Sediment Transport Mechanisms in a Lagoon with High River Discharge and Sediment Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. In Situ Suspended Sediment Concentration (SSC) Data Collection
3.2. The Modeling System
3.3. Model Set-up
- CAL: Simulation for model calibration for the period from 1 January 2013 until the end of 2015. Only the results for the year 2014–2015 were analyzed. The year 2013 was used as a spin up period.
- VAL: Simulation for model validation for the period 1 January 2015 until the end of 2016. The year 2015 was used as a spin up period.
- NoICE: Three-year-long simulation for analysis of ice influence on the sediment transport mechanisms in the Curonian Lagoon. Simulation period and set-up are the same as simulation CAL, but without ice cover data.
- LONG: Long-term simulation (13 years) for analysis of the sediment transport mechanisms in the Curonian Lagoon. Simulation period 2004–2016.
4. Results
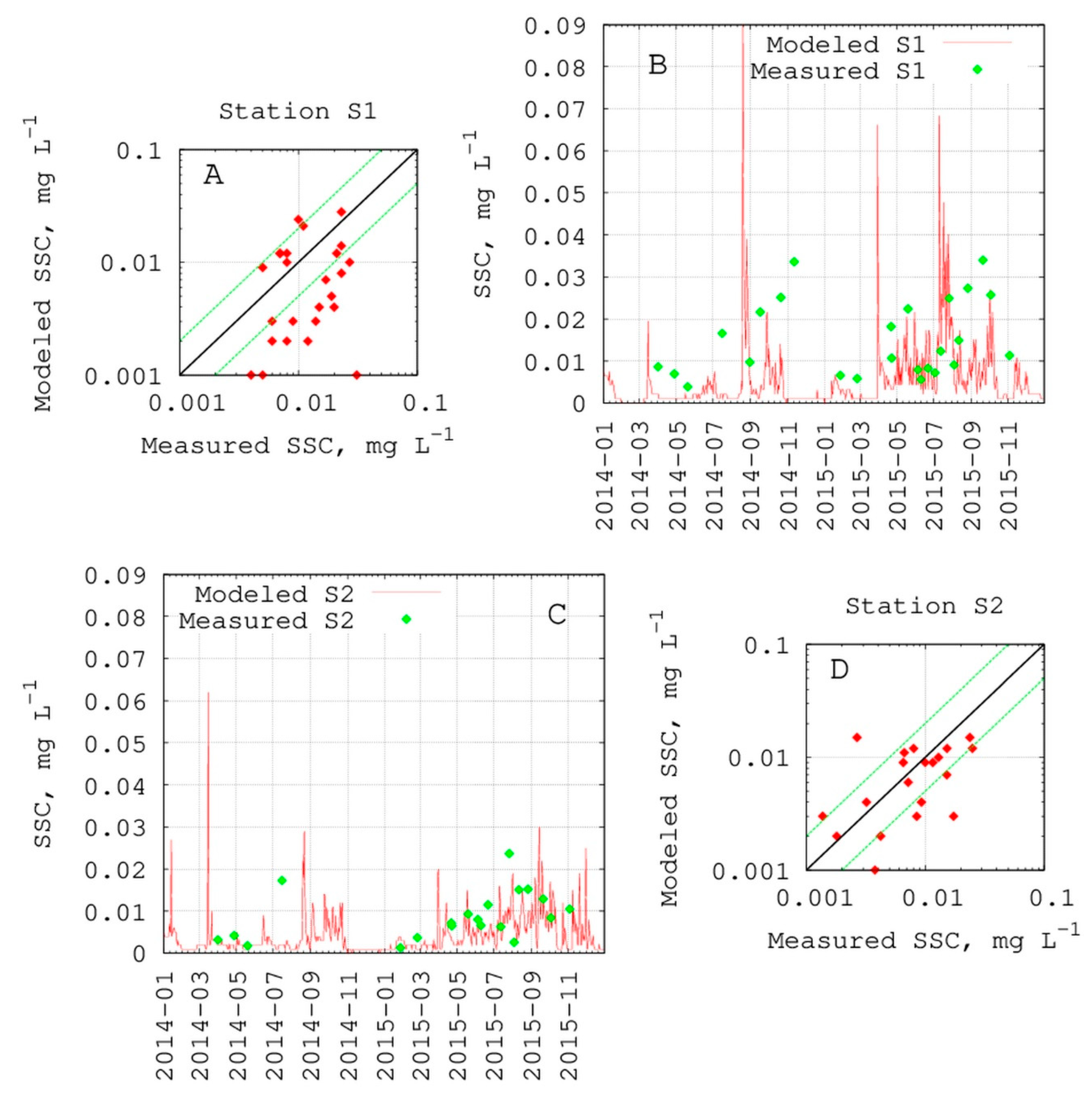
4.1. In Situ Suspended Sediment Observations
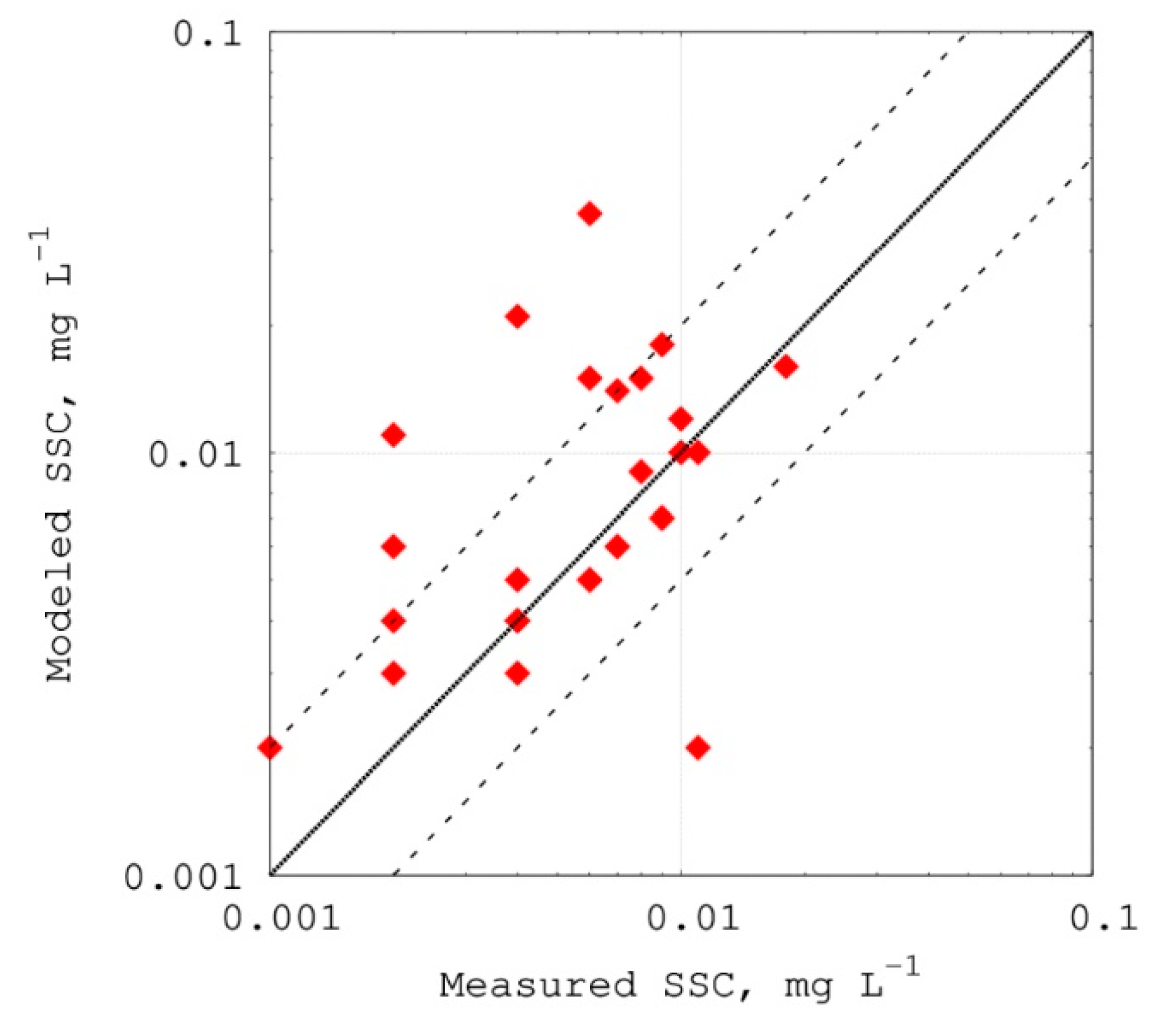
4.2. Model Calibration and Validation
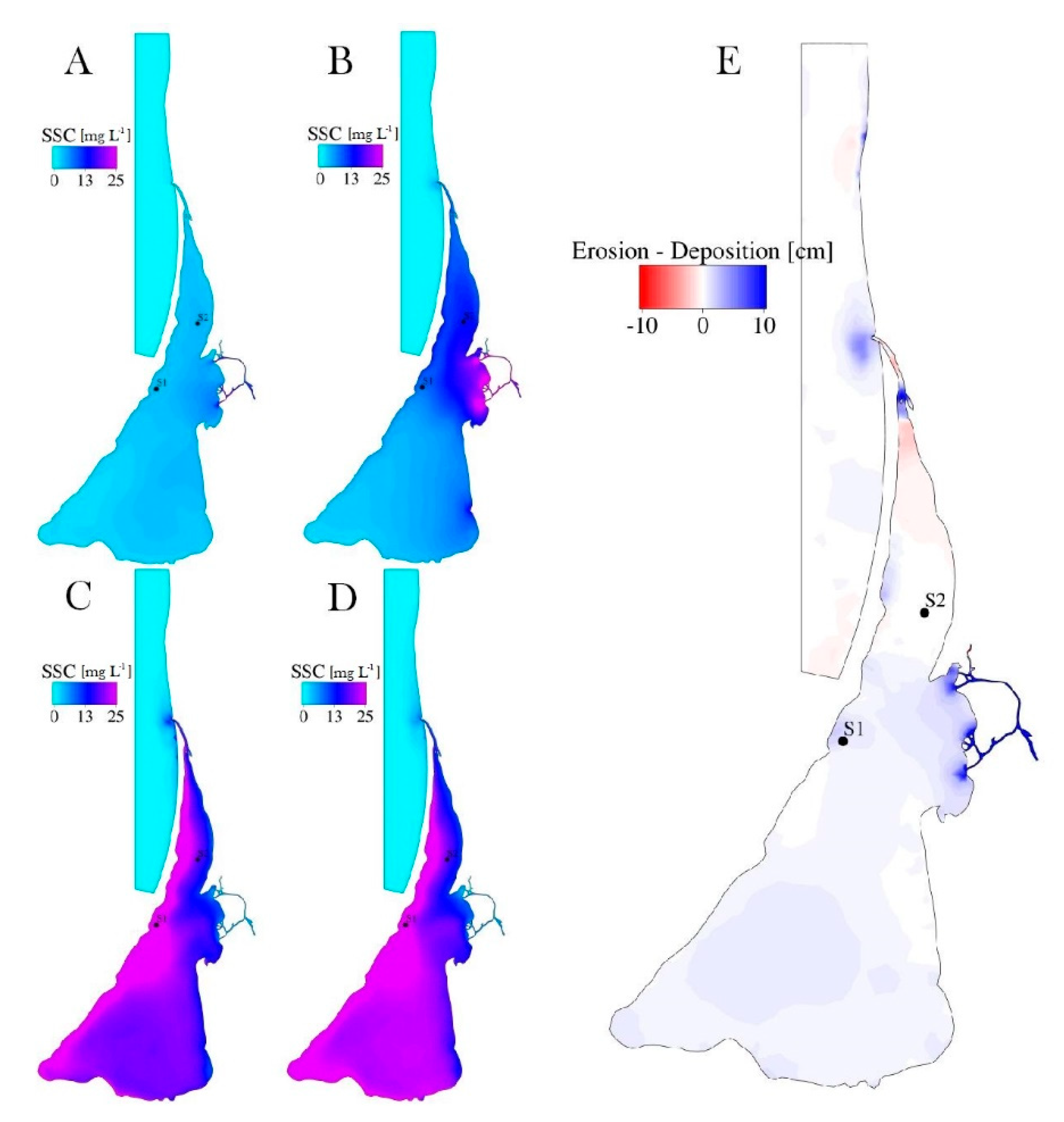
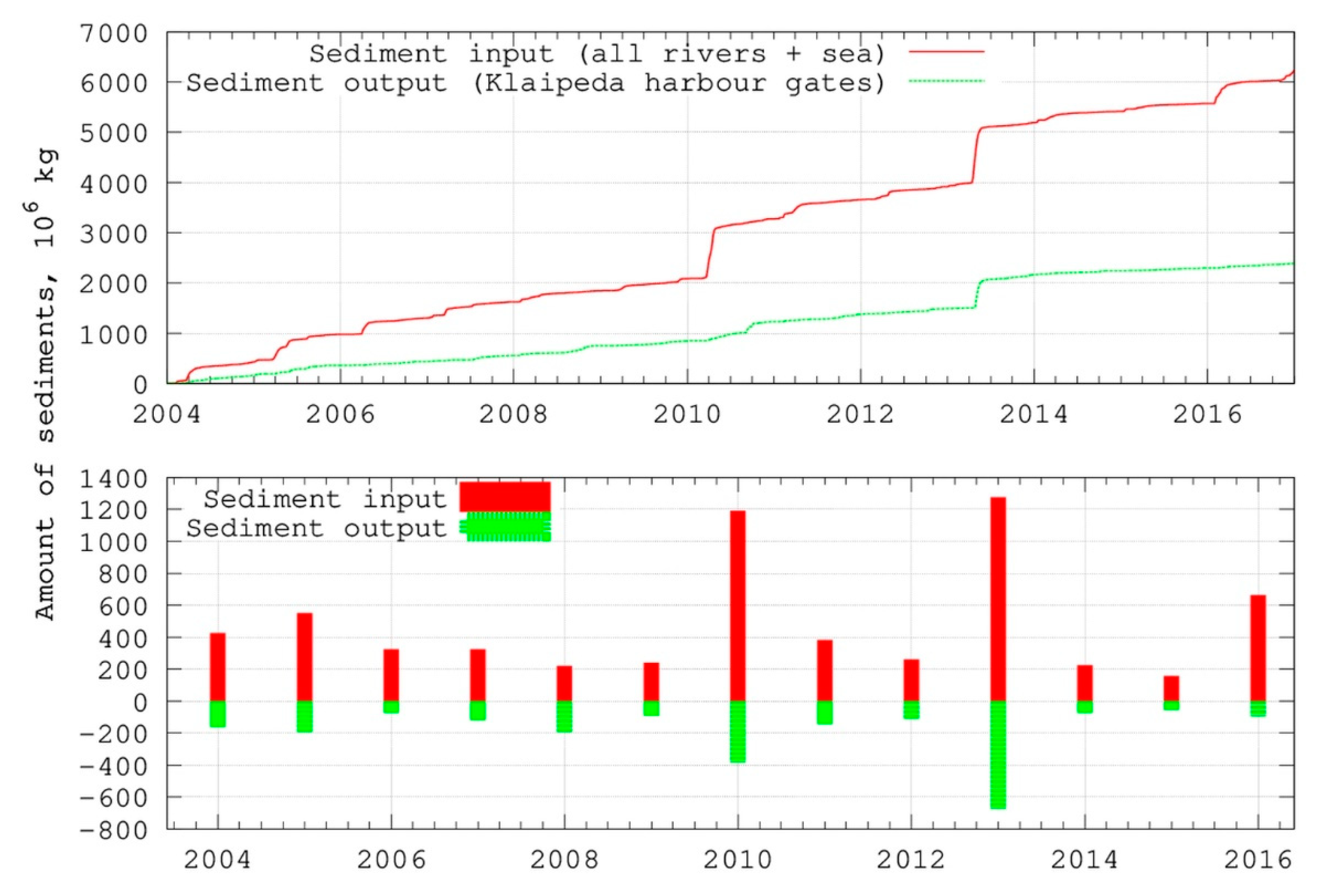
4.3. Long-Term Simulation Results
5. Discussion
5.1. In Situ Data and Sediment Rating Curve
5.2. An Introduced Formula for Settling Velocity
5.3. Analysis of Model Calibration and Validation Results
5.4. Factors Controlling Suspended Sediment Distribution
5.4.1. Impact of Ice Cover
5.4.2. Impact of Stormy Wind
5.5. Erosion-Accumulation Zones in the Curonian Lagoon
5.6. Model Results for Sediment Budget Calculation
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, Z.-G. Hydrodynamics and Water Quality; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-1-11-887715-9. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenreich, S.J.; Bernasconi, C. Climate Change and the European Water Dimension; EU Report No. 21553; Joint Research Center of European Commission: Ispra, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Maicu, F.; De Pascalis, F.; Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G. Hydrodynamics of the Po River-Delta-Sea System. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 6349–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, V.; Trincardi, F. Man made deltas. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Kettner, A. Sediment flux and the anthropocene. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 957–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, C.A.; Velásquez-Montoya, L. Modeling the sediment dynamics in the gulf of Urabá colombian Caribbean sea. Ocean Eng. 2017, 147, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.G.; Jin, K.R. Impacts of wind waves on sediment transport in a large, shallow lake. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2014, 19, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, B.; Lund-Hansen, L.C.; Beloshitskii, A. Comparative analyses of potential wind-wave impact on bottom sediments in the Vistula and Curonian lagoons. Baltica 2002, 15, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Teeter, A.M.; Johnson, B.H.; Berger, C.; Stelling, G.; Scheffner, N.W.; Garcia, M.H.; Parchure, T.M. Hydrodynamic and sediment transport modeling with emphasis on shallow-water, vegetated areas (lakes, reservoirs, estuaries and lagoons). Hydrobiologia 2001, 444, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataržytė, M.; Mėžinė, J.; Vaičiūtė, D.; Liaugaudaitė, S.; Mukauskaitė, K.; Umgiesser, G.; Schernewski, G. Fecal contamination in shallow temperate estuarine lagoon: Source of the pollution and environmental factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilius, M.; De Wit, R.; Bartoli, M. Response of sedimentary processes to cyanobacteria loading. J. Limnol. 2016, 75, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Swart, H.E.; Zimmerman, J.T.F. Morphodynamics of Tidal Inlet Systems. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, B.; Chechko, V.; Kileso, A.; Krek, E.; Topchaya, V. Hydrological and sedimentation conditions in a non-tidal lagoon during ice coverage – The example of Vistula Lagoon in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 216, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechko, V.A.; Topchaya, V.Y.; Chubarenko, B.V.; Pilipchuk, V.A. Distribution and composition of suspended matter in water and snow cover in Kaliningrad Bay. Water Resour. 2016, 43, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechko, V.A.; Blazchishin, A.I. Bottom deposits of the Vistula lagoon of the Baltic Sea. Baltica 2002, 15, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Galkus, A. Vandens cirkuliacija ir erdvine drumstumo dinamika vasara Kuršių marių ir Baltijos jūros Lietuvos akvatorijose [Summer water circulation and spatial turbidity dynamics in the Lithuanian waters of Curonian lagoon and Baltic Sea]. Geogr. Metrašt. 2003, 36, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Galkus, A.; Jokšas, K. Nuosėdinė Medžiaga Tranzitinėje Akvasistemoje [Sedimentary Material in the Transitional Aquasystem]; Institute of Geography: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1997; ISBN 9986909775.
- Pustelnikovas, O. Geochemistry of Sediments of the Curonian Lagoon (Baltic Sea); Institute of Geography: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1998; ISBN 978-9-98-690976-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pustelnikovas, O. Transport and accumulation of sediment and contaminants in the Lagoon of Kuršiu{ogonek}marios (Lithuania) and Baltic Sea. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 1994, 28, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimonis, E.; Gulbinskas, S.; Kuzavinis, M. The Curonian Lagoon bottom sediments in the Lithuanian water area. Baltica 2003, 16, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarin, C.; Razinkovas, A.; Gulbinskas, S.; Umgiesser, G.; Bliudžiute, L. Hydraulic regime-based zonation scheme of the Curonian Lagoon. Hydrobiologia 2008, 611, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemlys, P.; Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G.; Gulbinskas, S.; Bellafiore, D. Investigation of saline water intrusions into the Curonian Lagoon (Lithuania) and two-layer flow in the Klaipeda Strait using finite element hydrodynamic model. Ocean Sci. 2013, 9, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Zemlys, P.; Erturk, A.; Razinkovas-Baziukas, A.; Mėžinė, J.; Ferrarin, C. Seasonal renewal time variability in the Curonian Lagoon caused by atmospheric and hydrographical forcing. Ocean Sci. 2016, 12, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C. A Sediment Transport Model for the Lagoon of Venice; Universiteta Ca’Foscari: Venezia, Italia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Gailiušis, B.; Rimavičiūtė, E. Modelling of shoreface nourishment in the Lithuanian nearshore of the Baltic Sea. Geologija 2006, 53, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Gailiušis, B. Changes of Sediment Transport Induced by Reconstruction of Kalipėda seaport Entrance Channel. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2004, 2, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Žaromskis, R. Okeanai, Jūros ir Estuarijos [Oceans, Seas, Estuaries]; Debesija: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1996; ISBN 9986652022. [Google Scholar]
- Zilius, M.; Vybernaite-Lubiene, I.; Vaiciute, D.; Petkuviene, J.; Zemlys, P.; Liskow, I.; Voss, M.; Bartoli, M.; Bukaveckas, P.A. The influence of cyanobacteria blooms on the attenuation of nitrogen throughputs in a Baltic coastal lagoon. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkaityte, R.; Razinkovas, A. Seasonal changes in phytoplankton composition and nutrient limitation in a shallow Baltic lagoon. Boreal Environ. Res. 2007, 12, 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Gasiūnaitė, Z.R.; Daunys, D.; Olenin, S.; Razinkovas, A. The Curonian Lagoon. In Ecology of Baltic Coastal Waters; Schiewer, U., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 197–215. ISBN 978-3-54-073524-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gelumbauskaitė, L.Ž.; Grigelis, A.; Cato, I.; Repečka, M.; Kjellin, B. Bottom Topography and Sediment Maps of the Central Baltic Sea: Scale 1: 500,000. A Short Description. LGT Ser. Mar. Geol. Maps No. 1/SGU Ser. Geol. Maps Ba No. 54. Available online: https://www.dmu.dk/1_Viden/2_Miljoe-tilstand/3_vand/4_Charm/charm_res/data/WP1/Deliverable9/charm_all%20maps.htm (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Gulbinskas, S.; Žaromskis, R. The Curonian Lagoon Map for Fishery M 1:50 000; Lithuanian Deparment of Fisheries: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gailiušis, B.; Kovalenkovienė, M.; Jurgelėnaitė, A. Klaipėdos sąsiaurio tėkmės planinės struktūros pokyčių modeliavimas [Water balance of the Curonian Lagoon]. Energetika 1992, 2, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jakimavičius, D. Changes of Water Balance Elements of the Curonian Lagoon and Their Forecast Due to Anthropogenic and Natural Factors. Ph.D.Thesis, Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dailidiene, I.; Davuliene, L. Salinity trend and variation in the Baltic Sea near the Lithuanian coast and in the Curonian Lagoon in 1984–2005. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 74, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimonis, E.; Vaikutiene, G.; Gulbinskas, S. Seasonal and spatial variations of sedimentary matter and diatom transport in the Klaipėda Strait (Eastern Baltic). Baltica 2010, 23, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pustelnikovas, O. On the Eastern Baltic environment changes: A case study of the Curonian Lagoon area. Geologija 2008, 50, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T. A Practical Hand Book of Seawater Analysis, 2nd ed.; Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972; ISBN 978-0-66-011596-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Humphrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochemie und Physiologie der Pflanzen 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-0-08-030287-4. [Google Scholar]
- Catherine, A.; Escoffier, N.; Belhocine, A.; Nasri, A.B.; Hamlaoui, S.; Yéprémian, C.; Bernard, C.; Troussellier, M. On the use of the FluoroProbe ®, a phytoplankton quantification method based on fluorescence excitation spectra for large-scale surveys of lakes and reservoirs. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Ferrarin, C.; Cucco, A.; De Pascalis, F.; Bellafiore, D.; Ghezzo, M.; Bajo, M. Comparative hydrodynamics of 10 Mediterranean lagoons by means of numerical modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 2212–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Canu, D.M.; Cucco, A.; Solidoro, C. A finite element model for the Venice Lagoon. Development, set up, calibration and validation. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, U.; Ferrarin, C.; Amos, C.L.; Umgiesser, G.; Li, M.Z. Sedtrans05: An improved sediment-transport model for continental shelves and coastal waters with a new algorithm for cohesive sediments. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1223–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Cucco, A.; Umgiesser, G.; Bellafiore, D.; Amos, C.L. Modelling fluxes of water and sediment between Venice Lagoon and the sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G.; Cucco, A.; Hsu, T.W.; Roland, A.; Amos, C.L. Development and validation of a finite element morphological model for shallow water basins. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Umgiesser, G.; Roland, A.; Bajo, M.; De Pascalis, F.; Ghezzo, M.; Scroccaro, I. Sediment dynamics and budget in a microtidal lagoon—A numerical investigation. Mar. Geol. 2016, 381, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CERC. Shore Protection Manual: Volume I and II; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-8-57-811079-6.
- Van Ledden, M.; Van Kesteren, W.G.M.; Winterwerp, J.C. A conceptual framework for the erosion behaviour of sand-mud mixtures. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas; Aqua Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; ISBN 9080035629. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Z.; Amos, C.L. SEDTRANS96: The upgraded and better calibrated sediment-transport model for continental shelves. Comput. Geosci. 2001, 27, 619–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulsby, R. Dynamics of Marine Sands: A Manual for Practical Applications; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Funkquist, L. A unified model system for the Baltic Sea. Elsevier Oceanogr. Ser. 2003, 69, 516–518. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.L. Power of Flow Resistance in Open Channels; Manning’s Formula Revisited. In Channel Flow Resistance: Centennial of Manning’s Formula; Yen, B.C., Ed.; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-1-88-720-180-3. [Google Scholar]
- Vaikasas, S. Nemuno Žemupio Potvynių Tėkmių ir Nešmenų Dinamikos Modeliavimas [Flood Dynamics and Sedimentation-Diffusion Processes in the Lowland of the River Nemunas]; Technika: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2009; ISBN 978-9-95-528539-7. [Google Scholar]
- Idzelytė, R.; Kozlov, I.E.; Umgiesser, G. Remote Sensing of Ice Phenology and Dynamics of Europe’s Largest Coastal Lagoon (The Curonian Lagoon). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselman, N.E.M. Fitting and interpretation of sediment rating curves. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, C.L.; Bergamasco, A.; Umgiesser, G.; Cappucci, S.; Cloutier, D.; DeNat, L.; Flindt, M.; Bonardi, M.; Cristante, S. The stability of tidal flats in Venice Lagoon—the results of in-situ measurements using two benthic, annular flumes. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 211–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.G.; Van Rijn, L.C.; Damgaard, J.S.; Van De Graaff, J.; Ribberink, J.S. Intercomparison of research and practical sand transport models. Coast. Eng. 2002, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukaveckas, P.A.; Katarzyte, M.; Schlegel, A.; Spuriene, R.; Egerton, T.; Vaiciute, D. Composition and settling properties of suspended particulate matter in estuaries of the Chesapeake Bay and Baltic Sea regions. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2580–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, F.; Lubarsky, H.; Gerbersdorf, S.U.; Paterson, D.M. Surface adhesion measurements in aquatic biofilms using magnetic particle induction: MagPI. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2009, 7, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkaityte, R.; Razinkovas, A. Factors controlling phytoplankton blooms in a temperate estuary: Nutrient limitation and physical forcing. Hydrobiologia 2006, 555, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, E.; Kratzer, S.; Beltrán-Abaunza, J.M.; Harvey, E.T.; Vaičiūtė, D. Retrieval of suspended particulate matter from turbidity–model development, validation, and application to MERIS data over the Baltic Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1983–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remeikaite-Nikiene, N.; Lujaniene, G.; Garnaga, G.; Jokšas, K.; Garbaras, A.; Skipityte, R.; Barisevičiute, R.; Šilobritiene, B.; Stankevičius, A. Distribution of trace elements and radionuclides in the Curonian Lagoon and the Baltic Sea. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/OES Baltic International Symposium (BALTIC) on Ocean: Past, Present and Future, Klaipeda, Lithuania, 8–10 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Leipe, T.; Eidam, J.; Reinhard, L.; Hinrich, M.; Neumann, T.; Osadczuk, A.; Janke, W.; Puff, T.; Blanz, T.; Gingele, F.X.; et al. Das Oderhaff, Beiträge zur Rekonstruktion der holozänen geologischen Entwicklung und antropogenen Beeinflus sung des Oder Ästuars. Mar. Sci. Rep. 1998, 28, 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tavora, J.; Fernandes, E.H.L.; Thomas, A.C.; Weatherbee, R.; Schettini, C.A.F. The influence of river discharge and wind on Patos Lagoon, Brazil, Suspended Particulate Matter. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 4506–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, J.A. Trend analyses with river sediment rating curves. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimkus, A.; Vaikasas, S. Mathematical Modeling of the Suspended Sediment Dynamics in the Riverbeds and Valleys of Lithuanian Rivers and Their Deltas. In Water Pollution; Balkis, N., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 105–124. ISBN 978-9-53-307962-2. [Google Scholar]
- Vaikasas, S.; Rimkus, A. Hydraulic Modelling of Suspended Sediment Deposition in an Inundated Floodplain of the Nemunas Delta. Hydrol. Res. 2003, 34, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, S.; Krek, A.; Bubnova, E.; Danchenkov, A. Eutrophication and effects of algal bloom in the south–western part of the Curonian Lagoon alongside the Curonian Spit. Baltica 2018, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, R.C.; Droppo, I.G.; Wharton, G. Erodibility of cohesive sediment: The importance of sediment properties. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BACC II Author Team. Second Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-31-916005-4. [Google Scholar]
- Čerkasova, N. Nemunas River Watershed Input to the Curonian Lagoon: Discharge, Microbiological Pollution, Nutrient and Sediment Loads under Changing Climate. Ph.D. Thesis, Klaipėda University, Klaipėda, Lithuania, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg, P.L.; Ernstsen, V.B.; Andersen, T.J.; Winter, C.; Becker, M.; Kroon, A. The effect of successive storm events and seagrass coverage on sediment suspension in a coastal lagoon. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 212, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report—IPCC; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978-9-29-169143-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chubarenko, B.V.; Chubarenko, I.P. New way of natural geomorphological evolution of the Vistula Lagoon due to crucial artificial influence. In Geology of the Gdansk Basin, Baltic Sea; Yantarny Skaz: Kaliningrad, Russia, 2001; pp. 372–375. [Google Scholar]
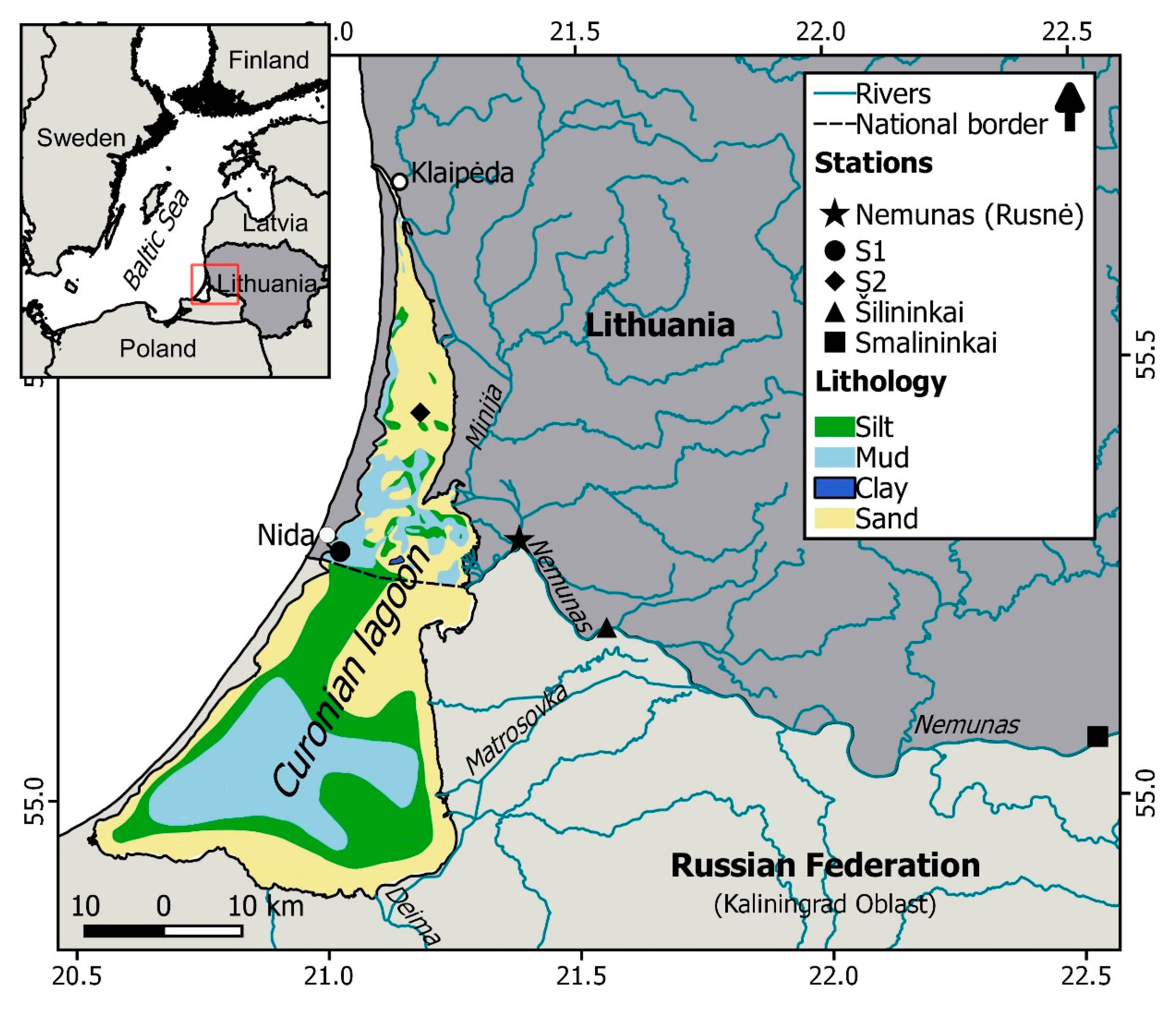
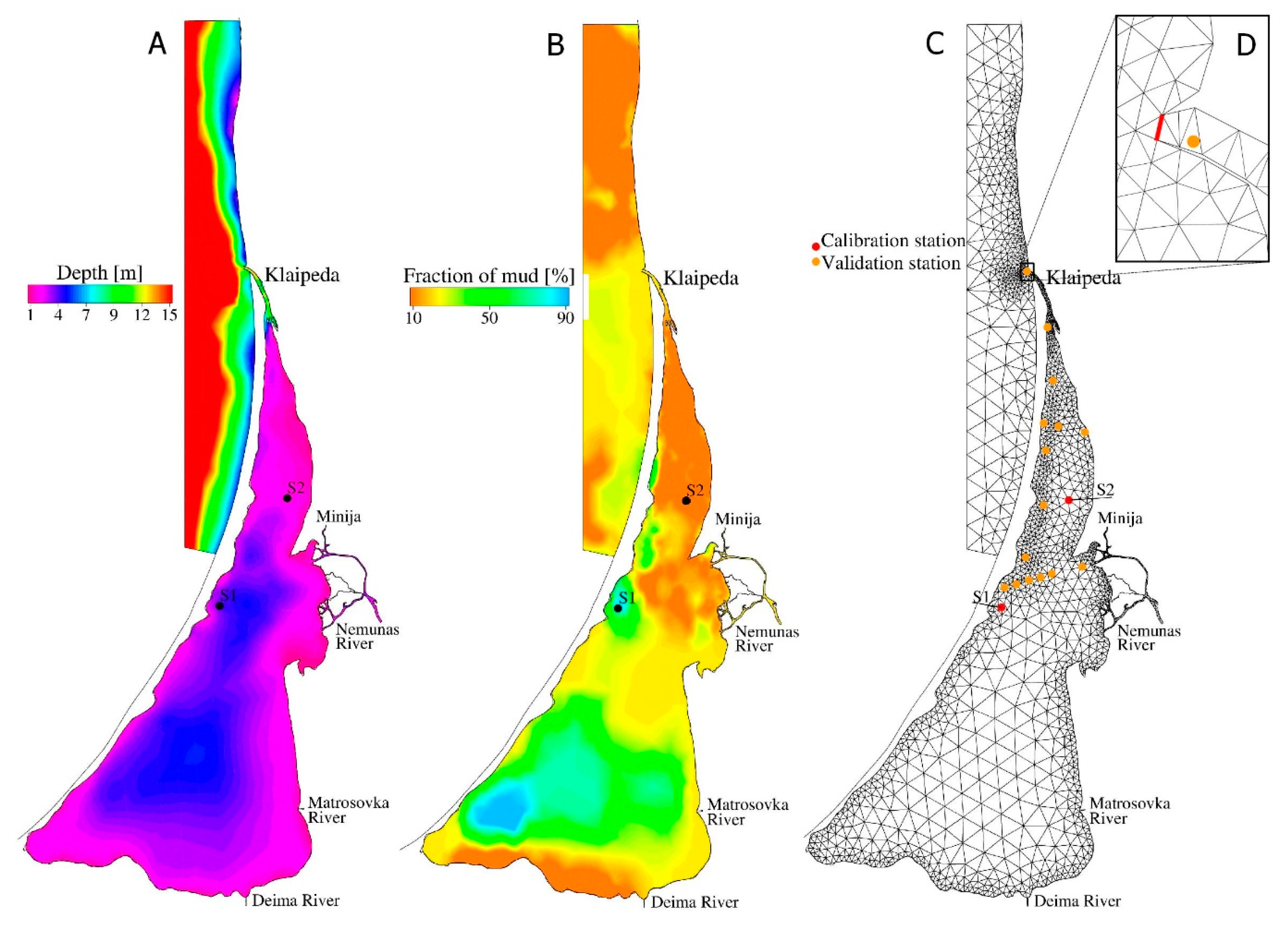
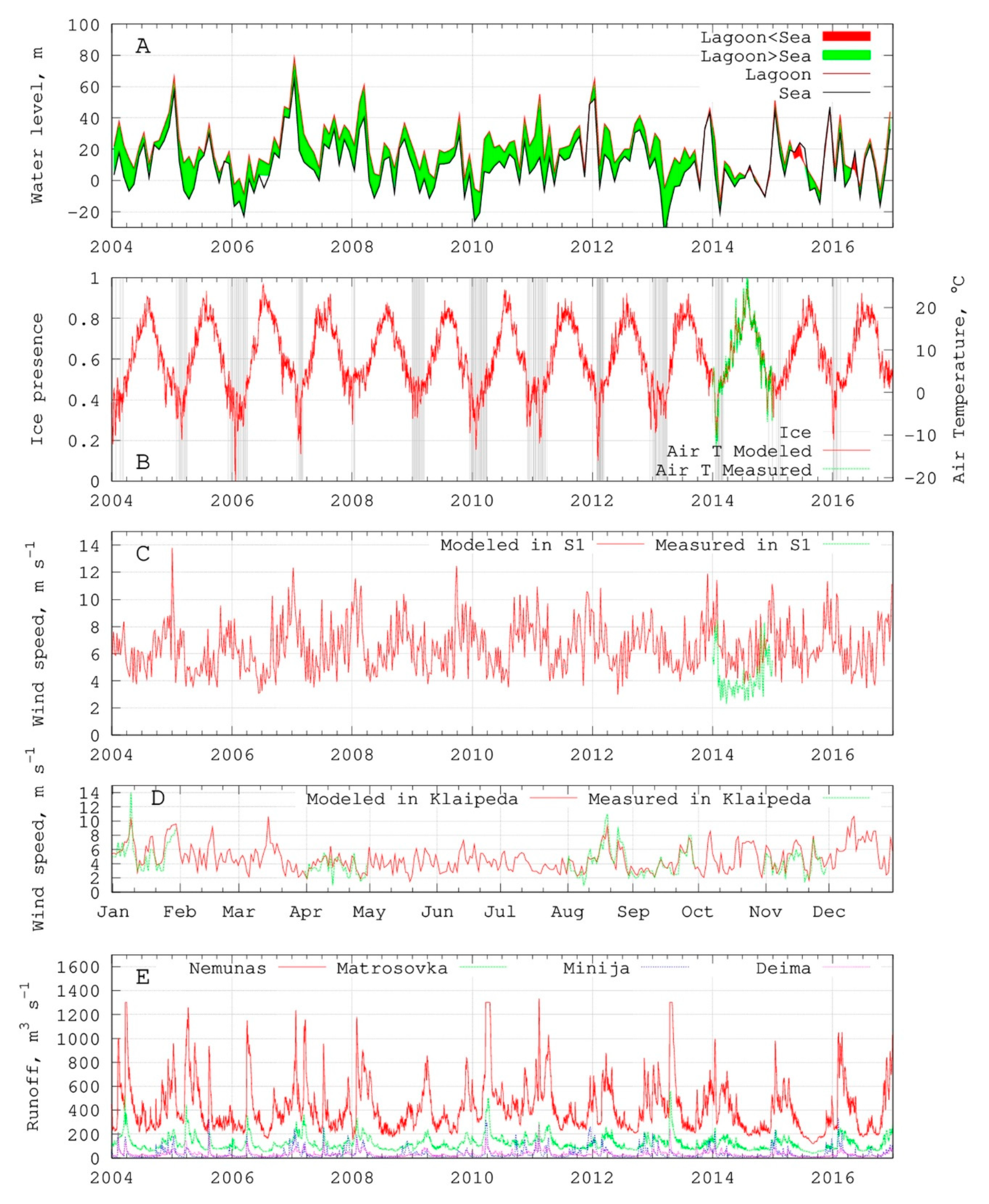
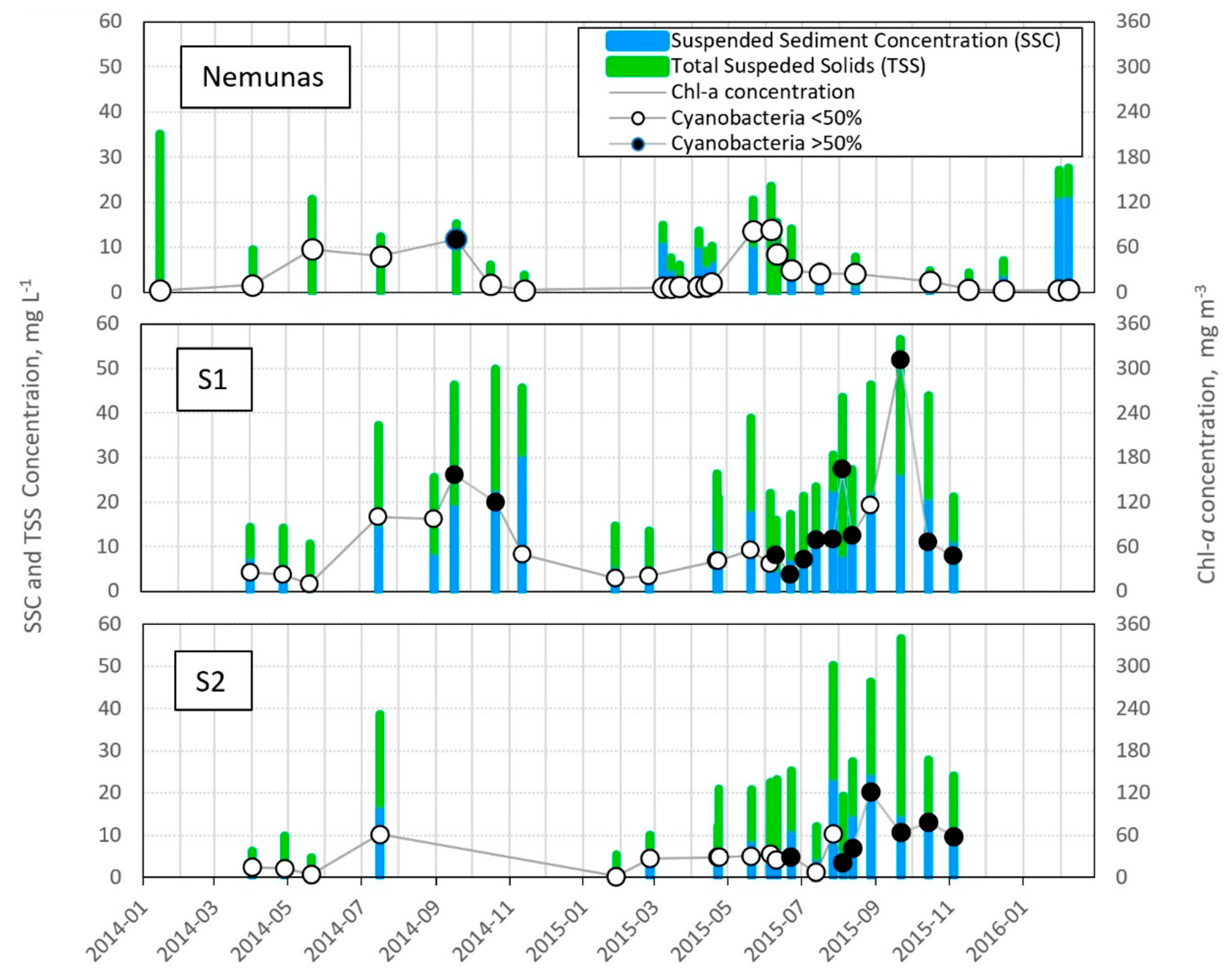


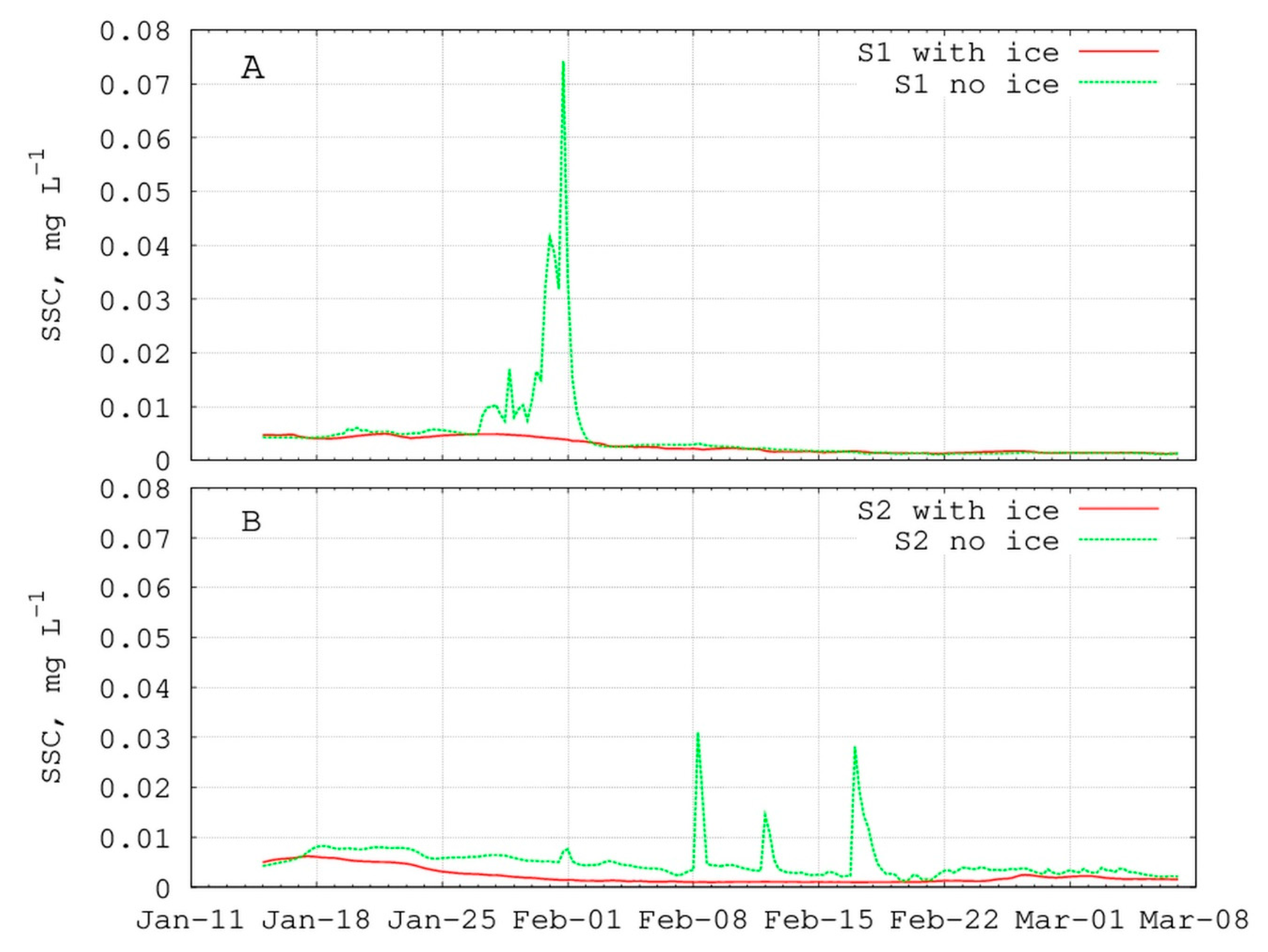
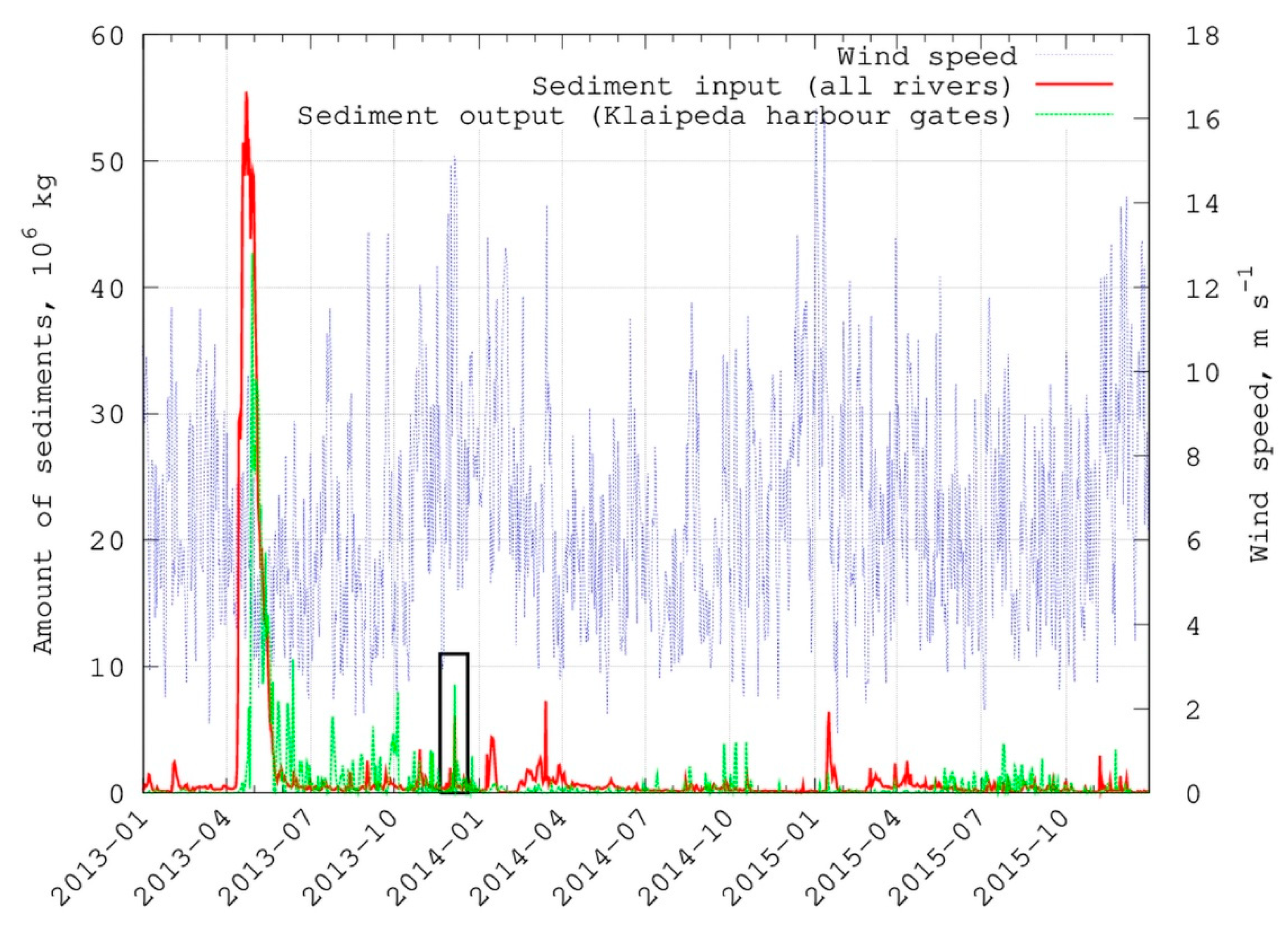
| Station | Location | Depth, m | Median Bottom Grain Size, µm | Percentage of Mud, % | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 55.286017 N | 3.35 | 35 | 77 | 25 |
| 21.021400 E | |||||
| S2 | 55.444483 N | 1.90 | 210 | 1.6 | 20 |
| 21.182733 E | |||||
| Nemunas | 55.298228 N | 2.00 | 350 | 1.8 | 24 |
| 21.380543 E |
| Data | Period | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Open sea boundary | 2004–2006 | DHI model MIKE 21 |
| 2007–2010 | SMHI model HIROMB | |
| 2011–2013 | IOW model MOM | |
| 2014–2016 | SMHI model HIROMB | |
| Meteo forcing | 2004–2008 | ECMWF model data |
| 2009–2010 | Lithuanian hydrometeorological service model HIRLAM | |
| 2011–2016 | ECMWF model data | |
| River discharges | 2004–2016 | Lithuanian hydrometeorological service |
| Ice coverage | 2004–2016 | Satellite data provided by KU MRI |
| Initial bottom sediment composition | - | Gelumbauskaitė et al. [31] and Gulbinskas and Žaromskis [32] |
| Name | Period | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CAL | 2013–2015 | Simulation for sediment model calibration (also used for sensitivity tests) |
| VAL | 2015–2016 | Simulation for model validation |
| NoICE | 2013–2015 | As CAL, but without ice cover data |
| LONG | 2004–2016 | 13-year simulation |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mėžinė, J.; Ferrarin, C.; Vaičiūtė, D.; Idzelytė, R.; Zemlys, P.; Umgiesser, G. Sediment Transport Mechanisms in a Lagoon with High River Discharge and Sediment Loading. Water 2019, 11, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101970
Mėžinė J, Ferrarin C, Vaičiūtė D, Idzelytė R, Zemlys P, Umgiesser G. Sediment Transport Mechanisms in a Lagoon with High River Discharge and Sediment Loading. Water. 2019; 11(10):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101970
Chicago/Turabian StyleMėžinė, Jovita, Christian Ferrarin, Diana Vaičiūtė, Rasa Idzelytė, Petras Zemlys, and Georg Umgiesser. 2019. "Sediment Transport Mechanisms in a Lagoon with High River Discharge and Sediment Loading" Water 11, no. 10: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101970
APA StyleMėžinė, J., Ferrarin, C., Vaičiūtė, D., Idzelytė, R., Zemlys, P., & Umgiesser, G. (2019). Sediment Transport Mechanisms in a Lagoon with High River Discharge and Sediment Loading. Water, 11(10), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11101970







