Abstract
Rapid economic development and population growth in China’s Yangtze River Delta (YRD) are exerting significant environmental pressure on the region’s land and water, especially in hilly areas where many drinking water reservoirs have been constructed. These areas, which are characterized by steep slopes and thin soils, provide critical services, including flood control, water resource supply, food production, and recreational opportunities for nearby highly developed and heavily populated areas of the delta. We contrast two of these areas—the well-studied Tianmu Lake watershed and the much larger Qiandao Lake watershed. Both face similar challenges from nitrogen and phosphorus pollution due to rapid socio-economic development, but differences in watershed size and distinctions related to political boundaries influence the range of approaches available to maintain water quality. We review experiences of controlling nutrient pollution in these watersheds as case studies, and based on that information, propose an integrated framework to minimize nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in similarly challenged watersheds. The framework, which is designed to be generalizable rather than prescriptive, emphasizes source control, delivery interception, and fate management of nutrients.
1. Introduction
Although serious environmental damage due to water pollution in populated, usually low-lying regions of the world is well documented [1,2,3,4,5,6], concern about this issue is now shifting to hilly watersheds, many of which serve as headwaters for downstream population centers. Human disturbance in these areas is intensifying, and pollution due to nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus is increasing [7,8,9,10]. The sources, transport, and retention of nutrients in these watersheds are tightly coupled with various human activities, a fact that renders narrow measures to control pollution ineffective [11,12,13,14]. A systems framework to guide nutrient management in threatened hilly watersheds is, therefore, desirable, as are integrative approaches that encompass the entire life cycles of polluting nutrients. Such a framework should be realistic and generalizable, providing reproducible and scalable insights that can be applied broadly.
China’s Yangtze River Delta (YRD) serves as an ideal research area to devise such a framework (Figure 1). It encompasses about 118,000 km2 of land and inland water and is among the most complex and human-impacted basins in the world [15,16]. The YRD is experiencing rapid development and significant population growth, mostly along the seaboard and in the low-lying, northern alluvial plain [17,18,19]. The environmental challenges facing these areas of the YRD, especially preservation of water resources, such as Taihu Lake, one of China’s largest and most nutrient-polluted water bodies, are well known [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
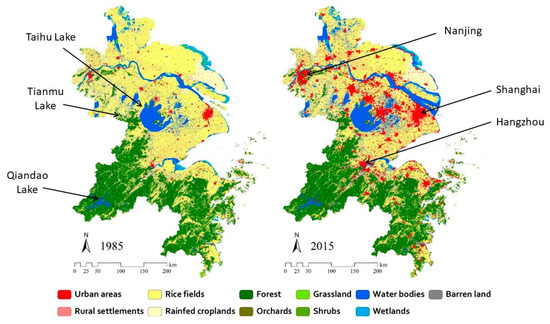
Figure 1.
The Yangtze River Delta of Eastern China showing land cover/land use as of 1985 and 2015. Taihu Lake, and the locations of Tianmu Lake and Qiandao Lake, are indicated on the left. Major cities are identified on the right.
The southern portion of the YRD, which is characterized by hilly watersheds with thin, easily erodible soils and large tracts of native forests (Figure 1), is now being imperiled by human caused N and P pollution [16,28,29,30,31,32,33]. This region is marked by an extensive network of dams and reservoirs that was constructed primarily for flood control, drinking water, and hydroelectric power [34,35,36,37]. There is growing pressure to divert water from the area’s reservoirs to meet the demands of nearby population centers; lake-based ecotourism and recreation are also expanding, and economic incentives are driving shifts toward agricultural intensification [14,38,39,40,41]. These dynamics are drawing attention to the causal nature of human activities and the need for integrated approaches to control nutrient pollution. The evaluation of the hilly watersheds of the YRD, therefore, offers an opportunity to comprehensively assess nutrient management options to preserve water quality.
Herein, we examine two hilly catchments in the YRD that are similarly threatened by human-caused N and P pollution, yet differ greatly in scale, intensity of management, and other contrasting characteristics [42,43,44,45,46,47]. This leads to practical insights for mitigation, not just in the YRD, but also in similar watersheds elsewhere [27]. We begin by reviewing the two YRD watersheds and the major determinants of water quality in them. We then generate an integrative framework to control N and P pollution in these and similar catchments. Our objective is to synthesize useful information from two well studied, model catchments into a widely useful, practical guide to control such pollution.
2. Study Areas
2.1. Tianmu Lake Watershed
The Tianmu Lake watershed covers an area of 153 km2 (Figure 2) centered on an 11.6 km2 reservoir that lies 19 m above sea level, and was impounded in 1961 [48]. The watershed provides headwaters for the much larger Taihu Lake basin, which has historically suffered from frequent harmful cyanobacterial blooms and has been the subject of intensive environmental management to reduce nutrient pollution [49]. Tianmu Lake receives a mean annual rainfall of 1394 mm [50], and is fed by inflows from small rivers and streams that descend from the surrounding hills (Figure 2), the highest of which rises to 531 m above sea level and forms the westernmost reaches of the Tianmu Mountains [51]. The lake lies within Liyang, a county-level city in Jiangsu Province, but a small portion of the surrounding watershed extends into neighboring Anhui province. Only 5% of the basin’s land is classified as urban, and the population is just 50,000 [52].
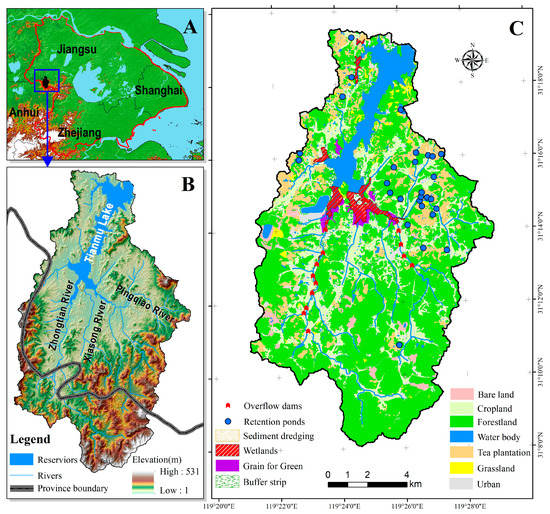
Figure 2.
The Tainmu Lake watershed. (A) Location of the watershed in the Yangtze River Delta. (B) Topographic map of the watershed showing the lake and the principal rivers that enter it. The dark line separates Jiangsu Province to the north from Anhui Province to the south. (C) Land cover/land use in the watershed as of 2017.
Tianmu Lake provides more than 1500 mW of hydroelectricity via two pumped storage power stations, as well as irrigation water and flood control [53,54,55,56]. It is also an important source of drinking water for the city of Liyang and nearby communities. Recognizing the potential of the area for recreation, the Jiangsu provincial government created the Tianmu Lake Tourist Resort in 1992 and took steps to protect the quality of the lake’s water, including reduction of water use for irrigation [14,56]. Recreation has consequently become a major contributor to the region’s economy and a key factor in management decisions for the lake, which has received the Chinese government’s highest, 5A rating as a scenic area.
Although land use models confirm the importance of ecological maintenance in the area surrounding Tianmu Lake, agriculture remains a major economic driver [33]. Almost all of the region’s valleys and many of the steeper, erodible slopes are cultivated [33,57]; and in contrast to the 1960s and earlier, when manure and other organic materials predominated as nutrient sources, chemical fertilizers are now applied extensively [14,45]. Although the ecological vulnerability of the watershed remains modest in comparison to other portions of the surrounding Taihu Lake basin, 15% of nearby land is at risk because of grain production, and vulnerability is increasing [46].
2.2. Qiandao Lake Watershed
The Qiandao Lake watershed is almost seventy times larger than the Tianmu Lake watershed and is located about 200 km south of it in Zhejiang and Anhui provinces (Figure 3). The lake drains a hilly and heavily forested area of 10,442 km2 with about two-million residents [58,59,60]. One of the largest freshwater reservoirs in China, Qiandao Lake was created by a dam on the Xin’an River in Zhejiang Province [61,62]. The dam, which was completed in 1959, lies southwest of Hangzhou, a beneficiary of the 845 mW of hydropower produced by the structure’s generators and a major recipient of the lake’s water for drinking as well [38]. The Xin’an River, which enters through the lake’s northwestern arm, provides almost 70% of inflows [63], but more than 50 smaller waterways of at least 10 km in length also enter the lake [64].
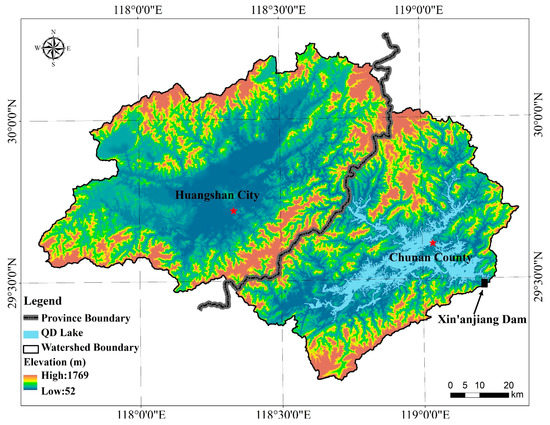
Figure 3.
The Qiandao Lake watershed. The dark line separates Anhui Province on the left from Zhejiang Province on the right.
Qiandao Lake is a deep water body with a surface area of 583 km2 and a lengthy, undulating shoreline with four main arms. Its surface area is punctuated by 1078 islands [65], which have greatly contributed to the lake’s official designation as a 5A scenic area for tourists, more than 17 million of whom visited the area in 2018 [39]. Tourism and recreation have created a few hotspots of development [66,67,68], but urban and associated growth in the basin has remained remarkably constant in comparison to adjacent areas of Zhejiang Province and the northern and coastal areas of the YRD.
The impoundment of Qiandao Lake submerged a rich river valley, triggering profound changes in land cover/land use in the surrounding basin. More than 120,000 farmers were displaced, and this reshaped agriculture in the region by reducing the amount of arable land available for crop production [62,67,69]. Some displaced farmers became fishermen or moved away [70], but many relocated to higher ground and cleared erodible land on steep slopes [71]. Other agricultural areas have appeared in protected zones near the shore, where they have illegally displaced natural vegetation that serves as an ecological buffer [71]. Some fields (Figure 4) even occupy land that temporarily emerges from the lake during drier parts of the year [69].

Figure 4.
The intrusion of small scale agriculture onto an ecological buffer zone near an inlet to Qiandao Lake.
Three-quarters of the Qiandao Lake watershed remains forested, but grain production has declined significantly in recent decades [47], so that cropland now occupies just 8.3% of its area. Agriculture has nevertheless responded to rapid socio-economic development and correspondingly improved living standards by expanding in other ways. Intensively managed tea plantations and orchards now occupy 4.5% and 2.3%, respectively, of the watershed, and greenhouses are also appearing. Most remaining cropland is northwest of the lake in Anhui Province, where agriculture is of small scale and dispersed in remote areas along minor streams [64]. Tea, on the other hand, is a growing factor for land use near the lake in Zhejiang Province, but it is only a minor activity in distant parts of the watershed [72,73]. These political and spatial distinctions have become important factors for the design of policy interventions to reduce N and P pollution in the watershed (Section 3.3).
3. Major Determinants of Water Quality
The preservation of clean surface water is usually the top priority in recreational areas, such as Qiandao Lake and Tianmu Lake, which place heavy emphasis on nature and ecotourism [73,74,75]. In reality, compromised water quality and sporadic algal blooms have been a chronic problem in both lakes for decades [76], due in part to pollution of water sources by manufacturing, quarrying, domestic activities, and recreational infrastructure. Construction of sewage treatment facilities, closure of industrial and quarrying sites, removal of livestock and poultry farms, and stringent enforcement of regulations have greatly reduced the contribution from these sources [14,77,78]. As a consequence, agriculture and fish are now major determinants of water quality in the two lakes [48,79,80].
3.1. Changes in Drainage Areas
Although pollution of Tianmu Lake has been apparent since the early 1990s, the release of nutrients from the surrounding terrain was of only of modest concern before the turn of the century [76]. This changed when favorable economics and supportive policies triggered changes in land use (Figure 5A) that included a sudden, rapid expansion of tea plantations in the watershed [77,78]. The area planted with tea has grown nearly six-fold since 2000 (Figure 5B), even as that devoted to crops has declined [81]. Indeed, the land area occupied by tea is now greater than the area covered by open water. Tea plantations typically form a buffer between forested areas, which comprise 54% of the watershed, and croplands, which comprise 16% of the watershed, and they tend to be clustered in the northern part of the watershed, near recreational areas (Figure 2). Although most plantations are on slopes of up to 15 degrees, some have been laid out on hillsides with slopes greater than 25 degrees [81].
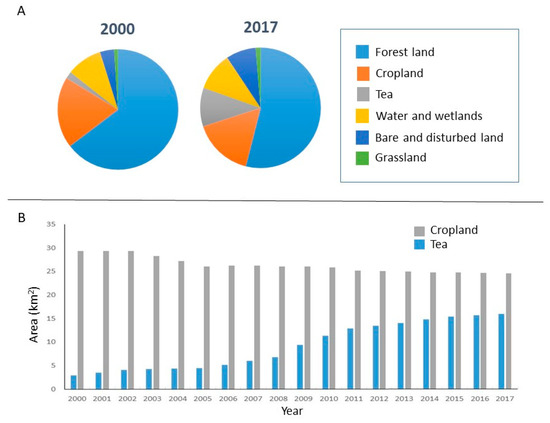
Figure 5.
Changes in land cover/land use in the Tianmu Lake watershed between 2000 and 2017. (A) Land cover/land use in the years 2000 and 2017. The category bare and disturbed land includes construction land, and in 2017, land removed from crop production and returned to its natural state. (B) Year by year changes in the area devoted to cropland and tea production.
Detailed information on total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) release from different land cover categories in the Tianmu Lake watershed is available, and that has facilitated hydrological modeling’s pinpointing of principal areas of concern [82,83]. Although forested areas remain the dominant land cover, they release relatively small amounts of TN and TP annually on a per hectare basis (Figure 6). Other land use categories represent varying degrees of disturbance. In each case, annual per hectare release of nutrients into the environment greatly overshadows that of forests—by a factor of three to eight in the case of TN and five to eight in the case of TP. The contribution of tea to nutrient runoff, especially that of TN, is disproportionately high (Figure 6) and associated with hotspots, most of which are near the lake [55]
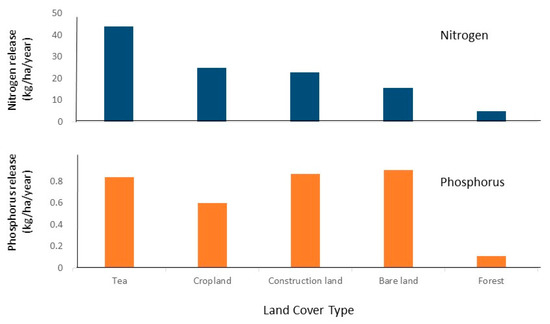
Figure 6.
Contributions of principal land cover types to rates of loss of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) in the Tianmu Lake watershed as of 2009 [82,83].
Release of TN and TP from tea plantations is a complex consequence of several factors. Tea provides significant economic returns, so it typically receives multiple seasonal applications of organic fertilizers (mostly manure but also some seed meal), as well as inorganic N and P at levels considered excessive [41,78]. The canopy cover of tea is never complete, and because the bushes are pruned in the spring, vegetation coverage is reduced from roughly 70% to about 30%, coincident with spring fertilization. This corresponds in time to the onset of the rainy season, when erosion is most likely [77]. Clearing land for tea also accounts for a portion of the basin’s bare areas in any given year, and this adds to nutrient runoff attributable to tea cultivation. In aggregate, these factors implicate tea plantations, due to their expansion over the past two decades, as a major target for reduction of nutrient flows into the lake.
The situation is similar for Qiandao Lake, where non-point release of TN and TP is the most significant threat to the water quality [69] and where 60% of the former and 80% of the latter is attributed to agriculture [84]. It is estimated that fertilizers account for 79% of TN loss and 88% of TP loss in the upper basin [71]. Although per hectare loss of TN, and to a lesser extent TP, from tea plantations is highly significant [63], grain cultivation on small, difficult to monitor farms is also a major source of nutrient runoff in the Qiandao Lake watershed [47,59,61,63,85]. High average chemical fertilization rates, which exceed internationally accepted standards by 60%, exacerbate this problem [69,71,84]. Agriculture has consequently been targeted in efforts to reduce TN and TP loads into the lake by 25% and 30%, respectively, by 2024 [84].
3.2. Changes in Water
Fish stocking and aquaculture have been important practices in Tianmu Lake for more than 50 years. Fish farms have, nevertheless, led to the destruction of wetlands adjacent to the lake [86], and they contribute pollutants in the form of residual feed and excreta [87]. Bighead carp and silver carp traditionally accounted for more than 95% of the caged species in the lake, with crucian carp included as a minor component of the mixture [14]. Bighead carp is particularly valuable from the perspective of tourism, which offers visitors a specialty cuisine based on this locally produced species [88,89], but it depletes zooplankton and can have disproportionately detrimental effects on the aquatic food chain [48,76].
These complex issues were addressed comprehensively, when in 2006, management of fish in Tianmu Lake was reoriented from economic to environmental focus [14]. The production of bighead carp was reduced from 600 to 400 metric tons per year, increasing the proportion of silver carp, which prefers phytoplankton as a food source and is beneficial to the lake [40]. Steps were also taken to enhance the breeding of wild fish, many of which are omnivorous and thus capable of removing a wide range of organic substances from the water [14]. Fishing for wild species is now prohibited, and the contribution of fish and aquaculture to the pollution of the lake has been curtailed [48,90,91].
Qiandao Lake offers a contrasting perspective. Although said to have the best water in the world, the lake experienced serious algal blooms in 1998–1999 and sporadically thereafter [47,58]. The 1998–1999 blooms coincided with a steep drop in the number of bighead carp and other wild carp species in the lake, thus implicating fish as regulators of water quality [85,92]. Carp populations in Qiandao Lake had been decimated by overfishing, much of it illegal [92,93]. Steps were consequently taken to re-establish carp; stocking levels were increased by an order of magnitude, and predator fish were removed [47,93]. One-quarter of Qiandao Lake was also designated a no-fishing zone to protect spawning areas, and fishing regulations were rigorously enforced [59,92]. These policies rapidly increased the quality of the lake’s water and have been maintained to ensure that desirable bighead and silver carp populations persist at levels that permit fish-harvest in the spring and summer [47,70,93].
Qiandao Lake and its river estuaries also support a significant aquaculture industry, but it is now strictly controlled [94,95]. Although this limits the polluting effects of nutrients from unconsumed feed and concentrated fish excreta, caged fish have been implicated as a source of pollution in estuaries [47]. Fish cages have been removed from sensitive stream areas [95], and the zone of the lake reserved for caged-culture is now limited to less than 1% of the lake’s total surface area. Only about one-third of caged areas is approved for artificially fed fish [96]. In spite of these restrictions, fish yields from aquaculture have risen substantially since 1998 [47], and caged Kaluga sturgeon from Qiandao Lake is now the world’s main source of caviar [97,98].
3.3. Policy Intervention
Knowledge of the important roles of agriculture and fish as determinants of water quality in Tianmu Lake and Qiandao Lake has led to a variety of steps to prevent nutrient pollution. These include the reforestation of highly erodible sites, the removal of farms from riverbanks, the promotion of organic farming, the rehabilitation of water infrastructure, the construction of wetland projects, and efforts to manage wild fish populations and regulate aquaculture [71,99,100]. Although such measures are potentially subject to constraints and opportunities imposed by political boundaries, borders have not become an issue in the small Tianmu Lake watershed, which lies almost entirely within Jiangsu Province (Figure 2). In contrast, the border between Zhejiang Province and Anhui Province bisects the Qiandao Lake watershed and decouples the lake, almost all of which lies in the former, from the polluted Xin’an River, which draws its inflows from the latter [46,85,101].
Economic and social factors exacerbate these spatial differences [94,99]. Personal income and per capita GDP in the Anhui portion of the watershed is less than that in the Zhejiang portion of the watershed and much less than that in the city of Hangzhou, which receives the benefit of the drinking water [59,62,99]. The major source of pollution (Anhui Province), the adjacent recipient of pollution (Zhejiang Province), and the more distant beneficiary of the lake (the city of Hangzhou) are consequently separated from one another—spatially and in terms of wealth, political organization, and actual and perceived benefits [63]. These distinctions add complexity, but they also make the Qiandao Lake watershed an ideal candidate for experimentation with payment for ecosystem services (PES) as a means to control water pollution.
Payment mechanisms for ecological protection of the Qiandao Lake watershed [99] were in fact first implemented in the late 1990s, coincident with algal blooms that then were polluting the lake. Zhejiang Province initiated transfers to Chun’an County, which surrounds the lake, and began to divert a portion of its earnings from tourism to preserve the lake’s environment [59]. Beijing also recognized the environmental fragility of the basin, designating it a key ecological function zone and providing funds for environmental remediation. These initial approaches became comprehensive, when in 2007 the basin was designated a demonstration zone for PES. In late 2011, the formal, three-year Xin’an River Basin Water Environment Pilot Implementation Plan became operational as the first trans-provincial PES scheme in the country [99].
Transboundary PES schemes are inherently contentious [102,103]. Disputes about rights and responsibilities are common, as are disagreements about who pays, who is compensated, and how costs and benefits are balanced [104]. Coordination is complex, as are negotiations on the details of environmental monitoring and assessment. All of these issues came into play at Qiandao Lake [59,99,101]. The economically disadvantaged Anhui Province did not want to consider sending funds to richer Zhejiang Province, which was willing to transfer funds to one of its poorer counties but hesitant to send funds across the border to another province. Zhejiang Province also asserted that Beijing should pay, because it receives benefits from hydroelectric power production by the dam.
As mediated by Beijing, the first three-year pilot agreement relied on joint monitoring of four equally weighted indices, including TN, TP, ammonia N, and the permanganate index, which were combined into a single index of water quality [98,105,106]. If water quality monitored at the point where the Xin’an River crosses from Anhui into Zhejiang Province exceeded the baseline standard established prior to the implementation of the PES scheme, Anhui Province would receive 100 million yuan from Zhejiang Province, but if the opposite was true, Zhejiang Province would receive 100 million yuan from Anhui Province [94,99]. In either case, Beijing would pay 300 million yuan a year to Anhui Province, which would match this sum with 100 million yuan [94,105].
The pilot experiment, which ran from 2012 through 2014, and a second agreement, which ran from 2015 through 2017, yielded mixed results. The concentration of ammonia N rose during the pilot period, but this was counterbalanced by declines in TN and TP, such that Anhui Province received compensation. Although reductions in TN and TP were not sustained during the second period [94,102,107], the PES scheme has, nevertheless, been reauthorized from 2018 through 2020, with weights of the four individual indices adjusted in an attempt to achieve desired reductions in TN and TP [30].
It is important to note that Anhui Province was granted great discretion in use of the PES funds to improve water quality [94,95,105]. Although some of the funds were used to build ecological restoration structures and reduce pollution from industrial and residential areas, agriculture and aquaculture emerged as priorities. Projects were funded to remove more than 6000 fish cages, convert over 300,000 ha of farmland to forest, establish ecological tea gardens, and prevent the over-fertilization of crops. This displaced many fishermen and farmers, who, according to surveys, are satisfied with the payments, even though their income has changed little [95]. All parties agree that reduction of TN and TP pollution from agriculture remains a top priority, so the most recent agreement emphasizes this issue as a means of improving water quality [107].
4. Integrative Management to Mediate Nutrient Loss
Tianmu Lake and Qiandao Lake exemplify reservoirs located in hilly, environmentally sensitive basins of the YRD and similar areas elsewhere, where traditional patterns of land use find themselves in conflict with pressures brought on by urbanization and economic development [30,74,80,108]. Water purity is of paramount importance in these areas, where TN and TP pollution from agriculture and aquaculture is a major contributor to low water quality, where recreation and tourism are economic drivers [48,69,79,80,90,108], and where efforts to control pollution are often reactive and first triggered by crisis events, such as the sudden appearance of algal blooms [59,82]. The above dynamics are occurring in similar lakes and watersheds located in other parts of the world, including North America [109], Latin America [110,111], Europe [112,113], and Asia [114,115,116]. Here, too, the complex challenges of nutrient pollution are apparent, but the responses are often uncoordinated and reactive [27,74,117,118,119].
By virtue of their location in the rapidly developing YRD, the Tianmu Lake and Qiandao Lake watersheds are under considerable environmental pressure and have been intensively investigated from a range of perspectives designed to reduce nutrient pollution. Nevertheless, they differ in several key characteristics that influence these efforts. The watersheds thus complement one another to facilitate the development of an integrated framework to prevent TN and TP pollution in similar areas (Figure 7). Although based on insights from two case studies, the framework is not meant to be constrained by site-specific factors, such as the expansion of tea or the availability of defined governmental policies. The framework is also not intended to be prescriptive; rather, it is designed to be used widely as a generalizable guide. It rests on three strategies that emphasize relationships and provide redundancy to the system: source control, delivery interception, and fate management. If, for example, the release of excess TN and TP into a basin cannot be prevented, the framework still offers options to manage pollution. The integrated nature of the framework also allows for functional overlaps among the strategies; e.g., PES schemes can both preclude nutrients from entering the system and prevent their delivery to the lake, and wetlands can both intercept nutrients and foster self-purification.
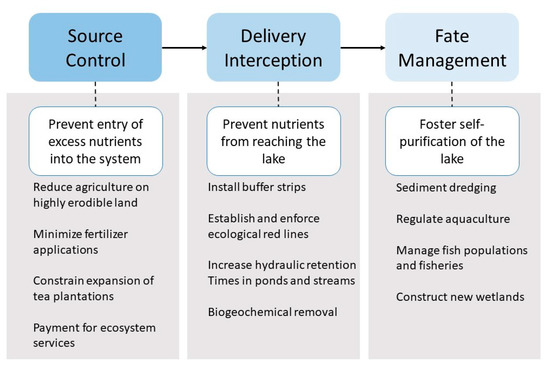
Figure 7.
The diagrammatic representation of an integrative three-stage approach to control TN and TP pollution in hilly watersheds. The framework is based on analyses of the Tianmu Lake and Qiandao Lake watersheds but is meant to be generalizable. Strategies are identified by blue boxes, with brief explanations below in white boxes. Actions, which are grouped under each of the gray boxes, are representative and not comprehensive.
The first and most desirable priority is simply to exclude unwanted nutrients from entering the basin of interest (Figure 7). Source control can take a variety of broad forms, some of which reflect specific governmental policies, such as the PES scheme in place at the Qiandao Lake watershed. Others, such as the 1991 directive from Beijing that prohibits agricultural fields on hillsides with slopes greater than 25 degrees, and the Grain for Green program, a generalized PES scheme that provides subsidies and other incentives to remove sensitive land from agricultural production [120,121], are not tailored to any specific ecological zone [81]. China has also established ecological red line areas that prohibit all forms of development in the most sensitive lakeshore areas and sharply curtail activities in others [22,71,122,123]. Although analogous regulatory strategies to exclude nutrients may be difficult to implement in other countries [103], a reduction of fertilizer application rates, checks on the expansion of agriculture, and the regulation of aquaculture, all are widely feasible approaches.
There are a variety of generalizable options to achieve the second priority, the interception of nutrients (Figure 7). These include contour planting, avoiding fertilization before heavy rain events, the application of protective mulches, and the construction of buffer strips below erodible land. Such measures have been examined in detail in the Tianmu Lake basin, where up to 75% of TN loads can be retained if appropriate measures are implemented [50]. Small upland ponds and cascading wetlands are both able to strongly buffer nutrient loads in hilly catchments [124,125,126]. The efficacy of the latter has been demonstrated along the Zhangtian River in the Tianmu Lake watershed (Figure 2). The river, which is known to be a major carrier of nutrients from agricultural fields [14,86], has been equipped with nine overflow dams, and in preliminary experiments, these have retained 38% of the incoming TN and 84% of the incoming TP. The adjacent Xiasong River, which still flows freely, achieves corresponding retention rates of just 10% and 48%, respectively.
The third priority, self-purification (Figure 7), can be achieved by several approaches, including the management of wild and caged fish populations to reduce nutrient loads and the preservation of wetlands [14,93,127,128,129]. The natural wetland that forms at the convergence of the Zhangtian, Xiasong, and Pingqiao rivers (Figure 2), for example, is known to represent a dynamic and critical component of Tianmu Lake’s capacity to self-purify [14,61,78]. This area has been functionally degraded by pollution from upstream aquaculture and agriculture [52], but it is now being dredged and is undergoing restoration [130]. These and similar projects in the Qiandao Lake watershed [84,100] exemplify the widespread attention being given to the management of fish and wetlands as a means of maintaining water quality [131,132].
5. Final Remarks and Broader Relevance
The environmentally sensitive hilly basins surrounding Tianmu Lake and Qiandao Lake in the YRD differ greatly in expanse and in the extent to which they are influenced by political boundaries, but they face a common set of challenges that are being faced by similar basins elsewhere [6,7,8,9,10,133], including those in areas that have transitioned from rural to urban [134,135]. Consideration of the two case studies from the YRD and the resulting framework for the control of nutrient pollution in basins with similar characteristics allows three main conclusions to be drawn. Each has implications for reducing nutrient loading in similar basins located away from the YRD [27,136].
The first conclusion is that watershed size and political boundaries are important factors. Smaller size and the absence of political entanglements enables rapid and responsive management decisions, and also easily facilitates the implementation of pilot projects to generate needed data. These dynamics allowed authorities at Tianmu Lake to enshrine long-term environmental benefits rather than short-term economic gains as the goal of watershed management [14]. They also enabled the city government of Liyang to join forces with the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, a unit of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, to establish the Tianmu Lake Watershed Ecological Observation Station in the basin, with the goal of developing technologies for comprehensive management of the Tianmu Lake watershed [137].
Larger watersheds that extend across multiple political boundaries do not enjoy these advantages, but size often generates interest from outside investors. Thus, the size and complexity of the Qiandao Lake watershed drew the attention of the central government, which resulted in the landmark Xin’an River Basin Water Environment Pilot Implementation Plan [99,107], and it also attracted the World Bank, which has funded large scale projects to preserve the water quality in the basin [84,100].
The second conclusion is that heightened interest in recreation, although a complicated issue [138], can be an important factor in preserving water quality. The economic potential of recreation was decisive in focusing the attention of local governments in both the Tianmu Lake [14] and Qiandao Lake [139] watersheds on management for long-term environmental benefits. Tourism can generate revenue for investment in measures, such as wetland reconstruction and rehabilitation, and it also draws attention to the management of fish populations and aquaculture activities as means to preserve water quality, both in the YRD [14,59] and in similar basins elsewhere [140,141,142].
The third and final conclusion is that approaches to reduce nutrient loading should be as integrated as possible and based on a comprehensive understanding of the underlying dynamics of the relevant watershed. The Tianmu Lake and Qiandao Lake watersheds have benefitted from important advances in this regard, and were thus used as case studies in the current analysis. Such understanding should encompass not just environmental issues, but also governance, socio-economic factors, and—as is clear from the considerations of fish and aquaculture in the case studies—the potential for trade-offs and synergies, some of which may be site-specific.
Author Contributions
S.G.P. conducted the literature review and drafted the manuscript. W.Z., H.L., D.C., and W.O. contributed data, assisted in preparing the figures, and provided critical interpretation, analysis, and synthesis of information, much of which has never been published in English. H.L. and W.Z. are responsible for the conceptual framework illustrated in Figure 7.
Funding
This work was supported by the Active Design Project for Agricultural and Social Development in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, grant number 20180417A06, awarded to H.L, and the National Natural Science Foundation, grant numbers 41877513 and 41701040, awarded to H.L.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the Nanjing Agricultural University-Michigan State University Asia Hub Program (grant number 2017-AH-10 awarded to W.O. and S.G.P.) for funding the collaboration that generated this paper. We thank Weimin Chen for insights on aquaculture and fisheries, and Jiaguo Qi, Yu Tao, and Jie Guo for advice, encouragement, and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, T.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, P. Urgency, development stage and coordination degree analysis to support differentiation management of water pollution emission control and economic development in the eastern coastal area of China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, A.; Nakura, Y.; Ishikawa, T. New direction for environmental water management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Feng, H.; Witherell, B.B.; Alebus, M.; Mahajan, M.D.; Zhang, W.; Yu, L. Causes, assessment, and treatment of nutrient (N and P) pollution in rivers, estuaries, and coastal waters. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Gu, B. Urban rivers as hotspots of regional nitrogen pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.J.; Wollheim, W.M.; Mulholland, P.J.; Webster, J.R.; Meyer, J.L.; Tank, J.L.; Marti, E.; Bowden, W.B.; Valett, H.M.; Hershey, A.E. Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 2001, 292, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Qiu, S.; Mao, S.; Bao, R.; Deng, H. Evaluating water resource accessibility in Southwest China. Water 2019, 11, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Carvalho, L.; Argillier, C.; Beklioglu, M.; Borja, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Hellsten, S. Managing aquatic ecosystems and water resources under multiple stress—An introduction to the MARS project. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 503, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Elser, J.J. Intensification of phosphorus cycling in China since the 1600s. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.M.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Burt, T.P.; Chan, N.I.; Elser, J.J.; Haygarth, P.M.; Sharpley, A.N. Long-term accumulation and transport of anthropogenic phosphorus in three river basins. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, S. Urbanization impacts on the structure and function of forested wetlands. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines-Young, R.; Potschin, M. The links between biodiversity, ecosystem services and human well-being. In Ecosystem Ecology: A New Synthesis; Raffaelli, D.G., Frid, C.L.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 110–139. [Google Scholar]
- Macintosh, K.A.; Mayer, B.K.; McDowell, R.W.; Powers, S.M.; Baker, L.A.; Boyer, T.H.; Rittmann, B.E. Managing diffuse phosphorus at the source versus at the sink. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11995–12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, G.; Chen, W.; Gao, R.; Nie, X.; Yu, Z.; Diao, Y.; Li, X. Current situation of good water quality reservoirs in hilly region of south-east China: Protection practices of Tianmuhu Reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 775–784. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huan, Y.; Wang, L.; Muhos, M.; Kess, P. Investment Environment of Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone; University of Oulu: Oulo, Finland, 2011; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.; Ban, Y. Urban growth and environmental impacts in Jing-Jin-Ji, the Yangtze, River delta and the Pearl River delta. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Recent Agriculture in the Yangtze Delta. A General Review; Agricultural Economics Research Institute: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 1–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, W.; Boelens, L. The interaction of city and water in the Yangtze River Delta, a natural/artificial comparison with Euro Delta. Sustainability 2018, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wei, Y.D.; Chen, W.; Yenneti, K. Urban land expansion and structural change in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10281–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Comparison of advantages and weaknesses among three major urban agglomerations in China. Asian Soc. Sci. 2008, 4, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; He, B. Analysis of the dynamic urban expansion based on multi-sourced data from 1998 to 2013: A case study of Jiangsu Province. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wong, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Hughes, A.C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q. Developing China’s ecological redline policy using ecosystem services assessments for land use planning. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X. Development and changes in industrial distribution in Shanghai in 1990. Contemp. China Hist. Stud. 2009, 16, 92–128. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; Jiang, N.; Yao, L. Land use and cover change during the rapid economic growth period from 1990 to 2010: A case study of Shanghai. Sustainability 2018, 10, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ou, W.; Guo, J. A land-cover-based approach to assessing ecosystem services supply and demand dynamics in the rapidly urbanizing Yangtze River Delta region. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Yang, G.; Ou, W.; Pueppke, S.; Sun, X.; Chen, G.; Tao, Q. Impact of land use change on multiple ecosystem services in the rapidly urbanizing Kunshan City of China: Past trajectories and future projections. Land Use Policy 2019, 85, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadouani, A.; Coggins, L.X. Science, technology and policy for water pollution control at the watershed scale: Current issues and future challenges. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; McDowell, R.W.; Kleinman, P.J. Phosphorus loss from land to water: Integrating agricultural and environmental management. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Swaney, D.P.; Hong, B.; Howarth, R.W.; Han, H.; Li, X. Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs and riverine phosphorus fluxes in highly populated headwater watersheds in China. Biogeochemistry 2015, 126, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, D.; Li, H. Spatio-temporal dynamics of water quality and their linkages with the watershed landscape in highly disturbed headwater watersheds in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35287–35300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Pearl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutropic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bi, J.; Lv, J.; Ma, Z.; Wang, C. Spatial multi-scale relationships of ecosystem services: A case study using a geostatistical methodology. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Jin, X.; Gan, L.; Jessup, L.H.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Yang, X.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, Y. Spatial identification and dynamic analysis of land use functions reveals distinct zones of multiple functions in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X. Drastic change in China’s lakes and reservoirs over the past decades. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Jin, C.; Zhu, J. Controlling cyanobacteria and its effectiveness: An evaluation in four reservoirs for drinking water supply. In Tropical and Sub-Tropical Reservoir Limnology in China; Han, B.-P., Liu, Z., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 343–362. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, C.; Wu, X.; Hu, C.; Tao, G.; Qing, Z. Survey of benthic animals in reservoirs in Jiangsu Province and its comprehensive evaluation. J. Lake Sci. 2004, 16, 43–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Zhou, G.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, Z. analysis on the basic characteristics of Jiangsu reservoir. Jiangsu Water Res. 2018, 7, 69–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hangzhou Second Water Source Qiandaohu Distribution Project. Available online: https://baike.baidu.com/item/千岛湖引水工程/10935578?fr=aladdin (accessed on 28 May 2019). (In Chinese).
- Statistical Communique of 2018 National Economic and Social Development in Chun’an County. Available online: http://www.qdh.gov.cn/art/2019/4/3/art_1388507_31968483.html?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg (accessed on 28 May 2019). (In Chinese)
- Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, F.; Perera, H.A.C.C. Status of reservoir fisheries in China and their effect on environment. In Tropical and Sub-Tropical Reservoir Limnology in China; Han, B.-P., Liu, Z., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Li, H.P.; Nie, X.F.; Xu, X.B. Nitrogen and phosphorus budget of different land use types in hilly area of Lake Taihu upper river basin. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 829–837. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Wu, J.; Lou, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J. Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Chen, Q.; Ren, K.; Chen, K. Vertical distribution and retention mechanism of nitrogen and phosphorus in soils with different macrophytes of a natural river mouth wetland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, R.; Huang, F.; Wu, J. Temporal trend and source apportionment of water pollution in different functional zones of Qiantang River, China. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Hudson, N.; Zhang, H.; Nie, X. Variations of farming systems and their impacts on surface water environment in past 60 years in intensive agricultural area of Taihu Region, China. J. Water Res. Protect. 2015, 7, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Yang, G.; Tan, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Li, H.; Wan, R.; Su, W.; Zhang, J. Ecological risk assessment of ecosystem services in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Luo, W.; Wu, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, B.; Phyoe, W.; Wang, F. Historical record of nutrients inputs into the Xin’an Reservoir and its potential environmental implication. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20330–20341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Ren, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Y.; He, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y. Response of water quality to the catchment development and protection in Tianmuhu Reservoir, China. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 809–817. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Lou, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Kendall, A.D.; Hyndman, D.W.; Diao, Y.; Geng, J.; Pang, J. Nitrogen transport and retention in a headwater catchment with dense distributions of lowland ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J. Soil erosion and regional ecological management in the headwater area of Eastern China—A case study in the Tianmu Mountains. In Hydrological Problems and Environmental Management in Highlands and Headwaters; Křeček, J., Rajwar, G.S., Haigh, M.J., Eds.; A. A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Huang, W.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Z.; Qin, J. Denitrification potential and influencing factors of the riparian zone soils in different watersheds, Taihu basin. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. Pumped hydroelectric storage. In Storing Energy; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.W.; Yang, J. Developments and characteristics of pumped storage power station in China. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 163, p. 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Province’s Largest Pumped Storage Station Put Into Operation. Available online: www.ourjiangsu.com/a/20171016/1508118973841.shtml (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, W.; Jiao, X. Agricultural water transfers in China: Current issues and perspectives. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Musyimi, Z. The response of grain production to changes in quantity and quality of cropland in Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 95, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhu, M. Spatial-temporal variations of water quality parameters in Xin’anjiang Reservoir (Lake Qiandao) and the water protection strategy. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 836–845. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, L. Chinese Practices of Ecological Compensation and Payments for Ecological and Environmental Services and its Policies in River Basins; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S. Present situation and management countermeasures of soil and water loss in Qiandaohu watershed. Soil Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. Shanxi 2001, 2, 41–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, L. Assessment of reservoir water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of Qiandao Lake, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Cao, F.; Jiang, C. Identification of sustainable development limiting factors and countermeasures of large deep lake—Exemplifying Qiandao Lake drainage area. Zhejiang Hydrotech. 2007, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Liang, T. Non-point source pollution modelling using soil and water assessment tool and its parameter sensitivity analysis in Xin’anjiang catchment, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.; Yan, Y. Effects of local, river-network and catchment factors on fish assemblages in the headwater streams of the Xin’an basin, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2017, 32, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, G. Building New China, Colonizing Kokonor; Lexington Books: Lanham, MD, USA, 2016; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- Agapiou, A.; Alexakis, D.; Sarris, A.; Themistocleous, K.; Papoutsa, C.; Hadjimitsis, D. Satellite-derived land use changes along the Xin’an river watershed for supporting water quality investigation for potential fishing grounds in Qiandao Lake, China. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 4–10 April 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Li, J.; Deng, J.; Lin, Y.; Ma, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, K.; Hong, Y. Eco-environmental vulnerability assessment of large drinking water resource: A case study of Qiandao Lake area, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 9, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yue, W.; Xu, H.; Wu, J.; He, Y. Environmental consequences of rapid urbanization in Zhejiang Province, East China. Int. J. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 7045–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Luo, D.; Luo, X.; Tang, D.; Chen, S. Agriculture non-point source pollution control measures of Qiandao lake area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 18, 126–129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Battle Lines Drawn to Fish in China’s Thousand Island Lake. Available online: https://www.scmp.com/news/china/society/article/2141266/battle-lines-drawn-fish-chinas-1000-island-lake (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Xu, Q. The Study of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Control Policy System. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Su, S.; Mai, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C. Quantifying determinants of cash crop expansion and their relative effects using logistic regression modeling and variance partitioning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Inheritance of the ecological culture with harmony between people and nature. In Chinese Dream and Practice in Zhejiang—Ecology; Pan, J., Shen, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 141–166. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Characterizing landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes for urbanization impacts at an eco-regional scale. Appl. Geog. 2012, 34, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, E.; Oh, T. (Eds.) The Water-Energy-Food Nexus. Human-Environmental Security in the Asia-Pacific Ring of Fire; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yun-lin, Z.; Chen, W.; Yang, D.; Huang, W.; Jiang, J. Relation of water environment of Tianmuhu Lake and fishery and tourism. Ecol. Sci. 2003, 22, 271–274. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Li, P.; Huang, Q.; Diao, Y.; Jiang, J. Characteristics of nitrogen loss via runoff from typical land uses in hilly area of Tianmuhu watershed. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 827–835. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Li, H.; Jiang, J.; Diao, Y.; Li, P. Spatiotemporal variation of riverine nutrients in a typical hilly watershed in Southeast China using multivariate statistics tools. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 983–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Couture, R.-M.; Larssen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, X.; Bu, X.; et al. Decline in Chinese lake phosphorus concentration accompanied by shift in sources since 2006. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Arhonditsis, G.B.; Gao, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, N.; Dong, F.; Shi, W. How successful are the restoration efforts of China’s lakes and reservoirs? Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, Z. Spatio-temporal change of tea plantation since 2000 and model-based prediction in the Tianhu Reservoir watershed. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 799–808. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, W.; Yang, G.; Xie, X. Reduction of nitrogen and phosphorus emission and zoning management targeting at water quality of lake or reservoir systems: A case study of Shahe Reservoir within Tianmuhu Reservoir area. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 785–795. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lidén, R.; Vasilyev, A.; Stålnacke, P.; Loigu, E.; Wittgren, H.B. Nitrogen source apportionment—A comparison between a dynamic and a statistical model. Ecol. Mod. 1999, 114, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/907641528515098050/pdf/China-Lake-and-River-PAD-05172018.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Luo, X.; Wen, J.; Luo, D.; Fong, Z. Changing characteristic and trend analysis of water quality of Qiandao Lake. Chin. J. Eco Agric. 2006, 14, 208–212. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Dong, Y. Variation of hydrological characteristics of Tianmu Lake and its effect on the Tianmuhu wetland and ecological environment of Tianmu Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2007, 5, 51–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Xiong, S.; Diana, J. Environmental impact of aquaculture and countermeasures to aquaculture pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 452–462. [Google Scholar]
- Tianmu Lake Tourist Region. Available online: http://www.changzhou.jiangsu.net/attraction/premier.php?name=Tianmu_Lake_Tourist_Region&city=Changzhou&id=97. (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- Tianmu Lake. Available online: http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/regional/2015-10/15/content_22186227.htm (accessed on 14 April 2019).
- He, R.R.; Gao, Y.X.; Wang, F.; Zhu, G.; Chen, W. Spatial-temporal distribution of nutrient and its causation in Tianmu Lake, China. J. Agro Environ. Sci. 2009, 28, 353–360. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Ciu, Y.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, M.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; Chen, W. Response of phytoplankton to nutrient reduction in Shahe Reservoir, Taihu catchment, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, L. The dilemma and path choice of reservoir fishery sustainable development based on the perspective of ecology: Verified by the illustration of Qiandao Lake aquatic environmental protection oriented fishery. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 3, 143–147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, M.; He, G.; Chen, L.; Hong, R. Impacts of aquatic environment protection oriented fishery on the structure of food web in Lake Qiandaohu. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 2774–2783. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, R. The implementation development of horizontal pilot eco-compensation policy in Xin’an River watershed in Anhui Province. China Econ. Trade Herald 2015, 13, 58–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.H.; Du, P.F. Evaluation on the effect of ecological compensation in Xin’an River basin. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 3, 63–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mims, S.D. Paddlefish: International status. In Paddlefish Aquaculture; Mims, S.D., Shelton, W.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 153–178. [Google Scholar]
- The World’s Best Caviar Doesn’t Come From Russia Anymore. Available online: https://bloomberg.com/news/articles/2017-09-19/the-world-s-best-caviar-doesn-t-come-from-russia-anymore (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- Chebanov, M.; Williot, P. An assessment of the characteristics of world production of Siberian sturgeon destined to human consumption. In The Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii, Brandt, 1869); Williot, P., Nonnotte, G., Chebanov, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 217–286. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Case Studies on Remuneration of Positive Externalities (RPE)/Payments for Environmental Services (PES); United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Disclosable Version of the ISR—Zhejiang Qiandao lake and Xin’an River Basin Water Resources and Ecological Environment Protection Project; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Huijin, L. Economic value of water resources of the upper reaches of the Xin’an River Basin, China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2012, 3, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Qin, F.; Wang, J. Payments for watershed services and practices in China: Achievements and challenges. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S. China’s domestic hydropolitics: An assessment and implications for international transboundary dynamics. Int. J. Water Res. Dev. 2018, 34, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Baoligao, B.; Jia, J. Benefits of Xin’an River water resources and ecological compensation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1073, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, G.H.; Zhao, Y. The first eco-compensation for crossing provinces of downstream and upstream in China: A model of Xinanjiang River. Environ. Protect. 2016, 14, 38–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, L.; Tang, L.; Gao, L.; Xie, G.; Cao, S.; Bai, Y.; Fang, C.; Bao, C.; Li, W.; et al. Principles and application of sustainable development. In Contemporary Ecology Research in China; Li, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 499–533. [Google Scholar]
- Horizontal Ecological Compensation Agreement for Upstream and Downstream of Xinanjiang River Basin; Zhejiang Provincial Ministry of Finance: Hangzhou, China, 2018.
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Shi, K.; Brookes, J.D.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Improving water quality in China: Environmental investment pays dividends. Water Res. 2017, 118, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putt, A.E.; MacIsaac, E.A.; Herunter, H.E.; Cooper, A.B.; Selbie, D.T. Eutrophication forcings on a peri-urban lake ecosystem: Context for integrated watershed to airshed management. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonansea, M.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Pinotti, L.; Ferrero, S. Using multi-temporal Landsat imagery and linear mixed models for assessing water quality parameters in Río Tercero reservoir (Argentina). Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrot, R.; Le Page, C.; Bommel, P.; Kuper, M. Articulating land and water dynamics with urbanization: An attempt to model natural resources management at the urban edge. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2004, 28, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereu, S.; Sušnik, J.; Trabucco, A.; Daccache, A.; Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia, L.; Renoldi, S.; Assimacopoulos, D. Operational resilience of reservoirs to climate change, agricultural demand, and tourism: A case study from Sardinia. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrent, J.; Barberis, E.; Gil-Sotres, F. Agriculture as a source of phosphorus for eutrophication in southern Europe. Soil Use Manag. 2007, 23 (Suppl. S1), 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Romshoo, S.H. Impact of anthropogenic activities on water quality of Lidder River in Kashmir Himalayas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4705–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharip, Z.; Zakaria, S. Lakes and reservoir in Malaysia: Management and research challenges. In Proceedings of the 12th World Lake Conference, Jaipur, India, 28 October–2 November 2007; Sengupta, M., Dalwani, R., Eds.; International Lake Environment Committee: Shiga, Japan, 2007; pp. 1349–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Mu, L.; Dai, L. Water quality of Lugu Lake: Changes, causes and measurements. Int. J. Sust. Dev. World Ecol. 2010, 15, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurence, W.F.; Sayer, J.; Cassman, K.G. Agricultural expansion and its impacts on tropical nature. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Global environmental impacts of agricultural expansion: The need for sustainable and efficient practices. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5995–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kateb, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Mosandl, R. Soil erosion and surface runoff on different vegetation covers and slope gradients: A field experiment in Southern Shaanxi Province, China. Catena 2013, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delang, C.O.; Yuan, Z. China’s Grain for Green Program; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–213. [Google Scholar]
- Rozelle, S. Grain to Green: Cost-effectiveness and sustainability of China’s conservations set-aside program. Land Econ. 2005, 81, 247–264. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fu, B.; Gao, G. Redlines for the greening of China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 33, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, G.; Barnett, J. China’s ambitious ecological red lines. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Krajewski, W.F.; Helmers, M.J.; Zhang, Z. Spatial variability and temporal persistence of event runoff coefficients for cropland hillslopes. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, B.; Nover, D.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Chen, W. Farm ponds in southern China: Challenges and solutions for conserving a neglected wetland ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Yin, C.; Tang, H. Nutrient retention by multipond systems: Mechanisms for the control of nonpoint source pollution. J. Environ. Q. 1998, 27, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salin, K.R.; Ataguba, G.A. Aquaculture and the environment: Towards sustainability. In Sustainable Aquaculture; Hai, F.I., Visvanathan, C., Boopathy, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; De Silva, S.S. Inland aquaculture: Trends and prospects. In Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends; Gui, J., Tang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, J., De Silva, S.S., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Simonit, S.; Perrings, C. Sustainability and the value of the ‘regulating’ services: Wetlands and water quality in Lake Victoria. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangsu Liyang Tianmu Lake Ecological Restoration Project. Available online: http://www.cn-natural.com/EN/pro3301.html (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- White, D.; Fennessy, S. Modeling the suitability of wetland restoration potential at the watershed scale. In Wetland Creation, Restoration and Conservation. The State of Science; Mitsch, W.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 359–378. [Google Scholar]
- Kusler, J.A.; Kentula, M.E. (Eds.) Wetland Creation and Restoration. The Status of Science; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Royer, T.V.; Tank, J.L.; David, M.B. Transport and fate of nitrate in headwater agricultural streams in Illinois. J. Environ. Q. 2004, 33, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccini, F.; Paliaga, G.; Piana, P.; Sacchini, A.; Watkins, C. The Bisagno stream catchment (Genoa, Italy) and its major floods: Geomorphic and land use variations in the last three centuries. Geomorphology 2016, 273, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, P.; Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Sacchini, A.; Watkins, C. Geomorphological landscape research and flood management in a heavily modified Tyrrhenian catchment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; de Jesus, C.; Boonchuwong, P.; Mohottala, K. The role of reservoir and lacustrine fisheries in rural development: Comparative evidence from Sri Lanka, Thailand and the Philippines. In Reservoir and Culture-based Fisheries: Biology and Management; De Silva, S., Ed.; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: Canberra, Australia, 2001; pp. 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Tianmu Lake Basin Ecological Observation Research Station Officially Unveiled. Available online: http://www.niglas.cas.cn/xwdt_1/zhxw/201712/t20171227_4923531.html (accessed on 29 May 2019). (In Chinese).
- Newsome, D.; Moore, S.A.; Dowling, R.K. Natural Area Tourism; Channel View Publications: Clevedon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 2018 National Economic and Social Development Statistics Bulletin, Xin’an County. Available online: http://www.qdh.gov.cn/art/2019/4/3/art_1388507_31968483.html?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg (accessed on 9 August 2019). (In Chinese)
- Ho, S.C. Status of limnological research and training in Malaysia. In Limnology in Developing Countries; Gopal, B., Wetzel, R.G., Eds.; International Association for Limnology: New Delhi, India, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 163–189. [Google Scholar]
- Baluyut, E.A. Introduction of fish stocking in lakes and reservoirs in South East Asia: A review. In Fish and Fisheries of Lakes and Reservoirs in Southeast Asia and Africa; van Dense, L.T., Morris, M.J., Eds.; Westbury Publishing: Otley, UK, 1999; pp. 117–141. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, S. (Ed.) Reservoir and Culture-based Fisheries: Biology and Management; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: Canberra, Australia, 2001; pp. 1–390. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).