 | 0.46 ** | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Sun, G.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y. Assessment of Lake Water Quality and Eutrophication Risk in an Agricultural Irrigation Area: A Case Study of the Chagan Lake in Northeast China. Water 2019, 11, 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112380
Liu X, Zhang G, Sun G, Wu Y, Chen Y. Assessment of Lake Water Quality and Eutrophication Risk in an Agricultural Irrigation Area: A Case Study of the Chagan Lake in Northeast China. Water. 2019; 11(11):2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112380
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuemei, Guangxin Zhang, Guangzhi Sun, Yao Wu, and Yueqing Chen. 2019. "Assessment of Lake Water Quality and Eutrophication Risk in an Agricultural Irrigation Area: A Case Study of the Chagan Lake in Northeast China" Water 11, no. 11: 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112380
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, G., Sun, G., Wu, Y., & Chen, Y. (2019). Assessment of Lake Water Quality and Eutrophication Risk in an Agricultural Irrigation Area: A Case Study of the Chagan Lake in Northeast China. Water, 11(11), 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112380








