Identifying the Drivers of Water Consumption in Single-Family Households in Joinville, Southern Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
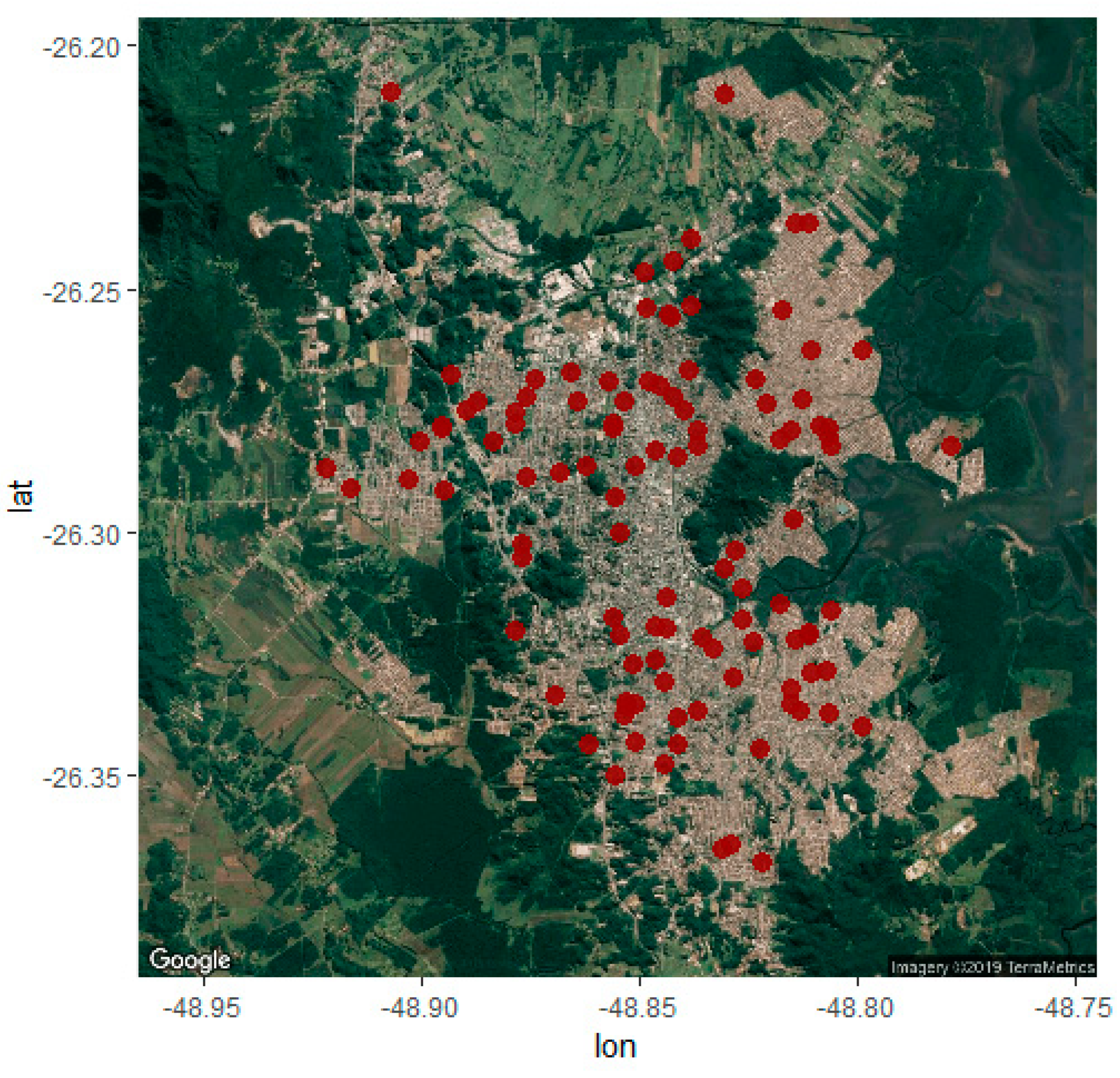
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Plan
2.2. Questionnaire Survey
2.3. Explanatory Data and Correlation Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
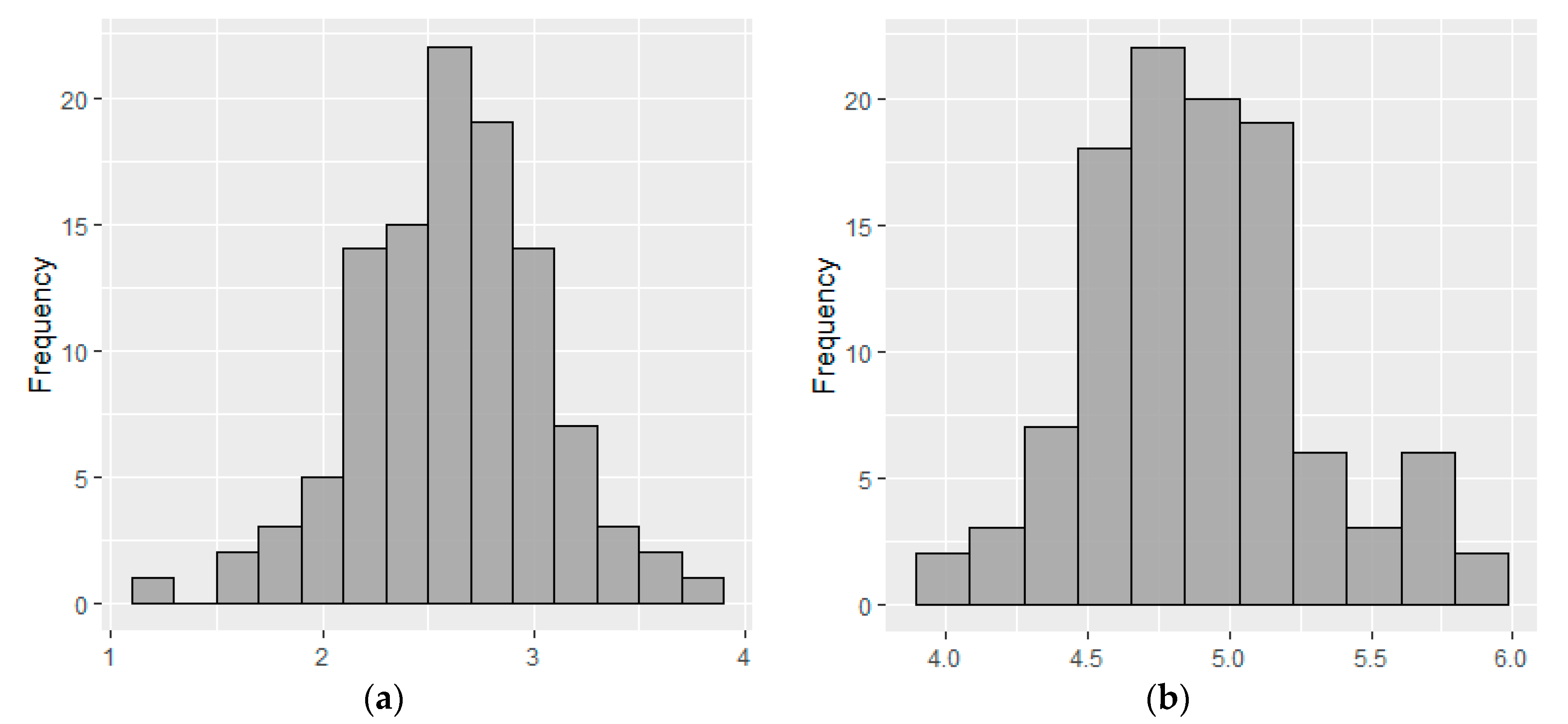
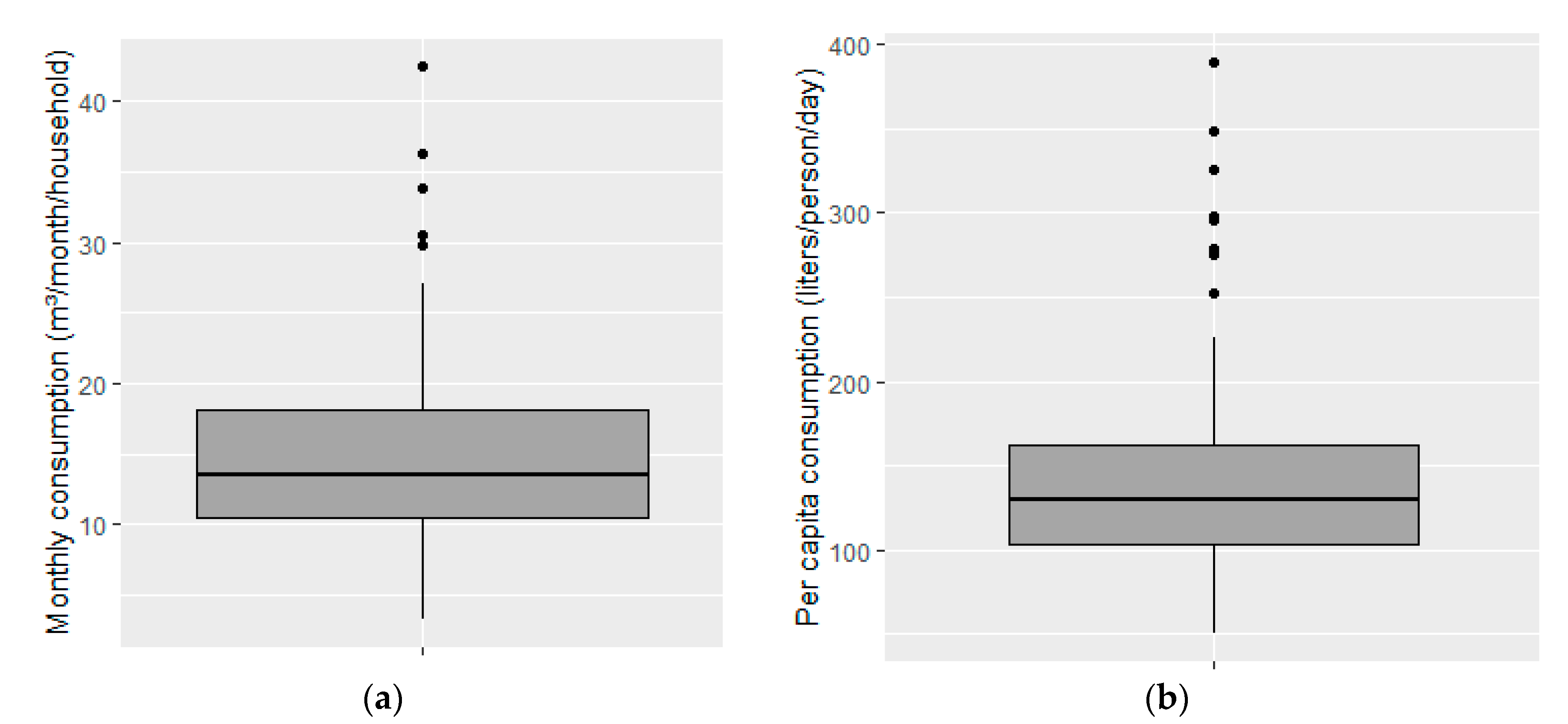
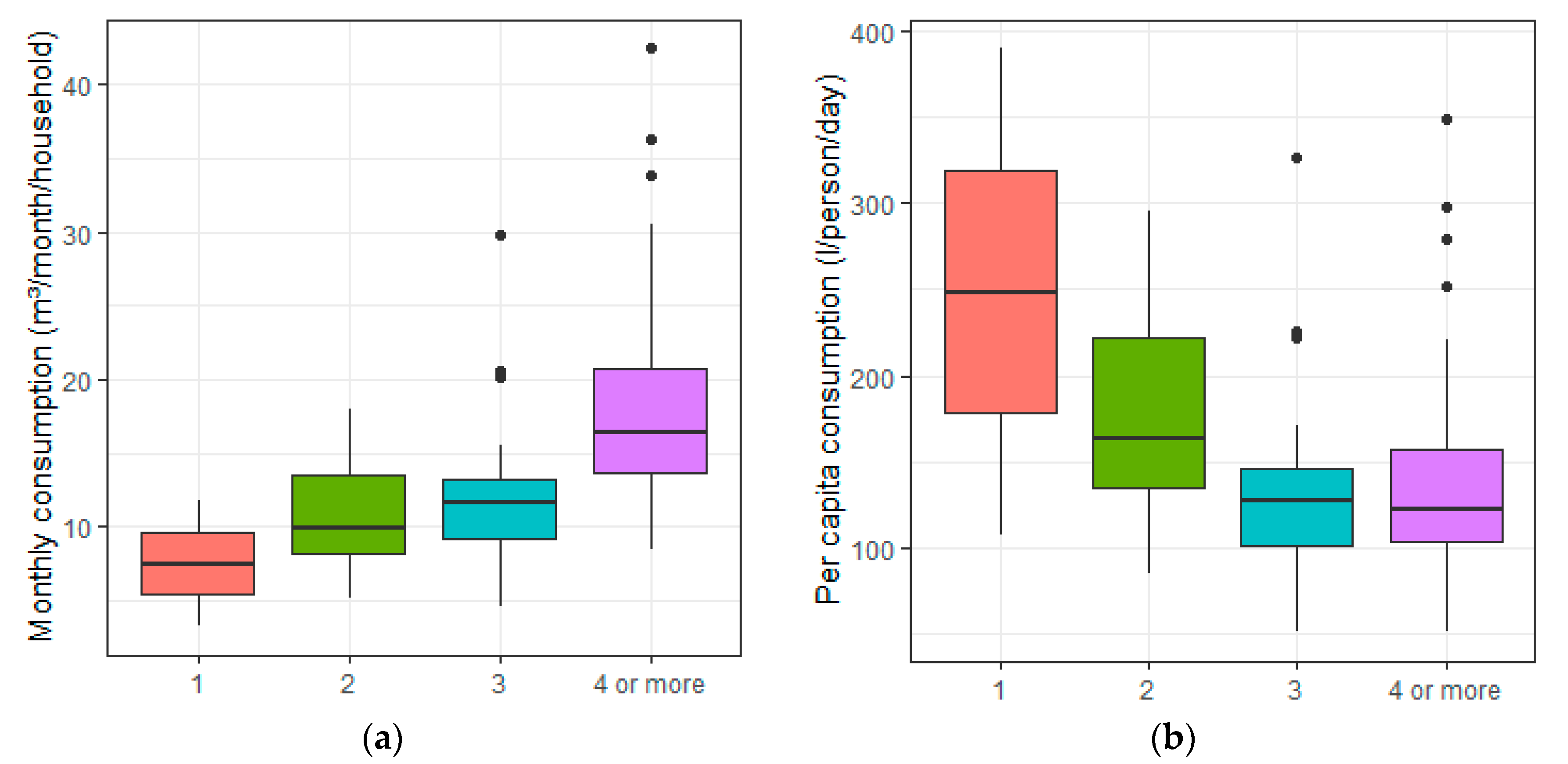
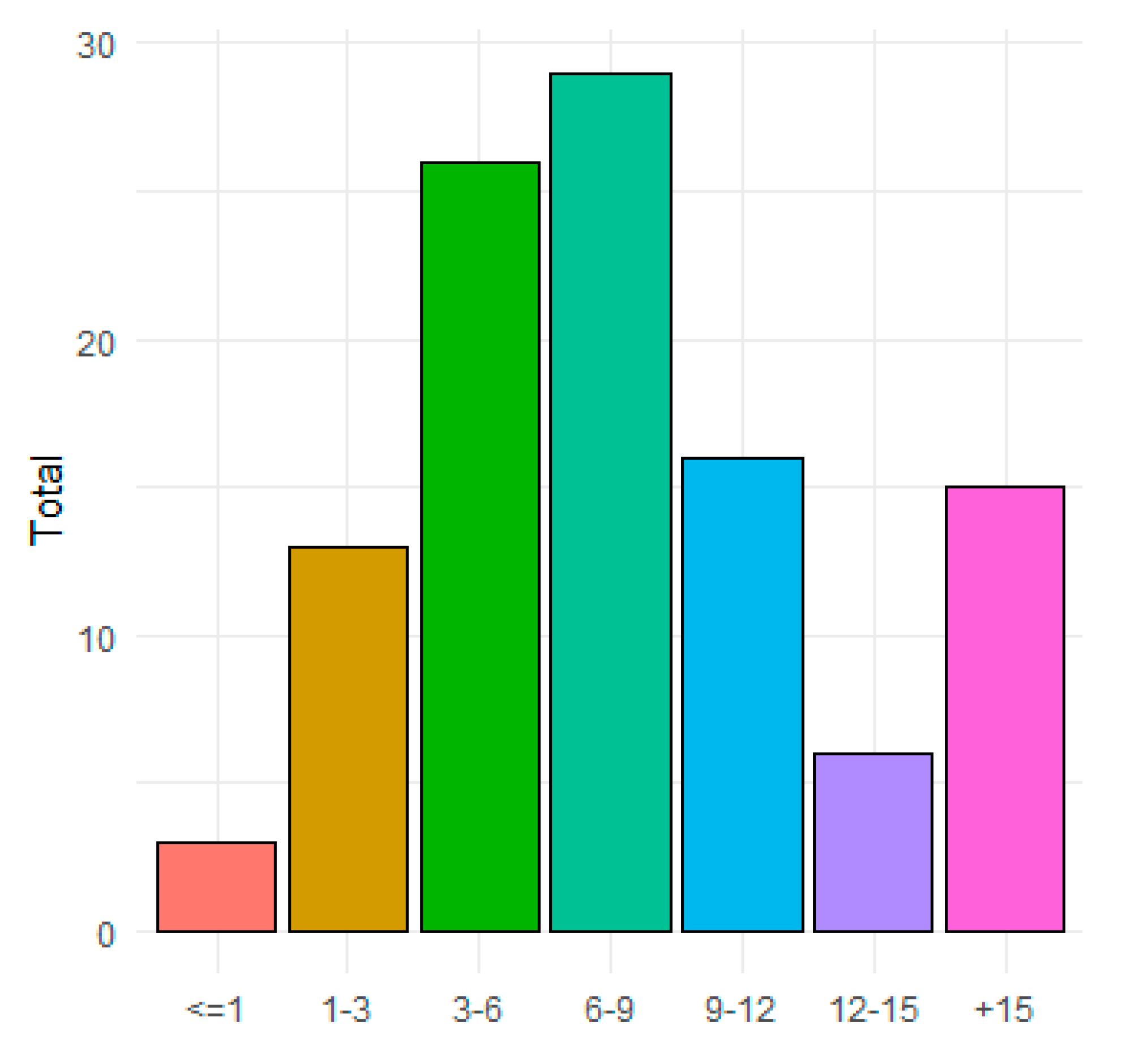
3.1. Water Consumption
3.2. Correlation Between Variables
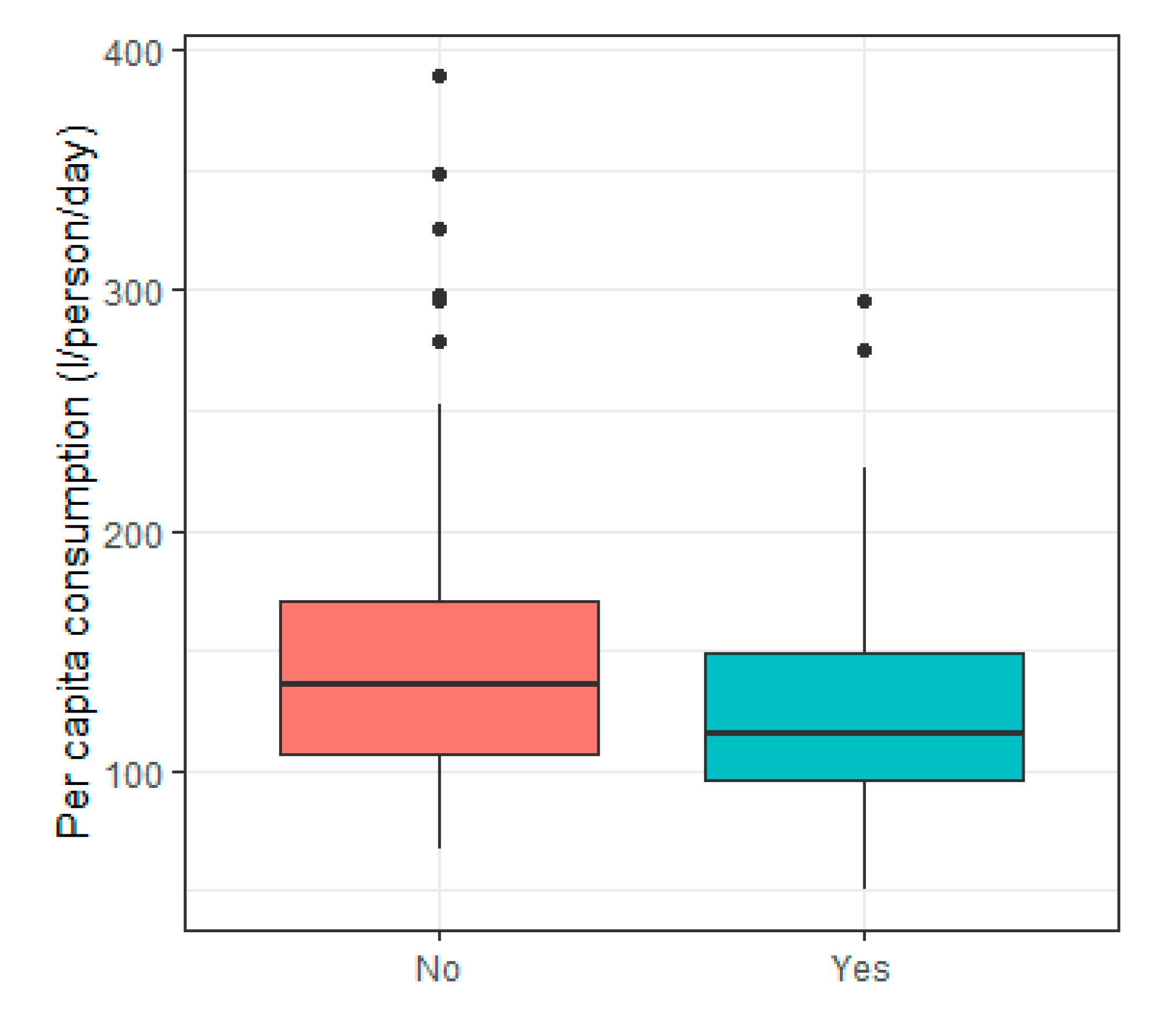
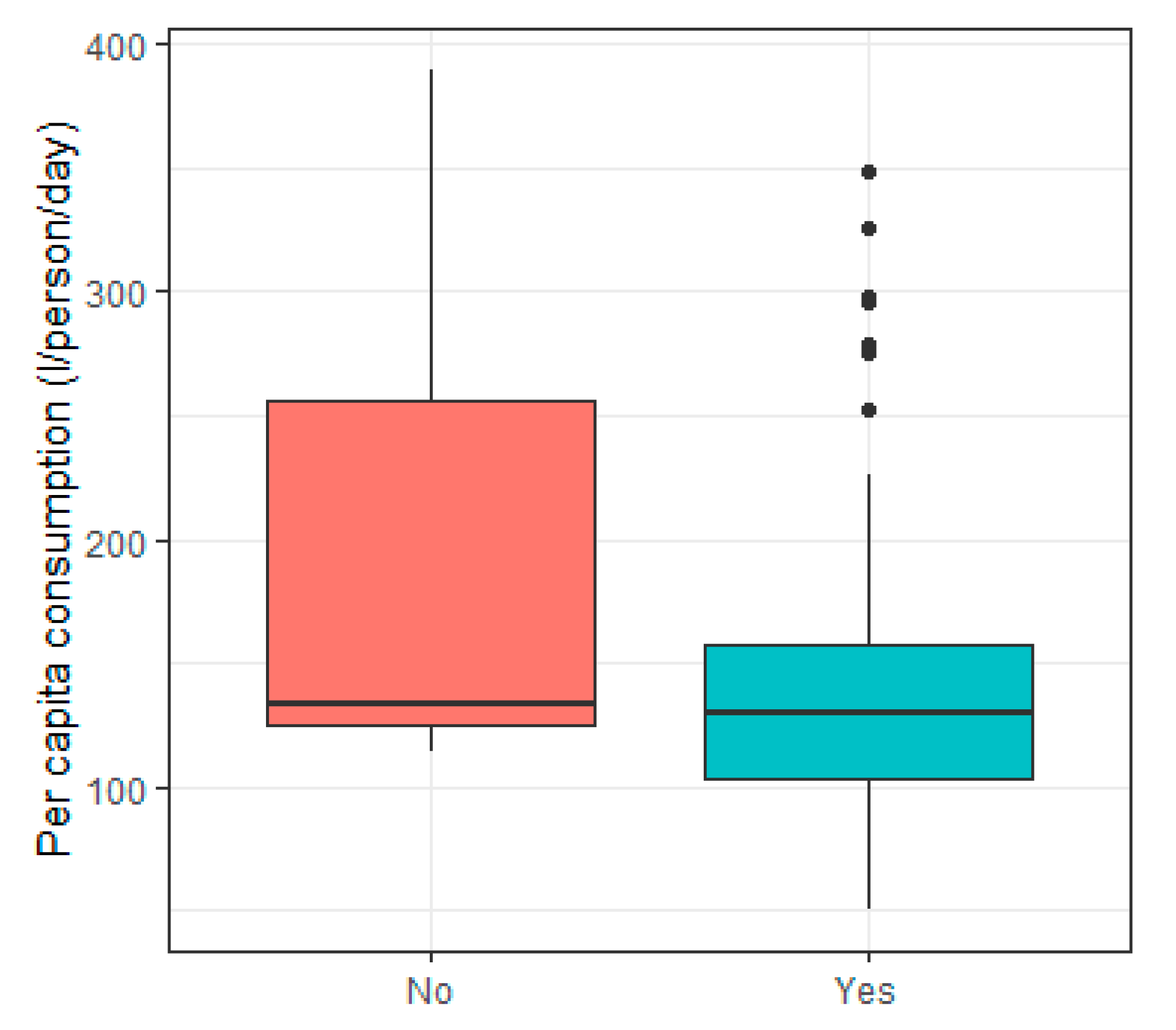
3.3. Surrounding Infrastructure
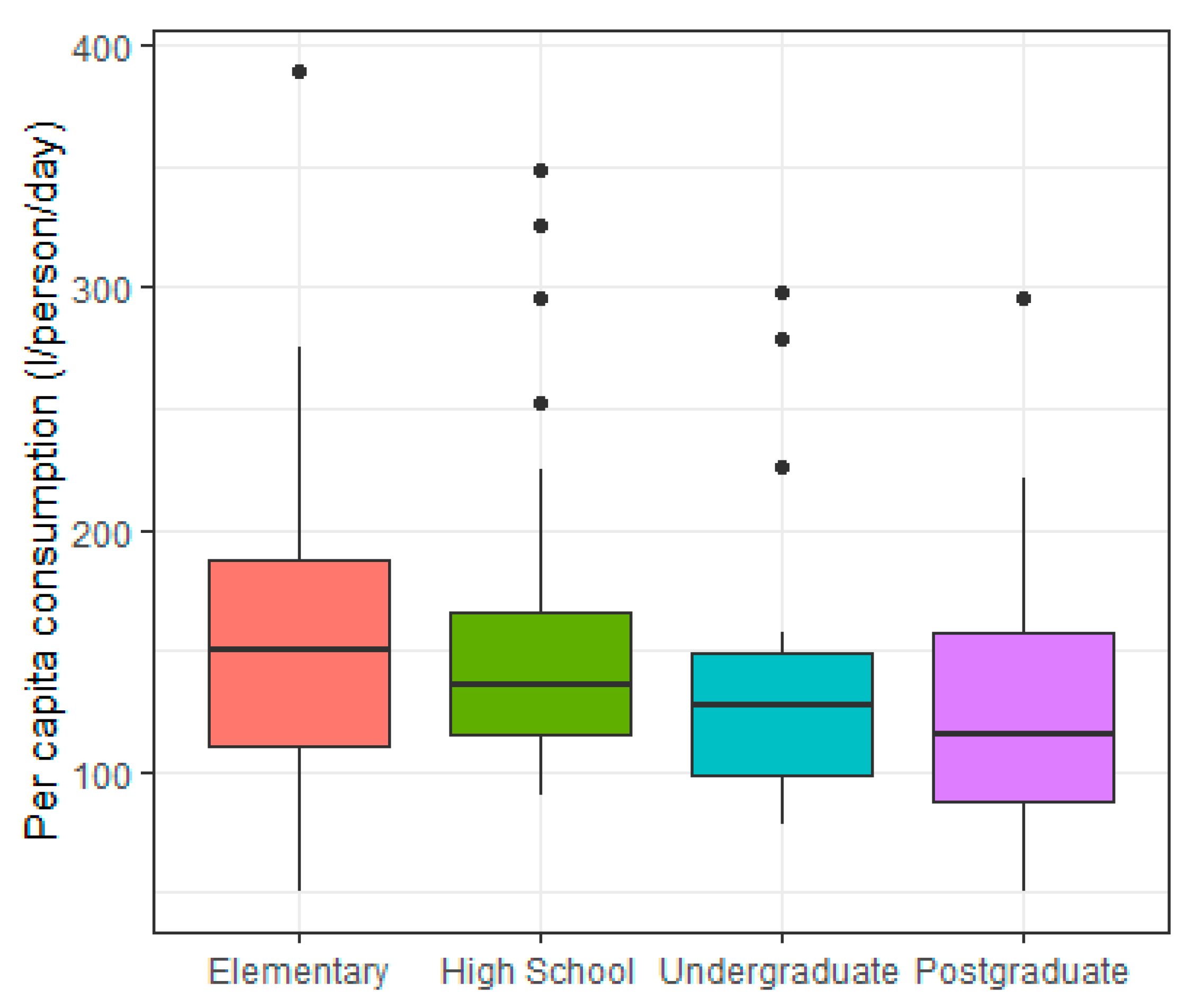
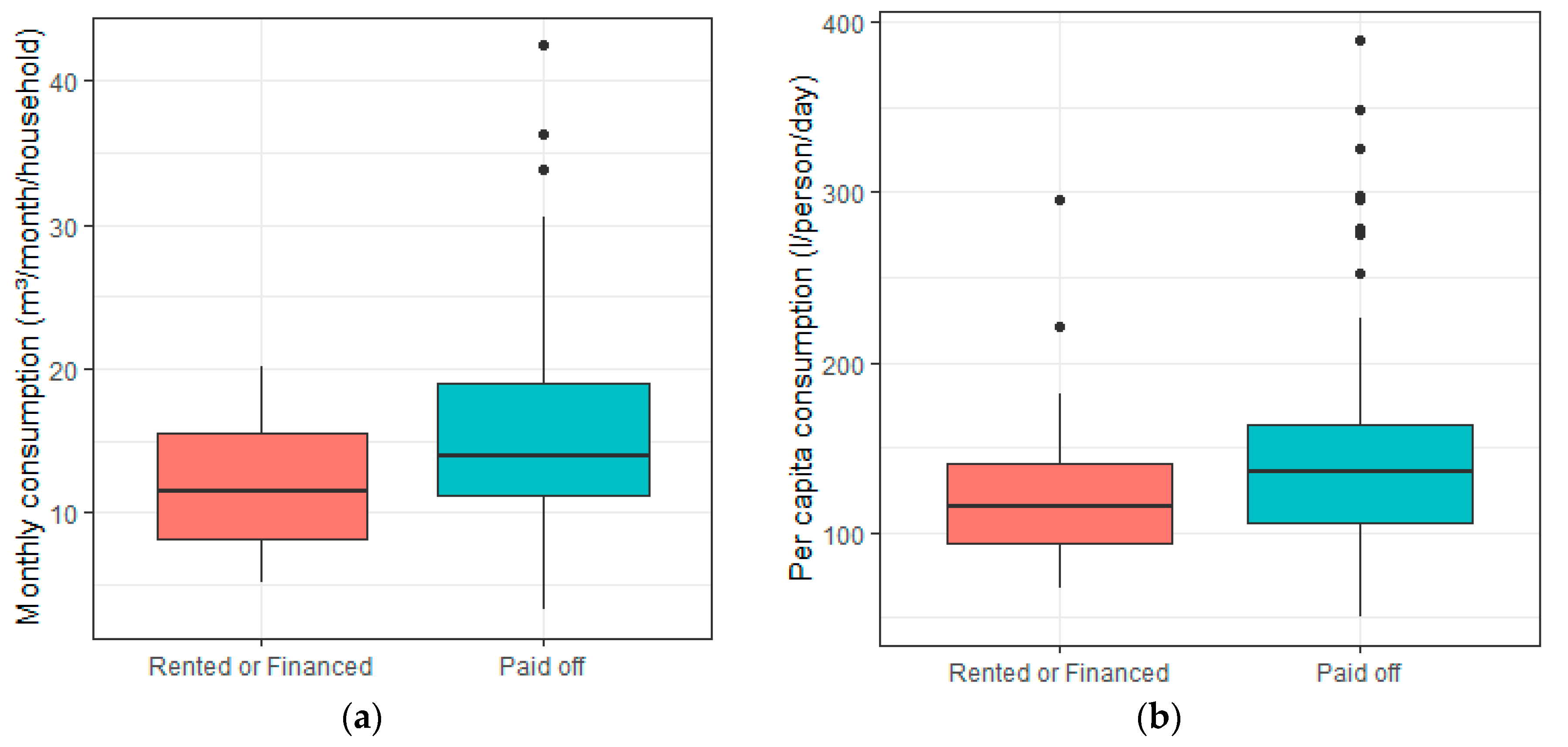
3.4. Socioeconomic and Demographic Characteristics
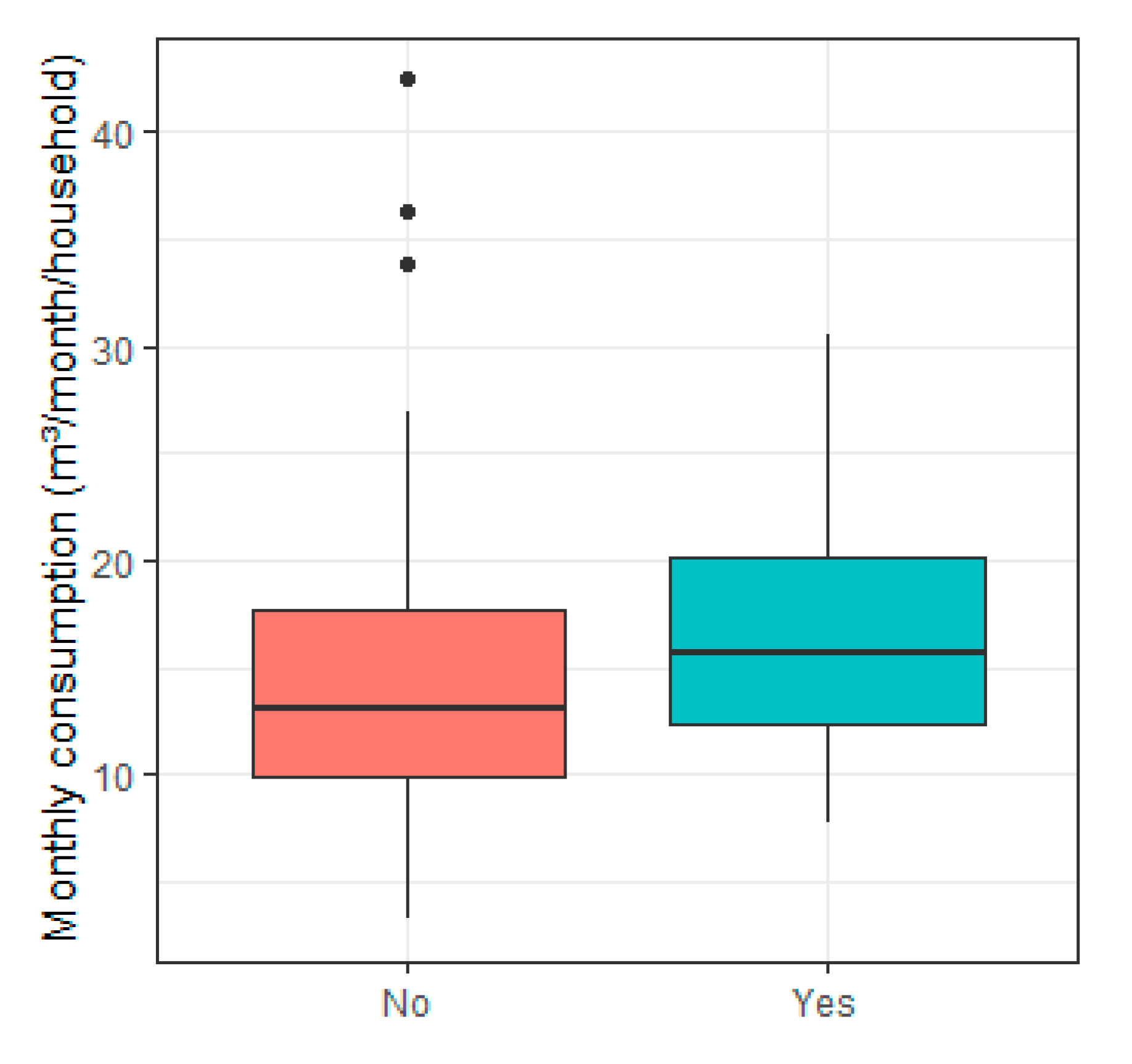
3.5. Constructive Features
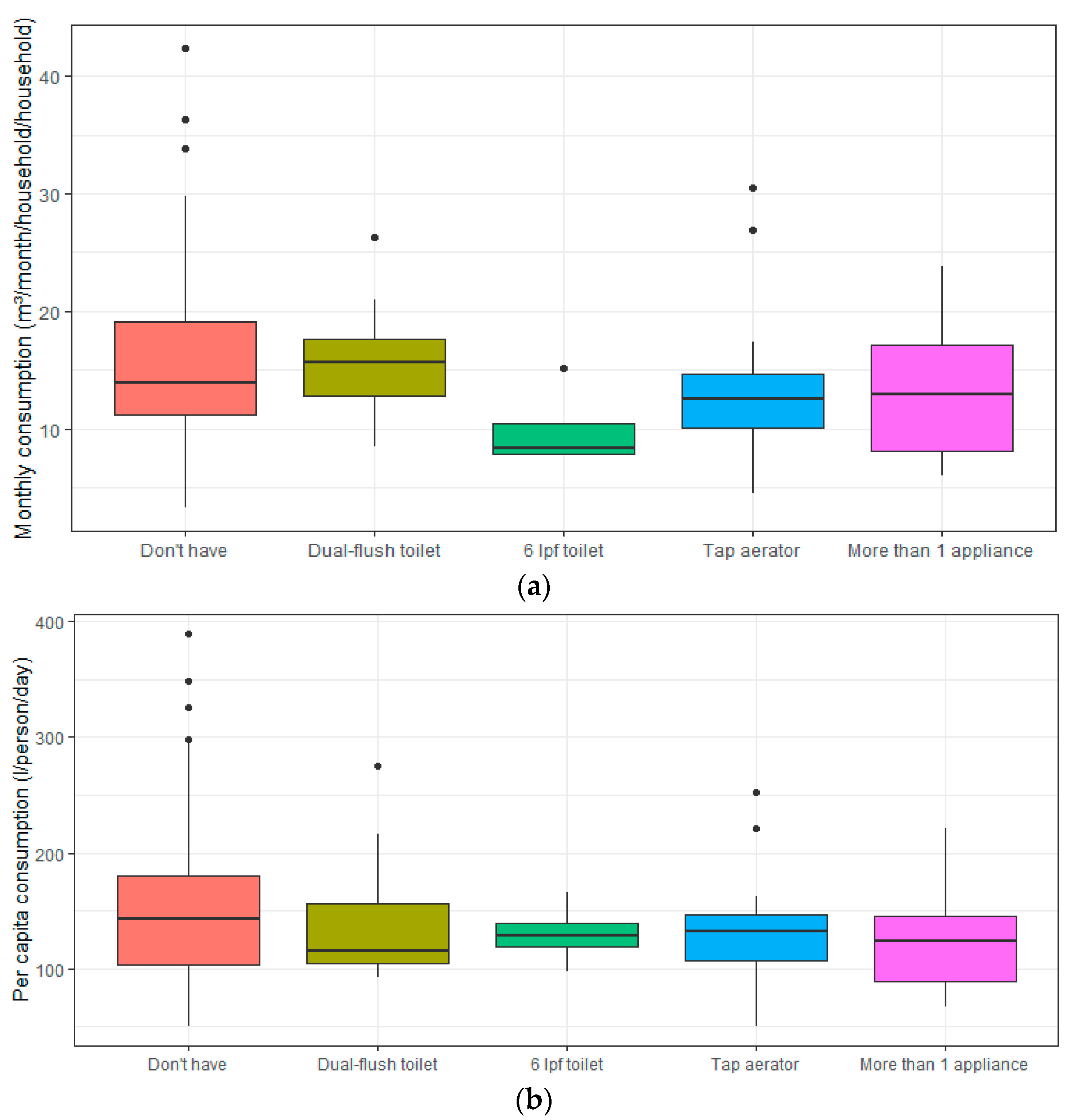
3.6. Installed Fixtures
3.7. Water-Use Habits
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adapa, S. Factors influencing consumption and anti-consumption of recycled water: Evidence from Australia. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN OCHA. Water Scarcity and Humanitarian Action: Key Emerging Trends and Challenges Brief; Policy Development and Studies Branch: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: https://www.unocha.org/es/publication/policy-briefs-studies/water-scarcity-and-humanitarian-action-key-emerging-trends-and (accessed on 2 June 2019).
- Marinoski, A.K.; Rupp, R.F.; Ghisi, E. Environmental benefit analysis of strategies for potable water savings in residential buildings. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, R.M.; Stewart, R.A.; Giurco, D.P.; Talebpour, M.R.; Mousavinejad, A. End use water consumption in households: Impact of socio-demographic factors and efficient devices. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 60, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, R.M.; Stewart, R.A.; Panuwatwanich, K.; Williams, P.R.; Hollingsworth, A.L. Quantifying the influence of environmental and water conservation attitudes on household end use water consumption. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauges, C.; Whittington, D. Estimation of water demand in developing countries: An overview. World Bank Res. Obs. 2009, 25, 263–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, W.A.; Memon, F.A.; Savic, D.A. Assessing and Modelling the Influence of Household Characteristics on Per Capita Water Consumption. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2931–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Gai, L.; Tong, Y.; Li, R. Urban water consumption and its influencing factors in China: Evidence from 286 cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Ana, D.; Mazzega, P. Socioeconomic analysis of domestic water end-use consumption in the Federal District, Brazil. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, A.O.; Alvarez-Chavez, C.R.; Ramos-Corella, M.A.; Soto-Hernandez, F. Determinants of domestic water consumption in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domene, E.; Saurí, D. Urbanisation and water consumption: Influencing factors in the metropolitan region of Barcelona. Urban Stud. 2006, 43, 1605–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontokosta, C.E.; Jain, R.K. Modeling the determinants of large-scale building water use: Implications for data-driven urban sustainability policy. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 18, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Salvati, N.; Guerrini, A. An empirical analysis of the determinants of water demand in Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 130, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, S.M.; Farias, M.M.M.W.E.C. Potential for rainwater harvesting in a dry climate: Assessments in a semiarid region in northeast Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPPUJ. Joinville Cidade em Dados 2018—Ambiente Construído. 2018. Available online: https://www.joinville.sc.gov.br/publicacoes/joinville-cidade-em-dados-2018/ (accessed on 21 January 2019).
- IBGE. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. 2018. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/sc/joinville/panorama (accessed on 21 January 2019).
- IBGE. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. 2010. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/sc/joinville/panorama (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- SANTA CATARINA. Secretaria de Estado da Fazenda. 2012. Available online: http://www.sef.sc.gov.br/ (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Galloway, A. Non-Probability Sampling. Encycl. Soc. Meas. 2005, 2, 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A Power Primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufféry, S. Data Mining and Statistics for Decision Making; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- R CORE TEAM. R: A language and Environment for Statistical Computing and Graphics; Version 3.4.3; The R Foundation: Auckland, New Zealand, 2019; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 18 June 2019).
- Lewis-Beck, M.S.; Bryman, A.; Liao, T.F. The SAGE Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldink, N.J. Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisi, E.; Oliveira, S.M. Potential for potable water savings by combining the use of rainwater and greywater in houses in southern Brazil. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Salvati, N.; Guerrini, A. Estimating the determinants of residential water demand in Italy. Water 2014, 5, 2929–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL. Lei n. 8.069 de 13 de Julho de 1990. Dispõe Sobre o Estatuto da Criança e do Adolescente e dá Outras Providências. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/l8069.htm (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- BRASIL. Lei n. 10.741 de 1 de Outubro de 2003. Dispõe Sobre o Estatuto do Idoso e dá Outras Providências. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/2003/l10.741.htm (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Pérez-Urdiales, M.; García-Valiñas, M.Á. Efficient water-using technologies and habits: A disaggregated analysis in the water sector. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 128, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.F.; Kalbusch, A.; Henning, E. Factors influencing water consumption in buildings in southern Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F.C.; Rueda, T.M.; Les, S.O. Cuadernos de I+D+I 4: Microcomponentes y Factores Explicativos del Consumo Doméstico de Agua en la Comunidad de Madrid. Canal de Isabel II. Available online: http://www.madrid.org/bvirtual/BVCM008675.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2019).
- Mayer, P.W.; DeOreo, W.B. Residential End Uses of Water; AWWARF: Denver, CO, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, M.; Coghlan, P. Domestic Water Use Study; Water Corporation: Perth, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, J.M.P.; Bocasanta, S.L.; Ávila, B.O.; Magtoto, M.; Jonck, A.V.; Gabriel, G.M.; De Andrade Guerra, J.B.S.O. The adoption of strategies for sustainable cities: A comparative study between Seattle and Florianopolis legislation for energy and water efficiency in buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domene, E.; Saurí, D.; Parés, M. Urbanization and Sustainable Resource Use: The Case of Garden Watering in the Metropolitan Region of Barcelona. Urban Geogr. 2005, 26, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, S.H.A.; Van Dorssen, A.J.; Brouwer, S. Enhancing domestic water conservation behavior: A review of empirical studies on influencing tatics. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavenhagen, M.; Buurman, J.; Tortajada, C. Saving water in cities: Assessing policies for residential water demand management in four cities in Europe. Cities 2018, 79, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, T.; Schaeffer, R.; Lucena, A.F.P.; Melo, S.; Dutra, R. Solar water heating technical economic potential in the household sector in Brazil. Renew. Energy 2019, 146, 1618–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardemil, J.M.; Starke, A.R.; Colle, S. Multi-objective optimization for reducing the auxiliary electric energy peak in low cost solar domestic hot-water heating systems in Brazil. Sol. Energy 2018, 163, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Variable | Minimum | 1st Quartile | Median | Mean | 3rd Quartile | Maximum | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly water consumption (m3/month/household) | 3.25 | 10.46 | 13.56 | 15.01 | 18.12 | 42.42 | 6.669 |
| Per capita water consumption (liters/person/day) | 50.64 | 103.68 | 130.36 | 144.91 | 162.06 | 389.54 | 63.370 |
| N | Description | LN Monthly Water Consumption | LN Per Capita Water Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | |||
| Surrounding infrastructure | |||
| 1 | Existence of public sewage collection system | - | −0.278 a |
| Socioeconomic and demographic characteristics | |||
| 2 | Total number of residents | 0.479 a | −0.283 a |
| 3 | Number of women | 0.204 a | −0.208 a |
| 4 | Educational level of the person responsible for the water bill | - | −0.226 a |
| 5 | House property (rented or financed) | −0.342 a | −0.233 b |
| Constructive features | |||
| 6 | Number of bathrooms | 0.237 a | - |
| 7 | Logarithm of building age (years) | 0.168 b | - |
| 8 | Built area (m2)—includes house area, garage, and shed | 0.288 a | 0.184 b |
| 9 | Presence of reservoir | - | −0.346 a |
| 10 | Water shortage in the household | 0.225 b | 0.254 a |
| Installed fixtures | |||
| 11 | Presence of water-efficient appliances (dual-flush toilets, 6 liters per flush toilet or tap aerators) | - | −0.217 b |
| 12 | Presence of aerators | −0.237 b | −0.226 b |
| 13 | Presence of 6 liters per flush toilets | −0.251 b | - |
| Consumption habits | |||
| 14 | Water reuse from washing machine | −0.239 b | - |
| 15 | Use of high-pressure washer for washing the car | 0.258 a | - |
| 16 | Use of high-pressure washer for washing outdoor areas | 0.318 a | - |
| 17 | Use of irrigator for garden watering | 0.382 a | 0.288 b |
| Characteristics | min | Median | Mean | Max | sd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of residents | 1 | 4 | 3.537 | 6 | 1.018 |
| # of women | 0 | 2 | 1.852 | 4 | 0.783 |
| # of children | 0 | 0 | 0.315 | 3 | 0.651 |
| # of teenagers | 0 | 0 | 0.231 | 2 | 0.466 |
| # of adults | 1 | 3 | 2.833 | 5 | 0.881 |
| # of elderly | 0 | 0 | 0.130 | 2 | 0.364 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, J.; Salfer, L.R.; Kalbusch, A.; Henning, E. Identifying the Drivers of Water Consumption in Single-Family Households in Joinville, Southern Brazil. Water 2019, 11, 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101990
Garcia J, Salfer LR, Kalbusch A, Henning E. Identifying the Drivers of Water Consumption in Single-Family Households in Joinville, Southern Brazil. Water. 2019; 11(10):1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101990
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Janine, Luis Ricardo Salfer, Andreza Kalbusch, and Elisa Henning. 2019. "Identifying the Drivers of Water Consumption in Single-Family Households in Joinville, Southern Brazil" Water 11, no. 10: 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101990
APA StyleGarcia, J., Salfer, L. R., Kalbusch, A., & Henning, E. (2019). Identifying the Drivers of Water Consumption in Single-Family Households in Joinville, Southern Brazil. Water, 11(10), 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101990







