Multi-Method Tracking of Monsoon Floods Using Sentinel-1 Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
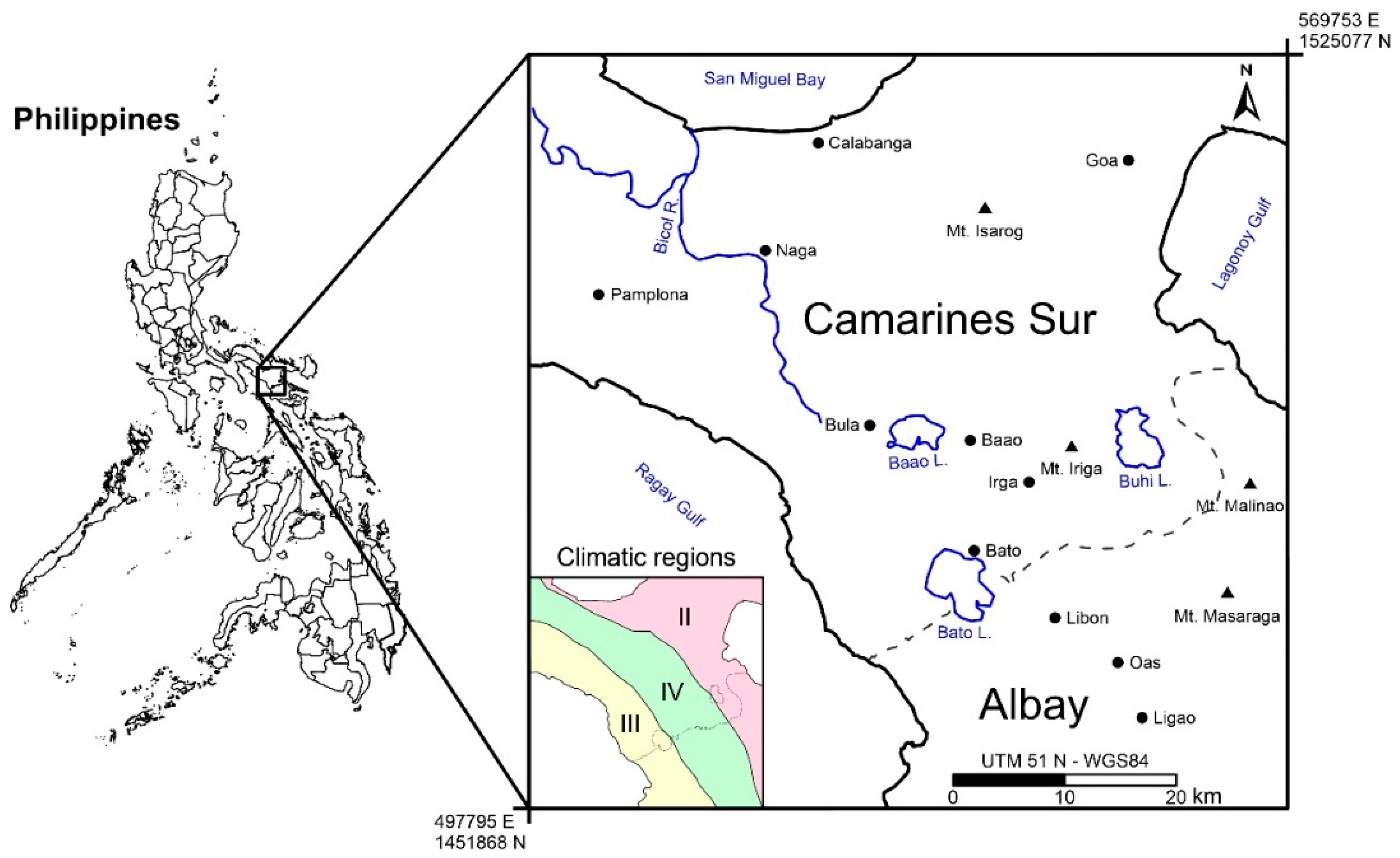
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
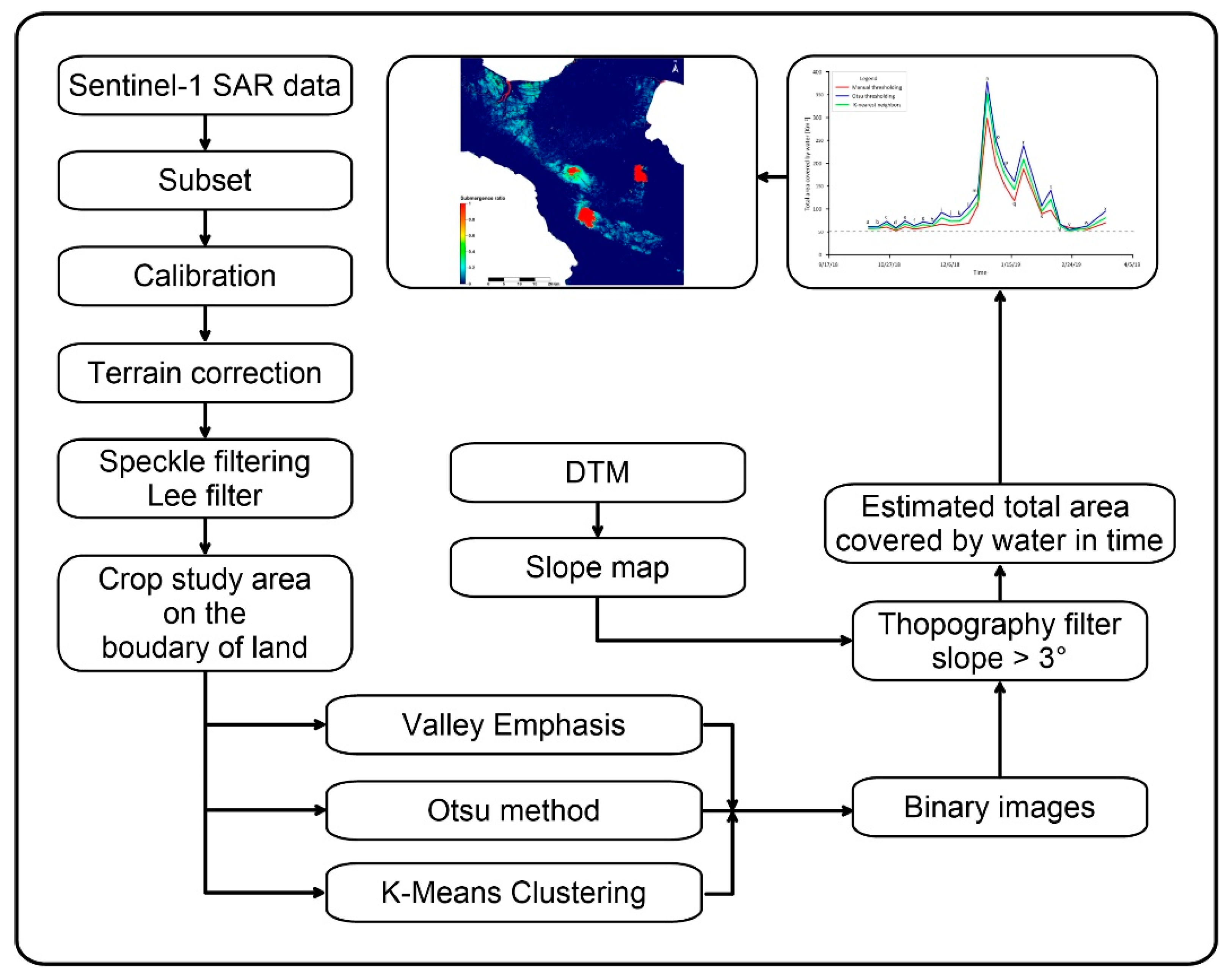
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
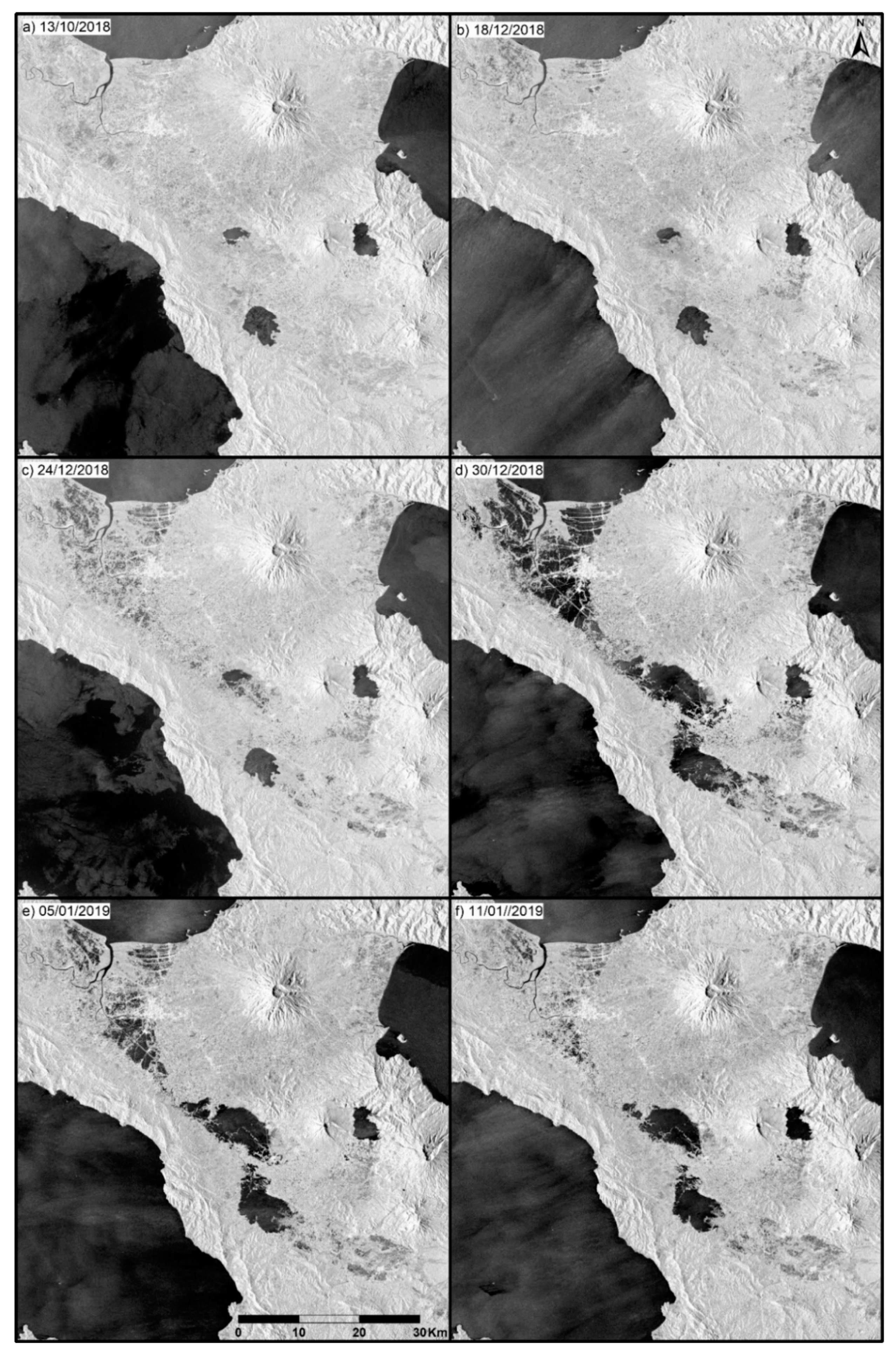
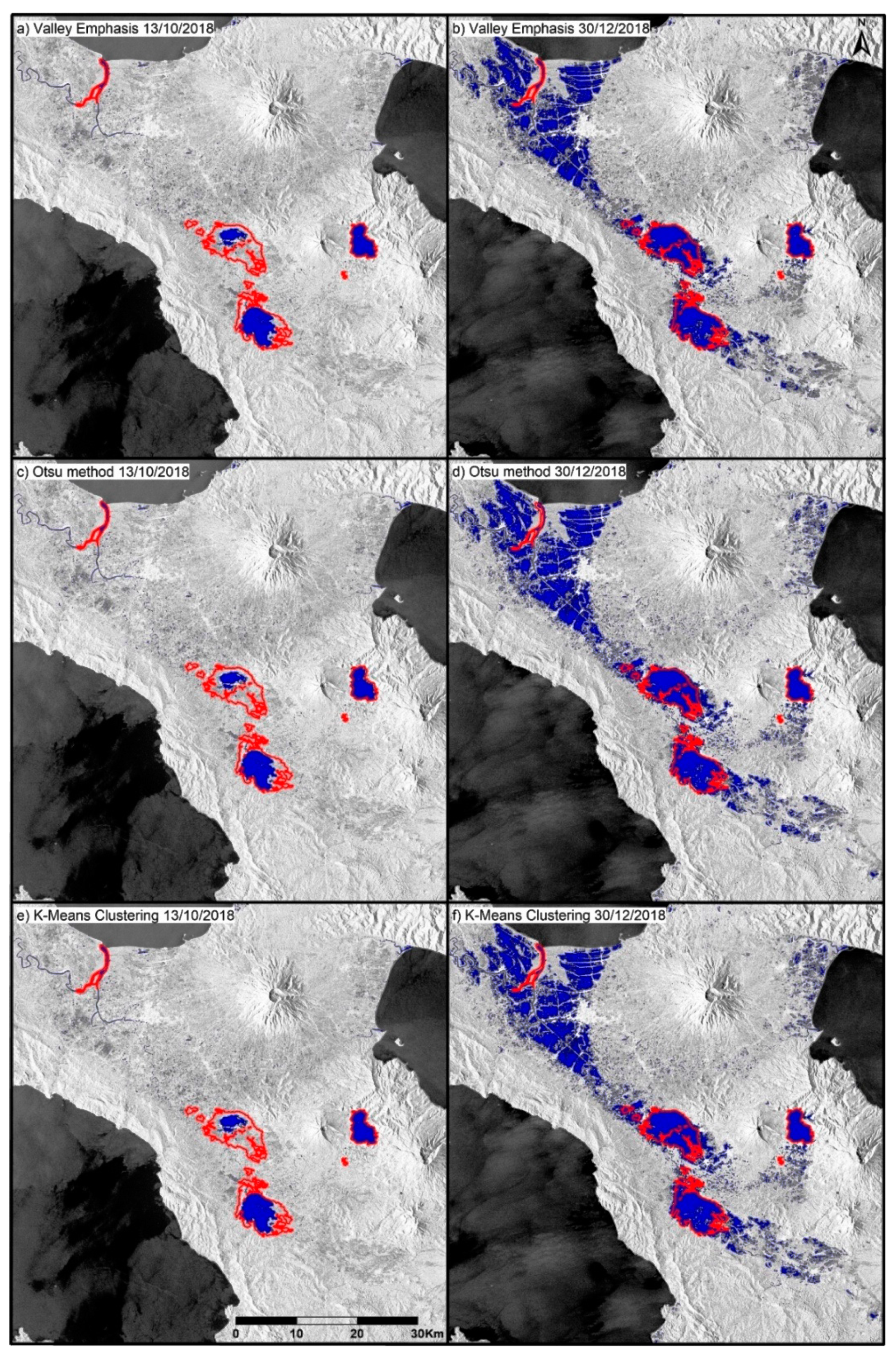
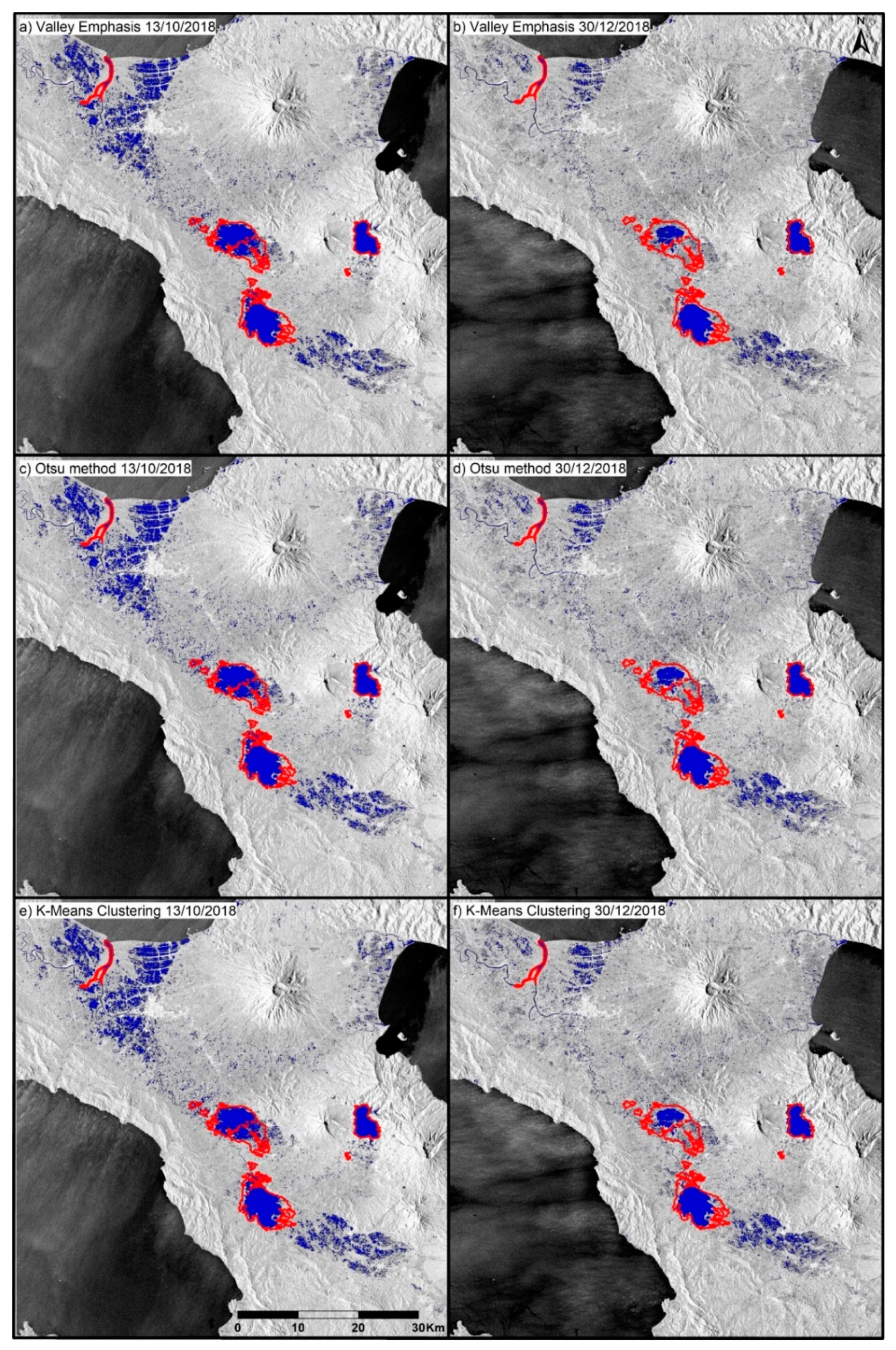
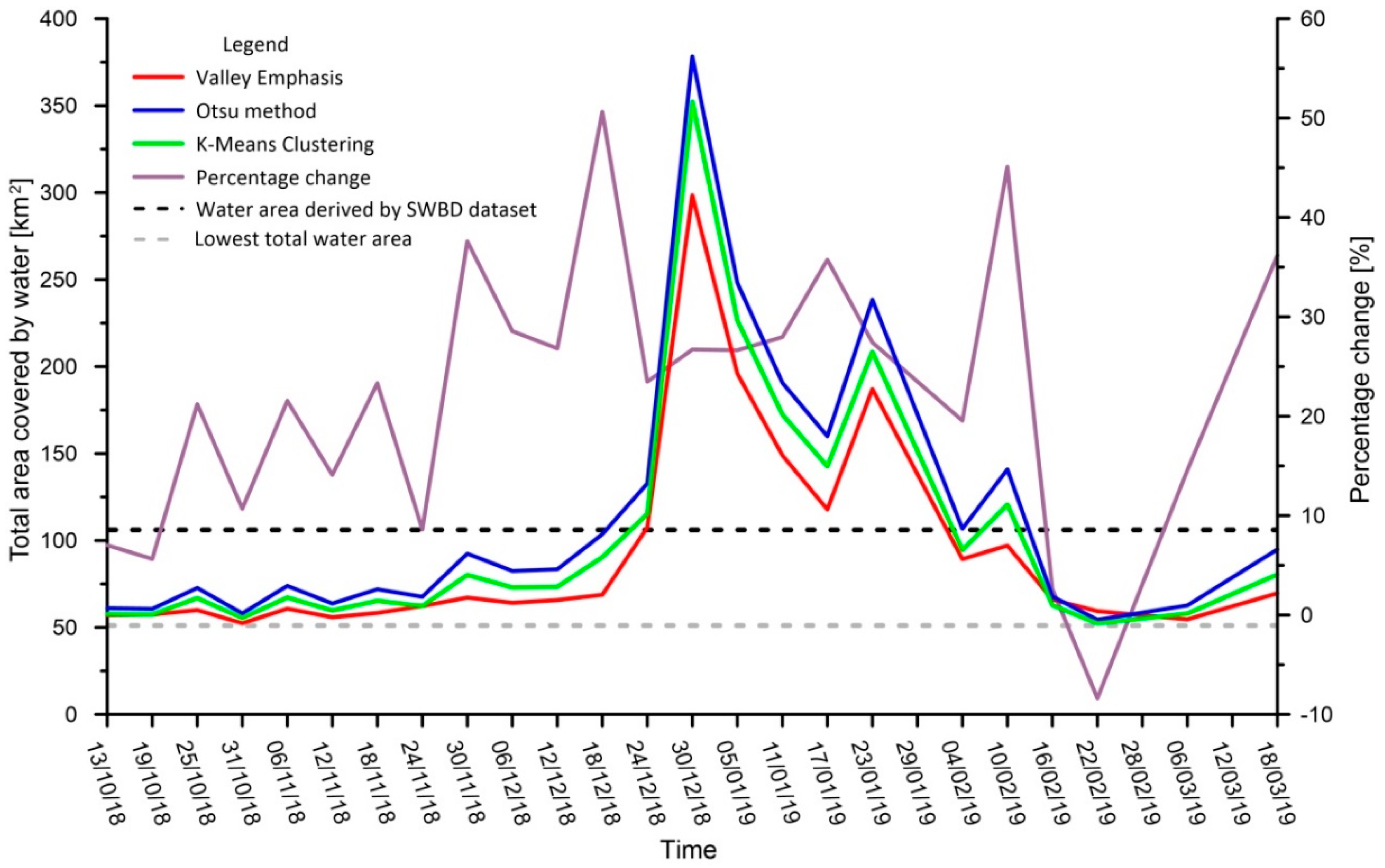
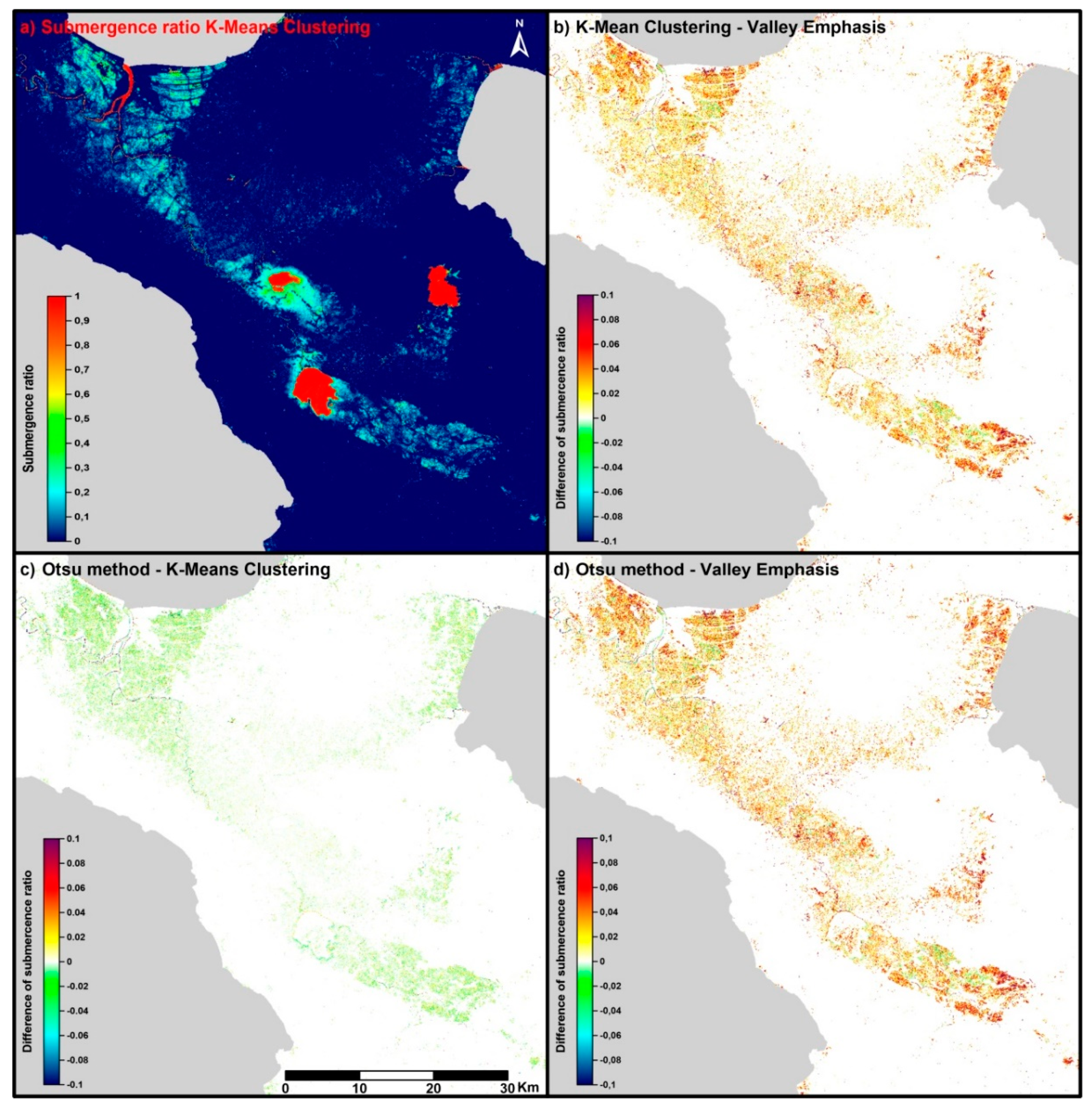
3.3. Extraction of the Water Body Area
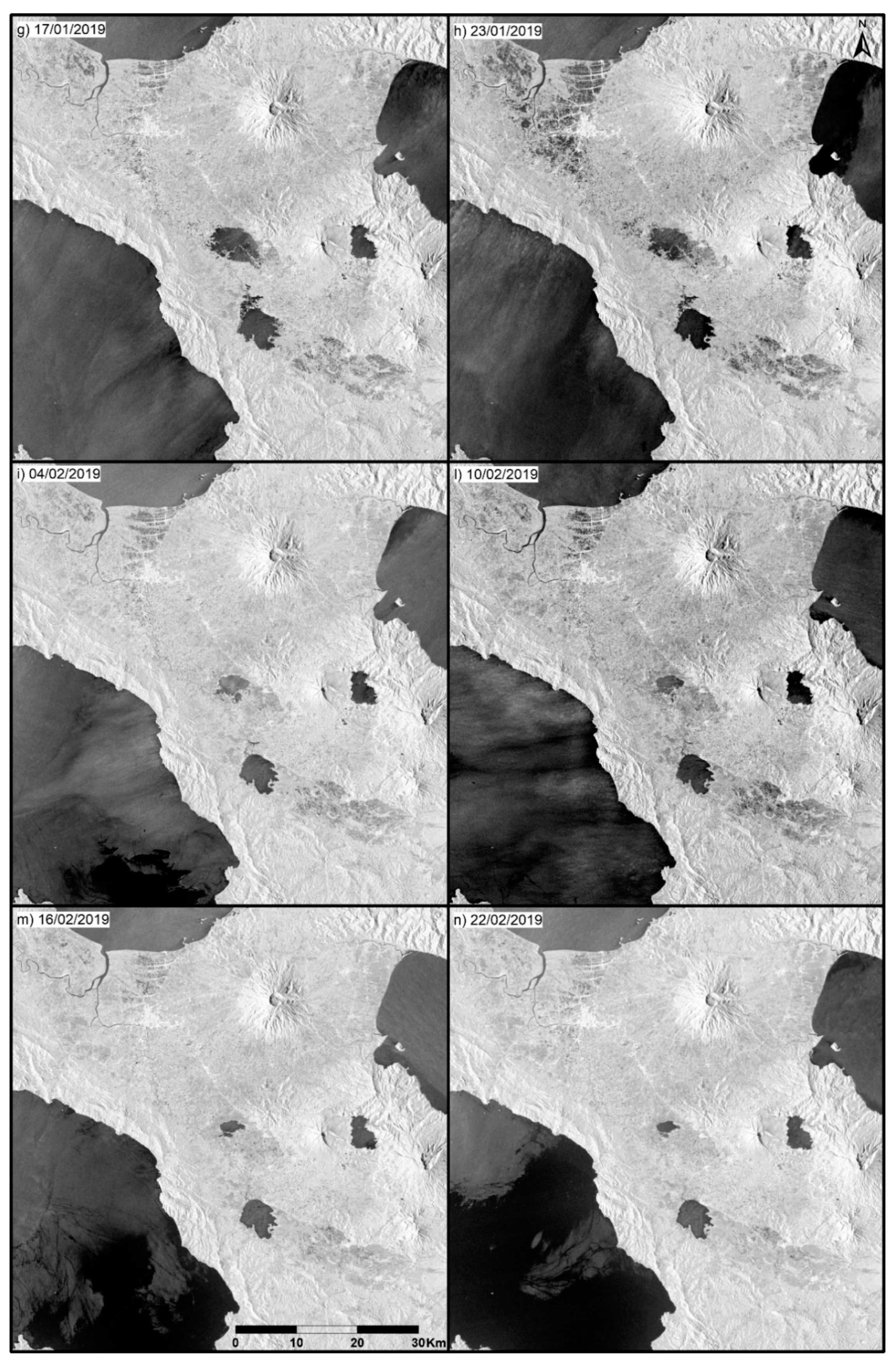
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Revellino, P.; Guerriero, L.; Mascellaro, N.; Fiorillo, F.; Grelle, G.; Ruzza, G.; Guadagno, F.M. Multiple Effects of Intense Meteorological Events in the Benevento Province, Southern Italy. Water 2019, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.H.; Sharif, H.O. Analysis of Damage Caused by Hydrometeorological Disasters in Texas, 1960–2016. Geosciences 2018, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ologunorisa, T.E.; Abawua, M.J. Flood risk assessment: A review. J. Appl. Sci. Eniron. Manag. 2005, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Re, M. Natural Catastrophes 2015, Annual Figures. Munich Re NatCat Service. 2016. Available online: https://www.munichre.com/site/corporate/get/params_E1254966961_Dattachment/1130647/Munich-Re-Overview-Natural-catastrophes-2015.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Jongman, B.; Ward, P.J.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Global exposure to river and coastal flooding: Long term trends and changes. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Schumann, G.; Bates, P.D.; Freer, J.E.; Beven, K.J. Flood-plain mapping: A critical discussion of deterministic and probabilistic approaches. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, L.; Mukolwem, M.M.; Di Baldassarre, G. Probabilistic flood maps to support decision-making: Mapping the value of information. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 1026–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, L.; Focareta, M.; Fusco, G.; Rabuano, R.; Guadagno, F.M.; Revellino, P. Flood hazard of major river segments, Benevento Province, Southern Italy. J. Maps 2018, 14, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoet, P.H.M.; Geys, J.; Nemmar, A.; Nemery, B. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C, Environmental Security; Korgan, F., Powell, A., Fedorov, O., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Klemas, V. Remote Sensing of Floods and Flood-Prone Areas: An Overview. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 31, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Henry, J.B.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Integration of SAR-derived river inundation areas, high-precision topographic data and a river flow model toward near real-time flood management. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussul, N.; Shelestov, A.; Shakun, S. Intelligent computations for flood monitoring. In Proceedings of the XIVth International Conference ‘Knowledge-Dialogue-Solution’ KDS, Varna, Bulgaria, 23 June–3 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Wang, D.; Mao, K.; Anagnostu., E.; Hong, Y. Inundation Extent Mapping by Synthetic Aperture Radar a Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Jacob, A.; Gamba, P. Spaceborne SAR data for global urban mapping at 30 m resolution using a robust urban extractor. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiage, L.M.; Walker, N.D.; Balasubramanian, S.; Baras, J. Application of Radarsat-1 synthetic aperture radar imagery to assess hurricane-related flooding of coastal Louisiana. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 5359–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolanos, S.; Stiff, D.; Brisco, B.; Pietroniro, A. Operational Surface Water Detection and Monitoring Using Radarsat 2. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, J.-P. A Change Detection Approach to Flood Mapping in Urban Areas Using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Davenport, I.J.; Neal, J.C.; Shumann, G.J.-P.; Bates, P.D. Near real-time flood detection in urban and rural areas using high resolution synthetic aperture radar images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Plank, S.; Cwik, K. The Use of Sentinel-1 Time-Series Data to Improve Flood Monitoring in Arid Areas. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, G. Monitoring monthly surface water dynamics of Dongting using Sentinel-1 data at 10 m. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, B.; McDonald, K.; Shimada, M.; Rosenqvist, A.; Schroeder, R.; Hess, L. Mapping Regional Inundation with Spaceborn L-Band SAR. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5440–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; D’Addabbo, A.; Lovergine, F.P.; Tijani, K.; Morea, A.; Nutricato, R.; Bovenga, F.; Nitti, D.O. Monitoring Flood Extent and Area Through Multisensor, Multi-temporal Remote Sensing: The Strymonas (Greece) River Flood. In Flood Monitoring through Remote Sensing; Springer Remote Sensing/Photogrammetry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakdaoui, S.; Emran, A.; Pradhan, B.; Lee, C.-W.; Fils, S.C.N. A Collaborative Change Detection Approach on Multi-Sensor Spatial Imagery for Desert Wetland Monitoring after a Flash Flood in Southern Morocco. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.J.-P.; Neal, J.C.; Mason, D.C.; Bates, P.D. The accuracy of sequential aerial photography and SAR data for observing urban flood dynamics, a case study of the UK summer 2007 floods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2536–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Henry, J.B.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Matgen, P. Demonstrating the high potential of remote sensing in hydraulic modelling and flood risk management. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry Society with the NERC Earth Observation Conference, Portsmouth, UK, 6–9 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Psomiadis, E. Flash flood area mapping utilizing Sentinel-1 radar data. In Proceedings of the SPIE Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications VII, Edinburgh, UK, 26–29 September 2016; p. 100051G. [Google Scholar]
- Bioresita, F.; Puissant, A.; Stumpf, A.; Malet, J.-P. A Method for Automatic and Rapid Mapping of Water Surface from Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L.; Wei, J.; Wu, H. An Unsupervised SAR Change Detection Method Based on Stochastic Subspace Ensemble Learning. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaffer, S.; Matgen, P.; Hollaus, M.; Wagner, W. Flood detection from multi-temporal SAR data using harmonic analysis and change detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Melgani, F. An Unsupervised Approach Based on the Generalized Gaussian Model to Automatic Change Detection in Multiple SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; De Vries, B.; Huang, C.; Lang, M.W.; Jones, J.W.; Creed, I.F.; Carroll, M.L. Automated Extraction of Surface Water Extent from Sentinel-1 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoudjit, A.; Guida, R. A Novel Automated Mapping of the Flood Extent on SAR Images Using a Supervised Classifier. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakmuenwai, P.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W. Automated Extraction of Inundated Areas from Multi-Temporal Dual-Polarizatio RADARSAT-2 Images of the 2011 Central Thailand Flood. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayik, C.; Abdikan, S.; Ozbulak, G.; Alasang, T.; Aydemir, S.; Sanli, F.B. Exploring multi-temporal Sentinal-1 SAR data for flood extend mapping. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Kuenzer, C.; Wendleder, A.; Hult, J.; Twele, A.; Roth, A.; Dech, S. Comparing four operational SAR-based water and flood detection approaches. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 3519–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajuelas, G.B. A Study of Rainfall Variations in the Philippines: 1950–1996. Sci. Diliman 2000, 12, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cinco, A.T.; Hilario, D.F.; de Guzman, G.R.; Ares, D.E. Climate trends and projections in the Philippines. In Proceedings of the 12th National Convention on Statistics (NCS), Mandaluyong City, Philippines, 1–2 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.B.; Chastanet, P.; Fellah, K.; Densos, Y.L. Envisat multipolarized ASAR for flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.S.; Matgen, P.; Pappenberger, F. Progress in integration of remote sensing-derived flood extent and stage data and hydraulic models. Rev. Geophys. 2009, 47, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B. Mapping and Monitoring Surface Water and Wetlands with Synthetic Aperture Radar. In Remote Sensing of Wetlands: Applications and Advances; Tiner, R., Lang, M., Klemas, V., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Giustarini, L.; Matgen, P.A. Hierarchical Split-Based Approach for Parametric Thresholding of SAR Images: Flood Inundation as Test Case. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6975–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C. Handbook of Radar Scattering Statistics for Terrain; Arthech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1989; ISBN 0890063362. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. Flattening gamma: Ratiometic terrain correction for SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Wen, J.H.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Chen, K.-S.; Chen, A.J. Improved sigma filter for speckle filtering of SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 202–213. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Jurkevich, I. Speckle Filtering of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: A review. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 8, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whoodhouse, I.H. Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shumann, G.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Bates, P. The utility of space-borne radar to render flood inundation maps based on multialgorithm ensembles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjusree, P.; Kumar, L.P.; Bhatt, C.M.; Rao, G.S.; Bhanumurthy, V. Optimization of threshold ranges for rapid flood inundation mapping by evaluating backscatter profiles of high incidence angle SAR Images. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2012, 3, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Fatoyinbo, T.E.; Policelli, F. Flood extent mapping for Namibia using change detection and thresholding with SAR. Int. J. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 9, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Speck, R.; Devereux, B.; Schumann, G.J.-P.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D. Flood detection in urban areas using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasbey, C. An analysis of histogram-based thresholding algorithms. CVGIP Graph. Models Image Process. 1993, 55, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Lei, B. A modified valley-emphasis method for automatic thresholding. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2012, 33, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bayanti, M.; El-Zaart, A. Automatic thresholding techniques for SAR images. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Soft Computing, Dubai, UAE, 2–3 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A.; Voigt, S. Towards operational near-real time flood detection using a split-based automatic thresholding procedure on high resolution TerraSAR-X data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Kersten, J.; Twele, A. A fully automated TerraSAR-X based flood service. ISPRS Int. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A.; Strobl, C.; Kersten, J.; Stein, E. A Multi-scale flood monitoring system based on fully automatic MODIS and TerraSAR-X processing chains. Remote Sens. 2013, 104, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostanche, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Puech, C.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Water level estimation and reduction of hydraulic model calibration uncertainties using satellite SAR images of floods. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 882–894. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.D. Automatic detection of surface water bodies from Sentinel-1 SAR images using Valley-Emphasis methods. Vietnam J. Earth Sci. 2015, 37, 328–343. [Google Scholar]
- Fuang, H.; Jargalsaikhan, D.; Tsai, H.-C.; Lin, C.-Y. An Improved Method for Image Thresholding based on the Valley-Emphasis Method. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 29 October–1 November 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histogram. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hou, B.; Liu, G. Using Combined Difference Image and k -Means Clustering for SAR Image Change Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T. Unsupervised Change Detection in Satellite Images Using Principal Component Analysis and k-Means Clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, K.S.; Ananthi, B. Color Skin Segmentation Using K-Means Cluster. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2009, 4, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.; Wegmüller, U.; Lamarche, C.; Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; Arino, O. Strengths and weaknesses of multi-year Envisat ASAR backscatter measurements to map permanent open water bodies at global scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SWBD. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission Water Body Data Set. Digital Media. 2005. Available online: https://dds.Cr.Usgs.Gov/srtm/version2_1/ (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Gahlaut, S. Determination of Surface Water Area Using Multitemporal SAR Imagery. Master’s Thesis, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruzza, G.; Guerriero, L.; Grelle, G.; Guadagno, F.M.; Revellino, P. Multi-Method Tracking of Monsoon Floods Using Sentinel-1 Imagery. Water 2019, 11, 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112289
Ruzza G, Guerriero L, Grelle G, Guadagno FM, Revellino P. Multi-Method Tracking of Monsoon Floods Using Sentinel-1 Imagery. Water. 2019; 11(11):2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112289
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuzza, Giuseppe, Luigi Guerriero, Gerardo Grelle, Francesco Maria Guadagno, and Paola Revellino. 2019. "Multi-Method Tracking of Monsoon Floods Using Sentinel-1 Imagery" Water 11, no. 11: 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112289
APA StyleRuzza, G., Guerriero, L., Grelle, G., Guadagno, F. M., & Revellino, P. (2019). Multi-Method Tracking of Monsoon Floods Using Sentinel-1 Imagery. Water, 11(11), 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112289





