Space–Time Kriging of Precipitation: Modeling the Large-Scale Variation with Model GAMLSS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
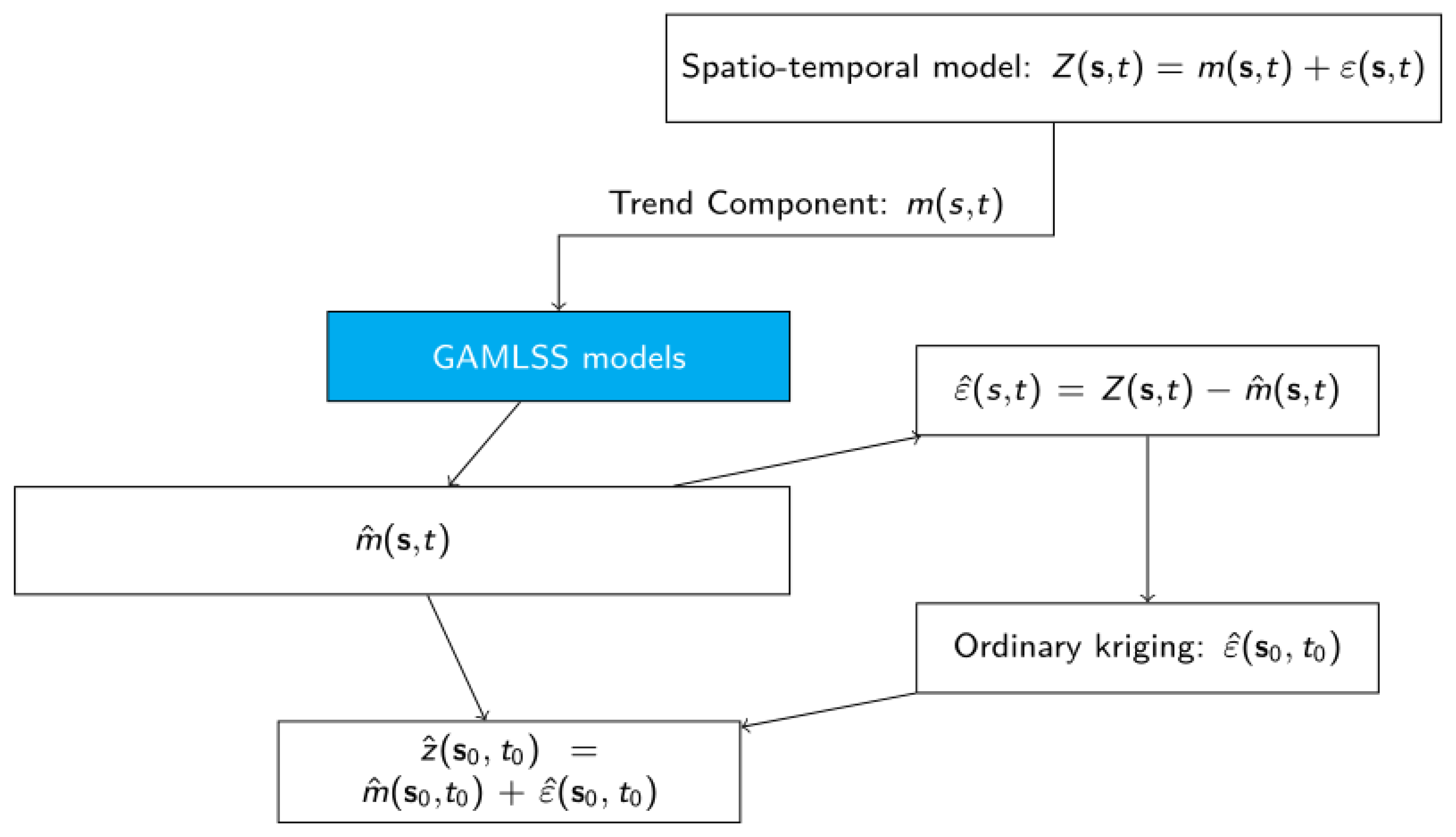
3. Methods
3.1. Trend Component
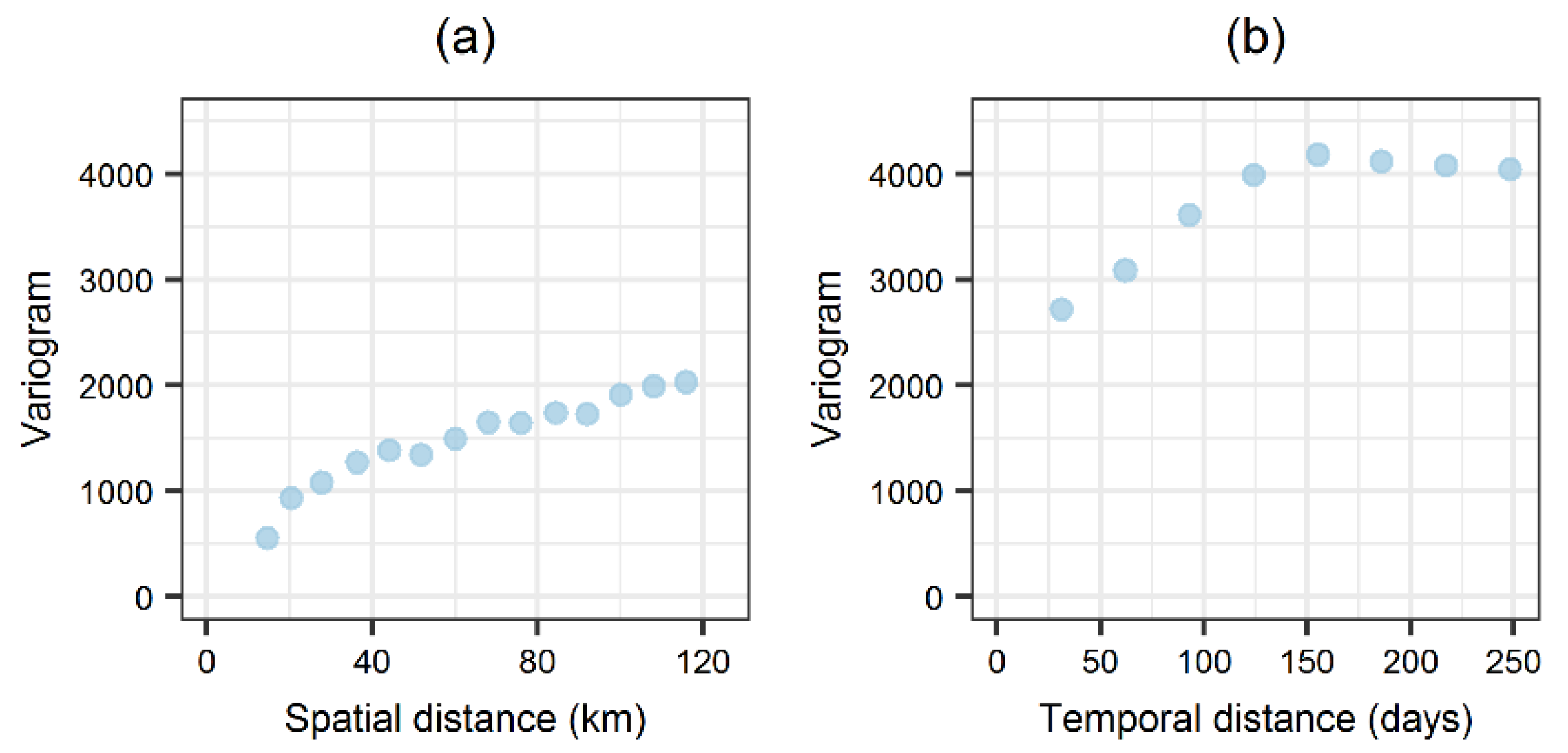
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variogram
3.3. Geostatistical Prediction
4. Results
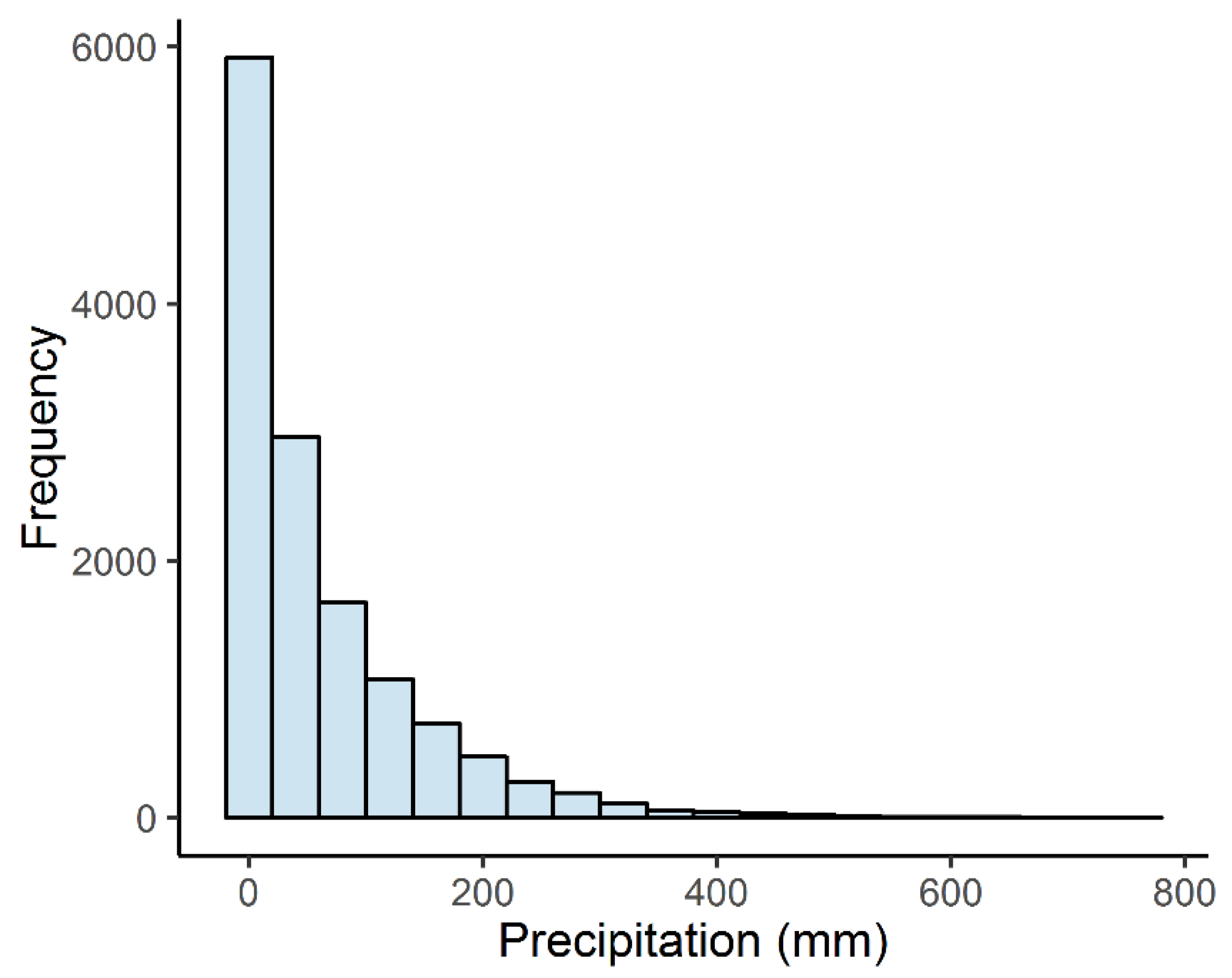
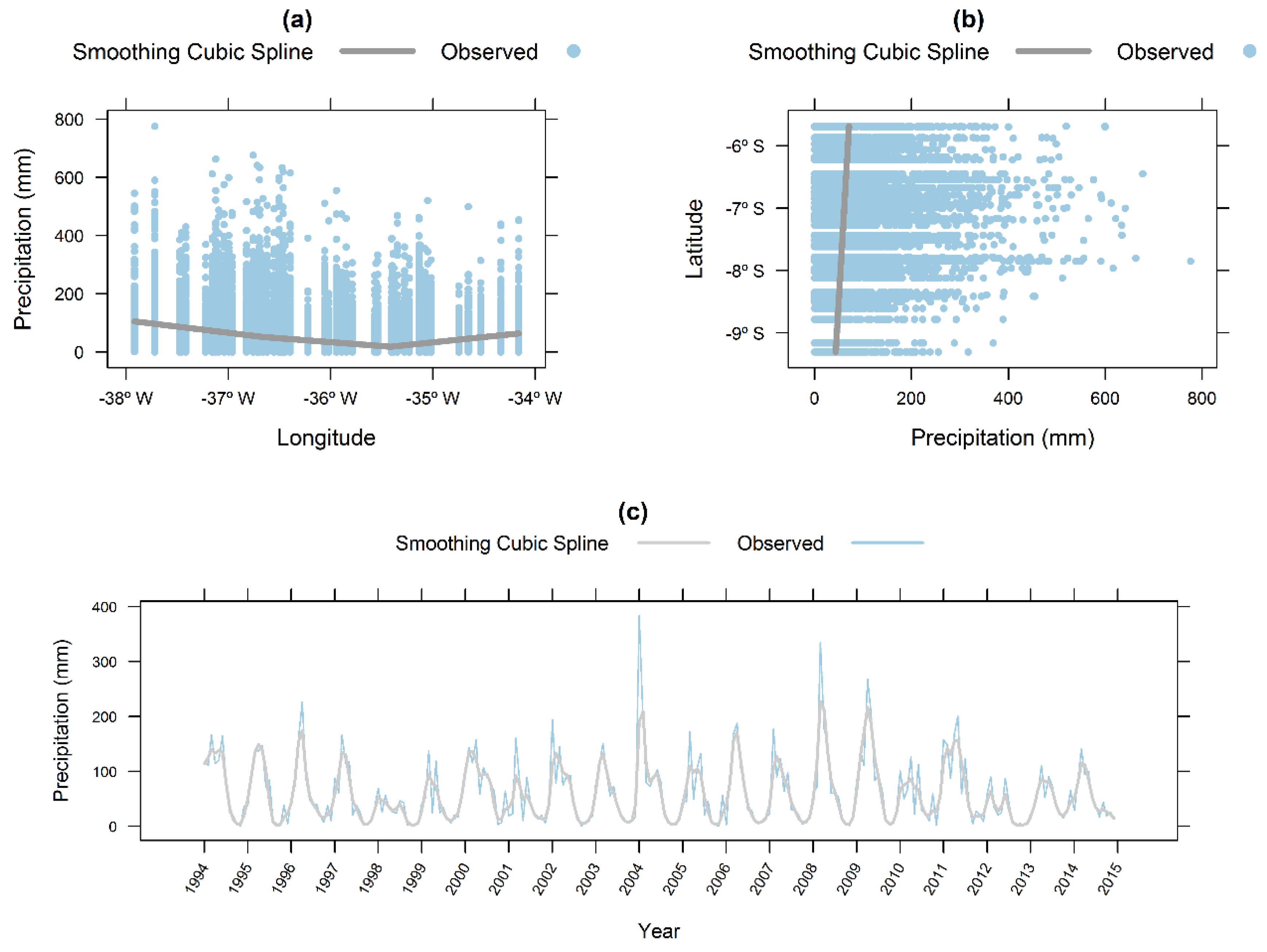
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
4.2. Trend Analysis
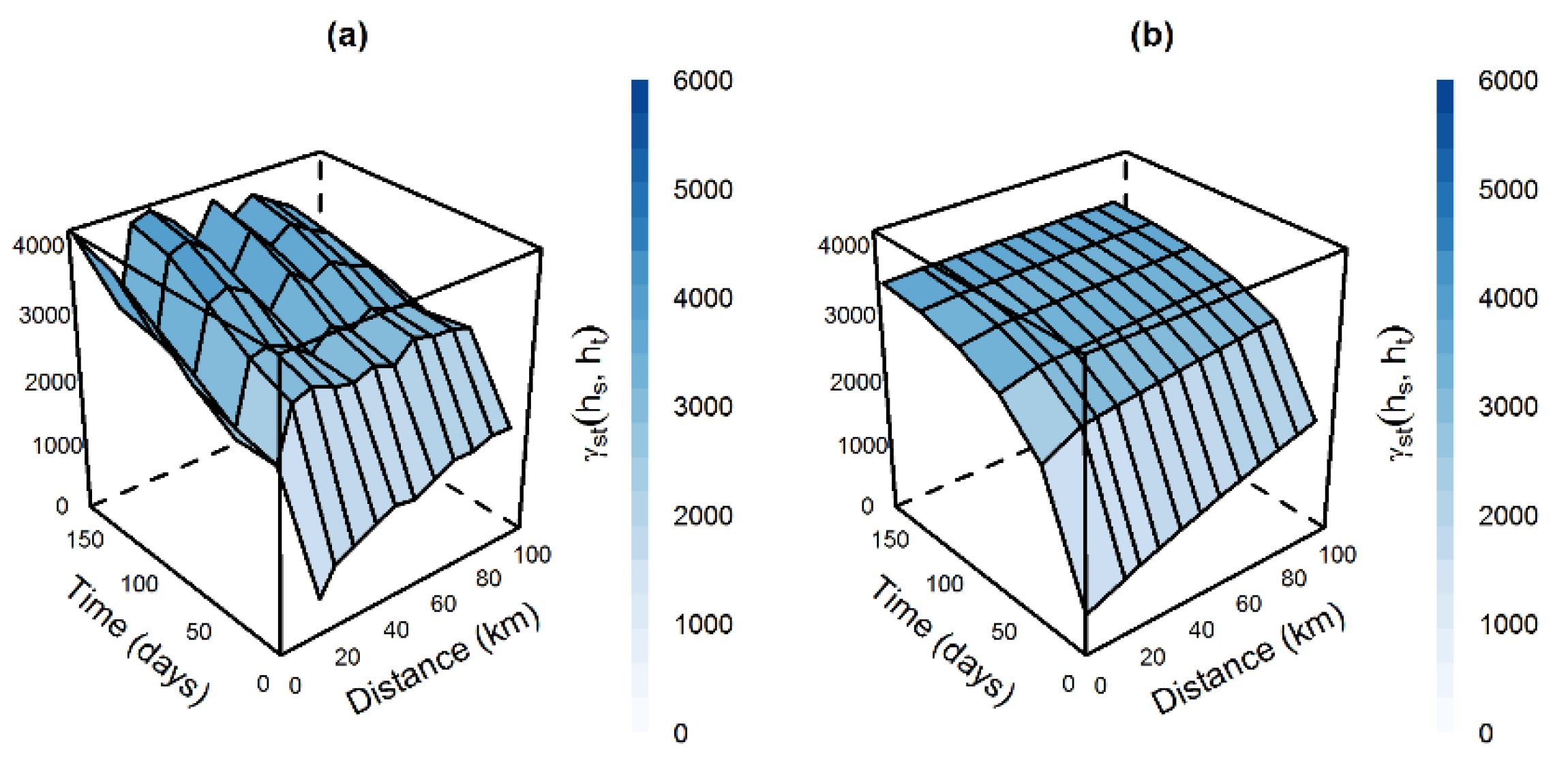
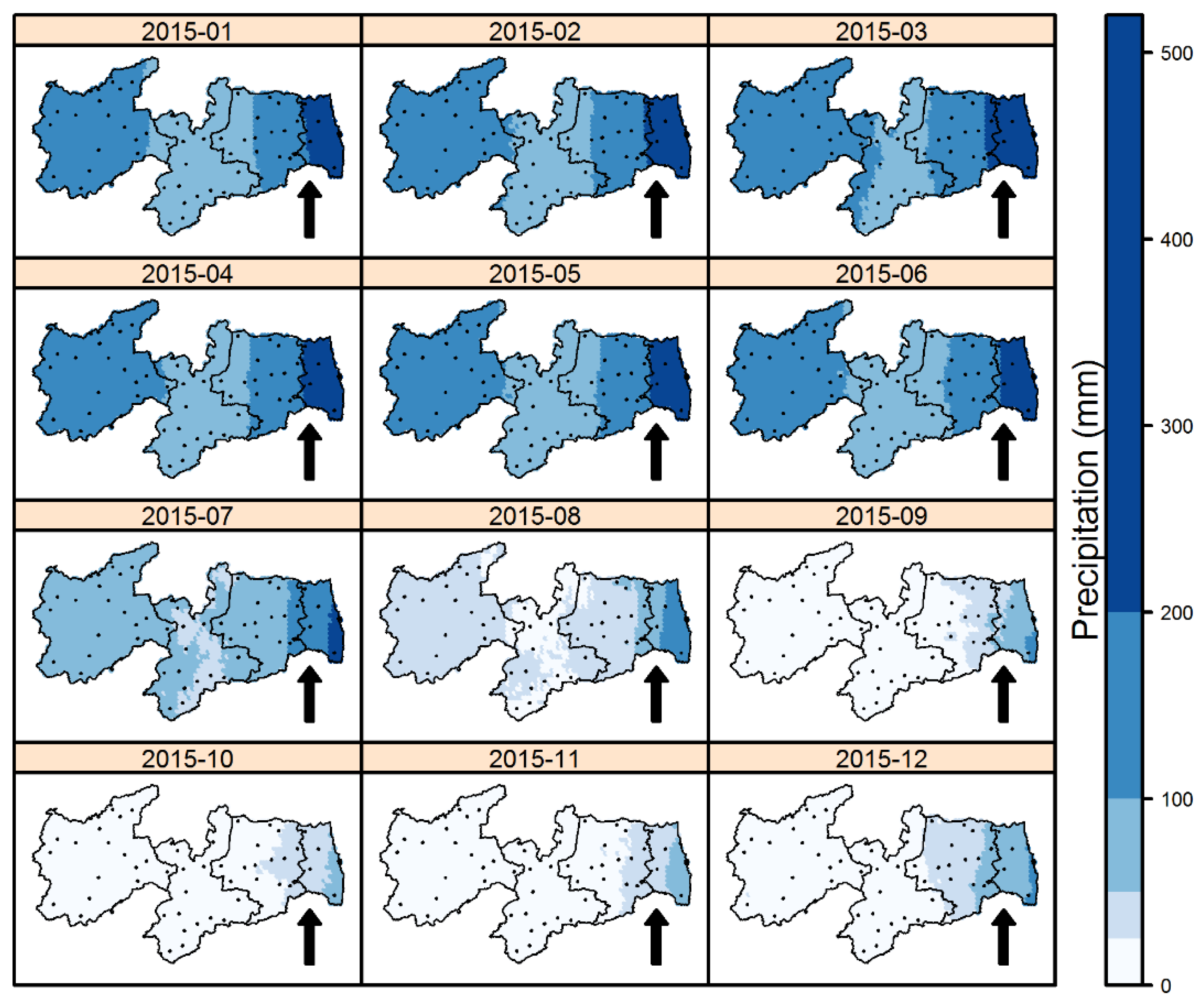
4.3. Geostatistical Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kilibarda, M.; Tadić, M.P.; Hengl, T.; Luković, J.; Bajat, B. Global geographic and feature space coverage of temperature data in the context of spatio-temporal interpolation. Spat. Stat. 2015, 14, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, W.A.; Melo, C.E.; Melo, O.O. Median Polish Kriging for space-time analysis of precipitation. Spat. Stat. 2017, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, R.; Mayr, G.J.; Messner, J.W.; Umlauf, N.; Zeileis, A. Spatio-temporal precipitation climatology over complex terrain using a censored additive regression model. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marengo, J.A.; Torres, R.R.; Alves, L.M. Drought in Northeast Brazil—past, present, and future. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, B.C.; de Baptista, G.M.; Meneses, P.R. Identification of hydromorphic areas by means of spectral analysis of remote sensing data, as support for the preparation of forensic reports issued to evaluation of rural properties. Rev. Bras. Geogr. Física 2014, 7, 1062–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, H.A.; Medeiros, E.A. Variabilidade no regime pluvial em duas mesorregiõres da Paraíba e sua relação com o fenômeno EL Niño Oscilação Sul. J. Environ. Anal. Prog. 2017, 2, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.A.C.; Gomes, O.M.; de Souza, F.A.S.; Paiva, W. De Análise Geoestatística da Precipitação Pluvial do Estado da Paraíba (Geostatistical Analysis of Precipitation in Paraiba State). Rev. Bras. Geogr. Física 2012, 4, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, P.R.M.; da Mello, V.S.; Bandeira, M.M.; de Marcedo, F.L.; Santos, D. Discriminação de cenários pluviométricos do estado da Paraíba utilizando distribuição Gama Incompleta e Teste Kolmogorov-Smirnov. Rev. Bras. Geogr. Física 2016, 9, 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gräler, B.; Gerharz, L.; Pebesma, E. Spatio-temporal analysis and interpolation of PM10 measurements in Europe. ETC/ACM Tech. Pap. 2011/10 2012, 8, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Perčec Tadić, M.; Pebesma, E.J. Spatio-temporal prediction of daily temperatures using time-series of MODIS LST images. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 107, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Shu, H.; Hu, H.; Xu, J. Spatiotemporal regression Kriging to predict precipitation using time-series MODIS data. Cluster Comput. 2017, 20, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.; Piairo, H.; García-Soidán, P.; Sousa, I. Spatial–temporal modellization of the NO2 concentration data through geostatistical tools. Stat. Methods Appt. 2016, 25, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Menezes, R.; Silva, M.E. Modelling spatio-temporal data with multiple seasonalities: The NO2 Portuguese case. Spat. Stat. 2017, 22, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinopoulos, M.; Rigby, R.A.; Heller, G.Z.; Voudouris, V.; De Bastiani, F. Flexible Regression and Smoothing Using GAMLSS in R; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, J.-M.; Fernández-Avilés, G.; Mateu, J. Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Geostatistical Modeling and Kriging; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schabenberger, O.; Gotway, C.A. Statistical Methods for Spatial Data Analysis; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Iaco, S.D.; Myers, D.E.; Posa, D. Space–time analysis using a general product–sum model. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2001, 52, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Martinez, F.; Mateu, J.; Montes, F. Model comparison and selection for stationary space–time models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2007, 51, 4577–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N.; Wikle, C.K. Statistics for Spatio-Temporal Data; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Iaco, S.D.; Myers, D.E.; Posa, D. Nonseparable space-time covariance models: Some parametric families. Math. Geol. 2002, 34, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilibarda, M.; Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Gräler, B.; Pebesma, E.; Perčec Tadić, M.; Bajat, B. Spatio-temporal interpolation of daily temperatures for global land areas at 1 km resolution. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2294–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M. Spatial Statistics and Spatio-Temporal Data; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cesare, L.D.; Myers, D.; Posa, D. Estimating and modeling space–time correlation structures. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2001, 51, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaco, S.D.; Palma, M.; Posa, D. Spatio-temporal geostatistical modeling for French fertility predictions. Spat. Stat. 2015, 14, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graler, B.; Pebesma, E.; Heuvelink, G. Spatio-temporal interpolation using gstat. Wp 2016, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivand, R.S.; Pebesma, E.; Gómez-Rubio, V. Hello World: Introducing Spatial Data. In Applied Spatial Data Analysis with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Marengo, J.A.; Alves, L.M.; Alvala, R.C.; Cunha, A.P.; Brito, S.; Moraes, O.L.L. Climatic Characteristics of the 2010–2016 Drought in the Semiarid Northeast Brazil Region. 2017. Available online: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0001-37652018000501973 (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- Souza, B.I.; Menezes, R.; Artigas, R.C. Efeitos da desertificação na composição de espécies do bioma Caatinga, Paraíba/Brasil. Investig. Geográficas 2015, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Macedo, M.J.; Guedes, R.; de Sousa, F.A.; Dantas, F. Analysis of the standardized precipitation index for the Paraíba state, Brazil. Ambient. e Agua-An Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 5, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, A.P.A.; Engle, N.L.; De Nys, E.; Molejón, C.; Martins, E.S. Drought preparedness in Brazil. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2014, 3, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.R.; McPhaden, M.J. Why did the 2011–2012 La Niña cause a severe drought in the Brazilian Northeast? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lei, L.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Zou, P.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B. Evaluation of spatio-temporal variogram models for mapping Xco2 using satellite observations: A case study in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, O.M.; dos Santos, C.A.C.; de Souza, F.A.S.; de Paiva, W.; de Olinda, R.A. Análise comparativa da precipitação no estado da paraíba utilizando modelos de regressão polinomial. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2015, 30, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
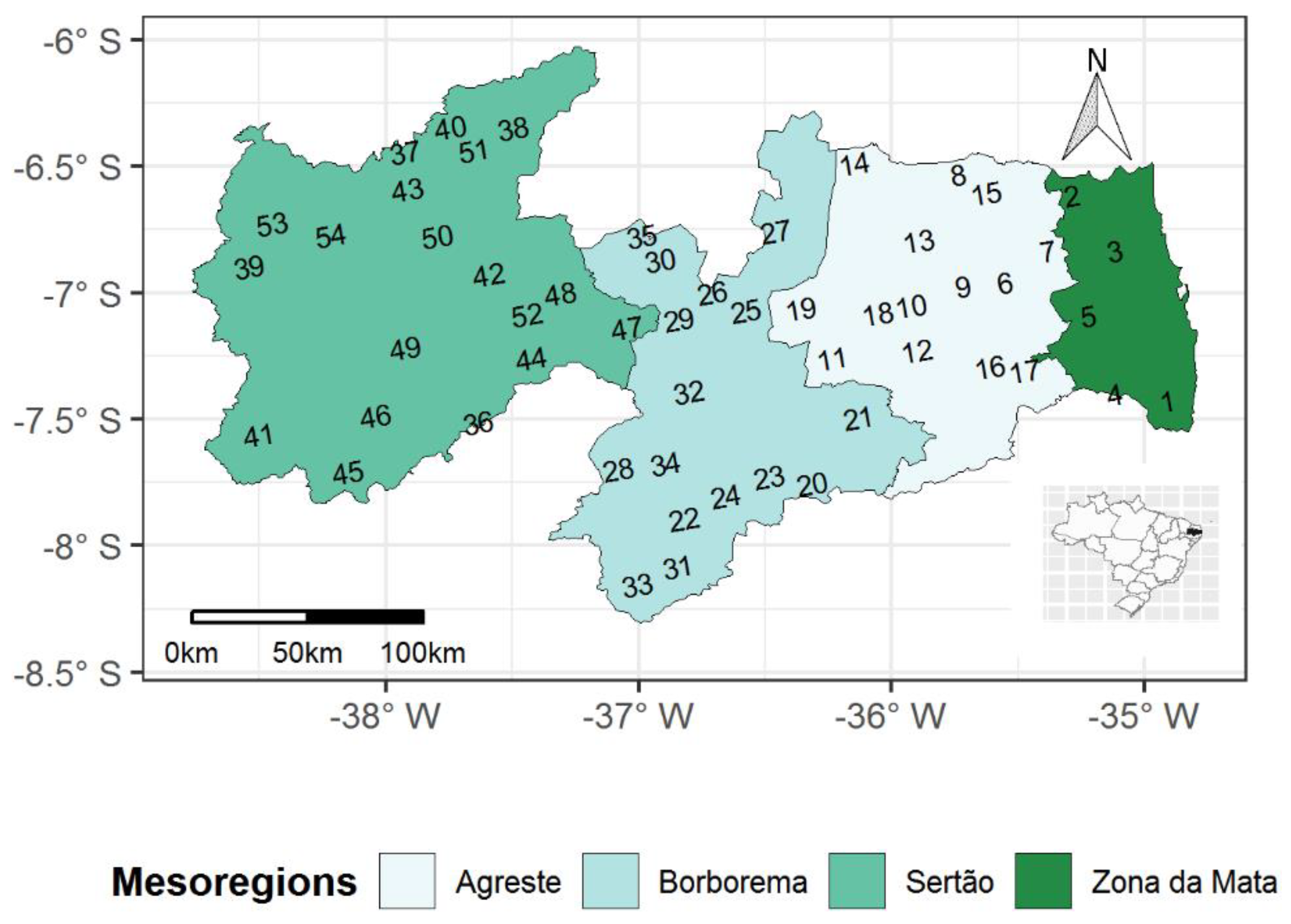
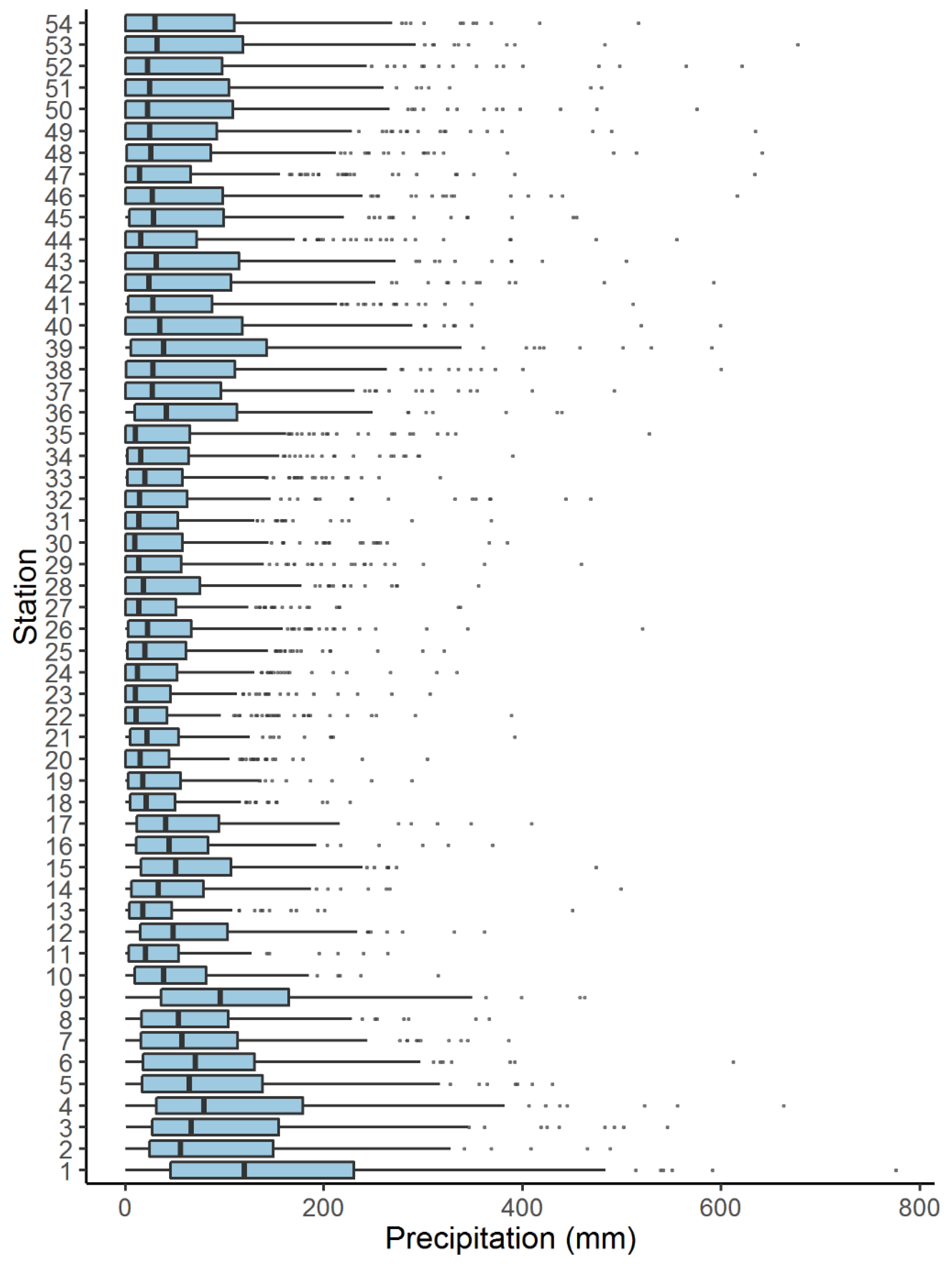
| ID | Mesoregion | Station | Lat | Long | Alt (m) | Quantiles | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5% | 50.0% | 97.5% | ||||||
| 1 | Zona da Mata | Alhandra | −7.43 | −34.91 | 56.28 | 6.49 | 119.85 | 481.71 |
| 2 | Zona da Mata | Jacaraú | −6.61 | −35.29 | 181.19 | 0.88 | 55.90 | 311.01 |
| 3 | Zona da Mata | Mamanguape | −6.84 | −35.12 | 16.62 | 2.60 | 66.70 | 403.02 |
| 4 | Zona da Mata | Pedras de Fogo | −7.40 | −35.12 | 175.36 | 4.71 | 79.25 | 399.52 |
| 5 | Zona da Mata | Sapé | −7.09 | −35.22 | 116.84 | 1.86 | 64.35 | 324.14 |
| 6 | Agreste | Alagoinha | −6.96 | −35.55 | 168.64 | 0.00 | 70.50 | 306.56 |
| 7 | Agreste | Araçagi | −6.83 | −35.39 | 104.62 | 0.00 | 56.95 | 290.73 |
| 8 | Agreste | Araruna | −6.53 | −35.74 | 575.41 | 0.00 | 53.40 | 235.32 |
| 9 | Agreste | Areia | −6.98 | −35.72 | 572.28 | 4.34 | 95.55 | 331.73 |
| 10 | Agreste | Areial | −7.05 | −35.93 | 693.09 | 0.00 | 38.55 | 182.72 |
| 11 | Agreste | Boa Vista | −7.26 | −36.24 | 486.00 | 0.00 | 20.30 | 127.07 |
| 12 | Agreste | Campina Grande | −7.23 | −35.90 | 544.37 | 0.93 | 48.00 | 244.28 |
| 13 | Agreste | Casserengue | −6.79 | −35.89 | 396.63 | 0.00 | 18.00 | 137.88 |
| 14 | Agreste | Cuité | −6.49 | −36.15 | 668.96 | 0.00 | 33.35 | 190.79 |
| 15 | Agreste | Dona Inês | −6.61 | −35.63 | 421.72 | 0.00 | 51.25 | 242.04 |
| 16 | Agreste | Ingá | −7.29 | −35.61 | 155.56 | 0.00 | 44.35 | 191.81 |
| 17 | Agreste | Mogeiro | −7.31 | −35.48 | 108.28 | 0.00 | 40.95 | 194.68 |
| 18 | Agreste | Pocinhos | −7.08 | −36.06 | 650.32 | 0.00 | 21.45 | 140.05 |
| 19 | Agreste | Soledade | −7.06 | −36.36 | 523.63 | 0.00 | 17.75 | 139.61 |
| 20 | Borborema | Barra de São Miguel | −7.75 | −36.32 | 488.63 | 0.00 | 15.30 | 142.21 |
| 21 | Borborema | Boqueirão | −7.49 | −36.14 | 355.08 | 0.00 | 21.65 | 148.11 |
| 22 | Borborema | Camalaú | −7.89 | −36.83 | 519.16 | 0.00 | 11.15 | 185.53 |
| 23 | Borborema | Caraúbas | −7.73 | −36.49 | 442.24 | 0.00 | 10.60 | 161.65 |
| 24 | Borborema | Congo | −7.80 | −36.66 | 491.99 | 0.00 | 12.25 | 164.82 |
| 25 | Borborema | Juazeirinho | −7.07 | −36.58 | 553.96 | 0.00 | 20.10 | 175.97 |
| 26 | Borborema | Junco do Seridó | −7.00 | −36.71 | 589.56 | 0.00 | 22.40 | 210.18 |
| 27 | Borborema | Pedra Lavrada | −6.76 | −36.46 | 521.82 | 0.00 | 13.55 | 180.72 |
| 28 | Borborema | Prata | −7.70 | −37.08 | 584.00 | 0.00 | 18.85 | 220.19 |
| 29 | Borborema | Salgadinho | −7.10 | −36.85 | 430.45 | 0.00 | 13.60 | 240.85 |
| 30 | Borborema | Santa Luzia | −6.87 | −36.92 | 311.24 | 0.00 | 9.80 | 246.99 |
| 31 | Borborema | São João do Tigre | −8.08 | −36.85 | 572.84 | 0.00 | 13.80 | 161.03 |
| 32 | Borborema | São José dos Cordeiros | −7.39 | −36.81 | 530.49 | 0.00 | 14.30 | 313.51 |
| 33 | Borborema | São Seb. do Umbuzeiro | −8.15 | −37.01 | 595.79 | 0.00 | 20.10 | 200.60 |
| 34 | Borborema | Sumé | −7.67 | −36.90 | 519.88 | 0.00 | 15.70 | 264.53 |
| 35 | Borborema | Várzea | −6.77 | −36.99 | 267.64 | 0.00 | 10.65 | 270.29 |
| 36 | Sertão | Agua Branca | −7.51 | −37.64 | 732.80 | 0.00 | 41.40 | 274.52 |
| 37 | Sertão | Bom Sucesso | −6.44 | −37.93 | 289.12 | 0.00 | 27.20 | 296.80 |
| 38 | Sertão | Brejo do Cruz | −6.35 | −37.50 | 200.67 | 0.00 | 27.70 | 320.60 |
| 39 | Sertão | Cajazeiras | −6.89 | −38.54 | 299.44 | 0.00 | 38.80 | 409.20 |
| 40 | Sertão | Catolé do Rocha | −6.34 | −37.75 | 298.89 | 0.00 | 34.55 | 301.66 |
| 41 | Sertão | Conceição | −7.56 | −38.50 | 388.28 | 0.00 | 27.90 | 272.48 |
| 42 | Sertão | Condado | −6.92 | −37.59 | 260.82 | 0.00 | 23.75 | 336.19 |
| 43 | Sertão | Lagoa | −6.59 | −37.91 | 275.56 | 0.00 | 31.30 | 314.85 |
| 44 | Sertão | Mãe D’Água | −7.26 | −37.43 | 411.10 | 0.00 | 15.65 | 277.71 |
| 45 | Sertão | Manaíra | −7.71 | −38.15 | 767.40 | 0.00 | 28.95 | 284.65 |
| 46 | Sertão | Nova Olinda | −7.48 | −38.04 | 321.00 | 0.00 | 27.55 | 326.82 |
| 47 | Sertão | Passagem | −7.14 | −37.05 | 305.04 | 0.00 | 14.65 | 273.24 |
| 48 | Sertão | Patos | −7.00 | −37.31 | 256.69 | 0.00 | 26.25 | 303.92 |
| 49 | Sertão | Piancó | −7.21 | −37.93 | 261.16 | 0.00 | 24.90 | 321.85 |
| 50 | Sertão | Pombal | −6.77 | −37.80 | 191.56 | 0.00 | 22.85 | 353.35 |
| 51 | Sertão | Riacho dos Cavalos | −6.44 | −37.65 | 206.93 | 0.00 | 24.45 | 269.48 |
| 52 | Sertão | Santa Teresinha | −7.08 | −37.45 | 307.16 | 0.00 | 22.55 | 368.42 |
| 53 | Sertão | São J. do Rio do Peixe | −6.73 | −38.45 | 248.20 | 0.00 | 31.90 | 325.64 |
| 54 | Sertão | Sousa | −6.77 | −38.22 | 235.44 | 0.00 | 30.30 | 327.17 |
| Parameter | Estimative | SE | t Value | p-Value | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −16.760 | 0.517 | −32.399 | < | 0.48 | ||
| < | < | 12.717 | < | |||
| 0.002 | < | 39.081 | < | |||
| < | < | −5.955 | < | |||
| 0.855 | 0.005 | 163.700 | < | |||
| −0.010 | 0.002 | −59.350 | < | |||
| MODEL | NORMAL | GAMMA | ZAGA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | |
| GAU + EXP | 36.099 | 21.881 | 0.813 | 36.652 | 22.065 | 0.807 | 36.116 | 21.920 | 0.812 |
| GAU + SPH | 36.881 | 22.414 | 0.805 | 36.708 | 22.090 | 0.807 | 37.596 | 22.895 | 0.797 |
| EXP + EXP | 34.710 | 21.011 | 0.827 | 35.381 | 21.253 | 0.821 | 34.598 | 20.970 | 0.828 |
| EXP + SPH | 34.991 | 21.181 | 0.824 | 35.388 | 21.262 | 0.821 | 35.342 | 21.430 | 0.820 |
| Component | Variogram Model | Nugget | Threshold | Range | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial () | Exponential | 0.757 | 4.350 | 171 km | 15.689 |
| Temporal () | Exponential | 17.479 | 52.058 | 47 days |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medeiros, E.S.d.; de Lima, R.R.; Olinda, R.A.d.; Dantas, L.G.; Santos, C.A.C.d. Space–Time Kriging of Precipitation: Modeling the Large-Scale Variation with Model GAMLSS. Water 2019, 11, 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112368
Medeiros ESd, de Lima RR, Olinda RAd, Dantas LG, Santos CACd. Space–Time Kriging of Precipitation: Modeling the Large-Scale Variation with Model GAMLSS. Water. 2019; 11(11):2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112368
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedeiros, Elias Silva de, Renato Ribeiro de Lima, Ricardo Alves de Olinda, Leydson G. Dantas, and Carlos Antonio Costa dos Santos. 2019. "Space–Time Kriging of Precipitation: Modeling the Large-Scale Variation with Model GAMLSS" Water 11, no. 11: 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112368
APA StyleMedeiros, E. S. d., de Lima, R. R., Olinda, R. A. d., Dantas, L. G., & Santos, C. A. C. d. (2019). Space–Time Kriging of Precipitation: Modeling the Large-Scale Variation with Model GAMLSS. Water, 11(11), 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112368






