Correlations of Stormwater Runoff and Quality: Urban Pavement and Property Value by Land Use at the Parcel Level in a Small Sized American City
Abstract
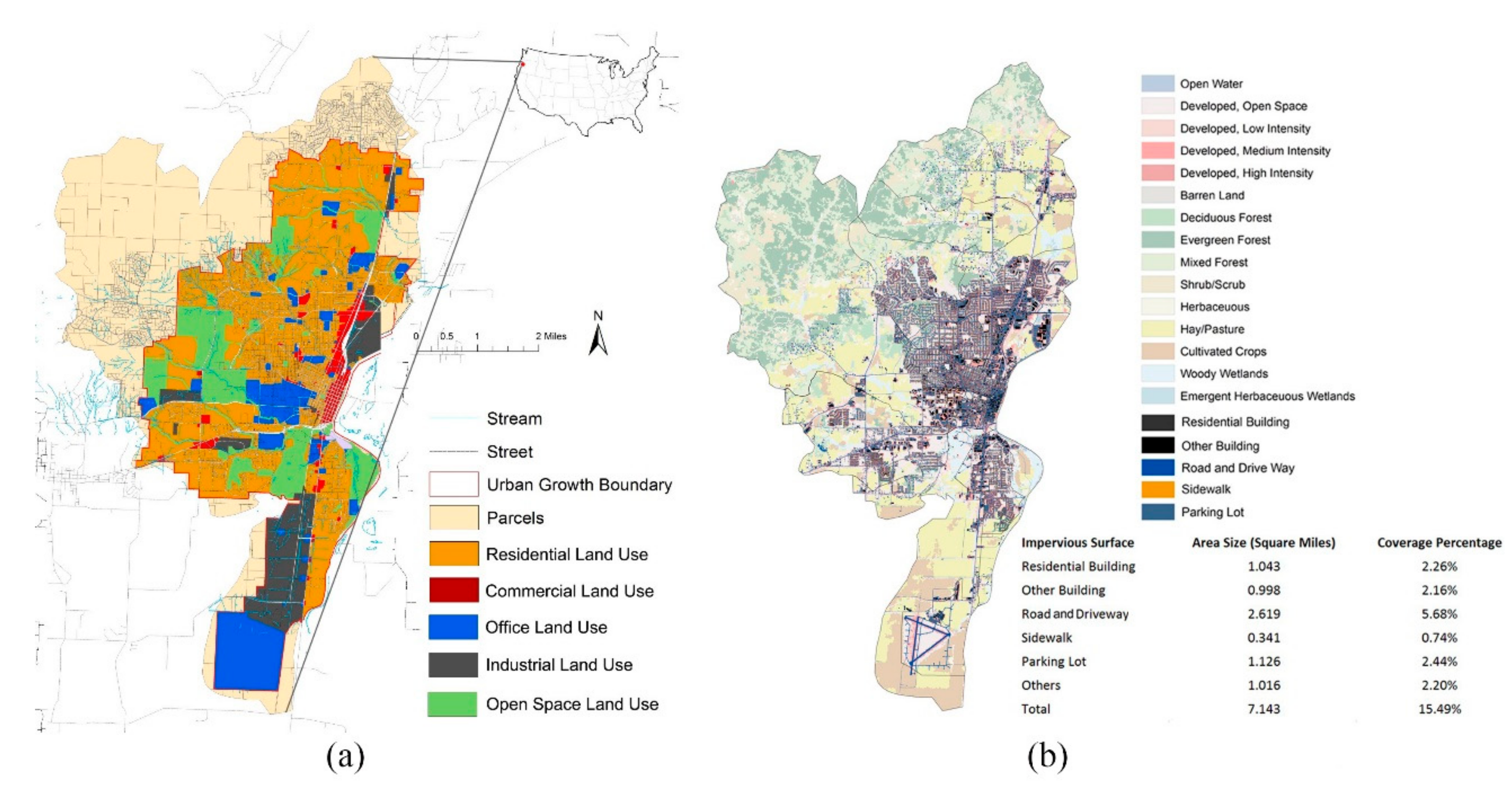
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Modelling Process
2.1. Stormwater Runoff Yield Modelling
2.2. Stormwater Purification
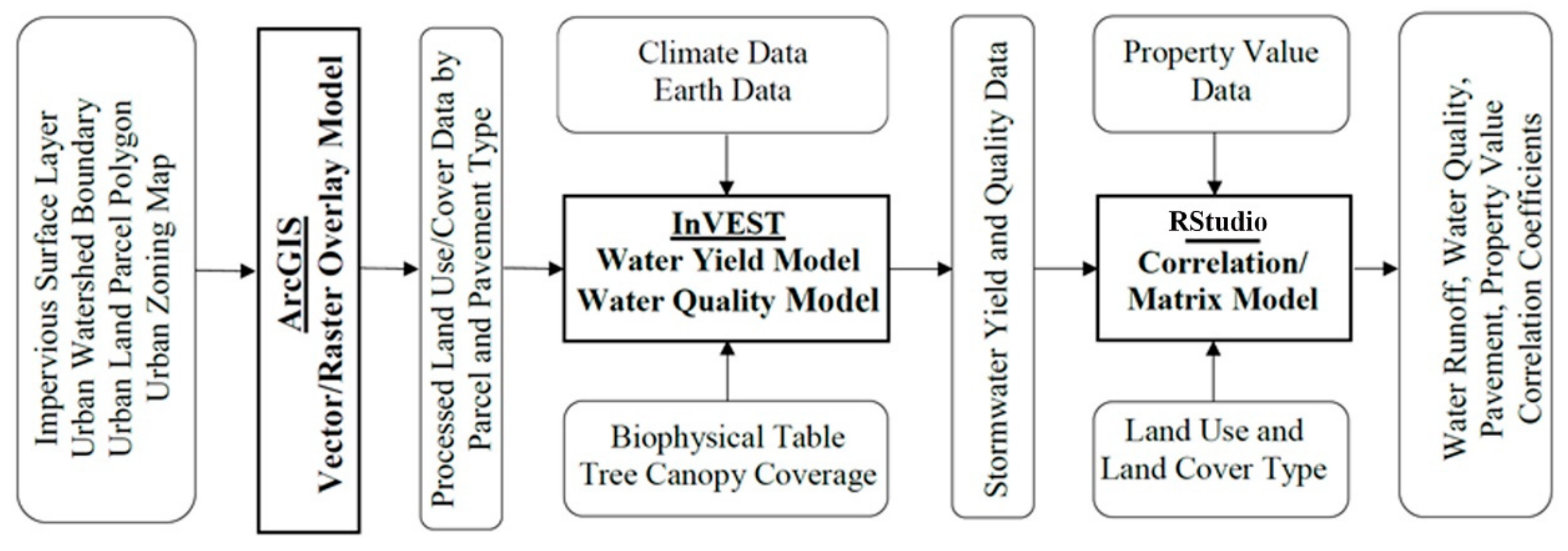
2.3. Research Framework and Data Processing
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Scatterplot Matrix for Commercial Land Use
3.2. Scatterplot Matrix for Industrial Land Use
3.3. Scatterplot Matrix for Residential Land Use
4. Conclusions and Research Limitations
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, C.L., Jr.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage: The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M.; Grabowiecki, P. Review of permeable pavement systems. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3830–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, B.S.; Tyner, J.S.; Yoder, D.C.; Buchanan, J.R. The Effect of Pervious Concrete on Water Quality Parameters: A Case Study. Water 2019, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, R.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Urban stormwater quality and treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, A.F.; Ward, D.A.; Woodington, W.G. The Effect of Asphalt Pavement on Stormwater Contamination; Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2010; Available online: https://digitalcommons.wpi.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1987&context=iqp-all (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Boatwright, J.; Stephenson, K.; Boyle, K.; Nienow, S. Subdivision infrastructure affecting stormwater runoff and residential property values. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 140, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule, M.; Memon, S.; Lee, B.-Y.; Umer, S.; Lee, C.-H. Stormwater runoff quality in correlation to land use and land cover development in Yongin, South Korea. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivkovich, B.R.; Mays, D.C. Predicting nonpoint stormwater runoff quality from land use. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvallis, O. Corvallis Urban Forestry Management Plan. Available online: https://archives.corvallisoregon.gov/public/ElectronicFile.aspx?dbid=0&docid=917700 (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Cox, E.; Longlands, S. The Role of Small and Medium-Sized Towns and Cities in Growing the Northern Powerhouse. Available online: https://www.ippr.org/files/publications/pdf/city-systems_June2016.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2019).
- Sýkora, L.; Mulíček, O. Territorial arrangements of small and medium-sized towns from a functional-spatial perspective. Tijdschr. Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2017, 108, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shen, G.; Woodfin, T.; Chen, T.; Song, K. Ecological and economic impacts of green roofs and permeable pavements at the city level: The case of Corvallis, Oregon. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2018, 61, 430–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.H.; Wenger, S.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Walsh, C.J.; Ladson, A.R.; Shuster, W.D.; Thurston, H.W.; Brown, R.R. Impediments and solutions to sustainable, watershed-scale urban stormwater management: Lessons from Australia and the United States. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, R. Spatial and temporal variation in local stormwater infrastructure use and stormwater management paradigms over the 20th century. Water 2016, 8, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livability. Top 100 Best Places to Live. Available online: https://livability.com/best-places/top-100-best-places-to-live/2018 (accessed on 16 April 2019).
- Oregon, S.O. Oregon’s 2010 Integrated Report Assessment Database and 303(d) List. Available online: https://www.deq.state.or.us/wq/assessment/rpt2010/search.asp (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.; Chan, K.M.; Daily, G.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Bonnette, M.R. Climate change and water-related ecosystem services: Impacts of drought in California, USA. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2016, 2, e01254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shen, G.; Wu, Y.; Brown, R.; Chen, T.; Wang, C. Urban Form, Growth, and Accessibility in Space and Time: Anatomy of Land Use at the Parcel-Level in a Small to Medium-Sized American City. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D. The Willamette River is among 10 Most ‘Endangered’ Rivers of 2019. Available online: https://www.statesmanjournal.com/story/news/2019/04/16/willamette-river-endangered-oregon-environment-american-rivers/3484349002/ (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Walsh, C.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Burns, M.J. Urban stormwater runoff: A new class of environmental flow problem. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. How much of the world’s land has been urbanized, really? A hierarchical framework for avoiding confusion. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbor, J.M. A practical method for estimating the impact of land use change on surface runoff, groundwater recharge and wetland hydrology. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1994, 60, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, B.; Grove, M.; Lowry, C.; Harbor, J. Assessing long-term hydrologic effects of land use change. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1997, 89, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, J.D.; Alig, R.J. Does land use planning slow the conversion of forest and farmlands? Growth Chang. 1999, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D.P. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzurik, A.A. Water Use and Public Policy in Florida. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1984, 110, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Wan, J.; Qin, M.; Qian, H.; Liu, C.; John, R.; Fan, P.; Chen, J. Urbanization dramatically altered the water balances of a paddy field dominated basin in Southern China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 12, 1941–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeška, T. The impact of impervious surfaces on ecohydrology and health in urban ecosystems of Banská Bystrica (Slovakia). Soil Water Res. 2016, 11, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Logan, K.E.; Kucharik, C.J. Impacts of urbanization on ecosystem goods and services in the US Corn Belt. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 519–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Thompson, J.R.; Kolka, R.K.; Franz, K.J.; Stewart, T.W. Using the Storm Water Management Model to predict urban headwater stream hydrological response to climate and land cover change. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzman, L.J.; Anderson, T.A.; Carr, D.L.; McIntyre, N.E. Local and landscape influences on PAH contamination in urban stormwater. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 142, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, D.M.; Walbridge, M.R. Urbanization and nutrient retention in freshwater riparian wetlands. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, A.; Rosas, K.G.; Lugo, A.E.; Ramos-González, O.M. Spatio-temporal variation in stream water chemistry in a tropical urban watershed. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, T.W.; Macdonald, N.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Miller, J.D.; Reynard, N. Current understanding of hydrological processes on common urban surfaces. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 40, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berland, A.; Shiflett, S.A.; Shuster, W.D.; Garmestani, A.S.; Goddard, H.C.; Herrmann, D.L.; Hopton, M.E. The role of trees in urban stormwater management. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Walsh, C.J.; Bos, D.; Nemes, V.; RossRakesh, S.; Prosser, T.; Hatt, B.; Birch, R. Restoration of stormwater retention capacity at the allotment-scale through a novel economic instrument. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.L.; Bos, D.G.; Walsh, C.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; RossRakesh, S. More than money: How multiple factors influence householder participation in at-source stormwater management. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2016, 59, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdaroglu, D.; Yigitcanlar, T. A parcel-scale assessment tool to measure sustainability through urban ecosystem components: The MUSIX model. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, T.; Li, Y. Effects of land use transitions due to rapid urbanization on ecosystem services: Implications for urban planning in the new developing area of China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.C.; Palmer, M.A.; Pizzuto, J.E.; Moglen, G.E.; Angermeier, P.L.; Hilderbrand, R.H.; Dettinger, M.; Hayhoe, K. Forecasting the combined effects of urbanization and climate change on stream ecosystems: From impacts to management options. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snyder, S.A.; Kilgore, M.A. The influence of multiple ownership interests and decision-making networks on the management of family forest lands: Evidence from the United States. Small-Scale For. 2018, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center, N.E.E.F. Stormwater Utility Fees: Considerations & Options for Interlocal Stormwater Working Group (ISWG). Available online: https://digitalcommons.usm.maine.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?referer=&httpsredir=1&article=1005&context=economicsfinance (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- EPA. U.S. Funding Stormwater Programs. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-10/documents/region3_factsheet_funding_0.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Redhead, J.W.; May, L.; Oliver, T.H.; Hamel, P.; Sharp, R.; Bullock, J.M. National scale evaluation of the InVEST nutrient retention model in the United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, Y.; Woodfin, T.; Zhu, R.; Chen, T. An approach to evaluate comprehensive plan and identify priority lands for future land use development to conserve more ecological values. Sustainability 2018, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST +VERSION+ User’s Guide. The Natural Capital Project, Stanford University, University of Minnesota, The Nature Conservancy, and World Wildlife Fund. U.S. Bureau of the Census. Available online: http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/41/4115800.html (accessed on 8 October 2016).
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. FaoRome 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Project, N.C. National Capital Project Dataset. Available online: https://naturalcapitalproject.stanford.edu/invest/ (accessed on 16 January 2019).
- Corvallis, C.O. NPDES Phase II Storm Water Management Program Plan. Available online: http://www.corvallisoregon.gov/modules/showdocument.aspx?documentid=4427 (accessed on 15 October 2015).
- Individual Sample Datasets for InVEST. Available online: http://data.naturalcapitalproject.org/invest-data/ (accessed on 1 October 2015).
- Arguez, A.; Durre, I.; Applequist, S.; Vose, R.S.; Squires, M.F.; Yin, X.; Heim, R.R., Jr.; Owen, T.W. NOAA’s 1981–2010 US climate normals: An overview. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesch, D.B. The national elevation dataset. In Digital Elevation Model Technologies and Applications: The DEM User’s Manual, 2nd ed.; Maune, D., Ed.; American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 99–118. ISBN 9781570830822. [Google Scholar]
- NRCS. Soil Survey Geographic Database. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/ (accessed on 8 May 2019).
- Consortium, P.N.E.R. Willamette River Basin Datasets. Available online: http://www.fsl.orst.edu/pnwerc/wrb/access.html (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Vigerstol, K.L.; Aukema, J.E. A comparison of tools for modeling freshwater ecosystem services. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2403–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, B., Jr. Paving over paradise: How land use regulations promote residential imperviousness. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 69, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.; Norman, J.M. Land use planning and surface heat island formation: A parcel-based radiation flux approach. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Bou-Zeid, E.; Smith, J.A. A coupled energy transport and hydrological model for urban canopies evaluated using a wireless sensor network. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 1643–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrić, S.; Leonhardt, G.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Processes improving urban stormwater quality in grass swales and filter strips: A review of research findings. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toor, G.S.; Occhipinti, M.L.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Majcherek, T.; Haver, D.; Oki, L. Managing urban runoff in residential neighborhoods: Nitrogen and phosphorus in lawn irrigation driven runoff. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Haver, D.; Pataki, D.E. Nitrogen budgets of urban lawns under three different management regimes in southern California. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reubold, T. Study: Lawn Fertilizers and Pet Waste Are the Major Sources of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Pollution in Urban Waters. Available online: http://environment.umn.edu/news/nitrogen-and-phosphorus-pollution-in-urban-watersheds/ (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Fenelon, S.E. Stormwater Management in the Industrial Environment. Available online: https://www.planning.org.nz/Folder?Action=View%20File&Folder_id=185&File=Fenelon.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Carmon, N.; Shamir, U. Water-sensitive planning: Integrating water considerations into urban and regional planning. Water Environ. J. 2010, 24, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, S.E.; Finlay, J.C.; Janke, B.D.; Nidzgorski, D.A.; Millet, D.B.; Baker, L.A. Contrasting nitrogen and phosphorus budgets in urban watersheds and implications for managing urban water pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4177–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aveni, M.; Berger, K.; Champion, J.; Felton, G.; Goatley, M.; Keeling, W.; Law, N.; Schwartz, S. Recommendations of the Expert Panel to Define Removal Rates for Urban Nutrient Management. Available online: https://www.chesapeakebay.net/documents/Final_CBP_Approved_Expert_Panel_Report_on_Urban_Nutrient_Management--short.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2019).
- Prudencio, L.; Null, S.E. Stormwater management and ecosystem services: A review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 033002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Z.; Fonseca, C.; Zeerak, R. Stormwater Utility Fees and Credits: A Funding Strategy for Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quality, D.O.E. Total Maximum Daily Loads. Available online: https://www.oregon.gov/deq/wq/tmdls/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 25 October 2019).







| Pixel | Ex_n/p | Gx_n/p | ALVx | Retx | Expx_n/p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E1 | G1 | ALV1 | 0 | ALV1 |
| 2 | E2 | G2 | ALV2 | Exp1 × E2 | Exp1 × G2 + ALV2 |
| 3 | E3 | G3 | ALV3 | Exp2 × E3 | Exp2 × G3 + ALV3 |
| 4 | E4 | G4 | ALV4 | Exp3 × E4 | Exp3 × G4 + ALV4 |
| x | Ex | Gx | ALVx | Exp(x−1) × Ex | Exp(x−1) × Gx + ALVx |
| Land Cover | Canopy_P | Sample Biophysical Table | Adjusted Biophysical Table | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kc | load_n | eff_n | load_p | eff_p | Kc | load_n | eff_n | load_p | eff_p | ||
| Building | 0% | 0.100 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.005 | 0.050 | 0.100 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.005 | 0.050 |
| Road and driveway | 15% | 0.100 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.005 | 0.050 | 0.235 | 0.609 | 0.133 | 0.005 | 0.133 |
| Sidewalk | 20% | 0.100 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.005 | 0.050 | 0.280 | 0.808 | 0.160 | 0.005 | 0.160 |
| Parking lot | 5% | 0.100 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.005 | 0.050 | 0.145 | 0.210 | 0.078 | 0.005 | 0.078 |
| Others (grass) | 25% | 0.650 | 11.000 | 0.400 | 1.500 | 0.400 | 0.888 | 9.250 | 0.450 | 1.126 | 0.450 |
| Urban tree | 100% | 1.000 | 4.000 | 0.600 | 0.005 | 0.600 | 1.000 | 4.000 | 0.600 | 0.005 | 0.600 |
| Dataset | Data Name | Source | Format Adjustment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate Dataset | Precipitation (P(x)) | Climate Prediction Center [52] | GIS Raster—GRID |
| Reference Evapotranspiration (ET0) | Climate Prediction Center [52] | GIS Raster—GRID | |
| Geographic Dataset | Digital Elevation Model | National Elevation Database [53] | GIS Raster—GRID |
| Plant Available Water Content (AWC) | Soil Survey Geographic Database [54] | GIS Raster—GRID | |
| Land Cover Data | Pacific Northwest Ecosystem Research Consortium [55] | GIS Raster—GRID | |
| Planning Dataset | Land Use | City of Corvallis, OR [9] | GIS Vector—Polygon |
| Urban Canopy (Canopy_P) | Urban Forestry Management Plan [50] | GIS Vector—Polygon | |
| Impervious Surface | City of Corvallis, OR [9] | GIS Vector—Polygon | |
| Parcel (x) | City of Corvallis, OR [9] | GIS Vector—Polygon | |
| Biophysical Dataset | Plant Evapotranspiration Coefficient (Kc) | FAO Crop Evapotranspiration [48] | N/A |
| Nutrient Loading Coefficient (load_n/p) | Natural Capital Project Dataset [49] | N/A | |
| Vegetation Filtering Coefficient (eff_n/p) | Natural Capital Project Dataset [49] | N/A |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L. Correlations of Stormwater Runoff and Quality: Urban Pavement and Property Value by Land Use at the Parcel Level in a Small Sized American City. Water 2019, 11, 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112369
Zhou L. Correlations of Stormwater Runoff and Quality: Urban Pavement and Property Value by Land Use at the Parcel Level in a Small Sized American City. Water. 2019; 11(11):2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112369
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Long. 2019. "Correlations of Stormwater Runoff and Quality: Urban Pavement and Property Value by Land Use at the Parcel Level in a Small Sized American City" Water 11, no. 11: 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112369
APA StyleZhou, L. (2019). Correlations of Stormwater Runoff and Quality: Urban Pavement and Property Value by Land Use at the Parcel Level in a Small Sized American City. Water, 11(11), 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112369




