Relationships between Wind Effect, Hydrodynamics and Water Level in the World’s Largest Coastal Lagoonal System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Telemac Model
2.2. Numerical Domain
2.3. Initial and Boundary Conditions
2.4. Model Calibration
2.5. Model Validation
2.6. Flushing Time
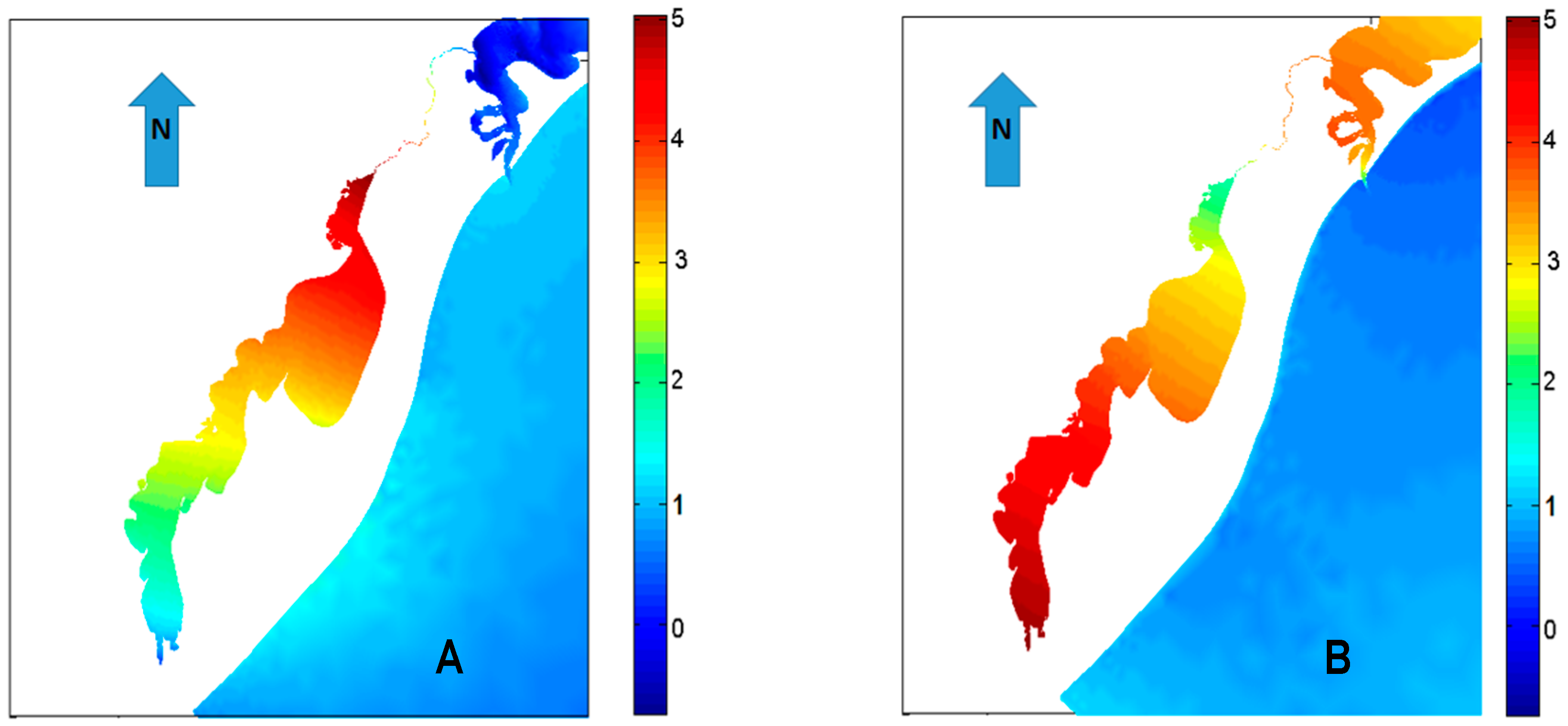
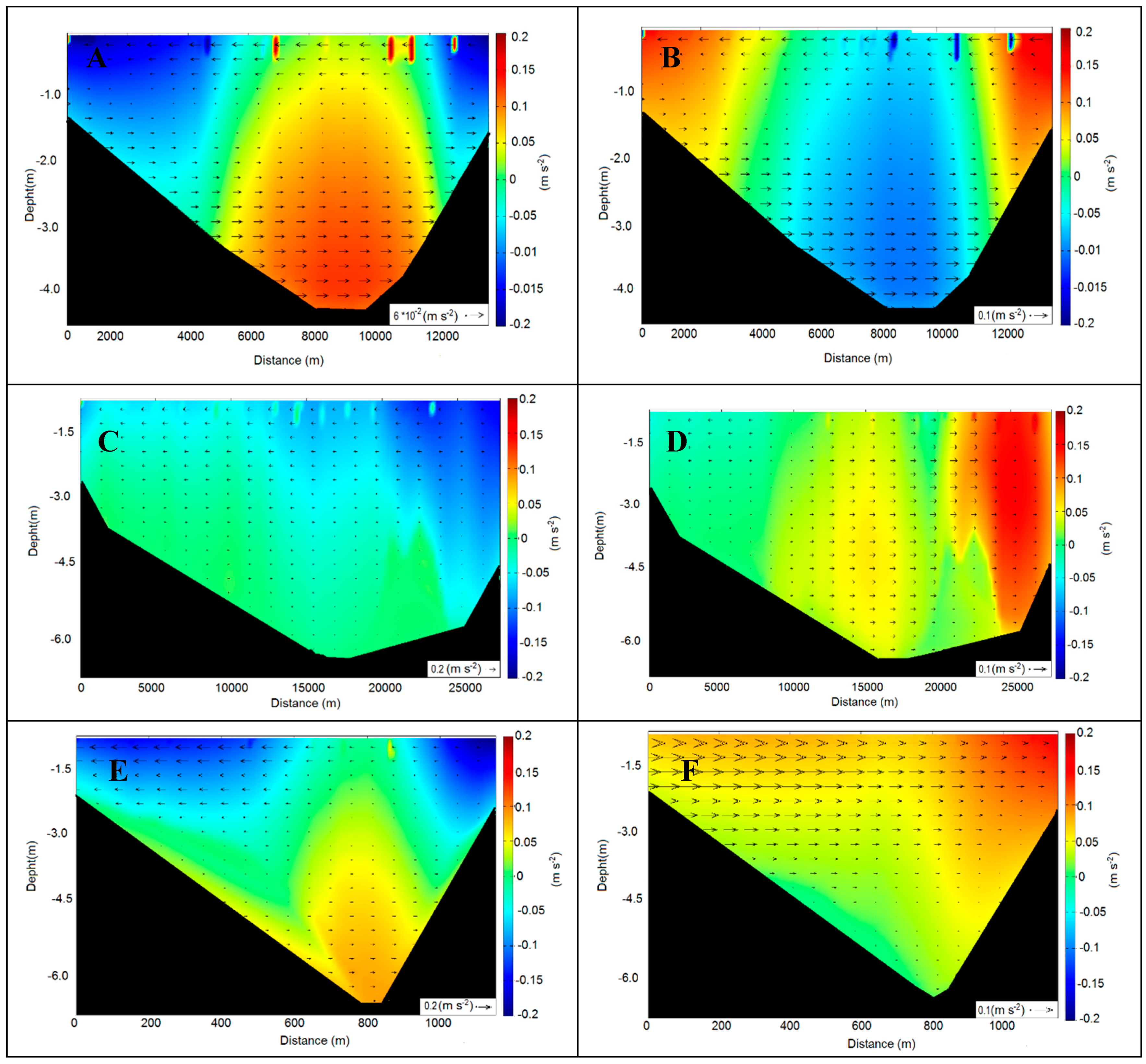
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Level
3.2. Currents
3.3. Cross Section Circulation
3.4. Discharges
4. Final Remarks and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miranda, L.B.; Castro, B.M.; Kjerfve, B. Princípios de Oceanografia Física de Estuários; Editora da Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro, L.; Iuppa, C.; Foti, E. Effect of partial use of Venice flood barriers. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelo, A.F.; Trombetta, T.B.; Lopes, B.V.; Marques, W.C.; Möller, O.O. Impacts of dredging on the hydromorphodynamics of the Patos Lagoon estuary, southern Brazil. Ocean Eng. 2019, 188, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjerfve, B. Comparative Oceanography of Coastal Lagoons. In Estuarine Variability; Wolf, D.A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Colvin, J.; Lazarus, S.; Splitt, M.; Weaver, R.; Taeb, P. Wind-driven setup in east central Florida’s Indian River Lagoon: Forcings and parametrizations. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 213, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costi, J.; Marques, W.C.; Kirinus, E.P.; Duarte, R.F.; Arigony-Neto, J. Water level variability of the Mirim-São Gonçalo System, a large, subtropical, semi-enclosed coastal complex. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 117, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mel, R.; Carniello, L.; D’Alpais, L. Addressing the effect of the Mo.S.E barriers closure on wind setup within the Venice Lagoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 225, 106249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.F.; Rangel, S.R.S. Rio Grande do Sul: Geografia Física e Vegetação; Editorial Sagra: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, E.F.; Rangel, S.R.S. Planície Costeira do Rio Grande do Sul: Geografia Física, Vegetação e Dinâmica Sócio-Demográfica; Editorial Sagra: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- CLM, Comissão da Lagoa Mirim. Barragem do São Gonçalo: Estudo Preliminar de Viabilidade; UFPEL: Pelotas, Brazil, 1970; Volume I, p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Gouvêa, T.; Zarnot, D.H.; Alba, J.M.F. Caracterização geoambiental e histórica do processo de desenvolvimento da bacia da Lagoa Mirim. In Sustentabilidade Socioambiental da Bacia da Lagoa Mirim; Embrapa Clima Temperado: Pelotas, Brazil, 2010; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, H.A.; Fernandes, E.H.L.; Möller, O.O.; Collares, G.L. Processos Hidrodinâmicos e Hidrológicos da Lagoa Mirim. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos. 2015, 20, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.F.; Pouey, J.L.O.; Rocha, C.B.; Portelinha, M.K.; Fernandes, J.M.; Piedras, S.R.N. O nível de água e a produção pesqueira na Lagoa Mirim. In Sustentabilidade Socioambiental da Bacia da Lagoa Mirim; Embrapa Clima Temperado: Pelotas, Brazil, 2010; pp. 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- IRGA. Instituto Rio Grandense do Arroz. Arroz Irrigado—Safra 2005/2006—Produção Municipal. 2006. Available online: http://www.irga.rs.gov.br/arquivos/20070117104152.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2010).
- SUDESUL. Plano de Desenvolvimento da Bacia da Lagoa Mirim; SUDESUL: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 1974; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, O.O.; Castaing, P.; Salomon, J.C.; Lazure, P. The influence of local and non-local forcing effects on the sub tidal circulation of Patos Lagoon. Estuaries 2001, 24, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelão, R.M.; Möller, O.O. Sobre a circulação tridimensional forçada por vento na Lagoa dos Patos. Atlântica 2003, 25, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, E.H.L.; Mariño Tapia, I.; Dyer, K.R.; Möller, O.O. The attenuation of tidal and sub tidal oscillations in the Patos Lagoon estuary. Ocean Dynam. 2004, 54, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.H.L.; Dyer, K.R.; Möller, O.O. Spatial gradients in the flow of Southern Patos Lagoon. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 20, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, W.C.; Möller, O.O. Variabilidade temporal em longo período da descarga fluvial e níveis de água da Lagoa dos Patos, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos 2009, 13, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, W.C.; Fernandes, E.H.; Monteiro, I.O.; Möller, O.O. Numerical modelling of the Patos Lagoon coastal plume, Brazil. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, W.C.; Fernandes, E.H.; Möller, O.O. Straining and advection contributions to the mixing process of the Patos Lagoon coastal plume, Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C06019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, W.C.; Fernandes, E.H.; Moraes, B.; Möller, O.O.; Malcherek, A. Dynamics of the Patos Lagoon coastal plume and its contribution to the deposition pattern of the southern Brazilian inner shelf. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, G. Qualidade das Águas no Canal de São Gonçalo—Rio Grande do Sul—Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, F.E.; Möller, O.O.; Mata, M.M. Regime shifts, trends and interannual variations of water level in Mirim Lagoon, southern Brazil. Pan-Am. J. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 5, 254–266. [Google Scholar]
- Hervouet, J.M. Hydrodynamics of Free Surface Flows: Modelling with the Finite Element Method; John Wiley& Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Smagorinsky, J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equation, I. The basic experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, G.; Häkkinen, S.; Ezer, T.; Patchen, R. A generalization of a Sigma Coordinate Ocean Model and an intercomparison of model vertical grids. In Ocean Forecasting: Conceptual Basis and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Walstra, L.C.; Van Rijn, L.C.; Blogg, H.; Van Ormondt, M. Evaluation of a Hydrodynamic Area Model Based on the COAST3D Data at Teignmouth 1999; Report TR121-EC MAST Project No. MAS3-CT97-0086, HR Wallinford: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. D4.1–D4.4. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, W.C.; Fernandes, E.H.; Rocha, L.A. Straining and advection contributions to the mixing process in the Patos Lagoon estuary, Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C03016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, M. Influence of ENSO and the South Atlantic Ocean on climate predictability over Southeastern South America. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, F.; Brugnoli, E.; Muniz, P.; Venturini, N.; Burone, L.; Hutton, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Pita, A.; Kandratavicius, N.; Verocai, J.; et al. Warm phase ENSO events modulate the continental freshwater supply and the trophic state of sediments in a large South American estuary. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.H.L.; Dyer, K.R.; Möller, O.O.; Niencheski, L.F.H. The Patos Lagoon hydrodynamics during an El Niño event (1998). Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csanady, G.T. Circulation in the Coastal Ocean; D. Reidel Pub.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Winant, C.D. Three-dimensional Wind-drive flow in an elongated, rotating basin. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2004, 34, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanay, R.; Valle-Levinson, A. Wind-Induced Circulation in Semi-enclosed Homogeneous, Rotating Basins. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 2520–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldo, E.E. Sedimentação, Predição do Padrão de Ondas e Dinâmica Sedimentar da Antepraia e Zona de Surfe do Sistema Lagunar da Lagoa dos Patos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- SEMA—Secretary of the Environment of Rio Grande do Sul. 2006. Available online: http://www.sema.rs.gov.br/conteudo.asp?cod_menu=57&cod_conteudo=6470 (accessed on 19 January 2015).
- Hartmann, C.; Schettini, C.A. Aspectos Hidrológicos na desembocadura da Laguna dos Patos, RS. Rev. Bras. Geociências. 1991, 21, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, P.C.; Odebrecht, C.; Niencheski, L.P. Nutrientes Dissolvidos. In O Estuário da Lagoa dos Patos: Um Século de Transformação; Seeliger, O., Ed.; FURG: Rio Grande, Brazil, 2010; pp. 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Odebrecht, C.; Bergesch, M.; Rorig, L.R.; Abreu, P.C. Phytoplankton interannual variability at Cassino Beach, Southern Brazil (1992–2007), with emphasis on the Surf Zone Diatom Asterionellopsis glacialis. Estuar. Coasts 2010, 33, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-C. The current and sea level variability in the Chesapeake and Delaware Canal. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 18343–18352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-C.; Garvine, C. Observations of wind-induced, subtidal variability in the Delaware Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 10589–10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Index | Excellent | Good | Reasonable | Poor | Bad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMAE | <0.2 | 0.2–0.4 | 0.4–0.7 | 0.7–1.0 | >1.0 |
| Cw | Cf | Cs |
|---|---|---|
| 1 × 10−5 | 0.4 | 0.01 |
| 5 × 10−3 | 0.6 | 0.1 |
| 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, H.; Fernandes, E.; Möller, O., Jr.; García-Rodríguez, F. Relationships between Wind Effect, Hydrodynamics and Water Level in the World’s Largest Coastal Lagoonal System. Water 2019, 11, 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112209
Oliveira H, Fernandes E, Möller O Jr., García-Rodríguez F. Relationships between Wind Effect, Hydrodynamics and Water Level in the World’s Largest Coastal Lagoonal System. Water. 2019; 11(11):2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112209
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Heline, Elisa Fernandes, Osmar Möller, Jr., and Felipe García-Rodríguez. 2019. "Relationships between Wind Effect, Hydrodynamics and Water Level in the World’s Largest Coastal Lagoonal System" Water 11, no. 11: 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112209
APA StyleOliveira, H., Fernandes, E., Möller, O., Jr., & García-Rodríguez, F. (2019). Relationships between Wind Effect, Hydrodynamics and Water Level in the World’s Largest Coastal Lagoonal System. Water, 11(11), 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112209






