Abstract
In this work we present a rapid and easy method to remove the totality of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions using ionic liquid (IL). Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction is employed. The IL 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bis((trifluoromethane)sulfonyl)imide ([C8C1im] [NTf2]) is formed in situ because of the mixture of 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([C8C1im]Cl) and lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Li[NTf2]) aqueous solutions. A cloud of microdroplets of IL formed by the dispersion generated through the precursors metathesis reaction allows the rapid and total extraction of bisphenol A (BPA). After centrifugation, the formed IL phase is deposited at the bottom of the flask and the total amount of BPA is extracted in the sedimented phase. The volume of IL is very low, in the order of microliters, which enables us to remove all the BPA from the solution. The technique studied is highly efficient, cost-effective, and presents less environmental impact than other extraction techniques, thus becoming an outstanding alternative to the most commonly used methods. BPA concentration is determined by high performance liquid chromatography by injecting the IL phase directly. An extraction kinetic model for the kinetic profile has been tested for this method, which allows to infer the ideal experimental conditions to execute the extraction method.
1. Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an important chemical agent employed in manufacturing of plastics, epoxy resins, polycarbonate, and flame retardants [1,2,3,4]. Trace residue level of BPA can interfere in the normal functioning of the endocrine system [5], and it may also act as a carcinogenic and mutagenic agent. Because of its large amount of production and numerous applications, BPA appears in the environment in high concentrations. Consequently, nowadays there is a major interest in developing techniques to remove BPA from different matrices, especially in water, because of its high toxicity and high resistance to natural degradation [6,7,8].
Several degradation techniques of BPA such as photocatalysis [6,9], oxidative degradation [10], and the use of reusable multifunctional electrodes have been developed recently. However, these techniques give rise to organic decomposition products that can sometimes be toxic and tedious to characterize. Therefore, alternative techniques to remove BPA are being investigated nowadays, remarkably the use of adsorbents [9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
In general, liquid–liquid extraction has not been widely employed as a research technique to remove BPA from aqueous solutions since the use of organic solvents becomes a detriment to the environment and implies a high cost. However, liquid–liquid microextraction techniques are environmentally friendly. Particularly, ionic liquids (ILs) are commonly used nowadays as organic phase because of its low vapor pressure, high thermal stability, and high capacity to solubilize different organic compounds [21,22,23,24,25]. Some authors have used IL to extract BPA from aqueous samples, but the rapid dispersion provided by the in situ IL formation does not occur. High temperatures and times are necessary, as well as cooling cycles. In addition, because of the high volume of extractant phase, the preconcentration factor and the detection limit are high, which limits the ultratrace analysis of BPA [26]. Other investigations show that IL can be used to extract phenolic compounds. However, the used volume is of the order of milliliters and high times are needed to carry out the extraction [27].
The main goal of this work is to remove BPA from aqueous solutions by means of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME). The developed technique comprises in situ IL formation by mixing two soluble reagents in a straightforward ion-exchange reaction producing a dispersion followed by formation of small drops of IL insoluble in water, which allows BPA to be extracted rapidly. After centrifugation, an insoluble IL phase remains at the bottom of the tube and can be easily separated from the aqueous phase and analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). It is worth pointing out that the volume of IL necessary to carry out the extraction is in the order of microliters because of the cloud of microdroplets formed that allows the total extraction of BPA to be rapid, not being a harm for the environment. The study has been complemented by characterizing the microextraction kinetics process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Materials
The bisphenol A standards were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (97% purity, Darmstadt, Germany). Ultrapure water was employed for preparation of 0.1 M solutions of these ILs.
Bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonamide lithium salt and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) were used in order to form the IL. Analytical grade acetonitrile was obtained from Panreac (Barcelona, Spain) and HPLC water from Macron (Valsamoggia, Italy). A volume of 2.54 mL of non-ionic surfactant Triton X-114 (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) were dissolved in 50 mL of water in order to obtain a 0.1 M solution. Working standard solutions were prepared by appropriate dilution of the stock solution by Milli-Q water.
2.2. Instrumentation and Analytical Conditions
HPLC analysis was performed on JASCO BS-4000 system equipped with a sample injector and an ultraviolet detector (UV-4075)(Madrid, Spain).
Chromatographic determination of BPA was performed on a C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 µm). The mobile phase was a solution of 60% acetonitrile and 40% water at a flow rate of 0.8 mL min−1. The injection volume was 10 µL and the monitoring wavelength was 230 nm.
2.3. General Procedure
A total of 10 mL of sample solution containing BPA in the 0.5–3 µg L−1 range, placed in a 15-mL glass tube, was heated in an ultrasonic bath for five minutes at 30 °C, after that 20 µL of pH 4 regulatory solution was added. Then, 100 µL of the [C8C1im]Cl solution and 100 µL of 0.1 mol L−1 Triton X-114 solution were added to the mix. After homogenizing by shaking manually, 100 µL of the Li[NTf2] solution was incorporated, observing a cloudy appearance of the mixture because of the dispersion phenomenon that takes place when the IL is formed. After centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 20 min, a low volume (33 ± 1 µL) of the IL was recovered in the bottom of the tube. Using a chromatographic-type syringe, 10 µL was taken, injected into the HPLC by triplicate procedure for the analysis using the instrumental and analytical conditions later described. Additionally, the concentration of BPA was determined by HPLC from aqueous solution before and after carrying out the microextraction process, observing that under the experimental conditions described, the compound is completely extracted from water to the IL phase, leaving the aqueous solution totally free of BPA.
2.4. Microextraction Kinetics Studies
The extraction kinetics of the BPA was examined by fitting the experimental data of the peak area vs. the exposure time, which can be described by the first-order mathematical model [28,29]:
where C is the saturation value (mV) and k is the rate constant of the extraction (s−1).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Acceptor Phase—The Ionic Liquid
Replacing the use of common organic solvents with ILs for the removal of pollutants in aqueous media is of great interest because of the unique properties of some ILs, especially those having low viscosity and low water solubility [30].
This procedure offers the possibility of getting a large surface in contact between the microdroplets and aqueous phase without the need of a specific disperser solvent as it can be seen in Figure 1.
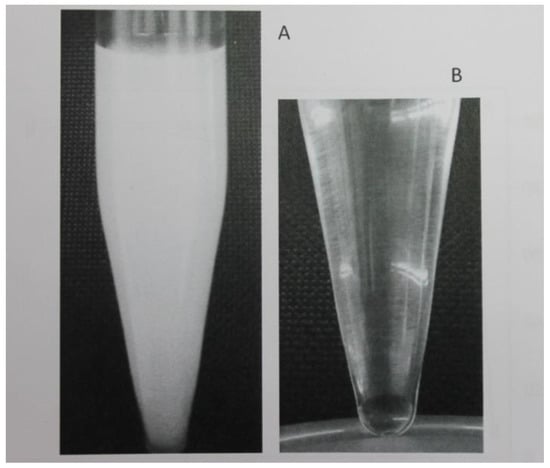
Figure 1.
(A) Rapid formation of a dispersed phase, (B) deposited after centrifugation.
If 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([C8C1im]Cl) is used to provide a voluminous cation, and it is mixed with lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Li[NTf2]) which would act as anion, and both reagents being insoluble in water, a turbidity is formed because of an insoluble 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bis((trifluoromethane)sulfonyl)imide ([C8C1im][NTf2]) produced in the reaction [30]. The metathesis reaction that takes place was then:
[C8C1im]Cl + Li[NTf2] → [C8C1im][NTf2] + LiCl
It was experimentally found that mixing 100 µL of 1 mol L−1 [C8C1im]Cl with 100 µL of 1 mol L−1 Li[NTf2] and 10 mL aqueous phase, followed by centrifugation, resulted in approximately 33 µL of IL in the bottom of the tube, which agrees with the theoretical prediction, taking into account the [C8C1im][NTf2] density [31]. The total BPA extraction is rapid and the whole procedure takes only a few minutes.
Preliminary experiments showed that, after centrifuging the turbid solution, some IL droplets remained on the walls of the centrifuge tube, and reproducibility was affected. To overcome this drawback, several anti-sticking agents [32], namely Triton X-100, Triton X-114, Tween 20, and Span 20, were assayed. Maximum and reproducible volumes for the recovered IL were obtained when the metathesis reaction was carried out in presence of 0.001 mol L−1 of Triton X-114.
3.2. Optimization of Removal Conditions
3.2.1. Optimization of Ionic Liquid Precursors Volumes
Different volumes of aqueous phase were tested with different proportions of IL precursors ([C8C1im]Cl and Li[NTf2]). Volumes of 5, 10, 15, and 20 mL of aqueous phase were taken and the volume of IL precursors was studied.
Volumes equal to 25, 50, and 100 µL of each precursor were added to carry out the dispersion and subsequent IL formation. For volumes of aqueous phase studied, the IL phase was hardly formed when the IL precursors volumes were 25 and 50 µL.
When the volume of each IL precursor was 100 µL the IL formed was 48 µL, with the volume of aqueous phase 5 ml. Total of 33 µL of IL was obtained when the volume of aqueous phase was 10 mL and 18 µL of IL achieved if aqueous phase is 15 mL. However, when the volume of aqueous phase is 20 ml the volume obtained from IL is 10 µL.
From the experiment it is depicted that the best concentration factor would be obtained taking a volume of aqueous phase of 20 mL. Nevertheless, a volume of 10 ml for the aqueous phase has been selected for two reasons. On the one hand, 33 µL of IL obtained are in agreement with the theoretical prediction about [C8C1im][NTf2] density, which implies that the aqueous solution is totally free of IL. On the other hand, 33 µL allows to perform the measurement by triplicate. This small volume of IL enables the procedure as a low-cost and environmentally friendly technique compared with the use of organic solvents.
3.2.2. Optimization of pH Conditions
Several experiments were carried out to determine the adequate pH for the extraction of BPA in the IL. The pH has been studied to obtain the maximum efficiency in the extraction of BPA from pH 1 to pH 10. As can be seen in Figure 2, the BPA maximum extraction is achieved in a pH range between 3 and 5. The pKa value of BPA ranges from 9.6 to 10.2 [33]. When pH increases, the hydrophobic interaction between IL and BPA decreases because of the deprotonation of BPA, and the removal of BPA also decreases. Subsequently, a value of pH 4 was selected to carry out the removal process. A non-linear fit of the experimental data was performed, non-theoretical, only for practical purposes (red solid line in Figure 2):
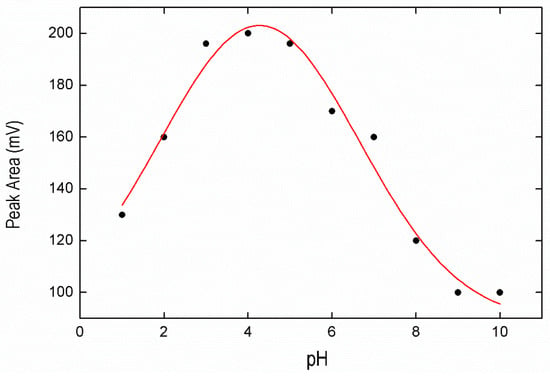
Figure 2.
Effect of pH on the bisphenol A (BPA) signal obtained from ionic liquid (IL) phase.
From the fit we obtained , , , (R2 = 0.964).
3.2.3. Optimization of Temperature Conditions and Incubation Time
The solution temperature plays a very important role in the extraction procedure. The temperature effect can influence the extraction efficiency. In the present work, this effect was studied within the range of 25–60 °C by heating the aqueous phase for 10 minutes prior to the addition of the IL precursors. As it is shown in Figure 3, the best extraction efficiency was obtained at 30 °C. Experimental data fit well to the following equation, non-theoretical, only for practical purposes (red solid line in Figure 3):
where . From the fit we obtained , , , (R2 = 0.9904).
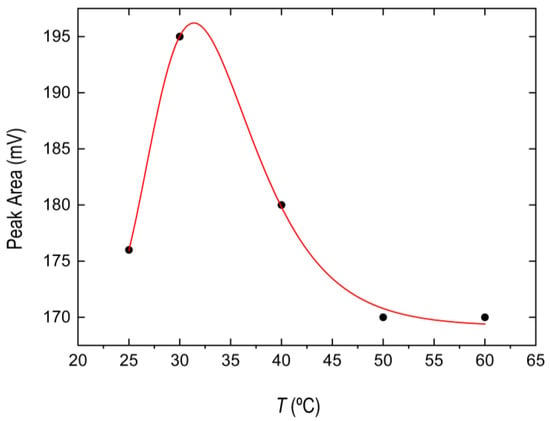
Figure 3.
Effect of the temperature on the BPA signal obtained from IL phase.
Incubation time of the samples was studied at 30 °C within the range of 2–30 min. As Figure 4 shows, the extraction performance of the BPA increased from 2 to 5 min, remaining constant for 30 min, becoming a fast technique that allows a wide working time range. Accordingly, we employed five minutes as heating time. The extraction kinetics was modeled via Equation (1) (red solid line in Figure 4), depicting C = 198.40 ± 1.93 mV, k = 0.57 ± 0.03 s−1 (R2 = 0.978).
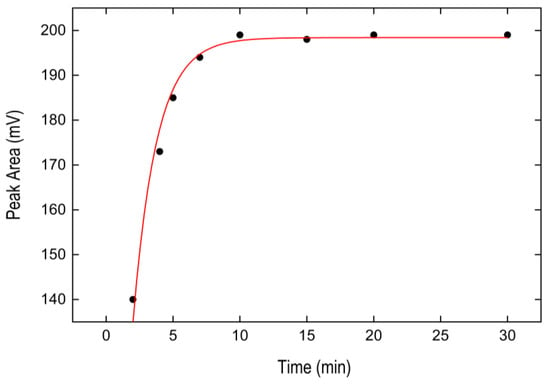
Figure 4.
Effect of incubation time at 30 °C on the BPA signal obtained from the IL phase. Solid line represents the fit of experimental data to Equation (1).
Same experiments were carried out using 50 µL of the commercial IL 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium-bis((trifluoromethane)sulfonyl)imide ([C8C1im][NTf2]), purchased from Solvionic (99.5% purity). It was subjected to ultrasounds for 2, 5, 10, 20, and 30 min. In all cases, after centrifuging for 15, 30, 45, and 60 min, the volume of IL at the bottom of the tube was only 10 µL, which does not allow to make the measurements by triplicate ensuring the reproducibility. In addition, when the ultrasound time was 2, 5, and 10 min it is not appreciated that BPA has been removed when the IL is injected into HPLC. The experiment was repeated using 100 µL of commercial IL. In this case, after centrifuging for 60 min, a volume of IL of 85 µL was recovered, indicating that not all of the IL had been removed from the aqueous solution. In addition, it was necessary to apply ultrasound for 30 min to achieve maximum BPA extraction, and it was not possible to remove the total, only 80% was acquired (See experimental conditions and results summary in Supplementary Material, Table S1). Therefore, the in situ formation of the IL provides better results, providing a higher extraction, reaching the total removal of the BPA, in just 2 min and without applying ultrasounds. In addition, the concentrations of the IL precursors used are low and the density values of the formed IL indicate that there are no residues of this in the aqueous solution.
3.2.4. Analytical Figures of Merit
Using the conditions described in the experimental section, a linear relationship between the analytical signal and the BPA concentration in the aqueous phase was verified in the 0.5–0.3 µg L−1 range (linear equation: y = 96.437x + 4736). Regression coefficient R2 = 0.997 and enrichment factor of 299 were achieved.
The detection limit, calculated on the basis of three times the standard deviation of y-residuals from the calibration graph (sy/x) was 0.19 µg L−1. The repeatability was estimated from ten consecutive experiments at the 0.5 µg L−1 level, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) was 5.2%. The reproducibility was calculated from ten measurements obtained on five consecutive days, and the RSD was 6.5%.
3.2.5. Recycling and Reuse Studies
To study the reusing process, the IL was separated from the aqueous solution and subjected to a new BPA extraction process by using ultrasound for 2, 5, 10, 20, and 30 min to disperse the IL in the aqueous sample. However, because of the small volume of IL (around 30 µL), after the centrifugation process to separate the phases, it is not sedimented at the bottom of the tube. Therefore, the IL formed by the in situ procedure cannot be reused.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we have developed a dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction technique by in situ formation of an IL through a metathesis reaction of its precursors. This approach allows us to use very low volumes of solvent leading to rapid and total removal of BPA from aqueous solutions. This procedure is a fast and efficient technique. Optimal experimental conditions were applied to achieve maximum BPA extraction, reaching the total removal at a pH value between 3 and 5, in just two minutes and at 30 °C. Additionally, in order to optimize the experimental conditions kinetic models have been tested to characterize the extraction process.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/11/10/2087/s1, Table S1: Experimental conditions and results for the use of commercial IL ([C8C1im][NTf2]) and in-situ IL.
Author Contributions
Y.V.-M., Ó.D.F.-O., and C.F.-L. performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and prepared the manuscript. M.C. and A.S.-M. performed the kinetic studies, analyzed the data, and prepared the figures and the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the University Centre of Defense at the Spanish Air Force Academy, MDE-UPCT, for the financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jiao, C.M.; Zhuo, J.L.; Chen, X.L.; Li, S.X.; Wang, H.J. Flame retardant epoxy resin based on bisphenol A epoxy resin modified by phosphoric acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, M.; Berti, C.; Binassi, E.; Fiorini, M.; Sullalti, S.; Acquasanta, F.; Karanam, S.; Brunelle, D.J. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated telechelic bisphenol A polycarbonate ionomers. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.M.; Zhang, G.S.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Dong, S.Y.; Wang, P. Application of nickel foam-supported Co3O4-Bi2O3 as a heterogeneous catalyst for BPA removal by peroxymonosulfate activation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassouane, F.; Ait-Amar, H.; Amrani, S.; Rodriguez-Couto, S. A promising laccase immobilization approach for Bisphenol A removal from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.D.; Gu, Y.Y.; Lan, H.Z.; Sun, Y.Y.; Gao, H.J. Functional graphene-gold nano-composite fabricated electrochemical biosensor for direct and rapid detection of bisphenol A. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, M.; Zoltowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Zgola-Grzeskowiak, A.; Ehrlich, H.; Jesionowski, T. Iron(III) phthalocyanine supported on a spongin scaffold as an advanced photocatalyst in a highly efficient removal process of halophenols and bisphenol A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 347, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Imam, M.A.; Hyder, A.H.M.G.; Jabbari, V.; Dominguez, N.; Noveron, J.C. Biosorption of bisphenol A and sulfamethoxazole from water using sulfonated coffee waste: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6602–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Jabbari, V.; Islam, M.T.; Turley, R.S.; Dominguez, N.; Kim, H.; Castro, E.; Hernandez-Viezcas, J.A.; Curry, M.L.; Lopez, J.; et al. Sustainable synthesis and remarkable adsorption capacity of MOF/graphene oxide and MOF/CNT based hybrid nanocomposites for the removal of Bisphenol A from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Johansson, E.M.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Jin, P.K. Photocatalytic activity and mechanism of bisphenol A removal over TiO2-x/rGO nanocomposite driven by visible light. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Gurmen, S.; Gafarli, I.; Khoei, S.; Safaltin, S.; Ozcelik, D.Y. Oxidative degradation of Bisphenol A by carbocatalytic activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate with reduced graphene oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.S.; Wang, H.W.; Ou, J.J.; Chen, L.F.; Ye, M.L. Construction of hierarchically porous monoliths from covalent organic frameworks (COFs) and their application for bisphenol A removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 355, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Ouada, S.; Ben Ali, R.; Leboulanger, C.; Ben Ouada, H.; Sayadi, S. Effect of Bisphenol A on the extremophilic microalgal strain Picocystis sp (Chlorophyta) and its high BPA removal ability. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2018, 158, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwak, S.Y. Rapid adsorption of bisphenol A from wastewater by beta-cyclodextrin-functionalized mesoporous magnetic clusters. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chen, B.L. Enhanced bisphenol A removal from stormwater in biochar-amended biofilters: Combined with batch sorption and fixed-bed column studies. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.G.; Vu, H.C.; Le, T.T.; Chang, Y.S. Activation of persulfate by a novel Fe(II)-immobilized chitosan/alginate composite for bisphenol A degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.X.; Piao, M.Y. Facile preparation of microscale hydrogel particles for high efficiency adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28562–28571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahari, A.M.; Shuo, C.W.; Sathishkumar, P.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Gu, F.L.; Buang, N.A.; Woei-Jye, L.; Gohari, R.J.; Yusop, Z. A reusable electrospun PVDF-PVP-MnO2 nanocomposite membrane for bisphenol A removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5801–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, A.; Chatzisymeon, E.; Chidichimo, F.; Beneduci, A.; Chidichimo, G. Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from water: Adsorption of Bisphenol-A by biobased hydrophobic functionalized cellulose. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Hernandez, C.; Kim, H.; Lin, Y.; Curry, M.L.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.; Noveron, J.C. Adsorptive removal of sulfamethoxazole and Bisphenol A from contaminated water using functionalized carbonaceous material derived from tea leaves. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Hernandez, C.; Castro, E.; Katla, S.K.; Kim, H.; Lin, Y.; Curry, M.L.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.; Noveron, J.C. Biomass conversion of saw dust to a functionalized carbonaceous materials for the removal of Tetracycline, Sulfamethoxazole and Bisphenol A from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4329–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Su, A.; Zhang, H.X. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of phenolic compounds from vegetable oils using a magnetic ionic liquid. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 3130–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Bai, H.; Xie, G.; Xiao, J. Trace determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental samples by temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1188, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa, L.B.A.; Padro, J.M.; Reta, M. Analysis of non-polar heterocyclic aromatic amines in beefburguers by using microwave-assisted extraction and dispersive liquid-ionic liquid microextraction. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Yao, S. Systematic investigation for extraction and separation of polyphenols in tea leaves by magnetic ionic liquids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Stark, A. Ionic liquids. In Green Solvent; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.X.; Gao, Y.Y.; Xie, G.H. Determination of bisphenol A, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-tert-octylphenol by temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-phase microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detector. Talanta 2011, 85, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Fan, Y.C.; Pei, Y.C.; Wu, K.; Wang, J.J.; Fan, M.H. Solvent extraction of selected endocrine-disrupting phenols using ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Lin, Q.; Luo, G.S.; Dai, Y.Y. Directly suspended droplet microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 566, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Zhang, D.F.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. Application of ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid phase microextraction for highly sensitive simultaneous determination of three endocrine disrupting compounds in food packaging. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Anderson, J.L. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using an in situ metathesis reaction to form an ionic liquid extraction phase for the preconcentration of aromatic compounds from water. Anal. Bioanalyt. Chem. 2009, 395, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Santos, L.; Fernandes, A.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M. An overview of the mutual solubilities of water-imidazolium-based ionic liquids systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 261, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, M.; Shemirani, F. Cold-induced aggregation microextraction: A novel sample preparation technique based on ionic liquids. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 613, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, C.A.; Dorn, P.B.; Klecka, G.M.; O’Block, S.T.; Harris, L.R. A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 2149–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).